Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Clinical Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of IPF Pathogenesis
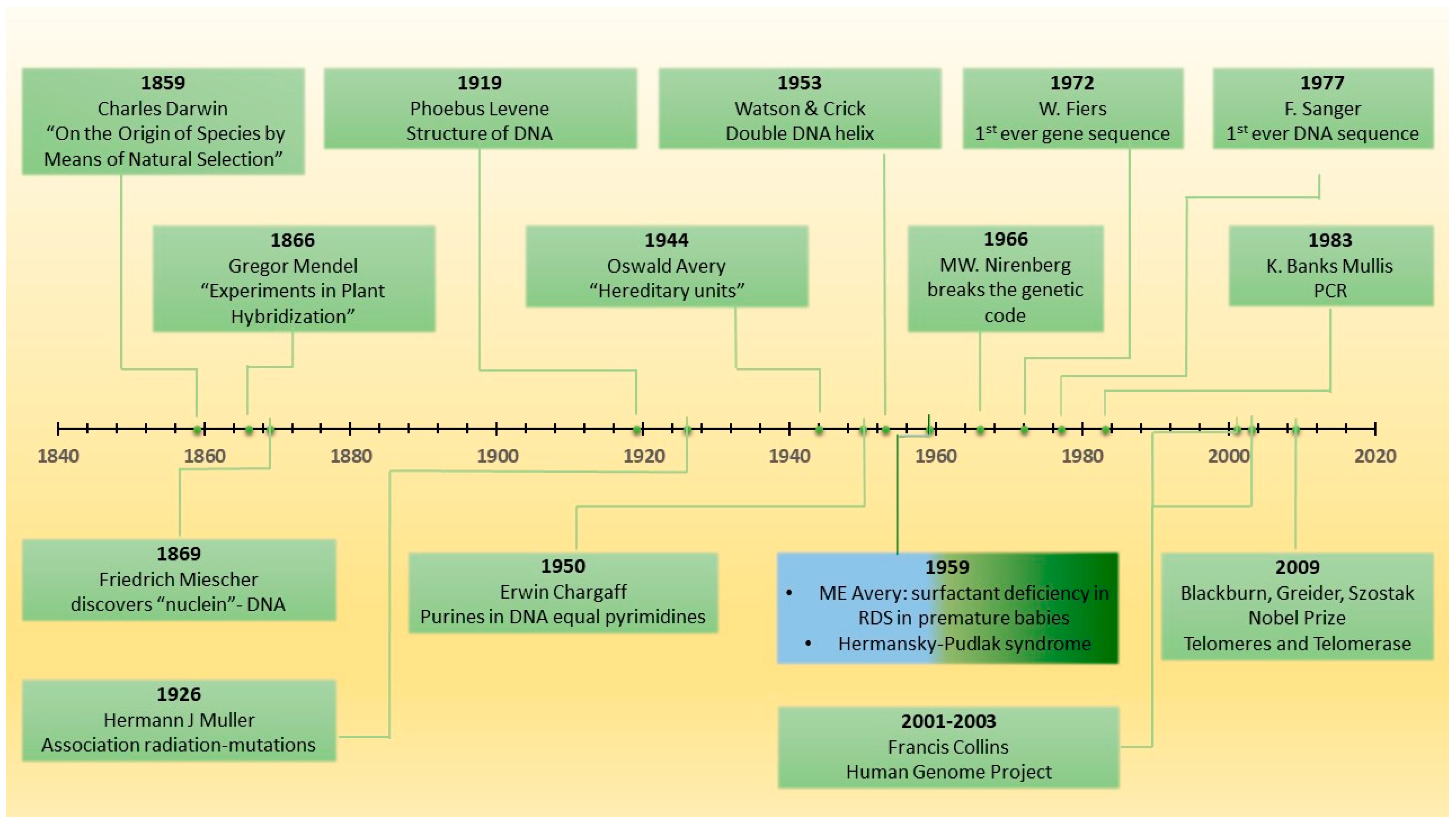
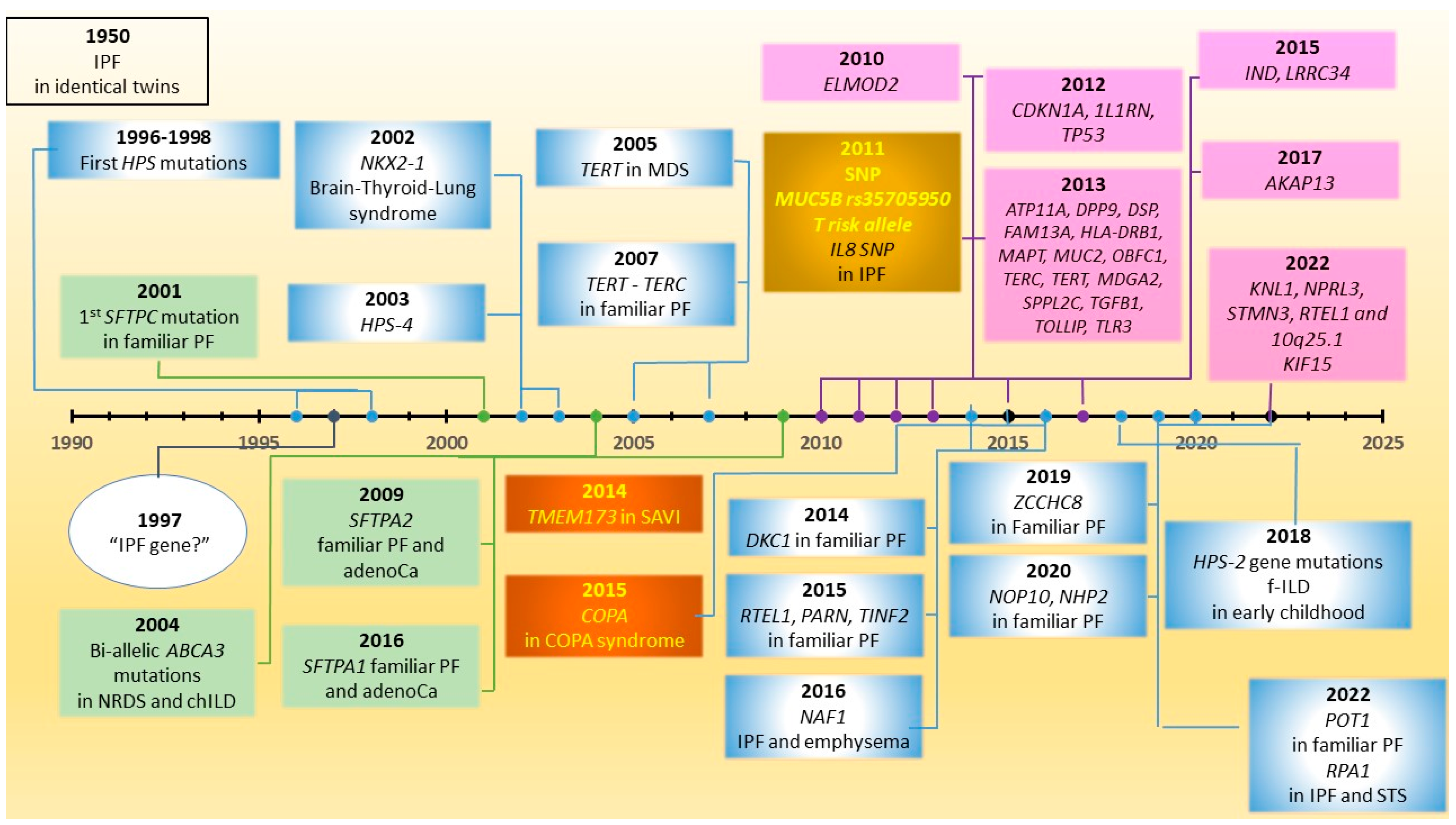
3. Historical Perspective on Genetics in IPF
4. Surfactant-Protein-Related Genes
5. Clinical Implications of Carriership of SRG Mutations
6. Telomere-Related Genes and Telomeropathy
7. Clinical Implications of Carriership of Pathogenic Variations in Telomere-Related Genes
8. Interferonopathies
8.1. STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy
8.2. Hermansky–Pudlak Syndrome
9. Clinical Implications of Other Rare Monogenic Forms of Pulmonary Fibrosis
10. Common Variants in IPF and MUC5B rs35705950
11. Clinical Implications of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and MUC5B rs35705950 T Risk Allele Carriership
12. Special Considerations
12.1. Children Diagnosed with ILD Reaching Adult Life
12.2. Genetic Testing for f-ILDs in Everyday Clinical Practice
13. Conclusions—Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, C.; Cottin, V. Epidemiology and real-life experience in progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Cottin, V. Spectrum of Fibrotic Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Suzuki, A.; Maher, T.M. Interstitial lung diseases. Lancet 2022, 400, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugashetti, J.V.; Adegunsoye, A.; Wu, Z.; Lee, C.T.; Srikrishnan, A.; Ghodrati, S.; Vo, V.; Renzoni, E.A.; Wells, A.U.; Garcia, C.K.; et al. Validation of Proposed Criteria for Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galioto, F.; Palmucci, S.; Astuti, G.M.; Vancheri, A.; Distefano, G.; Tiralongo, F.; Libra, A.; Cusumano, G.; Basile, A.; Vancheri, C. Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Focus on Their Clinical and Radiological Features. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, E.; Ruaro, B.; Giudici, F.; Wade, B.; Santagiuliana, M.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Simbolo, M.; Scarpa, A.; Tollot, S.; et al. Evaluation of Correlations between Genetic Variants and High-Resolution Computed Tomography Patterns in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropski, J.A.; Lawson, W.E.; Young, L.R.; Blackwell, T.S. Genetic studies provide clues on the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Dis. Model Mech. 2013, 6, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Le Guen, P.; Ghanem, M.; Taillé, C.; Dupin, C.; Dieudé, P.; Kannengiesser, C.; Crestani, B. The genetics of interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Newton, C.A. Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: Genetic Features and Clinical Implications. Chest 2021, 160, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmelpennink, M.C.; Meek, D.B.; Vorselaars, A.D.M.; Langezaal, L.C.M.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; van der Vis, J.J.; Veltkamp, M.; Grutters, J.C. Characterization of the PF-ILD phenotype in patients with advanced pulmonary sarcoidosis. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, M.; Bonella, F.; McCarthy, C. Unclassifiable, or simply unclassified interstitial lung disease? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2021, 27, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poellinger, A.; Berezowska, S.; Myers, J.L.; Huber, A.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Guler, S.; Geiser, T.; Harari, S.; Caminati, A.; Zompatori, M.; et al. The Octopus Sign-A New HRCT Sign in Pulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Myers, J.L. Diagnosis of usual interstitial pneumonia and distinction from other fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1275–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, D.A.; Sverzellati, N.; Travis, W.D.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Galvin, J.R.; Goldin, J.G.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A Fleischner Society White Paper. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegunsoye, A.; Vij, R.; Noth, I. Integrating Genomics Into Management of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2019, 155, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.A.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; Kozlitina, J.; Glazer, C.S.; Aravena, C.; Meyer, K.; Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere-related lung fibrosis is diagnostically heterogeneous but uniformly progressive. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Tabèze, L.; Thabut, G.; Nunes, H.; Cottin, V.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Prevot, G.; Tazi, A.; Cadranel, J.; Mal, H.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of TERT and TERC mutations in suspected genetic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyd, J.E. Pulmonary fibrosis in families. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, S47–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, M.P.; Speer, M.C.; Loyd, J.E.; Brown, K.K.; Herron, A.; Slifer, S.H.; Burch, L.H.; Wahidi, M.M.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Sporn, T.A.; et al. Clinical and pathologic features of familial interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, R.T.; Young, N.S. Telomere diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummala, H.; Walne, A.; Dokal, I. The biology and management of dyskeratosis congenita and related disorders of telomeres. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2022, 15, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Dupin, C.; Debray, M.P.; Cazes, A.; Crestani, B. Impact of genetic factors on fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Incidence and clinical presentation in adults. Presse Med. 2020, 49, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laenger, F.P.; Schwerk, N.; Dingemann, J.; Welte, T.; Auber, B.; Verleden, S.; Ackermann, M.; Mentzer, S.J.; Griese, M.; Jonigk, D. Interstitial lung disease in infancy and early childhood: A clinicopathological primer. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M. Chronic interstitial lung disease in children. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogee, L.M.; Hamvas, A. The past and future of genetics in pulmonary disease: You can teach an old dog new tricks. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Mathai, S.K.; Schwartz, D.A. Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Oldham, J.M.; Ma, S.F.; Dressen, A.; Paynton, M.L.; Kraven, L.M.; Obeidat, M.; Li, X.; Ng, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Susceptibility to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Stockwell, A.; Oldham, J.M.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Schwartz, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Flores, C.; Noth, I.; Yaspan, B.L.; Jenkins, R.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study across five cohorts identifies five novel loci associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2022, 77, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Blumhagen, R.Z.; Yang, I.V.; Walts, A.; Powers, J.; Walker, T.; Bishop, M.; Russell, P.; Vestal, B.; Cardwell, J.; et al. Resequencing Study Confirms That Host Defense and Cell Senescence Gene Variants Contribute to the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manali, E.D.; Kannengiesser, C.; Borie, R.; Ba, I.; Bouros, D.; Markopoulou, A.; Antoniou, K.; Kolilekas, L.; Papaioannou, A.I.; Tzilas, V.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Relationships in Inheritable Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Greek National Cohort Study. Respiration 2022, 101, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressen, A.; Abbas, A.R.; Cabanski, C.; Reeder, J.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Neighbors, M.; Bhangale, T.R.; Brauer, M.J.; Hunkapiller, J.; Reeder, J.; et al. Analysis of protein-altering variants in telomerase genes and their association with MUC5B common variant status in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A candidate gene sequencing study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Newton, C.A.; Wang, B.; Povysil, G.; Noth, I.; Martinez, F.J.; Raghu, G.; Goldstein, D.; Kim Garcia, C. Utility of whole genome sequencing in assessing risk and clinically-relevant outcomes for pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 2200577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraven, L.M.; Taylor, A.R.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Maher, T.M.; McDonough, J.E.; Mura, M.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A.; Huang, Y.; Noth, I.; et al. Cluster analysis of transcriptomic datasets to identify endotypes of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan-Guardela, B.M.; Herazo-Maya, J.D. Immunity, Ciliated Epithelium, and Mortality: Are We Ready to Identify Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Endotypes With Prognostic Significance? Chest 2022, 161, 1440–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Rosas, I.O. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 515–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, J.H.W.; Györfi, A.H.; Ramanujam, M.; Whitfield, M.L.; Königshoff, M.; Lafyatis, R. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagares, D.; Hinz, B. Animal and Human Models of Tissue Repair and Fibrosis: An Introduction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2299, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannella, K.M.; Wynn, T.A. Mechanisms of Organ Injury and Repair by Macrophages. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Tata, A.; Konkimalla, A.; Katsura, H.; Lee, R.F.; Ou, J.; Banovich, N.E.; Kropski, J.A.; Tata, P.R. Persistence of a regeneration-associated, transitional alveolar epithelial cell state in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, K.O. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis may be a disease of recurrent, tractional injury to the periphery of the aging lung: A unifying hypothesis regarding etiology and pathogenesis. Arch. Pathol Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; et al. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis is caused by elevated mechanical tension on alveolar stem cells. Cell 2021, 184, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froese, A.R.; Shimbori, C.; Bellaye, P.S.; Inman, M.; Obex, S.; Fatima, S.; Jenkins, G.; Gauldie, J.; Ask, K.; Kolb, M. Stretch-induced Activation of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L. The histologic diagnosis of usual interstitial pneumonia of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Where we are and where we need to go. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomos, I.P.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Aidinis, V.; Manali, E.D.; Bouros, E.; Bouros, D.; Papiris, S.A. Extracellular matrix remodeling in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It is the ‘bed’ that counts and not ‘the sleepers’. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. From pulmonary fibrosis to progressive pulmonary fibrosis: A lethal pathobiological jump. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L600–L607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. When things go wrong: Exploring possible mechanisms driving the progressive fibrosis phenotype in interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Murthy, M.; Balch, W.E.; Chandel, N.S.; Meiners, S.; Eickelberg, O.; Selman, M.; Pardo, A.; White, E.S.; Levy, B.D.; et al. Blue journal conference. Aging and susceptibility to lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moimas, S.; Salton, F.; Kosmider, B.; Ring, N.; Volpe, M.C.; Bahmed, K.; Braga, L.; Rehman, M.; Vodret, S.; Graziani, M.L.; et al. miR-200 family members reduce senescence and restore idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis type II alveolar epithelial cell transdifferentiation. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leavy, O.C.; Ma, S.F.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Maher, T.M.; Oldham, J.M.; Flores, C.; Noth, I.; Jenkins, R.G.; Dudbridge, F.; Wain, L.V.; et al. Proportion of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Risk Explained by Known Common Genetic Loci in European Populations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Porte, J.; Braybrooke, R.; Flores, C.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Oldham, J.M.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Ma, S.F.; Okamoto, T.; John, A.E.; et al. Genetic variants associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in people of European ancestry: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, J.S.; Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R. The contribution of genetic variants to disease depends on the ruler. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, C.R.; Donnelly, E.F.; Mehrad, M.; Ding, G.; Markin, C.R.; Douglas, K.; Wu, P.; Cogan, J.D.; Young, L.R.; Bartholmai, B.J.; et al. The Association between Exposures and Disease Characteristics in Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunninghake, G.M.; Goldin, J.G.; Kadoch, M.A.; Kropski, J.A.; Rosas, I.O.; Wells, A.U.; Yadav, R.; Lazarus, H.M.; Abtin, F.G.; Corte, T.J.; et al. Detection and Early Referral of Patients With Interstitial Lung Abnormalities: An Expert Survey Initiative. Chest 2022, 161, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunninghake, G.M.; Quesada-Arias, L.D.; Carmichael, N.E.; Martinez Manzano, J.M.; Poli De Frías, S.; Baumgartner, M.A.; DiGianni, L.; Gampala-Sagar, S.N.; Leone, D.A.; Gulati, S.; et al. Interstitial Lung Disease in Relatives of Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, R.K.; Rosas, I.O.; Hunninghake, G.M. Genetics and early detection in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, M.L.; Hewlett, J.C.; Ding, G.; Markin, C.R.; Douglas, K.; Mason, W.; Guttentag, A.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Cogan, J.D.; Reiss, S.; et al. Development and Progression of Radiologic Abnormalities in Individuals at Risk for Familial Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropski, J.A.; Young, L.R.; Cogan, J.D.; Mitchell, D.B.; Lancaster, L.H.; Worrell, J.A.; Markin, C.; Liu, N.; Mason, W.R.; Fingerlin, T.E.; et al. Genetic Evaluation and Testing of Patients and Families with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropski, J.A.; Pritchett, J.M.; Zoz, D.F.; Crossno, P.F.; Markin, C.; Garnett, E.T.; Degryse, A.L.; Mitchell, D.B.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Rickman, O.B.; et al. Extensive phenotyping of individuals at risk for familial interstitial pneumonia reveals clues to the pathogenesis of interstitial lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Gouya, L.; Nathan, N.; Crestani, B. Management of suspected monogenic lung fibrosis in a specialised centre. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Gouya, L.; Dupin, C.; Amselem, S.; Ba, I.; Bunel, V.; Bonniaud, P.; Bouvry, D.; Cazes, A.; et al. Pilot experience of multidisciplinary team discussion dedicated to inherited pulmonary fibrosis. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A.; Birchler, J.A.; Meyers, B.C. Focus on plant genetics: Celebrating Gregor Mendel’s 200th birth anniversary. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 2453–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K. After the genome: DNA and human disease. Cell 2001, 104, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jasny, B.R.; Kennedy, D. The human genome. Science 2001, 291, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peabody, J.W.; Peabody, J.W., Jr.; Hayes, E.W.; Hayes, E.W., Jr. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; its occurrence in identical twin sisters. Dis. Chest 1950, 18, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.P.; McAnulty, R.J.; Laurent, G.J. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: Is there a fibrosis gene? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogee, L.M.; Dunbar, A.E., 3rd; Wert, S.E.; Askin, F.; Hamvas, A.; Whitsett, J.A. A mutation in the surfactant protein C gene associated with familial interstitial lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.Q.; Lane, K.; Phillips, J., 3rd; Prince, M.; Markin, C.; Speer, M.; Schwartz, D.A.; Gaddipati, R.; Marney, A.; Johnson, J.; et al. Heterozygosity for a surfactant protein C gene mutation associated with usual interstitial pneumonitis and cellular nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis in one kindred. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.; Tanaka, T.; Ishida, M.; Kinoshita, A.; Fukuoka, J.; Takaki, M.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Kohno, S.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Surfactant protein C G100S mutation causes familial pulmonary fibrosis in Japanese kindred. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Moorsel, C.H.; van Oosterhout, M.F.; Barlo, N.P.; de Jong, P.A.; van der Vis, J.J.; Ruven, H.J.; van Es, H.W.; van den Bosch, J.M.; Grutters, J.C. Surfactant protein C mutations are the basis of a significant portion of adult familial pulmonary fibrosis in a dutch cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic defects in surfactant protein A2 are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, N.; Giraud, V.; Picard, C.; Nunes, H.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; Copin, B.; Galeron, L.; De Ligniville, A.; Kuziner, N.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; et al. Germline SFTPA1 mutation in familial idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and lung cancer. Hum. Mol Genet. 