Prenatal Diagnosis and Outcome of Umbilical–Portal–Systemic Venous Shunts: Experience of a Tertiary Center and Proposal for a New Complex Type
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables
2.4. Methods of Assessment
3. Results
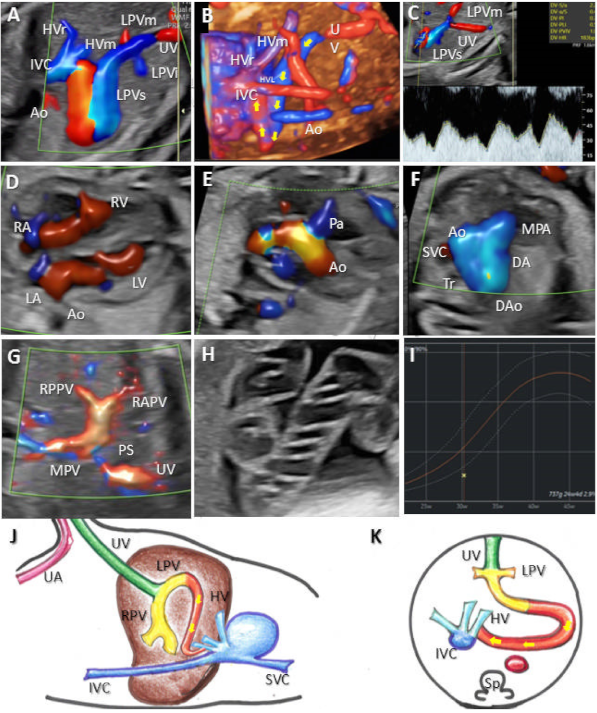
3.1. Umbilical–Systemic Shunts (USS, Type I)
3.2. Ductus Venosus–Systemic Shunts (DVSS, Type II)
3.3. Portal–Systemic Shunts (IHPSS, Type III)
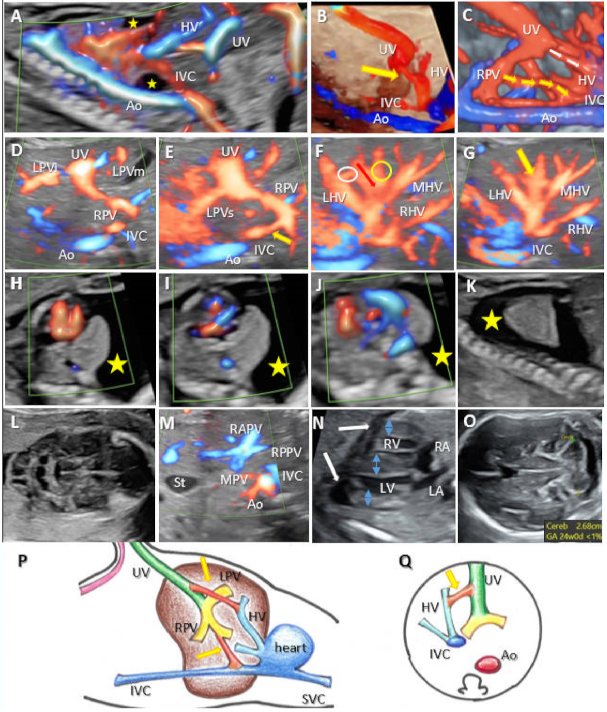
3.4. Complex Variants with Multiple Shunts (A Newly Described Category of UPSVS, Type IV)
3.5. Portal Venous System Characteristics in Relation to the Outcome
4. Discussion
4.1. Epidemiological Considerations
4.2. Early Detection
4.3. The Outcomes of UPSVS Types—Associated Structural Anomalies
4.4. Portal Venous System Implications
4.5. The Outcome of UPSVS Types—FGR
4.6. The Outcome of UPSVS Types—Genetics
4.7. Complex Variants with Multiple Shunts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fasouliotis, S.J.; Achiron, R.; Kivilevitch, Z.; Yagel, S. The human fetal venous system: Normal embryologic, anatomic, and physiologic characteristics and developmental abnormalities. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2002, 21, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stringer, M.D. The clinical anatomy of congenital portosystemic venous shunts. Clin.Anat. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Clin. Anat. Br. Assoc. Clin. Anatomists. 2008, 21, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioli, L.; Alberti, D.; Olivetti, L.; Rigamonti, W.; Codazzi, F.; Matricardi, L.; Fugazzola, C.; Chiesa, A. Congenital absence of portal vein with nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Eur. Radiol. 2000, 10, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, Y.; Hashizume, K.; Kitano, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Motoi, T.; Tange, T. Congenital extrahepatic portocaval shunt (Abernethy type 2), huge liver mass, and patent ductus arteriosus—A case report of its rare clinical presentation in a young girl. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003, 38, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.P.; Yoo, S.J.; Babyn, P.S. Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Pediatr. Radiol. 