Pulmonary Fibrosis Related to Amiodarone—Is It a Standard Pathophysiological Pattern? A Case-Based Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Pharmacology
1.2. Pathology
1.3. Clinical Presentation
1.4. Diagnostic
1.5. Imagistic Features
1.6. Differential Diagnosis
1.7. Treatment
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Case Presentation 1
2.2. Case Presentation 2
2.3. Case Presentation 3
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terzo, F.; Ricci, A.; D’Ascanio, M.; Raffa, S.; Mariotta, S. Amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity with an excellent response to treatment: A case report. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 29, 100974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Vaart, H.; Postma, D.S.; Timens, W.; Hylkema, M.N.; Willemse, B.W.M.; Boezen, H.M.; Vonk, J.M.; De Reus, D.M.; Kauffman, H.F.; Hacken, N.H.T.T. Acute effects of cigarette smoking on inflammation in healthy intermittent smokers. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.; Nandkeolyar, S.; Lan, H.; Desai, P.; Evans, J.; Hauschild, C.; Choksi, D.; Abudayyeh, I.; Contractor, T.; Hilliard, A. Amiodarone: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinicians. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkove, N.; Baltzan, M. Amiodarone Pulmonary Toxicity. Can. Respir. J. 2009, 16, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A.E.; Olshansky, B.; Naccarelli, G.V.; Kennedy, J.I.; Murphy, E.J.; Goldschlager, N. Practical Management Guide for Clinicians Who Treat Patients with Amiodarone. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancatelli, R.M.C.; Congedo, V.; Calvosa, L.; Ciacciarelli, M.; Polidoro, A.; Iuliano, L. Adverse reactions of Amiodarone. