From NTM (Nontuberculous mycobacterium) to Gordonia bronchialis—A Diagnostic Challenge in the COPD Patient
Abstract
1. Introduction
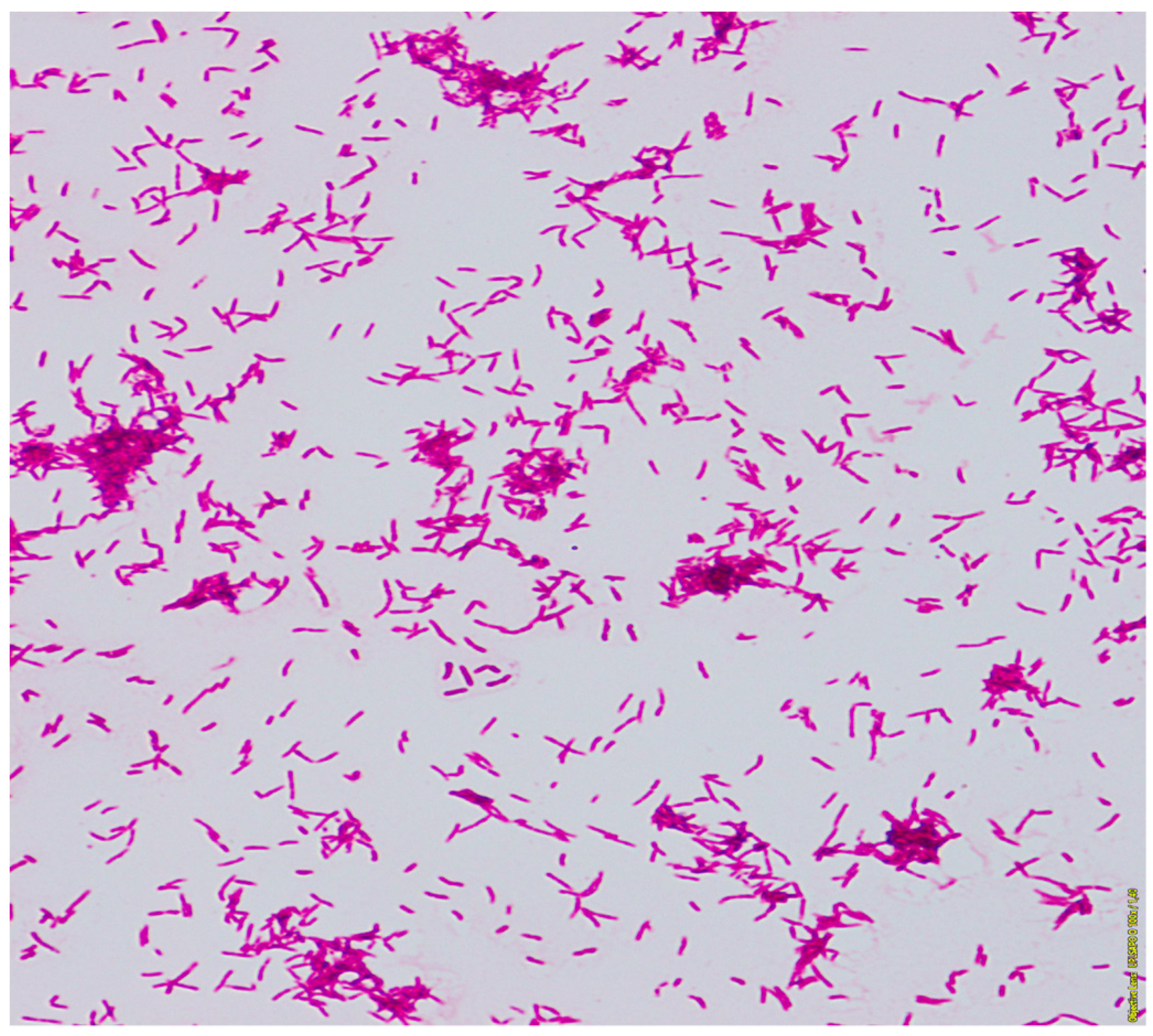
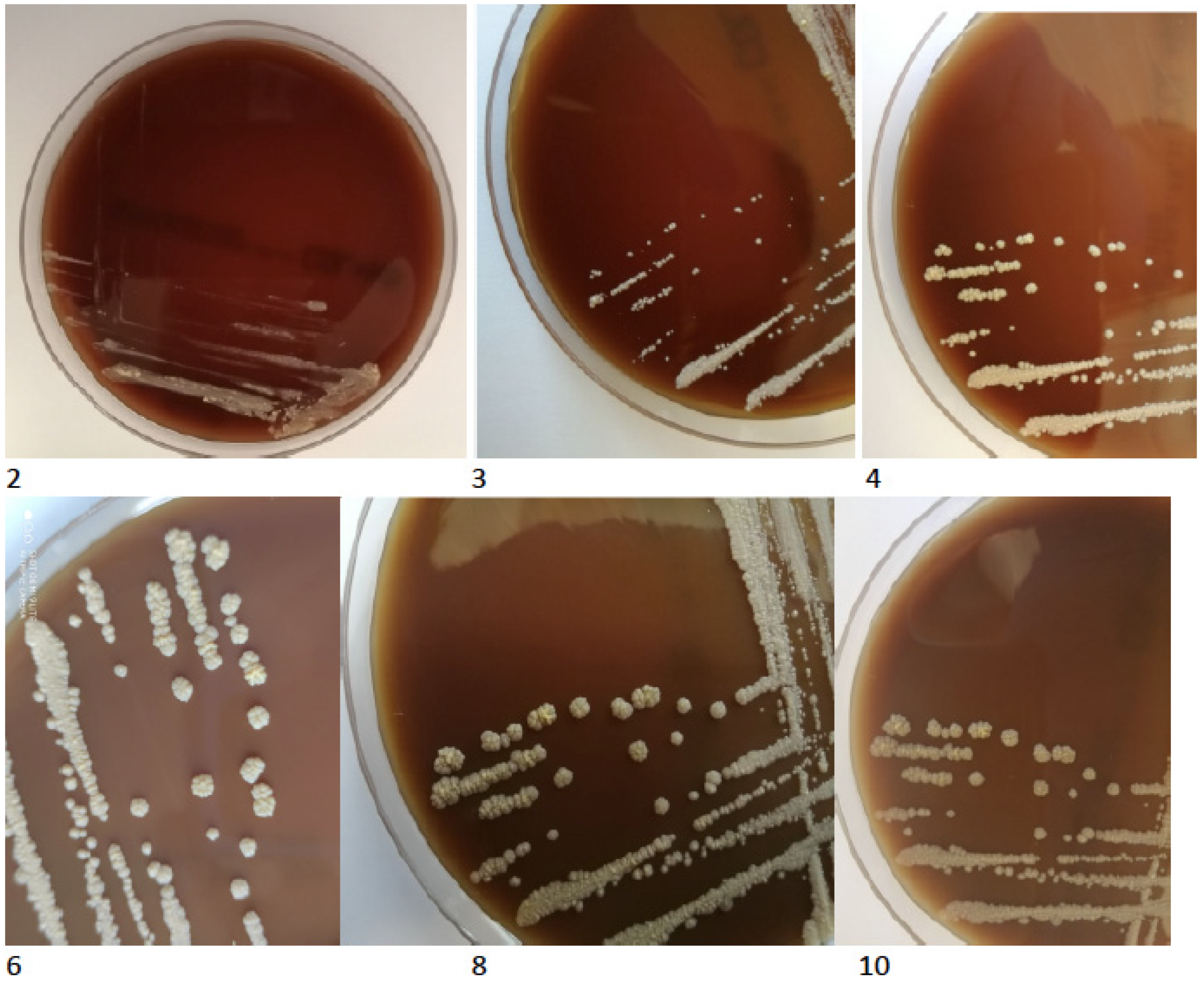
2. Case Presentation
3. Gene Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsukamura, M. Proposal of a new genus, Gordona, for slightly acid-fast organisms occurring in sputa of patients with pulmonary disease and in soil. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1971, 68, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A.; Onderdonk, A.B.; Cosimi, L.A.; Yawetz, S.; Lasker, B.A.; Bolcen, S.J.; Brown, J.M.; Marty, F.M. CASE REPORTS Gordonia bronchialis Bacteremia and Pleural Infection: Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, N.; Toumeh, A.; Georgescu, C. Tibial osteomyelitis caused by Gordonia bronchialis in an immunocompetent patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3119–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé-Álvarez, J.; Sáez-Nieto, J.A.; Escudero-Jiménez, A.; Barba-Rodríguez, N.; Galán-Ros, J.; Carrasco, G.; Muñoz-Izquierdo, M.P. Cutaneous abscess due to Gordonia bronchialis: Case report and literature review. Rev. Esp. Quim. 2016, 29, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.E.; Jung, C.J.; Won, C.H.; Chang, S.E.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, W.J. Case report of cutaneous nodule caused by Gordonia bronchialis in an immunocompetent patient after receiving acupuncture. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werno, A.M.; Anderson, T.P.; Chambers, S.T.; Laird, H.M.; Murdoch, D.R. Recurrent breast abscess caused by Gordonia bronchialis in an immunocompetent patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3009–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vidal, C.; Padilla, E.; Alcacer, P.; Campos, E.; Prieto, F.; Santos, C. Breast abscess caused by Gordonia bronchialis and the use of 16s rRNA gene sequence analysis for its definitive identification. JMM Case Rep. 2014, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Griesinger, L.; Wojewoda, C. Microbiology Case Study: A 42 Year Old Woman with a Lump in Her Left Breast. 2016. Available online: http://labmedicineblog.com/2016 (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Choi, R.; Strnad, L.; Flaxel, C.J.; Lauer, A.K.; Suhler, E.B. Gordonia bronchialis–Associated Endophthalmitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, J.C.M.; Whittier, S.; Scully, B.E.; McGregor, C.C.; Yin, M.T. Five cases of bacteraemia due to Gordonia species. