Lung Transplantation: CT Assessment of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD)
3. Diagnosis of CLAD
4. Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome
5. Restrictive Allograft Syndrome (RAS)
6. Overlap BOS/RAS: Mixed-Phenotype CLAD
7. When to Perform a CT Scan in the Setting of CLAD
8. Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in pre-CLAD and CLAD
9. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chambers, D.C.; Cherikh, W.S.; Goldfarb, S.B.; Hayes, D.; Kucheryavaya, A.Y.; Toll, A.E.; Khush, K.K.; Levvey, B.J.; Meiser, B.; Rossano, J.W.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Report-2018. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2018, 37, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Waddell, T.K.; Wagnetz, U.; Roberts, H.C.; Hwang, D.M.; Haroon, A.; Wagnetz, D.; Chaparro, C.; Singer, L.G.; Hutcheon, M.A.; et al. Restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS): A novel form of chronic lung allograft dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2011, 30, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, G.M.; Raghu, G.; Meyer, K.C.; Glanville, A.R.; Corris, P. A new classification system for chronic lung allograft dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, S.E.; Voss, R.; Verleden, G.M. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: Light at the end of the Tunnel? Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2019, 24, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, G.M.; Glanville, A.R.; Lease, E.D.; Fisher, A.J.; Calabrese, F.; Corris, P.A.; Ensor, C.R.; Gottlieb, J.; Hachem, R.R.; Lama, V.; et al. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: Definition, diagnostic criteria, and approaches to treatment—A consensus report from the pulmonary council of the ISHLT. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Herck, A.; Verleden, S.E.; Sacreas, A.; Heigl, T.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Dupont, L.J.; Yserbyt, J.; Verbeken, E.K.; Neyrinck, A.P.; Van Raemdonck, D.; et al. Validation of a post-transplant chronic lung allograft dysfunction classification system. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derhovanessian, A.; Todd, J.L.; Zhang, A.; Alice, Z.; Mayalall, A.; Copeland, C.A.F.; Shino, M.; Pavlisko, E.N.; Wallace, W.D.; Gregson, A.; et al. Validation and Refinement of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction Phenotypes in Bilateral and Single Lung Recipients. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Horie, M.; Sato, M.; Nakajima, D.; Shoushtarizadeh, H.; Binnie, M.; Azad, S.; Hwang, D.M.; Machuca, T.N.; Waddell, T.K.; et al. Low-dose computed tomography volumetry for subtyping chronic lung allograft dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhling, H.; Dettmer, S.; Greer, M.; Fuehner, T.; Avsar, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Gottlieb, J. Phenotyping Chronic lung allograft dysfunction using body plethysmography and computed tomography. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; Vos, R.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction phenotypes and treatment. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 2650–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, R.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, S.E.; Ruttens, D.; Vaneylen, A.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Dupont, L.J.; Verleden, G.M. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of azithromycin involved in treatment and prevention of chronic lung allograft rejection. Transplantation 2012, 94, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.C.; Raghu, G.; Verleden, G.M.; Corris, P.A.; Aurora, P.; Wilson, K.C.; Brozek, J.; Glanville, A.R. An international ISHLT/ATS/ERS clinical practice guideline: Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1479–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R.; Verleden, S.E.; De Wever, W.; De Vleeschauwer, S.I.; Willems-Widyastuti, A.; Scheers, H.; Dupont, L.J.