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 552–566. [Google Scholar]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averyanov, A.V. Difficult to Diagnose Rare Diffuse Lung Disease, 1st ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erven, L.; Schalij, M.J. Amiodarone: An effective antiarrhythmic drug with unusual side effects. Heart 2010, 96, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, W.; Israel, C.; Parwani, A. Klinische Besonderheiten der Therapie mit Amiodaron. Herzschr. Elektrophys. 2017, 28, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, S.M.; Stevenson, W.G.; Ackerman, M.J.; Bryant, W.J.; Callans, D.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Deal, B.J.; Dickfeld, T.; Field, M.E.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: Executive summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, e190–e252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malaviya, R.; Kipen, H.M.; Businaro, R.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Pulmonary toxicants and fibrosis: Innate and adaptive immune mechanisms. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 409, 115272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, D.L.; Malaviya, R.; Laskin, J.D. Role of Macrophages in Acute Lung Injury and Chronic Fibrosis Induced by Pulmonary Toxicants. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 168, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borthwick, L.A. The IL-1 cytokine family and its role in inflammation and fibrosis in the lung. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sulzer, D. Frequency-dependent modulation of dopamine release by nicotine. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meziani, L.; Mondini, M.; Petit, B.; Boissonnas, A.; De Montpreville, V.T.; Mercier, O.; Vozenin, M.