2016, 25, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulenin, S.; Nogee, L.M.; Annilo, T.; Wert, S.E.; Whitsett, J.A.; Dean, M. ABCA3 gene mutations in newborns with fatal surfactant deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.E.; Wert, S.E.; Whitsett, J.A.; Dean, M.; Nogee, L.M. ABCA3 mutations associated with pediatric interstitial lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, C.; Wittmann, T.; Reu, S.; Teusch, V.; Klemme, M.; Rauch, D.; Hengst, M.; Kappler, M.; Cobanoglu, N.; Sismanlar, T.; et al. Lung disease caused by ABCA3 mutations. Thorax 2017, 72, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manali, E.D.; Legendre, M.; Nathan, N.; Kannengiesser, C.; Coulomb-L’Hermine, A.; Tsiligiannis, T.; Tomos, P.; Griese, M.; Borie, R.; Clement, A.; et al. Bi-allelic missense ABCA3 mutations in a patient with childhood ILD who reached adulthood. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00066–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galambos, C.; Levy, H.; Cannon, C.L.; Vargas, S.O.; Reid, L.M.; Cleveland, R.; Lindeman, R.; deMello, D.E.; Wert, S.E.; Whitsett, J.A.; et al. Pulmonary pathology in thyroid transcription factor-1 deficiency syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamvas, A.; Deterding, R.R.; Wert, S.E.; White, F.V.; Dishop, M.K.; Alfano, D.N.; Halbower, A.C.; Planer, B.; Stephan, M.J.; Uchida, D.A.; et al. Heterogeneous pulmonary phenotypes associated with mutations in the thyroid transcription factor gene NKX2-1. Chest 2013, 144, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borie, R.; Funalot, B.; Epaud, R.; Delestrain, C.; Cazes, A.; Gounant, V.; Frija, J.; Debray, M.P.; Zalcman, G.; Crestani, B. NKX2.1 (TTF1) germline mutation associated with pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00356-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattes, E.; Lejeune, S.; Carsin, A.; Borie, R.; Gibertini, I.; Balinotti, J.; Nathan, N.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Thumerelle, C.; Fauroux, B.; et al. Heterogeneity of lung disease associated with NK2 homeobox 1 mutations. Respir. Med. 2017, 129, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Moorsel, C.H.M.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C. Genetic disorders of the surfactant system: Focus on adult disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogee, L.M. Genetic causes of surfactant protein abnormalities. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, W.E.; Crossno, P.F.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Roldan, J.; Cheng, D.S.; Lane, K.B.; Blackwell, T.R.; Xu, C.; Markin, C.; Ware, L.B.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in alveolar epithelial cells is prominent in IPF: Association with altered surfactant protein processing and herpesvirus infection. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L1119–L1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.; Guttentag, S.H.; Deterding, R.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Goralski, J.L.; Chatterjee, S.; Mulugeta, S.; Beers, M.F. A non-BRICHOS SFTPC mutant (SP-CI73T) linked to interstitial lung disease promotes a late block in macroautophagy disrupting cellular proteostasis and mitophagy. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L33–L47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, M.F.; Hawkins, A.; Maguire, J.A.; Kotorashvili, A.; Zhao, M.; Newitt, J.L.; Ding, W.; Russo, S.; Guttentag, S.; Gonzales, L.; et al. A nonaggregating surfactant protein C mutant is misdirected to early endosomes and disrupts phospholipid recycling. Traffic 2011, 12, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzen, J.; Wagner, B.D.; Venosa, A.; Kopp, M.; Tomer, Y.; Russo, S.J.; Headen, A.C.; Basil, M.C.; Stark, J.M.; Mulugeta, S.; et al. An SFTPC BRICHOS mutant links epithelial ER stress and spontaneous lung fibrosis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, M.F.; Mulugeta, S. The biology of the ABCA3 lipid transporter in lung health and disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, M.; Wang, Y.; Gerard, R.D.; Mendelson, C.R.; Garcia, C.K. Surfactant protein A2 mutations associated with pulmonary fibrosis lead to protein instability and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22103–22113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezaki, A.; Tsukumo, S.I.; Setoguchi, Y.; Ledford, J.G.; Goto, H.; Hosomichi, K.; Uehara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Yasutomo, K. A homozygous SFTPA1 mutation drives necroptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, A.; Szinnai, G.; Castanet, M.; Sura-Trueba, S.; Tron, E.; Broutin-L’Hermite, I.; Barat, P.; Goizet, C.; Lacombe, D.; Moutard, M.L.; et al. Five new TTF1/NKX2.1 mutations in brain-lung-thyroid syndrome: Rescue by PAX8 synergism in one case. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2266–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shin, D.; Lee, G.; Bae, H. Loss of SP-A in the Lung Exacerbates Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomer, Y.; Wambach, J.; Knudsen, L.; Zhao, M.; Rodriguez, L.R.; Murthy, A.; White, F.V.; Venosa, A.; Katzen, J.; Ochs, M.; et al. The common ABCA3(E292V) variant disrupts AT2 cell quality control and increases susceptibility to lung injury and aberrant remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L291–L307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, J.A.; Rutherford, E.N.; Abreu, S.; Chambers, J.E.; Ellis, M.O.; van Schadewijk, A.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Marciniak, S.J. Novel insights into surfactant protein C trafficking revealed through the study of a pathogenic mutant. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Moorsel, C.H.; Hoffman, T.W.; van Batenburg, A.A.; Klay, D.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C. Understanding Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia: A Gene-Based Review of Stressed Lungs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 304186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, M.; Butt, A.; Borie, R.; Debray, M.P.; Bouvry, D.; Filhol-Blin, E.; Desroziers, T.; Nau, V.; Copin, B.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; et al. Functional assessment and phenotypic heterogeneity of SFTPA1 and SFTPA2 mutations in interstitial lung diseases and lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M.; Lorenz, E.; Hengst, M.; Schams, A.; Wesselak, T.; Rauch, D.; Wittmann, T.; Kirchberger, V.; Escribano, A.; Schaible, T.; et al. Surfactant proteins in pediatric interstitial lung disease. Pediatr Res. 2016, 79, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, T.; Peca, D.; Menchini, L.; Schiavino, A.; Boldrini, R.; Esposito, F.; Danhaive, O.; Cutrera, R. Surfactant Protein C-associated interstitial lung disease; three different phenotypes of the same SFTPC mutation. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Moorsel, C.H.; Ten Klooster, L.; van Oosterhout, M.F.; de Jong, P.A.; Adams, H.; Wouter van Es, H.; Ruven, H.J.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C. SFTPA2 Mutations in Familial and Sporadic Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayasaka, I.; Cho, K.; Akimoto, T.; Ikeda, M.; Uzuki, Y.; Yamada, M.; Nakata, K.; Furuta, I.; Ariga, T.; Minakami, H. Genetic basis for childhood interstitial lung disease among Japanese infants and children. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Nong, G.; Liu, X.; Ji, W.; Zhao, D.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, K. Genetic basis of surfactant dysfunction in Chinese children: A retrospective study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klay, D.; Platenburg, M.; van Rijswijk, R.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. ABCA3 mutations in adult pulmonary fibrosis patients: A case series and review of literature. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, M.; Darde, X.; Ferreira, M.; Chantot-Bastaraud, S.; Campana, M.; Plantier, L.; Nathan, N.; Amselem, S.; Toutain, A.; Diot, P.; et al. The clinical course of interstitial lung disease in an adult patient with an ABCA3 homozygous complex allele under hydroxychloroquine and a review of the literature. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2022, 39, e2022019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.G.; Thakkar, D.; Buchanan, P.; Graf, N.; Wheatley, J. ABCA3 deficiency from birth to adulthood presenting as paediatric interstitial lung disease. Respirol. Case Rep. 2020, 8, e00633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S. Etiologic spectrum of interstitial lung diseases in Chinese children older than 2 years of age. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, C.; Reu, S.; Teusch, V.; Schams, A.; Grimmelt, A.C.; Barker, M.; Brand, J.; Gappa, M.; Kitz, R.; Kramer, B.W.; et al. Genotype alone does not predict the clinical course of SFTPC deficiency in paediatric patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbar, R.; Shih, F.; Baga, M.; Torlakovic, E.; Ramlall, K.; Skomro, R.; Cockcroft, D.W.; Lemire, E.G. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia with mutation in surfactant protein C in familial pulmonary fibrosis. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klay, D.; Hoffman, T.W.; Harmsze, A.M.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Systematic review of drug effects in humans and models with surfactant-processing disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M.; Kappler, M.; Stehling, F.; Schulze, J.; Baden, W.; Koerner-Rettberg, C.; Carlens, J.; Prenzel, F.; Nährlich, L.; Thalmeier, A.; et al. Randomized controlled phase 2 trial of hydroxychloroquine in childhood interstitial lung disease. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, A.L.; Wambach, J.A.; Sinn, P.L.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Gene Therapy Potential for Genetic Disorders of Surfactant Dysfunction. Front. Genome Ed. 2021, 3, 785829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinting, S.; Höppner, S.; Schindlbeck, U.; Forstner, M.E.; Harfst, J.; Wittmann, T.; Griese, M. Functional rescue of misfolding ABCA3 mutations by small molecular correctors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, W.B.; Zhang, Q.; Faro, A.; Sweet, S.C.; Eghtesady, P.; Hamvas, A.; Cole, F.S.; Wambach, J.A. Outcomes of Lung Transplantation for Infants and Children with Genetic Disorders of Surfactant Metabolism. J. Pediatr. 2017, 184, 157–164.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiri, K.D.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Weissler, J.C.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Shay, J.W.; Garcia, C.K. Adult-onset pulmonary fibrosis caused by mutations in telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulliamy, T.J.; Walne, A.; Baskaradas, A.; Mason, P.J.; Marrone, A.; Dokal, I. Mutations in the reverse transcriptase component of telomerase (TERT) in patients with bone marrow failure. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2005, 34, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walne, A.J.; Dokal, I. Telomerase dysfunction and dyskeratosis congenita. Cytotechnology 2004, 45, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mason, P.J.; Bessler, M. The genetics of dyskeratosis congenita. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuch, A.A. The molecular genetics of the telomere biology disorders. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulliamy, T.J.; Marrone, A.; Knight, S.W.; Walne, A.; Mason, P.J.; Dokal, I. Mutations in dyskeratosis congenita: Their impact on telomere length and the diversity of clinical presentation. Blood 2006, 107, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, S.A.; Stewart, B.J.; Weksler, B.B.; Baerlocher, G.M.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Chanock, S.J.; Alter, B.P. Mutations in the reverse transcriptase component of telomerase (TERT) in patients with bone marrow failure. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2006, 37, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrone, A.; Walne, A.; Tamary, H.; Masunari, Y.; Kirwan, M.; Beswick, R.; Vulliamy, T.; Dokal, I. Telomerase reverse-transcriptase homozygous mutations in autosomal recessive dyskeratosis congenita and Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome. Blood 2007, 110, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, N.S.; Knight, S.W.; Vulliamy, T.J.; Klauck, S.M.; Wiemann, S.; Mason, P.J.; Poustka, A.; Dokal, I. X-linked dyskeratosis congenita is caused by mutations in a highly conserved gene with putative nucleolar functions. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revy, P.; Kannengiesser, C.; Bertuch, A.A. Genetics of human telomere biology disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Armanios, M. Telomere-mediated lung disease. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1703–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Bouvry, D.; Cottin, V.; Gauvain, C.; Cazes, A.; Debray, M.P.; Cadranel, J.; Dieude, P.; Degot, T.; Dominique, S.; et al. Regulator of telomere length 1 (RTEL1) mutations are associated with heterogeneous pulmonary and extra-pulmonary phenotypes. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyelles, M.; O’Donohue, M.F.; Kermasson, L.; Lainey, E.; Borie, R.; Lagresle-Peyrou, C.; Nunes, H.; Cazelles, C.; Fourrage, C.; Ollivier, E.; et al. NHP2 deficiency impairs rRNA biogenesis and causes pulmonary fibrosis and Høyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannengiesser, C.; Manali, E.D.; Revy, P.; Callebaut, I.; Ba, I.; Borgel, A.; Oudin, C.; Haritou, A.; Kolilekas, L.; Malagari, K.; et al. First heterozygous NOP10 mutation in familial pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropski, J.A.; Reiss, S.; Markin, C.; Brown, K.K.; Schwartz, D.A.; Schwarz, M.I.; Loyd, J.E.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Blackwell, T.S.; Cogan, J.D. Rare Genetic Variants in PARN Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis in Families. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.D.; Choi, J.; Zaidi, S.; Xing, C.; Holohan, B.; Chen, R.; Choi, M.; Dharwadkar, P.; Torres, F.; Girod, C.E.; et al. Exome sequencing links mutations in PARN and RTEL1 with familial pulmonary fibrosis and telomere shortening. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gable, D.L.; Gaysinskaya, V.; Atik, C.C.; Talbot, C.C., Jr.; Kang, B.; Stanley, S.E.; Pugh, E.W.; Amat-Codina, N.; Schenk, K.M.; Arcasoy, M.O.; et al. ZCCHC8, the nuclear exosome targeting component, is mutated in familial pulmonary fibrosis and is required for telomerase RNA maturation. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelich, J.; Aramburu, T.; van der Vis, J.J.; Showe, L.; Kossenkov, A.; van der Smagt, J.; Massink, M.; Schoemaker, A.; Hennekam, E.; Veltkamp, M.; et al. Telomere dysfunction implicates POT1 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S.E.; Gable, D.L.; Wagner, C.L.; Carlile, T.M.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Khalil, S.E.; DeZern, A.E.; Rojas-Duran, M.F.; Applegate, C.D.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the RNA biogenesis factor NAF1 predispose to pulmonary fibrosis-emphysema. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 351ra107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysinskaya, V.; Stanley, S.E.; Adam, S.; Armanios, M. Synonymous Mutation in DKC1 Causes Telomerase RNA Insufficiency Manifesting as Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2020, 158, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Stanley, S.E.; Wagner, C.L.; Hamilton, M.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Armanios, M. Exome sequencing identifies mutant TINF2 in a family with pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2015, 147, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vis, J.J.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Hennekam, F.A.M.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Pulmonary Fibrosis and a TERT Founder Mutation With a Latency Period of 300 Years. Chest 2020, 158, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sahoo, S.S.; Honda, M.; Granger, S.L.; Goodings, C.; Sanchez, L.; Künstner, A.; Busch, H.; Beier, F.; Pruett-Miller, S.M.; et al. Gain-of-function mutations in RPA1 cause a syndrome with short telomeres and somatic genetic rescue. Blood 2022, 139, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Kacher, R.; Jaillet, M.; Colicchio, B.; Vasarmidi, E.; Mailleux, A.; Dieterlen, A.; Kannengiesser, C.; Borie, C.; Oudrhiri, N.; Junker, S.; et al. Lung Fibroblasts from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients Harbor Short and Unstable Telomeres Leading to Chromosomal Instability. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratz, K.E.; Haley, L.; Danoff, S.K.; Blackford, A.L.; DeZern, A.E.; Gocke, C.D.; Duffield, A.S.; Armanios, M. Cancer spectrum and outcomes in the Mendelian short telomere syndromes. Blood 2020, 135, 1946–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratz, K.E. Extrahematopoietic manifestations of the short telomere syndromes. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2020, 2020, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.L.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Talbot, C.C., Jr.; Abraham, R.S.; Hamm, D.; Gable, D.L.; Kanakry, C.G.; Applegate, C.D.; Siliciano, J.; Jackson, J.B.; et al. Short telomere syndromes cause a primary T cell immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5222–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomos, I.; Karakatsani, A.; Manali, E.D.; Kottaridi, C.; Spathis, A.; Argentos, S.; Papiris, S.A. Telomere length across different UIP fibrotic-Interstitial Lung Diseases: A prospective Greek case-control study. Pulmonology 2022, 28, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.C.