Inflammatory Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Ectasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Outcomes of Interest
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Results
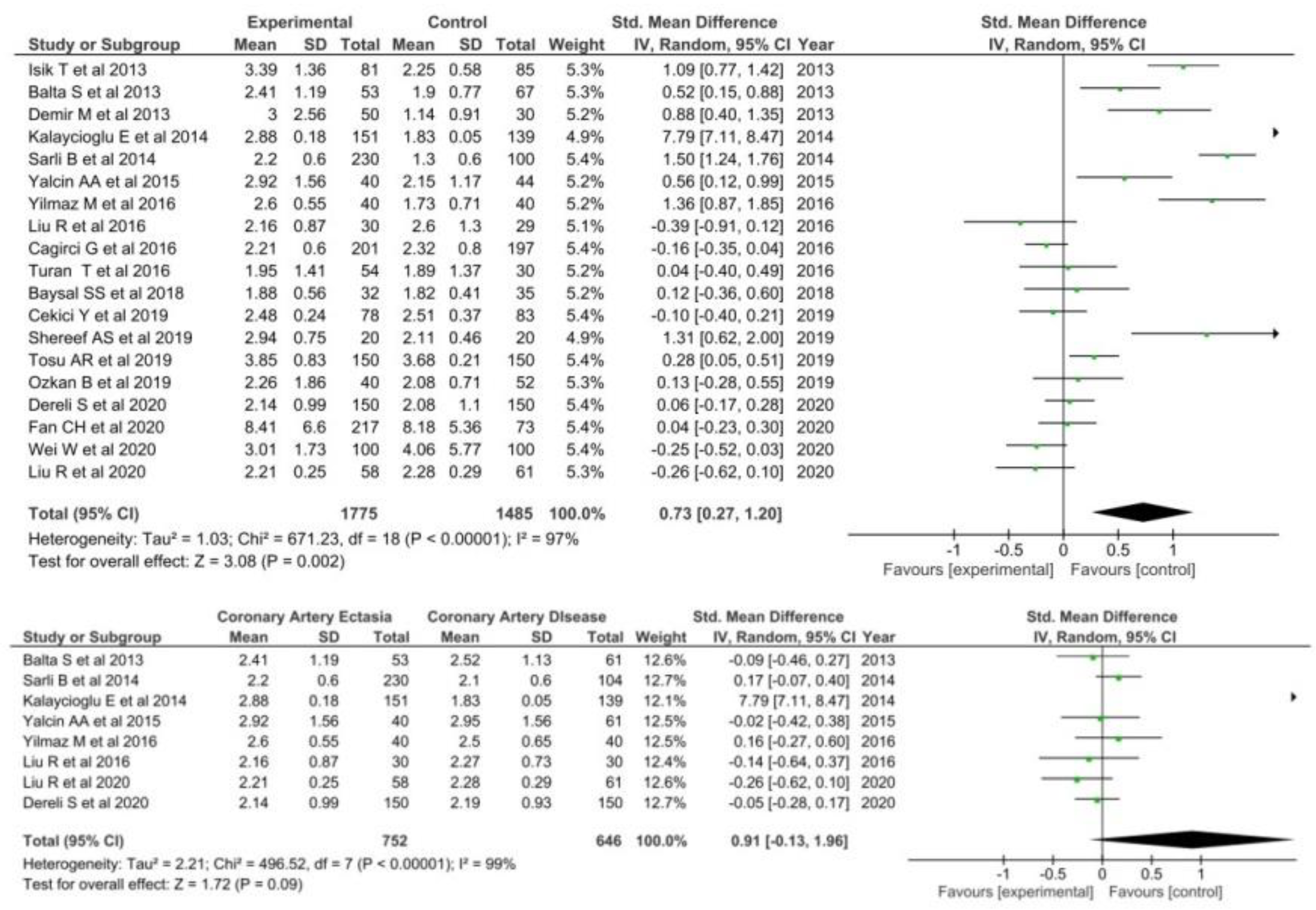
3.1.1. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio
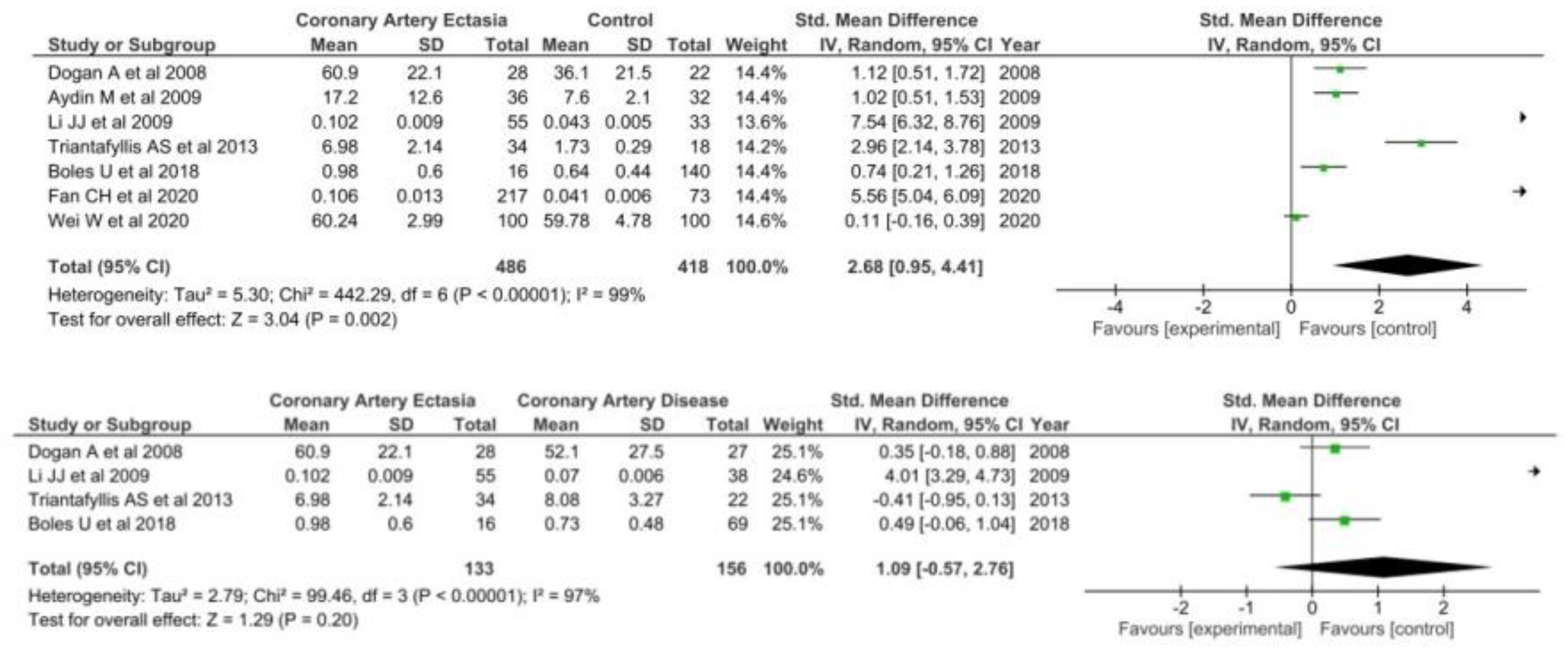
3.1.2. High Sensitivity CRP
3.1.3. IL-6
3.1.4. TNF-a
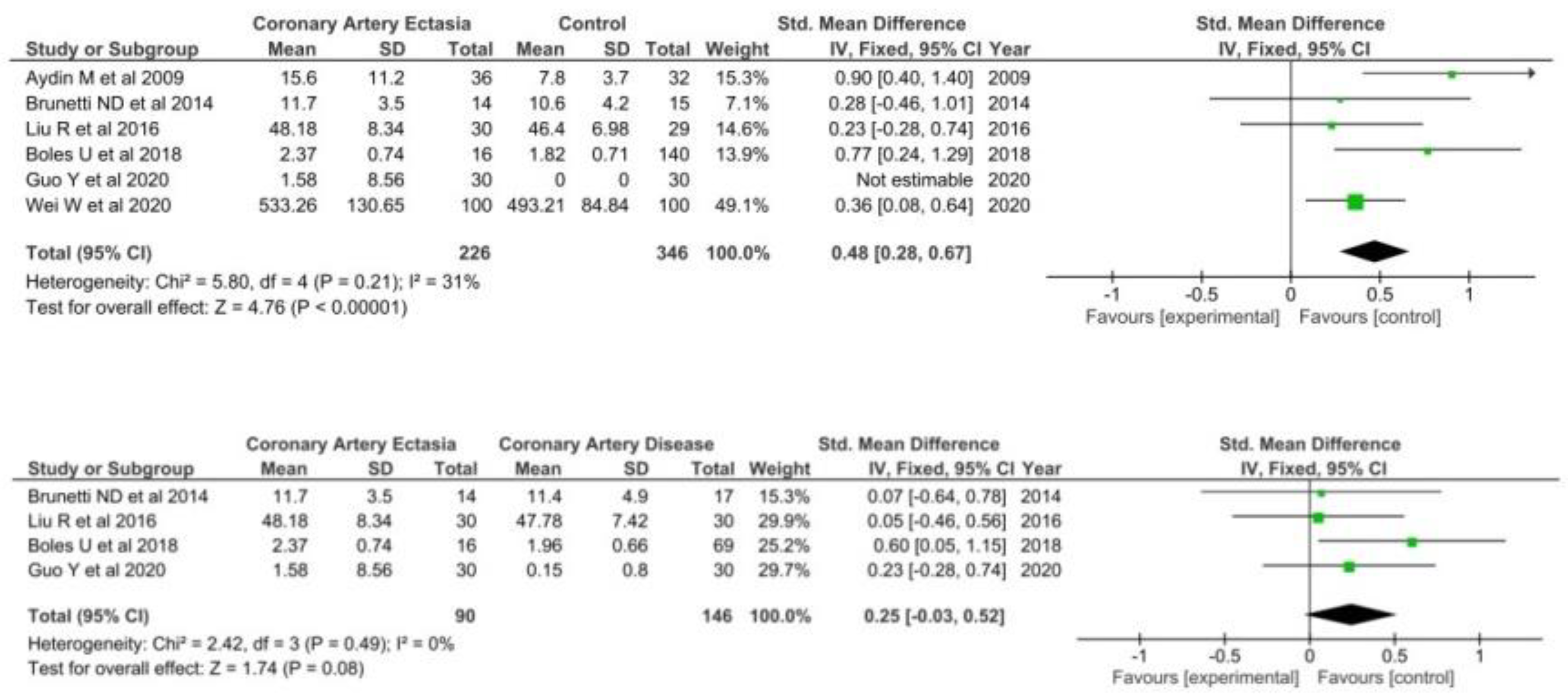
3.1.5. Red Cell Distribution
3.2. Sensitivity Analyses
3.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
Assessment of Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboeata, A.S.; Sontineni, S.P.; Alla, V.M.; Esterbrooks, D.J. Coronary artery ectasia: Current concepts and interventions. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitan, A.; Roguin, A. Coronary artery ectasia: New insights into pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Coron. Artery Dis. 2016, 27, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devabhaktuni, S.; Mercedes, A.; Diep, J.; Ahsan, C. Coronary Artery Ectasia-A Review of Current Literature. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 12, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-M. Inflammatory mediators of coronary artery ectasia. J. Vasc. Bras. 2014, 13, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, Q.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.H.; Li, J.J. Relation of diabetes to coronary artery ectasia: A meta-analysis study. Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 2014, 14, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, U.; Eriksson, P.; Zhao, Y.; Henein, M.Y. Coronary artery ectasia: Remains a clinical dilemma. Coron. Artery Dis. 2010, 21, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, U.; Wiklund, U.; David, S.; Ahmed, K.; Henein, M.Y. Coronary artery ectasia carries a worse prognosis: A long-term follow-up study. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekaran, P.; Stanojevic, D.; Drees, T.; Fritzlen, J.; Haghnegahdar, M.; McCullough, M.; Gupta, K. Prognostic significance, angiographic characteristics and impact of antithrombotic and anticoagulant therapy on outcomes in high versus low grade coronary artery ectasia: A long-term follow-up study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliazzo, S.; Nigro, O.; Bertù, L.; Guasti, L.; Grandi, A.M.; Ageno, W.; Dentali, F. Prognostic role of neutrophils to lymphocytes ratio in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentali, F.; Nigro, O.; Squizzato, A.; Gianni, M.; Zuretti, F.; Grandi, A.M.; Guasti, L. Impact of neutrophils to lymphocytes ratio on major clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 266, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Chen, S.Y. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predict mortality and major adverse cardiac events in acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 52, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.; Chen, K.; Rha, S.W.; Lim, H.E.; Li, G.; Liu, T. Usefulness of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Res. 2015, 46, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Cheng, X. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in aortic disease: A meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1733–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, C.D.; Parajuli, A.; Gale, H.J.; Bulteel, N.S.; Schuetz, P.; de Jager, C.P.C.; Baillie, J.K. The utility of peripheral blood leucocyte ratios as biomarkers in infectious diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, J.; Pan, F. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zeng, A.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, R. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and their correlation with activity: A meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Song, G.G. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, mean platelet volume and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in Behçet’s disease and their correlation with disease activity: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Paliogiannis, P.; Castagna, F.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Passiu, G.; Zinellu, A. Meta-analysis of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; McNamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Amir, E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.M.; Tao, S.M.; Liu, G.L. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in relation to the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Xiao, D.; Guo, J.; Chahan, B.; Wang, Z. Neutrophil–lymphocyte count ratio as a diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connel, D.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 1 February 2009).
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.T.S. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Demirkol, S.; Celik, T.; Kucuk, U.; Unlu, M.; Arslan, Z.; Yokusoglu, M. Association between coronary artery ectasia and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio. Angiology 2013, 64, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarli, B.; Baktir, A.O.; Saglam, H.; Arinc, H.; Kurtul, S.; Sivgin, S.; Akpek, M.; Kaya, M.G. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with severity of coronary artery ectasia. Angiology 2014, 65, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.H.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, X.L.; Huang, Z.H.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.L. Anti-inflammatory effects of rosuvastatin treatment on coronary artery ectasia patients of different age groups. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, B.; Örsçelik, Ö.; Yaroğlu, H.Y.; Balcı, Ş.; Özcan, M.K.; Çelik, A.; Özcan, İ.T. Association between serum adropin levels and isolated coronary artery ectasia in patients with stable angina pectoris. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2019, 22, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çekici, Y.; Kılıç, S.; Saraçoğlu, E.; Çetin, M.; Veysel Düzen, İ.; Yılmaz, M. The Relationship between Blood Viscosity and Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2019, 35, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, S.S.; Koç, Ş.; Güneş, A.; Altiparmak, I.H. Endothelium biomarkers endocan and thrombomodulin levels in isolated coronary artery ectasia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4677–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagirci, G.; Kucukseymen, S.; Yuksel, I.O.; Bayar, N.; Koklu, E.; Guven, R.; Arslan, S. The relationship between Vitamin D and coronary artery ectasia in subjects with a normal c-reactive protein level. Korean Circ. J. 2017, 47, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Turan, T.; Akyuz, A.R.; Aykan, A.C.; Kul, S.; Cirakoglu, O.F.; Aslan, A.O.; Celik, S. Plasma Endocan Levels in Patients With Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia. Angiology 2016, 67, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. Neutrophil serine proteases and their endogenous inhibitors in coronary artery ectasia patients. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2016, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shereef, A.; Kandeel, N. Predictors for coronary artery ectasia. J. Indian Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Sheng, Q.; Liang, S.; Zhao, H. Peripheral blood soluble elastin and elastase as auxiliary diagnostic indicators for coronary artery ectasia. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, S.; Çerik, İ.B.; Kaya, A.; Bektaş, O. Assessment of the Relationship Between C-Reactive Protein-to-Albumin Ratio and the Presence and Severity of Isolated Coronary Artery Ectasia. Angiology 2020, 71, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycıoğlu, E.; Gökdeniz, T.; Aykan, A.C.; Gül, I.; Boyacı, F.; Gürsoy, O.M.; Çelik, Ş. Comparison of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with coronary artery ectasia versus patients with obstructive coronary artery disease. Kardiol. Pol. 2014, 72, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işik, T.; Ayhan, E.; Uyarel, H.; Tanboǧa, I.H.; Kurt, M.; Uluganyan, M.; Eksik, A. Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with presence of isolated coronary artery ectasia. Türk Kardiyoloji Derneği Arşivi 2013, 41, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, A.A.; Topuz, M.; Akturk, I.F.; Celik, O.; Erturk, M.; Uzun, F.; Duran, M.; Karadeniz, M.; Sarikamis, C.; Oner, E. Is there a correlation between coronary artery ectasia and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio? Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2015, 21, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, M.; Korkmaz, H.; Bilen, M.N.; Uku, Ö.; Kurtoğlu, E. Could neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio be an indicator of coronary artery disease, coronary artery ectasia and coronary slow flow? J. Int. Med. Res. 2016, 44, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosu, A.R.; Çinar, T.; Güler, A.; Kahraman, S.; Gürbak, İ. Monosit/yüksek yoğunluklu lipoprotein oranının koroner arter ektaziyi öngörmedeki yararı. Turk. J. Clin. Lab. 2019, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. Difference in inflammation, atherosclerosis, and platelet activation between coronary artery aneurysm and coronary artery ectasia. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 5811–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.; Demir, C.; Keceoglu, S. The Relationship Between Blood Monocyte Count and Coronary Artery Ectasia. Cardiol. Res. 2014, 5, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundi, H.; Gök, M.; Çetin, M.; Kızıltunç, E.; Çiçekcioğlu, H.; Güven Çetin, Z.; Örnek, E. Relationship between platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and the presence and severity of coronary artery ectasia. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2016, 16, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-J.; Guo, Y.-L.; Zhu, C.-G.; Qing, P.; Xu, R.-X.; Wu, N.-Q.; Li, J.J. Association of alkaline phosphatase with isolated coronary artery ectasia. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2014, 74, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, M.; Kundi, H.; Kiziltunc, E.; Topcuoglu, C.; Örnek, E. The relationship between serum endocan levels and the presence/severity of isolated coronary artery ectasia. Cardiovasc. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 7, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, A.; Michowitz, Y.; Abashidze, A.; Miller, H.; Keren, G.; George, J. Temporal association between circulating proteolytic, inflammatory and neurohormonal markers in patients with coronary ectasia. Atherosclerosis 2005, 179, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogdu, O.; Koc, F.; Kalay, N.; Yarlioglues, M.; Elcik, D.; Karayakali, M.; Kaya, M.G. Assessment of red cell distribution width (RDW) in patients with coronary artery ectasia. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2012, 18, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.; Tuzun, N.; Turker, Y.; Akcay, S.; Kaya, S.; Ozaydin, M. Matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory markers in coronary artery ectasia: Their relationship to severity of coronary artery ectasia. Coron. Artery Dis. 2008, 19, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagli, N.; Ozturk, U.; Karaca, I.; Yavuzkir, M.; Koca, S.; Akbulut, H.; Balin, M. Adiponectin levels in coronary artery ectasia. Heart Vessels 2009, 24, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicek, Y.; Durakoglugil, M.E.; Erdogan, T.; Yilmaz, A.; Uydu, H.A.; Saglam, H.; Temiz, A. Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels in patients with isolated coronary artery ectasia. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2012, 33, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyel, A.; Sahinarslan, A.; Kiziltunc, E.; Yıldız, U.; Alsancak, Y.; Akboga, M.K.; Ozdemir, M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels in isolated coronary artery ectasia. Can. J. Cardiol. 2011, 27, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiloglu, A.K.; Can, R.; Nazli, C.; Ocal, A.; Ergene, O.; Tinaz, G.; Kisioglu, N. Ectasia and severe atherosclerosis: Relationships with Chlamydia pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori, and inflammatory markers. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2005, 32, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Aciksari, G.; Uygun, T.; Atici, A.; Aciksari, K.; Toprak, A.E.; Onur, I.; Caliskan, M. Association between galectin-3 levels and isolated coronary artery ectasia. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2020, 31, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, W.; Kappary, M.; Baghdady, Y.; Shehata, M. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) and high sensitivity C—Reactive protein (hs-CRP) in coronary artery ectasia. Egypt. Heart J. 2013, 65, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, J.; Yoo, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choe, K.H. Vascular endothelial function and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with isolated coronary artery ectasia and exercise-induced angina pectoris. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 145, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, M.; Parisi, Q.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.G.L.; Pristipino, C.; Cianflone, D.; Crea, F. New insights into molecular mechanisms of diffuse coronary ectasiae: A possible role for VEGF. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 106, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, T.; Demir, B.; Tosun, V.; Ungan, İ.; Kural, A.; Çiftçi, R.; Fatullayev, F. Relationship between interleukin-17A and isolated coronary ectasia. Cytokine 2019, 115, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, H.; Erbay, A.R.; Yasar, A.S.; Balci, M.; Bicer, A.; Yetkin, E. Comparison of C-reactive protein levels in patients with coronary artery ectasia versus patients with obstructive coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Hong, L.-F.; Jia, Y.-J.; Nie, S.-P.; Guo, Y.-L.; Xu, R.-X.; Li, J.J. Significance of red cell distribution width measurement for the patients with isolated coronary artery ectasia. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-J.; Nie, S.-P.; Qian, X.-W.; Zeng, H.-S.; Zhang, C.