Diagnostic Performance of the Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Parkinson’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
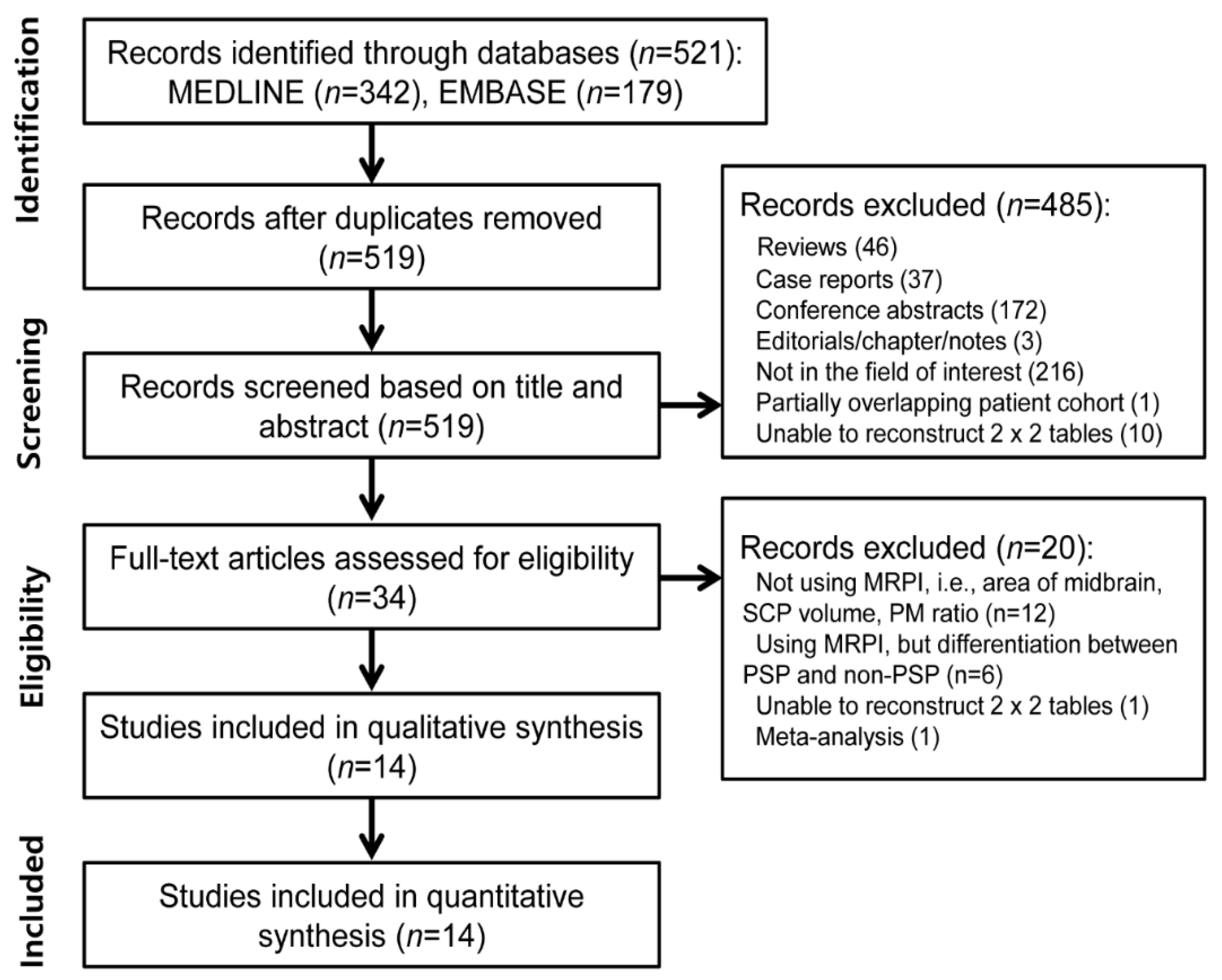
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
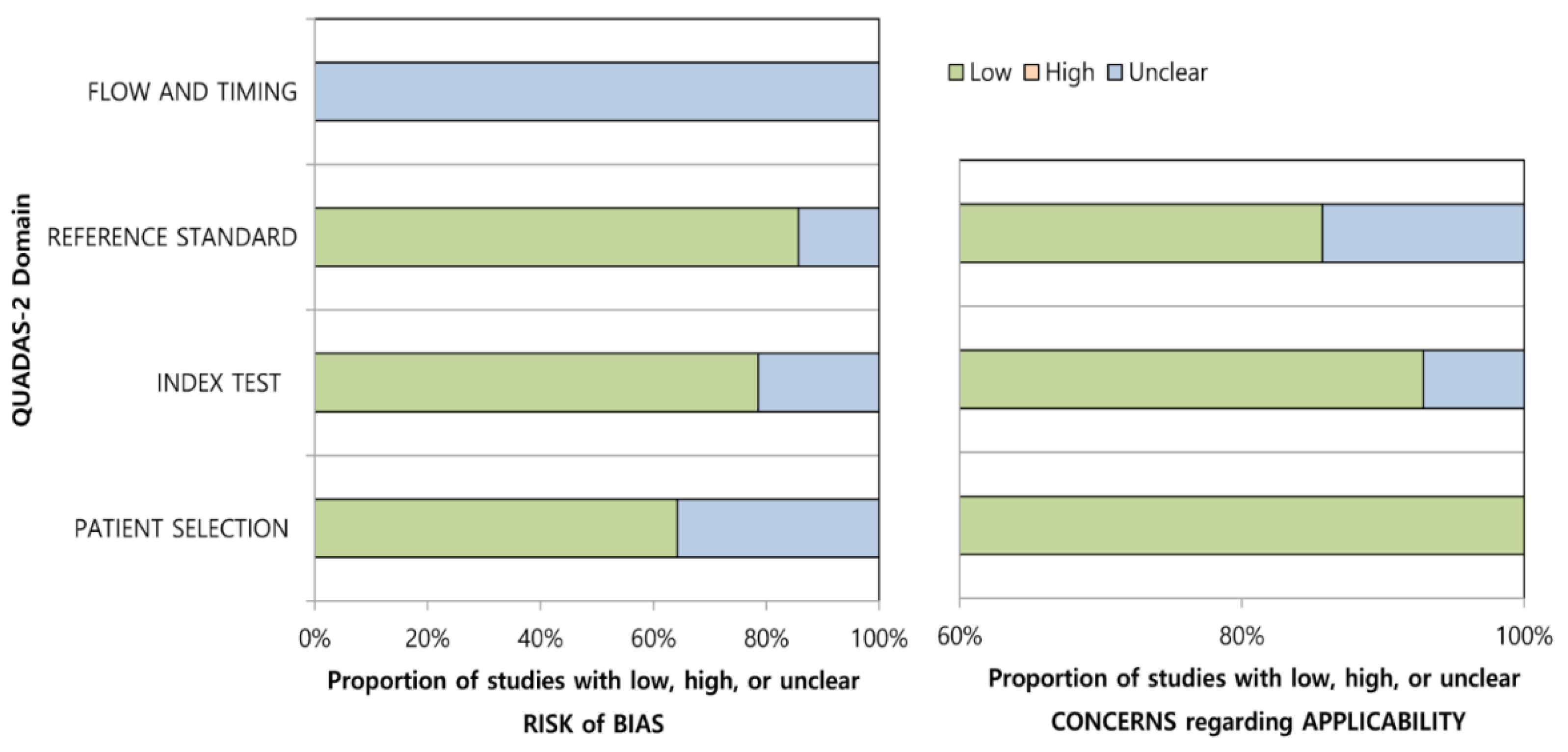
3.3. Quality Assessment
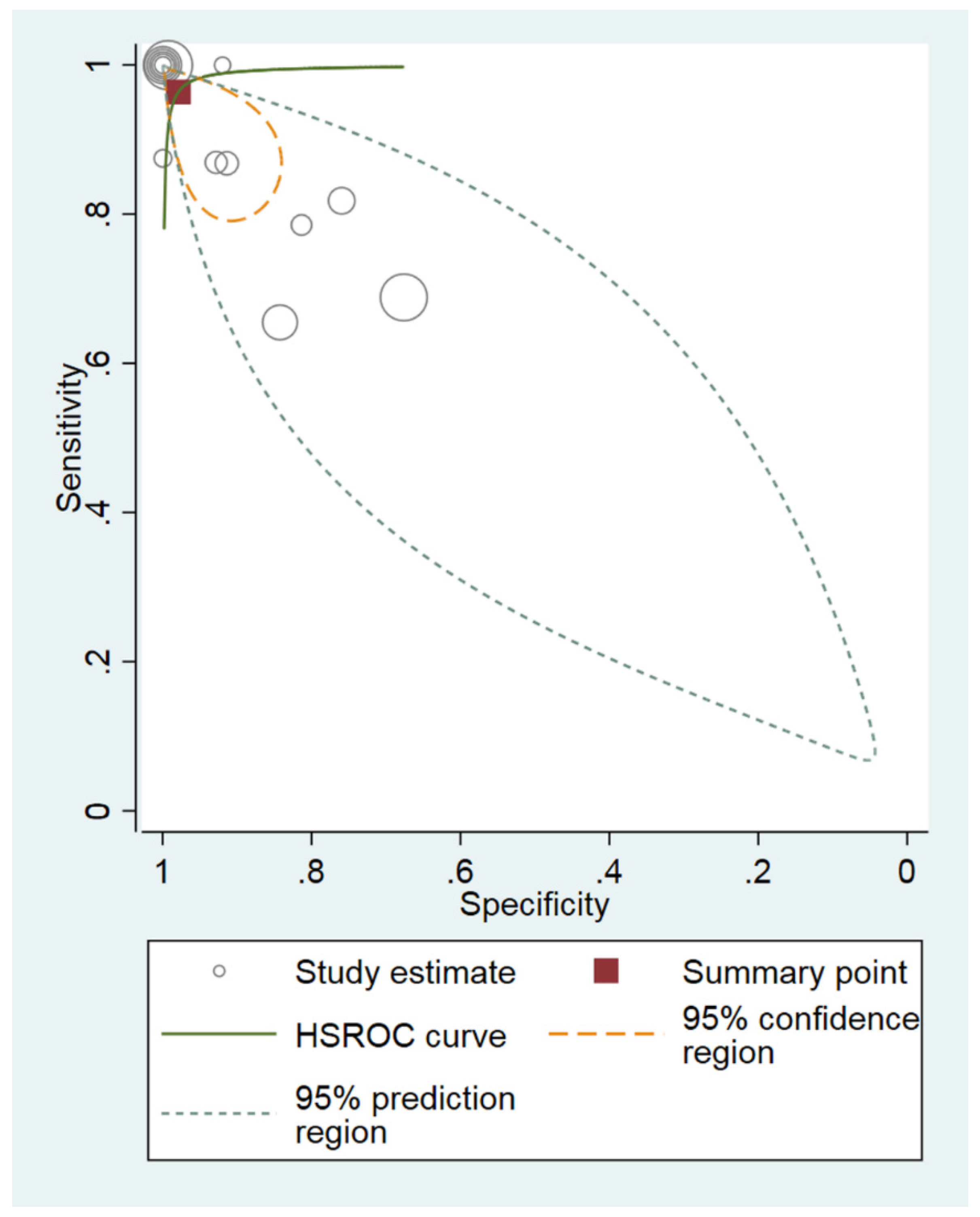
3.4. Diagnostic Performance of the MRPI
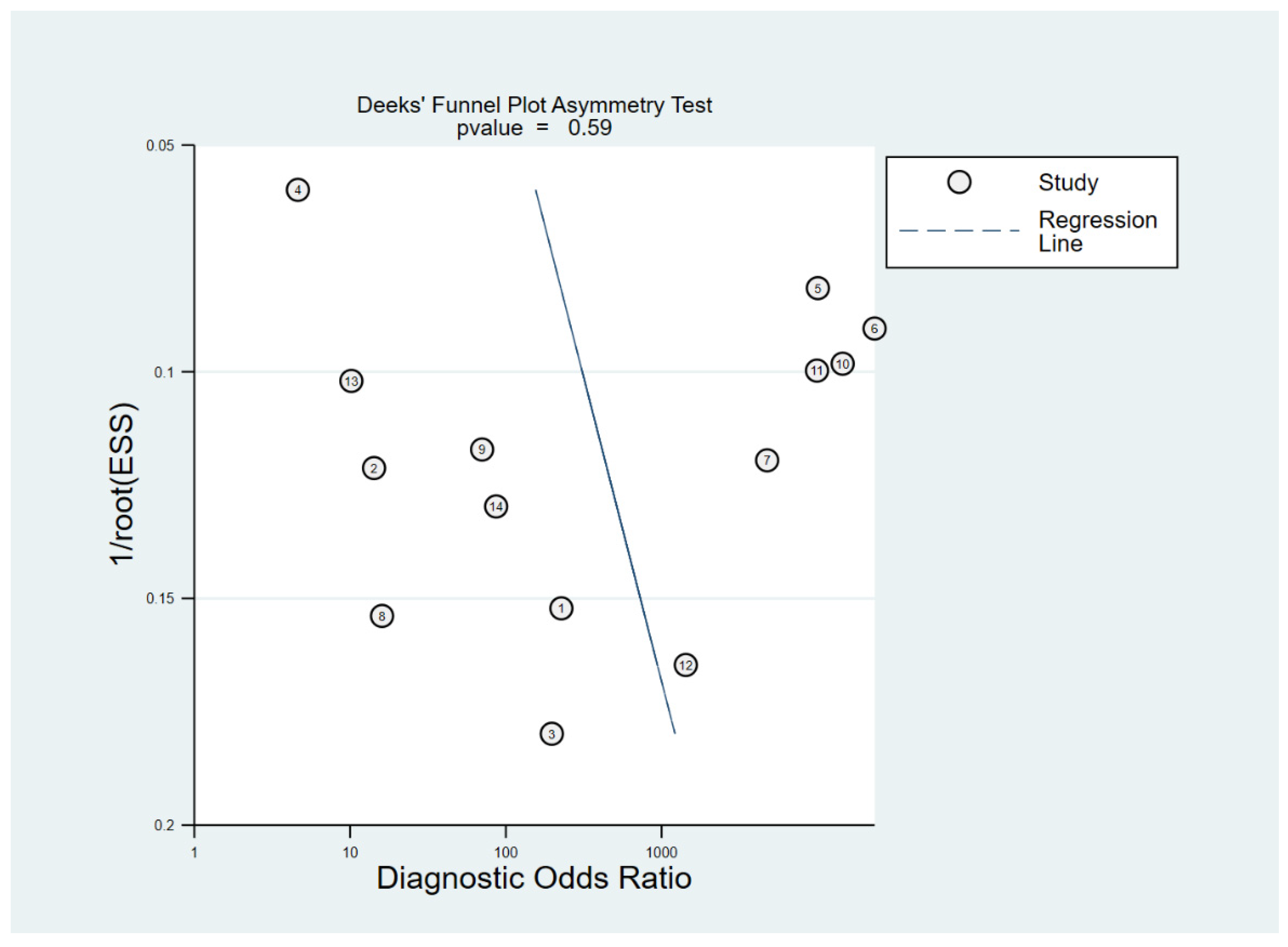
3.5. Meta-Regression
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Hentz, J.G.; Shill, H.A.; Caviness, J.N.; Driver-Dunckley, E.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Sue, L.I.; Jacobson, S.A.; Belden, C.M.; et al. Low clinical diagnostic accuracy of early vs. advanced Parkinson disease: Clinicopathologic study. Neurology 2014, 83, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Lees, A.J. The accuracy of diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes in a specialist movement disorder service. Brain 2002, 125, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvan, I.; Agid, Y.; Calne, D.; Campbell, G.; Dubois, B.; Duvoisin, R.C.; Goetz, C.G.; Golbe, L.I.; Grafman, J.; Growdon, J.H.; et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): Report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 1996, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, P.; Madetko, N.; Koziorowski, D.; Friedman, A. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy-Parkinsonism Predominant (PSP-P)-A Clinical Challenge at the Boundaries of PSP and Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Muller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta-Barba, A.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Martinez-Horta, S.; Busteed, L.; Pascual-Sedano, B.; Illan-Gala, I.; Marin-Lahoz, J.; Aracil-Bolanos, I.; Perez-Perez, J.; Sampedro, F.; et al. Cognitive and behavioral profile of progressive supranuclear palsy and its phenotypes. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 3400–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necpal, J.; Borsek, M.; Jelenova, B. “Parkinson’s disease” on the way to progressive supranuclear palsy: A review on PSP-parkinsonism. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4927–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schocke, M.F.; Seppi, K.; Esterhammer, R.; Kremser, C.; Mair, K.J.; Czermak, B.V.; Jaschke, W.; Poewe, W.; Wenning, G.K. Trace of diffusion tensor differentiates the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppi, K.; Schocke, M.F.; Esterhammer, R.; Kremser, C.; Brenneis, C.; Mueller, J.; Boesch, S.; Jaschke, W.; Poewe, W.; Wenning, G.K. Diffusion-weighted