-C.; Deutsch, E. CSF1R inhibition prevents radiation pulmonary fibrosis by depletion of interstitial macrophages. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Peng, B.; Cui, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Qin, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhao, L.; et al. Distribution of toxic chemicals in particles of various sizes from mainstream cigarette smoke. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venosa, A.; Malaviya, R.; Choi, H.; Gow, A.J.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Characterization of distinct macrophage subpopulations during nitrogen mustard-induced lung injury and fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasleton, P.; Flieder, D.B. (Eds.) Spencer’s Pathology of the Lung, 6th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papiris, S.A.; Triantafillidou, C.; Kolilekas, L.; Markoulaki, D.; Manali, E.D. Amiodarone: Review of Pulmonary Effects and Toxicity. Drug Saf. 2010, 33, 539–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, W.H. Cationic amphiphilic drug-induced phospholipidosis. Toxicol. Pathol. 1997, 25, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Shiga, T.; Matsuda, N.; Hagiwara, N.; Kasanuki, H. Incidence and predictors of pulmonary toxicity in japanese patients receiving low-dose amiodarone. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo Clinic. Lymphoid Hyperplasia and Eosinophilic Pneumonia as Histologic Manifestations of Amiodarone-Induced Lung Toxicity. Available online: https://mayoclinic.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/lymphoid-hyperplasia-and-eosinophilic-pneumonia-as-histologic-man/fingerprints/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Baron, E.; Mok, W.K.; Jayawardena, M.; Reall, G.; Elfaki, H.; Thirumaran, M.; Dwarakanath, A. Amiodarone lung: Under recognised but not forgotten. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2021, 51, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschlager, N.; Epstein, A.E.; Naccarelli, G.; Olshansky, B.; Singh, B. Practical guidelines for clinicians who treat patients with amiodarone. Practice Guidelines Subcommittee, North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, A.C.; Camus, P. Iatrogenic pulmonary lesions. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 35, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shi, J.; Tang, H. Animal models of drug-induced pulmonary fibrosis: An overview of molecular mechanisms and characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 699–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Saraya, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Hiraoka, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Yano, K.; Ishii, H.; Furuse, J.; Goya, T.; Takizawa, H.; et al. High-Resolution Computed Tomography Findings for Patients with Drug-Induced Pulmonary Toxicity, with Special Reference to Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis-Like Patterns in Gemcitabine-Induced Cases. Oncologist 2013, 18, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.S.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.-H. The diagnostic utility of chest computed tomography scoring for the assessment of amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, C.; Syed, J.; Pollak, P.T.; Koren, G. Falling between the cracks: A case of amiodarone toxicity. CMAJ 2011, 183, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiblmair, M.; Berghaus, T.; Haeckel, T.; Wagner, T.; von Scheidt, W. Amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity: An under-recognized and severe adverse effect? Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2010, 99, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeoch, S.; Weatherley, N.; Swift, A.J.; Oldroyd, A.; Johns, C.; Hayton, C.; Giollo, A.; Wild, J.M.; Waterton, J.C.; Buch, M.; et al. Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelandt, M.; Demedts, M.; Callebaut, W.; Coolen, D.; Slabbynck, H.; Bockaert, J.; Kips, J.; Brie, J.; Ulburghs, M.; De Boeck, K.; et al. Epidemiology of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in flanders: Registration by pneumologists in 1992–1994. Working group on ILD, VRGT. Vereniging voor Respiratoire Gezondheidszorg en Tuberculosebestrijding. Acta Clin. Belg. 1995, 50, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, C.; Horinouchi, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Kohno, T.; Okusaka, T.; Ueno, H.; Tamura, K.; Ohe, Y.; Zembutsu, H. Whole genome sequencing to identify predictive markers for the risk of drug-induced interstitial lung disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.R.; Monahan, K.H.; Packer, D. Pulmonary Vein Stenosis Complicating Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Clinical Spectrum and Interventional Considerations. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 2, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankikian, J.; Favelle, O.; Guillon, A.; Guilleminault, L.; Cormier, B.; Jonville-Béra, A.; Perrotin, D.; Diot, P.; Marchand-Adam, S. Initial characteristics and outcome of hospitalized patients with amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, B.; Sami, M.; Rubin, A.; Kostis, J.; Shorofsky, S.; Slee, A.; Greene, H.L. Use of amiodarone for atrial fibrillation in patients with preexisting pulmonary disease in the AFFIRM study. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollin, L.; Maillet, I.; Quesniaux, V.; Holweg, A.; Ryffel, B. Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor nintedanib in experimental models of lung fibrosis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 349, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meter, M.; Prusac, I.K.; Glavaš, D.; Meter, D. Acute respiratory failure on a low dose of amiodarone–is it an underdiagnosed and undertreated condition? Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 34, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bangalore, S.; Kumari, R.; Grosu, H.; Jean, R. Amiodarone-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome masquerading as acute heart failure. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 43, e311–e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmarajan, T.S.; Shah, A.B.; Dharmarajan, L. Amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity: Potentially fatal, recognize early during life! J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1363–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarand, J.; Lee, A.; Leigh, R. Amiodaronoma: An unusual form of amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity. CMAJ 2007, 176, 1411–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Richeldi, L. Interstitial Lung Disease; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera-Rego, J.O.; Luzurriaga Navas, J.D.; Yanes Quintana, A.A. Acute amiodarone pulmonary toxicity with low impregnation dose: Case report. Medwave 2020, 20, e7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiffel, J.A. Adverse Events with Amiodarone—Will the List Ever End? J. Innov. Card. Rhythm Manag. 2018, 9, 3077–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Baumann, H.; Fichtenkamm, P.; Schneider, T.; Biscoping, J.; Henrich, M. Rapid onset of amiodarone induced pulmonary toxicity after lung lobe resection–A case report and review of recent literature. Ann. Med. Surg. (Lond) 2017, 21, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, P.; Trohman, R.G. Prescribing AmiodaroneAn Evidence-Based Review of Clinical Indications. JAMA 2007, 298, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, J.; Agrawal, N.; Marballi, A.; Agrawal, S.; Rawat, N.; Sule, S.; Lehrman, S.G. Amiodarone induced pulmonary toxicity: An unusual response to steroids. Am. J. Case Rep. 2012, 13, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Avery, A.J.; Neil, K.E.; Johnson, C.; Dewey, M.E.; Stockley, I.H. Incidence and possible causes of prescribing potentially hazardous/contraindicated drug combinations in general practice. Drug Saf. 2005, 28, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.G.; Connolly, S.J.; Dorian, P.; Green, M.; Humphries, K.H.; Klein, G.J.; Sheldon, R.; Talajic, M.; Kerr, C.R. Antiarrhythmic use from 1991 to 2007, insights from the Canadian Registry of Atrial Fibrillation (CARAF I and II). Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
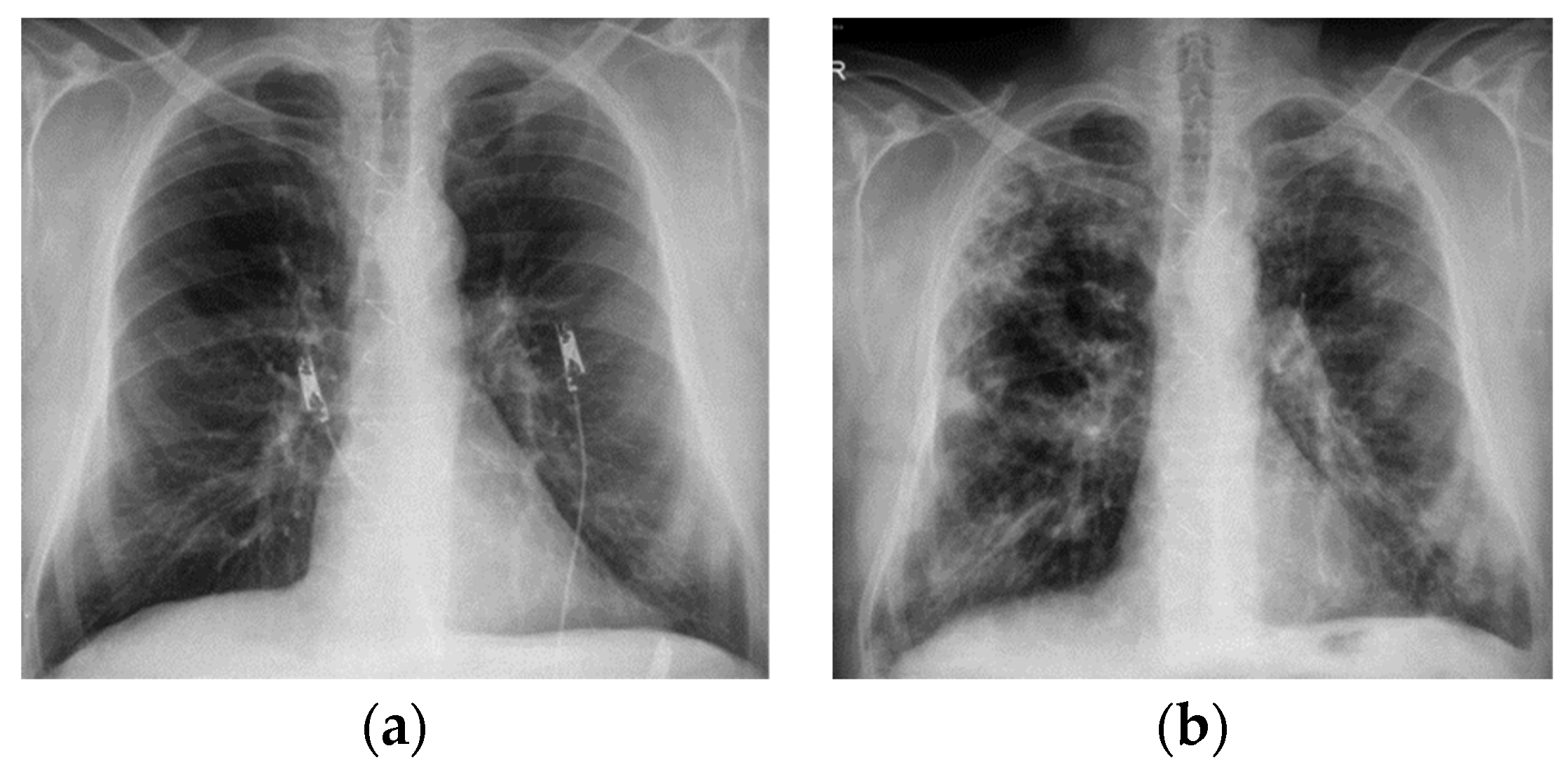
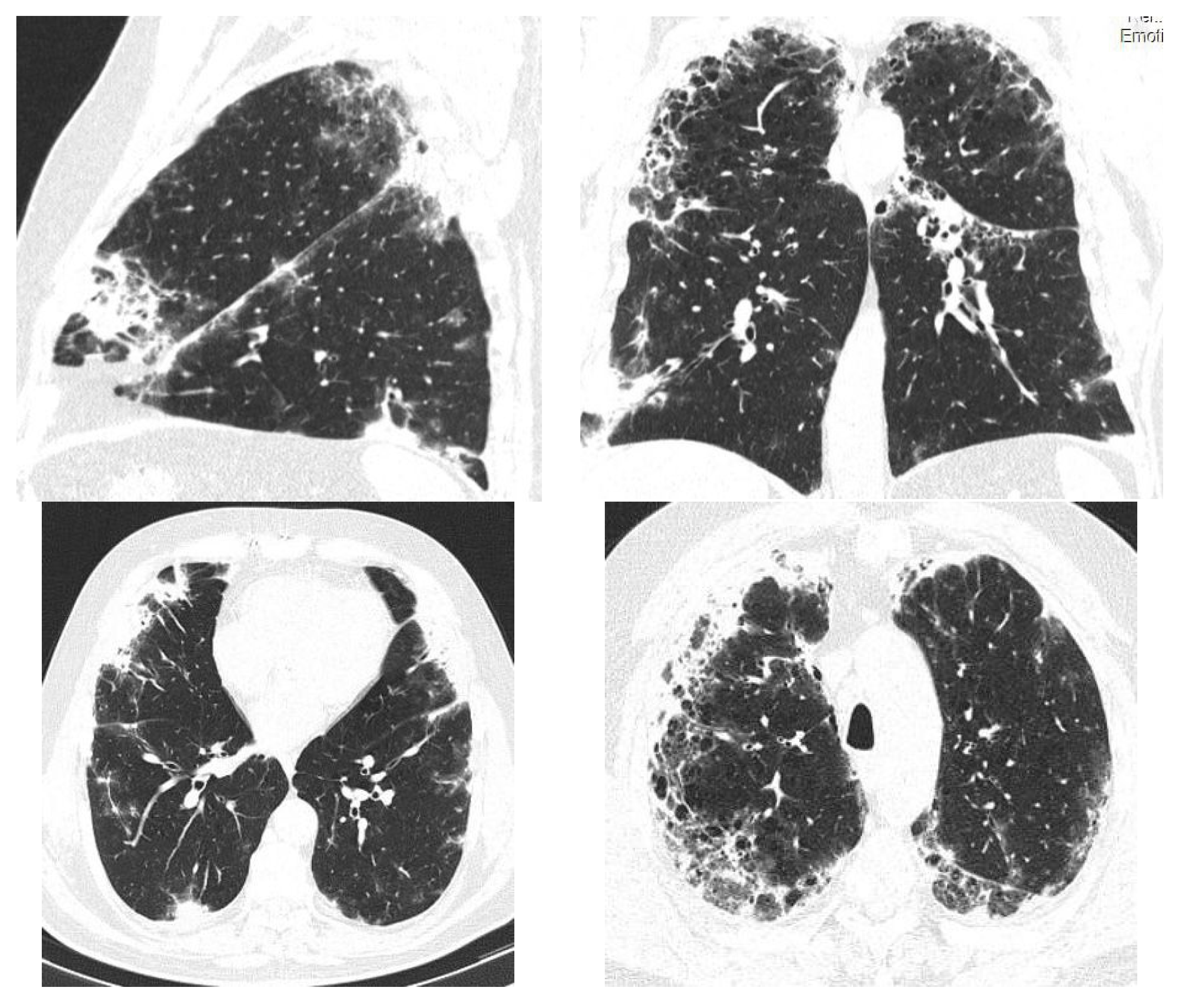

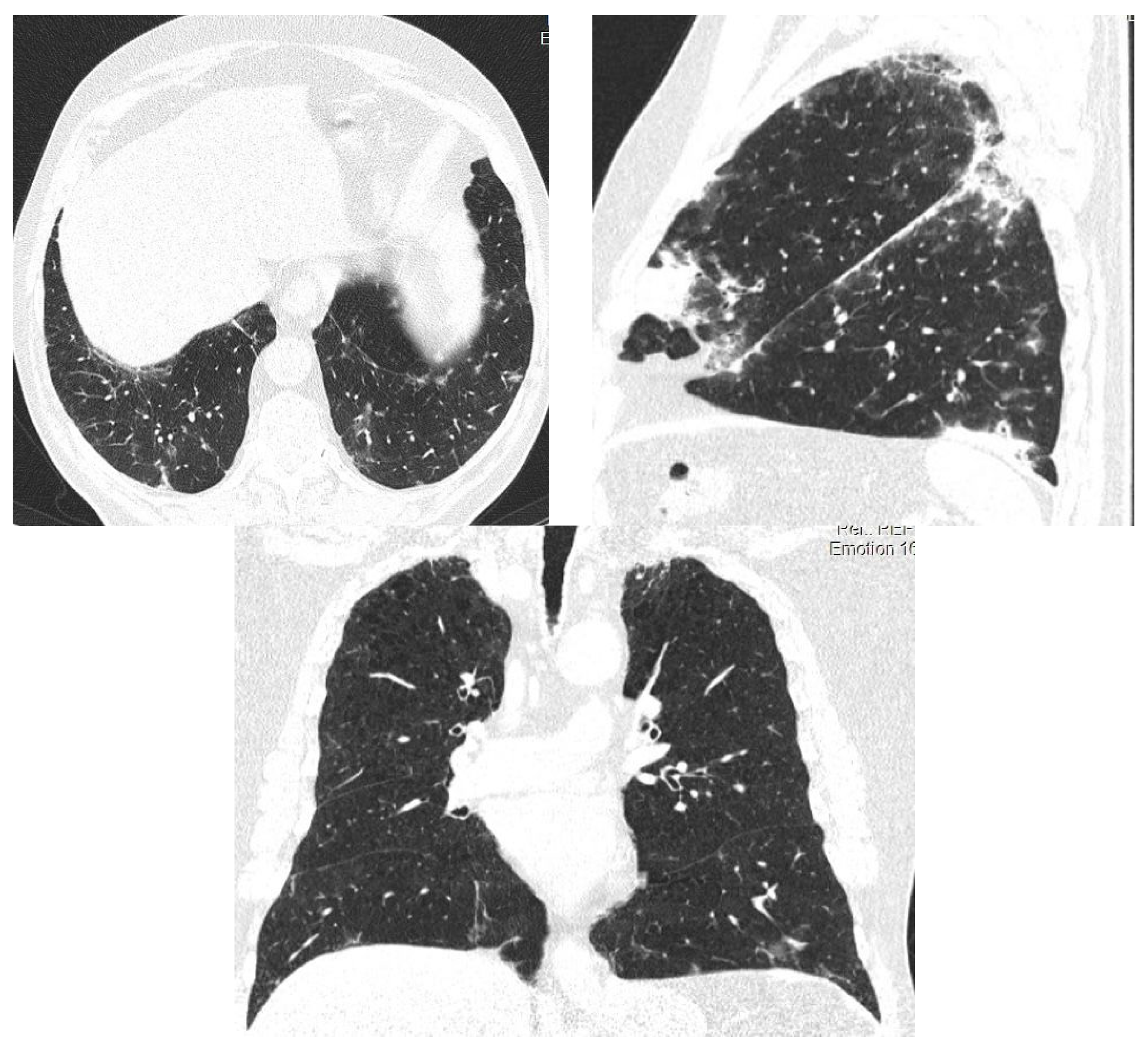
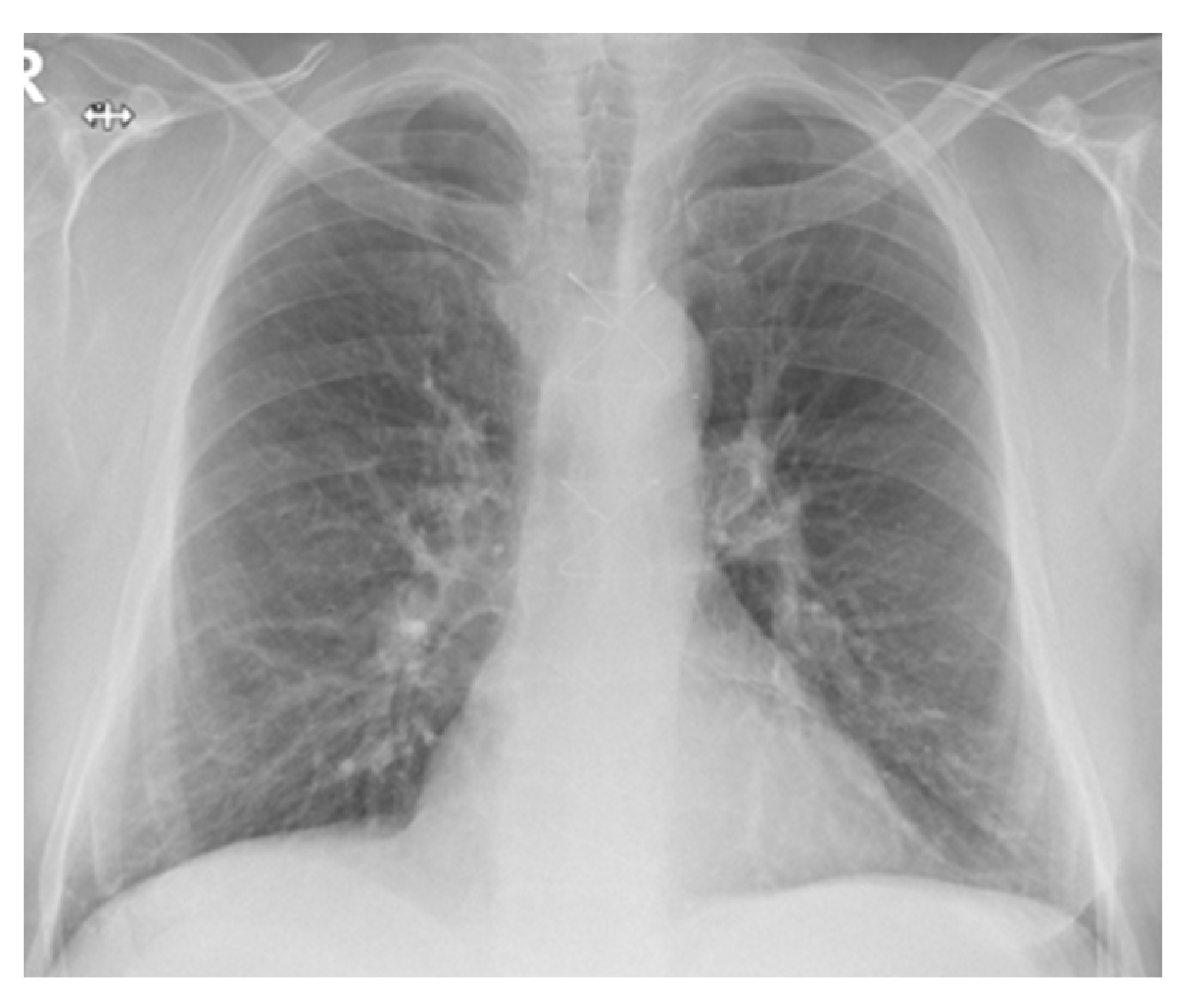
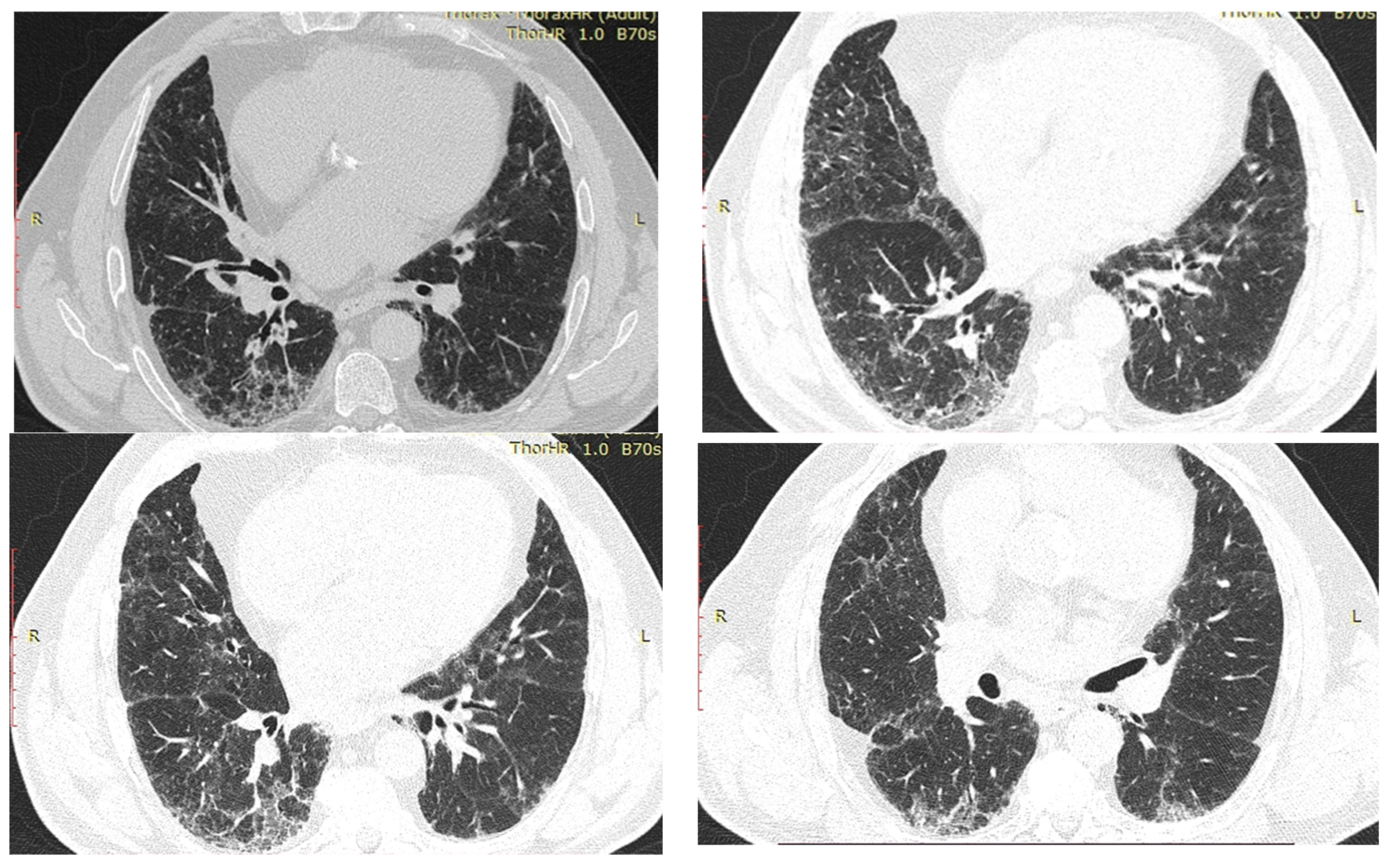
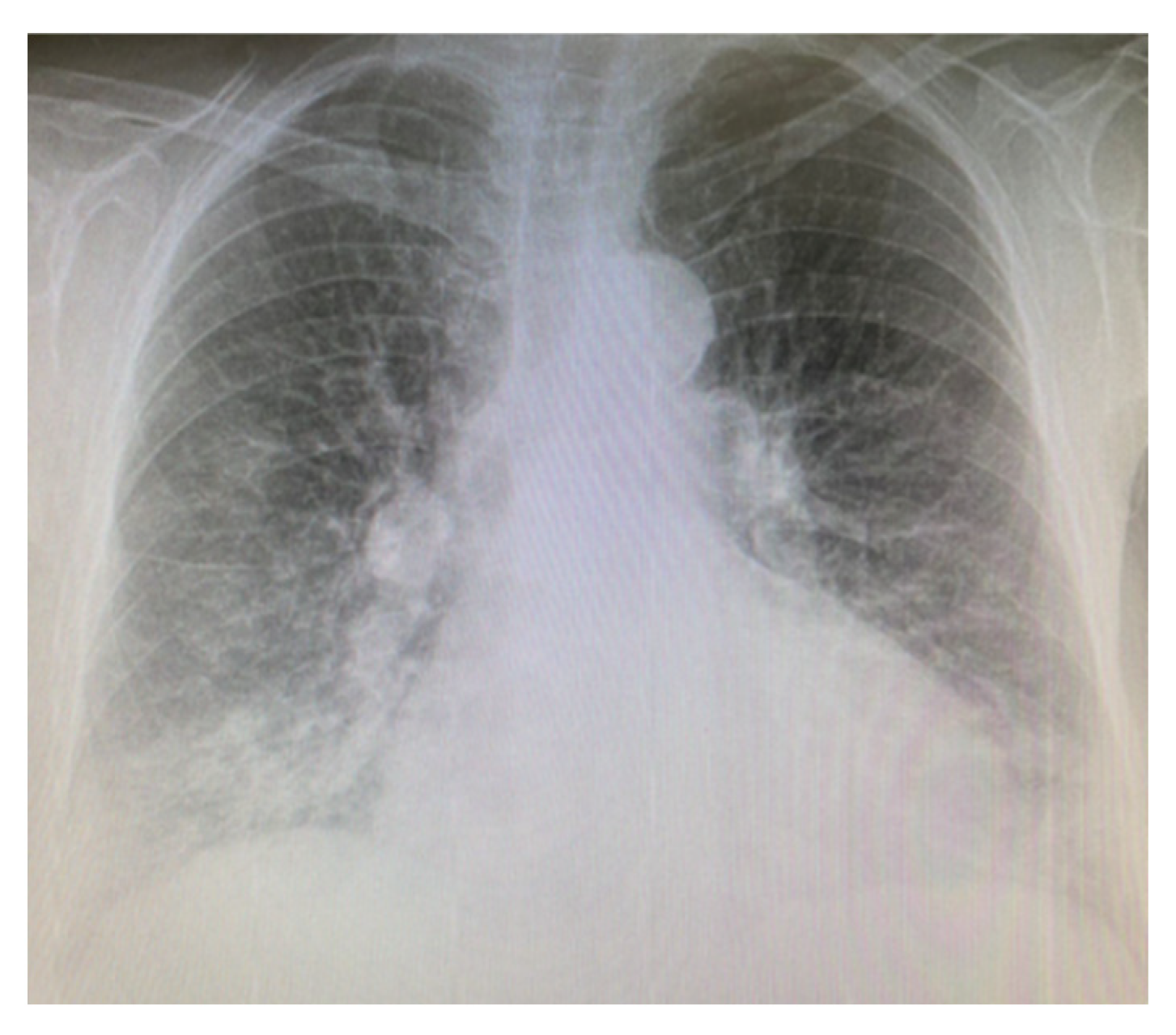
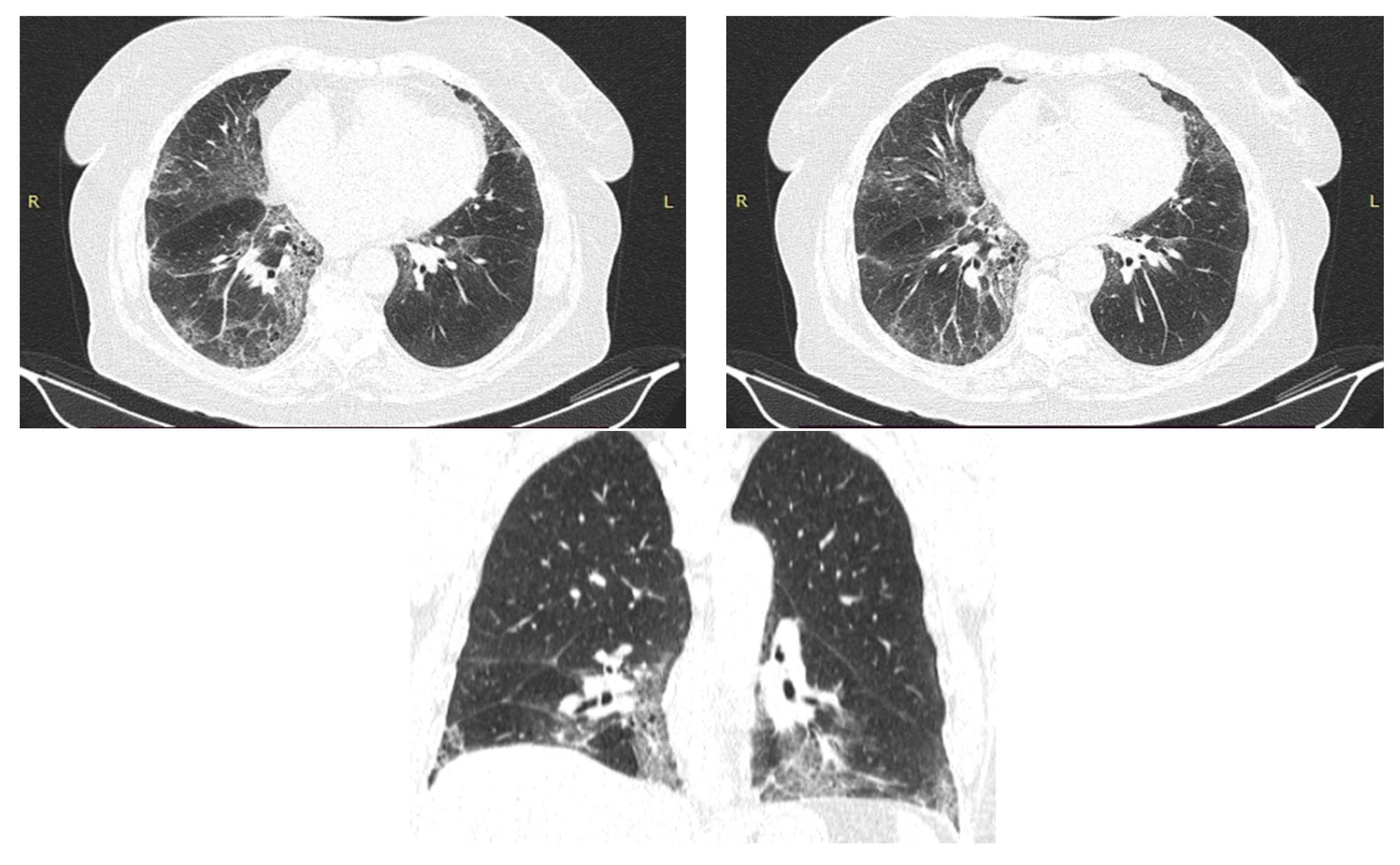
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). High-resolution CT often shows honeycomb changes, traction bronchiectasis and a reticular pattern that is predominantly in the periphery of the lower lobes. |
