Clinical Implications of (Pro)renin Receptor (PRR) Expression in Renal Tumours
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
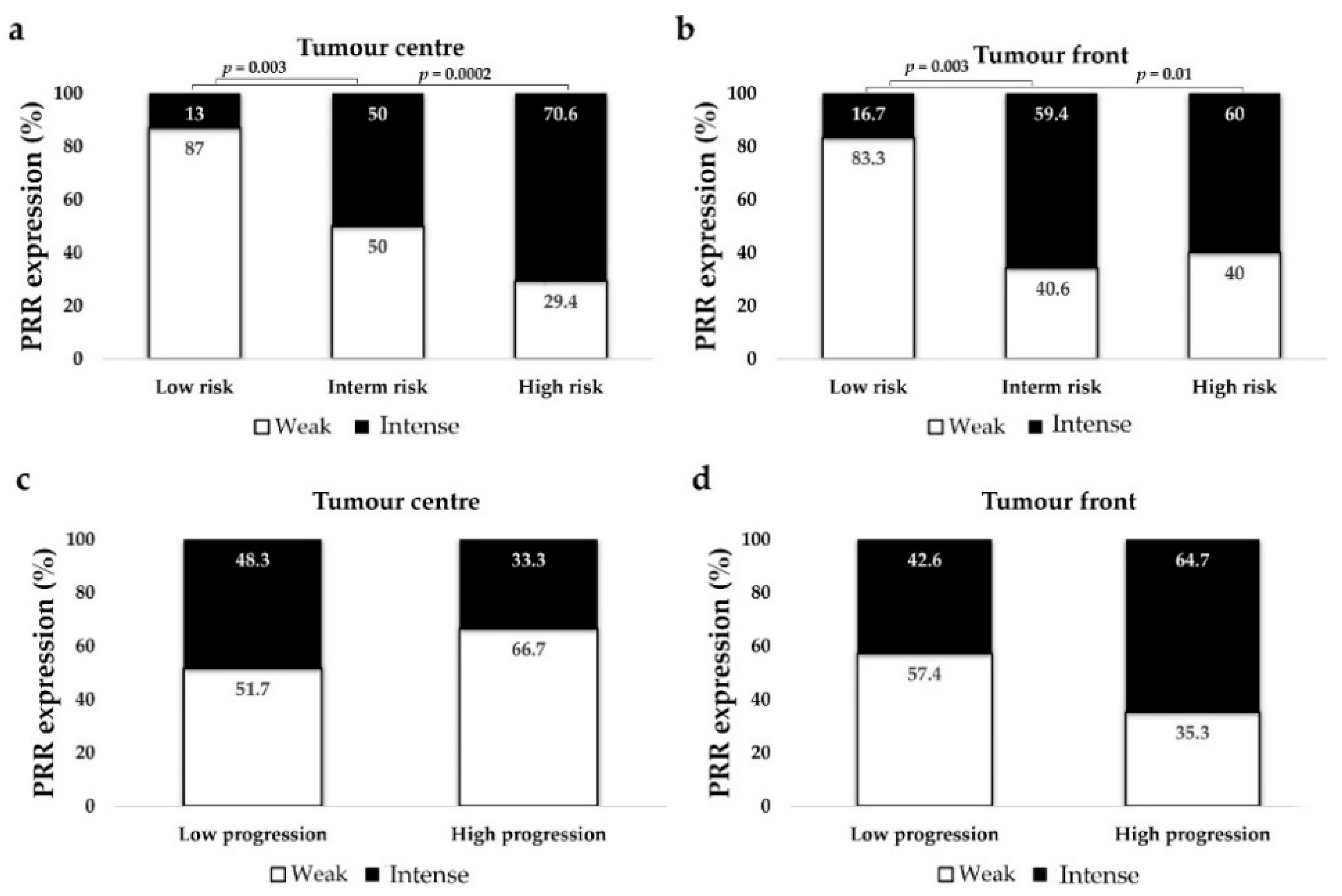
3. Results
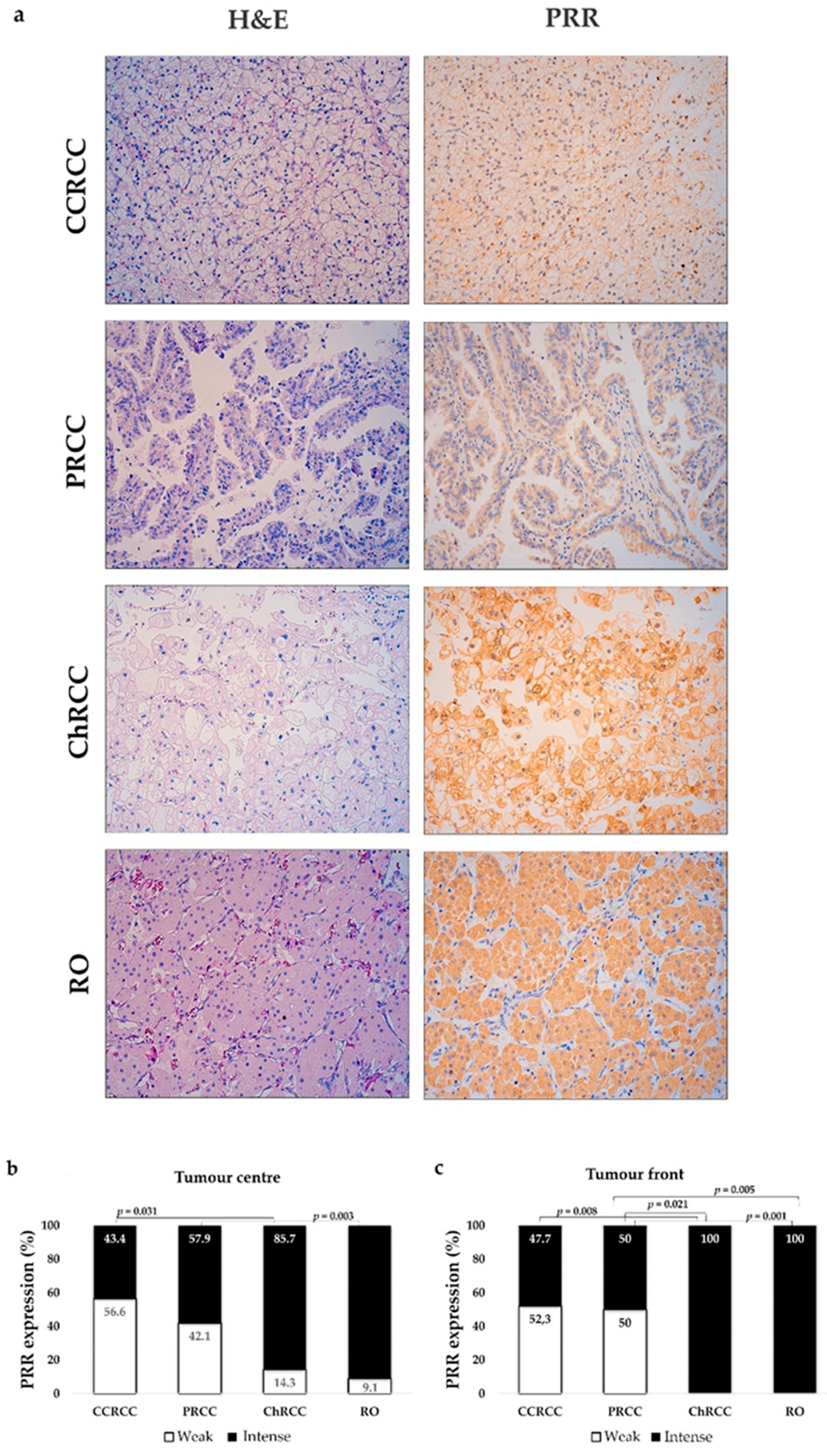
3.1. Kidney Tumours Express PRR
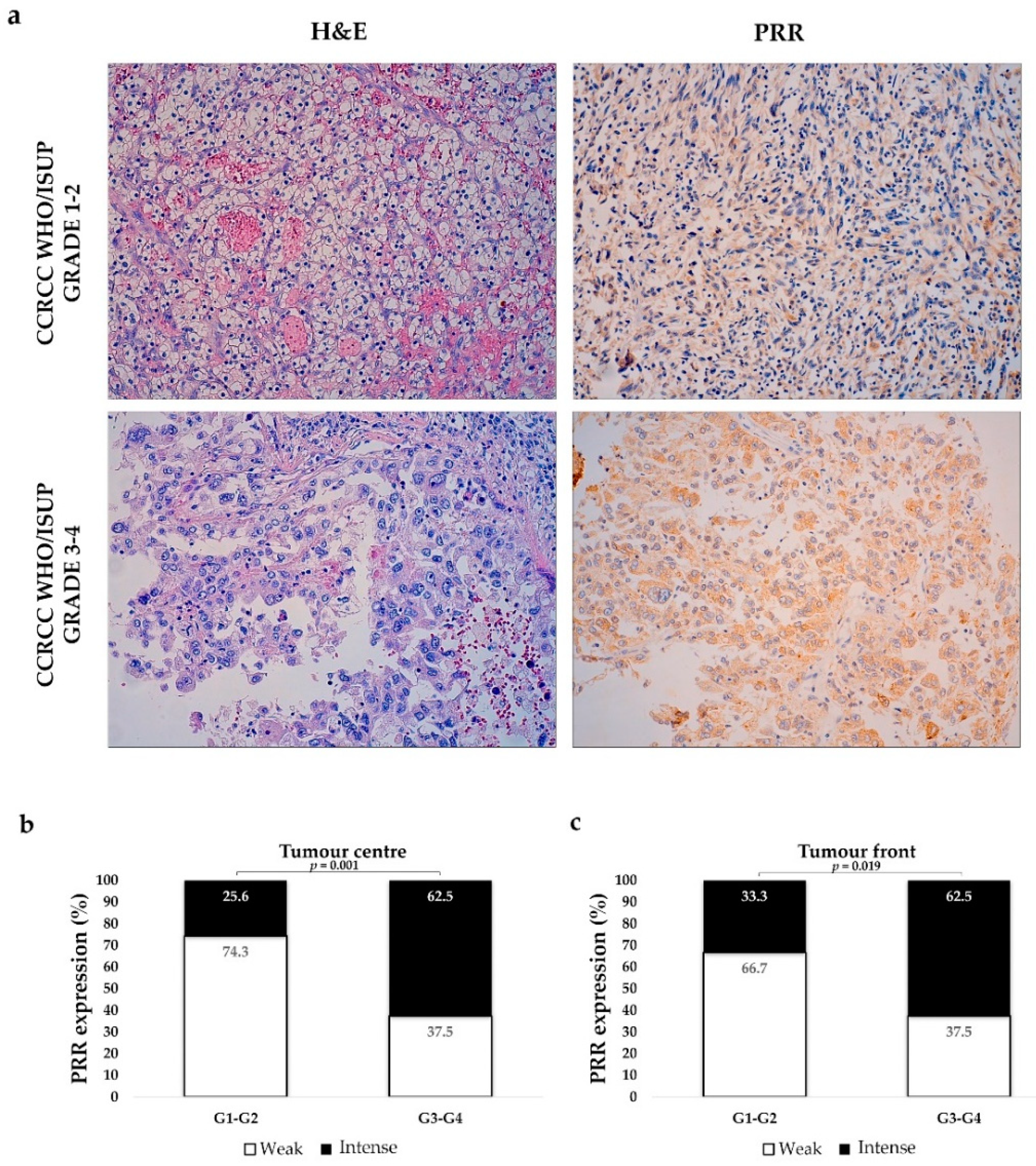
3.2. PRR Expression in CCRCC Changes Depending on Tumour Aggressiveness
3.2.1. PRR Expression is Higher in High Grade CCRCCs
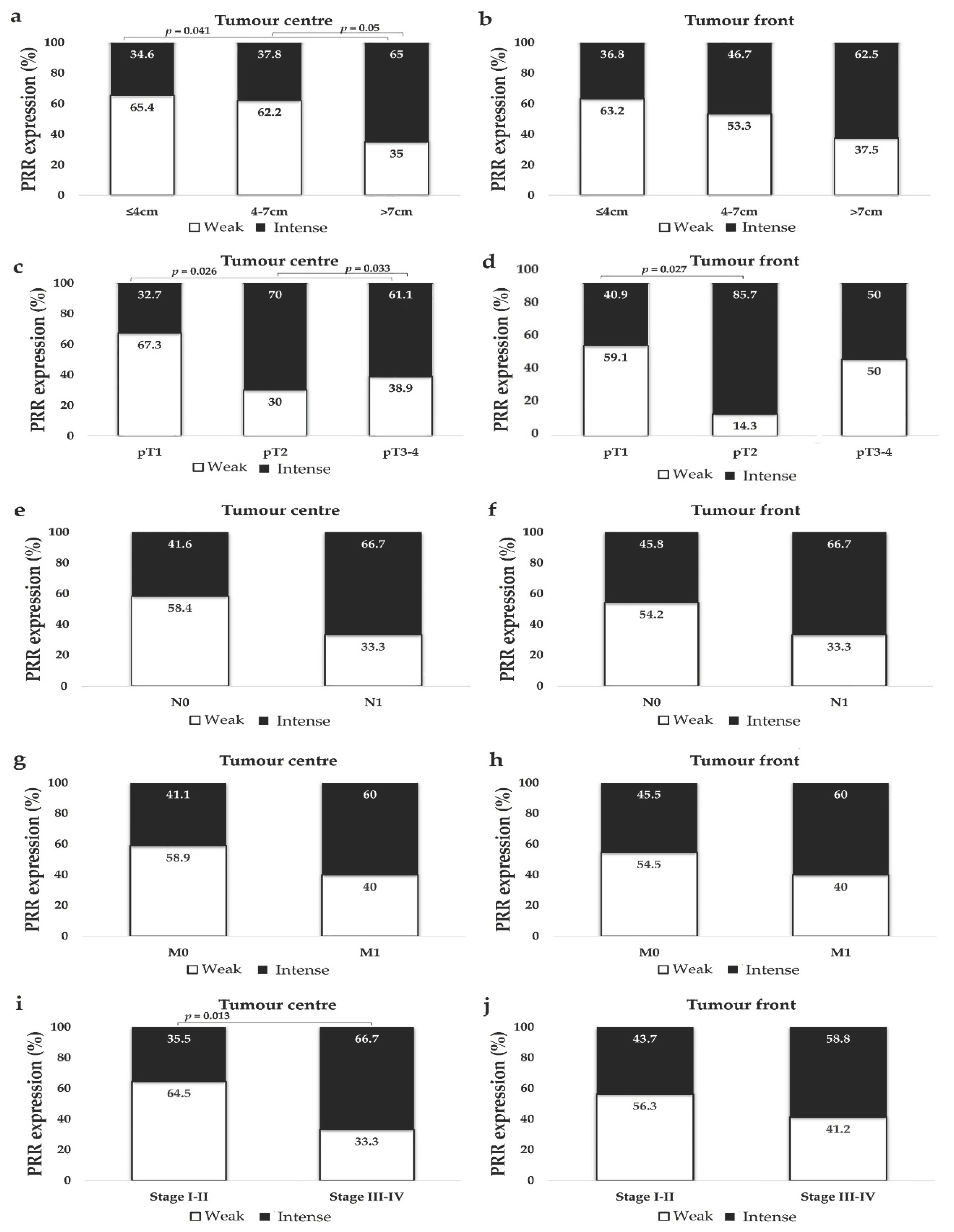
3.2.2. PRR Staining is Stronger in Large Tumours
3.2.3. PRR Expression is Higher in CCRCCs with Higher Local Invasion (pT)
3.2.4. PRR Expression Does Not Vary Significantly in Metastasized and Not Metastasized CCRCCs
3.2.5. PRR Expression is Significantly Higher in High Stage Tumours
3.2.6. PRR Expression is Higher in CCRCC Patients with Intermediate and High Mortality Risk (UISS)
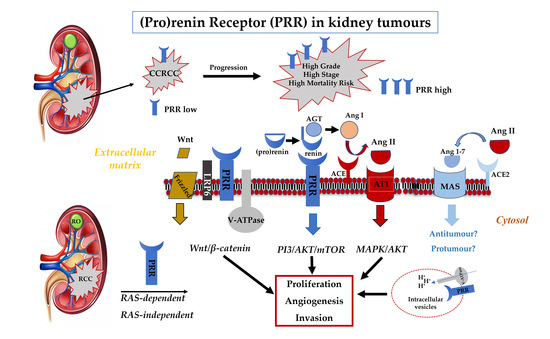
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Thandra, K.C.; Saginala, K.; Mohammed, A.; Vakiti, A.; Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esther, J.; Hale, P.; Hahn, A.W.; Agarwal, N.; Maughan, B.L. Treatment Decisions for Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma in Older Patients: The Role of TKIs and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Drugs Aging 2019, 36, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, G.T.; Cheng, L. Neoplasms of the kidney. In Urologic Surgical Pathology, 3rd ed.; Bostwick, D.G., Cheng, L., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 76–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, K.L.; Morais, C.; Bernard, A.; Saunders, N.; Samaratunga, H.; Gobe, G.; Wood, S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of immunohistochemical biomarkers that differentiate chromophobe renal cell carcinoma from renal oncocytoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turajlic, S.; Xu, H.; Litchfield, K.; Rowan, A.; Horswell, S.; Chambers, T.; O’Brien, T.; Lopez, J.I.; Watkins, T.B.; Nicol, D.; et al. Deterministic Evolutionary Trajectories Influence Primary Tumor Growth: TRACERx Renal. Cell 2018, 173, 595–610.