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, P.; Deziel, P.J.; Wengenack, N.L. Gordonia bacteremia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sng, L.H.; Koh, T.H.; Toney, S.R.; Floyd, M.; Butler, W.R.; Tan, B.H. Bacteremia caused by Gordonia bronchialis in a patient with sequestrated lung. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2870–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.Y.W.; Wu, A.K.L.; Leung, W.-S.; Cheung, I.; Tsang, C.-C.; Chen, J.H.K.; Chan, J.F.W.; Tse, C.W.S.; Lee, R.A.; Lau, S.K.P.; et al. Gordonia Species as Emerging Causes of Continuous-Ambulatory-Peritoneal-Dialysis-Related Peritonitis Identified by 16S rRNA and secA1 Gene Sequencing and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukackiene, D.; Rimsevicius, L.; Kiveryte, S.; Marcinkeviciene, K.; Bratchikov, M.; Zokaityte, D.; Tyla, R.; Laucyte-Cibulskiene, A.; Miglinas, M. A case of successfully treated relapsing peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis caused by Gordonia bronchialis in a farmer. Nephrol. Ther. 2018, 14, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Wing Ma, T.; Chow, K.M.; Ching-Ha Kwan, B.; Lee, K.P.; Leung, C.B.; Kam-Tao Li, P.; Szeto, C.C. Peritoneal-dialysis related peritonitis caused by Gordonia species: Report of four cases and literature review. Nephrology 2014, 19, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Titécat, M.; Loïez, C.; Courcol, R.J.; Wallet, F. Difficulty with Gordonia bronchialis identification by Microflex mass spectrometer in a pacemaker-induced endocarditis. JMM Case Rep. 2014, 1, e003681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mormeneo Bayo, S.; Palacián Ruíz, M.P.; Asin Samper, U.; Millán Lou, M.I.; Pascual Catalán, A.; Villuendas Usón, M.C. Pacemaker-induced endocarditis by Gordonia bronchialis. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Yamamoto, D.; Yokota, A.; Suzuki, A.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Gordonan, an Acidic Polysaccharide with Cell Aggregation-Inducing Activity in Insect BM-N4 Cells, Produced by Gordonia sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richet, H.M.; Craven, P.C.; Brown, J.M.; Lasker, B.A.; Cox, C.D.; McNeil, M.M.; Tice, A.D.; Jarvis, W.R.; Tablan, O.C. A cluster of Rhodococcus (Gordona) bronchialis sternal-wound infections after coronary-artery bypass surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.N.; Gerry, J.S.; Busowski, M.T.; Klochko, A.Y. Gordonia bronchialis sternal wound infection in 3 patients following open heart surgery: Intraoperative transmission from a health worker. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2012, 33, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambesh, P.; Kapoor, A.; Elsheshtawy, M.; Shetty, V.; Lin, Y.S.; Kamholz, S.; Kazmi, D.H.; Elsheshtawy, M.; Shetty, V.; Lin, Y.S.; et al. Sternal Osteomyelitis by Gordonia Bronchialis in an Immunocompetent Patient after Open Heart Surgery. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Misuk, J.; Hyo-Lim, H.; Sang-Ho, C.; Yang-Soo, K.; Cheol-Hyun, C.; Heungsup, S.; Mi-Na, K. Sternal osteomyelitis caused by Gordonia bronchialis after open-heart surgery. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 46, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, V.; Fazii, P.; Favaro, M.; Astolfi, D.; Polilli, E.; Pompilio, A.; Vannucci, M.; D’Amario, C.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Fontana, C.; et al. Tuberculosis-like pneumonias by the aerobic actinomycetes Rhodococcus, Tsukamurella and Gordonia. Microbes. Infect. 2012, 14, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Lozano, J.; Pérez-Llantada, E.; Agüero, J.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; De Alegria, C.R.; Martinez-Martinez, L.L.; Calvo, J.; Perez-Llantada, E.; Aguero, J.; Rodriguez-Fernadez, A.; et al. Sternal wound infection caused by Gordonia bronchialis: Identification by MALDI-TOF MS. JMM Case Rep. 2016, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, A.J.; Bender, J.; Byington, C.L.; Korgenski, K.; Daly, J.; Petti, C.A.; Pavia, A.T.; Ampofo, K. Gordonia Species: Emerging Pathogens in Pediatric Patients That Are Identified by 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Brown, J.M.; Nunez, V.H.; Morey, R.E.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Pellegrini, G.J.; Kessler, H.A. Native valve endocarditis due to Gordonia polyisoprenivorans: Case report and review of literature of bloodstream infections caused by Gordonia species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Sande, E.; Brun-Otero, M.; Campo-Cerecedo, F.; Esteban, E.; Aguilar, L.; García-De-Lomas, J. Etiological misidentification by routine biochemical tests of bacteremia caused by Gordonia terrae infection in the course of an episode of acute cholecystitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2645–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blanc, V.; Dalle, M.; Markarian, A.; Debunne, M.V.; Duplay, E.; Rodriguez-Nava, V.; Boiron, P. Gordonia terrae: A difficult-to-diagnose emerging pathogen? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1076–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



| Sample 2 | ||||||||