| Hypersensitivity pneumonitis | Exposure history. Specific IgG antibodies. Pulmonary infiltrates and suspected nonspecific interstitial pneumonia or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. |
| Infectious pathologies | Purulent sputum, unilateral localization. Procalcitonin value elevated. |
| Heart failure. Acute cardiogenic pulmonary oedema | Kerley lines and peri bronchial oedema. Subpleural patchy areas in pulmonary oedema. |
| BOOP | Procalcitonin value unchanged. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budin, C.E.; Cocuz, I.G.; Sabău, A.H.; Niculescu, R.; Ianosi, I.R.; Ioan, V.; Cotoi, O.S. Pulmonary Fibrosis Related to Amiodarone—Is It a Standard Pathophysiological Pattern? A Case-Based Literature Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123217
Budin CE, Cocuz IG, Sabău AH, Niculescu R, Ianosi IR, Ioan V, Cotoi OS. Pulmonary Fibrosis Related to Amiodarone—Is It a Standard Pathophysiological Pattern? A Case-Based Literature Review. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123217
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudin, Corina Eugenia, Iuliu Gabriel Cocuz, Adrian Horațiu Sabău, Raluca Niculescu, Ingrid Renata Ianosi, Vladimir Ioan, and Ovidiu Simion Cotoi. 2022. "Pulmonary Fibrosis Related to Amiodarone—Is It a Standard Pathophysiological Pattern? A Case-Based Literature Review" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123217
APA StyleBudin, C. E., Cocuz, I. G., Sabău, A. H., Niculescu, R., Ianosi, I. R., Ioan, V., & Cotoi, O. S. (2022). Pulmonary Fibrosis Related to Amiodarone—Is It a Standard Pathophysiological Pattern? A Case-Based Literature Review. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123217