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeniuk-Wojtaś, A.; Stec, R.; Szczylik, C.A. Are primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases of renal cell carcinoma the same cancer? Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2016, 34, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczuk, P.; Szczylik, C.A.; Porta, C.; Czarnecka, A.M. Renin angiotensin system deregulation as renal cancer risk factor. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5059–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyhrquist, F.Y.; Saijonmaa, O. Renin-angiotensin system revisited. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Soto-Reyes, E.; Vidal-Millán, S.; Sánchez-Corona, J. The renin-angiotensin system meets the hallmarks of cancer. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2015, 16, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, A.; Yatabe, M.S. The (pro)renin receptor in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolley-Hitze, T.; Jouan, F.; Martin, B.; Mottier, S.; Edeline, J.; Moranne, O.; Le Pogamp, P.; Belaud-Rotureau, M.-A.; Patard, J.-J.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; et al. Angiotensin-2 receptors (AT1-R and AT2-R), new prognostic factors for renal clear-cell carcinoma? Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrinaga, G.; Pérez, I.; Sanz, B.; Blanco, L.; Lopez, J.I.; Candenas, M.L.; Pinto, F.M.; Gil, J.; Irazusta, J.; Varona, A. Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE and ACE2) are downregulated in renal tumors. Regul. Pept. 2010, 165, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errarte, P.; Beitia, M.; Perez, I.; Manterola, L.; Lawrie, C.H.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; Unda, M.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. Expression and activity of angiotensin-regulating enzymes is associated with prognostic outcome in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizman, D.; Huang, P.; Eisenberger, M.A.; Pili, R.; Kim, J.J.