Elastic Modulus and Elasticity Ratio of Malignant Breast Lesions with Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography: Variations with Different Region of Interest and Lesion Size
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barr, R. Sonographic breast elastography: A primer. J. Ultrasound Med. 2012, 31, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddi, A.; Bonardi, M.; Alessi, S. Breast elastography: A literature review. J. Ultrasound 2012, 15, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennisson, J.-L.; Deffieux, T.; Fink, M.; Tanter, M. Ultrasound elastography: Principles and techniques. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youk, J.H.; Son, E.J.; Gweon, H.M.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.A. Comparison of strain and shear wave elastography for the differentiation of benign from malignant breast lesions, combined with B-mode ultrasonography: Qualitative and quantitative assessments. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiou, A.; Tardivon, A.; Tanter, M.; Sigal-Zafrani, B.; Bercoff, J.; Deffieux, T.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Fink, M.; Neuenschwander, S. Breast lesions: Quantitative elastography with supersonic shear imaging: Preliminary results. Radiology 2010, 256, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicki, A.; Dobruch-Sobczak, K. Introduction to ultrasound elastography. J. Ultrason. 2016, 16, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youk, J.H.; Gweon, H.M.; Son, E.J. Shear-wave elastography in breast ultrasonography: The state of the art. Ultrasonography 2017, 36, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skerl, K.; Vinnicombe, S.; Giannotti, E. Influence of region of interest size and ultrasound lesion size on the performance of 2D shear wave elastography (SWE) in solid breast masses. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Hwang, J.Y.; Park, J.S.; Koh, S.H.; Park, S.Y. Impact of region of interest (ROI) size on the diagnostic performance of shear wave elastography in differentiating solid breast lesions. Acta Radiol. 2017, 59, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youk, J.H.; Son, E.J.; Han, K.; Gweon, H.M.; Kim, J.A. Performance of shear-wave elastography for breast masses using different region-of-interest (ROI) settings. Acta. Radiol. 2018, 59, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olgun, D.Ç.; Korkmazer, B.; Kılıç, F. Use of shear wave elastography to differentiate benign and malignant breast lesions. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 20, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, F.W.