Blood–Brain Barrier Impairment in Patients Living with HIV: Predictors and Associated Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Demographic and Clinical Features
3.2. Antiretroviral Naïve and Treated Participants
3.3. Blood–Brain Barrier Impairment and CSF Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data. Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Trunfio, M.; Vai, D.; Montrucchio, C.; Alcantarini, C.; Livelli, A.; Tettoni, M.; Orofino, G.; Audagnotto, S.; Imperiale, D.; Bonora, S.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of new and old cognitive screening tools for HIV–associated neurocognitive disorders. HIV Med. 2018, 19, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, R.; Cysique, L.A. HIV–Associated Neurocognitive Disorders: A Global Perspective. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2017, 23, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, A.; Alberione, M.C.; Romito, A.; Imperiale, D.; Ghisetti, V.; Audagnotto, S.; Lipani, F.; Raviolo, F.; Di Perri, G.; Bonora, S. Prevalence and predictors of blood–brain barrier damage in the HAART era. J. Neurovirol. 2014, 20, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazza, M.; Pirrone, V.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonnemacher, M.R. Breaking down the barrier: The effects of HIV–1 on the blood–brain barrier. Brain Res. 2011, 1399, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivey, N.S.; MacLean, A.G.; Lackner, A.A. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and the blood–brain barrier. J. Neurovirol. 2009, 15, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, A.; Atzori, C.; Romito, A.; Vai, D.; Audagnotto, S.; Stella, M.L.; Montrucchio, C.; Imperiale, D.; Di Perri, G.; Bonora, S. Blood brain barrier impairment is associated with cerebrospinal fluid markers of neuronal damage in HIV–positive patients. J. Neurovirol. 2016, 22, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eugenin, E.A.; Clements, J.E.; Zink, M.C.; Berman, J.W. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection of Human Astrocytes Disrupts Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity by a Gap Junction–Dependent Mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9456–9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Podany, A.; Al–Harthi, L.; Wallace, J. The far–reaching HAND of cART: cART effects on astrocytes. