In Vivo Super-Resolution Cardiac Diffusion Tensor MRI: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
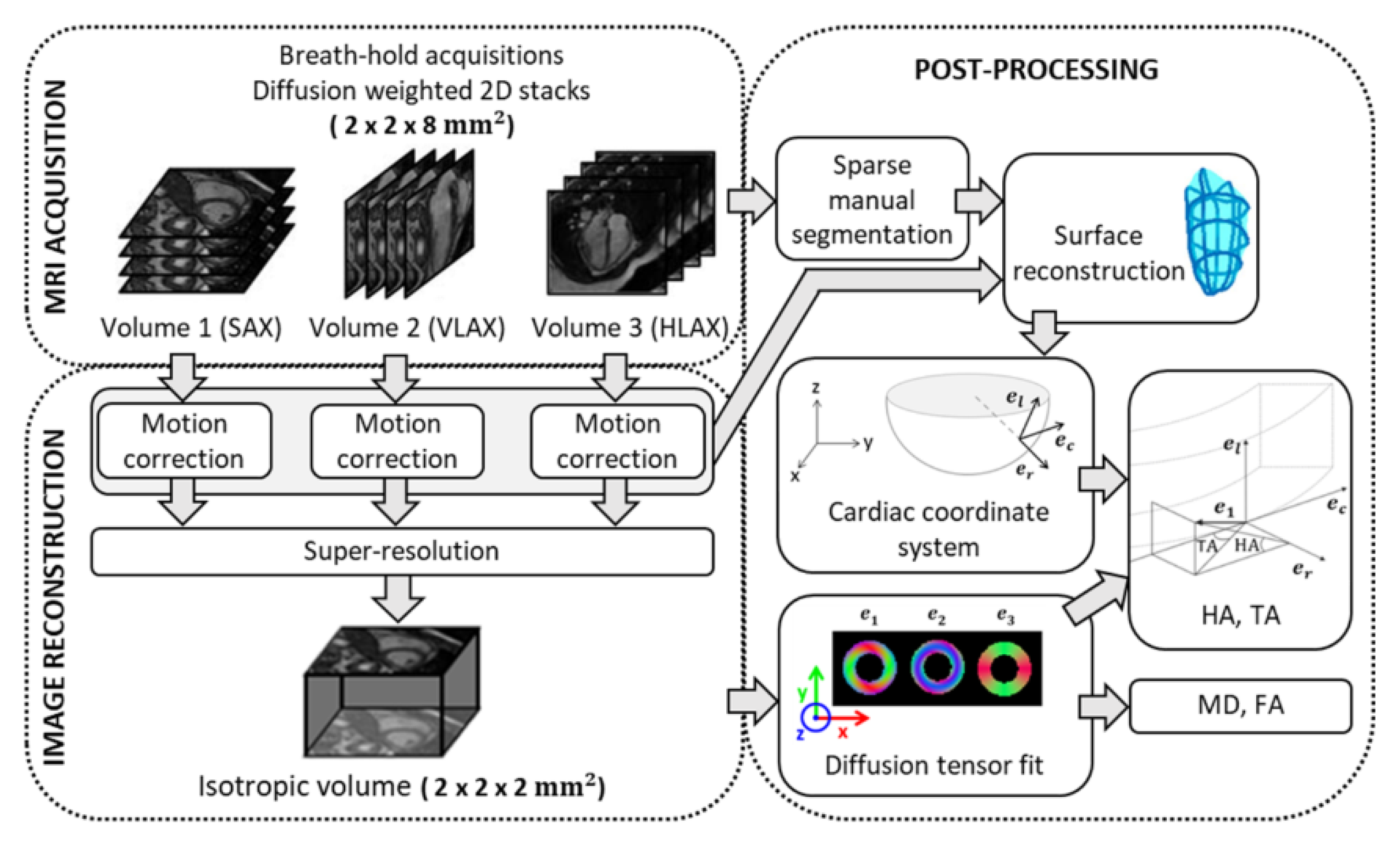
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Super-Resolution Reconstruction
2.2. Numerical Simulations
2.2.1. Numerical Phantom
2.2.2. Data Analysis
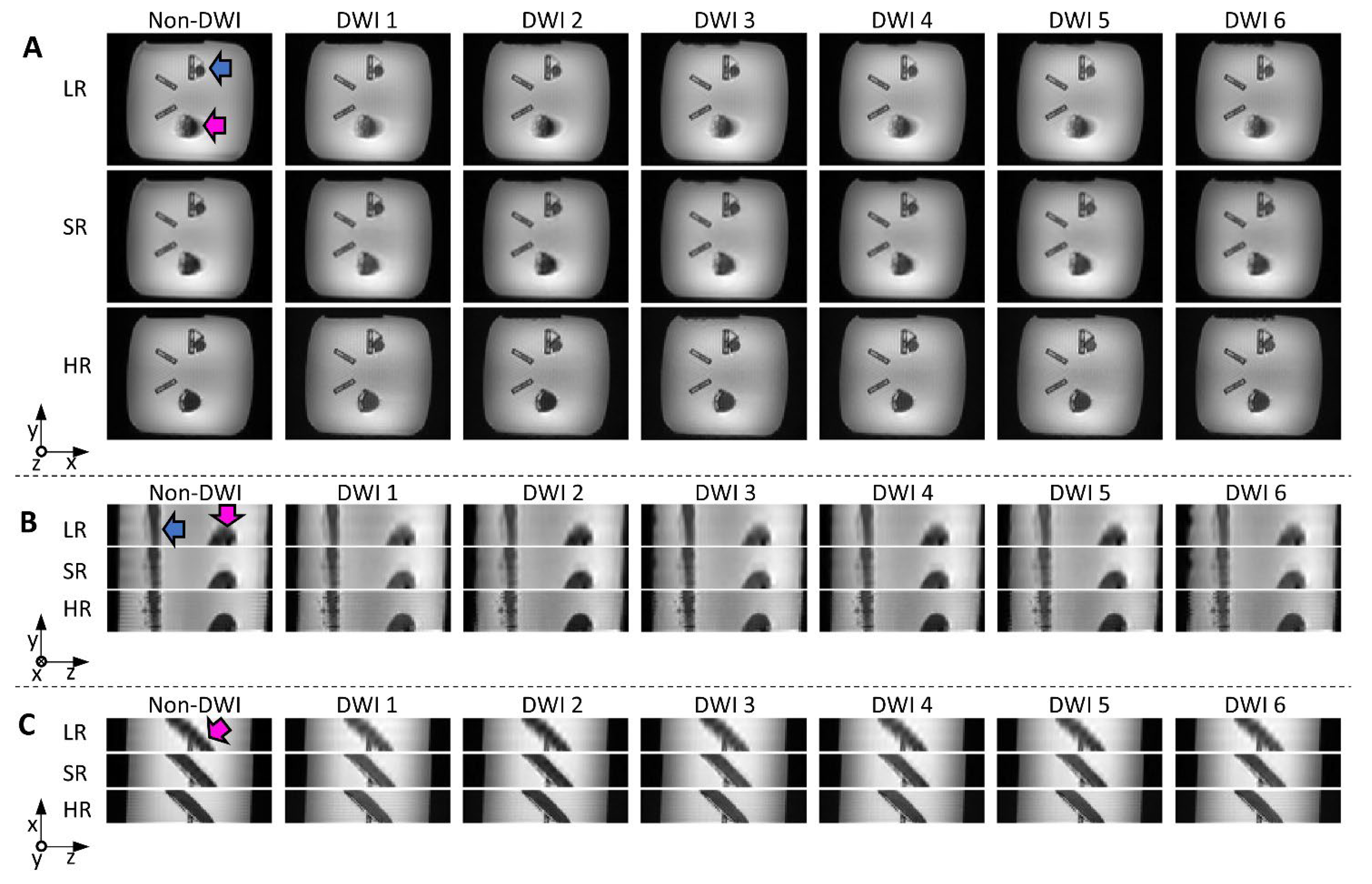
2.3. Physical Phantom
2.3.1. Setup and Data Acquisition
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
2.4. In Vivo Data
2.4.1. Data Acquisition
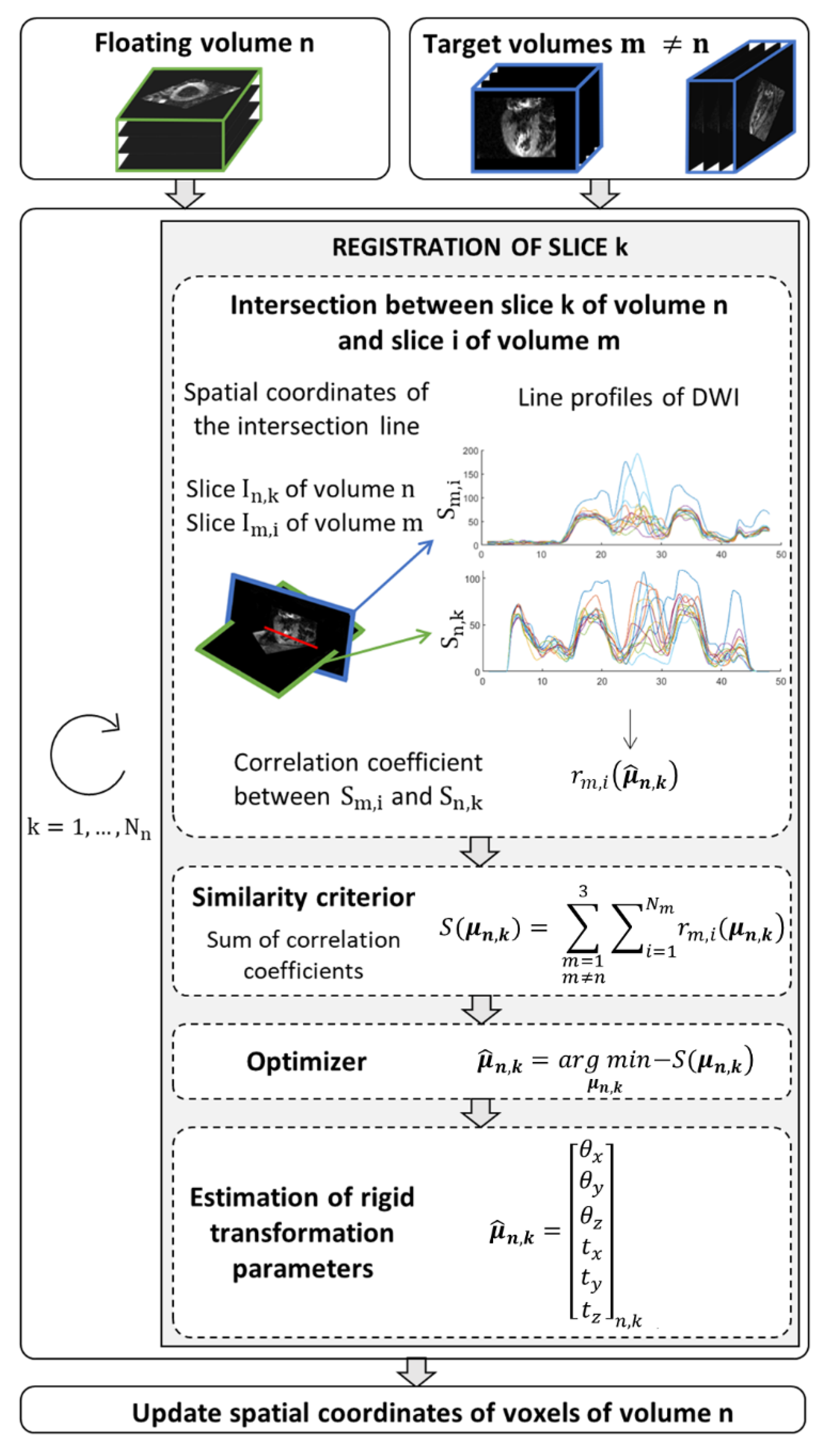
2.4.2. Motion Correction Strategy
2.4.3. Post-Processing
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Numerical Phantom
3.2. Physical Phantom
3.3. In Vivo Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aumentado-Armstrong, T.; Kadivar, A.; Savadjiev, P.; Zucker, S.W.; Siddiqi, K. Conduction in the Heart Wall: Helicoidal Fibers Minimize Diffusion Bias. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stephenson, R.S.; Atkinson, A.; Kottas, P.; Perde, F.; Jafarzadeh, F.; Bateman, M.; Iaizzo, P.A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Anderson, R.H.; et al. High Resolution 3-Dimensional Imaging of the Human Cardiac Conduction System from Microanatomy to Mathematical Modeling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielles-Vallespin, S.; Khalique, Z.; Ferreira, P.F.; de Silva, R.; Scott, A.D.; Kilner, P.; McGill, L.-A.; Giannakidis, A.; Gatehouse, P.D.; Ennis, D.; et al. Assessment of Myocardial Microstructural Dynamics by In Vivo Diffusion Tensor Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielles-Vallespin, S.; Scott, A.; Ferreira, P.; Khalique, Z.; Pennell, D.; Firmin, D. Cardiac Diffusion: Technique and Practical Applications. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 52, 348–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, P.; Beg, M.F.; Miller, M.I.; Winslow, R.L. Measuring and Mapping Cardiac Fiber and Laminar Architecture Using Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1047, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Song, S.-K.; Liu, W.; McLean, M.; Allen, J.S.; Tan, J.; Wickline, S.A.; Yu, X. Remodeling of Cardiac Fiber Structure after Infarction in Rats Quantified with Diffusion Tensor MRI. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H946–H954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sosnovik, D.E.; Wang, R.; Dai, G.; Wang, T.; Aikawa, E.; Novikov, M.; Rosenzweig, A.; Gilbert, R.J.; Wedeen, V.J. Diffusion Spectrum MRI Tractography Reveals the Presence of a Complex Network of Residual Myofibers in Infarcted Myocardium. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ennis, D.B.; Kindlmann, G. Orthogonal Tensor Invariants and the Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Images. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 55, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, I.; McClymont, D.; Zdora, M.-C.; Whittington, H.J.; Davidoiu, V.; Lee, J.; Lygate, C.A.; Rau, C.; Zanette, I.; Schneider, J.E. Validation of Diffusion Tensor MRI Measurements of Cardiac Microstructure with Structure Tensor Synchrotron Radiation Imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2017, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoeck, C.T.; Kalinowska, A.; von Deuster, C.; Harmer, J.; Chan, R.W.; Niemann, M.; Manka, R.; Atkinson, D.; Sosnovik, D.E.; Mekkaoui, C.; et al. Dual-Phase Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging with Strain Correction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamper, U.; Boesiger, P.; Kozerke, S. Diffusion Imaging of the in Vivo Heart Using Spin Echoes–Considerations on Bulk Motion Sensitivity. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, E.; Wu, H.H.; Ennis, D.B. Convex Optimized Diffusion Encoding (CODE) Gradient Waveforms for Minimum Echo Time and Bulk Motion–Compensated Diffusion-Weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welsh, C.L.; DiBella, E.V.R.; Hsu, E.W. Higher-Order Motion-Compensation for In Vivo Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Rats. IEEE Transac. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoeck, C.T.; von Deuster, C.; Genet, M.; Atkinson, D. Kozerke Sebastian Second-order Motion-compensated Spin Echo Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Human Heart. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, C.; Fan, Z.; Xie, Y.; Pang, J.; Speier, P.; Bi, X.; Kobashigawa, J.; Li, D. In Vivo Diffusion-Tensor MRI of the Human Heart on a 3 Tesla Clinical Scanner: An Optimized Second Order (M2) Motion Compensated Diffusion-Preparation Approach. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielles-Vallespin, S.; Mekkaoui, C.; Gatehouse, P.; Reese, T.G.; Keegan, J.; Ferreira, P.F.; Collins, S.; Speier, P.; Feiweier, T.; Silva, R.; et al. In Vivo Diffusion Tensor MRI of the Human Heart: Reproducibility of Breath-hold and Navigator-based Approaches. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Deuster, C.; Stoeck, C.T.; Genet, M.; Atkinson, D.; Kozerke, S. Spin Echo versus Stimulated Echo Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the in Vivo Human Heart. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkaoui, C.; Reese, T.G.; Jackowski, M.P.; Cauley, S.F.; Setsompop, K.; Bhat, H.; Sosnovik, D.E. Diffusion Tractography of the Entire Left Ventricle by Using Free-Breathing Accelerated Simultaneous Multisection Imaging. Radiology 2016, 282, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulin, K.; Croisille, P.; Feiweier, T.; Delattre, B.M.A.; Wei, H.; Robert, B.; Beuf, O.; Viallon, M. In Vivo Free-Breathing DTI and IVIM of the Whole Human Heart Using a Real-Time Slice-Followed SE-EPI Navigator-Based Sequence: A Reproducibility Study in Healthy Volunteers. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.Z.; Tunnicliffe, E.M.; Frost, R.; Koopmans, P.J.; Tyler, D.J.; Robson, M.D. Accelerated Human Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging Using Simultaneous Multislice Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.; Marques, P.; Alves, V.; Sousa, N. A Hitchhiker’s Guide to Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poot, D.H.J.; Jeurissen, B.; Bastiaensen, Y.; Veraart, J.; Hecke, W.V.; Parizel, P.M.; Sijbers, J. Super-Resolution for Multislice Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenkiste, G.V.; Jeurissen, B.; Veraart, J.; den Dekker, A.J.; Parizel, P.M.; Poot, D.H.J.; Sijbers, J. Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Diffusion Parameters from Diffusion-Weighted Images with Different Slice Orientations. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, I.; McClymont, D.; Carruth, E.; Omens, J.; McCulloch, A.; Schneider, J.E. Improved Compressed Sensing and Super-Resolution of Cardiac Diffusion MRI with Structure-Guided Total Variation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Habas, P.A.; Rousseau, F.; Glenn, O.A.; Barkovich, A.J.; Studholme, C. Intersection Based Motion Correction of Multislice MRI for 3-D in Utero Fetal Brain Image Formation. IEEE Transac. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plenge, E.; Poot, D.H.J.; Bernsen, M.; Kotek, G.; Houston, G.; Wielopolski, P.; van der Weerd, L.; Niessen, W.J.; Meijering, E. Super-Resolution Methods in MRI: Can They Improve the Trade-off between Resolution, Signal-to-Noise Ratio, and Acquisition Time? Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, A.; Estroff, J.A.; Warfield, S.K. Robust Super-Resolution Volume Reconstruction From Slice Acquisitions: Application to Fetal Brain MRI. IEEE Transac. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prévost, C.; Usevich, K.; Comon, P.; Brie, D. Hyperspectral Super-Resolution With Coupled Tucker Approximation: Recoverability and SVD-Based Algorithms. IEEE Transac. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odille, F.; Bustin, A.; Liu, S.; Chen, B.; Vuissoz, P.-A.; Felblinger, J.; Bonnemains, L. Isotropic 3D Cardiac Cine MRI Allows Efficient Sparse Segmentation Strategies Based on 3D Surface Reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Med 2018, 79, 2665–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, A.; Ferry, P.; Codreanu, A.; Beaumont, M.; Liu, S.; Burschka, D.; Felblinger, J.; Brau, A.C.S.; Menini, A.; Odille, F. Impact of Denoising on Precision and Accuracy of Saturation-Recovery-Based Myocardial T1 Mapping. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbany, M.; Bustin, A.; Poujol, J.; Thomassin-Naggara, I.; Felblinger, J.; Vuissoz, P.-A.; Odille, F. One-Millimeter Isotropic Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging: Evaluation of a Superresolution Strategy in Terms of Signal-to-Noise Ratio, Sharpness and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2588–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.L.; Wedeen, V.J.; Weisskoff, R.M.; Rosen, B.R. White Matter Tract Visualization by Echo-Planar MRI. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Meeting of SMRM, ISMRM, New York, NY, USA, 14–20 August 1993; Volume 289. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhani, M.; Sappa, A.D. Implicit B-Spline Fitting Using the 3L Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 893–896. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, P.G.; Atkinson, D.; Hill, D.L.G.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Anisotropic Noise Propagation in Diffusion Tensor MRI Sampling Schemes. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 49, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.K.; Cercignani, M. Twenty-Five Pitfalls in the Analysis of Diffusion MRI Data. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, C.A.; Lebel, R.M.; Wilman, A.H.; Beaulieu, C. The Effect of Concomitant Gradient Fields on Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudela, R.; Muñoz-Moreno, E.; López-Gil, X.; Soria, G. Effects of Orientation and Anisometry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisitions on Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Structural Connectomes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, A.D.; Nielles-Vallespin, S.; Ferreira, P.F.; Khalique, Z.; Gatehouse, P.D.; Kilner, P.; Pennell, D.J.; Firmin, D.N. An In-Vivo Comparison of Stimulated-Echo and Motion Compensated Spin-Echo Sequences for 3 T Diffusion Tensor Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance at Multiple Cardiac Phases. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2018, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edelman, R.R.; Gaa, J.; Wedeen, V.J.; Loh, E.; Hare, J.M.; Prasad, P.; Li, W. In Vivo Measurement of Water Diffusion in the Human Heart. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994, 32, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Reese, T.G.; Tseng, W.-Y.I.; Wedeen, V.J. Cardiac Diffusion MRI without Motion Effects. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 48, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Dataset | SNR | MD | FA | HA Mean (°) | HA Min (°) | HA Max (°) | TA Mean (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT | - | - | 42.07 | 34.57 | 49.57 | 0 | |
