α-Lipoic Acid Improves Hepatic Metabolic Dysfunctions in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RNA Interference
2.2. Evaluation of PBGD Enzymatic Activity
2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
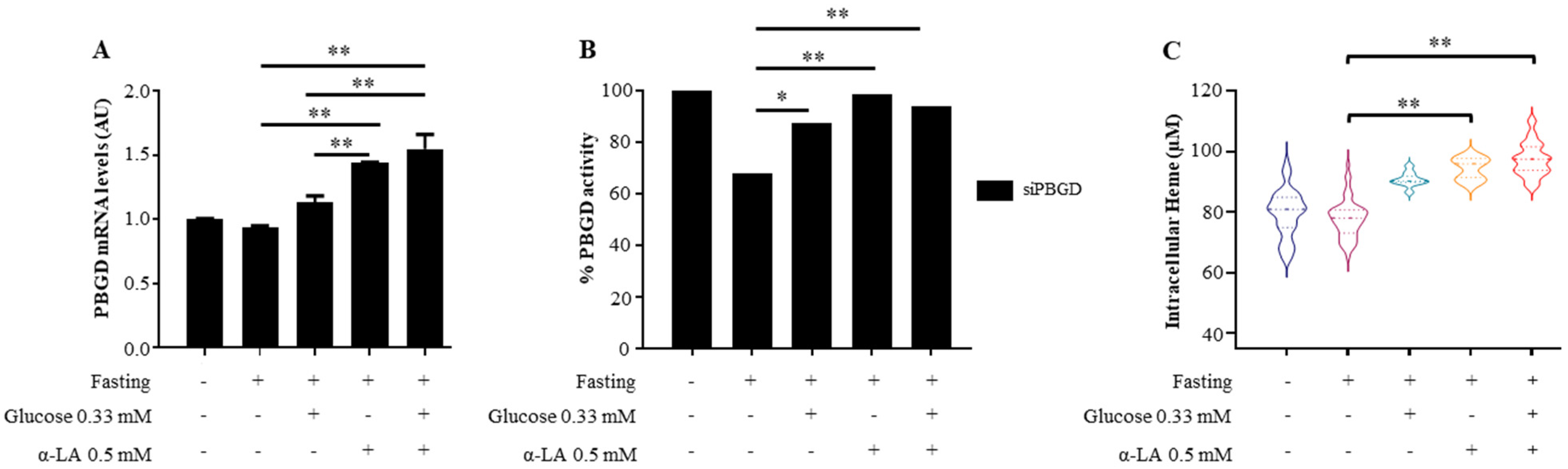
3.1. α-Lipoic Acid Improved Heme Production in siPBGD Cells
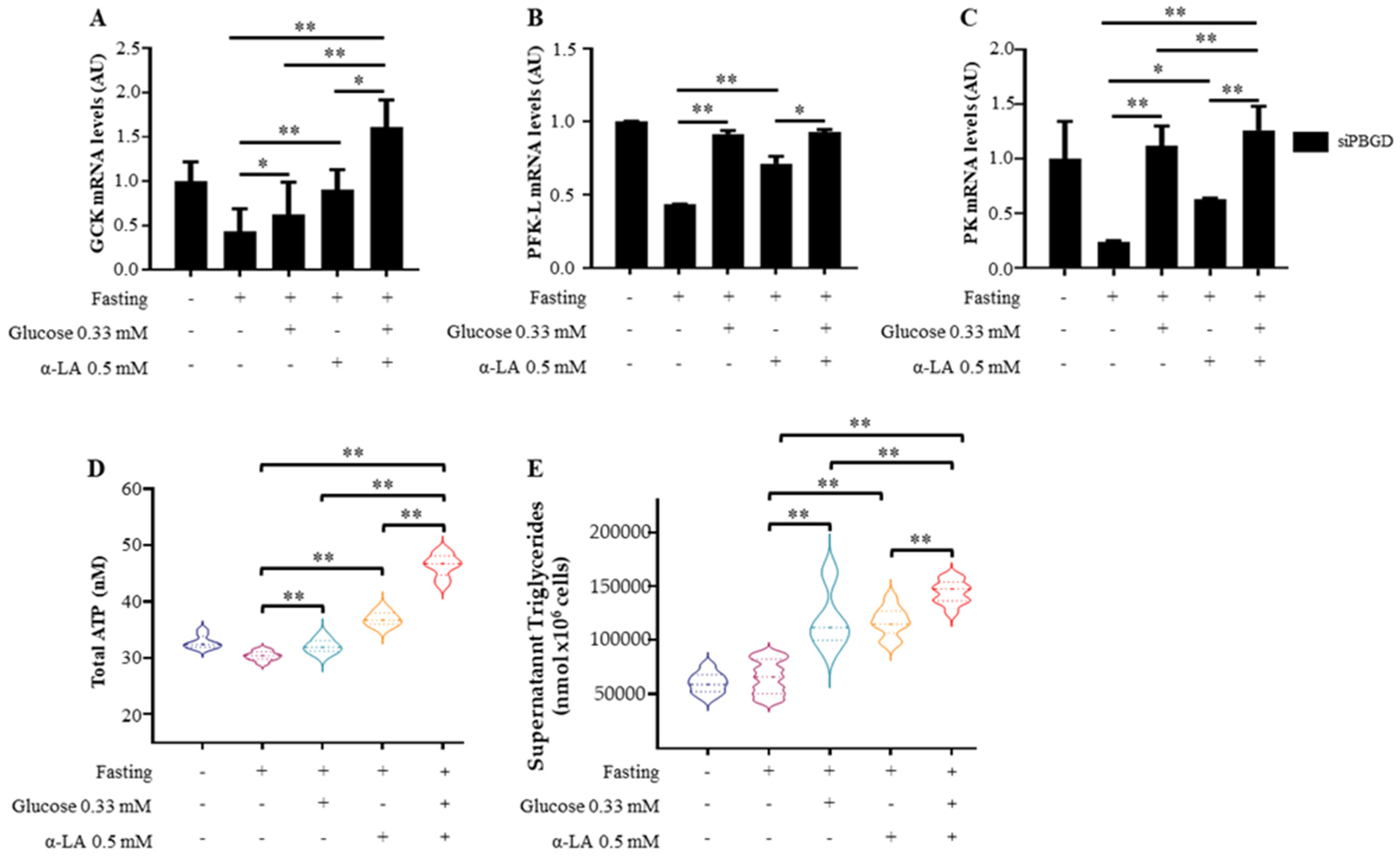
3.2. α-Lipoic Acid Stimulates Glucose Utilization and Provides Energy Supplies during Fasting
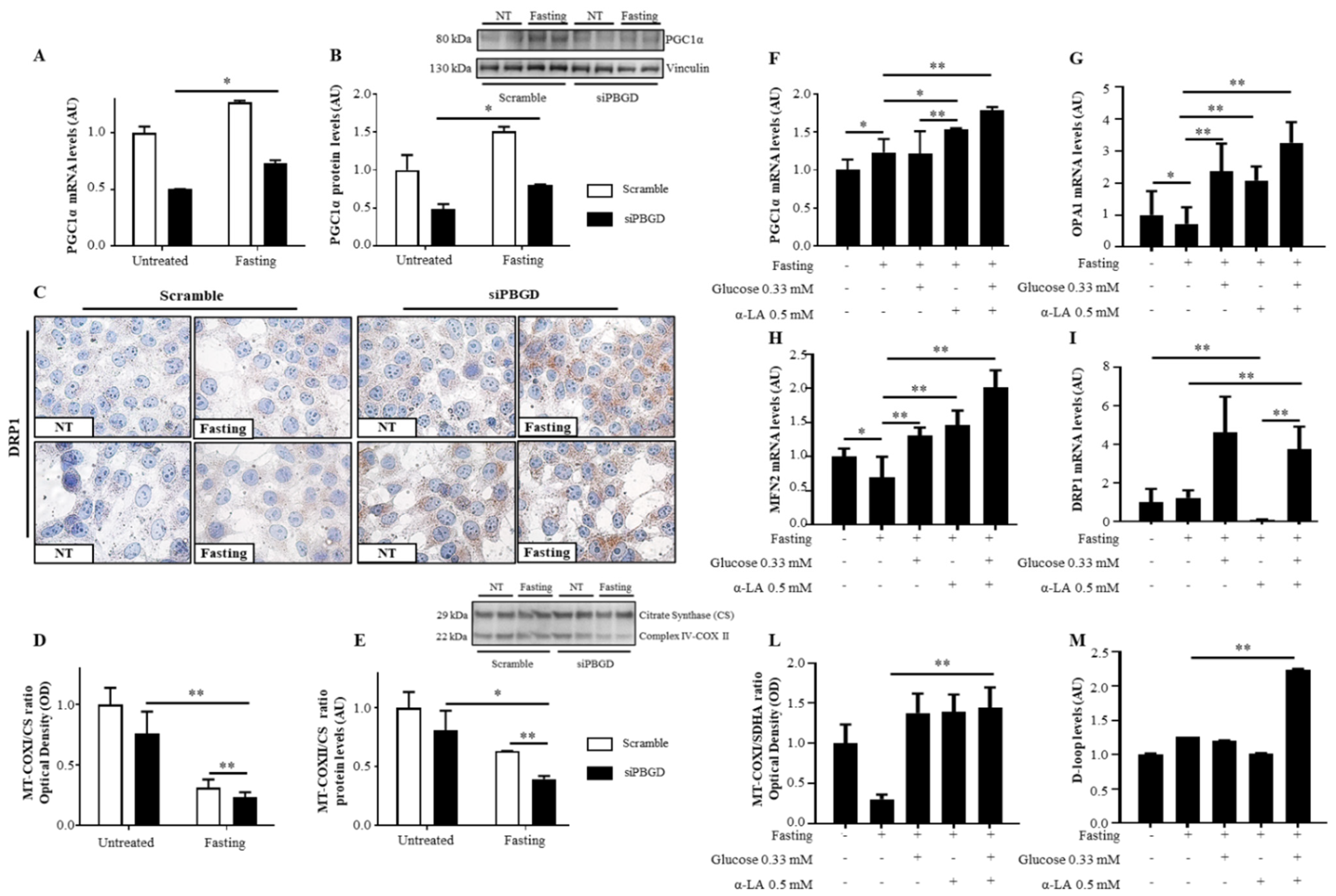
3.3. α-Lipoic Acid Recovered Mitobiogenesis: The Dual Role of PGC1α
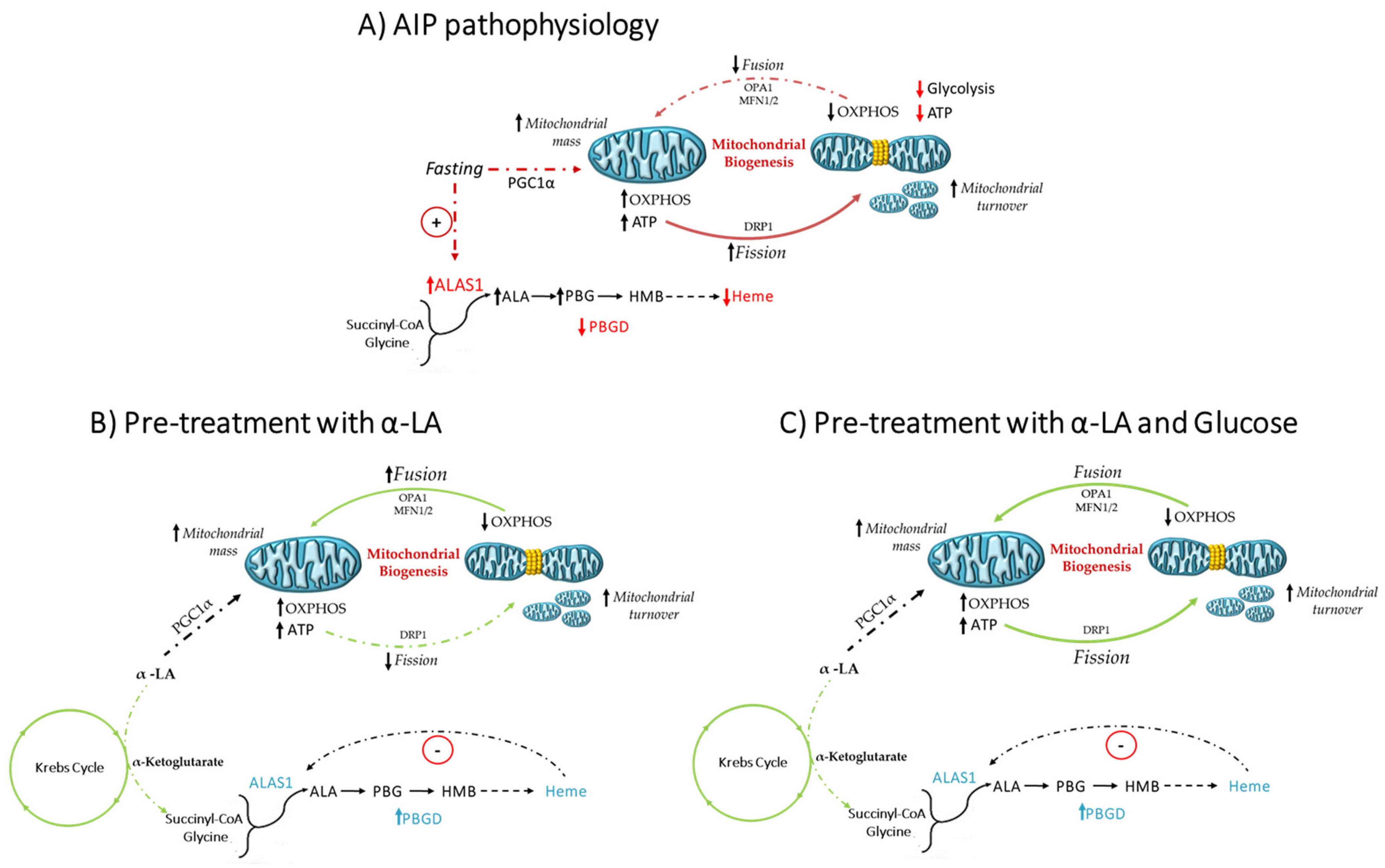
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Rudnick, S.; Cengia, B.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Acute Hepatic Porphyrias: Review and Recent Progress. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenglet, H.; Schmitt, C.; Grange, T.; Manceau, H.; Karboul, N.; Bouchet-Crivat, F.; Robreau, A.M.; Nicolas, G.; Lamoril, J.; Simonin, S.; et al. From a dominant to an oligogenic model of inheritance with environmental modifiers in acute intermittent porphyria. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Shaw, K.; Phillips, A.D.; Cooper, D.N. The Human Gene Mutation Database: Building a comprehensive mutation repository for clinical and molecular genetics, diagnostic testing and personalized genomic medicine. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischik, E.; Kauppinen, R. An update of clinical management of acute intermittent porphyria. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2015, 8, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, H.P.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Augusto, O.; Bechara, E.J.H. Free radical generation during δ-Aminolevulinic acid autoxidation: Induction by hemoglobin and connections with porphyrinpathies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 271, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.J.W.; Cantrill, R.C. δ-Aminolaevulinic acid and amino acid neurotransmitters. In The Biological Effects of Glutamic Acid and Its Derivatives; Najjar, V.