| L.P. | Description | Scientific Name | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E Value | Per. Ident | Accession |
| 1 | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 | 586 | 586 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−167 | 100.00% | NR_074529.1 |
| 2 | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 | 586 | 586 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−167 | 100.00% | NR_027594.1 |
| 3 | Gordonia effusa strain IFM 10200 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia effusa | 580 | 580 | 100% | 1.0 × 10−165 | 99.68% | NR_041008.1 |
| 4 | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 strain NCTC 10667 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 | 575 | 575 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−164 | 99.37% | NR_119065.1 |
| 5 | Gordonia soli strain CC-AB07 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia soli | 575 | 575 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−164 | 99.37% | NR_043331.1 |
| 6 | Gordonia rubripertincta strain ATCC 14352 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia rubripertincta | 569 | 569 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−162 | 99.05% | NR_119117.1 |
| 7 | Gordonia westfalica strain Kb2 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia westfalica | 569 | 569 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−162 | 99.05% | NR_025468.1 |
| 8 | Gordonia rubripertincta strain N4 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia rubripertincta | 569 | 569 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−162 | 99.05% | NR_104572.1 |
| 9 | Gordonia namibiensis strain NAM-BN063A 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia namibiensis | 569 | 569 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−162 | 99.05% | NR_025165.1 |
| 10 | Gordonia hankookensis strain ON-33 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia hankookensis | 569 | 569 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−162 | 99.05% | NR_104507.1 |
| Sample 3 | ||||||||
| L.P. | Description | Scientific Name | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E Value | Per. Ident | Accession |
| 1 | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 | 575 | 575 | 100% | 5.0 × 10−164 | 100.00% | NR_074529.1 |
| 2 | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 | 575 | 575 | 100% | 5.0 × 10−164 | 100.00% | NR_027594.1 |
| 3 | Gordonia effusa strain IFM 10200 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia effusa | 569 | 569 | 100% | 3.0 × 10−162 | 99.68% | NR_041008.1 |