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindpani, K.; McNamara, L.G.; Smith, N.R.; Vinnakota, C.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Faull, R.L.; Kwakowsky, A. Vascular Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Prelude to the Pathological Process or a Consequence of It? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, D.A.; Sweeney, M.D.; Montagne, A.; Sagare, A.P.; D’Orazio, L.M.; Pachicano, M.; Sepehrband, F.; Nelson, A.R.; Buennagel, D.P.; Harrington, M.G.; et al. Blood–brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smail, R.C.; Brew, B.J. HIV–associated neurocognitive disorder. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 152, 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Reiber, H. External quality assessment in clinical neurochemistry: Survey of analysis for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteins based on CSF/serum quotients. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinori, A.; Arendt, G.; Becker, J.T.; Brew, B.J.; Byrd, D.A.; Cherner, M.; Clifford, D.B.; Cinque, P.; Epstein, L.G.; Goodkin, K.; et al. Updated research nosology for HIV–associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology 2007, 69, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madihi, S.; Syed, H.; Lazar, F.; Zyad, A.; Benani, A. A Systematic Review of the Current Hepatitis B Viral Infection and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Situation in Mediterranean Countries. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagnelli, E.; Stroffolini, T.; Sagnelli, C.; Pirisi, M.; Babudieri, S.; Colloredo, G.; Russello, M.; Coppola, N.; Gaeta, G.B.; Cacopardo, B.; et al. Gender differences in chronic liver diseases in two cohorts of 2001 and 2014 in Italy. Infection 2018, 46, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, E.P. Sex Differences in HIV Infection. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018, 15, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, P.M.; Martin-Thormeyer, E. HIV, Cognition and Women. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2009, 19, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, L.H.; Neigh, G.N.; Sundermann, E.E.; Xu, Y.; Scully, E.P.; Maki, P.M. Sex Differences in Neurocognitive Function in Adults with HIV: Patterns, Predictors, and Mechanisms. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namagga, J.K.; Rukundo, G.Z.; Voss, J.G. Prevalence and Risk Factors of HIV–Associated Neurocognitive Disorders in Rural Southwestern Uganda. J. Assoc. Nurses AIDS Care 2019, 30, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, R.; Umlauf, A.; Luca, A.; Gianella, S.; Radoi, R.; Ruta, S.M.; Marcotte, T.D.; Ene, L.; Achim, C.L. Sex–based differences in neurocognitive functioning in HIV–infected young adults. AIDS 2018, 32, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.A.; Liang, W.S.; Fernandez, E.G.; Bullock, K.M.; Thysell, J.A.; Banks, W.A. Genetics and sex influence peripheral and central innate immune responses and blood–brain barrier integrity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulle, S.; Hagberg, L.; Gisslen, M. Effects of antiretroviral treatment on blood–brain barrier integrity and intrathecal immunoglobulin production in neuroasymptomatic HIV–1—infected patients. HIV Med. 2005, 6, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimy, E.; Li, F.Y.; Hagberg, L.; Fuchs, D.; Robertson, K.; Meyerhoff, D.J.; Zetterberg, H.; Price, R.W.; Gisslén, M.; Spudich, S. Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption Is Initiated During Primary HIV Infection and Not Rapidly Altered by Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, A.; Celani, L.; Trunfio, M.; Orofino, G.; Imperiale, D.; Atzori, C.; Arena, V.; D’Ettorre, G.; Guaraldi, G.; Gisslen, M.; et al. Alzheimer’s Dementia in People Living With HIV. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougea, A.; Spantideas, N.; Galanis, P.; Gkekas, G.; Thomaides, T. Optimal treatment of HIV–associated neurocognitive disorders: Myths and reality. A critical review. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, 204993611983822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, A.; Romito, A.; Atzori, C.; Ghisetti, V.; Cardellino, C.; Audagnotto, S.; Scarvaglieri, E.; Lipani, F.; Imperiale, D.; Di Perri, G.; et al. Blood Brain Barrier Impairment in HIV–Positive Naïve and Effectively Treated Patients: Immune Activation Versus Astrocytosis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017, 12, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, P.; He, J.J. HIV/neuroAIDS biomarkers. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 157, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurain, N.S.; Hanson, B.A.; Hotton, A.L.; Weber, K.M.; Cohen, M.H.; Landay, A.L. The Association of Human Cytomegalovirus with Biomarkers of Inflammation and Immune Activation in HIV–1–Infected Women. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2016, 32, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perello, R.; Vergara, A.; Monclus, E.; Jimenez, S.; Montero, M.; Saubi, N.; Moreno, A.; Eto, Y.; Inciarte, A.; Mallolas, J.; et al. Cytomegalovirus infection in HIV–infected patients in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deayton, J.R.; Sabin, C.A.; Johnson, M.A.; Emery, V.C.; Wilson, P.; Griffiths, P.D. Importance of cytomegalovirus viraemia in risk of disease progression and death in HIV–infected patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Lancet 2004, 363, 2116–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellner, M.D.; Durand, K.; Correa, R.M.; Redini, L.; Yampolsky, C.; Colobraro, A.; Sevlever, G.; Teyssié, A.R.; Benetucci, J.; Picconi, M.A. Circulating Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in HIV–infected patients and its relation with primary brain lymphoma. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehee, A.; Asselot, C.; Piolot, T.; Jacomet, C.; Rozenbaum, W.; Vidaud, M.; Garbarg-Chenon, A.; Nicolas, J.C. Quantification of Epstein–Barr virus load in peripheral blood of human immunodeficiency virus–infected patients using real–time PCR. J. Med. Virol. 2001, 65, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupia, T.; Milia, M.G.; Atzori, C.; Gianella, S.; Audagnotto, S.; Imperiale, D.; Mighetto, L.; Pirriatore, V.; Gregori, G.; Lipani, F.; et al. Presence of Epstein–Barr virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid is associated with greater HIV RNA and inflammation. AIDS 2020, 34, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R. The blood brain barrier in HIV infection. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bertrand, L.; Nair, M.; Toborek, M. Solving the Blood–Brain Barrier Challenge for the Effective Treatment of HIV Replication in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | cART-Naïve | cART-Treated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 147 | 317 | |
| Age | Years | 44.1 (38.0–51.7) | 49.2 (42.8–57.5) |
| Sex | Female | 41 (27.9) | 88 (27.8) |
| BMI | Kg/m2 | 18.5 (12.8–21.7) | 23.9 (22.2–25.8) |
| Ancestry | European | 119 (84.4) | 216 (86.4) |
| African | 14 (9.9) | 28 (11.2) | |
| South American | 6 (4.3) | 6 (2.4) | |