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M. Survival determinants in lung transplant patients with chronic lung allograft dysfunction. Transplantation 2011, 92, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Meyts, I.; Vos, R.; Geudens, N.; De Wever, W.; Verbeken, E.K.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Dupont, L.J.; Verleden, G.M. A dichotomy in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation revealed by azithromycin therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, P.A.; Vos, R.; Verleden, G.M.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Veschakelen, J.A. Thin-section computed toography findings before and after azithromycin treatment of neutrophilic reversible lung allograft dysfunction. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, R.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, S.E.; De Vleeschauwer, S.I.; Willems-Widyastuti, A.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Schoonis, A.; Nawrot, T.S.; Dupont, L.J.; Verleden, G.M. A randomised controlled trial of azithromycin to prevent chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 37, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruttens, D.; Verleden, S.E.; Vandermeulen, E.; Bellon, H.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Somers, J.; Schoonis, A.; Schaevers, V.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Neyrinck, A.; et al. Prophylactic azithromycin therapy after lung transplantation: Post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.L.; Palmer, S. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: The final frontier for lung transplantation. Chest 2011, 140, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, V.G.; Taylor, D.E.; Dhillon, G.S.; Knower, M.T.; McFadden, P.M.; Fuchs, D.M.; Kantrow, S.P. Success of lung transplantation without surveillance bronchoscopy. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2002, 21, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, P.; Dass, C.; Kumaran, M.; Simpson, S. High-resolution CT findings of obstructive phenotypes of chronic lung allograft dysfunction: More than just bronchiolitis oblierans syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, W13–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankier, A.A.; Van Muylem, A.; Knoop, C.; Estenne, M.; Gevenois, P.A. Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome in Heart-Lung Transplant Recipients: Diagnosis with Expiratory CT. Radiology 2001, 218, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M.J.; Bhalla, S.; Guttierrez, F.R.; Hildebolt, C.; Sweet, S. Post-lung transplantation bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: Usefulness of expiratory thin-section CT for diagnosis. Radiology 2001, 220, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, P.A.; Dodd, J.D.; Coxson, H.O.; Storness-Bliss, C.; Paré, P.D.; Mayo, J.R.; Levy, R.D. Bronchiolitis obliterans following lung transplantation: Early detection using computed tomographic scanning. Thorax 2006, 61, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konen, E.; Gutierrez, C.; Chaparro, C.; Murray, C.P.; Chung, T.; Crossin, J.; Hutcheon, M.A.; Paul, N.S.; Weisbrod, G.L. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome in lung trnsplant recipients: Can thin-section CT findings predict disease before its clinical appearance? Radiology 2004, 231, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; Ruttens, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; Bellon, H.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Dupont, L.J.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.; Vos, R. Restrictive chronic lung allograft dysfunction: Where are we now? J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R.; Vanaudenaerde, B.; Dupont, L.; Yserbyt, J.; Van Raemdonck, D.; Verleden, S. Current views on chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbeldam, A.; Barthels, C.; Coolen, J.; Verschakelen, J.A.; Verleden, S.E.; Vos, R.; Verleden, G.M.; De Wever, W. Restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation: New radiological insights. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 27, 2810–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Hwang, D.M.; Waddell, T.K.; Singer, L.G.; Keshavjee, S. Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2013, 32, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, E.; Sato, M.; Saito, T.; Wagnetz, U.; Roberts, H.C.; Chaparro, C.; Waddell, T.K.; Singer, L.G.; Hutcheon, M.A.; Keshavjee, S.; et al. Restrictive allograft syndrome post lung transplantation is characterized by pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Thüsen, J.H.; Vandermeulen, E.; Vos, R.; Weynand, B.; Verbeken, E.K.; Verleden, S.E. The histomorphological spectrum of restrictive chronic lung allograft dysfunction and implications for prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, M.A.; Osadolor, T.; Khiroya, R.; Salcedo, M.T.; Robertus, J.L.; Rice, A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Roman, A.; Monforte, V. Restrictive allograft syndrome and idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: Do they really have the same histology? Histopathology 2017, 70, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; Vasilescu, D.M.; McDonough, J.E.; Ruttens, D.; Vos, R.; Vandermeulen, E.; Bellon, H.; Geenens, R.; Verbeken, E.K.; Verschakelen, J.; et al. Linking clinical phenotypes of chronic lung allograft dysfunction to changes in lung structure. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskeva, M.; McLean, C.; Ellis, S.; Bailey, M.; Williams, T.; Levvey, B.; Snell, G.I.; Westall, G.P. Acute Fibrinoid Organizing Pneumonia after Lung Transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, D.; Nador, R.G.; English, J.C.; Yee, J.; Levy, R.; Bergeron, C.; Swiston, J.R.; Mets, O.M.; Muller, N.L.; Bilawich, A.-M. Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Review of CT and Pathologic Findings. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; de Jong, P.A.; Ruttens, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Verschakelen, J.