2003, 33, 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, M.; Yokoya, S.; Hachiya, Y.; Hachiya, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Hoshino, K.; Saji, T. Two hyperandrogenic adolescent girls with congenital portosystemic shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2001, 160, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, S.; Kitayama, Y.; Usui, N.; Kuroda, S.; Nose, K.; Sawai, T.; Okada, A. Patent ductus venosus with a hypoplastic intrahepatic portal system presenting intrapulmonary shunt: A case treated with banding of the ductus venosus. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2000, 35, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier, S.; Delarue, A.; Rouault, F.; Roman, C.; Bre´aud, J.; Petit, P. Congenital portocaval fistula associated with hepatopulmonary syndrome: Ligation vs liver transplantation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Mawatari, H.; Mizoguchi, N.; Eguchi, T.; Sakura, N. Clinical features and outcome of eight infants with intrahepatic porto-venous shunts detected in neonatal screening for galactosaemia. Acta. Paediatr. Oslo. Nor. 1992 1998, 87, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Tajima, G.; Bahagia, A.D.; Sakamoto, A.; Ono, H.; Sakura, N.; Naito, K.; Hamakawa, M.; Yoshii, C.; Kubota, M.; et al. Differential diagnosis of neonatal mild hypergalactosaemia detected by mass screening: Clinical significance of portal vein imaging. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2004, 27, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeggi, E.T.; Fouron, J.C.; Hornberger, L.K.; Proulx, F.; Oberhänsli, I.; Yoo, S.J.; Fermont, L. Agenesis of the ductus venosus that is associated with extrahepatic umbilical vein drainage: Prenatal features and clinical outcome. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2002, 187, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perles, Z.; Nir, A.; Nadjari, M.; Ergaz, Z.; Raas-Rothschild, A.; Rein, A.J. Absent ductus venosus in the fetus: Review of the literature and first report of direct umbilical venous drainage to the coronary sinus. Fetal. Diagn. Ther. 2003, 18, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, C.; Kamil, D.; Geipel, A.; Kohl, T.; Knöpfle, G.; Hansmann, M.; Gembruch, U. Absence of ductus venosus-importance of umbilical venous drainage site. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2006, 28, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acherman, R.J.; Evans, W.N.; Galindo, A.; Collazos, J.C.; Rothman, A.; Mayman, G.A.; Luna, C.F.; Rollins, R.; Kip, K.T.; Berthody, D.P.; et al. Diagnosis of absent ductus venosus in a population referred for fetal echocardiography: Association with a persistent portosystemic shunt requiring postnatal device occlusion. J. Ultrasound Med. 2007, 26, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, O.; Valsky, D.V.; Messing, B.; Cohen, S.M.; Lipschuetz, M.; Yagel, S. Shunt diameter in agenesis of the ductus venosus with extrahepatic portosystemic shunt impacts on prognosis. