Pepsinogen and Serum IgG Detection Is a Valuable Diagnostic Method for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Low-Prevalence Country: A Report from Sri Lanka
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. H. pylori Infection Status and Pepsinogen Level
2.3. Anti-H. pylori IgG Test and PG Test from Serology
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. H. pylori Infection Status
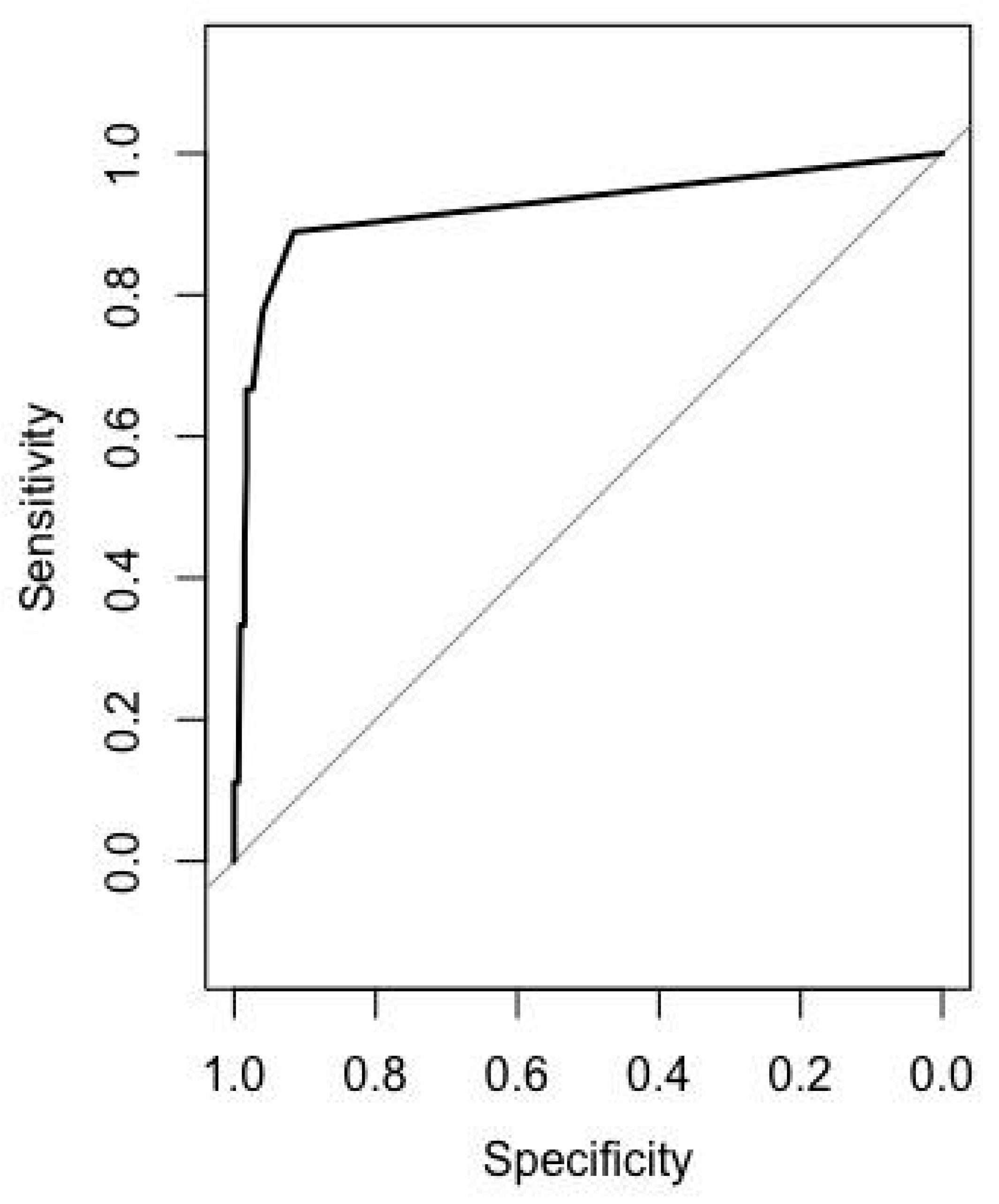
3.2. Determination of H. pylori Infection Status by Anti-H. pylori IgG
3.3. Endoscopy Diagnosis and Histology Examination
3.4. Analysis of Serum PG and Gastric Cancer Risk Determination by the ABC Method
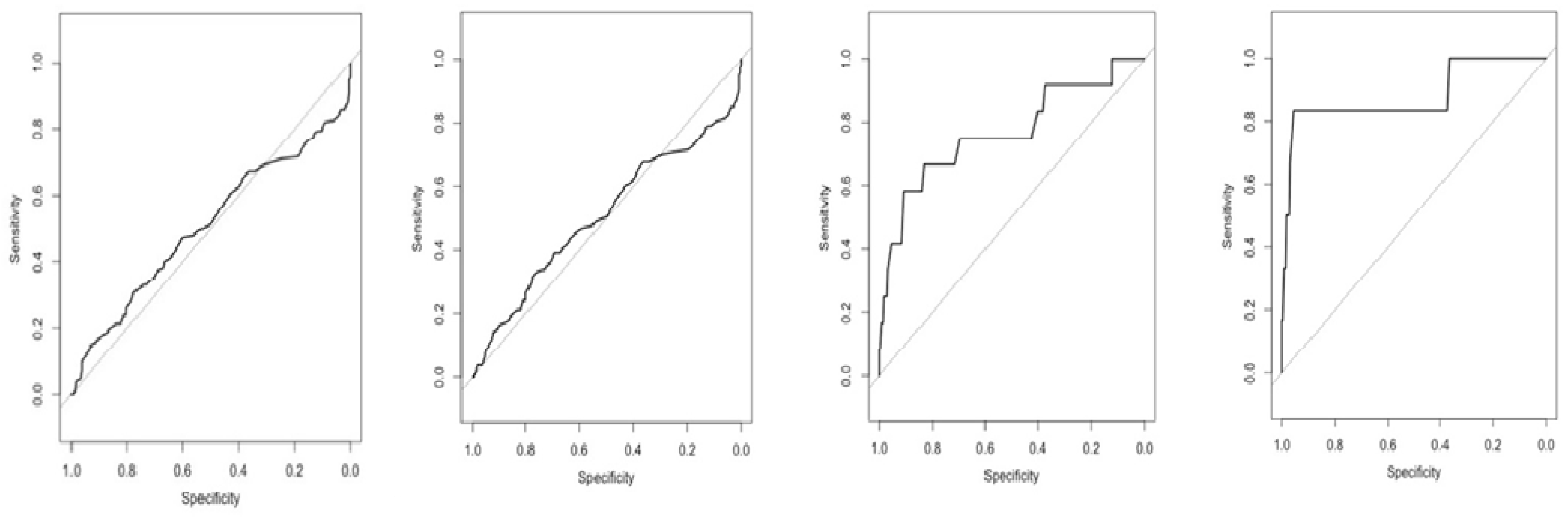
3.5. Diagnostic Value of Pepsinogen to Discriminate Gastric Mucosa Status
3.6. Diagnostic Value of PG to Discriminate Gastric Mucosa Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marshall, B.; Warren, J. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1984, 323, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Ojo, O.; Fujimoto, S.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Gutierrez, O.; El-Zimaity, H.M.T.; Reddy, R.; Arnqvist, A.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins and gastroduodenal disease. Gut 2006, 55, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, P.; Houghton, J. Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerdörffer, E.; Rudolph, B.; Neubauer, A.; Thiede, C.; Lehn, N.; Eidt, S.; Stolte, M. MALT Lyphoma Study Group Regression of primary gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. Lancet 1995, 345, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Ebrahimtabar, F.; Zamani, V.; Miller, W.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Shokri-Shirvani, J.; Derakhshan, M. System-atic review with meta–analysis: The worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathi, P.; Satpathi, S.; Mohanty, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Behera, P.K.; Maity, A.B. Helicobacter pylori infection in dyspeptic patients in an industrial belt of India. Trop. Dr. 2016, 47, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaichone, R.-K.; Mahachai, V.; Shiota, S.; Uchida, T.; Ratanachu-Ek, T.; Tshering, L.; Tung, N.L.; Fujioka, T.; Moriyama, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Extremely high prevalence of Helicobacter pyloriinfection in Bhutan. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2806–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftab, H.; Miftahussurur, M.; Subsomwong, P.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, A.K.A.; Matsumoto, T.; Suzuki, R.; Yamaoka, Y. Two pop-ulations of less-virulent Helicobacter pylori genotypes in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, N.; Holton, J.; Vaira, D.; DeSilva, M. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Sri Lanka as Determined by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2675–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- WHO. 2019 Health SDG Profile: Sri Lanka; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, N.; Perera, N.; Vaira, D.; Holton, J. Helicobacter pylori in School Children From the Western Province of Sri Lanka. Helicobacter 2001, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubhayawardana, N.; Weerasekera, M.; Weerasekera, D.; Samarasinghe, K.; Gunasekera, C.; Fernando, N. Detection