Recognizing Atypical Presentations of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Importance of CSF Biomarkers in Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Neuroimaging
2.3. Neuropsychological Testing
2.4. CSF Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.; Schneider, J.; Bienias, J.; Evans, D.A.; Wilson, R.S. Mild cognitive impairment is related to Alzheimer pathology and cerebral infarctions. Neurology 2005, 64, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, M. Primary progressive aphasia: Clinicopathological correlations. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, H.; Toyoshima, Y.; Tada, M.; Oyake, M.; Aida, I.; Tomita, I.; Satoh, A.; Tsujihata, M.; Takahashi, H.; Nishizawa, M.; et al. Pathology and sensitivity of current clinical criteria in corticobasal syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutch, S.J.; Lehmann, M.; Schott, J.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Rossor, M.N.; Fox, N.C. Posterior cortical atrophy. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.F.; Joshi, A.; Tassniyom, K.; Teng, E.; Shapira, J.S. Clinicopathologic differences among patients with behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 2013, 80, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, A.; Nordlund, A.; Jonsson, M.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Ohrfelt, A.; Stalhammar, J.; Eckerstrom, M.; Carlsson, M.; Olsson, E.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease–subcortical vascular disease spectrum in a hospital-based setting: Overview of results from the Gothenburg MCI and dementia studies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peavy, G.M.; Edland, S.D.; Toole, B.M.; Hansen, L.A.; Galasko, D.R.; Mayo, A.M. Phenotypic differences based on staging of Alzheimer’s neuropathology in autopsy-confirmed dementia with Lewy bodies. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 31, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.; Lowe, V.; Senjem, M.; Weigand, S.D.; Kemp, B.J.; Shiung, M.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Klunk, W.E.; Mathis, C.A.; et al. 11C PiB and structural MRI provide complementary information in imaging of Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Brain 2008, 131, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinuevo, J.L.; Blennow, K.; Dubois, B.; Engelborghs, S.; Lewczuk, P.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; Teunissen, C.E.; Parnetti, L. The clinical use of cerebrospinal fluid biomarker testing for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis: A consensus paper from the Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Standardization Initiative. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Dubois, B.; Fagan, A.M.; Lewczuk, P.; de Leon, M.J.; Hampel, H. Clinical utility of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, D.; Bensaïdane, R.; Laforce, R. Untangling Alzheimer’s Disease Clinicoanatomical Heterogeneity Through Selective Network Vulnerability—An Effort to Understand a Complex Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; Hampel, H.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Blennow, K.; DeKosky, S.T.; Gauthier, S.; Selkoe, D.; Bateman, R.; et al. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: The IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, A.; Kapaki, E.; Boban, M.; Engelborghs, S.; Hermann, D.M.; Huisa, B.; Jonsson, M.; Kramberger, M.G.; Lossi, L.; Malojcic, B.; et al. Biochemical markers in vascular cognitive impairment associated with subcortical small vessel disease—A consensus report. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaki, E.; Liappas, I.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Theotoka, I.; Rabavilas, A. The diagnostic value of tau protein, beta-amyloid (1-42) and their ratio for the discrimination of alcohol-related cognitive disorders from Alzheimer’s disease in the early stages. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2005, 20, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Kapaki, E.; Kararizou, E.; Mitsonis, C.; Sfagos, C.; Vassilopoulos, D. Cerebrospinal fluid tau protein is increased in neurosyphilis: A discrimination from syphilis without nervous system involvement? Sex. Transm. Dis. 2007, 34, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Kaselimis, D.; Kourtidou, E.; Constantinides, V.; Bougea, A.; Potagas, C.; Evdokimidis, I.; Kapaki, E. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers as a Diagnostic Tool of the Underlying Pathology of Primary Progressive Aphasia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 55, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, A.H.; Herukka, S.K.; Andreasen, N.; Baldeiras, I.; Bjerke, M.; Blennow, K.; Engelborghs, S.; Frisoni, G.B.; Gabryelewicz, T.; Galluzzi, S.; et al. Recommendations for CSF AD biomarkers in the diagnostic evaluation of dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Leys, D.; Barkhof, F.; Huglo, D.; Weinstein, H.C.; Vermersch, P.; Kuiper, M.; Steinling, M.; Wolters, E.C.; Valk, J. Atrophy of medial temporal lobes on MRI in “probable” Alzheimer’s disease and normal ageing: Diagnostic value and neuropsychological correlates. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, L. Clinical dementia rating (CDR). Psychopharmacol. Bull. 1988, 24, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.; Folstein, S.; McHugh, P.R. Mini-Mental State: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Touchon, J.; Portet, F.; Ousset, P.J.; Vellas, B.; Michel, B. “The 5 words”: A simple and sensitive test for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Presse Med. 2002, 31, 1696–1699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Slachevsky, A.; Litvan, I.; Pillon, B. The FAB: A Frontal Assessment Battery at bedside. Neurology 2000, 55, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royall, D.R.; Cordes, J.A.; Polk, M. CLOX: An executive clock drawing task. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, G.; Hermsdörfer, J.; Glindemann, R.; Rorden, C.; Karnath, H.O. Pantomime of tool use depends on integrity of left inferior frontal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, G.; Hartmann, K.; Schlott, I. Defective pantomime of object use in left brain damage: Apraxia or asymbolia? Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodglass, H.; Kaplan, E.; Barresi, B. Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination, 3rd ed.; Pearson: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Del Campo, M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Bertolotto, A.; Engelborghs, S.; Hampel, H.; Simonsen, A.H.; Kapaki, E.; Kruse, N.; Le Bastard, N.; Lehmann, S.; et al. Recommendations to standardize preanalytical confounding factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers: An update. Biomark. Med. 2012, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Weintraub, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mendez, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Ogar, J.M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Black, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 2011, 76, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; Bak, T.H.; Bhatia, K.P.; Borroni, B.; Boxer, A.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Grossman, M.; Hallett, M.; et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration. Neurology 2013, 80, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Agid, Y.; Calne, D.; Campbell, G.; Dubois, B.; Duvoisin, R.C.; Goetz, C.G.; Golbe, L.I.; Grafman, J.; Growdon, J.H.; et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): Report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 1996, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefer, M.; Untenberg, A. The differential diagnosis and treatment of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2012, 109, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Tan, L.; Cao, L.; Zhu, X.C.; Jiang, T.; Tan, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Tsai, R.M.; Jia, J.P.; et al. Application of the IWG-2 Diagnostic Criteria for Alzheimer’s Disease to the ADNI. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, R.W.; Toombs, J.; Slattery, C.F.; Nicholas, J.M.; Andreasson, U.; Magdalinou, N.K.; Blennow, K.; Warren, J.D.; Mummery, C.J.; Rossor, M.N.; et al. Dissecting IWG-2 typical and atypical Alzheimer’s disease: Insights from cerebrospinal fluid analysis. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Mattsson, N.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Scheltens, P.; van der Flier, W.M.; Rabinovici, G.D. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and cerebral atrophy in distinct clinical variants of probable Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.F. Early-onset Alzheimer disease. Neurol. Clin. 2017, 35, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff-Radford, J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Apostolova, L.G.; Bouwman, F.H.; Carrillo, M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Schott, J.M.; Jones, D.T.; Murray, M.E. New insights into atypical Alzheimer’s disease in the era of biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M.; Gall, C.; Thompson, J.C.; Richardson, A.M.; Neary, D.; du Plessis, D.; Pal, P.; Mann, D.M.; Snowden, J.S.; Jones, M. Classification and pathology of primary progressive aphasia. Neurology 2013, 81, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Navarro, S.; Lladó, A.; Rami, L.; Castellvi, M.; Bosch, B.; Bargallo, N.; Lomena, F.; Rene, R.; Montagut, N.; Antonell, A.; et al. Neuroimaging and biochemical markers in the three variants of primary progressive aphasia. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, R.; Coppi, E.; Ferrari, L.; Bernasconi, M.P.; Pinto, P.; Passerini, G.; Comi, G.; Magnani, G. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers can play a pivotal role in the diagnostic work up of primary progressive aphasia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 43, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norise, C.; Ungrady, M.; Halpin, A.; Jester, C.; McMillan, C.T.; Irwin, D.J.; Cousins, K.A.; Grossman, M. Clinical Correlates of Alzheimer’s Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid Analytes in Primary Progressive Aphasia. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, D.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Santos-Santos, M.A.; Seeley, W.; Miller, B.L.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Keulen, M.A.; Groot, C.; van Berckel, B.N.M.; et al. Prevalence of amyloid-β pathology in distinct variants of primary progressive aphasia. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Petropoulou, O.; Bougea, A.; Vekrellis, K.; Evdokimidis, I.; Stamboulis, E.; Kapaki, E. CSF biomarkers β-amyloid, tau proteins and a-synuclein in the differential diagnosis of Parkinson-plus syndromes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 382, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonenboom, N.; Reesink, F.; Verwey, N.; Kester, M.I.; Teunissen, C.E.; van de Ven, P.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid markers for differential dementia diagnosis in a large memory clinic cohort. Neurology 2012, 78, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech-Azeddine, R.; Hogh, P.; Juhler, M.; Gjerris, F.; Waldemar, G. Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Clinical comorbidity correlated with cerebral biopsy findings and outcome of cerebrospinal fluid shunting. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaki, E.N.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Tzerakis, N.G.; Sfagos, C.; Seretis, A.; Kararizou, E.; Vassilopoulos, D. Cerebrospinal fluid tau, phospho-tau181 and beta-amyloid1-42 in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A discrimination from Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Lee, E.B.; Xie, S.X.; Law, A.; Jackson, E.M.; Arnold, S.E.; Clark, C.M.; Shaw, L.M.; Grady, M.S.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Phosphorylated tau/amyloid beta 1–42 ratio in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid reflects outcome in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golomb, J.; Wisoff, J.; Miller, D.C.; Boksay, I.; Kluger, A.; Weiner, H.; Salton, J.; Graves, W. Alzheimer’s disease comorbidity in normal pressure hydrocephalus: Prevalence and shunt response. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnell, K.; Religa, D.; Eriksdotter, M. Differences in drug therapy between dementia disorders in the Swedish dementia registry: A nationwide study of over 7000 patients. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
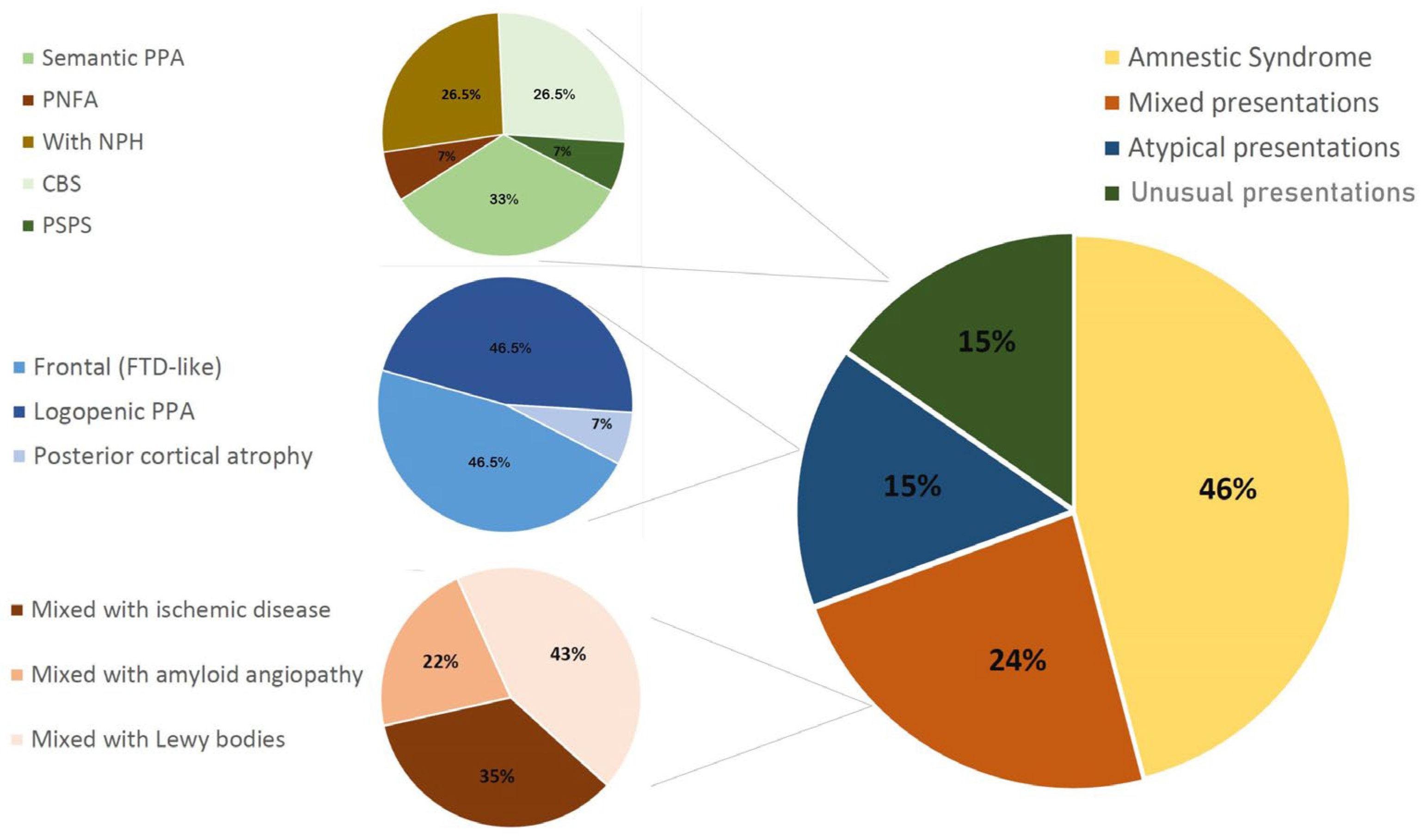

| Clinical Presentation | Percentage | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Typical AD (“hippocampal” amnestic) | 45.92% | 33.49–61.44% |
| Mixed disease | 23.47% | 14.88–35.22% |
| Mixed with cerebrovascular disease | 13.27% | 7.06–22.68% |
| Mixed with ischemic disease | 8.16% | 3.52–16.09% |
| Mixed with amyloid angiopathy | 5.10% | 1.67–11.91% |
| Mixed with Lewy bodies | 10.20% | 4.89–18.77% |