-F.; Ghai, S.; Moshonov, H. Diagnostic performance of quantitative shear wave elastography in the evaluation of solid breast masses: Determination of the most discriminatory parameter. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, S.; Choi, Y. Diagnostic performance of shear wave elastography of the breast according to scanning orientation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, W.A.; Cosgrove, D.O.; Doré, C.J.; Schäfer, F.K.; Svensson, W.E.; Hooley, R.J.; Ohlinger, R.; Mendelson, E.B.; Balu-Maestro, K.; Locatelli, M.; et al. Shear-wave elastography improves the specificity of breast US: The BE1 multinational study of 939 masses. Radiology 2012, 262, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Jung, H.K.; Ko, K.H.; Lee, J.T.; Yoon, J.H. Diagnostic performances of shear wave elastography: Which parameter to use in differential diagnosis of solid breast masses? Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.; Whelehan, P.; Thomson, K.; Brauer, K.; Jordan, L.; Purdie, C.; McLean, D.; Baker, L.; Vinnicombe, S.; Thompson, A. Differentiating benign from malignant solid breast masses: Value of shear wave elastography according to lesion stiffness combined with greyscale ultrasound according to BI-RADS classification. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhan, W.; Chang, C.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, C.; Sun, J.; Grant, E.G. Breast lesions: Evaluation with shear wave elastography, with special emphasis on the “stiff rim” sign. Radiology 2014, 272, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.M.; Park, I.A.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.H.; Bae, M.S.; Koo, H.R.; Yi, A.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, N.; Moon, W.K. Stiffness of tumours measured by shear-wave elastography correlated with subtypes of breast cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, J.T.; Ko, K.H. Shear-wave elastography in the diagnosis of solid breast masses: What leads to false-negative or false-positive results? Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R. Elastography: A Practical Approach; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chamming’s, F.; Hangard, C.; Gennisson, J.L.; Reinhold, C.; Fournier, L.S. Diagnostic Accuracy of Four Levels of Manual Compression Applied in Supersonic Shear Wave Elastography of the Breast. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
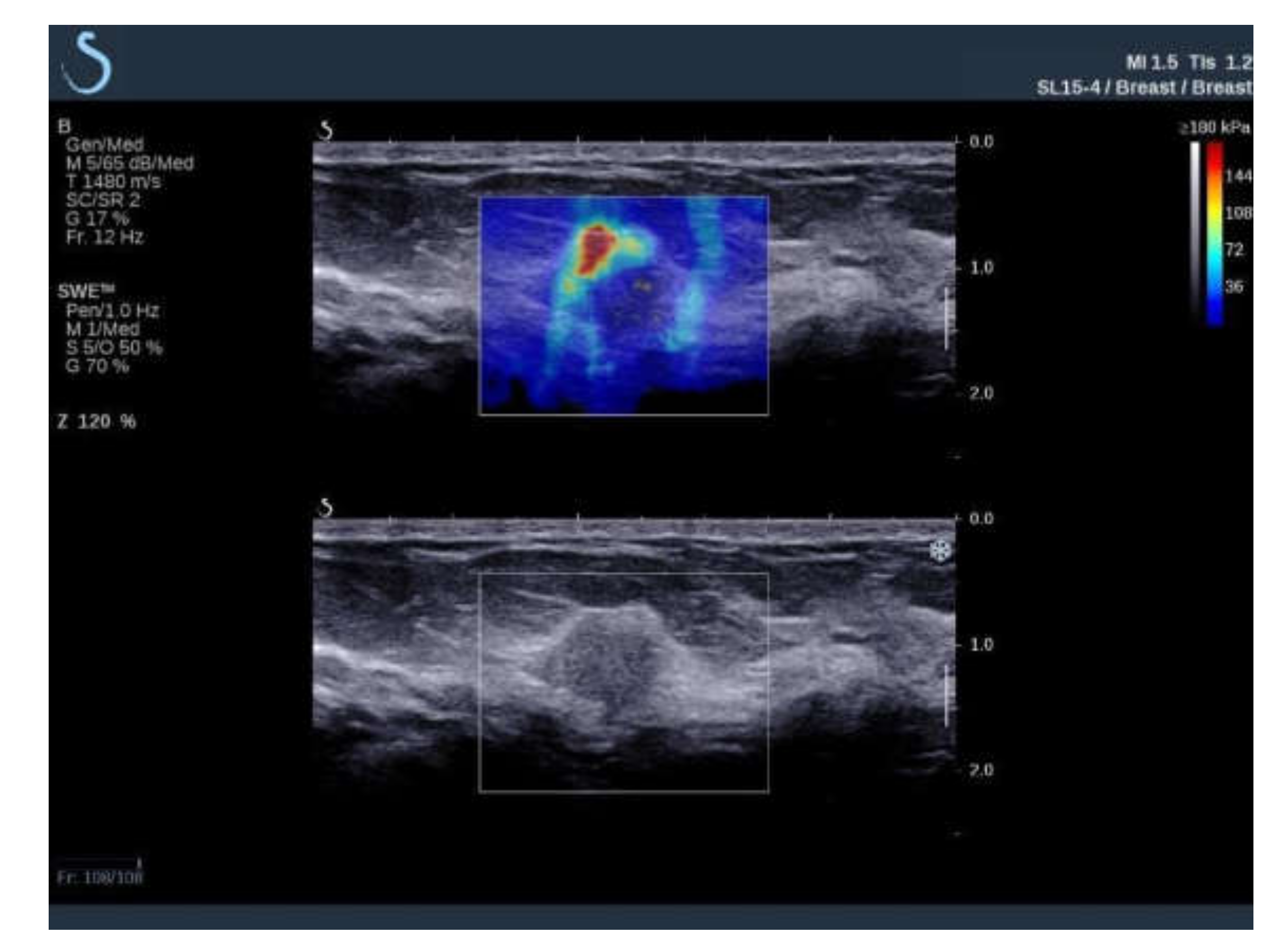
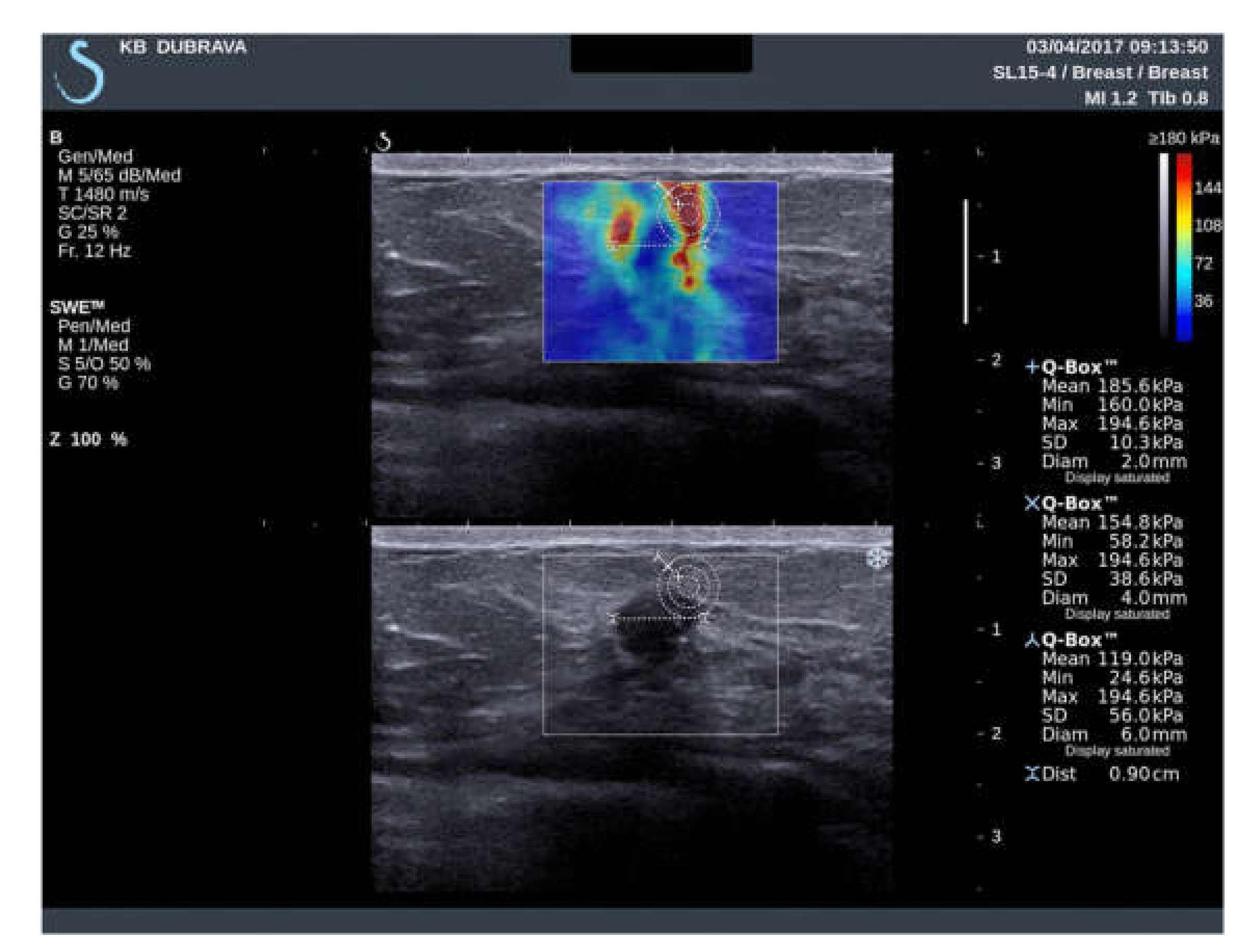
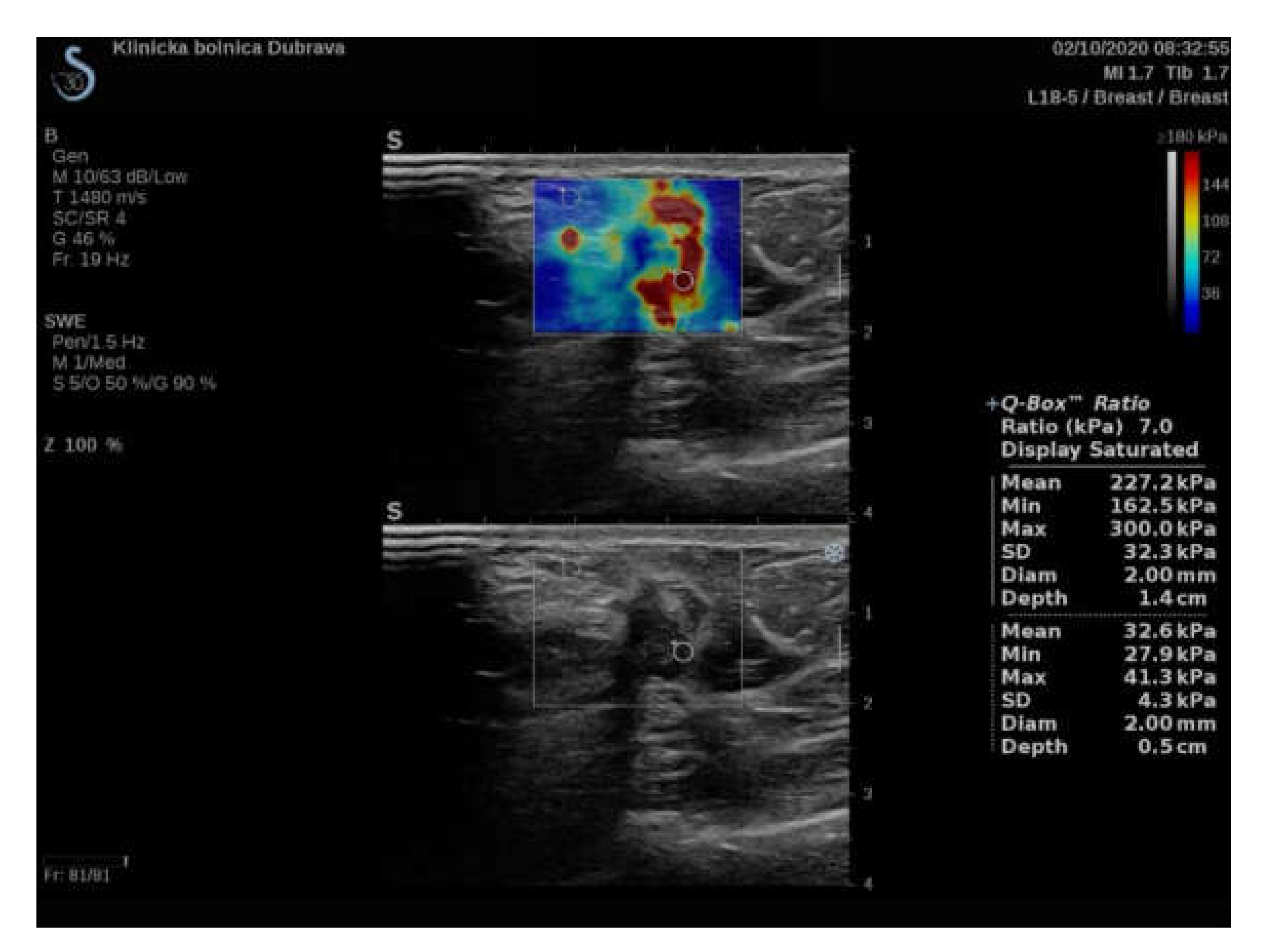