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short telomeres are a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Strong, M.A.; DeZern, A.E.; Stanley, S.E.; Takemoto, C.M.; Danilova, L.; Applegate, C.D.; Bolton, S.G.; Mohr, D.W.; et al. Diagnostic utility of telomere length testing in a hospital-based setting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2358–E2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansner, J.M.; Rosas, I.O.; Ebert, B.L. Pulmonary fibrosis, bone marrow failure, and telomerase mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1551–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M.; Alder, J.K.; Parry, E.M.; Karim, B.; Strong, M.A.; Greider, C.W. Short telomeres are sufficient to cause the degenerative defects associated with aging. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.P. Molecular Mechanisms of Alveolar Epithelial Stem Cell Senescence and Senescence-Associated Differentiation Disorders in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells 2022, 11, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roake, C.M.; Artandi, S.E. Regulation of human telomerase in homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.R.; Wyatt, H.D.; Ting, N.S.; Beattie, T.L. hTERT mutations associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis affect telomerase activity, telomere length, and cell growth by distinct mechanisms. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M.; Blackburn, E.H. The telomere syndromes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Molina, M.; Borie, R. Clinical implications of telomere dysfunction in lung fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehian, S.; Semple, T.; Pabary, R. Childhood interstitial lung disease: Short lessons from telomeres. Thorax 2021, 76, 1250–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Cogan, J.D.; Brown, A.F.; Anderson, C.J.; Lawson, W.E.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Loyd, J.E.; Chen, J.J.; Armanios, M. Ancestral mutation in telomerase causes defects in repeat addition processivity and manifests as familial pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silhan, L.L.; Shah, P.D.; Chambers, D.C.; Snyder, L.D.; Riise, G.C.; Wagner, C.L.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Orens, J.B.; Mewton, J.F.; Danoff, S.K.; et al. Lung transplantation in telomerase mutation carriers with pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Hirschi, S.; Le Pavec, J.; Mal, H.; Bergot, E.; Jouneau, S.; Naccache, J.M.; Revy, P.; Boutboul, D.; et al. Severe hematologic complications after lung transplantation in patients with telomerase complex mutations. J. Heart. Lung Transpl. 2015, 34, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips-Houlbracq, M.; Mal, H.; Cottin, V.; Gauvain, C.; Beier, F.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Sidali, S.; Mornex, J.F.; Hirschi, S.; Roux, A.; et al. Determinants of survival after lung transplantation in telomerase-related gene mutation carriers: A retrospective cohort. Am. J. Transpl. 2022, 22, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, A.C.; Neely, M.L.; Frankel, C.W.; Kelly, F.L.; Petrovski, S.; Durheim, M.T.; Bush, E.; Snyder, L.; Goldstein, D.B.; Todd, J.L.; et al. Lung Transplant Outcomes in Patients With Pulmonary Fibrosis With Telomere-Related Gene Variants. Chest 2019, 156, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Messika, J.; Courtwright, A.; Mornex, J.F.; Hirschi, S.; Roux, A.; Le Pavec, J.; Quêtant, S.; Froidure, A.; Lazor, R.; et al. Airway complications in lung transplant recipients with telomere-related interstitial lung disease. Clin. Transpl. 2022, 36, e14552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Rosas, I.O.; Cui, Y.; McKane, C.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Camp, P.C.; Raby, B.A.; Goldberg, H.J.; El-Chemaly, S. Short telomeres, telomeropathy, and subclinical extrapulmonary organ damage in patients with interstitial lung disease. Chest 2015, 147, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pavec, J.; Dauriat, G.; Gazengel, P.; Dolidon, S.; Hanna, A.; Feuillet, S.; Pradere, P.; Crutu, A.; Florea, V.; Boulate, D.; et al. Lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Presse Med. 2020, 49, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, I.; Mannem, H.; Winters, S.A.; Hoji, A.; Silveira, F.; McNally, E.; Pipeling, M.R.; Lendermon, E.A.; Morrell, M.R.; Pilewski, J.M.; et al. Impaired Cytomegalovirus Immunity in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Lung Transplant Recipients with Short Telomeres. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Boutboul, D.; Tabeze, L.; Brunet-Possenti, F.; Lainey, E.; Debray, M.P.; Cazes, A.; Crestani, B. Pneumocystosis revealing immunodeficiency secondary to TERC mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Anstrom, K.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lasky, J.A.; Martinez, F.J. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.A.; Zhang, D.; Oldham, J.M.; Kozlitina, J.; Ma, S.F.; Martinez, F.J.; Raghu, G.; Noth, I.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere Length and Use of Immunosuppressive Medications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, C.R.; Myllymäki, M.; Redd, R.; Padmanaban, S.; Karunakaran, D.; Tesmer, V.; Tsai, F.D.; Gibson, C.J.; Rana, H.Q.; Zhong, L.; et al. The clinical and functional effects of TERT variants in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2021, 138, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, E.M.; Alder, J.K.; Qi, X.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Armanios, M. Syndrome complex of bone marrow failure and pulmonary fibrosis predicts germline defects in telomerase. Blood 2011, 117, 5607–5611, Erratum in Blood 2016, 127, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papiris, S.A.; Tsirigotis, P.; Kannengiesser, C.; Kolilekas, L.; Gkirkas, K.; Papaioannou, A.I.; Revy, P.; Giouleka, P.; Papadaki, G.; Kagouridis, K.; et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A dangerous liaison. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz de Leon, A.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Katzenstein, A.L.; Godwin, J.D.; Raghu, G.; Glazer, C.S.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Girod, C.E.; Garrity, E.R.; Xing, C.; et al. Telomere lengths, pulmonary fibrosis and telomerase (TERT) mutations. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratz, K.E.; Gaysinskaya, V.; Cosner, Z.L.; DeBoy, E.A.; Xiang, Z.; Kasch-Semenza, L.; Florea, L.; Shah, P.D.; Armanios, M. Somatic reversion impacts myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia evolution in the short telomere disorders. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e147598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, R.T.; Regal, J.A.; Kleiner, D.E.; Schrump, D.S.; Peterson, N.R.; Pons, V.; Chanock, S.J.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Young, N.S. A spectrum of severe familial liver disorders associate with telomerase mutations. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, R.T.; Brudno, J.; Mehta, P.; Kovacs, J.J.; Wu, C.; Zago, M.A.; Chanock, S.J.; Boyer, T.D.; Young, N.S. Constitutional telomerase mutations are genetic risk factors for cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.C.; Ningarhari, M.; Rebouissou, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. The role of telomeres and telomerase in cirrhosis and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, K.L.; Chang, S.; Millard, M.; Schreiber-Agus, N.; DePinho, R.A. Inhibition of experimental liver cirrhosis in mice by telomerase gene delivery. Science 2000, 287, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgy, A.I.; Jonassaint, N.L.; Stanley, S.E.; Koteish, A.; DeZern, A.E.; Walter, J.E.; Sopha, S.C.; Hamilton, J.P.; Hoover-Fong, J.; Chen, A.R.; et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome is a frequent cause of dyspnea in the short telomere disorders. Chest 2015, 148, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, T.W.; van der Vis, J.J.; Biesma, D.H.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Extrapulmonary manifestations of a telomere syndrome in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are associated with decreased survival. Respirology 2022, 27, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Rochwerg, B.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, C.A.; Azuma, A.; Behr, J.; Brozek, J.L.; Collard, H.R.; Cunningham, W.; Homma, S.