PSORS1 Locus Genotyping Profile in Psoriasis: A Pilot Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SNP Selection
2.2. Molecular Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Allelic Discrimination Analysis
2.5. PSORS1C1 Relative Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Clinical Assessment of Psoriasis Patients
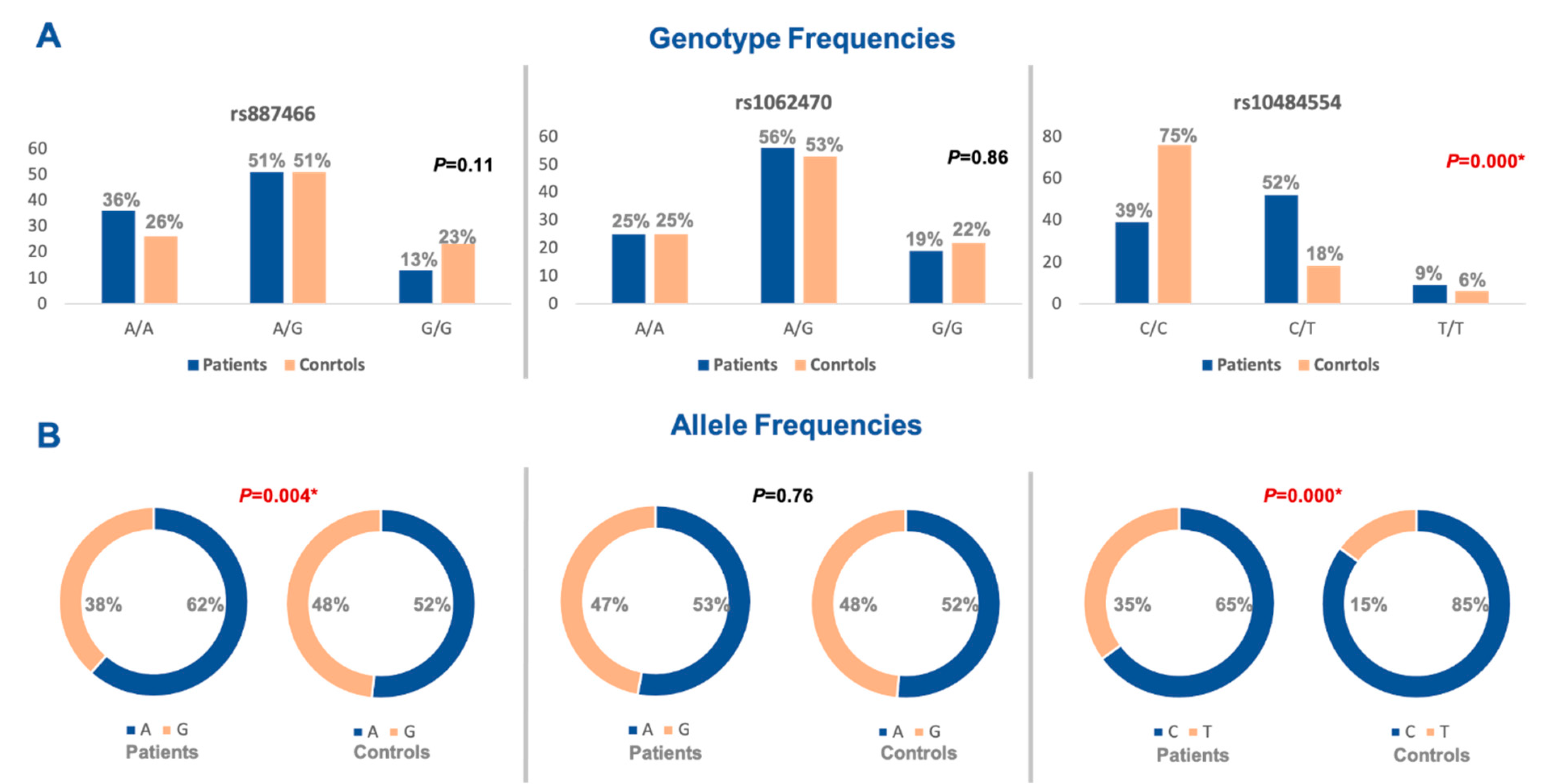
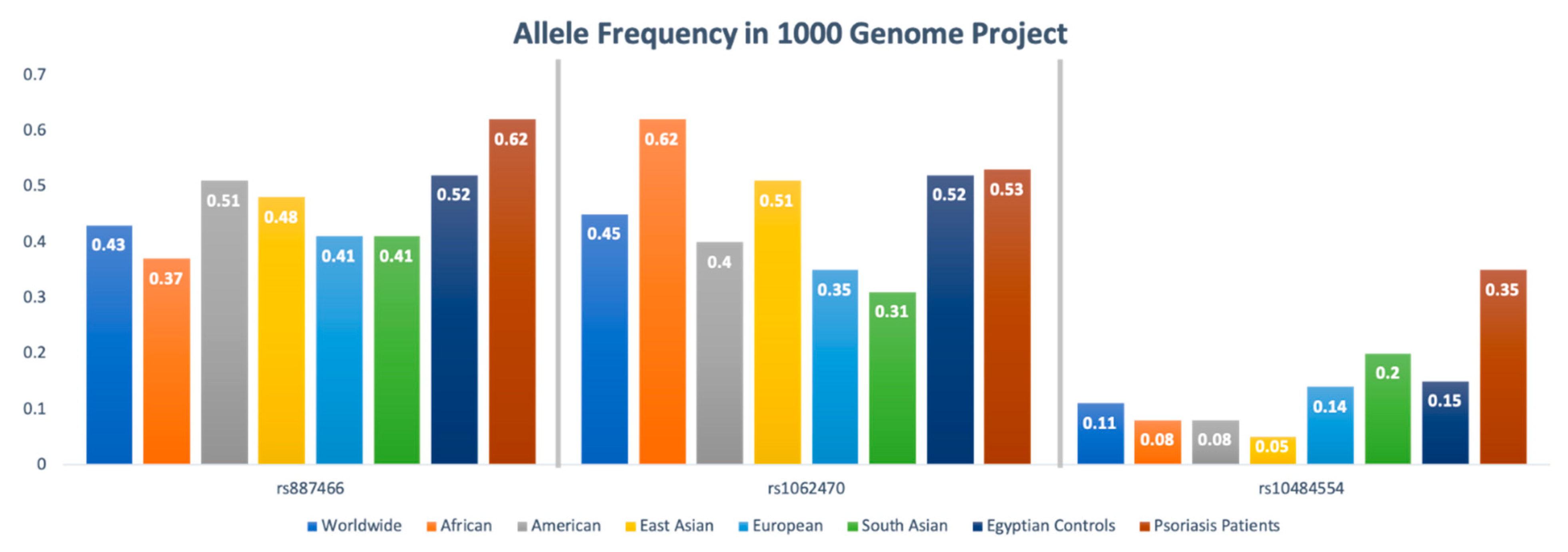
3.3. Allelic Discrimination Analysis
3.4. Association of PSORS1 Locus Gene Variants with Psoriasis Risk
3.5. Association of PSORS1 Locus Haplotypes with Psoriasis Severity
3.6. Relative Expression Analysis of Plasma PSORS1C1 in Psoriasis
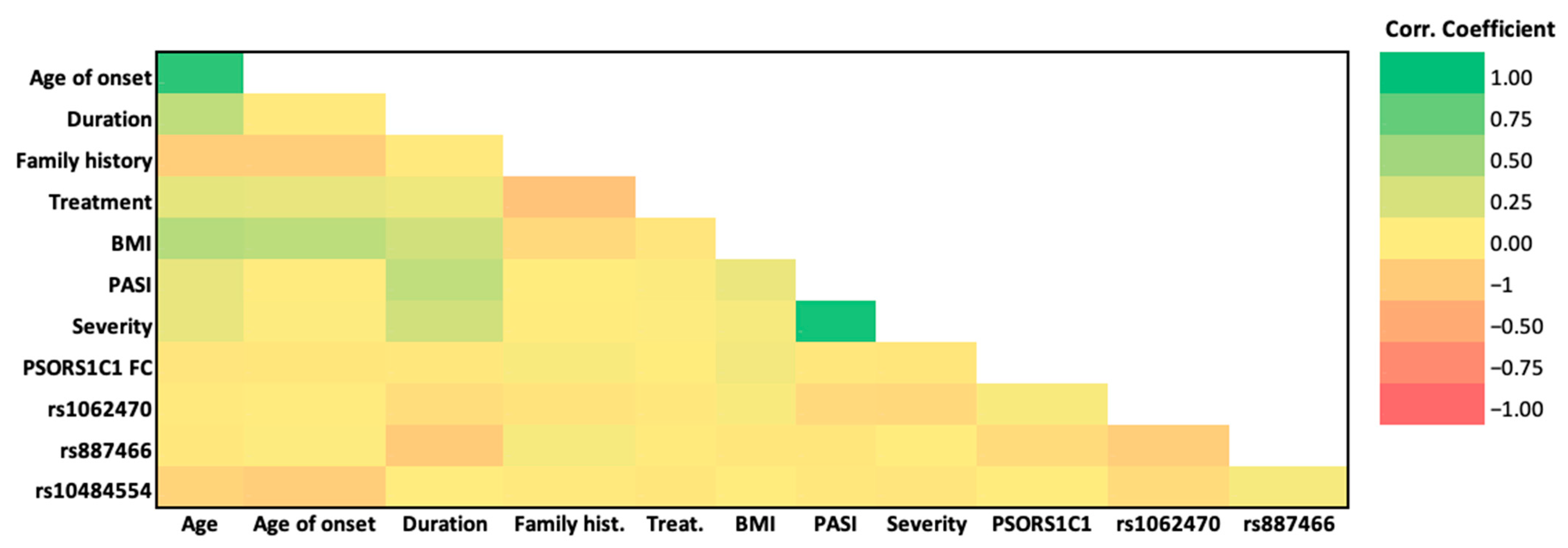
3.7. Association of the Studied SNPs, PSORS1C1 Gene Expression, and Clinicopathological Features
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Springate, D.A.; Parisi, R.; Kontopantelis, E.; Reeves, D.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Incidence, Prevalence and Mortality of Patients with Psoriasis: A U.K. Population-Based Cohort Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasch, M.C. Nail Psoriasis: A Review of Treatment Options. Drugs 2016, 76, 675–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, F.M.; Richardson, B.C. Epigenetics in Human Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2008, 41, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; Cinelli, E.; Megna, M. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab in psoriasis patients who failed ustekinumab and/or anti-interleukin-17 treatment: A real-life 52-week retrospective study. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; Cinelli, E.; Megna, M. Guselkumab and risankizumab for psoriasis: A 44-week indirect real-life comparison. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generali, E.; Ceribelli, A.; Stazi, M.A.; Selmi, C. Lessons Learned from Twins in Autoimmune and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 83, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.-J.; Sun, L.-D.; Soltani-Arabshahi, R.; Bowcock, A.M.; Nair, R.P.; Stuart, P.; Elder, J.T.; Schrodi, S.J.; Begovich, A.B.; Abecasis, G.R.; et al. Multiple Loci within the Major Histocompatibility Complex Confer Risk of Psoriasis. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.P.; Stuart, P.; Henseler, T.; Jenisch, S.; Chia, N.V.; Westphal, E.; Schork, N.J.; Kim, J.; Lim, H.W.; Christophers, E.; et al. Localization of Psoriasis-Susceptibility Locus PSORS1 to a 60-Kb Interval Telomeric to HLA-C. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 66, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clop, A.; Bertoni, A.; Spain, S.L.; Simpson, M.A.; Pullabhatla, V.; Tonda, R.; Hundhausen, C.; Di Meglio, P.; De Jong, P.; Hayday, A.C.; et al. An In-Depth Characterization of the Major Psoriasis Susceptibility Locus Identifies Candidate Susceptibility Alleles within an HLA-C Enhancer Element. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, F. The Genetic Basis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, F.; Toal, I.K.; Evans, J.C.; Allen, M.H.; Patel, S.; Tillman, D.; Burden, D.; Barker, J.N.W.N.; Trembath, R.C. Haplotype Analysis of Distantly Related Populations Implicates Corneodesmosin in Psoriasis Susceptibility. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.; Sirotkin, K. DbSNP—Database for Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Other Classes of Minor Genetic Variation. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Valentovic, M.A.; Rankin, G.O. Effects of Cytochrome P450 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Methadone Metabolism and Pharmacodynamics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.L.; Achuthan, P.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D884–D891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. G:Profiler: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Conversions of Gene Lists (2019 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.J.; Chow, C.; Morgenstem, H.; Luger, T.A.; Ellis, C.N. Comparison of 3 Methods for Measuring Psoriasis Severity in Clinical Studies (Part 2 of 2): Use of Quality of Life to Assess Construct Validity of LS-PGA, PASI and Static Physician’s Global Assessment. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greshake, B.; Bayer, P.E.; Rausch, H.; Reda, J. OpenSNP-a Crowdsourced Web Resource for Personal Genomics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, A.; Matusiak, Ł.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Nowak, I.; Kuśnierczyk, P. HLA-C*06:02-Independent, Gender-Related Association of PSORS1C3 and PSORS1C1/CDSN Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms with Risk and Severity of Psoriasis. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2018, 293, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, X.; Guinó, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A Web Tool for the Analysis of Association Studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejaoui, Y.; Witte, M.; Abdelhady, M.; Eldarouti, M.; Abdallah, N.M.A.; Elghzaly, A.A.; Tawhid, Z.; Gaballah, M.A.; Busch, H.; Munz, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Psoriasis in an Egyptian Population. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Helms, C.; Liao, W.; Zaba, L.C.; Duan, S.; Gardner, J.; Wise, C.; Miner, A.; Malloy, M.J.; Pullinger, C.R.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Identifies New Disease Loci. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Képíró, L.; Széll, M.; Kovács, L.; Keszthelyi, P.; Kemény, L.; Gyulai, R. The Association of HLA-C and ERAP1 Polymorphisms in Early and Late Onset Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients of Hungary. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiel, B.; Kisiel, K.; Szymański, K.; Mackiewicz, W.; Biało-Wójcicka, E.; Uczniak, S.; Fogtman, A.; Iwanicka-Nowicka, R.; Koblowska, M.; Kossowska, H.; et al. The Association between 38 Previously Reported Polymorphisms and Psoriasis in a Polish Population: High Predicative Accuracy of a Genetic Risk Score Combining 16 Loci. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Martínez, A.; Gallardo-Blanco, H.; Cerda-Flores, R.; Torres-Muñoz, I.; Gómez-Flores, M.; Salas-Alanís, J.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Martínez-Garza, L. Candidate Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Psoriasis: A Pilot Study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Strange, A.; Capon, F.; Spencer, C.C.; Knight, J.; Weale, M.E.; Allen, M.H.; Barton, A.; Band, G.; Bellenguez, C.; Bergboer, J.G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies New Psoriasis Susceptibility Loci and an Interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, A.; Matusiak, Ł.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Nowak, I.; Łuszczek, W.; Kuśnierczyk, P. The Association of ERAP1 and ERAP2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Their Haplotypes with Psoriasis Vulgaris Is Dependent on the Presence or Absence of the HLA-C* 06: 02 Allele and Age at Disease Onset. Hum. Immunol. 