of clar-ithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori strains in a dyspeptic patient population in Sri Lanka by polymerase chain reac-tion-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 33, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörhendi, N.; Soós, A.; Engh, M.A.; Tinusz, B.; Szakács, Z.; Pécsi, D.; Mikó, A.; Sarlós, P.; Hegyi, P.; Eröss, B. Accuracy of theHelicobacter pyloridiagnostic tests in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Rengifo, D.F.; Mendoza, B.; Jaramillo, C.; Rodríguez-Urrego, P.; Vera-Chamorro, J.F.; Alvarez, J.; Delgado, M.D.P.; Jimenez-Soto, L.F. Helicobacter pylori culture as a key tool for diagnosis in Colombia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2019, 13, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessède, E.; Arantes, V.; Mégraud, F.; Coelho, L.G. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Biomarkers forHelicobacter pyloriinfection and gastroduodenal diseases. Biomark. Med. 2014, 8, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, D.; Krumm, N.; Wener, M.H.; Yeh, M.M.; Truong, C.D.; Reddi, D.M.; Liu, Y.; Swanson, P.; Schmidt, R.A.; Bryan, A. Serology Is More Sensitive Than Urea Breath Test or Stool Antigen for the Initial Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Gastritis When Compared with Histopathology. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamashima, C.; for the JPHC Study Group; Sasazuki, S.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S. Receiver operating characteristic analysis of prediction for gastric cancer development using serum pepsinogen and Helicobacter pylori antibody tests. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrebinska, S.; Daugule, I.; Santare, D.; Isajevs, S.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Rudzite, D.; Kikuste, I.; Vanags, A.; Tolmanis, I.; Atstupens, J.; et al. Accuracy of two plasma antibody tests and faecal antigen test for non-invasive detection of H. pylori in middle-aged Caucasian general population sample. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Diagnostic Methods ofHelicobacter pyloriInfection for Epidemiological Studies: Critical Im-portance of Indirect Test Validation. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Jung, H.C. The Role of Serum Pepsinogen in the Detection of Gastric Cancer. Gut Liver 2010, 4, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, S.; Thrift, A.P.; Green, L.; Shah, R.; Verstovsek, G.; Rugge, M.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Serag, H.B. Clinical manifesta-tions of Helicobacter pylori–negative gastritis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, M.; Miki, K.; Wong, R.N.S.; Tatematsu, M.; Furihata, C.; Konishi, T.; Matsushima, M.; Tanji, M.; Sano, J.; Kurokawa, K.; et al. Methylation and Expression of Human Pepsinogen Genes in Normal Tissues and Their Alteration in Stomach Cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1991, 82, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, X. The potential value of serum pepsinogen for the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis among the health check-up populations in China: A diagnostic clinical research. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, H.; Mitsushima, T.; Yamaji, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Wada, R.; Kokubo, T.; Doi, H.; Yoshida, H.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Predicting the development of gastric cancer from combining Helicobacter pylori antibodies and serum pepsinogen sta-tus: A prospective endoscopic cohort study. Gut 2005, 54, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.K.; Park, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Jeon, C.H.; Lee, H.J.; Chae, H.D. The Role of Serum Pepsinogen in Detection of Gastric Cancer. J. Korean Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2009, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kikuchi, S.; Kato, M.; Mabe, K.; Kawai, T.; Furuta, T.; Inoue, K.; Ito, M.; Yoshihara, M.; Kodama, M.; Murakami, K. Optimal Criteria and Diagnostic Ability of Serum Pepsinogen Values for Helicobacter pylori Infection. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Z.; Huang, C.-Z.; Hu, W.-X.; Liu, Y.; Yao, X.-Q. Gastric Cancer Screening by Combined Determination of Serum Helicobacter pylori Antibody and Pepsinogen Concentrations. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Hiratsuka, R.; Kawase, Y.; Tominaga, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Sakagami, S.; Ishida, S. Gastric Cancer Screening by Combined Assay for Serum Anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG Antibody and Serum Pepsinogen Levels-The ABC Method. Digestion 2016, 93, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K. Gastric cancer screening by combined assay for serum anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG antibody and serum pepsinogen levels-“ABC method”. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2011, 87, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broutet, N.; the Eurohepygast Study Group; Plebani, M.; Sakarovitch, C.; Sipponen, P.; Megraud, F. Pepsinogen A, pep-sinogen C, and gastrin as markers of atrophic chronic gastritis in European dyspeptics. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, M.; Hamada, G.S.; Nishimoto, I.N.; Kowalski, L.P.; Iriya, K.; Gama-Rodrigues, J.J.; Tsugane, S. Ethnic differences in serum pepsinogen levels among Japanese and non-Japanese Brazilian gastric cancer patients and controls. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2000, 24, 564–571. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, T.L.; Fock, K.M.; Dhamodaran, S.; Teo, E.K.; Tan, J. Racial differences in Helicobacter pylori, serum pepsinogen and gastric cancer incidence in an urban Asian population. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syam, A.F.; Miftahussurur, M.; Makmun, D.; Nusi, I.A.; Zain, L.H.; Zulkhairi; Akil, F.; Uswan, W.B.; Simanjuntak, D.; Uchida, T.; et al. Risk Factors and Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Five Largest Islands of Indonesia: A Preliminary Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, M. and A. Meining, The updated Sydney system: Classification and grading of gastritis as the basis of diagnosis and treatment. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 15, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.K.; Kuo, F.C.; Liu, C.J.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Wu, J.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Huang, Y.K.; Wu, D.C. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection: Current options and developments. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 11221–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Ichinose, M.; Ishikawa, K.B.; Yahagi, N.; Matsushima, M.; Kakei, N.; Tsukada, S.; Kido, M.; Ishihama, S.; Shimizu, Y.; et al. Clinical application of serum pepsinogen I and II levels for mass screening to detect gastric cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1993, 84, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Morita, M.; Sasajima, M.; Hoshina, R.; Kanda, E.; Urita, Y. Usefulness of gastric cancer screening using the serum pepsinogen test method. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, M.; Ohwada, S.; Ishida, F.; KUDO, S. Serum Helicobacter Pylori IgG Titers are Predictive of H. pylori Infection Status. Showa Univ. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 28, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Sawada, N.; Goto, A.; Shimazu, T.; Yamaji, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Tsugane, S.; JPHC Study Group. High-Negative Anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG Antibody Titers and Long-Term Risk of Gastric Cancer: Results from a Large-Scale Population-Based Cohort Study in Japan. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Sharma, R.P.; Shrestha, P.K.; Suzuki, R.; Uchida, T.; Yamaoka, Y. Molecular Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Nepal: Specific Ancestor Root. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftab, H.; Yamaoka, Y.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, A.A.; Subsomwong, P.; Miftahussurur, M.; Uchida, T.; Malaty, H.M. Validation of diagnostic tests and epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2018, 12, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.K.; Kafle, P.; Puri, P.; Chaulagai, B.; Sidhu, J.S.; Hassan, M.; Paudel, M.S.; Kanth, R.; Gayam, V. An association of Helicobacter pylori infection with endoscopic and histological findings in the Nepalese population. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Waskito, L.A.; Syam, A.F.; Nusi, I.A.; Wibawa, I.; Rezkitha, Y.; Siregar, G.; Yulizal, O.K.; Akil, F.; Uwan, W.B.; et al. Analysis of risks of gastric cancer by gastric mucosa among Indonesian ethnic groups. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafiah, A.; Binmaeil, H.; Raja Ali, R.A.; Mohamed Rose, I.; Lopes, B.S. Molecular characterization and prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori isolates in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3051–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.; Piazuelo, M.B. The gastric precancerous cascade. J. Dig. Dis. 2012, 13, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, R.; Zhang, B.; Li, C. Chronic Atrophic Gastritis: A Review. J. Environ. Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2018, 37, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantuya, B.; El-Serag, H.B.; Matsumoto, T.; Ajami, N.J.; Oyuntsetseg, K.; Azzaya, D.; Uchida, T.; Yamaoka, Y. Gastric Microbiota in Helicobacter pylori-Negative and -Positive Gastritis Among High Incidence of Gastric Cancer Area. Cancers 2019, 11, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Waskito, L.A. Gastric microbiota and Helicobacter pylori in Indonesian population. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leja, M.; Park, J.Y.; Murillo, R.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Isajevs, S.; Kikuste, I.; Rudzite, D.; Krike, P.; Parshutin, S.; Polaka, I.; et al. Multicentric randomised study of Helicobacter pylori eradication and pepsinogen testing for prevention of gastric cancer mortality: The GISTAR study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.P.; Gong, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Y. Serum pepsinogen levels and their influencing factors: A population-based study in 6990 Chinese from North China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 13, 6562–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.H.; Bai, X.J.; Han, L.L.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, X.F. Changes with aging in gastric biomarkers levels and in biochemical factors associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in asymptomatic Chinese population. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5945–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.X.; Pu, H.; Huh, N.H.; Yokota, K.; Oguma, K.; Namba, M. Helicobacter pylori induces pepsinogen secretion by rat gastric cells in culture via a cAMP signal pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.C.; Blot, W.J.; Zhang, L.; Kneller, R.W.; Li, J.Y.; Jin, M.L.; Chang, Y.S.; Zeng, X.R.; Zhao, L.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr.; et al. Serum pepsinogens in relation to precancerous gastric lesions in a population at high risk for gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1993, 2, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Shen, S.; Dong, N.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q.; Sun, L.; Yuan, Y. Correlation between negative expression of pepsinogen C and a series of phenotypic markers of gastric cancer in different gastric diseases. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4068–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, T.H.; Chiu, S.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Yen, A.M.; Fann, J.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Chou, C.K.; Chiu, H.M.; Shun, C.T.; Wu, M.S.; et al. Serum Pepsinogen as a Predictor for Gastric Cancer Death: A 16-Year Community-based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, e186–e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.C.; Isomoto, H.; Moriyama, M.; Fujioka, T.; Machado, J.C.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter and gastric malignancies. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, H.; Kanmura, S.; Maeda, T.; Iwaya, H.; Arima, S.; Sasaki, F.; Nasu, Y.; Tanoue, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Ido, A. Helicobacter pylori eradication improves the quality of life regardless of the treatment outcome: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Medicine 2017, 96, e9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiso, M.; Yoshihara, M.; Ito, M.; Inoue, K.; Kato, K.; Nakajima, S.; Mabe, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Uemura, N.; Yada, T.; et al. Characteristics of gastric cancer in negative test of serum anti-Helicobacter pylori antibody and pepsinogen test: A multicenter study. Gastric Cancer. 2017, 20, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Subject Characteristics | Total Subjects | Positive Result (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture | Histology | Culture and Histology | ||