imaging discriminates progressive supranuclear palsy from PD, but not from the parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2003, 60, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Saini, J.; Kesavadas, C.; Sarma, P.S.; Kishore, A. Utility of susceptibility-weighted MRI in differentiating Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. Neuroradiology 2010, 52, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burciu, R.G.; Ofori, E.; Shukla, P.; Planetta, P.J.; Snyder, A.F.; Li, H.; Hass, C.J.; Okun, M.S.; McFarland, N.R.; Vaillancourt, D.E. Distinct patterns of brain activity in progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, L.A.; Jager, H.R.; Paviour, D.C.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Ling, H.; Williams, D.R.; Kallis, C.; Holton, J.; Revesz, T.; Burn, D.J.; et al. The midbrain to pons ratio: A simple and specific MRI sign of progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2013, 80, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, H.; Yagishita, A.; Terada, H.; Barkovich, A.J.; Kutomi, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Furui, S.; Shimizu, T.; Uchigata, M.; Matsumura, K.; et al. New and reliable MRI diagnosis for progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2005, 64, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paviour, D.C.; Price, S.L.; Stevens, J.M.; Lees, A.J.; Fox, N.C. Quantitative MRI measurement of superior cerebellar peduncle in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2005, 64, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longoni, G.; Agosta, F.; Kostic, V.S.; Stojkovic, T.; Pagani, E.; Stosic-Opincal, T.; Filippi, M. MRI measurements of brainstem structures in patients with Richardson’s syndrome, progressive supranuclear palsy-parkinsonism, and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Arabia, G.; Salsone, M.; Novellino, F.; Giofre, L.; Paletta, R.; Messina, D.; Nicoletti, G.; Condino, F.; Gallo, O.; et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance parkinsonism index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from probable or possible Parkinson disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, S.; Arabia, G.; Antonini, A.; Weis, L.; Marcante, A.; Tessitore, A.; Cirillo, M.; Tedeschi, G.; Zanigni, S.