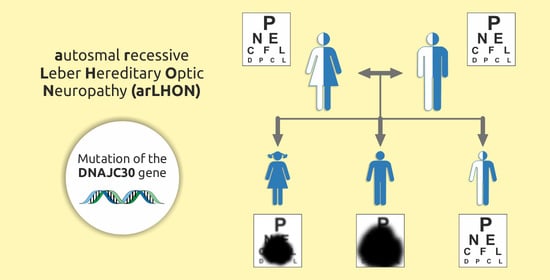
Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family
Abstract
1. Introduction
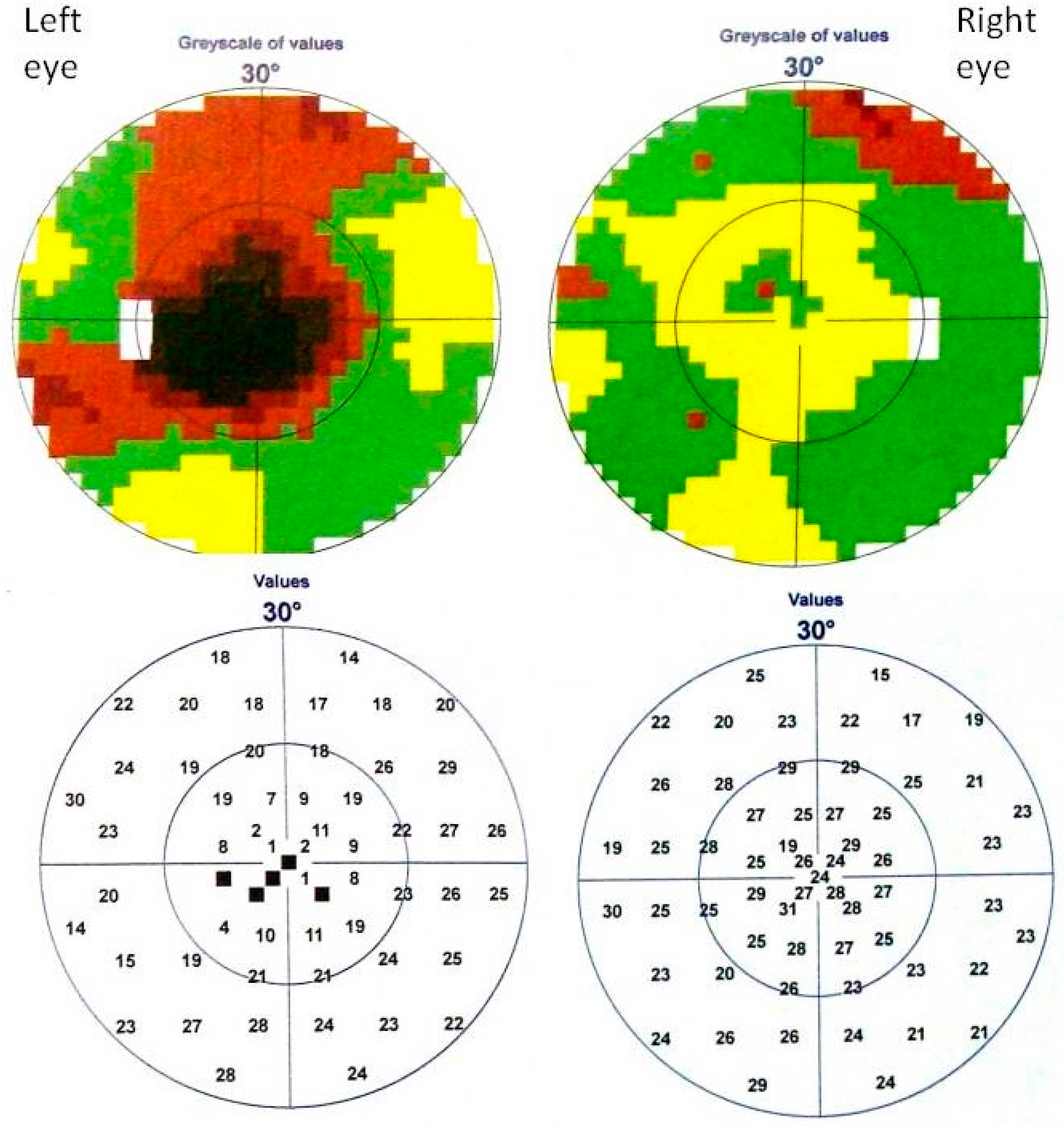
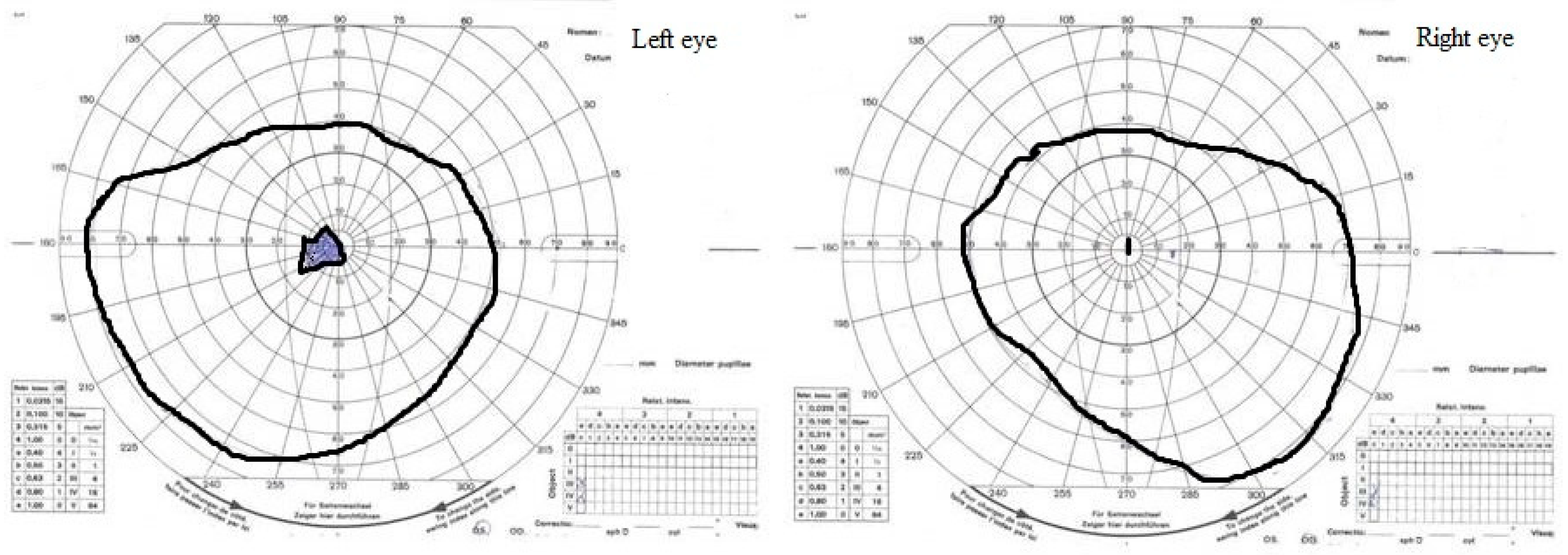
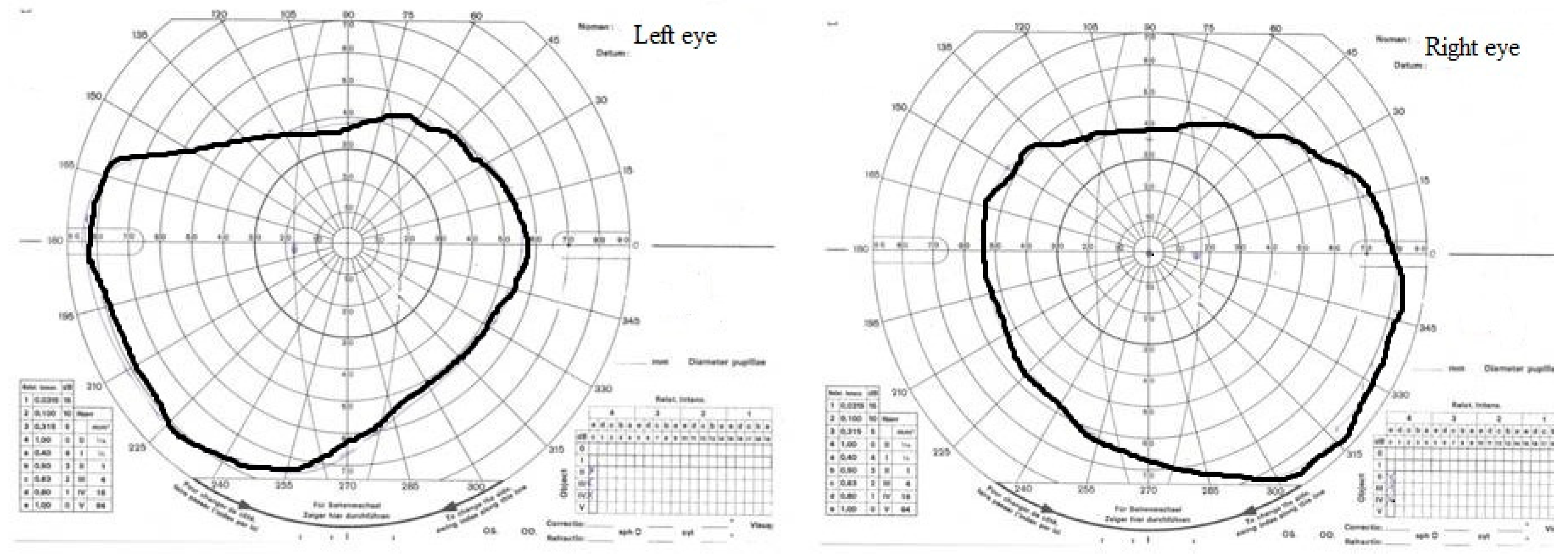
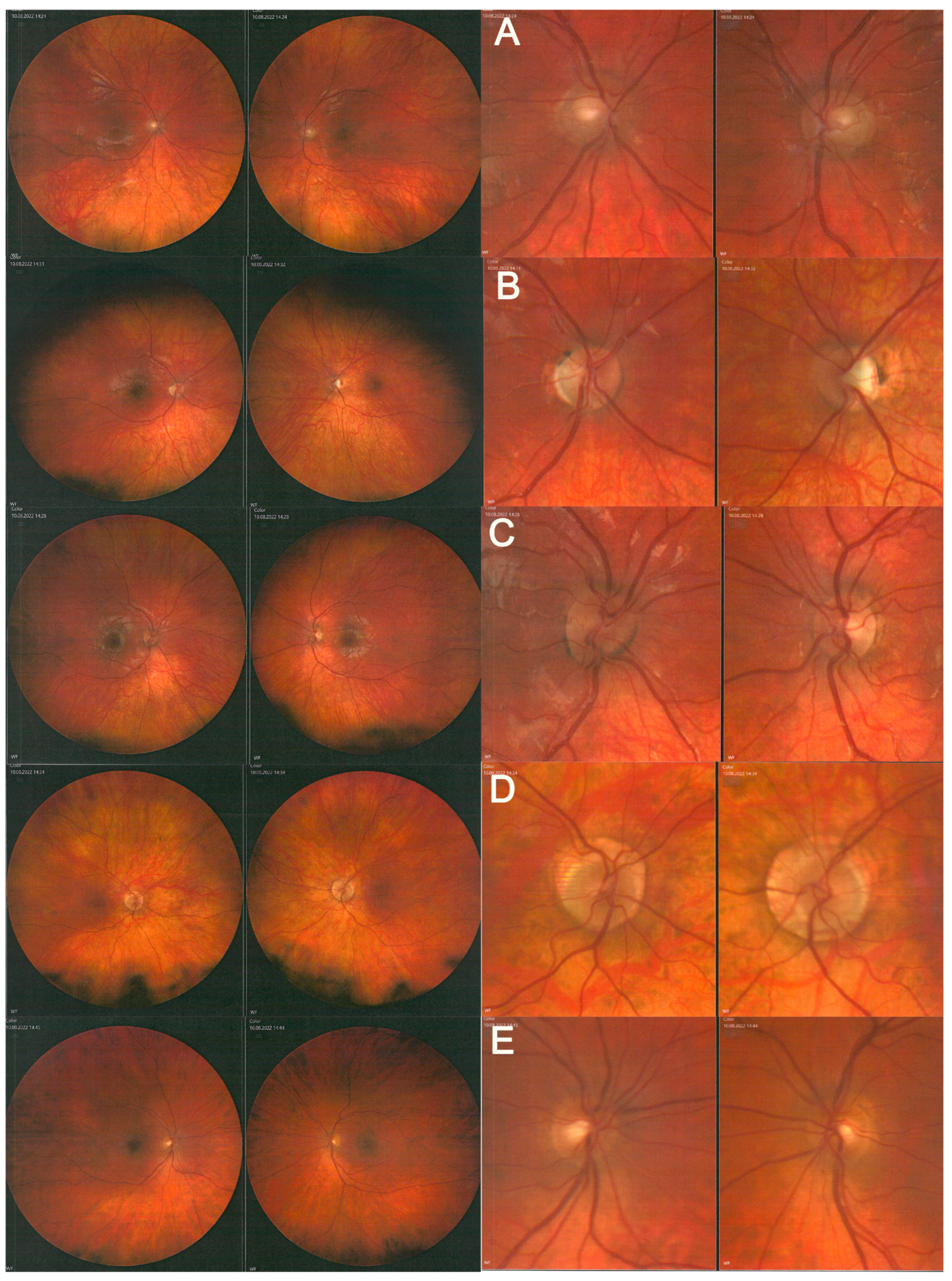
2. Case Study
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Chinnery, P.F. Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. In GeneReviews®; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Amore, G.; Romagnoli, M.; Carbonelli, M.; Barboni, P.; Carelli, V.; La Morgia, C. Therapeutic Options in Hereditary Optic Neuropathies. Drugs 2021, 81, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieninger, S.; Xiao, T.; Weisschuh, N.; Kohl, S.; Rüther, K.; Kroisel, P.M.; Brockmann, T.; Knappe, S.; Kellner, U.; Lagrcze, W.; et al. DNAJC30 disease-causing gene variants in a large Central European cohort of patients with suspected Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy and optic atrophy. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odom, J.V.; Bach, M.; Brigell, M.; Holder, G.E.; McCulloch, D.L.; Mizota, A.; Tormene, A.P. International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision: ISCEV standard for clinical visual evoked potentials—(2016 update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, A.G.; Frishman, L.J.; Grigg, J.; Hamilton, R.; Jeffrey, B.G.; Kondo, M.; Li, S.; McCulloch, D.L. ISCEV Standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2022 update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2022, 144, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortlock, K.E.; Binns, A.; Aldebasi, Y.H.; North, R.V. Inter-subject, inter-ocular and inter-session repeatability of the photopic negative response of the electroretinogram recorded using DTL and skin electrodes. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2010, 121, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueven, N. Idebenone for Leber’s hereditaty optic neuropathy. Drugs Today 2016, 52, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, B.C.; von Livonius, B.; Priglinger, C.; Banik, R.; Matloob, S.; Tamhankar, M.A.; Castillo, L.; Friedburg, C.; Halfpenny, C.A.; Lincoln, J.A.; et al. Real-World Clinical Experience with Idebenone in the treatment of Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. Neuro-Ophthalmology 2020, 40, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suno, M.; Nagaoka, A. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by idebenone in brain mitochondria in the presence of succinate. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1989, 8, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.S.; Mahroo, O.A.; Mollon, J.D.; Yu-Wai-Man, P. Retinal Ganglion Cells—Diversity of Cell Types and Clinical Relevance. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 661938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkman, M.A.; You-Wai-Man, P.; Korsten, A.; Lonhardt, M.; Dimitriadis, K.; De Coo, I.F.; Klopstock, T.; Chinnery, P.F. Gene-enviroment interaction in Leber hereditary optic neuropaty. Brain 2009, 132, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emperador, S.; Lopez-Gallardo, E.; Hernandez-Ainsa, C.; Habbane, M.; Montoya, J.; Bayona-Bafaluy, M.P.; Ruiz-Pesini, E. Ketogenic treatment reduces the percentage of a LHON heteroplasmic mutation and increases mtDNA amount of a LHON homoplasmic mutation. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, G.; Majamaa, K.; Turnbull, D.M.; Thorburn, D.; Chinnery, P.F. Treatment for mitochondrial disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 4, CD004426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellouze, S.; Augustin, S.; Bouaita, A.; Bonnet, C.; Simonutti, C.; Forster, V.; Picaud, S.; Sahel, J.-A.; Corral-Debrinski, M. Optimized allotropic expression of the human mitochondrial ND4 prevents blindness in a rat model of mitochondrial dysfunction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuer, W.J.; Schiffman, J.C.; Davis, J.L.; Porciatti, V.; Gonzalez, P.; Koilkonda, R.D.; Yuan, H.; Lalwani, A.; Lam, B.L.; Guy, J. Gene Therapy for Leber Herediatry Optic Neuropathy. Opthalmology 2016, 123, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, J.; Feuer, W.J.; Davis, J.L.; Porciatti, V.; Gonzalez, P.J.; Koilkonda, R.D.; Yuan, H.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Lam, B.L. Gene therapy for Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: Low- and medium-dose visual results. Ophthalomology 2017, 124, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadun, A.A.; Chicani, C.F.