Optical Biosensors for Diagnostics of Infectious Viral Disease: A Recent Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Viral Infectious Diseases
2.1. COVID-19
2.2. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
2.3. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
2.4. Hepatitis
2.5. Dengue
2.6. Biomarkers
3. Literature Overview (State of the Art)
4. Safety and Security
5. Objective of the Present Review
6. Optical Diagnostics
6.1. Colorimetric Sensors

6.2. Fluorescence/Chemiluminescence-Based Approaches
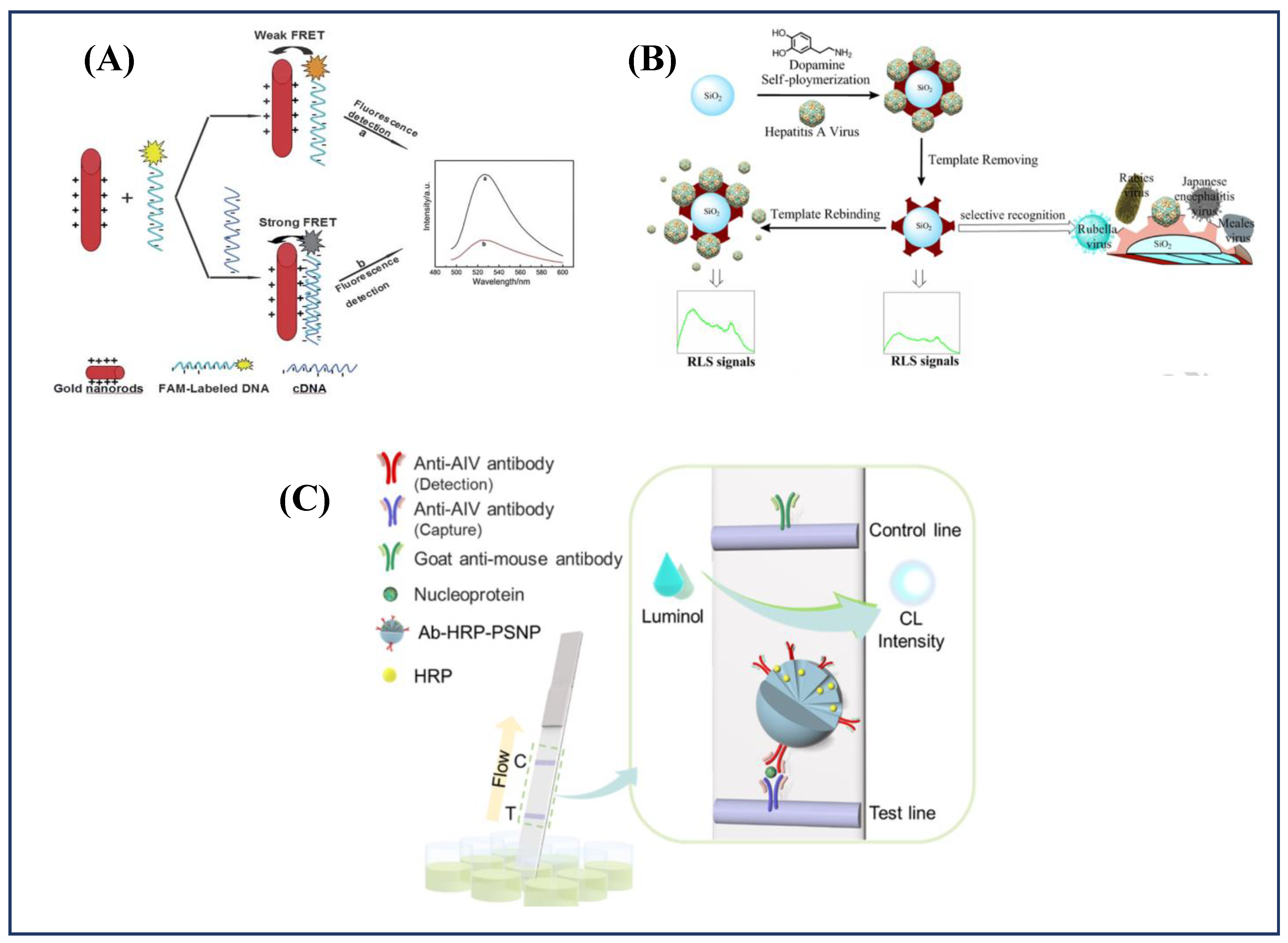
6.3. Surface Plasmon Based Approaches

6.4. Photonic Sensors
| S. No. | Antigen/Analyte | Bio-Element | Real Sample | Detection Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rotavirus | Secondary fluorescent Ab | - | 6.35 µg mL−1 to 1.27 mg mL−1 | 2.54 µg mL−1 | [24] |
| 2. | Epstein–Barr virus (EBNA-1) protein | EBNA-1 Antibody | PBS | 0.0–10.0 µg mL−1 | 1.0 × 10−3 µg mL−1 | [22] |
| 3. | HIV-1 | Antibody | PBS Plasma | 104–108 copies mL−1 102–107 copies mL−1 | - | [65] |
| 4. | DENV E Protein | Antibody | BSA/PBS | 1.0 pM–1.0 nM | 1.0 pM | [207] |
| 5. | Influenza Virus | Antibody | Human Saliva | 1 pg mL−1–100 ng mL−1 | 1.0 ng mL−1 | [23] |
| 6. | SARS-CoV-2 | Antibody | Human Serum | - | 26.7 ng mL−1 | [208] |
| 7. | Human Papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPs) | Antibody | Buffer and Serum (10%) | 0.70–5.80 nM | 1.5 nM | [209] |
| 8. | Rotavirus | Rotavirus Antibody | Water | 102–105 PFU/mL | <103 PFU/mL | [210] |
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carter, M.J. Enterically infecting viruses: Pathogenicity, transmission and significance for food and waterborne infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 1354–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maal-Bared, R.; Brisolara, K.; Munakata, N.; Bibby, K.; Gerba, C.; Sobsey, M.; Schaefer, S.; Swift, J.; Gary, L.; Sherchan, S.; et al. Implications of SARS-CoV-2 on current and future operation and management of wastewater systems. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goud, K.Y.; Reddy, K.K.; Khorshed, A.; Kumar, V.S.; Mishra, R.K.; Oraby, M.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Kim, H.; Gobi, K.V. Electrochemical diagnostics of infectious viral diseases: Trends and challenges. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.; Wilkins, E. Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of Biological Warfare Agents. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemer, G.S.; Stedman, K.M. A novel virus genome discovered in an extreme environment suggests recombination between unrelated groups of RNA and DNA viruses. Biol. Direct. 2012, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, D.T.N.; Wang, H.; Sugiarto, S.; Li, T.; Ang, W.H.; Lee, C.; Pastorin, G. Advances in nanomaterials and their applications in point of care (POC) devices for the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Tiwari, S.; Jayant, R.; Vashist, A.; Nikkhah-Moshaie, R.; El-Hage, N.; Nair, M. Electrochemical Biosensors for Early Stage Zika Diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 35, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D. Saliva and viral infections. Periodontology 2000 2016, 70, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. 25 May 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---25-may-2021 (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical Biosensing for the Diagnosis of Viral Infections and Tropical Diseases. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 753–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliy, O.I.; Zaitsev, B.D.; Larionova, O.S.; Borodina, I.A. Virus Detection Methods and Biosensor Technologies. Biophysics 2019, 64, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, K.; Bardani, E.; Kallemi, P.; Kalantidis, K. Viral Detection: Past, Present, and Future. BioEssays 2019, 41, 1900049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, A.M.; Mazon, T. Early diagnosis of Zika infection using a ZnO nanostructures-based rapid electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2019, 203, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, H.A.M.; Zucolotto, V. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for zika virus identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzgar, D.; Sampath, R.; Rounds, M.A.; Ecker, D.J. The value and validation of broad spectrum biosensors for diagnosis and biodefense. Virulence 2013, 4, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Tiwari, S.; Deb, M.K.; Marty, J.L. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): A global pandemic and treatment strategies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Uh, M.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-K. Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor using nanopatterned gold particles on the surface of an optical fiber. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.J.; Hyun, M.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Ko, S. A self-assembled fusion protein-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Talanta 2009, 79, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, J.C.; Su, L.; Chen, Y.A.; Chen, C.; Chou, C. Localized surface plasmon coupled fluorescence fiber-optic biosensor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nucleocapsid protein detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 14th OptoElectronics and Communications Conference, Hong Kong, China, 13–17 July 2009; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.P. Interferometric Biosensors. In Principles of Bacterial Detection: Biosensors, Recognition Receptors and Microsystems; Zourob, M., Elwary, S., Turner, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 169–211. [Google Scholar]