| Atypical presentations | 15.31% | 8.57–25.25% |
| Frontal (FTD-like) | 7.14% | 2.87–14.72% |
| Logopenic PPA | 7.14% | 2.87–14.72% |
| Posterior cortical atrophy | 1.02% | 0.03–5.69% |
| Unusual presentations | 15.31% | 8.57–25.25% |
| Non-logopenic PPA | 6.12% | 2.25–13.33% |
| Semantic PPA | 5.10% | 1.67–11.91% |
| PNFA | 1.02% | 0.03–5.69% |
| With NPH | 4.08% | 1.11–10.45% |
| CBS | 4.08% | 1.11–10.45% |
| PSPS | 1.02% | 0.03–5.69% |
| Typical | Mixed | Atypical | Unusual | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 45 (45.92) | 23 (23.47) | 15 (15.31) | 15 (15.31) | |
| f/m | 26/19 | 12/11 | 9/6 | 6/9 | NS * |
| Education (y) † | 12.3 ± 4.4 | 11.8 ± 4.9 | 11.1 ± 5.6 | 10.9 ± 4.5 | NS § |
| Age (y) † | 62.9 ± 11.6 a | 74.0 ± 5.8 b | 65.4 ± 5.9 | 70.5 ± 9.8 | 0.0007 § |
| Age at onset † | 59.1 ± 12.1 | 70.1 ± 6.8 c | 60.7 ± 5.9 | 66.8 ± 9.1 | 0.0009 § |
| Duration (y) † | 3.9 ± 3.6 | 3.8 ± 3.8 | 4.8 ± 4.2 | 4.0 ± 3.8 | NS § |
| Early onset (%) | 33 (73.33) | 6 (26.09) d | 11 (73.33) | 8 (53.33) | 0.0014 * |
| MMSE ‡ | 17 (12–20) | 20 (10–24) | 16 (7–22) | 14 (5–21) | NS # |
| FAB ‡ | 7 (3–13) | 9 (4–14) | 7 (4–12) | 6 (2–13) | NS # |
| 5wIRt ‡ | 2.5 (0–4.75) | 4.5 (3.25–5) | 3.5 (0.75–5) | 4 (0–5) | NS # |
| 5wDRt ‡ | 0.5 (0–2) | 2 (0.25–5) | 1 (0–5) | 1 (0–5) | NS # |
| CLOX1 ‡ | 4 (0–10) | 5 (2–9) | 3.5 (1.5–6) | 3 (0.5–8) | NS # |
| CLOX2 ‡ | 7 (0–12) | 5 (4–10) | 7 (3.75–11.25) | 9 (2–13) | NS # |
| VAMTA | 3 (3–4) e | 3 (2–3) | 2 (1–2) | 2.5 (2–3) | 0.001 # |
| Aβ42 (pg/mL) ** | 430 (359–496) 421 ± 91.3 | 399 (367–477) 415 ± 86.2 | 427 (369–497) 440 ± 77.5 | 454 (380–503) 435 ± 94 | NS †† |
| τT (pg/mL) ** | 844 (561–1220) 900 ± 354 | 713 (575–963) 754 ± 262 | 903 (679–1248) 1104 ± 819 | 682 (527–876) 927 ± 886 | NS †† |
| τP-181 (pg/mL) ** | 80 (76–112) 98.3 ± 33.4 | 97 (70–115) 94.2 ± 22.5 | 97 (75–115) 116 ± 62.3 | 92 (73–105) 119 ± 81.9 | NS †† |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paraskevas, G.P.; Constantinides, V.C.; Boufidou, F.; Tsantzali, I.; Pyrgelis, E.-S.; Liakakis, G.; Kapaki, E. Recognizing Atypical Presentations of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Importance of CSF Biomarkers in Clinical Practice. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123011
Paraskevas GP, Constantinides VC, Boufidou F, Tsantzali I, Pyrgelis E-S, Liakakis G, Kapaki E. Recognizing Atypical Presentations of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Importance of CSF Biomarkers in Clinical Practice. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123011
Chicago/Turabian StyleParaskevas, George P., Vasilios C. Constantinides, Fotini Boufidou, Ioanna Tsantzali, Efstratios-Stylianos Pyrgelis, Georgios Liakakis, and Elisabeth Kapaki. 2022. "Recognizing Atypical Presentations of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Importance of CSF Biomarkers in Clinical Practice" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123011
APA StyleParaskevas, G. P., Constantinides, V. C., Boufidou, F., Tsantzali, I., Pyrgelis, E.-S., Liakakis, G., & Kapaki, E. (2022). Recognizing Atypical Presentations of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Importance of CSF Biomarkers in Clinical Practice. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123011