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Barboni, P.; Thoolen, M.; Shrader, W.D.; Kubis, K.; Carelli, V.; Miller, G. Effect of EPI-743 on the clinical course of the mitochondrial disease Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poincenot, L.; Pearson, A.L.; Karanjia, R. Demographics of a Large International Population of Patients Affected by Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. Ophthalmol. AAO J. 2020, 127, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PATIENT | Examination Date | EYE | Pattern VEP P100 | Flash VEP P2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1° | 15′ | 1.4 Hz | ||||||
| L [ms] | A [µV] | L [ms] | A [µV] | L [ms] | A [µV] | |||
| middle child 12-year-old | January | R | 125 | 14.4 | 121 | 17.2 | 104 | 19.8 |
| L | 164 | 5.2 | NM | NM | 115 | 18.2 | ||
| May | R | 120 | 8.2 | 129 | 4.9 | 110 | 19.1 | |
| L | 145 | 4.9 | NM | NM | 107 | 14.2 | ||
| August | R | 149 | 5.12 | 129 | 1.95 | 109 | 13.7 | |
| L | 145 | 4.09 | 102 | 1.95 | 106 | 10.3 | ||
| eldest child | 10-year-old | R | 105 | 7.4 | 129 | 5.1 | NP | NP |
| L | 109 | 7.4 | 128 | 8.9 | NP | NP | ||
| 17-year-old | R | 98 | 6.2 | 118 | 2.6 | 151 | 10.3 | |
| L | 103 | 6.3 | 115 | 2.9 | 149 | 11.5 | ||
| youngest child | 10-year-old | R | 104 | 25.7 | 108 | 19.0 | 102 | 18.1 |
| L | 113 | 28.5 | 118 | 20.8 | 107 | 31.0 | ||
| PATIENT | EYE | LA 3 ERG | LA 30 Hz ERG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-Wave | b-Wave | Peak | |||||
| IT [ms] | A [µV] | IT [ms] | A [µV] | IT [ms] | A [µV] | ||
| Reference ranges children | 9.8↔14.0 | −2.9↔−16.8 | 25.3↔30.5 | 21.0↔68.6 | 23.2↔28.1 | 20.0↔57.1 | |