- Guider, R.; Gandolfi, D.; Chalyan, T.; Pasquardini, L.; Samusenko, A.; Pederzolli, C.; Pucker, G.; Pavesi, L. Sensitivity and Limit of Detection of biosensors based on ring resonators. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 6, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Liao, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Huang, J.-J. Surface plasmons coupled two-dimensional photonic crystal biosensors for Epstein-Barr virus protein detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Ozawa, S.; Okuda, N.; Yanagida, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Hatsuzawa, T. Reflectometric detection of influenza virus in human saliva using nanoimprint lithography-based flexible two-dimensional photonic crystal biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, B.; Park, Y.; Park, J. Direct label-free detection of Rotavirus using a hydrogel based nanoporous photonic crystal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 7384–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Chang, Y.F.; Chen, K.H.; Su, L.C.; Lee, C.W.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Chou, C. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus nucleocapsid protein in human serum using a localized surface plasmon coupled fluorescence fiber-optic biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A. Brief Review on Integrated Planar Waveguide-Based Optical Sensor. In Planar Waveguide Optical Sensors: From Theory to Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 9–69. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.S.; Grace, W.K.; Grace, K.M.; Hartman, N.; Swanson, B.I. Pathogen detection using single mode planar optical waveguides. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospíšilová, M.; Kuncová, G.; Trögl, J. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Fiber-Optic Bio-Sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 25208–25259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keighron, J.; Ewing, A.; Cans, A.-S. Analytical tools to monitor exocytosis: A focus on new fluorescent probes and methods. Analyst 2012, 137, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Hayat, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Catanante, G.; Bhand, S.; Marty, J.L. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2) Quenching Based Aptasensing Platform: Application to Ochratoxin A Detection. Toxins 2015, 7, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltomaa, R.; Glahn-Martínez, B.; Benito-Peña, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Optical Biosensors for Label-Free Detection of Small Molecules. Sensors 2018, 18, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Khan, R.; Catanante, G.; Sherazi, T.A.; Bhand, S.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Designed Strategies for Fluorescence-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, L.G.; Huertas, C.S.; Lechuga, L.M. Prospects of optical biosensors for emerging label-free RNA analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborský, P.; Švitel, J.; Katrlík, J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddali, H.; Miles, C.E.; Kohn, J.; O’Carroll, D.M. Optical Biosensors for Virus Detection: Prospects for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19. Chembiochem A Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2020, 22, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Hayat, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Catanante, G.; Shahid, S.A.; Bhand, S.; Marty, J.L. Design of a fluorescence aptaswitch based on the aptamer modulated nano-surface impact on the fluorescence particles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65579–65587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh, P.; Hejazi, M.; Gharaatifar, N.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Baradaran, B.; de la Guardia, M. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic virus. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paules, C.I.; Marston, H.D.; Fauci, A.S. Coronavirus Infections—More Than Just the Common Cold. JAMA 2020, 323, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olwenyi, O.A.; Dyavar, S.R.; Acharya, A.; Podany, A.T.; Fletcher, C.V.; Ng, C.L.; Reid, S.P.; Byrareddy, S.N. Immuno-epidemiology and pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Overview and Infection Prevention and Control Priorities in Non-Us Healthcare Settings. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/non-us-settings/overview/index.html (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Archila, P.A.; Danies, G.; Molina, J.; Truscott de Mejía, A.-M.; Restrepo, S. Towards Covid-19 Literacy: Investigating the Literacy Levels of University Students in Colombia. Sci. Educ. 2021, 30, 785–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, W.G.