2018, 79, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Spencer, C.C.A.; Pointon, J.J.; Su, Z.; Harvey, D.; Kochan, G.; Oppermann, U.; Dilthey, A.; Pirinen, M.; Stone, M.A.; et al. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in Ankylosing Spondylitis Implicates Peptide Handling in the Mechanism for HLA-B27 in Disease Susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Chandra, A.; Chakraborty, J.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Senapati, S.; Chatterjee, G.; Chatterjee, R. Associations of ERAP1 Coding Variants and Domain Specific Interaction with HLA-C∗06 in the Early Onset Psoriasis Patients of India. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.Y.P.C.; Barton, A.; Worthington, J.; Thomson, W.; Silman, A.J.; Bruce, I.N. HLA-Cw6 and HLA-DRB1*07 Together Are Associated with Less Severe Joint Disease in Psoriatic Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, H.L.; Bowes, J.; Smith, R.L.; Flynn, E.; Parslew, R.; Alsharqi, A.; McHugh, N.J.; Barker, J.N.W.N.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Barton, A.; et al. Identification of Loci Associated with Late-Onset Psoriasis Using Dense Genotyping of Immune-Related Regions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shen, F. Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bakker, P.I.W.; McVean, G.; Sabeti, P.C.; Miretti, M.M.; Green, T.; Marchini, J.; Ke, X.; Monsuur, A.J.; Whittaker, P.; Delgado, M.; et al. A High-Resolution HLA and SNP Haplotype Map for Disease Association Studies in the Extended Human MHC. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.T.; Chou, C.T.; Shiao, Y.M.; Lin, M.W.; Yu, C.W.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lee, D.D.; Liu, H.N.; Wang, W.J.; et al. Psoriasis Vulgaris in Chinese Individuals Is Associated with PSORS1C3 and CDSN Genes: Genetics of Psoriasis in Chinese Individuals. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S.J.; Sánchez, F.; Carlén, L.M.; Mallbris, L.; Ståhle, M.; O’Brien, K.P. HLA-Cw*0602 Associates More Strongly to Psoriasis in the Swedish Population than Variants of the Novel 6p21.3 Gene PSORS1C3. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2005, 85, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesueur, F.; Oudot, T.; Heath, S.; Foglio, M.; Lathrop, M.; Prud’homme, J.-F.; Fischer, J. ADAM33, a New Candidate for Psoriasis Susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Matsui, S.; Fukushima, M.; Yasuda, H.; Miyauchi, H.; Miyachi, Y. Prognostic Factor Analysis for Plaque Psoriasis. Dermatology 2005, 211, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, D.; Sundström, A.; Eriksson, M.; Schmitt-Egenolf, M. Severity of Psoriasis Differs between Men and Women: A Study of the Clinical Outcome Measure Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) in 5438 Swedish Register Patients. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X. PSORS1C1 May Be Involved in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol. Lett. 2013, 153, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
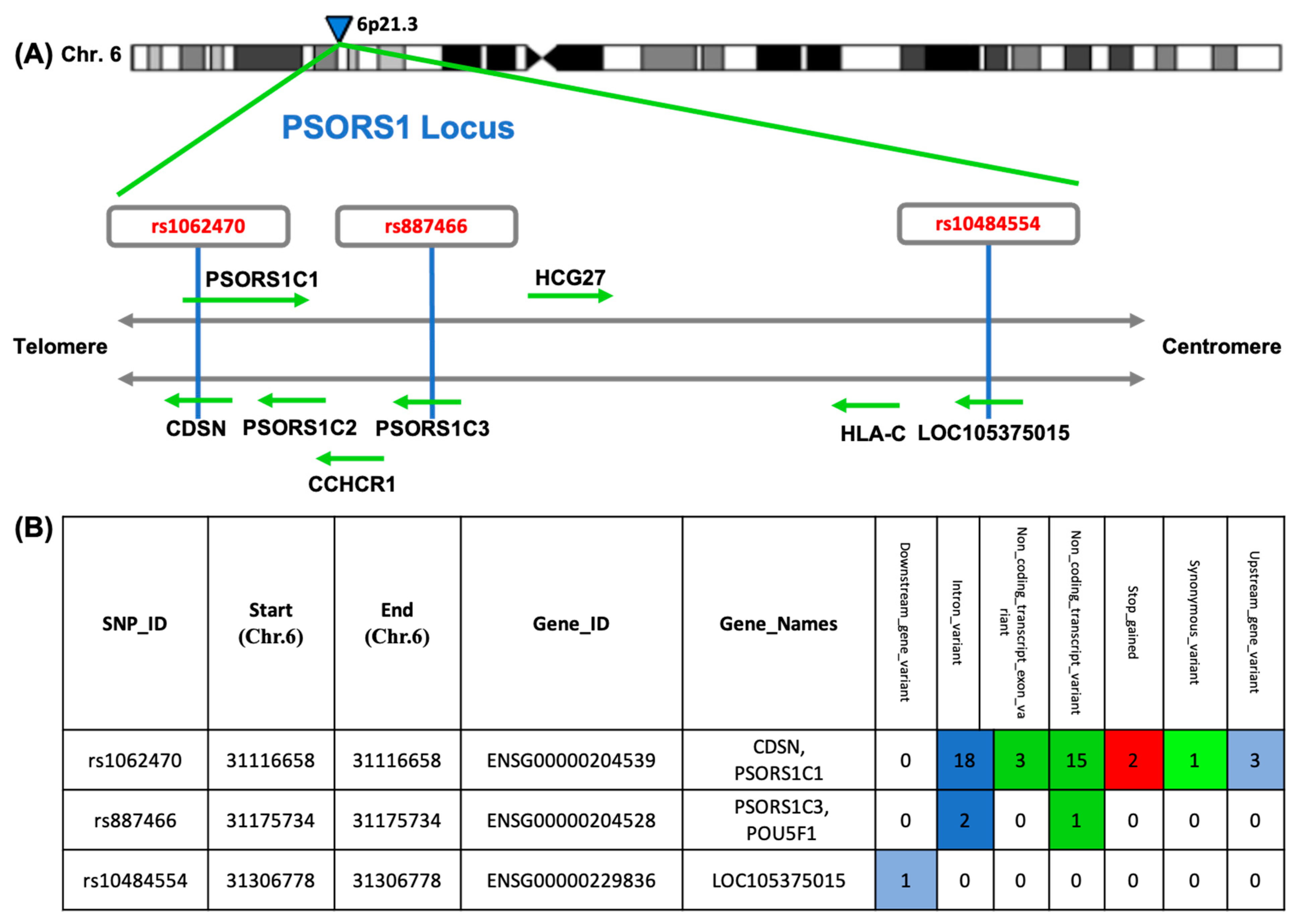

| Cases (n = 100) | Control (n = 100) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | ||
| Age (years) | |||||
| ● Min.–Max. | 18.0–60.0 | 20.0–62.0 | 0.134 | ||
| ● Mean ± SD. | 41.74 ± 14.08 | 39.17 ± 11.65 | |||
| ● Median (IQR) | 42.0 (31.50–56.0) | 37.0 (30.0–49.0) | |||
| Gender | |||||
| ● Male | 47 | 47.0 | 55 | 55.0 | 0.258 |
| ● Female | 53 | 53.0 | 45 | 45.0 | |
| Special habits | |||||
| ● Non-smoker | 77 | 77.0 | 72 | 72.0 | 0.417 |
| ● Smoker | 23 | 23.0 | 28 | 28.0 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
| ● Min.–Max. | 19.0–36.21 | 19.55–35.63 | 0.112 | ||
| ● Mean ± SD. | 26.80 ± 3.99 | 27.70 ± 3.93 | |||
| ● Median (IQR) | 25.91 (24.13–29.45) | 27.43 (25.0–30.8) | |||
| Disease Characteristic | No. | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age of onset | ||
| ● vEOP | 21 | 21.0 |
| ● mEOP | 42 | 42.0 |
| ● LOP | 37 | 37.0 |
| ● Min.–Max. | 3.0–59.0 | |
| ● Mean ± SD. | 35.07 ± 13.43 | |
| ● Median (IQR) | 36.0 (24.13–29.45) | |
| Severity | ||
| ● Mild | 45 | 45.0 |
| ● Moderate | 31 | 31.0 |
| ● Severe | 24 | 24.0 |
| Duration (years) | ||
| ● Min.–Max. | 0.50–30.0 | |
| ● Mean ± SD. | 6.75 ± 6.22 | |
| ● Median (IQR) | 5.0 (25.0–30.80) | |
| Family history | ||
| ● No | 84 | 84.0 |
| ● Yes | 16 | 16.0 |
| Treatment | ||
| ● No Treatment | 41 | 41.0 |
| ● On Treatment | 59 | 59.0 |