| HR 30dir | 70.8 | 1.69 ± 0.11 | 0.31 ± 0.06 | 42.40 ± 0.56 | 33.71 ± 5.51 | 49.64 ± 1.70 | −2.03 ± 3.35 |
| HR | 64.8 | 1.71 ± 0.09 | 0.34 ± 0.07 | 43.21 ± 1.26 | 31.76 ± 4.10 | 52.19 ± 3.05 | −0.15 ± 2.67 |
| LR-Tra3 | 68.8 | 1.72 ± 0.21 | 0.32 ± 0.14 | 44.07 ± 1.06 | 36.96 ± 2.15 | 52.05 ± 2.45 | −0.97 ± 1.98 |
| SR | 81.5 | 1.68 ± 0.12 | 0.35 ± 0.09 | 41.53 ± 1.10 | 31.90 ± 3.31 | 49.48 ± 2.36 | −1.17 ± 2.34 |
| LR-Tra | 67.4 | 1.73 ± 0.21 | 0.32 ± 0.14 | 44.34 ± 1.34 | 34.75 ± 1.83 | 52.28 ± 2.38 | −1.34 ± 1.89 |
| LR-Coro | 76.8 | 1.72 ± 0.24 | 0.31 ± 0.15 | 39.93 ± 3.16 | 26.81 ± 7.13 | 49.46 ± 2.76 | −0.25 ± 3.11 |
| LR-Sag | 75.7 | 1.72 ± 0.20 | 0.35 ± 0.14 | 40.28 ± 2.85 | 28.01 ± 4.59 | 52.71 ± 3.84 | −1.72 ± 3.57 |
| Dataset | TA (°) | FA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | −0.993 ± 0.007 | −2.22 ± 24.13 | 1.35 ± 0.28 | 0.35 ± 0.14 |
| SAX | −0.873 ± 0.010 | −0.15 ± 32.39 | 1.50 ± 0.43 | 0.46 ± 0.19 |
| HLAX | −0.643 ± 0.013 | −2.80 ± 32.81 | 1.40 ± 0.43 | 0.42 ± 0.18 |
| VLAX | −0.635 ± 0.013 | −4.04 ± 31.52 | 1.30 ± 0.42 | 0.45 ± 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Bars, A.-L.; Moulin, K.; Ennis, D.B.; Felblinger, J.; Chen, B.; Odille, F. In Vivo Super-Resolution Cardiac Diffusion Tensor MRI: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040877
Le Bars A-L, Moulin K, Ennis DB, Felblinger J, Chen B, Odille F. In Vivo Super-Resolution Cardiac Diffusion Tensor MRI: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(4):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Bars, Anne-Lise, Kevin Moulin, Daniel B. Ennis, Jacques Felblinger, Bailiang Chen, and Freddy Odille. 2022. "In Vivo Super-Resolution Cardiac Diffusion Tensor MRI: A Feasibility Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 4: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040877
APA StyleLe Bars, A.-L., Moulin, K., Ennis, D. B., Felblinger, J., Chen, B., & Odille, F. (2022). In Vivo Super-Resolution Cardiac Diffusion Tensor MRI: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics, 12(4), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040877