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Cao, B.; Pasnick, S.; Jamil, S. Novel Wuhan (2019-nCoV) Coronavirus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, P7–P8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Nie, H.; Lu, H. Comorbid Chronic Diseases are Strongly Correlated with Disease Severity among COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, D.; Kim, T.H.; Johnstone, J.; Lam, P.P.; Science, M.; Kuster, S.P.; Fadel, S.A.; Tran, D.; Fernandez, E.; Bhatnagar, N.; et al. Populations at risk for severe or complicated influenza illness: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2013, 347, f5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F. Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funari, R.; Chu, K.-Y.; Shen, A.Q. Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein by gold nanospikes in an opto-microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.M.A.; Chowdhury, S.S.; Kabir, E. Numerical Analysis of a Highly Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. Plasmonics 2021, 16, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, D.; Bhatia, H.; Sai, V.V.R.; Satija, J. P-FAB: A Fiber-Optic Biosensor Device for Rapid Detection of COVID-19. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumla, A.; Hui, D.S.; Perlman, S. Middle East respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2015, 386, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, N.; Shaib, H. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A review. Germs 2019, 9, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, A.A.; Grant, R.; Assiri, A.; Elhakim, M.; Malik, M.R.; Van Kerkhove, M.D. MERS-CoV infection among healthcare workers and risk factors for death: Retrospective analysis of all laboratory-confirmed cases reported to WHO from 2012 to 2 June 2018. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Gautret, P. Asymptomatic Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: Extent and implications for infection control: A systematic review. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 27, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layqah, L.A.; Eissa, S. An electrochemical immunosensor for the corona virus associated with the Middle East respiratory syndrome using an array of gold nanoparticle-modified carbon electrodes. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, R. Identification of a Novel Inhibitor against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Viruses 2017, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilianski, A.; Mielech, A.M.; Deng, X.; Baker, S.C. Assessing activity and inhibition of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus papain-like and 3C-like proteases using luciferase-based biosensors. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11955–11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, M.; Hwang, J.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, D.-R.; Lee, K.-S.; Kang, M. Development of Label-Free Colorimetric Assay for MERS-CoV Using Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teengam, P.; Siangproh, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Multiplex Paper-Based Colorimetric DNA Sensor Using Pyrrolidinyl Peptide Nucleic Acid-Induced AgNPs Aggregation for Detecting MERS-CoV, MTB, and HPV Oligonucleotides. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5428–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. The evolution of HIV-1 and the origin of AIDS. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, C.L.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Zhao, G.; Handley, S.A.; Ghebremichael, M.S.; Lim, E.S.; Lankowski, A.; Baldridge, M.T.; Wilen, C.B.; Flagg, M.; et al. Altered Virome and Bacterial Microbiome in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, H.F.; Javed, A.; Sumbal; Afroze, B.; Ali, Q.; Akbar, K.; Nadeem, T.; Rana, M.A.; Nazar, Z.A.; Nasir, I.A.; et al. HIV Diagnosis and Treatment through Advanced Technologies. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Scott, I.; Whitmore, R.; Foster, H.; Fujimura, S.; Schmitz, J.; Levy, J. Low-level HIV infection of plasmacytoid dendritic cells: Onset of cytopathic effects and cell death after PDC maturation. Virology 2004, 329, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, J.; Njau, B.; Hobbie, A.; Mtuy, T.; Masaki, M.L.; Shayo, A.; van Zwetselaar, M.; Masnick, M.; Flaherty, B.; Brown, D.S.; et al. Using discrete choice experiments to design interventions for heterogeneous preferences: Protocol for a pragmatic randomised controlled trial of a preference-informed, heterogeneity-focused, HIV testing offer for high-risk populations. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e039313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, H.; Lidstone, E.A.; Jahangir, M.; Inci, F.; Hanhauser, E.; Henrich, T.J.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Cunningham, B.T.; Demirci, U. Nanostructured Optical Photonic Crystal Biosensor for HIV Viral Load Measurement. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, L.; Shamsipur, M.; Samandari, L.; Sheibani, S. HIV biosensors for early diagnosis of infection: The intertwine of nanotechnology with sensing strategies. Talanta 2020, 206, 120201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Hepatitis: Review. SA Pharm. J. 2015, 82, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.J. Drug-Induced Autoimmune-Like Hepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 958–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, D.B.; Wright, T.; Thomas, D.L.; Seeff, L.B. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1147–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, A. Chapter 70: Hepatitis viruses. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.; Ijaz, S.; Banks, M. Hepatitis E: An emerging infection in developed countries. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ); Ricci, A.; Allende, A.; Bolton, D.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; Fernandez Escamez, P.S.; Herman, L.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lindqvist, R.; et al. Public health risks associated with hepatitis E virus (HEV) as a food-borne pathogen. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukomolov, S. Viral Hepatitis: Selected Issues of Pathogenesis and Diagnostics; BoD–Books on Demand; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dakl, A.A.A.; Alnuaimy, W.A. Epidemiology of Hepatitis B and C in Al-Muthanna Province. Prof. RK Sharma 2020, 14, 419. [Google Scholar]
- Dionne-Odom, J.; Tita, A.T.N.; Silverman, N.S. #38: Hepatitis B in pregnancy screening, treatment, and prevention of vertical transmission. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavi, K.; Sravani, D.; Durga, S.; Durga, P.; Pavan, P.; Babu, P.; Raviteja, K. Hepatitis review on current and future scenario. J. Silico Vitr. Pharm. 2017, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, A.; Sharafeldin, N.; El-Hoseiny, M.; El-Daly, M.; Abdel-Hamid, M.; Aidi, S.; Sultan, Y.; El-Sayed, N.; Mohamed, M.; Fontanet, A. Community transmission of hepatitis B virus in Egypt: Results from a case-control study in Greater Cairo. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, C.W.; Simard, E.P.; Finelli, L.; Fiore, A.E.; Bell, B.P. Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Epidemiology and Vaccination. Epidemiol. Rev. 2006, 28, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, C.; Silvestri, C.; Voller, F. Update on Hepatitis C Epidemiology: Unaware and Untreated Infected Population Could Be the Key to Elimination. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.W.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Sullivan, P.S. Estimates of state-level chronic hepatitis C virus infection, stratified by race and sex, United States, 2010. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibbell, J.E.; Iqbal, K.; Patel, R.C.; Suryaprasad, A.; Sanders, K.J.; Moore-Moravian, L.; Serrecchia, J.; Blankenship, S.; Ward, J.W.; Holtzman, D. Increases in hepatitis C virus infection related to injection drug use among persons aged ≤30 years—Kentucky, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia, 2006–2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P. Epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of hepatitis D: Update and challenges ahead. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Chen, D.-S.; Chen, P.-J. Natural Course and Treatment of Hepatitis D Virus Infection. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2006, 105, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Shen, D.-T.; Ji, D.-Z.; Han, P.-C.; Zhang, W.-M.; Ma, J.-F.; Chen, W.-S.; Goyal, H.; Pan, S.; Xu, H.-G. Prevalence and burden of hepatitis D virus infection in the global population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2019, 68, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, G.; Fan, J. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescence biosensor for hepatitis C virus DNA detection based on δ-FeOOH and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Talanta 2020, 209, 120550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, E.G.; Castilla, V.; Damonte, E.B. Functional entry of dengue virus into Aedes albopictus mosquito cells is dependent on clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Verlaeten, O.; Cabié, A.; Kaidomar, S.P.; Moravie, V.; Martial, J.; Najioullah, F.; Plumelle, Y.; Fonteau, C.; Dussart, P.; et al. Influence of the Dengue Serotype, Previous Dengue Infection, and Plasma Viral Load on Clinical Presentation and Outcome During a Dengue-2 and Dengue-4 Co-Epidemic. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crill, W.D.; Hughes, H.R.; Delorey, M.J.; Chang, G.-J.J. Humoral Immune Responses of Dengue Fever Patients Using Epitope-Specific Serotype-2 Virus-Like Particle Antigens. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/about/index.html (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Badaru, O.; Adetona, K.; Ahmed, M.; Akanbi, O.; Foncham, J.; Kadavil, S.; Likaj, L.; Raza, S. Global epidemiology of dengue hemorrhagic fever: An update. J. Hum. Virol. Retrovirol. 2017, 5, 00179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.-T.; Linster, M.; Mendenhall, I.H.; Su, Y.C.F.; Smith, G.J.D. Avian influenza viruses in humans: Lessons from past outbreaks. Br. Med. Bull. 2019, 132, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capua, I.; Alexander, D.J. Avian influenza and human health. Acta Trop. 2002, 83, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha Kamil, Y.; Al-Rekabi, S.H.; Yaacob, M.H.; Syahir, A.; Chee, H.Y.; Mahdi, M.A.; Abu Bakar, M.H. Detection of dengue using PAMAM dendrimer integrated tapered optical fiber sensor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, N.A.S.; Fen, Y.W.; Abdullah, J.; Chik, C.E.N.C.E.; Mahdi, M.A. Development of an optical sensor based on surface plasmon resonance phenomenon for diagnosis of dengue virus E-protein. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2018, 20, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashchenko, O.; Shelby, T.; Banerjee, T.; Santra, S. A Comparison of Optical, Electrochemical, Magnetic, and Colorimetric Point-of-Care Biosensors for Infectious Disease Diagnosis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1162–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.S. Virus entry: Molecular mechanisms and biomedical applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermali, M.; Khalsa, R.K.; Pillai, K.; Ismail, Z.; Harky, A. The role of biomarkers in diagnosis of COVID-19—A systematic review. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, G.; Maccaferri, M.; Ruini, C.; Tomasi, A.; Ozben, T. Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression. Crit Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Ajmal, M.; Ashraf, G.; Muhammad, N.; Aziz, A.; Iftikhar, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. The role of biosensors in coronavirus disease-2019 outbreak. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 23, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stol, K.; Nijman, R.G.; van Herk, W.; van Rossum, A.M.C. Biomarkers for Infection in Children: Current Clinical Practice and Future Perspectives. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, S7–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotru, S.; Klimuntowski, M.; Ridha, H.; Uddin, Z.; Askhar, A.A.; Singh, G.; Howlader, M.M.R. Electrochemical sensing: A prognostic tool in the fight against COVID-19. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for detecting viral and bacterial infections using host biomarkers: A review. Analyst 2021, 145, 7825–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapasi, A.J.; Dittrich, S.; González, I.J.; Rodwell, T.C. Host Biomarkers for Distinguishing Bacterial from Non-Bacterial Causes of Acute Febrile Illness: A Comprehensive Review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, M.U.; Blyth, C.C.; West, R.; Lang, J.; Rahman, T.; Granland, C.; de Gier, C.; Borland, M.L.; Thornton, R.B.; Kirkham, L.-A.S.; et al. Combination of clinical symptoms and blood biomarkers can improve discrimination between bacterial or viral community-acquired pneumonia in children. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Scholl, A.; Averhoff, P.; Zychlinsky, A. How do neutrophils and pathogens interact? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prilutsky, D.; Shneider, E.; Shefer, A.; Rogachev, B.; Lobel, L.; Last, M.; Marks, R.S. Differentiation between Viral and Bacterial Acute Infections Using Chemiluminescent Signatures of Circulating Phagocytes. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4258–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-reactive protein: A critical update. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, C.; Prkno, A.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Schlattmann, P. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation, and Pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tripathy, S.; Jyoti, A.; Singh, S.G. Recent advances in biosensors for diagnosis and detection of sepsis: A comprehensive review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124–125, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Marco, C.; Galeno, H.; Villagra, E.; Vera, L.; Lagos, N.; Becerra, N.; Mora, J.; Bermúdez, A.; et al. Serum levels of interleukin-6 are linked to the severity of the disease caused by Andes Virus. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, M. Defense against filoviruses used as biological weapons. Antivir. Res. 2003, 57, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, R.M. The potential use of influenza virus as an agent for bioterrorism. Antivir. Res. 2003, 57, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noah, D.L.; Huebner, K.D.; Darling, R.G.; Waeckerle, J.F. The history and threat of biological warfare and terrorism. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 20, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daaboul, G.G.; Lopez, C.A.; Yurt, A.; Goldberg, B.B.; Connor, J.H.; Ünlü, M.S. Label-free optical biosensors for virus detection and characterization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2011, 18, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Erdem, Ö.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. An alternative medical diagnosis method: Biosensors for virus detection. Biosensors 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, M.L.; Mach, K.E.; Wong, P.K.; Liao, J.C. Advances and challenges in biosensor-based diagnosis of infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.A. Wearable miniaturized electrochemical sensors: Benefits and challenges. In Electrochemistry: Volume 15; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; Volume 15, pp. 147–185. [Google Scholar]