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstaetter, C.; Plath, H.; Hansmann, M. Prenatal diagnosis of abnormalities of the fetal venous system. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2000, 15, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokollik, C.; Bandsma, R.H.J.; Gana, J.C.; van den Heuvel, M.; Ling, S.C. Congenital portosystemic shunt: Characterization of a multisystem disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, B.; Lachaux, A.; Gottrand, F.; De Smet, S. Prenatally diagnosed congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2018, 31, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiron, R.; Gindes, L.; Kivilevitch, Z.; Kuint, J.; Kidron, D.; Boyanover, Y.; Yakobson, J.; Heggesh, J. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital agenesis of the fetal portal venous system. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2009, 34, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiron, R.; Kivilevitch, Z. Fetal umbilical-portal-systemic venous shunt: In-utero classification and clinical significance. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2016, 47, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Tao, G.; Cong, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Z. Prenatal sonographic characteristics and postnatal outcomes of umbilical-portal-systemic venous shunts under the new in-utero classification: A retrospective study. Medicine 2019, 98, e14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagel, S.; Kivilevitch, Z.; Cohen, S.M.; Valsky, D.V.; Messing, B.; Shen, O.; Achiron, R. The fetal venous system, part I: Normal embryology, anatomy, hemodynamics, ultrasound evaluation and Doppler investigation. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2010, 35, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagel, S.; Cohen, S.M.; Valsky, D.V.; Shen, O.; Lipschuetz, M.; Messing, B. Systematic examination of the fetal abdominal precordial veins: A cohort study. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2015, 45, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salomon, L.J.; Alfirevic, Z.; Bilardo, C.M.; Chalouhi, G.E.; Ghi, T.; Kagan, K.O.; Lau, T.K.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Raine-Fenning, N.J.; Stirnemann, J.; et al. ISUOG practice guidelines: Performance of first-trimester fetal ultrasound scan. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Salomon, L.J.; Alfirevic, Z.; Berghella, V.; Bilardo, C.; Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Johnsen, S.L.; Kalache, K.; Leung, K.Y.; Malinger, G.; Munoz, H.; et al. Practice guidelines for performance of the routine mid-trimester fetal ultrasound scan. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, D.G.; Cara, M.L.; Tudorache, S.; Antsaklis, P.; Novac, L.V.; Antsaklis, A.; Cernea, N. Agenesis of ductus venosus in sequential first and second trimester screening. Prenat. Diagn. 2014, 34, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitzelmann, R.; Forster, I.; Willi, U.V. Hypergalactosaemia in a newborn: Self-limiting intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1997, 156, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, R.D.; Ruican, D.; Zorilă, G.-L.; Istrate-Ofiţeru, A.-M.; Badiu, A.M.; Iliescu, D.G. Feasibility of Fetal Portal Venous System Ultrasound Assessment at the FT Anomaly Scan. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, P.; Marasini, M.; Caruso, G.; Lituania, M.; Marzullo, A.; Volpe, G.; Gentile, M. Prenatal diagnosis of ductus venosus agenesis and its association with cytogenetic/congenital anomalies. Prenat. Diagn. 2002, 22, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, R.S.; Winsberg, F.; Stancato-Pasik, A.; Sterling, K.M. Color Doppler sonography of vascular malformations of the liver. J. Ultrasound Med. 1993, 12, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, M.; Ohhama, Y.; Nishi, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujita, S.; Take, H.; Adachi, M.; Tachibana, K.; Aida, N.; Kato, K.; et al. Congenital absence of the portal vein and role of liver transplantation in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2001, 36, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, F.; Blanc, T.; Gauthier, F.; Abella, S.F.; Branchereau, S. Congenital portosystemic vascular malformations. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 21, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Muneuchi, J.; Ihara, K.; Yuge, T.; Kanaya, Y.; Yamaki, S.; Hara, T. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with congenital portosystemic venous shunt: A previously unrecognized association. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e892–e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautz, T.B.; Tantemsapya, N.; Rowell, E.; Superina, R.A. Management and classification of type II congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, O.