| n test positive | 353 | 6 (1.6) | 7 (1.9) | 9 (2.5) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 189 | 4 (2.1) | 5 (2.6) | 6 (3.2) |
| Female | 164 | 2 (1.2) | 2 (1.2) | 3 (1.8) |
| p-value | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.51 | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Sinhalese | 309 | 4 (1.3) | 5 (1.6) | 6 (1.9) |
| Muslim | 25 | 1 (4.0) | 1 (4.0) | 1 (4.0) |
| Tamil | 19 | 1 (5.2) | 1 (5.2) | 2 (10.5) |
| p-value | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.06 | |
| Histology Culture-Negative | Histology Culture-Positive | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. pylori-IgG Positive | H. pylori-IgG Negative | H. pylori-IgG Positive | H. pylori-IgG Negative | |
| Normal | 2 | 196 | 0 | 0 |
| Chronic gastritis | 1 | 20 | 1 | 0 |
| Mild atrophy | 7 | 108 | 5 | 1 |
| Moderate atrophy | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| Metaplasia | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 14 | 330 | 7 | 2 |
| PGI | PGII | PGI/PGII | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All sample summary | |||
| Median | 77.9 | 12.2 | 6.3 |
| Min | 2 | 2.6 | 0.1 |
| Max | 783 | 348 | 25 |
| IQR | 98.5 | 12.4 | 2.8 |
| H. pylori infection status (median; IQR) | |||
| Positive (n = 23) * | 69.9; 74.1 | 16.9; 17.5 | 4.1; 1.8 |
| Negative (n = 339) | 78.5; 99.1 | 12; 12.05 | 6.3; 2.9 |
| p-value | 0.31 | 0.19 | <0.001 |
| Gender (median; IQR) | |||
| Male (n = 189) | 92.8; 109.8 | 13.7; 16.7 | 6.3; 2.7 |
| Female (n = 164) | 68.2; 111.3 | 11.2; 18.3 | 6.1; 7.7 |
| p-value | 0.0018 | 0.0089 | 0.28 |
| Parameters | Chronic Gastritis | Mild Atrophy | Moderate Atrophy | Metaplasia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGI | PGI/PGII Ratio | PGI | PGI/PGII Ratio | PGI | PGI/PGII Ratio | PGI | PGI/PGII Ratio | |
| True positive | 64 | 13 | 56 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| True negative | 104 | 197 | 118 | 218 | 187 | 331 | 192 | 337 |
| False positive | 94 | 1 | 102 | 2 | 154 | 10 | 155 | 10 |
| False negative | 91 | 142 | 77 | 121 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 41.29 | 8.38 | 42.11 | 9.02 | 33.33 | 33.33 | 50 | 66.67 |
| Specificity (%) | 52.53 | 99.5 | 53.64 | 99.1 | 54.84 | 97.07 | 55.33 | 97.12 |
| Positive likelihood | 0.89 | 16.61 | 0.91 | 9.93 | 0.74 | 11.37 | 1.12 | 23.13 |
| Negative likelihood | 1.18 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 0.92 | 1.21 | 0.69 | 0.9 | 0.3432 |
| PPV | 40.5 | 92.85 | 49.39 | 85.73 | 2.52 | 28.51 | 1.08 | 28.45 |
| NPV | 53.34 | 58.12 | 46.3 | 64.28 | 95.9 | 97.65 | 98.47 | 99.41 |
| Accuracy | 47.59 | 59.49 | 49.29 | 65.16 | 54.11 | 94.9 | 55.24 | 96.6 |
| AUC | New Cut-Off | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Control | Case | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic gastritis | |||||||
| PGI | 0.5335 | 92.45 | 62.12 | 48.38 | 198 | 155 | 0.28 |
| PGII | 0.5552 | 17.45 | 71.22 | 40.64 | 0.07 | ||
| PGI/PGII ratio | 0.5081 | 9.75 | 93.43 | 14.83 | 0.79 | ||
| Mild atrophy | |||||||
| PGI | 0.529 | 92.45 | 60.91 | 48.12 | 220 | 133 | 0.36 |