- Citartan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.; Tominaga, J.; Tang, T.-H. Label-free methods of reporting biomolecular interactions by optical biosensors. Analyst 2013, 138, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharatape, A.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. Optical biomarker-based biosensors for cancer/infectious disease medical diagnoses. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2019, 27, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Mashinchian, O.; Ayoubi, B.; Jamali, A.A.; Mobed, A.; Losic, D.; Omidi, Y.; de la Guardia, M. Optical and electrochemical DNA nanobiosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochia, R. Developments in biosensors for CoV detection and future trends. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhalim, I.; Zourob, M.; Lakhtakia, A. Surface plasmon resonance for biosensing: A mini-review. Electromagnetics 2008, 28, 214–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.A.; Wagner, K.; Parikh, P.; Hassan, U. Smartphone Based Microfluidic Biosensor for Leukocyte Quantification at the Point-of-Care. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Healthcare Innovations and Point of Care Technologies,(HI-POCT), Bethesda, MD, USA, 20–22 November 2019; pp. 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mukundan, H.; Anderson, A.S.; Grace, W.K.; Grace, K.M.; Hartman, N.; Martinez, J.S.; Swanson, B.I. Waveguide-Based Biosensors for Pathogen Detection. Sensors 2009, 9, 5783–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, J.M.; Im, M.; Choi, Y.K. Integration of field effect transistor-based biosensors with a digital microfluidic device for a lab-on-a-chip application. Lab. Chip 2012, 12, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.-F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Tan, J.; Chen, J.; Du, L.; Sun, T.; Shen, J.; Chen, K.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3C-like proteinase N terminus is indispensable for proteolytic activity but not for enzyme dimerization: Biochemical and thermodynamic investigation in conjunction with molecular dynamics simulations. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor technique: A review. J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, N.; Sacher, E.; Mandeville, R.; Meunier, M. Surface plasmon resonance detection of E. coli and methicillin-resistant S. aureus using bacteriophages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 37, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussrow, A.; Baksh, M.M.; Bornhop, D.J.; Finn, M. Universal sensing by transduction of antibody binding with backscattering interferometry. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussrow, A.; Enders, C.S.; Castro, A.R.; Cox, D.L.; Ballard, R.C.; Bornhop, D.J. The potential of backscattering interferometry as an in vitro clinical diagnostic tool for the serological diagnosis of infectious disease. Analyst 2010, 135, 1535–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Gai, Z.; Tao, Y.; Schmitt, J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Wang, J. Dual-functional plasmonic photothermal biosensors for highly accurate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5268–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaja, S.; Hilgenberg, J.D.; Collins, J.L.; Shah, A.A.; Koulen, P.; Wawro, D.D.; Zimmerman, S.; Magnusson, R. Detection of novel biomarkers for ovarian cancer with an optical nanotechnology detection system enabling label-free diagnostics. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 081412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, N.; Zhang, Y.; Mellor, C.; Benson, T. Photonic biosensor chip for early-stage cancer diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2015 17th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Budapest, Hungary, 5–9 July 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, L.C.; Lunn, G.; Coico, R. Biosafety: Guidelines for working with pathogenic and infectious microorganisms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2009, 13, Unit 1A.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.Y.; Nguyen, B.T.T.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Chin, L.K.; Wei, M.; Yap, P.H.; Zhou, X.; et al. On-Chip Optical Detection of Viruses: A Review. Adv. Photonics Res. 2021, 2, 2000150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosendahl Huber, S.K.; Luimstra, J.J.; van Beek, J.; Hoppes, R.; Jacobi, R.H.J.; Hendriks, M.; Kapteijn, K.; Ouwerkerk, C.; Rodenko, B.; Ovaa, H.; et al. Chemical Modification of Influenza CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes Enhances Their Immunogenicity Regardless of Immunodominance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crux, N.B.; Elahi, S. Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) and Immune Regulation: How Do Classical and Non-Classical HLA Alleles Modulate Immune Response to Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Infections? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.M.; Cvelbar, U.; Abdulhalim, I. A comprehensive review on plasmonic-based biosensors used in viral diagnostics. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ongagna-Yhombi, S.Y.; Lu, Z.; Centeno-Tablante, E.; Colt, S.; Cao, X.; Ren, Y.; Cárdenas, W.B.; Mehta, S.; Erickson, D. Rapid Diagnostic Platform for Colorimetric Differential Detection of Dengue and Chikungunya Viral Infections. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5415–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, V.X.T.; Wong, T.I.; Zheng, X.T.; Tan, Y.N.; Zhou, X. Colorimetric biosensors for point-of-care virus detections. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Enein, H.; Stefan, R.-I.; Van Staden, J. Chemiluminescence-Based (Bio)Sensors—An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1999, 29, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; Geiss, B.J.; Henry, C.S. Review—Chemical and Biological Sensors for Viral Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, S.Y. Recent Trends in Nanomaterials-Based Colorimetric Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Viruses. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Wei, G. Recent advances in the design of colorimetric sensors for environmental monitoring. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 2195–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VS, A.P.; Joseph, P.; Daniel, K.; Susithra, L.; Kinoshita, T.; Muthusamy, S. Colorimetric sensors for rapid detection of various analytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, C.; Wen, J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Jiang, L.; He, H. Development and Evaluation of a Polydiacetylene Based Biosensor for the Detection of H5 Influenza Virus. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 219, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, S.; Saadun, R.; Azmi, N.E.; Ariffin, N.; Abdullah, J.; Yusof, N.A.; Sidek, H.; Hajian, R. Label-Free Dengue Detection Utilizing PNA/DNA Hybridization Based on the Aggregation Process of Unmodified Gold Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 839286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanawarut, R.; Su, X. Colorimetric Detection of DNA Using Unmodified Metallic Nanoparticles and Peptide Nucleic Acid Probes. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6122–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, E.G.; O’Dell, D.; Mehta, S.; Erickson, D. Mitigating the Hook Effect in Lateral Flow Sandwich Immunoassays Using Real-Time Reaction Kinetics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5095–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, N.K.; Hanson, J.E.; Glick, G.D.; Brown, J.H.; Crowther, R.L.; Park, S.J.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Binding of influenza virus hemagglutinin to analogs of its cell-surface receptor, sialic acid: Analysis by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and x-ray crystallography. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 9609–9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, W.; Brown, J.H.; Cusack, S.; Paulson, J.C.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature 1988, 333, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Portner, A.; Scroggs, R.; Uchikawa, M.; Koyama, N.; Matsuo, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Takimoto, T. Receptor Specificities of Human Respiroviruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4604–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Gaston, M.A.; Weiss, A.A.; Zhang, P. Colorimetric viral detection based on sialic acid stabilized goldnanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Kim, J.; Tran, V.T.; Suzuki, T.; Neethirajan, S.; Lee, J.; Park, E.Y. In situ self-assembly of gold nanoparticles on hydrophilic and hydrophobic substrates for influenza virus-sensing platform. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yu, X.; He, H.; Cao, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.-Y. Smartphone-Based Point-of-Care Microfluidic Platform Fabricated with a ZnO Nanorod Template for Colorimetric Virus Detection. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, F.; Wang, K.; Chen, G. Colorimetric detection of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA based on DNA-templated copper nanoclusters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 909, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, M.; An, J.; Luo, M.; Lyu, Y.; Hu, N.; Guo, W.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Magnetic Separation and Enzymatic Catalysis Conjugated Colorimetric Immunosensor for Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Detection. Microchem. J. 2021, 106155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Balapure, A.; Khaja, M.N.; Ganesan, R.; Dutta, J.R. Naked-eye colorimetric detection of HCV RNA mediated by a 5′ UTR-targeted antisense oligonucleotide and plasmonic gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2021, 146, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, E.; Lara-Mayorga, I.M.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Zhang, Y.S.; Martínez-Chapa, S.O.; Santiago, G.T.-d.; Alvarez, M.M. Colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for cost-effective and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2: The change in color in LAMP-based assays quantitatively correlates with viral copy number. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, B.D.; Cennamo, M.; Minopoli, A.; Campanile, R.; Censi, S.B.; Terracciano, D.; Portella, G.; Velotta, R. Colorimetric Test for Fast Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Nasal and Throat Swabs. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-P.; Cho, E.; Yun, D.; Kim, T.; Lee, I.-S.; Jung, S. Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Influenza Antigen Based on an Antibody-Polydiacetylene Conjugate and Its Coated Polyvinylidene Difluoride Membrane. Polymers 2017, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, J.; Sharma, A.; Jang, J. Vertical flow-based paper immunosensor for rapid electrochemical and colorimetric detection of influenza virus using a different pore size sample pad. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, J.; Tran, V.T.; Lee, D.K.; Ahmed, S.R.; Hong, J.C.; Lee, J.; Park, E.Y.; Lee, J. Magnetic Nanozyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Ultrasensitive Influenza A Virus Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12534–12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Yeom, G.; Jang, H.; Park, C.