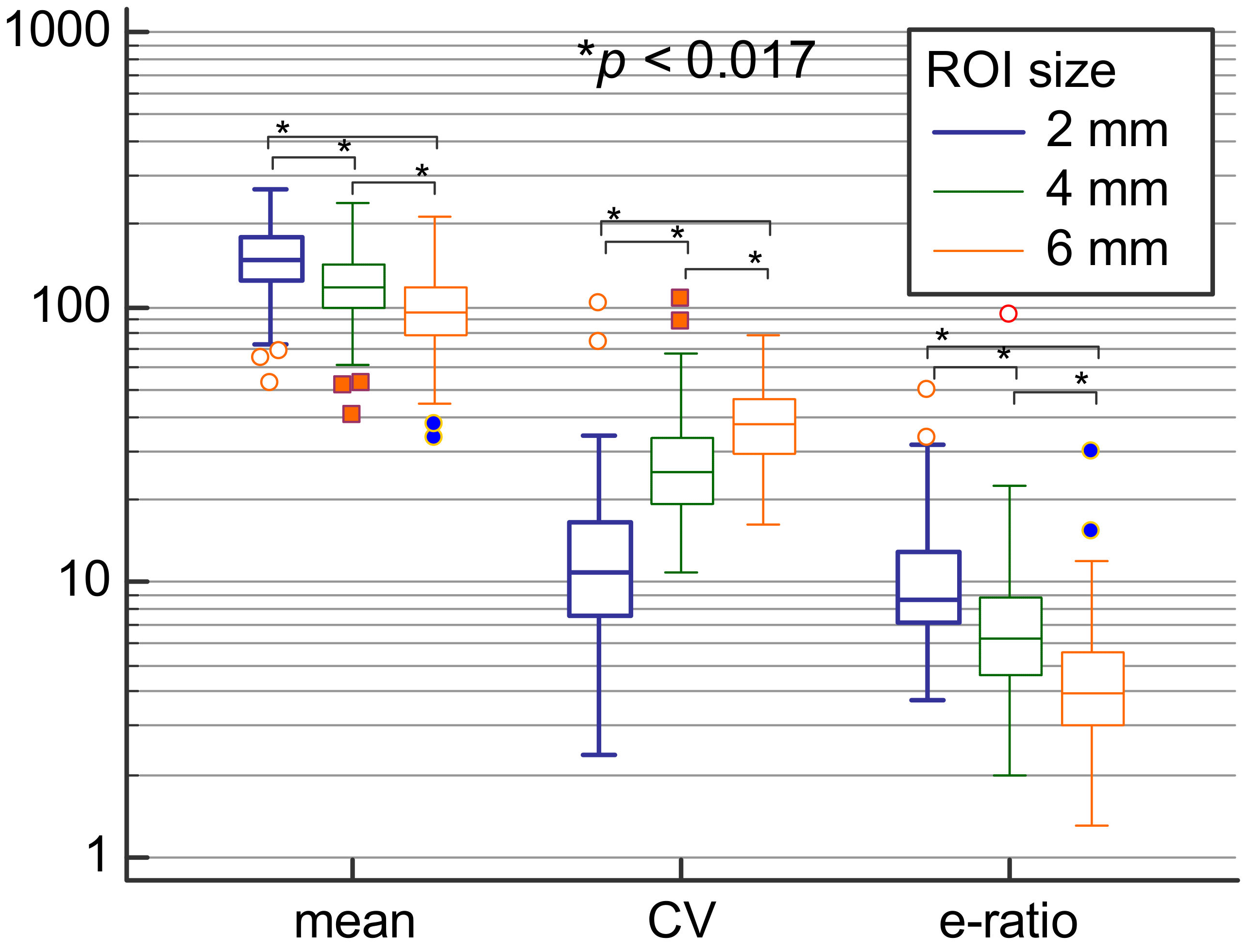
| Variable | ROI 2 mm (1) | ROI 4 mm (2) | ROI 6 mm (3) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emean (kPa) | 148.85 | 117.55 | 95.65 | <0.001 * (1 vs. 2; 1 vs. 3; 2 vs. 3) * |
| Sd (kPa) | 16.6 | 31.15 | 36.65 | <0.001 * (1 vs. 2; 1 vs. 3; 2 vs. 3) * |
| Coeff. var. (%) | 10.9 | 25.22 | 37.77 | <0.001 * (1 vs. 2; 1 vs. 3; 2 vs. 3) * |
| Emin (kPa) | 108.35 | 50.8 | 23.85 | <0.001 * (1 vs. 2; 1 vs. 3; 2 vs. 3) * |
| Emax (kPa) | 184.45 | 184.45 | 184.45 | 0.236 |
| e-ratio | 8.7 | 6.3 | 3.95 | <0.001 * (1 vs. 2; 1 vs. 3; 2 vs. 3) * |
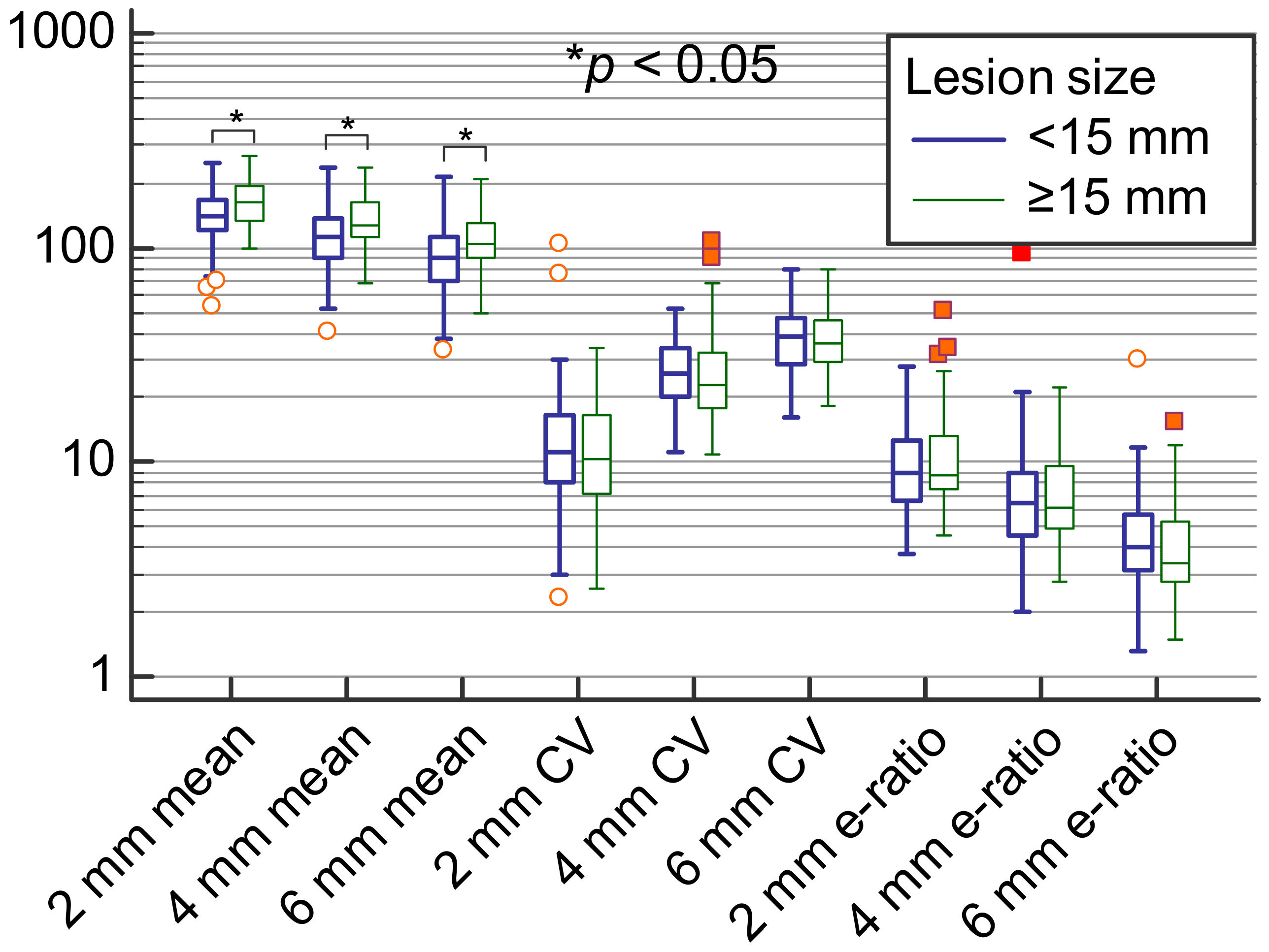
| Variable | Lesion Size < 15 mm | Lesion Size ≥ 15 mm | p Value | Correlation with Lesion Size as a Cont. Variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nm of patients | 95 | 55 | - | - |
| Emean ROI 2 mm (kPa) | 141.8 IQR (119.6–165.9) | 161.7 IQR (134.95–190.6) | 0.003 * | Rho = 0.4; p < 0.001 * |
| Sd ROI 2 mm (kPa) | 16.6 IQR (11–23) | 16.6 IQR (11.35–23.3) | 0.729 | Rho = 0.18; p = 0.030 * |
| Coeff. var. ROI 2 mm (%) | 11.1 IQR (8.08–16.42) | 10.1 IQR (6.7–16.32) | 0.245 | Rho = −0.01; p = 0.894 |
| Emin ROI 2 mm (kPa) | 104.9 IQR (79.4–127.4) | 123.8 IQR (91.3–154.6) | 0.015 * | Rho = 0.3; p < 0.001 * |