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, e3–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justet, A.; Thabut, G.; Manali, E.; Molina Molina, M.; Kannengiesser, C.; Cadranel, J.; Cottin, V.; Gondouin, A.; Nunes, H.; Magois, E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of pirfenidone in patients carrying telomerase complex mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justet, A.; Klay, D.; Porcher, R.; Cottin, V.; Ahmad, K.; Molina Molina, M.; Nunes, H.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Naccache, J.M.; Manali, E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and carrying a telomere-related gene mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsley, D.M.; Dumitriu, B.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Weinstein, B.; Chen, C.; Hardy, N.; Mihalek, A.D.; Lingala, S.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Danazol Treatment for Telomere Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackintosh, J.A.; Pietsch, M.; Lutzky, V.; Enever, D.; Bancroft, S.; Apte, S.H.; Tan, M.; Yerkovich, S.T.; Dickinson, J.L.; Pickett, H.A.; et al. TELO-SCOPE study: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial of danazol for short telomere related pulmonary fibrosis. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2021, 8, e001127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, M.C.; Katzen, J.; Engler, A.E.; Guo, M.; Herriges, M.J.; Kathiriya, J.J.; Windmueller, R.; Ysasi, A.B.; Zacharias, W.J.; Chapman, H.A.; et al. The Cellular and Physiological Basis for Lung Repair and Regeneration: Past, Present, and Future. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 482–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jesus, A.A.; Marrero, B.; Yang, D.; Ramsey, S.E.; Sanchez, G.A.M.; Tenbrock, K.; Wittkowski, H.; Jones, O.Y.; Kuehn, H.S.; et al. Activated STING in a vascular and pulmonary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.; Frémond, M.L. Lung Inflammation in STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI). Cells 2022, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, C.; Thouvenin, G.; Kannengiesser, C.; Dubus, J.C.; Jeremiah, N.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Crestani, B.; Belot, A.; Thivolet-Béjui, F.; Secq, V.; et al. Severe Pulmonary Fibrosis as the First Manifestation of Interferonopathy (TMEM173 Mutation). Chest 2016, 150, e65–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, F.; Betrains, A.; Doubel, P.; Willemsen, M.; Cleemput, V.; Vanderschueren, S.; Corveleyn, A.; Meyts, I.; Sprangers, B.; Crow, Y.J.; et al. Adult-Onset ANCA-Associated Vasculitis in SAVI: Extension of the Phenotypic Spectrum, Case Report and Review of the Literature. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkin, L.B.; Jessen, B.; Wiszniewski, W.; Vece, T.J.; Jan, M.; Sha, Y.; Thamsen, M.; Santos-Cortez, R.L.; Lee, K.; Gambin, T.; et al. COPA mutations impair ER-Golgi transport and cause hereditary autoimmune-mediated lung disease and arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.; Hrovat-Schaale, K.; Prigione, I.; Yu, C.H.; Laohamonthonkul, P.; Harapas, C.R.; Low, R.R.J.; De Nardo, D.; Dagley, L.F.; Mlodzianoski, M.J.; et al. Deficiency in coatomer complex I causes aberrant activation of STING signalling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepelley, A.; Martin-Niclós, M.J.; Le Bihan, M.; Marsh, J.A.; Uggenti, C.; Rice, G.I.; Bondet, V.; Duffy, D.; Hertzog, J.; Rehwinkel, J.; et al. Mutations in COPA lead to abnormal trafficking of STING to the Golgi and interferon signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vece, T.J.; Watkin, L.B.; Nicholas, S.; Canter, D.; Braun, M.C.; Guillerman, R.P.; Eldin, K.W.; Bertolet, G.; McKinley, S.; de Guzman, M.; et al. Copa Syndrome: A Novel Autosomal Dominant Immune Dysregulatory Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, S.; Tsui, J.; Mariani, M.; Pastorino, C.; Caorsi, R.; Sacco, O.; Ravelli, A.; Shum, A.K.; Gattorno, M.; Picco, P. Type I interferon pathway activation in COPA syndrome. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 187, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Gochuico, B.R. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome pulmonary fibrosis: A rare inherited interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansky, F.; Pudlak, P. Albinism associated with hemorrhagic diathesis and unusual pigmented reticular cells in the bone marrow: Report of two cases with histochemical studies. Blood 1959, 14, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Bailin, T.; Fukai, K.; Feng, G.H.; Ho, L.; Mao, J.I.; Frenk, E.; Tamura, N.; Spritz, R.A. Positional cloning of a gene for Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, a disorder of cytoplasmic organelles. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Angelica, E.C.; Shotelersuk, V.; Aguilar, R.C.; Gahl, W.A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Altered trafficking of lysosomal proteins in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome due to mutations in the beta 3A subunit of the AP-3 adaptor. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.D.; Huizing, M.; Claassen, D.A.; White, J.; Gahl, W.A. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 4 (HPS-4): Clinical and molecular characteristics. Hum. Genet. 2003, 113, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann, S.; Schulz, A.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Dieckmann, N.M.; Niethammer, K.; Fuchs, S.; Eckl, K.M.; Plank, R.; Werner, R.; Altmüller, J.; et al. Mutations in AP3D1 associated with immunodeficiency and seizures define a new type of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Blood 2016, 127, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizing, M.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; Wang, J.A.; Pri-Chen, H.; Hess, R.A.; Fischer, R.; O’Brien, K.J.; Merideth, M.A.; Gahl, W.A.; Gochuico, B.R. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: Mutation update. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 543–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengst, M.; Naehrlich, L.; Mahavadi, P.; Grosse-Onnebrink, J.; Terheggen-Lagro, S.; Skanke, L.H.; Schuch, L.A.; Brasch, F.; Guenther, A.; Reu, S.; et al. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2 manifests with fibrosing lung disease early in childhood. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochuico, B.R.; Huizing, M.; Golas, G.A.; Scher, C.D.; Tsokos, M.; Denver, S.D.; Frei-Jones, M.J.; Gahl, W.A. Interstitial lung disease and pulmonary fibrosis in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2, an adaptor protein-3 complex disease. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicary, G.W.; Vergne, Y.; Santiago-Cornier, A.; Young, L.R.; Roman, J. Pulmonary Fibrosis in Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhani, F.N.; Brantly, M.L.; Markello, T.C.; Helip-Wooley, A.; O’Brien, K.; Hess, R.; Huizing, M.; Gahl, W.A.; Gochuico, B.R. Alveolar macrophage dysregulation in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, J.; Bodine, S.P.M.; Lamattina, A.M.; Ma, D.D.; Shrestha, S.; Maynard, D.M.; Bishop, K.; Nwokeji, A.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; Testa, L.C.; et al. Dysregulated myosin in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome lung fibroblasts is associated with increased cell motility. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyerla, T.A.; Rusiniak, M.E.; Borchers, M.; Jahreis, G.; Tan, J.; Ohtake, P.; Novak, E.K.; Swank, R.T. Aberrant lung structure, composition, and function in a murine model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L643–L653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, P.W.; Oiso, N.; Gautam, R.; Suzuki, T.; Swank, R.T.; Spritz, R.A. The Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 1 (HPS1) and HPS4 proteins are components of two complexes, BLOC-3 and BLOC-4, involved in the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20332–20337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atochina-Vasserman, E.N.; Bates, S.R.; Zhang, P.; Abramova, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gonzales, L.; Tao, J.Q.; Gochuico, B.R.; Gahl, W.; Guo, C.J.; et al. Early alveolar epithelial dysfunction promotes lung inflammation in a mouse model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.R.; Gulleman, P.M.; Bridges, J.P.; Weaver, T.E.; Deutsch, G.H.; Blackwell, T.S.; McCormack, F.X. The alveolar epithelium determines susceptibility to lung fibrosis in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, T.; Sato, S.; Upagupta, C.; Kolb, M. What have we learned from basic science studies on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.J.; Introne, W.J.; Akal, O.; Akal, T.; Barbu, A.; McGowan, M.P.; Merideth, M.A.; Seward, S.L., Jr.; Gahl, W.A.; Gochuico, B.R. Prolonged treatment with open-label pirfenidone in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome pulmonary fibrosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 125, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuto, L.; Qayum, S.; Kim, H.; Robbins, H.; Shah, L.; Dimango, A.; Magda, G.; Grewal, H.; Lemaitre, P.; Stanifer, B.P.; et al. Lung Transplantation for Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated With Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome. A Single-center Experience. Transpl. Direct 2022, 8, e1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin Gedik, K.; Lamot, L.; Romano, M.; Demirkaya, E.; Piskin, D.; Torreggiani, S.; Adang, L.A.; Armangue, T.; Barchus, K.; Cordova, D.R.; et al. The 2021 European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology/American College of Rheumatology Points to Consider for Diagnosis and Management of Autoinflammatory Type I Interferonopathies: CANDLE/PRAAS, SAVI, and AGS. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frémond, M.L.; Legendre, M.; Fayon, M.; Clement, A.; Filhol-Blin, E.; Richard, N.; Berdah, L.; Roullaud, S.; Rice, G.I.; Bondet, V.; et al. Use of ruxolitinib in COPA syndrome manifesting as life-threatening alveolar haemorrhage. Thorax 2020, 75, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griese, M.; Seidl, E.; Hengst, M.; Reu, S.; Rock, H.; Anthony, G.; Kiper, N.; Emiralioğlu, N.; Snijders, D.; Goldbeck, L.; et al. International management platform for children’s interstitial lung disease (chILD-EU). Thorax 2018, 73, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a complex genetic disorder. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2016, 127, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fingerlin, T.E.; Murphy, E.; Zhang, W.; Peljto, A.L.; Brown, K.K.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.E.; Cosgrove, G.P.; Lynch, D.; Groshong, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthagen, N.M.; van Moorsel, C.H.; Barlo, N.P.; Kazemier, K.M.; Ruven, H.J.; Grutters, J.C. Association between variations in cell cycle genes and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, V.; Bruce, S.; Rintahaka, J.; Hodgson, U.; Laitinen, T.; Alenius, H.; Kinnula, V.L.; Myllärniemi, M.; Matikainen, S.; Kere, J. ELMOD2, a candidate gene for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, regulates antiviral responses. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.H.; Park, B.L.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.W.; Park, J.S.; Kim, D.J.; Jang, A.S.; Park, J.S.; Shin, H.K.; Uh, S.T.; et al. A promoter SNP rs4073T>A in the common allele of the interleukin 8 gene is associated with the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via the IL-8 protein enhancing mode. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noth, I.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.F.; Flores, C.; Barber, M.; Huang, Y.; Broderick, S.M.; Wade, M.S.; Hysi, P.; Scuirba, J.; et al. Genetic variants associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility and mortality: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, D.N.; Armstrong, M.E.; Trujillo, G.; Cooke, G.; Keane, M.P.; Fallon, P.G.; Simpson, A.J.; Millar, A.B.; McGrath, E.E.; Whyte, M.K.; et al. The Toll-like receptor 3 L412F polymorphism and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Povysil, G.; Kobeissy, P.H.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Amelotte, M.; Jaouadi, H.; Newton, C.A.; Maher, T.M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; et al. Rare and Common Variants in KIF15 Contribute to Genetic Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, M.A.; Wise, A.L.; Speer, M.C.; Steele, M.P.; Brown, K.K.; Loyd, J.E.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Zhang, W.; Gudmundsson, G.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimasu, Y.; Ohshimo, S.; Bonella, F.; Tanaka, S.; Ishikawa, N.; Hattori, N.; Kohno, N.; Guzman, J.; Costabel, U. MUC5B promoter polymorphism in Japanese patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2015, 20, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peljto, A.L.; Selman, M.; Kim, D.S.; Murphy, E.; Tucker, L.; Pardo, A.; Lee, J.S.; Ji, W.; Schwarz, M.I.; Yang, I.V.; et al. The MUC5B promoter polymorphism is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in a Mexican cohort but is rare among Asian ancestries. Chest 2015, 147, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.A.; Lee, J.S.; Ebstein, E.; Furukawa, H.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Gazal, S.; Kannengiesser, C.; Ottaviani, S.; Oka, S.; Tohma, S.; et al. MUC5B Promoter Variant and Rheumatoid Arthritis with Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, H.; Peljto, A.L.; Walts, A.D.; Cardwell, J.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Lee, J.S.; Fernández Pérez, E.R.; Wolters, P.J.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Common idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis risk variants are associated with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Thorax 2022, 77, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Hennessy, C.E.; Liu, N.; Schwarz, M.I.; Evans, C.M.; Fontenot, A.P.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Muc5b plays a role in the development of inflammation and fibrosis in hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2022, 323, L329–L337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Newton, C.A.; Arnould, I.; Elicker, B.M.; Henry, T.S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Golden, J.A.; Jones, K.D.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; et al. The MUC5B promoter polymorphism and telomere length in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: An observational cohort-control study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, B.D.; Putman, R.K.; Araki, T.; Nishino, M.; Gudmundsson, G.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Zilhao Nogueira, N.R.; Dupuis, J.; Xu, H.; et al. Overlap of Genetic Risk between Interstitial Lung Abnormalities and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathai, S.K.; Humphries, S.; Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S.; Powers, J.; Walts, A.D.; Markin, C.; Woodward, J.; Chung, J.H.; Brown, K.K.; et al. MUC5B variant is associated with visually and quantitatively detected preclinical pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2019, 74, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, R.K.; Gudmundsson, G.; Araki, T.; Nishino, M.; Sigurdsson, S.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Eiríksdottír, G.; Aspelund, T.; Ross, J.C.; San José Estépar, R.; et al. The MUC5B promoter polymorphism is associated with specific interstitial lung abnormality subtypes. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancil, I.T.; Michalski, J.E.; Davis-Hall, D.; Chu, H.W.; Park, J.A.; Magin, C.M.; Yang, I.V.; Smith, B.J.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Schwartz, D.A. Pulmonary fibrosis distal airway epithelia are dynamically and structurally dysfunctional. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, F.; Sasse, S.K.; Kurche, J.S.; Gruca, M.A.; Cardwell, J.H.; Okamoto, T.; Chu, H.W.; Hou, X.; Poirion, O.B.; Buchanan, J.; et al. The MUC5B-associated variant rs35705950 resides within an enhancer subject to lineage- and disease-dependent epigenetic remodeling. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e144294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, L.A.; Hennessy, C.E.; Solomon, G.M.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Estrella, A.; Hara, N.; Hill, D.B.; Kissner, W.J.; Markovetz, M.R.; Grove Villalon, D.E.; et al. Muc5b overexpression causes mucociliary dysfunction and enhances lung fibrosis in mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Is a Genetic Disease Involving Mucus and the Peripheral Airways. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, S192–S197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helling, B.A.; Gerber, A.N.; Kadiyala, V.; Sasse, S.K.; Pedersen, B.S.; Sparks, L.; Nakano, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Evans, C.M.; Yang, I.V.; et al. Regulation of MUC5B Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Cox, M.J.; Willis-Owen, S.A.; Mallia, P.; Russell, K.E.; Russell, A.M.; Murphy, E.; Johnston, S.L.; Schwartz, D.A.; Wells, A.U.; et al. The role of bacteria in the pathogenesis and progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Blumhagen, R.Z.; Fingerlin, T.E. Evolution of the Gain-of-Function MUC5B Promoter Variant. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Cardwell, J.; Konigsberg, I.R.; Moore, C.M.; Zhang, W.; Sasse, S.K.; Gally, F.