| Other | 2 (1.4) | 0 | |
| Risk Factors | Males who have sex with males | 44 (33.6) | 66 (28.1) |
| Heterosexuals | 41 (31.3) | 60 (25.5) | |
| Intravenous drug users | 24 (18.3) | 80 (34.0) | |
| Other | 6 (4.6) | 6 (2.6) | |
| Unknown | 15 (11.5) | 23 (9.8) | |
| Comorbidities | Liver cirrhosis | 6 (4.2) | 27 (10.9) |
| Psychiatric disorders | 25 (19.4) | 46 (19.0) | |
| Past syphilis | 30 (21.4) | 54 (22.0) | |
| Chronic HCV | 24 (16.8) | 70 (28.2) | |
| Chronic HBV | 14 (9.9) | 32 (12.9) | |
| Toxoplasma positive serology | 15 (31.2) | 29 (42.0) | |
| Active smoking | 45 (30.7) | 89 (28.0) | |
| Characteristics | ART-Naïve (n = 147) | ART-Treated (n = 317) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Asymptomatic/control | 8 (5.8) | 64 (23.7) |
| Primary infection | 1 (0.7) | – | |
| Late presentation | 77 (55.8) | 17 (6.3) | |
| Other CNS disorders | 11 (8.0) | 44 (16.3) | |
| CNS opportunistic infections | 19 (13.8) | 34 (12.6) | |
| HIV-related encephalitis/escape/rebound | 2 (1.4) | 7 (2.6) | |
| HAND | 14 (10.1) | 77 (28.5) | |
| White matter hyperintensity | 2 (1.4) | 11 (4.1) | |
| Syphilis | 1 (0.7) | 13 (4.8) | |
| Neuro syphilis | 3 (2.2) | 3(1.1) | |
| RMN | White matter hyperintensities | 87 (64.4) | 150 (68.8) |
| Therapy | PI | – | 41 (12.9) |
| INSTI | – | 88 (28) | |
| MVC | – | 16 (5) | |
| NNRTI | – | 55 (17.4) | |
| Number of drugs | – | 3 | |
| Characteristics | ART-Naïve (n = 147) | ART-Treated (n = 317) | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nadir CD4+ (cell/mm3) | 49 (20–118) | 97 (26.5–208) | 0.002 |
| CD4+ (cell/mm3) | 57 (23–117) | 366.5 (154.25–620.5) | <0.001 |
| HIV DNA (copies/106 PBMCs) | 478.5 (138.25–2462.5) | 123 (29–395) | 0.002 |
| Serum HIV RNA (log10 cps/mL) | 5.42 (4.93–5.95) | 1.28 (0.42–1.91) | <0.001 |
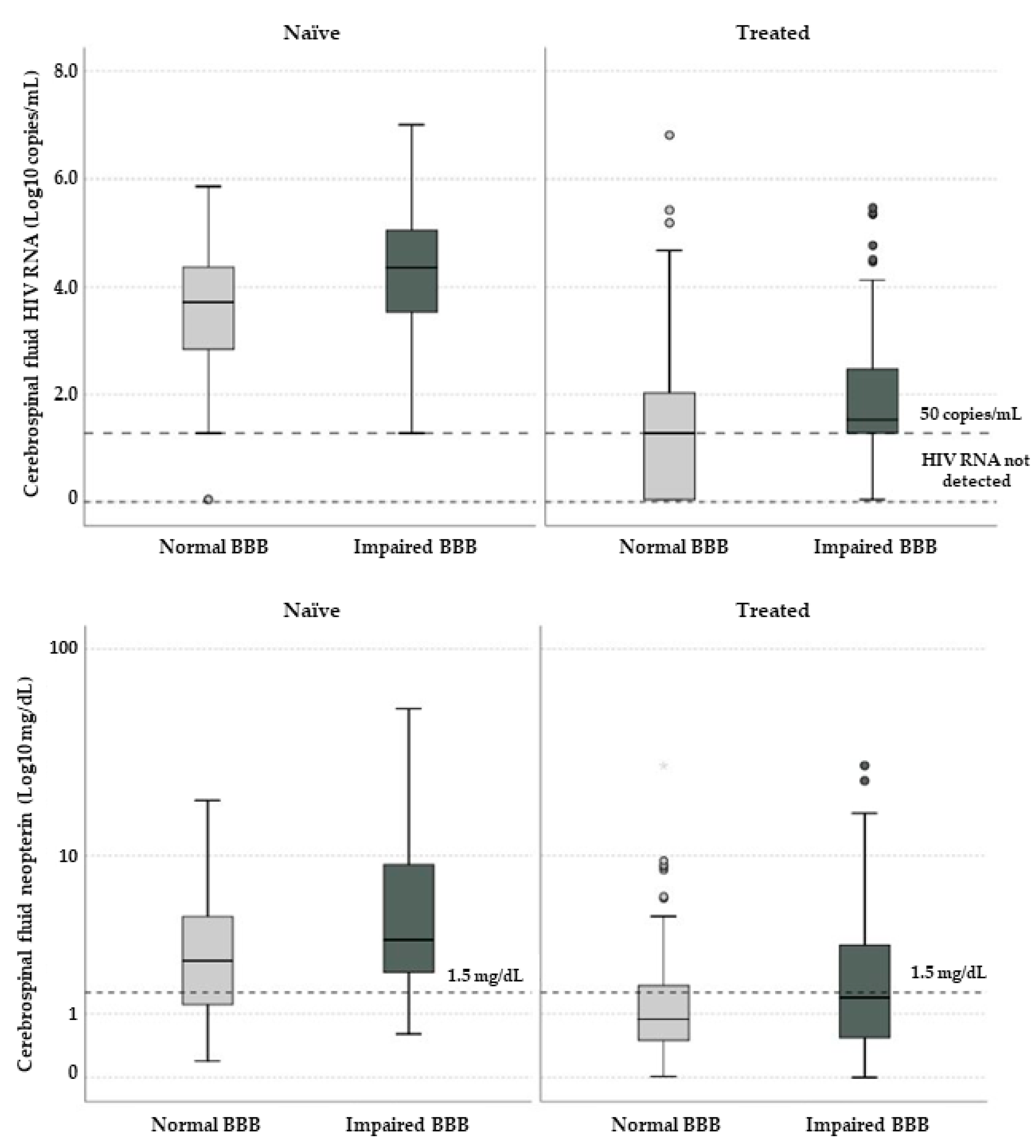
| CSF HIV RNA (log10 cps/mL) | 3.88 (3.07–4.7) | 1.28 (0.04–2.08) | <0.001 |
| HIV duration (months) | 1.23 (0.43–125.63) | 143.37 (44.98–225.96) | <0.001 |
| Viral suppression (months) | 0 (0–0) | 18 (3.8–73) | <0.001 |
| CSF cells | 0 (0–3) | 0 (0–2) | 0.266 |
| CSF proteins | 49 (39–68.25) | 48 (38–63) | 0.557 |
| CSF glucose | 50 (45–57) | 48 (51–63) | <0.001 |
| Serum HIV RNA < 50 cps/mL | 1 (0.7) | 196 (70.8) | <0.001 |
| CSF HIV RNA < 50 cps/mL | 5 (3.6) | 178 (63.3) | <0.001 |
| NADIR CD4 < 200 cells/mm3 | 117 (84.2) | 164 (71.3) | 0.005 |