| middle child | R | 12.9 (82%) | −9.0 (66%) | 27.7 (47%) | 39.3 (54%) | 24.3 (40%) | 36.7 (65%) |
| L | 13.1 (91%) | −5.2 (12%) | 28.0 (63%) | 30.2 (20%) | 24.8 (62%) | 25.1 (18%) | |
| eldest child | R | 13.0 (83%) | −3.3 (3%) | 30.0 (95%) | 25.3 (10%) | 27.2 (96%) | 26.9 (25%) |
| L | 10.9 (15%) | −3.5 (4%) | 28.6 (74%) | 23.8 (9%) | 26.8 (95%) | 23.7 (16%) | |
| youngest child | R | 11.8 (51%) | −9.6 (73%) | 29.0 (87%) | 43.4 (70%) | 25.4 (86%) | 48.1 (92%) |
| L | 11.9 (56%) | −8.8 (60%) | 28.8 (83%) | 38.9 (53%) | 25.4 (87%) | 43.6 (82%) | |
| Reference ranges adults | 6.6↔13.6 | −1.2↔−18.5 | 24.0↔32.1 | 11.1↔72.6 | 23.4↔28.6 | 13.9↔67.4 | |
| mother | R | 12.7 (76%) | −1.8 (4%) | 27.9 (14%) | 5.6 (1%) | 24.7 (17%) | 6.8 (0%) |
| L | 11.3 (34%) | −3.1 (8%) | 28.3 (24%) | 10.8 (2%) | 25.2 (35%) | 11.9 (1%) | |
| father | R | 11.1 (24%) | −4.3 (18%) | 28.8 (36%) | 27.7 (46%) | 26.1 (70%) | 28.4 (54%) |
| L | 10.9 (18%) | −2.8 (7%) | 30.5 (83%) | 23.0 (28%) | 26.2 (74%) | 21.8 (25%) | |
| PATIENT | DATE | EYE | IT [ms] | A [µV] | W-Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| middle child | January | R | 64 (29%) | 15.1 (0%) | 0.79 (0%) |
| L | 78 (69%) | 2.5 (1%) | 1.00 (4%) | ||
| February | R | 60 (21%) | −3.5 (27%) | 1.08 (48%) | |
| L | 61 (21%) | −4.7 (44%) | 1.16 (69%) | ||
| March | R | 42 (14%) | −4.0 (35%) | 0.90 (34%) | |
| L | 46 (16%) | −3.5 (21%) | 0.97 (74%) | ||
| May | R | 40 (13%) | −5.6 (80%) | 0.96 (71%) | |
| L | 43 (14%) | −4.1 (37%) | 0.95 (65%) | ||
| August | R | 39 (21%) | −6.6 (87%) | 1.11 (99%) | |
| L | 39 (22%) | −5.3 (67%) | 1.12 (100%) | ||