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Branchereau, S.; Pariente, D.; Gauthier, F.; Jacquemin, E. Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Recognition, evaluation, and management. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kivilevitch, Z.; Gindes, L.; Deutsch, H.; Achiron, R. In-utero evaluation of the fetal umbilical-portal venous system: Two- and three-dimensional ultrasonic study. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2009, 34, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorincour, G.; Droullé, P.; Guibaud, L. Prenatal diagnosis of umbilicoportosystemic shunts: Report of 11 cases and review of the literature. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Chiaie, L.; Neuberger, P.; Von Kalle, T. Congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: Prenatal diagnosis and possible influence on fetal growth. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2008, 32, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wu, H.; Zhu, L.; Cong, X.; Li, Q.; Tang, F.; Tao, G. Prenatal Ultrasound Analysis of Umbilical-Portal-Systemic Venous Shunts Concurrent with Trisomy 21. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.P.; Hudgins, L.; Hannibal, M. Kabuki Syndrome; 1 September 2011 [updated 15 July 2021]; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Mirzaa, G.M., Amemiya, A., Eds.; GeneReviews® [Internet]; University of Washington: Seattle, WC, USA, 2011; pp. 1993–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Iliescu, D.G.; Tudorache, S.; Cernea, D. Agenesis of ductus venosus with complex intra- and extrahepatic umbilical drainage. J. Obs. Gynaecol Res. 2014, 40, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, L.F.; Sherer, D.M.; Romero, R.; Silva, M.; Amundson, G.M.; Treadwell, M.C. Prenatal sonographic findings of agenesis of the right and left portal veins and associated intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. J. Ultrasound Med. 1995, 14, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
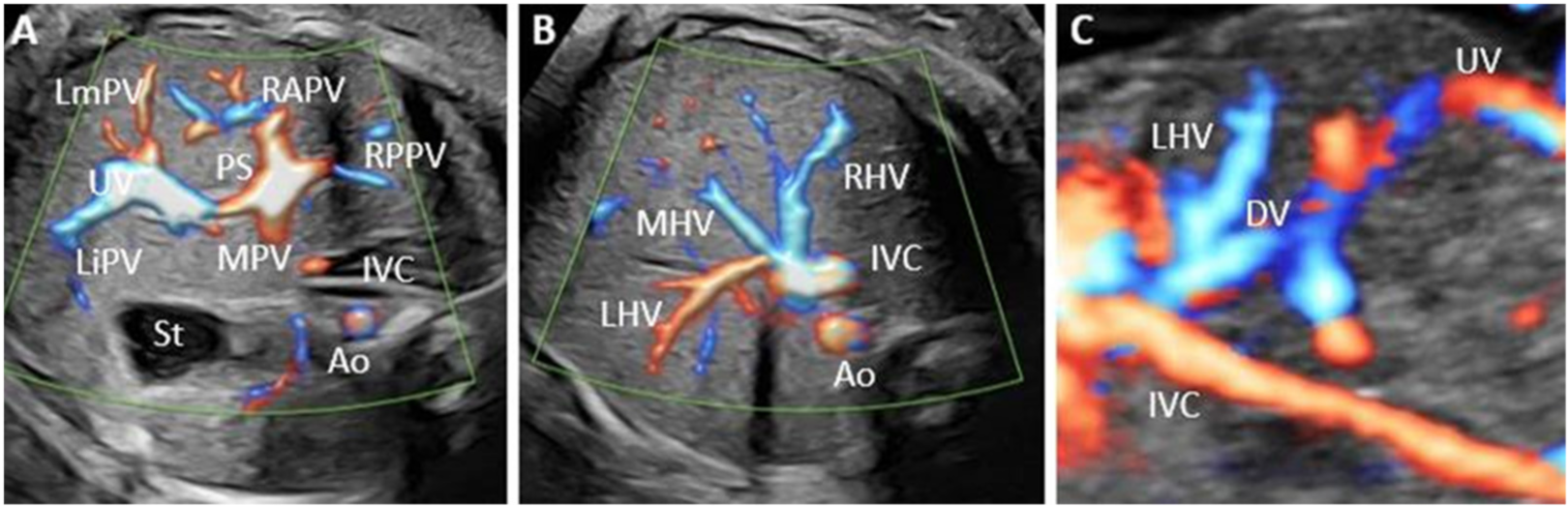
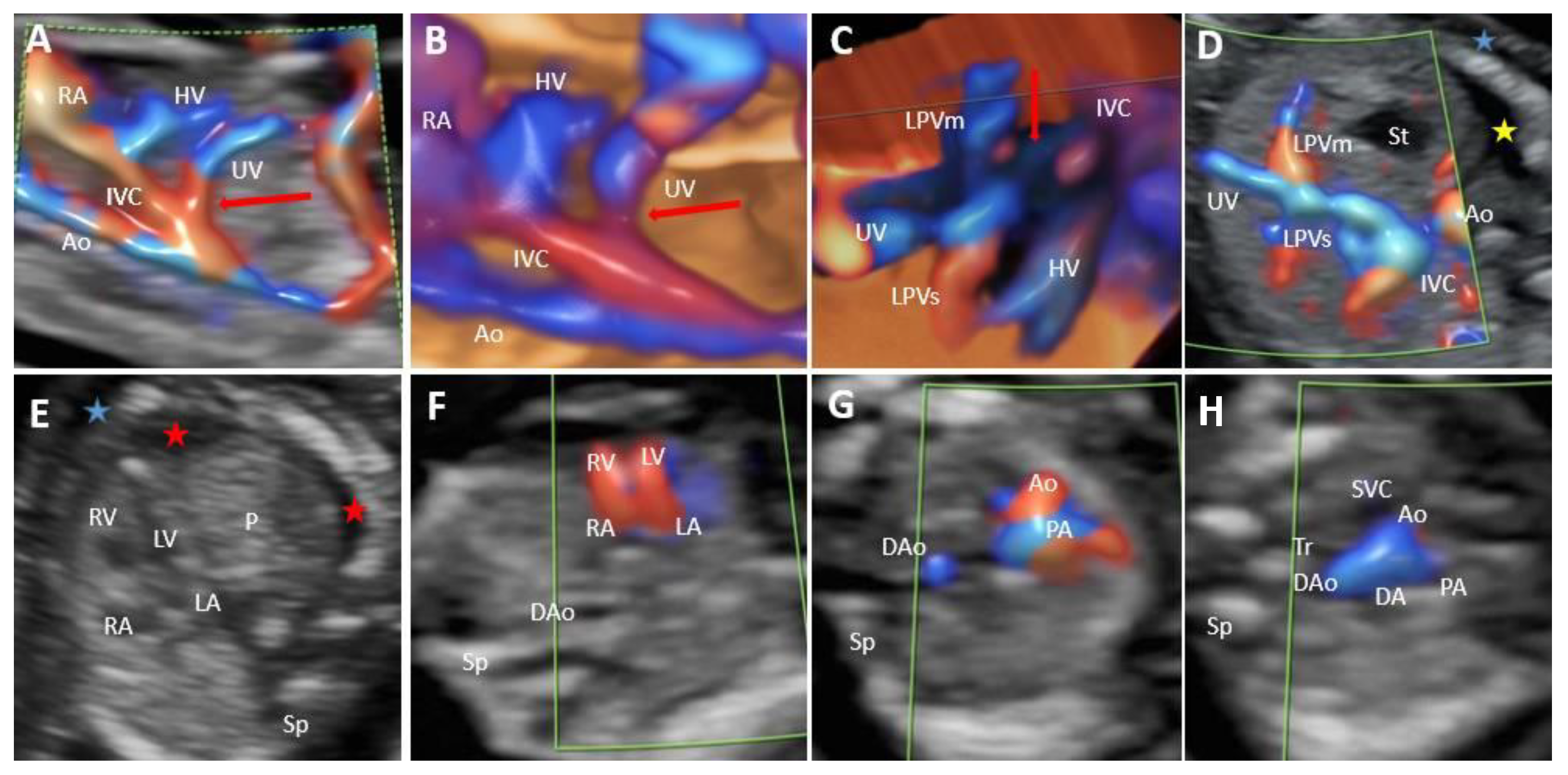
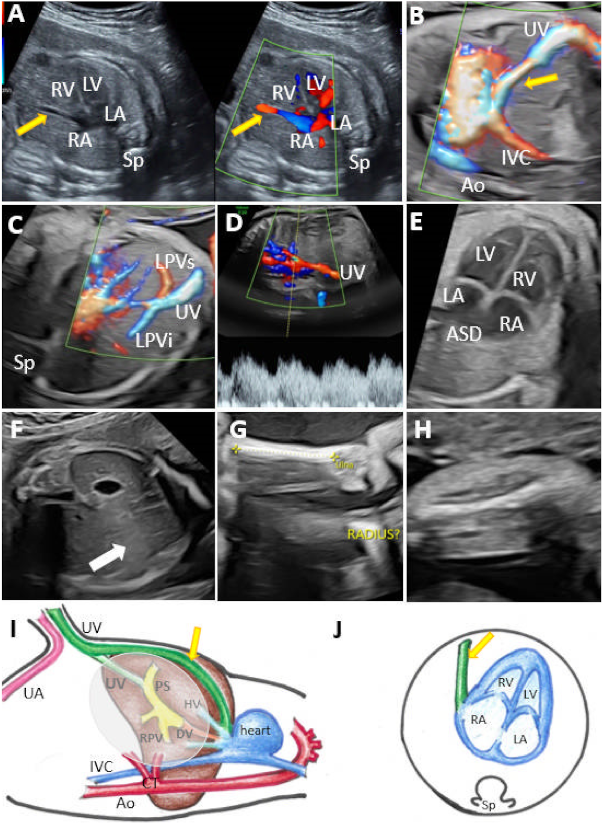
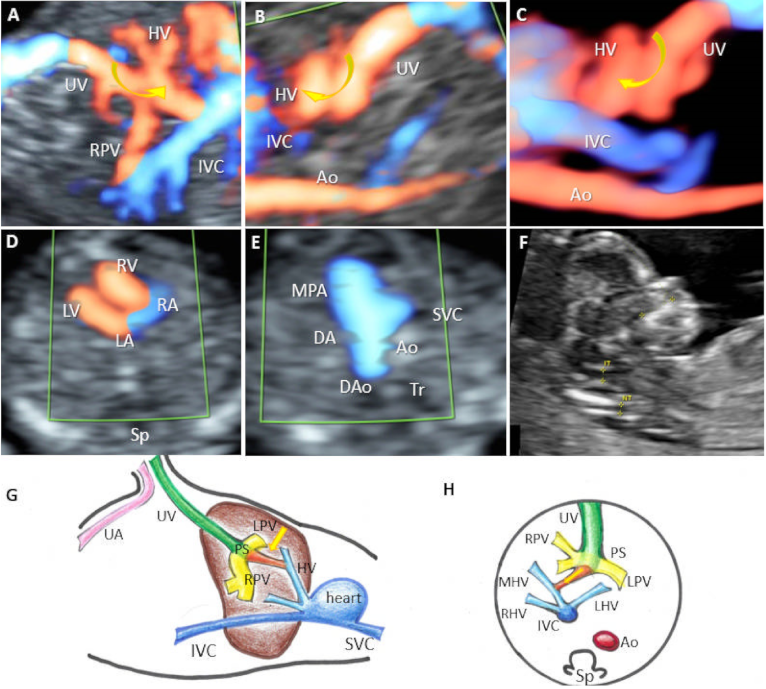
| Case | GA (Weeks) | Type of Shunt | Drainage | DV | PVS | Additional Sonographic Findings | Outcome | Intrauterine Genetic Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current study 2017–2022 | ||||||||
| 1 | 13 | I | IVC | ADV | PPVSA | Hydrops | TOP | 45X |
| 2 | 13 | I | IVC | ADV | TPVSA | - | TOP | N |