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index: Diagnostic accuracy of a fully automated algorithm in comparison with the manual measurement in a large Italian multicentre study in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2665–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamani, W.M.; Mubarak, F.; Barakzai, M.D.; Ahmed, M.S. Role of magnetic resonance planimetry and magnetic resonance parkinsonism index in discriminating Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: A retrospective study based on 1.5 and 3 T MRI. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2017, 10, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrone, A.; Morelli, M.; Nigro, S.; Quattrone, A.; Vescio, B.; Arabia, G.; Nicoletti, G.; Nistico, R.; Salsone, M.; Novellino, F.; et al. A new MR imaging index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy-parkinsonism from Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 54, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrone, A.; Nicoletti, G.; Messina, D.; Fera, F.; Condino, F.; Pugliese, P.; Lanza, P.; Barone, P.; Morgante, L.; Zappia, M.; et al. MR imaging index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson disease and the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Radiology 2008, 246, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, C.S.; Patil, K.B.; Sawant, N.; Gupta, S. Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in differentiating progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson’s disease and controls in Indian patients. Neurol. India 2016, 64, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, P.; Migda, B.; Madetko, N.; Duszynska-Was, K.; Drzewinska, A.; Charzynska, I.; Starczynski, M.; Szepelska, A.; Krolicki, L.; Friedman, A. The Role of Frontal Assessment Battery and Frontal Lobe Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography in the Differential Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Variants and Corticobasal Syndrome-A Pilot Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 630153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picillo, M.; Tepedino, M.F.; Abate, F.; Erro, R.; Ponticorvo, S.; Tartaglione, S.; Volpe, G.; Frosini, D.; Cecchi, P.; Cosottini, M.; et al. Midbrain MRI assessments in progressive supranuclear palsy subtypes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, X. Diagnostic validity of magnetic resonance parkinsonism index in differentiating patients with progressive supranuclear palsy from patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 66, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, W.R.; Lees, A.J. The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvan, I.; Agid, Y.; Jankovic, J.; Goetz, C.; Brandel, J.P.; Lai, E.C.; Wenning, G.; D’Olhaberriague, L.; Verny, M.