| eldest child | March | R | 73 (92%) | −3.9 (34%) | 0.83 (10%) |
| L | 75 (94%) | −3.0 (10%) | 0.82 (8%) | ||
| August | R | 46 (33%) | −3.4 (18%) | 0.93 (48%) | |
| L | 44 (33%) | −2.8 (6%) | 0.88 (20%) | ||
| youngest child | August | R | 61 (74%) | −4.9 (59%) | 0.98 (70%) |
| L | 59 (70%) | −4.8 (58%) | 0.94 (48%) | ||
| mother | August | R | 77 (95%) | −1.8 (1%) | 0.77 (3%) |
| L | 58 (40%) | −2.1 (3%) | 0.82 (14%) | ||
| father | August | R | 57 (29%) | −5.5 (81%) | 0.99 (87%) |
| L | 56 (21%) | −5.0 (71%) | 1.06 (96%) |
| PATIENT | EYE | MACULA | DISC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILM-RPE Thickness [µm] | Mean GCL + IPL Thickness [µm] | Mean RNFL Thickness [µm] | ||
| middle child | R | 251 | 54 | 80 |
| L | 247 | 52 | 75 | |
| eldest child | R | 233 | 52 | 66 |
| L | 233 | 53 | 67 | |
| youngest child | R | 253 | 66 | 89 |
| L | 254 | 64 | 81 | |
| mother | R | 284 | 70 | 65 |
| L | 287 | 67 | 65 | |
| father | R | 270 | 82 | 91 |
| L | 270 | 81 | 92 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pojda-Wilczek, D.; Wójcik, J.; Kmak, B.; Krawczyński, M.R. Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701
Pojda-Wilczek D, Wójcik J, Kmak B, Krawczyński MR. Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701
Chicago/Turabian StylePojda-Wilczek, Dorota, Justyna Wójcik, Bożena Kmak, and Maciej Robert Krawczyński. 2022. "Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701
APA StylePojda-Wilczek, D., Wójcik, J., Kmak, B., & Krawczyński, M. R. (2022). Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701