| 3 | 24 | I | Cardiac | ADV | PPVSA | Bilateral short humerus Unilateral absence of the radius Syndactyly Gallbladder agenesis ASD | NO FOLLOW-UP | T21 |
| 4 | 26 | I | Cardiac | ADV | TPVSA | Persistent left superior vena cava esophageal atresia | Growth and motor retardation at 6 months | Invasive genetics declined |
| 5 | 16 | I | Cardiac | ADV | TPVSA | Hypoplastic left heart syndrome DORV; nasal hypoplasia | IUFD | T21 |
| 6 | 16 | I | HV | ADV | PPVSA | - | NO FOLLOW-UP | Invasive genetics declined |
| 7 | 15 | I | HV | ADV | TPVSA | Aorto umbilical fistula Hygroma | TOP | T21 |
| 8 | 13 | I | IVC | ADV | TPVSA | Hydrops | IUFD | Normal FISH |
| 9 | 15 | I | IVC | ADV | TPVSA | Hydrops Dextrocardia Aorto umbilical fistula Cheilognathopalatoschisis Ventriculomegaly | IUFD | Translocation 46,XX,add(12)(q24) |
| 10 | 20 | I | IVC | ADV | TPVSA | Aberrant right subclavian artery Small stomach | TOP | T 21 |
| 11 | 13 | II | HV | Short DV-like | N | - | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | Invasive genetics declined |
| 12 | 20 | II | HV | Short DV-like | N | Interrupted inferior vena cava with hemizygous continuation | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | N |
| 13 | 14 | II | HV | Short DV-like | N | Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Asymmetric diaphragm Club foot | TOP | N |
| 14 | 13 | II | IVC | Short DV-like | N | - | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | Invasive genetics declined |
| 16 | 30 | IIIa | HV | ADV | N | FGR Hyper-coiled umbilical cord | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | N |
| 17 | 28 | IIIa | HV | ADV | PPVSA | FGR Duodenal atresia Esophageal atresia Right aortic arch | Growth and motor retardation at 6 months | mos 47, XY, +mar [15]/46, XY [38] |
| 18 | 18 | IV | Complex drainage HV + IVC | short DV | N | Pleural effusion Cardiomyopathy FGR Mitral and tricuspid regurgitation | GAB neonatal death | Normal FISH |
| 19 | 13 | IV | Complex HV + cardiac | ADV | N | Hygroma SUA Thymus agenesis Ascites Pleural effusion | IUFD | N |
| 20 | 18 | IV | Complex IVC + HV | ADV | N | SUA Non-visible gallbladder Coarctation of the aorta | GAB Kabuki Syndrome motor retardation at 6 months follow-up | N |
| The previous study, 2010–2013 | ||||||||
| 21 | 13+6 | IIIa | HV | ADV | N | - | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | N |
| 22 | 13+3 | IIIa | HV | ADV | N | - | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | N |
| 23 | 13 | I | IVC | ADV | N | Hydronephrosis | GAB Good at 6 months follow-up | N |