| Emax ROI 2 mm (kPa) | 171.8 IQR (137.9–192) | 192 IQR (171.85–221.6) | 0.001 * | Rho = 0.44; p < 0.001 * |
| e-ratio ROI 2 mm | 8.8 IQR (6.6–12.75) | 8.6 IQR (7.5–12.95) | 0.201 | Rho = 0.19; p = 0.023 * |
| Emean ROI 4 mm (kPa) | 111.3 IQR (89.15–135.55) | 128.6 IQR (111.9–161.8) | 0.001 * | Rho = 0.42; p < 0.001 * |
| Sd ROI 4 mm (kPa) | 31 IQR (21.9–37.65) | 32.8 IQR (24.15–40.1) | 0.256 | Rho = 0.21; p = 0.009 * |
| Coeff. var. ROI 4 mm (%) | 25.7 IQR (20.72–34.14) | 22.7 IQR (17.93–32.1) | 0.154 | Rho = −0.1; p = 0.219 |
| Emin ROI 4 mm (kPa) | 49.3 IQR (32.3–66.9) | 57.2 IQR (40.05–82) | 0.063 | Rho = 0.26; p = 0.002 * |
| Emax ROI 4 mm (kPa) | 171.8 IQR (137.9–192) | 192 IQR (171.85–214.6) | 0.001 * | Rho = 0.43; p < 0.001 * |
| e-ratio ROI 4 mm | 6.3 IQR (4.55–8.8) | 6.3 IQR (4.95–10.05) | 0.638 | Rho = 0.14; p = 0.092 |
| Emean ROI 6 mm (kPa) | 89.4 IQR (69.8–110.1) | 105.1 IQR (89.65–129.8) | 0.001 * | Rho = 0.4; p < 0.001 * |
| Sd ROI6 mm (kPa) | 34.5 IQR (24.75–43.45) | 39.7 IQR (32.95–46.55) | 0.005 * | Rho = 0.39; p < 0.001 * |
| Coeff. var. ROI6 (kPa) | 38.4 IQR (28.82–46.59) | 35.7 IQR (29.24–44.9) | 0.785 | Rho = 0.01; p = 0.942 |
| Emin ROI 6 mm (kPa) | 23.1 IQR (15.1–38.45) | 25.4 IQR (10.85–41.1) | 0.685 | Rho = 0.09; p = 0.295 |
| Emax ROI 6 mm (kPa) | 171.8 IQR (137.9–192) | 192 IQR (171.85–221.6) | 0.001 * | Rho = 0.43; p < 0.001 * |