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R. Functional and computed tomographic evolution and survival of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, A.R.; Verleden, G.M.; Todd, J.L.; Benden, C.; Calabrese, F.; Gottlieb, J.; Hachem, R.R.; Levine, D.; Meloni, F.; Palmer, S.M.; et al. Chronic lung allograft lung dysfunction: Definition and update of restrictive allograft syndrome. A consensus report from the Pulmonary Council of the ISHLT. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konen, E.; Weisbrod, G.L.; Pakhale, S.; Chung, T.; Paul, N.S.; Hutcheon, M.A. Fibrosis of the Upper Lobes: A Newly Identified Late-Onset Complication After Lung Transplantation? Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, S.E.; Ruttens, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; Bellon, H.; Dubbeldam, A.; De Wever, W.; Dupont, L.J.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M.; et al. Predictors of survival in restrictive chronic lung allograft dysfunction after lung transplanttion. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, S.E.; Gheysens, O.; Goffin, K.E.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verbeken, E.K.; Weynand, B.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, S.E.; Von Der Thüsen, J.; Van Herck, A.; Weynand, B.; Verbeken, E.; Verschakelen, J.; Dubbeldam, A.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Vos, R.; Verleden, G.M.; et al. Identification and characterization of chronic lung allograft dysfunction patients with mixed phenotype: A single-center study. Clin. Transplant. 2020, 34, e13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, S.; Shin, H.-O.; Vogel-Claussen, J.; Westphal, M.; Haverich, A.; Warnecke, G.; Welte, T.; Wacker, F.; Gottlieb, J.; Suhling, H. CT at onset of chronic lung allograft dysfunction in lung transplant patients predicts development of the restrictive phenotype and survival. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 94, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazourian, L.; Ash, S.; Meserve, E.E.; Diaz, A.; Estepar, R.S.J.; El-Chemaly, S.Y.; Rosas, I.O.; Divo, M.; Fuhlbrigge, A.L.; Camp, P.C.; et al. Quantitative computed tomography assessment of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortani Barbosa, E.J.; Shou, H.; Simpson, S.; Gee, J.; Tustison, N.; Lee, J.C. Quantitative computed tomography metrics from the transplanted lung can predict forced expiratory volume in the first second after lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Imaging 2018, 33, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortani Barbosa, E.J.; Simpson, S.; Lee, J.C.; Tustison, N.; Gee, J.; Shou, H. Multivariate modeling using quantitative CT metrics may improve accuracy of diagnosis of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortani Barbosa, E.J.; Lanclus, M.; Vos, W.; Van Holsbeke, C.; De Baker, W.; De Baker, J.; Lee, J. Machine learning algorithms utilizing quantitative CT features may predict eventual onset of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation. Acad. Radiol. 2018, 25, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, M.; Saito, T.; Moseley, J.; D’Errico, L.; Salazar, P.; Nakajima, D.; Brock, K.; Yasufuku, K.; Binnie, M.; Keshavjee, S.; et al. The role of biomechanical anatomical modeling via computed tomography for identification of restrictive allograft syndrome. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, M.; Salazar, P.; Saito, T.; Binnie, M.; Brock, K.; Yasufuku, K.; Azad, S.; Keshavjee, S.; Martinu, T.; Paul, N. Quantitative chest CT for subtyping chronic lung allograft dysfunction and its association with survival. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Levy, L.; Houbois, C.; Salazar, P.; Saito, T.; Pakkal, M.; O’Brien, C.; Sajja, S.; Brock, K.; Yasufuku, K.; et al. Lung density analysis using quantitative chest CT for early prediction of chronic lung allo-graft dysfunction. Transplantation 2019, 103, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
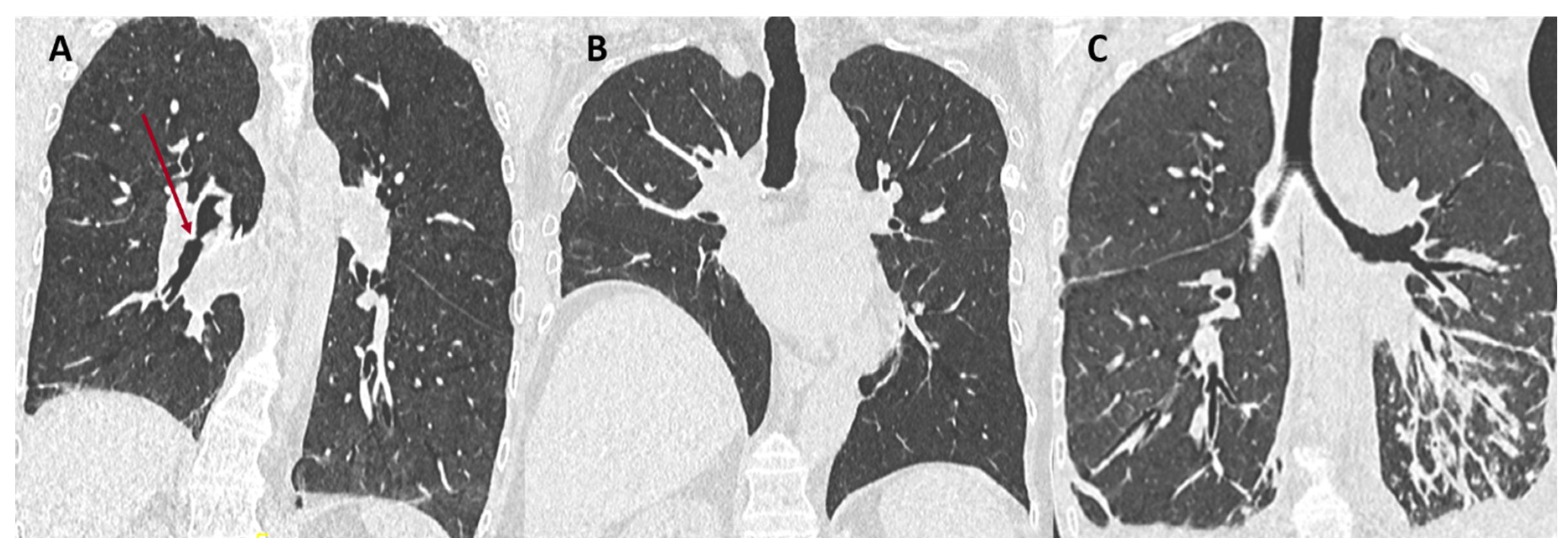
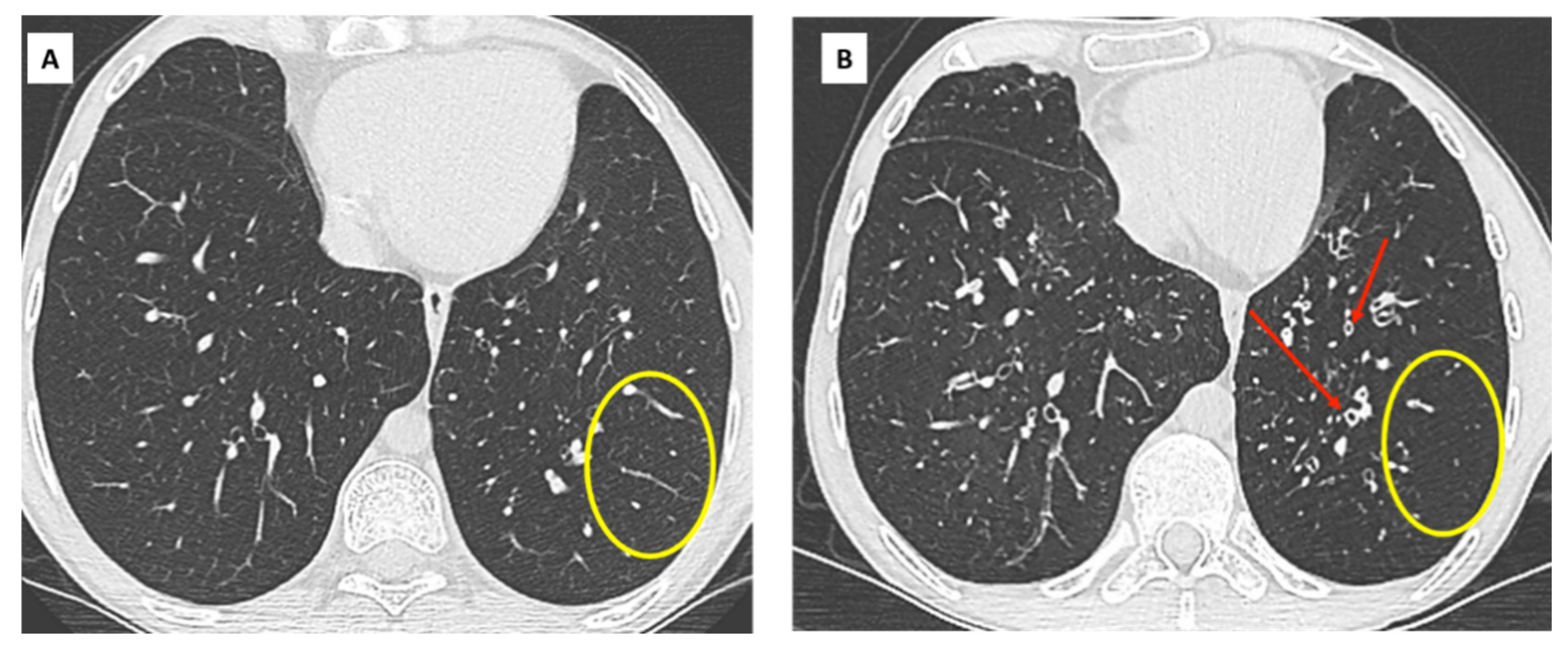
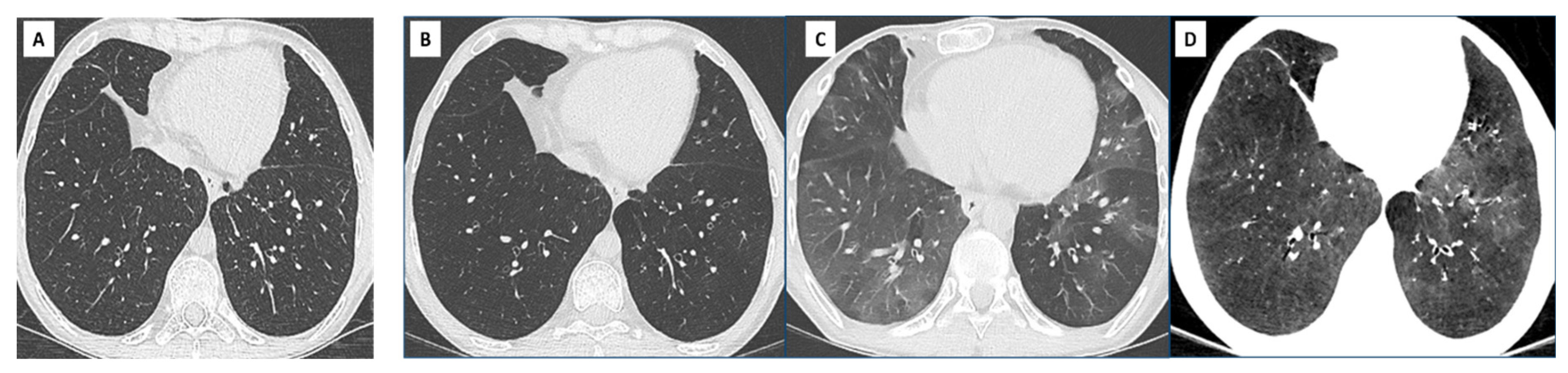