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Walts, A.; Powers, J.; et al. Colocalization of Gene Expression and DNA Methylation with Genetic Risk Variants Supports Functional Roles of MUC5B and DSP in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Mathai, S.K.; Stancil, I.T.; Ma, X.; Hernandez-Gutierrez, A.; Becerra, J.N.; Marrero-Torres, E.; Hennessy, C.E.; Hatakka, K.; Wartchow, E.P.; et al. Aberrant Multiciliogenesis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, P.C.; Soares, M.L.; Vasconcelos, C.D.; Ferreira, A.C.; Lima, B.A.; Manduchi, E.; Moore, J.H.; Melo, N.; Novais-Bastos, H.; Pereira, J.M.; et al. Predictive value of common genetic variants in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis survival. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.H.; Peljto, A.L.; Chawla, A.; Talbert, J.L.; McKean, D.F.; Rho, B.H.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; Schwartz, D.A.; Lynch, D.A. CT Imaging Phenotypes of Pulmonary Fibrosis in the MUC5B Promoter Site Polymorphism. Chest 2016, 149, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Chawla, A.; Peljto, A.L.; Cool, C.D.; Groshong, S.D.; Talbert, J.L.; McKean, D.F.; Brown, K.K.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; et al. CT scan findings of probable usual interstitial pneumonitis have a high predictive value for histologic usual interstitial pneumonitis. Chest 2015, 147, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peljto, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Ma, S.F.; Garcia, J.G.; Richards, T.J.; Silveira, L.J.; Lindell, K.O.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.E.; et al. Association between the MUC5B promoter polymorphism and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. JAMA 2013, 309, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vis, J.J.; Snetselaar, R.; Kazemier, K.M.; ten Klooster, L.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H. Effect of Muc5b promoter polymorphism on disease predisposition and survival in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Respirology 2016, 21, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatabu, H.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Richeldi, L.; Brown, K.K.; Wells, A.U.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Verschakelen, J.; Nicholson, A.G.; Beasley, M.B.; Christiani, D.C.; et al. Interstitial lung abnormalities detected incidentally on CT: A Position Paper from the Fleischner Society. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Putman, R.K.; Hatabu, H.; Gao, W.; Dupuis, J.; Latourelle, J.C.; Nishino, M.; Zazueta, O.E.; Kurugol, S.; Ross, J.C.; et al. Development and Progression of Interstitial Lung Abnormalities in the Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.A.; Granger, B.; Debray, M.P.; Ebstein, E.; Louis-Sidney, F.; Kedra, J.; Doyle, T.J.; Borie, R.; Constantin, A.; Combe, B.; et al. A Risk Score to Detect Subclinical Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonella, F.; Campo, I.; Zorzetto, M.; Boerner, E.; Ohshimo, S.; Theegarten, D.; Taube, C.; Costabel, U. Potential clinical utility of MUC5B und TOLLIP single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the management of patients with IPF. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, J.M.; Ma, S.F.; Martinez, F.J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Raghu, G.; Schwartz, D.A.; Valenzi, E.; Witt, L.; Lee, C.; Vij, R.; et al. TOLLIP, MUC5B, and the Response to N-Acetylcysteine among Individuals with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, A.; Pabary, R. Pulmonary alveolarproteinosis in children. Breathe 2020, 16, 200001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Spartà, G.; Kiritsi, D.; Weibel, L.; Moeller, A.; Vega-Warner, V.; Waters, A.; He, Y.; Anikster, Y.; Esser, P.; et al. Integrin α3 mutations with kidney, lung, and skin disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlens, J.; Johnson, K.T.; Bush, A.; Renz, D.; Hehr, U.; Laenger, F.; Hogg, C.; Wetzke, M.; Schwerk, N.; Rayment, J.H. Heterogenous Disease Course and Long-term Outcome of Children’s Interstitial Lung Disease Related to Filamin A Gene Variants. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griese, M. Etiologic Classification of Diffuse Parenchymal (Interstitial) Lung Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A. Paediatric interstitial lung disease: Not just kid’s stuff. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Antoniou, K.; Bonella, F.; Crestani, B.; Fabre, A.; Froidure, A.; Galvin, L.; Griese, M.; Grutters, J.C.; et al. European Respiratory Society Statement on Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koucký, V.; Pohunek, P.; Vašáková, M.; Bush, A. Transition of patients with interstitial lung disease from paediatric to adult care. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00964–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.A.; Oldham, J.M.; Applegate, C.; Carmichael, N.; Powell, K.; Dilling, D.; Schmidt, S.L.; Scholand, M.B.; Armanios, M.; Garcia, C.K.; et al. The Role of Genetic Testing in Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Perspective From the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation Genetic Testing Work Group. Chest 2022, 162, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.O.; Ren, P.; Avila, N.A.; Chow, C.K.; Franks, T.J.; Travis, W.D.; McCoy, J.P., Jr.; May, R.M.; Wu, H.P.; Nguyen, D.M.; et al. Early interstitial lung disease in familial pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, B.A.; Fox, G.; Bhatia, R.; Sala, E.; Noble, B.; Denic, N.; Fernandez, D.; Duguid, N.; Dohey, A.; Kamel, F.; et al. A Newfoundland cohort of familial and sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients: Clinical and genetic features. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Cordier, J.F. Velcro crackles: The key for early diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Richeldi, L. Neglected evidence in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolo, P.; Ryerson, C.J.; Putman, R.; Oldham, J.; Salisbury, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Valenzuela, C.; Guler, S.; Jones, S.; Wijsenbeek, M.; et al. Early diagnosis of fibrotic interstitial lung disease: Challenges and opportunities. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Telomeropathy Dyskeratosis Congenita | Hermansky–Pudlak | SAVI | COPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical and Laboratory Manifestations | |||
| Skin: hyperpigmentation, nail dystrophy, hyperhidrosis, hair loss | Oculocutaneous albinism, photophobia, strabismus, nystagmus | Non-healing ulcers on cheeks, nose, fingers, toes, soles | Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage Lung fibrosis |
| Oral: Leukoplakia, ulcerations, atrophic glossitis, periodontitis, dental carries, lichenoid lesions, hyperpigmentation, neoplasms | Bleeding disorders | Failure to thrive in children | Renal disease lupus nephritis |
| Lung fibrosis Liver cirrhosis | Lung fibrosis (HPS1, HPS4, and AP3B1 genes) | Lung fibrosis | Arthritis |
| Bone-marrow failure, anemia | Kidney’s disease | Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytosis, T-cell lymphopenia | Cystic lung disease |
| Skull and CNS: microcephalia, cerebral hypoplasia, mental retardation, deafness | Granulomatous colitis | Myositis | |
| Hypogonadism | Joint stiffness | ||
| Esophageal stenosis | |||
| Osteoporosis | |||
| Short stature | |||
| Skeletal malformations | |||
| Epiphora | |||
| Genetic Variants | |||
| Interferonopathies | |||
| 17genes implicated: ACD, CTC1, DCLRE1B, DKC1, NHP2, NOP10, PARN, POT1, RPA1, RTEL1, STN1, TERC, TERT, TINF2, WRAP53, and ZCCHC8 | 10 genes implicated: AP3B1, HPS1, HPS3, HPS4, HPS5, HPS6, and less commonly, AP3D1, BLOC1S3, BLOC1S6, and DTNBP1 inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | STING1 | COPA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papiris, S.A.; Kannengiesser, C.; Borie, R.; Kolilekas, L.; Kallieri, M.; Apollonatou, V.; Ba, I.; Nathan, N.; Bush, A.; Griese, M.; et al. Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Clinical Perspective. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122928
Papiris SA, Kannengiesser C, Borie R, Kolilekas L, Kallieri M, Apollonatou V, Ba I, Nathan N, Bush A, Griese M, et al. Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Clinical Perspective. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122928
Chicago/Turabian StylePapiris, Spyros A., Caroline Kannengiesser, Raphael Borie, Lykourgos Kolilekas, Maria Kallieri, Vasiliki Apollonatou, Ibrahima Ba, Nadia Nathan, Andrew Bush, Matthias Griese, and et al. 2022. "Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Clinical Perspective" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122928
APA StylePapiris, S. A., Kannengiesser, C., Borie, R., Kolilekas, L., Kallieri, M., Apollonatou, V., Ba, I., Nathan, N., Bush, A., Griese, M., Dieude, P., Crestani, B., & Manali, E. D. (2022). Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Clinical Perspective. Diagnostics, 12(12), 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122928