| 4 | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 strain NCTC 10667 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia bronchialis DSM 43247 | 564 | 564 | 100% | 1.0 × 10−160 | 99.36% | NR_119065.1 |
| 5 | Gordonia soli strain CC-AB07 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia soli | 564 | 564 | 100% | 1.0 × 10−160 | 99.36% | NR_043331.1 |
| 6 | Gordonia rubripertincta strain ATCC 14352 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia rubripertincta | 558 | 558 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−159 | 99.04% | NR_119117.1 |
| 7 | Gordonia westfalica strain Kb2 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia westfalica | 558 | 558 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−159 | 99.04% | NR_025468.1 |
| 8 | Gordonia rubripertincta strain N4 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia rubripertincta | 558 | 558 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−159 | 99.04% | NR_104572.1 |
| 9 | Gordonia namibiensis strain NAM-BN063A 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia namibiensis | 558 | 558 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−159 | 99.04% | NR_025165.1 |
| 10 | Gordonia hankookensis strain ON-33 16S ribosomal RNA, partial sequence | Gordonia hankookensis | 558 | 558 | 100% | 6.0 × 10−159 | 99.04% | NR_104507.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franczuk, M.; Klatt, M.; Filipczak, D.; Zabost, A.; Parniewski, P.; Kuthan, R.; Jakubowska, L.; Augustynowicz-Kopeć, E. From NTM (Nontuberculous mycobacterium) to Gordonia bronchialis—A Diagnostic Challenge in the COPD Patient. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020307
Franczuk M, Klatt M, Filipczak D, Zabost A, Parniewski P, Kuthan R, Jakubowska L, Augustynowicz-Kopeć E. From NTM (Nontuberculous mycobacterium) to Gordonia bronchialis—A Diagnostic Challenge in the COPD Patient. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020307
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranczuk, Monika, Magdalena Klatt, Dorota Filipczak, Anna Zabost, Paweł Parniewski, Robert Kuthan, Lilia Jakubowska, and Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć. 2022. "From NTM (Nontuberculous mycobacterium) to Gordonia bronchialis—A Diagnostic Challenge in the COPD Patient" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020307
APA StyleFranczuk, M., Klatt, M., Filipczak, D., Zabost, A., Parniewski, P., Kuthan, R., Jakubowska, L., & Augustynowicz-Kopeć, E. (2022). From NTM (Nontuberculous mycobacterium) to Gordonia bronchialis—A Diagnostic Challenge in the COPD Patient. Diagnostics, 12(2), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020307