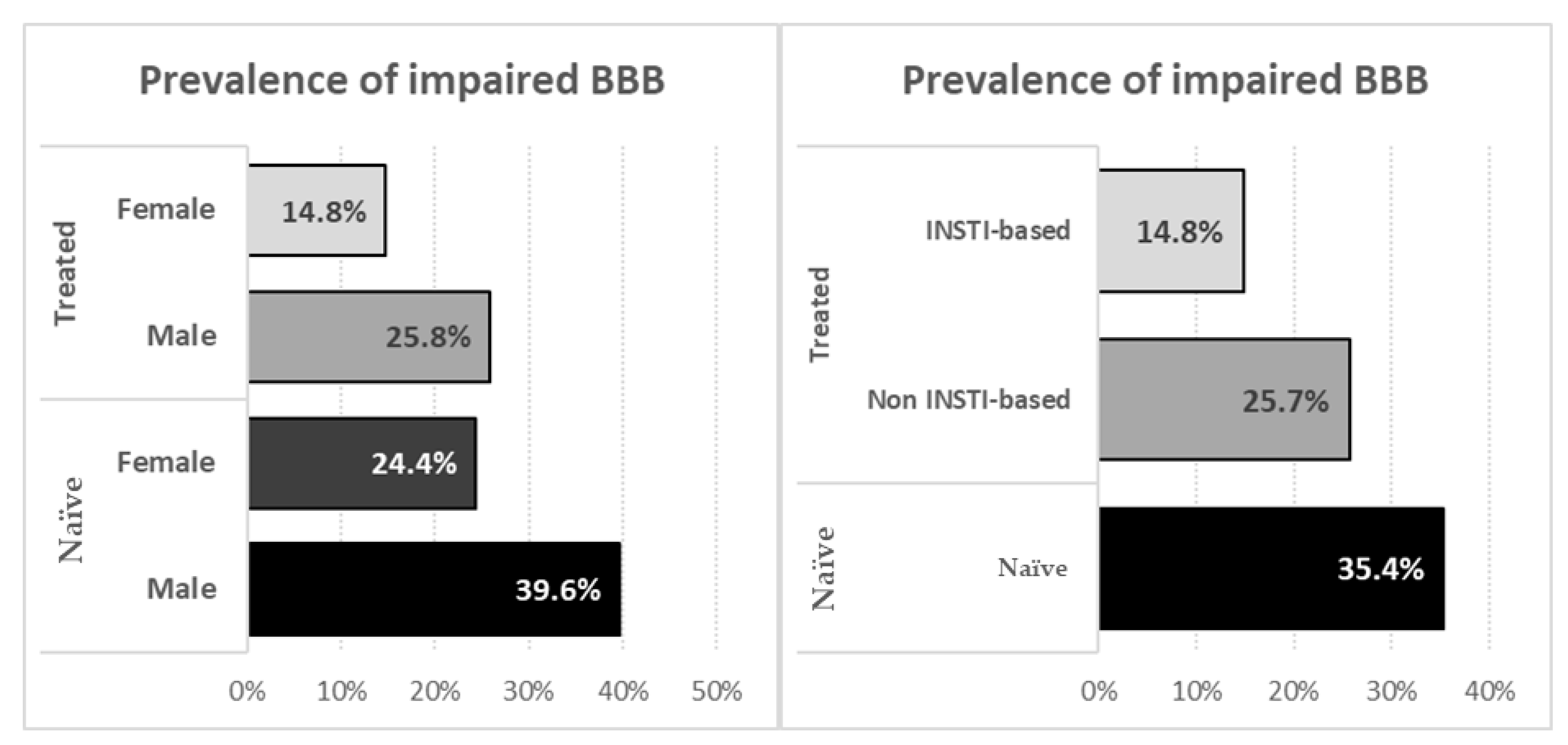
| BBB impairment | 52 (35.4) | 72 (22.7) | 0.005 |
| CSAR | 6.2 (4.3–8.7) | 5.6 (4.1–7.6) | 0.119 |
| Intrathecal IgG Synthesis | 0 (0–25) | 0 (0–20) | 0.280 |
| t–Tau | 165 (96–293) | 222 (129–350) | 0.045 |
| p–Tau | 33 (25–41) | 37 (27–51) | 0.040 |
| Aβeta42 | 962 (704–1142) | 919 (736–1171) | 0.901 |
| S100Beta | 145 (48–260) | 129 (70.25–219.5) | 0.758 |
| Neopterin | 2.9 (1.4–5.7) | 0.9 (0.5–1.9) | <0.001 |
| JCV DNA+ | 8 (5.6) | 17 (5.1) | 1.000 |
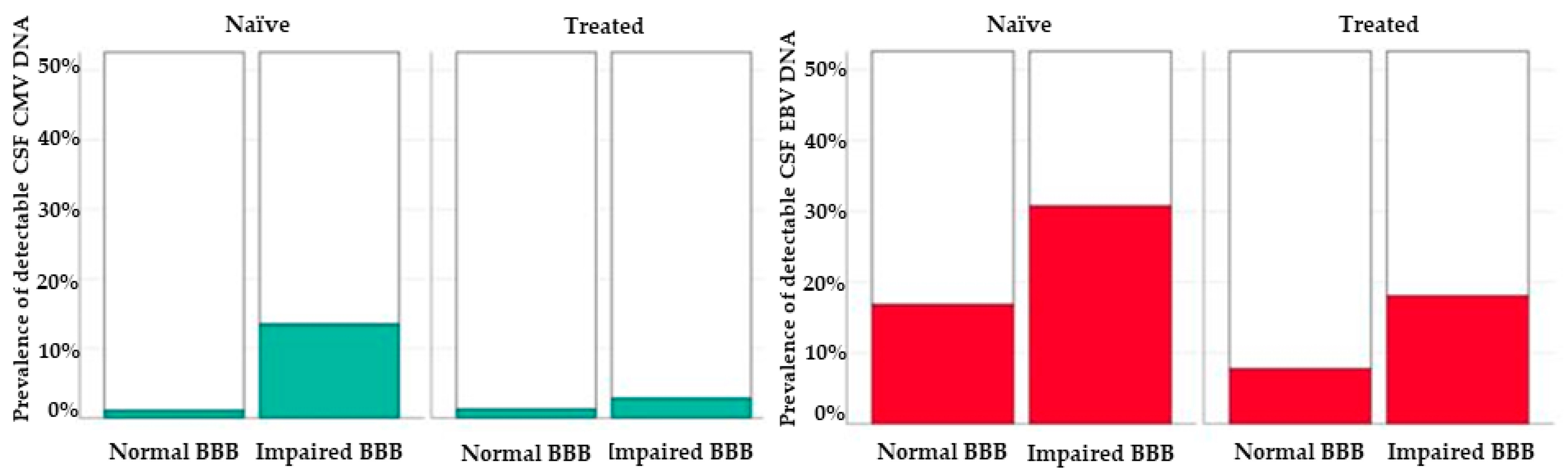
| EBV DNA+ | 32 (22.3) | 32 (10.1) | 0.001 |
| CMV DNA+ | 8 (5.6) | 5 (1.5) | 0.030 |
| Characteristics | Naïve Features | cART-Treated Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact BBB | BBBi | p Values | Intact BBB | BBBi | p Values | |
| n | 95 (64.6) | 52 (35.4) | – | 245 (77.3) | 72 (22.7) | – |
| Female sex | 31 (32.6) | 10 (19.2) | 0.088 | 75 (30.6) | 13 (18.1) | 0.037 |
| Age | 46 (39–52) | 41 (37–49) | 0.034 | 49 (43–57) | 48 (42–56) | 0.854 |
| CD4+ (cell/mm3) | 47 (20–110) | 72 (36–218) | 0.132 | 371 (155–628) | 357 (145–593) | 0.910 |
| Nadir CD4+ (cell/mm3) | 46 (15–107) | 71 (26–149) | 0.089 | 95 (25–202) | 100 (31–229) | 0.283 |
| Nadir CD4 < 200 cells/mm3 | 78 (87.6) | 39 (78.0) | 0.152 | 132 (73.3) | 32 (64.0) | 0.218 |
| Serum HIV RNA (Log10 cps/mL) | 5.4 (4.9–5.9) | 5.6 (4.9–6.0) | 0.098 | <1.28 (<1.28–1.80) | <1.28 (<1.28–2.32) | 0.598 |
| Serum HIV RNA < 50 cps/mL | 1 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 1.00 | 157 (72.7) | 39 (63.9) | 0.204 |
| HIV DNA (copies/106 PBMCs) | 478 (76–2324) | 903 (160–12064) | 0.291 | 91 (<50–362) | 147 (70–829) | 0.160 |
| HIV duration (months) | – | – | – | 143 (45–226) | 142 (42–225) | 0.929 |
| Viral suppression (months) | – | – | – | 17 (2.5–65) | 29 (9–95) | 0.115 |
| History of CNS opportunistic infections | 6 (6.3) | 13 (25) | 0.002 | 18 (7.3) | 16 (22.2) | 0.001 |
| Receiving NNRTIs | – | – | – | 38 (15.5) | 17 (23.6) | 0.114 |
| Receiving PIs | – | – | – | 31 (12.7) | 10 (13.9) | 0.842 |
| Receiving INSTIs | – | – | – | 75 (30.9) | 13 (18.3) | 0.050 |
| CSF cells ≥ 5/mm3 | 12 (13) | 21 (41.2) | <0.001 | 20 (9.5) | 17 (27.9) | 0.001 |
| CSF proteins | 40 (34–49) | 75 (56–90) | <0.001 | 43 (34–52) | 81 (66–107) | <0.001 |
| CSF glucose | 51 (45–58) | 48 (42–54) | 0.022 | 57 (52–63) | 56 (50–65) | 0.940 |
| CSF HIV RNA (Log10 cps/mL) | 3.71 (2.82–4.39) | 4.36 (3.49–5.09) | 0.002 | <1.28 (<1.28–2.03) | 1.53 (<1.28–2.66) | 0.029 |