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Hammers, H.; Carducci, M.A. Angiotensin system inhibitors and outcome of sunitinib treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective examination. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; DeRosa, L.; Le Teuff, G.; Albiges, L.; Escudier, B. Hypertension and angiotensin system inhibitors: impact on outcome in sunitinib-treated patients for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, R.R.; Rodriguez, G.E.; Lin, X.; Kaymakcalan, M.D.; Hamnvik, O.-P.R.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Bhatt, R.S.; Simantov, R.; Choueiri, T.K. Angiotensin System Inhibitors and Survival Outcomes in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.; Delarue, F.; Burcklé, C.; Bouzhir, L.; Giller, T.; Sraer, J.-D. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 109, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke-Kaiser, H.; Zollmann, F.S.; Schefe, J.H.; Unger, T. Signal transduction of the (pro)renin receptor as a novel therapeutic target for preventing end-organ damage. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 33, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nishiyama, A.; Matsuyama, M.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y. The (pro)renin receptor: a novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target for various cancers. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, Y.; Fujimori, T.; Nguyen, G.; Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Ichihara, A.; Kitada, K.; Nakano, D.; Kobori, H.; Kohno, M.; et al. (Pro)renin receptor is crucial for Wnt/β-catenin-dependent genesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arundhathi, A.; Chuang, W.-H.; Chen, J.-K.; Wang, S.-E.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liao, W.-N.; Chen, H.-W.; Teng, Y.-M.; Pai, C.-C.; et al. Prorenin receptor acts as a potential molecular target for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55437–55448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Celerier, J.; Chapuis, B.C.; Nguyen, G.; Wostl, W.; Maerki, H.P.; Janzer, R.