| Age of Onset | vEOP (n = 21) | mEOP (n = 42) | LOP (n = 37) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | ||
| Gender | |||||||
| - Male | 3 | 14.3 | 22 | 52.4 | 22 | 59.5 | 0.003 * |
| - Female | 18 | 85.7 | 20 | 47.6 | 15 | 40.5 | |
| PASI | |||||||
| - Min.–Max. | 3.50–38.30 | 2.0–40.50 | 1.50–35.60 | 0.564 | |||
| - Mean ± SD. | 12.28 ± 7.84 | 14.72 ± 9.56 | 13.29 ± 9.31 | ||||
| - Median | 11.50 | 12.25 | 12.50 | ||||
| SNP | Model | Genotype | Patients | Controls | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs887466 | Codominant | A/A | 36 | 26 | Reference | |
| A/G | 51 | 51 | 0.72 (0.38–1.36) | 0.3 | ||
| G/G | 13 | 23 | 0.4 (0.17–0.95) | 0.038 * | ||
| Dominant | A/A | 36 | 26 | Reference | ||
| A/G-G/G | 64 | 74 | 0.62 (0.34–1.14) | 0.13 | ||
| Recessive | A/A-A/G | 87 | 77 | Reference | ||
| G/G | 13 | 23 | 0.5 (0.23–1.05) | 0.068 | ||
| Over-dominant | A/A-G/G | 49 | 49 | Reference | ||
| A/G | 51 | 51 | 1.0 (0.57–1.74) | 1.0 | ||
| Allelic Model | A | 123 | 103 | Reference | ||
| G | 77 | 97 | 0.66 (0.44–0.99) | 0.04 * | ||
| rs1062470 | Codominant | A/A | 25 | 25 | Reference | |
| A/G | 56 | 53 | 1.05 (0.54–2.06) | 0.87 | ||
| G/G | 19 | 22 | 0.86 (0.37–1.97) | 0.72 | ||
| Dominant | A/A | 25 | 25 | Reference | ||
| A/G-G/G | 75 | 75 | 1.04 (0.66–1.62) | 0.87 | ||
| Recessive | A/A-A/G | 81 | 78 | Reference | ||
| G/G | 19 | 22 | 0.83 (0.41–1.65) | 0.6 | ||
| Over-dominant | A/A-G/G | 44 | 77 | Reference | ||
| A/G | 56 | 53 | 1.84 (1.09–3.13) | 0.02 * | ||
| Allelic Model | A | 106 | 103 | Reference | ||
| G | 94 | 97 | 0.94 (0.63–1.39) | 0.76 | ||
| rs10484554 | Codominant | C/C | 39 | 76 | Reference | |
| C/T | 52 | 18 | 5.63 (2.9–10.9) | <0.001 * | ||
| T/T | 9 | 6 | 2.92 (0.97–8.8) | 0.05 * | ||
| Dominant | C/C | 39 | 76 | Reference | ||
| C/T-T/T | 61 | 24 | 5 (2.7–9.1) | <0.001 * | ||
| Recessive | C/C-C/T | 91 | 94 | Reference | ||
| T/T | 9 | 6 | 1.54 (0.53–4.52) | 0.42 | ||
| Over-dominant | C/C-T/T | 48 | 82 | Reference | ||
| C/T | 52 | 18 | 5 (2.59–9.4) | <0.001 * | ||
| Allelic Model | C | 130 | 170 | Reference | ||
| T | 70 | 30 | 3 (1.88–4.95) | <0.001 * | ||
| rs887466 | rs1062470 | rs10484554 | Frequency | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G | A | C | 0.199 | Reference | - |
| 2 | A | G | C | 0.1954 | NA (NA–NA) | NA |
| 3 | A | A | C | 0.1672 | 0.4 (−0.06–0.85) | 0.089 |