| 24 | 13 | I | IVC | ADV | N | Cystic hygroma Abnormal facial profile-flat face Hypertelorism (ST findings) Skeletal: short femur and humerus, abnormal hands and feet (ST findings) Pyelectasis (ST finding) Choanal hypoplasia (neonatal finding) Restrictive respiratory disease | GAB Poor neonatal outcome Sudden infant death at 2 months | 46 XY, 10p- |
| 25 | 13+5 | I | Cardiac | ADV | TPVSA | Cystic hygroma Renal pyelectasis Hypoplastic left heart | TOP | Invasive genetics declined |
| 26 | 11 | I | IVC | ADV | Not assessed (early termination) | Hydrops Atrio-ventricular septal defect Frontal bossing | TOP | N |
| 27 | 13+4 | I | Cardiac | ADV | TPVSA | Heterotaxy syndrome Pulmonary atresia Abnormal right subclavian artery Kyphoscoliosis | TOP ST | N |
| 28 | 13+2 | I | HV | ADV | PPVSA | Hydrops (ST finding) Hypoplastic left heart Single umbilical artery Short long bones (ST finding) | TOP ST | Invasive genetics declined |
| 29 | 12+6 | I | HV | ADV | PPVSA | Cystic hygroma Hydrops Hypoplastic left heart | TOP | 45 X |
| 30 | 11+1 | I | Cardiac | ADV | Not assessed (early termination) | Hydrops Univentricular heart Abnormal face Absent NB Holoprosencephaly Microcephaly Skeletal abnormalities: spinal deformities, distorted feet, arm micromelia Lateral body wall defect Absent bladder | TOP | N |
| 31 | 11+3 | I | Cardiac | ADV | Not assessed (early termination) | Hydrops Body-stalk syndrome | TOP | N |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagy, R.D.; Iliescu, D.G. Prenatal Diagnosis and Outcome of Umbilical–Portal–Systemic Venous Shunts: Experience of a Tertiary Center and Proposal for a New Complex Type. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040873
Nagy RD, Iliescu DG. Prenatal Diagnosis and Outcome of Umbilical–Portal–Systemic Venous Shunts: Experience of a Tertiary Center and Proposal for a New Complex Type. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(4):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040873
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagy, Rodica Daniela, and Dominic Gabriel Iliescu. 2022. "Prenatal Diagnosis and Outcome of Umbilical–Portal–Systemic Venous Shunts: Experience of a Tertiary Center and Proposal for a New Complex Type" Diagnostics 12, no. 4: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040873
APA StyleNagy, R. D., & Iliescu, D. G. (2022). Prenatal Diagnosis and Outcome of Umbilical–Portal–Systemic Venous Shunts: Experience of a Tertiary Center and Proposal for a New Complex Type. Diagnostics, 12(4), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040873