-Y. Chronic inflammatory status in patients with coronary artery ectasia. Cytokine 2009, 46, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, M.; Tekin, I.O.; Dogan, S.M.; Yildirim, N.; Arasli, M.; Sayin, M.R.; Aktop, Z. The levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with isolated coronary artery ectasia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllis, A.S.; Kalogeropoulos, A.S.; Rigopoulos, A.G.; Sakadakis, E.A.; Toumpoulis, I.K.; Tsikrikas, S.; Rizos, I. Coronary artery ectasia and inflammatory cytokines: Link with a predominant Th-2 immune response? Cytokine 2013, 64, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, U.; Johansson, A.; Wiklund, U.; Sharif, Z.; David, S.; McGrory, S.; Henein, M.Y. Cytokine Disturbances in Coronary Artery Ectasia Do Not Support Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, N.D.; Salvemini, G.; Cuculo, A.; Ruggiero, A.; De Gennaro, L.; Gaglione, A.; Di Biase, M. Coronary artery ectasia is related to coronary slow flow and inflammatory activation. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, S. Neutrophil activation and neutrophil derived neutrophil extracellular trap formation in patients with coronary artery ectasia. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keser, A.; Özbek, K.; Ulucan, Ş.; Katlandur, H.; Bilgi, M.; Özdil, H. Relationship between red cell distribution width levels and severity of coronary artery ectasia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Özbek, K.; Katlandur, H.; Keser, A.; Ulucan, Ş.; Özdil, H.; Ülgen, M.S. Is there a relationship between mean platelet volume and the severity of coronary ectasia? Biomed. Res. 2016, 27, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, T.; Kurt, M.; Ayhan, E.; Uyarel, H.; Tanboga, I.H.; Korkmaz, A.F.; Sevimli, S. Relation of red cell distribution width with presence and severity of coronary artery ectasia. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2012, 18, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.; Neupane, B.; Proskuriakova, E.; Jada, K.; Kakieu Djossi, S.; Mostafa, J.A. Pharmacologic Management of Coronary Artery Ectasia. Cureus 2021, 13, e17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Danielson, E.; Fonseca, F.A.H.; Genest, J.; Gotto, A.M.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Glynn, R.J. Rosuvastatin to Prevent Vascular Events in Men and Women with Elevated C-Reactive Protein. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrachatis, D.A.; Giannopoulos, G.V.; Deftereos, S.G. Colchicine administered early in acute myocardial infarction: Ready, set … go? Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidorf, S.M.; Fiolet, A.T.L.; Mosterd, A.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Schut, A.; Opstal, T.S.J.; Thompson, P.L. Colchicine in Patients with Chronic Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Glynn, R.J. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rola, P.; Włodarczak, A.; Barycki, M.; Doroszko, A. Use of the Shock Wave Therapy in Basic Research and Clinical Applications-From Bench to Bedsite. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola, P.; Doroszko, A.; Derkacz, A. The Use of Low-Level Energy Laser Radiation in Basic and Clinical Research. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 23, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawsara, A.; Núñez Gil, I.J.; Alqahtani, F.; Moreland, J.; Rihal, C.S.; Alkhouli, M. Management of Coronary Artery Aneurysms. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markis, J.E.; Joffe, C.D.; Cohn, P.F.; Feen, D.J.; Herman, M.V.; Gorlin, R. Clinical significance of coronary arterial ectasia. Am. J. Cardiol. 1976, 37, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.P.; Chuang, N.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Hsu, C.A.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, J.K.; Wu, C.K.; Hwang, J.J.; Lin, L.Y.; et al. Genome-wide methylation profiles in coronary artery ectasia. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yin, D.; Song, W.; Dou, K. Diffuse coronary artery dilation predicted worse long-term outcomes in patients with coronary artery Ectasia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 319, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, R. Underlying factors relating to acute myocardial infarction for coronary artery ectasia patients. Medicine 2020, 99, e21983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrachatis, D.A.; Papathanasiou, K.A.; Kazantzis, D.; Sanz-Sánchez, J.; Giotaki, S.G.; Raisakis, K.; Kaoukis, A.; Kossyvakis, C.; Deftereos, G.; Reimers, B.; et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Ectasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051026
Vrachatis DA, Papathanasiou KA, Kazantzis D, Sanz-Sánchez J, Giotaki SG, Raisakis K, Kaoukis A, Kossyvakis C, Deftereos G, Reimers B, et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Ectasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051026
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrachatis, Dimitrios A., Konstantinos A. Papathanasiou, Dimitrios Kazantzis, Jorge Sanz-Sánchez, Sotiria G. Giotaki, Konstantinos Raisakis, Andreas Kaoukis, Charalampos Kossyvakis, Gerasimos Deftereos, Bernhard Reimers, and et al. 2022. "Inflammatory Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Ectasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051026
APA StyleVrachatis, D. A., Papathanasiou, K. A., Kazantzis, D., Sanz-Sánchez, J., Giotaki, S. G., Raisakis, K., Kaoukis, A., Kossyvakis, C., Deftereos, G., Reimers, B., Avramides, D., Siasos, G., Cleman, M., Giannopoulos, G., Lansky, A., & Deftereos, S. (2022). Inflammatory Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Ectasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051026