| 4 | A | G | T | 0.1508 | 0.3 (−0.12–0.72) | 0.16 |
| 5 | A | A | T | 0.1015 | −0.36 (−0.77–0.04) | 0.082 |
| 6 | G | G | C | 0.0884 | −0.73 (−1.21–−0.24) | 0.0038 * |
| 7 | G | A | T | 0.0623 | −0.32 (−0.8–0.17) | 0.2 |
| 8 | G | G | T | 0.0354 | 0.92 (0.18–1.66) | 0.015 * |
| Age | Age of Onset | Duration | Family History | Treatment | BMI | PASI | Severity | PSORS1C1 FC | rs1062470 | rs887466 | rs10484554 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | R | 1 | 0.896 ** | 0.367 ** | −0.237 * | 0.175 | 0.416 ** | 0.163 | 0.164 | −0.056 | −0.021 | −0.039 | −0.184 |
| P | . | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.018 | 0.083 | <0.001 | 0.106 | 0.103 | 0.583 | 0.832 | 0.698 | 0.067 | |
| Age of onset | R | 0.896 ** | 1 | −0.023 | −0.225 * | 0.158 | 0.375 ** | 0.022 | 0.054 | −0.05 | 0.022 | 0.046 | −0.227 * |
| P | <0.001 | . | 0.824 | 0.024 | 0.118 | <0.001 | 0.831 | 0.596 | 0.624 | 0.83 | 0.653 | 0.023 | |
| Duration | R | 0.367 ** | −0.023 | 1 | −0.017 | 0.125 | 0.279 ** | 0.354 ** | 0.275 ** | −0.034 | −0.111 | −0.251 * | 0.033 |
| P | <0.001 | 0.824 | . | 0.866 | 0.218 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.736 | 0.27 | 0.012 | 0.745 | |
| Family history | R | −0.237 * | −0.225 * | −0.017 | 1 | −0.310 ** | −0.15 | 0.005 | −0.005 | 0.075 | −0.071 | 0.084 | −0.018 |
| P | 0.018 | 0.024 | 0.866 | . | 0.002 | 0.147 | 0.963 | 0.96 | 0.46 | 0.483 | 0.407 | 0.855 | |
| Treatment | R | 0.175 | 0.158 | 0.125 | −0.310 ** | 1 | −0.06 | 0.062 | 0.056 | 0.027 | −0.038 | −0.013 | −0.046 |
| P | 0.083 | 0.118 | 0.218 | 0.002 | . | 0.578 | 0.542 | 0.581 | 0.788 | 0.706 | 0.9 | 0.649 | |
| BMI | R | 0.416 ** | 0.375 ** | 0.279 ** | −0.146 | −0.057 | 1 | 0.147 | 0.082 | 0.118 | 0.076 | −0.051 | −0.001 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.147 | 0.578 | . | 0.145 | 0.417 | 0.242 | 0.454 | 0.612 | 0.994 | |
| PASI | R | 0.163 | 0.022 | 0.354 ** | 0.005 | 0.062 | 0.147 | 1 | 0.930 ** | −0.037 | −0.134 | −0.049 | −0.038 |
| P | 0.106 | 0.831 | <0.001 | 0.963 | 0.542 | 0.145 | . | <0.001 | 0.716 | 0.183 | 0.63 | 0.705 | |
| Severity | R | 0.164 | 0.054 | 0.275 ** | −0.005 | 0.056 | 0.082 | 0.930 ** | 1 | −0.051 | −0.156 | 0.015 | −0.062 |
| P | 0.103 | 0.596 | 0.006 | 0.96 | 0.581 | 0.417 | <0.001 | . | 0.611 | 0.12 | 0.881 | 0.539 | |