-C.; Corvol, P.; Gasc, J.-M. Renin and angiotensinogen expression and functions in growth and apoptosis of human glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchi, M.; Shibayama, Y.; Ogawa, D.; Miyake, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Tamiya, T. (Pro)renin receptor is crucial for glioma development via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shibayama, Y.; Zhang, A.; Ohsaki, H.; Asano, E.; Suzuki, Y.; Kushida, Y.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T.; Wang, Z.; et al. (Pro)renin receptor promotes colorectal cancer through the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway despite constitutive pathway component mutations. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitia, M.; Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Errarte, P.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; Loizate, A.; Etxezarraga, M.C.; Sanz, B.; Larrinaga, G. (Pro)renin Receptor Expression Increases throughout the Colorectal Adenoma-Adenocarcinoma Sequence and It Is Associated with Worse Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nishiyama, H.; Kaneko, K.; Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Sasano, H.; Takahashi, K. Expression of (pro)renin receptor in breast cancers and its effect on cancer cell proliferation. Biomed. Res. 2014, 35, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforce, S.J.; Lumbers, E.R.; De Meaultsart, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Proietto, A.; Otton, G.; Scurry, J.; Verrills, N.M.; Scott, R.J.; Pringle, K.G. Expression of renin–angiotensin system (RAS) components in endometrial cancer. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, S.B.; Byrd, D.R.; Compton, C.C.; Fritz, A.G.; Greene, F.L.; Trotti, A. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Delahunt, B.; Eble, J.N.; Egevad, L.; Samaratunga, H. Grading of renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2018, 74, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Frank, I.; Leibovich, B.C.; Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Zincke, H.; Blute, M.L. Impact of tumour size on the predictive ability of the pT3a primary tumour classification for renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2006, 177, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, I.; Blute, M.L.; Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Weaver, A.L.; Zincke, H. An outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: the SSIGN score. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisman, A.; Pantuck, A.J.; Dorey, F.; Said, J.W.; Shvarts, O.; Quintana, D.; Gitlitz, B.J.; Dekernion, J.B.; Figlin, R.A.; Belldegrun, A.S. Improved Prognostication of Renal Cell Carcinoma Using an Integrated Staging System. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Drake, C.G. Kidney Cancer. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2020, 47, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K. Targeting the renin-angiotensin system to improve cancer treatment: Implications for immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Song, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Yang, L.; Meng, R.; Tao, T.; Wang, S.; et al. Ang-(1-7) promotes the migration and invasion of human renal cell carcinoma cells via Mas-mediated AKT signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Wang, X. The SARS-CoV-2 host cell receptor ACE2 correlates positively with immunotherapy response and is a potential protective factor for cancer progression. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, L.-C.; Song, X.; Lu, J.-R.; Jin, Z. KRT6 interacting with notch1 contributes to progression of renal cell carcinoma, and aliskiren inhibits renal carcinoma cell lines proliferation in vitro. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 9182–9188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sitaram, R.T.; Landström, M.; Roos, G.; Ljungberg, B. Significance of PI3K signalling pathway in clear cell renal cell carcinoma in relation to VHL and HIF status. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Krause, M.; Samoylenko, A.; Vainio, S. Wnt Signaling in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2016, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.C.; Williams, D.E.; Liu, L.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Mullins, J.J.; Mitchell, K.D. Enhancement of renin and prorenin receptor in collecting duct of Cyp1a1-Ren2 rats may contribute to development and progression of malignant hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2011, 300, F581–F588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, G.A.; Lara, L.S.; Luffman, C.; Seth, D.M.; Prieto, M.C. The soluble form of the (pro)renin [s(P)RR] is augmented in the collecting duct and urine of chronic angiotensin II-dependent hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2011, 57, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, A.; Aizaki, Y.; Kusano, K.-I.; Kishi, F.; Susumu, T.; Iida, S.; Ishiura, S.; Nishimura, S.; Shichiri, M.; Senbonmatsu, T. The (pro)renin receptor is cleaved by ADAM19 in the Golgi leading to its secretion into extracellular space. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohba, K.; Endo, M.; Sato, S.; Kashio-Yokota, Y.; Hirose, T.; Takahashi, K. (Pro)renin receptor/ATP6AP2 is required for autophagy and regulates proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Genes Cells 2020, 25, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kaneko, K.; Ohba, K.; Morimoto, R.; Hirose, T.; Satoh, F.; Totsune, K.; Takahashi, K. Increased expression of (pro)renin receptor in aldosterone-producing adenomas. Peptides 2013, 49, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recarti, C.; Seccia, T.M.; Caroccia, B.; Gonzales-Campos, A.; Ceolotto, G.; Lenzini, L.; Petrelli, L.; Belloni, A.S.; Rainey, W.E.; Nussberger, J.; et al. Expression and functional role of the prorenin receptor in the human adrenocortical zona glomerulosa and in primary aldosteronism. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | CCRCC Patients (n = 83) |