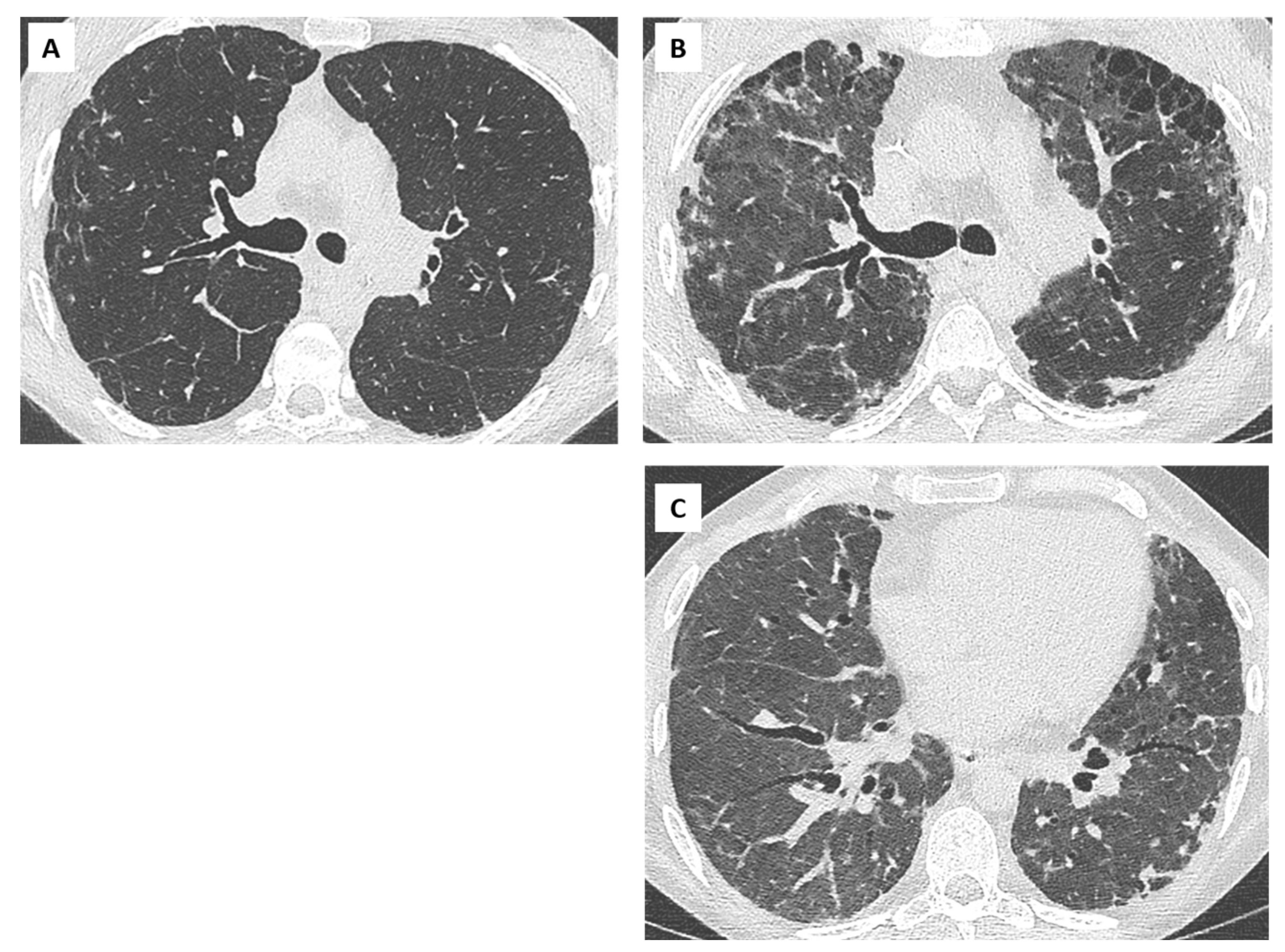
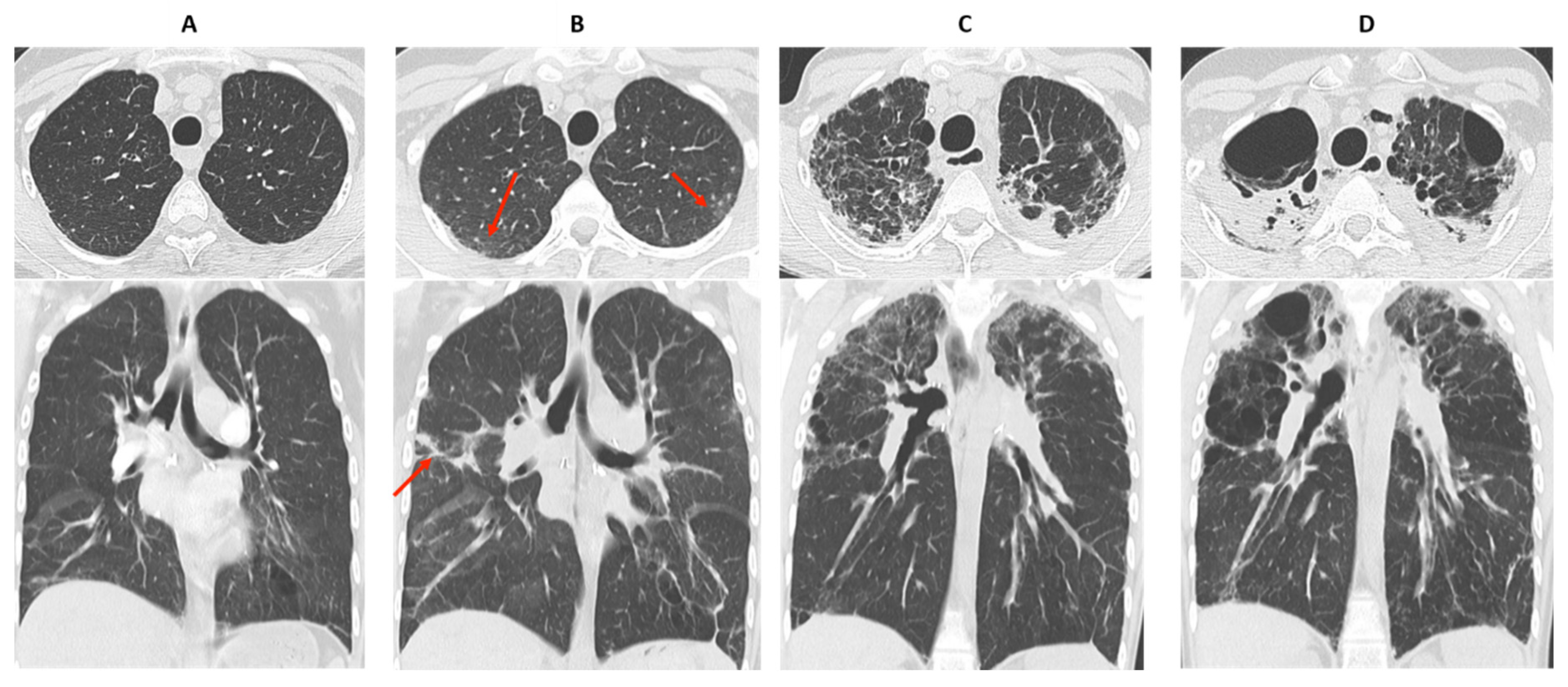
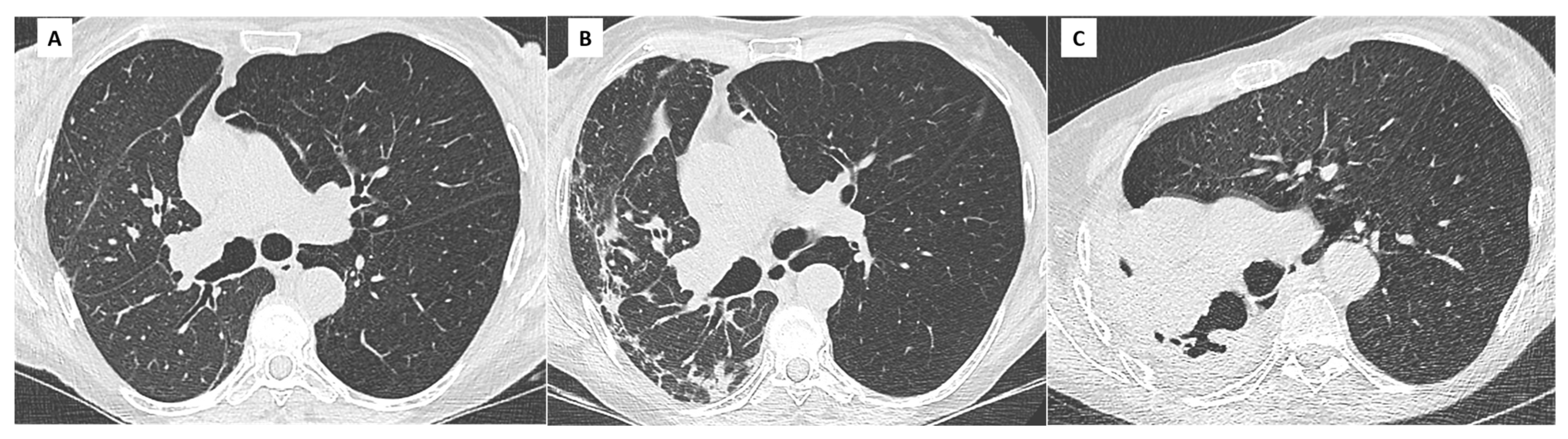
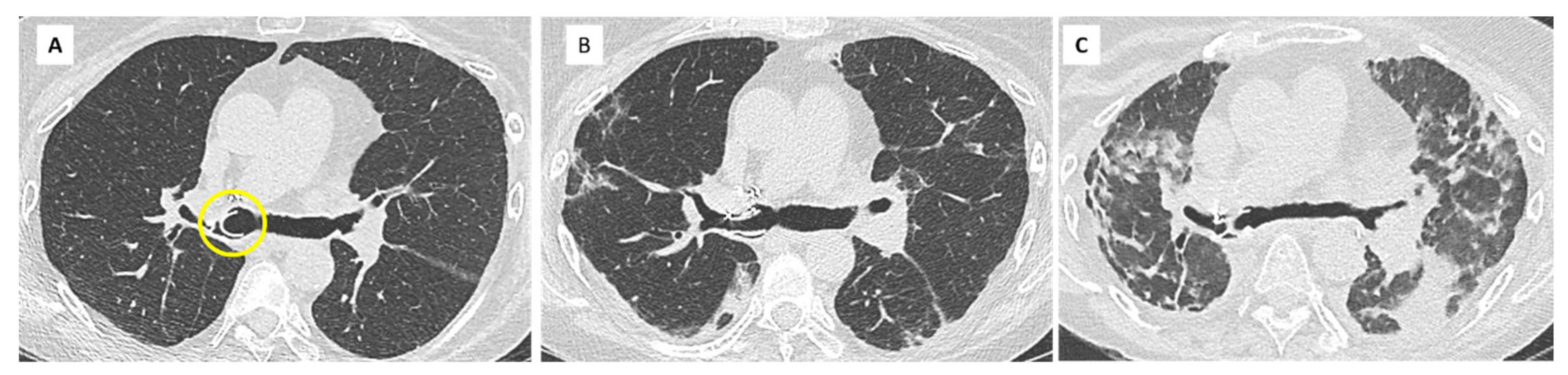
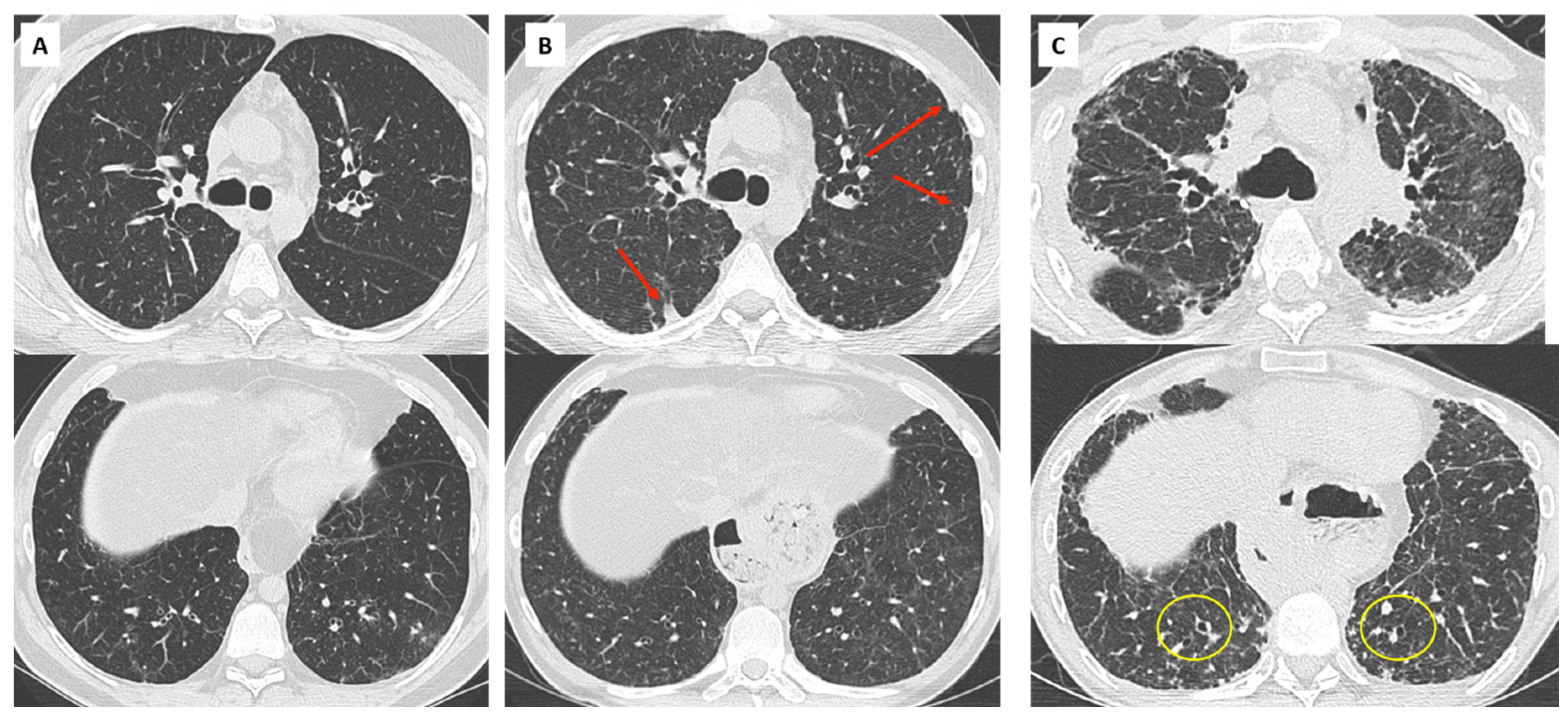
| (A) Processes and diseases responsible for chronic lung function decline. Stability for at least 6 months allows recalculation of a new baseline FEV1: |
|
| (B) Processes and diseases responsible for a potentially reversible functional decline: |
|
| Stage | Spirometry |
|---|---|
| CLAD 0 | FEV1 > 80% FEV1 baseline |
| CLAD 1 | FEV1 > 65–80% FEV1 baseline |
| CLAD 2 | FEV1 > 50–65% FEV1 baseline |
| CLAD 3 | FEV1 > 35–50% FEV1 baseline |
| CLAD 4 | FEV1 ≤ 35% FEV1 baseline |
| KERRYPNX | Obstruction (FEV1/FVC < 0.7) | Restriction (TLC Decline ≥ 10% from Baseline) | Opacities on Chest X ray/CT |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOS | Yes | No | No |
| RAS | No | Yes | Yes |
| Mixed | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Undefined | Yes | No | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brun, A.-L.; Chabi, M.-L.; Picard, C.; Mellot, F.; Grenier, P.A. Lung Transplantation: CT Assessment of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050817
Brun A-L, Chabi M-L, Picard C, Mellot F, Grenier PA. Lung Transplantation: CT Assessment of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD). Diagnostics. 2021; 11(5):817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050817
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrun, Anne-Laure, Marie-Laure Chabi, Clément Picard, François Mellot, and Philippe A. Grenier. 2021. "Lung Transplantation: CT Assessment of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD)" Diagnostics 11, no. 5: 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050817
APA StyleBrun, A.-L., Chabi, M.-L., Picard, C., Mellot, F., & Grenier, P. A. (2021). Lung Transplantation: CT Assessment of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD). Diagnostics, 11(5), 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050817