| PSORS1C1 FC | R | −0.056 | −0.05 | −0.034 | 0.075 | 0.027 | 0.118 | −0.037 | −0.051 | 1 | 0.074 | −0.126 | 0.008 |
| P | 0.583 | 0.624 | 0.736 | 0.46 | 0.788 | 0.242 | 0.716 | 0.611 | . | 0.465 | 0.212 | 0.938 | |
| rs1062470 | R | −0.021 | 0.022 | −0.111 | −0.071 | −0.038 | 0.076 | −0.134 | −0.156 | 0.074 | 1 | −0.231 * | −0.127 |
| P | 0.832 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 0.483 | 0.706 | 0.454 | 0.183 | 0.12 | 0.465 | . | 0.021 | 0.209 | |
| rs887466 | R | −0.039 | 0.046 | −0.251 * | 0.084 | −0.013 | −0.05 | −0.049 | 0.015 | −0.126 | −0.231 * | 1 | 0.081 |
| P | 0.698 | 0.653 | 0.012 | 0.407 | 0.9 | 0.612 | 0.63 | 0.881 | 0.212 | 0.021 | . | 0.425 | |
| rs10484554 | R | −0.184 | −0.227 * | 0.033 | −0.018 | −0.046 | −0 | −0.038 | −0.062 | 0.008 | −0.127 | 0.081 | 1 |
| P | 0.067 | 0.023 | 0.745 | 0.855 | 0.649 | 0.994 | 0.705 | 0.539 | 0.938 | 0.209 | 0.425 | . |
| SNP | Genotype Frequency | Allele Frequency | Level of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs1062470 | 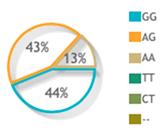 | 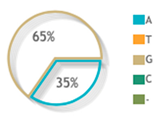 | 4 publications |
| rs887466 | 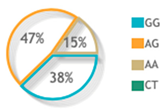 | 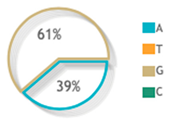 | 7 publications |
| rs10484554 | 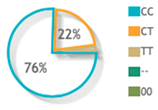 | 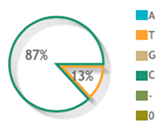 | 39 publications |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tawfik, N.Z.; Abdallah, H.Y.; Hassan, R.; Hosny, A.; Ghanem, D.E.; Adel, A.; Atwa, M.A. PSORS1 Locus Genotyping Profile in Psoriasis: A Pilot Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051035
Tawfik NZ, Abdallah HY, Hassan R, Hosny A, Ghanem DE, Adel A, Atwa MA. PSORS1 Locus Genotyping Profile in Psoriasis: A Pilot Case-Control Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051035
Chicago/Turabian StyleTawfik, Noha Z., Hoda Y. Abdallah, Ranya Hassan, Alaa Hosny, Dina E. Ghanem, Aya Adel, and Mona A. Atwa. 2022. "PSORS1 Locus Genotyping Profile in Psoriasis: A Pilot Case-Control Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051035
APA StyleTawfik, N. Z., Abdallah, H. Y., Hassan, R., Hosny, A., Ghanem, D. E., Adel, A., & Atwa, M. A. (2022). PSORS1 Locus Genotyping Profile in Psoriasis: A Pilot Case-Control Study. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051035