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; et al. Accuracy of clinical criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome). Neurology 1996, 46, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M. Group Q-QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.; Park, S.H. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part, I. General Guidance and Tips. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.W.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.; Park, S.H. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part II. Statistical Methods of Meta-Analysis. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, C.M.; Gatsonis, C.A. A hierarchical regression approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Stat. Med. 2001, 20, 2865–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Park, S.H. Successful Publication of Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Korean J. Radiol. 2016, 17, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, W.L.; Buntinx, F.; Bouter, L.M.; Montori, V.M.; de Vet, H.C.; van der Windt, D.A.; Bezemer, P.D. Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: Didactic guidelines. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2002, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Macaskill, P.; Irwig, L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M.; Smith, G.D. Systematic reviews in health care: Investigating and dealing with publication and other biases in meta-analysis. BMJ 2001, 323, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.S.; Youn, J.; Jang, W.; Oh, E.; Lee, P.H.; Koh, S.B.; Ahn, T.B.; Cho, J.W. Midbrain atrophy in patients with presymptomatic progressive supranuclear palsy-Richardson’s syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 66, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, M.; Hirai, T.; Nakaura, T.; Kitajima, M.; Yamashita, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamada, K.; Uetani, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Wang, Y. Combining quantitative susceptibility mapping to the morphometric index in differentiating between progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 406, 116443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Ma, H.I.; Kim, Y.J. Utility of the Midbrain Tegmentum Diameter in the Differential Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paviour, D.C.; Price, S.L.; Jahanshahi, M.; Lees, A.J.; Fox, N.C. Regional brain volumes distinguish PSP, MSA-P, and PD: MRI-based clinico-radiological correlations. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, W.; Abe, T.; Haji, S.; Murakami, N.; Osaki, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Harada, M.; Kaji, R. “One line”: A method for differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2019, 140, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, C.; Cerasa, A.; Castiglioni, I.; Gallivanone, F.; Augimeri, A.; Lopez, M.; Arabia, G.; Morelli, M.; Gilardi, M.C.; Quattrone, A. Machine learning on brain MRI data for differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 222, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherfler, C.; Gobel, G.; Muller, C.; Nocker, M.; Wenning, G.K.; Schocke, M.; Poewe, W.; Seppi, K. Diagnostic potential of automated subcortical volume segmentation in atypical parkinsonism. Neurology 2016, 86, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talai, A.S.; Ismail, Z.; Sedlacik, J.; Boelmans, K.; Forkert, N.D. Improved Automatic Morphology-Based Classification of Parkinson’s Disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2019, 29, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, D.; Hatano, T.; Kamagata, K.; Okuzumi, A.; Oji, Y.; Mori, A.; Hori, M.; Aoki, S.; Hattori, N. Neuromelanin imaging and midbrain volumetry in progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.B.; Mitchell, T.; Burciu, R.G.; Yang, J.; Nigro, S.; Quattrone, A.; Quattrone, A.; Jeromin, A.; McFarland, N.R.; Okun, M.S.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Neurofilament Light in the Differentiation of Parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, C.; Acarer, A.; Guneyli, S.; Akyuz, E.; Aydin, E.; Colakoglu, Z.; Kitis, O.; Calli, M.C. MRI evaluation of progressive supranuclear palsy: Differentiation from Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Neurol. Res. 2019, 41, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, B.; Mangesius, S.; Krismer, F.; Wenning, G.K.; Hussl, A.; Scherfler, C.; Gizewski, E.R.; Schocke, M.; Esterhammer, R.; Quattrone, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of MR planimetry in clinically unclassifiable parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 82, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangesius, S.; Hussl, A.; Krismer, F.; Mahlknecht, P.; Reiter, E.; Tagwercher, S.; Djamshidian, A.; Schocke, M.; Esterhammer, R.; Wenning, G.; et al. MR planimetry in neurodegenerative parkinsonism yields high diagnostic accuracy for PSP. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 46, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangesius, S.; Mariotto, S.; Ferrari, S.; Pereverzyev, S., Jr.; Lerchner, H.; Haider, L.; Gizewski, E.R.; Wenning, G.; Seppi, K.; Reindl, M.; et al. Novel decision algorithm to discriminate parkinsonism with combined blood and imaging biomarkers. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2020, 77, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, F.; Shiraishi, S.; Kitajima, M.; Ogasawara, K.; Tsuda, N.; Tomiguchi, S.; Yamashita, Y. Diagnostic Performance of (123)I-FPCIT SPECT Specific Binding Ratio in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Use of Core Clinical Features and MRI for Comparison. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.C.; Choi, S.M.; Choi, K.H.; Nam, T.S.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Yoon, W. MRI measurements of brainstem structures in patients with vascular parkinsonism, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Velonakis, G.; Toulas, P.; Stamboulis, E.; Kapaki, E. MRI Planimetry and Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in the Differential Diagnosis of Patients with Parkinsonism. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussl, A.; Mahlknecht, P.; Scherfler, C.; Esterhammer, R.; Schocke, M.; Poewe, W.; Seppi, K. Diagnostic accuracy of the magnetic resonance Parkinsonism index and the midbrain-to-pontine area ratio to differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson’s disease and the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, L.; Kassubek, J.; Sudmeyer, M.; Hilker, R.; Hattingen, E.; Egger, K.; Amtage, F.; Pinkhardt, E.H.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; et al. Manual MRI morphometry in Parkinsonian syndromes. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, C.; Ozkaynak, S.S.; Eseroglu, E.; Karaali, K. Contribution of the Mesencephalon Indices to Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsonian Disorders. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2020, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, H.; Granberg, T.; Hashim, F.; Westman, E.; Svenningsson, P. Automated brainstem volumetry can aid in the diagnostics of parkinsonian disorders. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2020, 79, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanigni, S.