| e-ratio ROI 6 mm | 4 IQR (3.15–5.7) | 3.4 IQR (2.85–5.35) | 0.335 | Rho = −0.05; p = 0.527 |
| ROI 2 mm vs. 4 mm mean difference | 26.3 IQR (18.55–37.95) | 26.2 IQR (21.4–38.75) | 0.408 | Rho = 0.13; p = 0.116 |
| ROI 2 mm vs. 6 mm mean difference | 47.4 IQR (34.05–64.6) | 52.7 IQR (41.45–69) | 0.116 | Rho = 0.22; p = 0.006 * |
| ROI 4 mm vs. 6 mm mean difference | 22.2 IQR (15.65–26) | 26.1 IQR (18.25–32.2) | 0.008 * | Rho = 0.32; p < 0.001 * |
| Variable | e-Ratio ROI 2 mm | e-Ratio ROI 4 mm | e-Ratio ROI 6 mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROI 2 mm vs. 4 mm mean difference | Rho = 0.14; p = 0.088 | Rho = 0.07; p = 0.388 | Rho = −0.01; p = 0.952 |
| ROI 2 mm vs. 6 mm mean difference | Rho = 0.25; p = 0.002 * | Rho = 0.2; p = 0.017 * | Rho = 0.08; p = 0.362 |
| ROI 4 mm vs. 6 mm mean difference | Rho = 0.39; p < 0.001 * | Rho = 0.39; p < 0.001 * | Rho = 0.22; p = 0.007 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulum, A.; Ivanac, G.; Divjak, E.; Biondić Špoljar, I.; Džoić Dominković, M.; Bojanić, K.; Lucijanić, M.; Brkljačić, B. Elastic Modulus and Elasticity Ratio of Malignant Breast Lesions with Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography: Variations with Different Region of Interest and Lesion Size. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061015
Bulum A, Ivanac G, Divjak E, Biondić Špoljar I, Džoić Dominković M, Bojanić K, Lucijanić M, Brkljačić B. Elastic Modulus and Elasticity Ratio of Malignant Breast Lesions with Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography: Variations with Different Region of Interest and Lesion Size. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(6):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulum, Antonio, Gordana Ivanac, Eugen Divjak, Iva Biondić Špoljar, Martina Džoić Dominković, Kristina Bojanić, Marko Lucijanić, and Boris Brkljačić. 2021. "Elastic Modulus and Elasticity Ratio of Malignant Breast Lesions with Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography: Variations with Different Region of Interest and Lesion Size" Diagnostics 11, no. 6: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061015
APA StyleBulum, A., Ivanac, G., Divjak, E., Biondić Špoljar, I., Džoić Dominković, M., Bojanić, K., Lucijanić, M., & Brkljačić, B. (2021). Elastic Modulus and Elasticity Ratio of Malignant Breast Lesions with Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography: Variations with Different Region of Interest and Lesion Size. Diagnostics, 11(6), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061015