| PGII | 0.5517 | 17.45 | 71.82 | 42.11 | 0.1 | ||
| PGI/PGII ratio | 0.5055 | 7.65 | 76.36 | 33.08 | 0.86 | ||
| Moderate atrophy | |||||||
| PGI | 0.4785 | 111 | 66.28 | 50 | 341 | 12 | 0.8 |
| PGII | 0.6987 | 14.55 | 60.12 | 83.33 | 0.019 | ||
| PGI/PGII ratio | 0.7652 | 4.75 | 83.28 | 66.67 | 0.0017 | ||
| Metaplasia | |||||||
| PGI | 0.6804 | 15.15 | 98.84 | 50 | 347 | 6 | 0.13 |
| PGII | 0.7207 | 18.15 | 69.16 | 83.33 | 0.064 | ||
| PGI/PGII ratio | 0.8804 | 3.25 | 95.39 | 83.33 | 0.0014 |
| ABC Method According to Criteria by Miki, n | |||||
| Total | A | B | C | D | |
| Number in each group | 353 | 335 | 7 | 1 | 10 |
| Histology of gastric tissue | |||||
| Metaplasia | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Moderate atrophic | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Mild atrophic | 121 | 111 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| Chronic gastritis | 22 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Normal | 198 | 197 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sri Lanka-modified criteria, n | |||||
| Total | A | B | C | D | |
| Number in each group | 353 | 323 | 19 | 3 | 8 |
| Histology of gastric tissue | |||||
| Metaplasia | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Moderate atrophic | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Mild atrophic | 121 | 104 | 11 | 2 | 4 |
| Chronic gastritis | 22 | 19 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Normal | 198 | 195 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doohan, D.; Fauzia, K.A.; Rathnayake, J.; Lamawansa, M.D.; Waskito, L.A.; Tuan, V.P.; Dashdorj, A.; Kabamba, E.T.; Phuc, B.H.; Ansari, S.; et al. Pepsinogen and Serum IgG Detection Is a Valuable Diagnostic Method for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Low-Prevalence Country: A Report from Sri Lanka. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081364
Doohan D, Fauzia KA, Rathnayake J, Lamawansa MD, Waskito LA, Tuan VP, Dashdorj A, Kabamba ET, Phuc BH, Ansari S, et al. Pepsinogen and Serum IgG Detection Is a Valuable Diagnostic Method for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Low-Prevalence Country: A Report from Sri Lanka. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(8):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081364
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoohan, Dalla, Kartika Afrida Fauzia, Jeewantha Rathnayake, Meegahalande Durage Lamawansa, Langgeng Agung Waskito, Vo Phuoc Tuan, Azzaya Dashdorj, Evariste Tshibangu Kabamba, Bui Hoang Phuc, Shamshul Ansari, and et al. 2021. "Pepsinogen and Serum IgG Detection Is a Valuable Diagnostic Method for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Low-Prevalence Country: A Report from Sri Lanka" Diagnostics 11, no. 8: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081364
APA StyleDoohan, D., Fauzia, K. A., Rathnayake, J., Lamawansa, M. D., Waskito, L. A., Tuan, V. P., Dashdorj, A., Kabamba, E. T., Phuc, B. H., Ansari, S., Akada, J., Matsumoto, T., Uchida, T., Matsuhisa, T., & Yamaoka, Y. (2021). Pepsinogen and Serum IgG Detection Is a Valuable Diagnostic Method for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Low-Prevalence Country: A Report from Sri Lanka. Diagnostics, 11(8), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081364