| CSF HIV RNA < 50 cps/mL | 4 (4.3) | 1 (2.1) | 0.660 | 143 (65.3) | 35 (56.5) | 0.233 |
| CSAR | 5.0 (3.8–6.0) | 9.6 (8.3–12.8) | <0.001 | 4.9 (3.8–6.2) | 10.4 (8.8–13.4) | <0.001 |
| Intrathecal IgG Synthesis (%) | 38 (40.4) | 15 (29.4) | 0.210 | 76 (33.8) | 17 (25.8) | 0.234 |
| tau | 134 (93–306) | 173 (136–285) | 0.282 | 225 (134–344) | 212 (113–403) | 0.865 |
| p–Tau | 31 (24–41) | 34 (27–42) | 0.423 | 36 (26–51) | 39 (29–50) | 0.648 |
| Aβeta42 | 925 (734–1144) | 1017 (580–1149) | 0.947 | 918 (726–1165) | 950 (752–1284) | 0.665 |
| S100Beta | 151 (55–281) | 102 (38–229) | 0.410 | 121 (71–202) | 178 (60–351) | 0.269 |
| Neopterin | 2.52 (1.19–4.80) | 3.42 (2.10–9.80) | 0.029 | 0.88 (0.50–1.70) | 1.38 (0.50–3.40) | 0.048 |
| JCV DNA+ | 3 (3.2) | 5 (9.6) | 0.131 | 10 (4.1) | 7 (9.7) | 0.075 |
| EBV DNA+ | 16 (16.8) | 16 (30.8) | 0.061 | 19 (7.8) | 13 (18.1) | 0.015 |
| CMV DNA+ | 1 (1.1) | 7 (13.5) | 0.003 | 3 (1.2) | 2 (2.8) | 0.319 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caligaris, G.; Trunfio, M.; Ghisetti, V.; Cusato, J.; Nigra, M.; Atzori, C.; Imperiale, D.; Bonora, S.; Di Perri, G.; Calcagno, A. Blood–Brain Barrier Impairment in Patients Living with HIV: Predictors and Associated Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050867
Caligaris G, Trunfio M, Ghisetti V, Cusato J, Nigra M, Atzori C, Imperiale D, Bonora S, Di Perri G, Calcagno A. Blood–Brain Barrier Impairment in Patients Living with HIV: Predictors and Associated Biomarkers. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(5):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050867
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaligaris, Giulia, Mattia Trunfio, Valeria Ghisetti, Jessica Cusato, Marco Nigra, Cristiana Atzori, Daniele Imperiale, Stefano Bonora, Giovanni Di Perri, and Andrea Calcagno. 2021. "Blood–Brain Barrier Impairment in Patients Living with HIV: Predictors and Associated Biomarkers" Diagnostics 11, no. 5: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050867
APA StyleCaligaris, G., Trunfio, M., Ghisetti, V., Cusato, J., Nigra, M., Atzori, C., Imperiale, D., Bonora, S., Di Perri, G., & Calcagno, A. (2021). Blood–Brain Barrier Impairment in Patients Living with HIV: Predictors and Associated Biomarkers. Diagnostics, 11(5), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050867