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; Manners, D.N.; Testa, C.; Gibertoni, D.; Evangelisti, S.; Sambati, L.; Guarino, M.; De Massis, P.; Gramegna, L.L.; et al. Accuracy of MR markers for differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2016, 11, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author (Year of Publication) | Institution | Duration of Patient Recruitment | No. of Patients (n) | PSP (n) | PD (n) | Mean Age of PD Patients (SD) | Mean Age of PD Patients (SD) | M:F (PSP) | M:F (PD) | Study Design | Consecutive Enrollment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constantinides VC, et al., (2018) | National and Kapodistrian University of Athens | 2011–2014 | 42 | 24 | 18 | 63.2 (6.8) | 64.4 (9.3) | 13:11 | 10:8 | prospective | yes |
| Hussl A, et al., (2010) | Medical University Innsbruck | NA | 97 | 22 | 75 | 68.7 (9.1) | 64.8 (9.7) | 11:11 | 46:29 | NA | NA |
| Longoni G, et al., (2011) | University of Belgrade | 1998.01–2008.11 | 35 | 10 | 25 | 62.5 | 65.5 | 3:7 | 6:19 | retrospective | yes |
| Möller L, et al., (2017) | Five German academic centers (Universities in Marburg, Dusseldorf, Frankfurt, Freiburg, and Ulm) | 2009–2013 | 310 | 106 | 204 | 69.0 (0.6) | 64.0 (0.8) | 60:46 | 136:68 | retrospective | NA |
| Morelli M, et al., (2011) | NA | NA | 340 | 42 | 298 | 70.26 (6.0) | NA | 31:11 | 198:100 | NA | NA |
| Nigro S, et al., (2019) | Seven different Italian movement disorder centers | NA | 192 | 37 | 155 | NA | NA | NA | NA | retrospective | NA |
| Nizamani WM, et al., (2017) | Khan University Hospital | 2006.01–2015.12 | 68 | 34 | 34 | 66.8 (6.3) | 66.8 (6.3) | 19:15 | 20:14 | retrospective | yes |
| Oktay C, et al., (2020) | Neurology Department, Movement Disorder Clinic | 2015.11–2017.03 | 57 | 14 | 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | retrospective | NA |
| Picillo M, et al., (2020) | University of Salerno and University of Pisa | 2015.11–2018.12 | 73 | 38 | 35 | 71 | 68 | 23:15 | 26:9 | retrospective | yes |
| Quattrone A, et al., (2018) | University of Catanzaro | 2009–2017 | 99 | 46 | 53 | 70.4 (5.2) | 70.3 (5.2) | 25:21 | 39:14 | NA | yes |
| Quattrone A, et al., (2008) | NA | 2002.06–2006.05 | 141 | 33 | 108 | 69.3 (6.1) | 65.8 (9.0) | 23:10 | 62:46 | prospective | yes |
| Sankhla CS, et al., (2016) | P.D. Hinduja National Hospital | 2012.03–2014.03 | 39 | 26 | 13 | 66.2 (7.4) | 56.5 (11.2) | 18:8 | 9:4 | NA | yes |
| Sjöström H, et al., (2020) | Karolinska University Hospital | 2001–2015 | 169 | 29 | 140 | 69.1 (6.7) | 65.3 (9.8) | 11:18 | 48:92 | retrospective | yes |
| Zanigni S, et al., (2016) | NA | 2010–2014 | 65 | 23 | 42 | 72.8 (7.1) | 64.7 (10.5) | 12:11 | 29:13 | retrospective | yes |