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, T.S.; Pahernik, S.; Scheruebl, I.; Jauch, K.W.; Thasler, W.E. Cellular damage to human hepatocytes through repeated application of 5-aminolevulinic acid. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Solis-Villa, C.; Hakenberg, J.; Qiao, W.; Srinivasan, R.R.; Yasuda, M.; Balwani, M.; Doheny, D.; Peter, I.; Chen, R.; et al. Acute Intermittent Porphyria: Predicted Pathogenicity of HMBS Variants Indicates Extremely Low Penetrance of the Autosomal Dominant Disease. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, S.M.; de San Martín Viale, L.C.; Mazzetti, M.B. Response of glucose metabolism enzymes in an acute porphyria model. Role of reactive oxygen species. Toxicology 2005, 216, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantes, M.; Serrano-Mendioroz, I.; Benito, M.; Molinet-Dronda, F.; Delgado, M.; Vinaixa, M.; Sampedro, A.; de Enriquez Salamanca, R.; Prieto, E.; Pozo, M.A.; et al. Glucose metabolism during fasting is altered in experimental porphobilinogen deaminase deficiency. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homedan, C.; Schmitt, C.; Laafi, J.; Gueguen, N.; Desquiret-Dumas, V.; Lenglet, H.; Karim, Z.; Gouya, L.; Deybach, J.-C.; Simard, G.; et al. Mitochondrial energetic defects in muscle and brain of a Hmbs−/− mouse model of acute intermittent porphyria. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5015–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Gan, L.; Zhang, B.; Desnick, R.J.; Yasuda, M. Characterization of the hepatic transcriptome following phenobarbital induction in mice with AIP. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.; Lenglet, H.; Yu, A.; Delaby, C.; Benecke, A.; Lefebvre, T.; Letteron, P.; Paradis, V.; Wahlin, S.; Sandberg, S.; et al. Recurrent attacks of acute hepatic porphyria: Major role of the chronic inflammatory response in the liver. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balwani, M.; Sardh, E.; Ventura, P.; Peiró, P.A.; Rees, D.C.; Stölzel, U.; Bissell, D.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Windyga, J.; Anderson, K.E.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of RNAi Therapeutic Givosiran for Acute Intermittent Porphyria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanellas, A.; Ávila, M.A.; Anderson, K.E.; Deybach, J.C. Current and innovative emerging therapies for porphyrias with hepatic involvement. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solares, I.; Izquierdo-Sánchez, L.; Morales-Conejo, M.; Jericó, D.; Castelbón, F.J.; Córdoba, K.M.; Sampedro, A.; Lumbreras, C.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Enríquez de Salamanca, R.; et al. High Prevalence of Insulin Resistance in Asymptomatic Patients with Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Liver-Targeted Insulin as a Novel Therapeutic Approach. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.; Bylesjö, I.; Lithner, F. Effects of diabetes mellitus on patients with acute intermittent porphyria. J. Intern. Med. 1999, 245, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.Y.; Lo, Y.M.; Xu, J.H.; Chang, W.C.; Huang, D.W.; Wu, J.S.; Yang, C.H.; Huang, W.C.; Shen, S.C. Alpha-lipoic acid alleviates NAFLD and triglyceride accumulation in liver via modulating hepatic NLRP3 inflammasome activation pathway in type 2 diabetic rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanabadi, A.; Mahboob, S.; Amirkhizi, F.; Hosseinpour-Arjmand, S.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. Oral α-lipoic acid supplementation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Effects on adipokines and liver histology features. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4941–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinpour-Arjmand, S.; Amirkhizi, F.