|---|---|
| Diameter | |
| ≤4 cm | 26 |
| >4 to 7cm | 37 |
| >7 cm | 20 |
| WHO/ISUP grade | |
| Low G1-G2 | 43 |
| High G3-G4 | 40 |
| Local invasion (pT) | |
| Organ-confined pT1-pT2 | 65 |
| Not confined pT3-pT4 | 18 |
| Lymph node invasion (N) | |
| No | 77 |
| Yes | 6 |
| Distant metastasis (M) | |
| No | 73 |
| Yes | 10 |
| TNM Stage | |
| Not-advanced (I-II) | 62 |
| Advanced (III-IV) | 21 |
| SSIGN (tumour progression) | |
| Low progression | 62 |
| High progression | 21 |
| UISS (mortality risk) | |
| Low | 23 |
| Intermediate | 42 |
| High | 17 |
| Patients’ Survival | |
| Alive | 62 |
| Dead of disease | 15 |
| Dead by other causes | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solano-Iturri, J.D.; Echevarría, E.; Unda, M.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Pérez-Fernández, A.; Angulo, J.C.; López, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. Clinical Implications of (Pro)renin Receptor (PRR) Expression in Renal Tumours. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020272
Solano-Iturri JD, Echevarría E, Unda M, Loizaga-Iriarte A, Pérez-Fernández A, Angulo JC, López JI, Larrinaga G. Clinical Implications of (Pro)renin Receptor (PRR) Expression in Renal Tumours. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020272
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolano-Iturri, Jon Danel, Enrique Echevarría, Miguel Unda, Ana Loizaga-Iriarte, Amparo Pérez-Fernández, Javier C. Angulo, José I. López, and Gorka Larrinaga. 2021. "Clinical Implications of (Pro)renin Receptor (PRR) Expression in Renal Tumours" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020272
APA StyleSolano-Iturri, J. D., Echevarría, E., Unda, M., Loizaga-Iriarte, A., Pérez-Fernández, A., Angulo, J. C., López, J. I., & Larrinaga, G. (2021). Clinical Implications of (Pro)renin Receptor (PRR) Expression in Renal Tumours. Diagnostics, 11(2), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020272