| Author (Year of Publication) | Magnet Strength (T) | Vendor | Scanner | Sequence | Section Thickness (mm) | Number of Readers | Experience of Readers | Measurement Method for the MRPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constantinides VC, et al., (2018) | 1.5 or 3 | Philips | NA | T1 or 3D T1 turbo field echo | 1–5 | 1 | NA | Manual |
| Hussl A, et al., (2010) | 1.5 | Siemens | Magnetom Symphony | Native 3D T1 | 1.2 | NA | NA | Manual |
| Longoni G, et al., (2011) | 1.5 | Siemens | Magnetom Avanto | 3D T1 MP-RAGE | NA | 1 | NA | Manual |
| Möller L, et al., (2017) | 1.5 or 3 | Siemens | Magnetom Trio | T1 3D MP-RAGE | 1 or 1.2 | 2 | NA | Manual |
| Morelli M, et al., (2011) | 1.5 | GE | Signa | T1 volumetric spoiled gradient echo | 0.6 | 2 | >10 yrs | Manual |
| Nigro S, et al., (2019) | 3 | GE | Discovery MR750, Signa HDx | 3D T1 | 1–1.2 | 2 | >8 yrs | Manual |
| Nizamani WM, et al. (2017) | 1.5 or 3 | Siemens | Avanto, Vantage | T1 volumetric spoiled gradient echo, T2, FLAIR | 0.6, 4, 4 | 2 | NA | Manual |
| Oktay C, et al., (2020) | 3 | Siemens | Spectra | 3D T1 MP-RAGE | 1 | 2 | 20/5 yrs | Manual |
| Picillo M, et al., (2020) | 1.5 or 3 | Siemens | Skyra | 3D T1 | NA | 1 | >15 yrs | Manual |
| Quattrone A, et al., (2018) | 3 | GE | MR750 | 3D T1 volumetric spoiled gradient echo | 1 | 2 | >10 yrs | Automatic |
| Quattrone A, et al., (2008) | 1.5 | GE | Signa | T1 volumetric spoiled gradient echo | 0.6 | 2 | NA | Manual |
| Sankhla CS, et al., (2016) | 1.5 or 3 | NA | NA | T1 volumetric spoiled gradient echo | NA | 1 | NA | Manual |
| Sjöström H, et al., (2020) | 1.5 or 3 | Siemens | Aera, Avanto, Symphony, Trio | 3D T1 MP-RAGE | NA | 2 | NA | Automatic |
| Zanigni S, et al., (2016) | 1.5 | GE | Signa | 3D volumetric T1—FSPGR | NA | 3 | NA | Manual |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Suh, C.H.; Shim, W.H.; Kim, S.J. Diagnostic Performance of the Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Parkinson’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010012
Kim S, Suh CH, Shim WH, Kim SJ. Diagnostic Performance of the Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Parkinson’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seongken, Chong Hyun Suh, Woo Hyun Shim, and Sang Joon Kim. 2022. "Diagnostic Performance of the Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Parkinson’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010012
APA StyleKim, S., Suh, C. H., Shim, W. H., & Kim, S. J. (2022). Diagnostic Performance of the Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index in Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Parkinson’s Disease: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010012