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. The effect of alpha-lipoic acid on inflammatory markers and body composition in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 44, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.J.; Lee, F.Y.; Wu, S.J.; Chang, W.J. Determination of erythrocyte porphobilinogen deaminase activity using porphobilinogen as substrate. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1987, 168, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, P.E.; Badminton, M.N.; Rees, D.C. Update review of the acute porphyrias. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 176, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.D. Heme biosynthesis and the porphyrias. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storjord, E.; Dahl, J.A.; Landsem, A.; Ludviksen, J.K.; Karlsen, M.B.; Karlsen, B.O.; Brekke, O.-L. Lifestyle factors including diet and biochemical biomarkers in acute intermittent porphyria: Results from a case-control study in northern Norway. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Diz, L.; Murcia, M.A.; Gris, J.L.; Pons, A.; Monteagudo, C.; Martínez-Tomé, M.; Jiménez-Monreal, A.M. Assessing nutritional status of acute intermittent porphyria patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrick, A.L.; Fisher, B.M.; Moore, M.R.; Cathcart, S.; McColl, K.E.L.; Goldberg, A. Elevation of blood lactate and pyruvate levels in acute intermittent porphyria—A reflection of haem deficiency? Clin. Chim. Acta 1990, 190, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, E.; Granata, F. Nutrients and Porphyria: An Intriguing Crosstalk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homedan, C.; Laafi, J.; Schmitt, C.; Gueguen, N.; Lefebvre, T.; Karim, Z.; Desquiret-Dumas, V.; Wetterwald, C.; Deybach, J.-C.; Gouya, L.; et al. Acute intermittent porphyria causes hepatic mitochondrial energetic failure in a mouse model. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 51, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, J.; Kostrzewska, E.; Michalak, T.; Zawirska, B.; Medrzejewski, W.; Gregor, A. Abnormalities in liver function and morphology and impaired aminopyrine metabolism in hereditary hepatic porphyrias. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Stattmann, M.; Cicvaric, A.; Monje, F.J.; Coiro, P.; Hotka, M.; Ricken, G.; Hainfellner, J.; Greber-Platzer, S.; Yasuda, M.; et al. Severe hydroxymethylbilane synthase deficiency causes depression-like behavior and mitochondrial dysfunction in a mouse model of homozygous dominant acute intermittent porphyria. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, T.; Sishtla, K.; Park, B.; Repass, M.J.; Corson, T.W. Heme Synthesis Inhibition Blocks Angiogenesis via Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Iscience 2020, 23, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balwani, M.; Wang, B.; Anderson, K.E.; Bloomer, J.R.; Bissell, D.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Phillips, J.D.; Desnick, R.J. Acute hepatic porphyrias: Recommendations for evaluation and long-term management. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willandt, B.; Langendonk, J.G.; Biermann, K.; Meersseman, W.; D’Heygere, F.; George, C.; Verslype, C.; Monbaliu, D.; Cassiman, D. Liver Fibrosis Associated with Iron Accumulation Due to Long-Term Heme-Arginate Treatment in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Case Series. JIMD Rep. 2016, 25, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Storjord, E.; Dahl, J.A.; Landsem, A.; Fure, H.; Ludviksen, J.K.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Karlsen, B.O.; Berg, K.S.; Mollnes, T.E.; Nielsen, E.W.; et al. Systemic inflammation in acute intermittent porphyria: A case-control study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 187, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7522–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.; Mansouri, A.; Martelli, A.; Bayart, S.; Manceau, H.; Callebaut, I.; Moulouel, B.; Gouya, L.; Puy, H.; Kannengiesser, C.; et al. GLRX5 mutations impair heme biosynthetic enzymes ALA synthase 2 and ferrochelatase in Human congenital sideroblastic anemia. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilas, G.L.; Aldonatti, C.; San Martín de Viale, L.C.; de Ríos Molina, M.C. Effect of alpha lipoic acid amide on hexachlorobenzene porphyria. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1999, 47, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Székely, E.; Szentmihályi, K.; Tasnádi, G.; Várnai, K.; Blázovics, A. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on the porphyria cutanea tarda patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and heavy drinkers. Z. Gastroenterol. 2005, 43, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longo, M.; Paolini, E.; Meroni, M.; Duca, L.; Motta, I.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Di Pierro, E.; Dongiovanni, P. α-Lipoic Acid Improves Hepatic Metabolic Dysfunctions in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091628
Longo M, Paolini E, Meroni M, Duca L, Motta I, Fracanzani AL, Di Pierro E, Dongiovanni P. α-Lipoic Acid Improves Hepatic Metabolic Dysfunctions in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(9):1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091628
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongo, Miriam, Erika Paolini, Marica Meroni, Lorena Duca, Irene Motta, Anna Ludovica Fracanzani, Elena Di Pierro, and Paola Dongiovanni. 2021. "α-Lipoic Acid Improves Hepatic Metabolic Dysfunctions in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Proof-of-Concept Study" Diagnostics 11, no. 9: 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091628
APA StyleLongo, M., Paolini, E., Meroni, M., Duca, L., Motta, I., Fracanzani, A. L., Di Pierro, E., & Dongiovanni, P. (2021). α-Lipoic Acid Improves Hepatic Metabolic Dysfunctions in Acute Intermittent Porphyria: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Diagnostics, 11(9), 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11091628