-J.; Kim, M.-G. Highly sensitive and universal detection strategy based on a colorimetric assay using target-specific heterogeneous sandwich DNA aptamer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1123, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, Q.; Duan, Y. Fluorescent labels in biosensors for pathogen detection. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 35, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggoner, A. Fluorescent labels for proteomics and genomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, K.; Han, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y. A gold nanorods-based fluorescent biosensor for the detection of hepatitis B virus DNA based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Analyst 2013, 138, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, F.; Xu, H.; Lv, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, A. Immunochromatographic assay for quantitative and sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen using highly luminescent quantum dot-beads. Talanta 2015, 142, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. A virus resonance light scattering sensor based on mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymers for high sensitive and high selective detection of Hepatitis A Virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Rong, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. A fluorescent aptasensor for H5N1 influenza virus detection based-on the core–shell nanoparticles metal-enhanced fluorescence (MEF). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K.; Hatanaka, K. Development of tetraphenylethylene-based fluorescent oligosaccharide probes for detection of influenza virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, S.; Katsura, H.; Zhao, D.; Ozawa, M.; Ando, T.; Shoemaker, J.E.; Ishikawa, I.; Yamada, S.; Neumann, G.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Multi-spectral fluorescent reporter influenza viruses (Color-flu) as powerful tools for in vivo studies. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-P.; Chen, S.-R.; Liu, S.-W.; Tang, X.-Y.; Qin, L.; Qiu, G.-H.; Chen, J.-X.; Chen, W.-H. Platforms Formed from a Three-Dimensional Cu-Based Zwitterionic Metal–Organic Framework and Probe ss-DNA: Selective Fluorescent Biosensors for Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 ds-DNA and Sudan Virus RNA Sequences. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 12206–12214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Qiang, L.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y. Rapid and sensitive triple-mode detection of causative SARS-CoV-2 virus specific genes through interaction between genes and nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1154, 338330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; He, J.A.; Chen, W.; Ho, H.P.; Kong, S.K.; Wang, C.; Long, J.; Fong-Chuen Loo, J.; Gu, D. Development of peptide-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) for diagnosis of dengue virus infection in human. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 556, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.; Park, J.; Seok, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, M.-G.; Song, C.-S.; Lee, J. A Size-Selectively Biomolecule-Immobilized Nanoprobe-Based Chemiluminescent Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Detection of Avian-Origin Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartman, M.T.; Kaidarova, Z.; Hirschkorn, D.; Sacher, R.A.; Fridey, J.; Garratty, G.; Gibble, J.; Smith, J.W.; Newman, B.; Yeo, A.E.; et al. Long-term increases in lymphocytes and platelets in human T-lymphotropic virus type II infection. Blood 2008, 112, 3995–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.-J.; Ren, M.; Liang, L.; Zhang, C.-Y. Controllable fabrication of bio-bar codes for dendritically amplified sensing of human T-lymphotropic viruses. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4942–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Lan, G.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Ali, Z.; Tang, Y.; Mou, X.; et al. Magnetic beads-based chemiluminescent assay for ultrasensitive detection of pseudorabies virus. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 3337–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, A.; Wei, F.; Lei, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y. A simple and rapid capillary chemiluminescence immunoassay for quantitatively detecting human serum HBsAg. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouri, S.; Ghourchian, H.; Shourian, M.; Boutorabi, M. A gold nanoparticle-based immunosensor for the chemiluminescence detection of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Kou, G.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ni, W.; Wu, W.; Tang, S.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Clinical application of Chemiluminescence Microparticle Immunoassay for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 130, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukli, N.; Le Mene, M.; Schnuriger, A.; Cuervo, N.S.; Laroche, C.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Gozlan, J. High Incidence of False-Positive Results in Patients with Acute Infections Other than COVID-19 by the Liaison SARS-CoV-2 Commercial Chemiluminescent Microparticle Immunoassay for Detection of IgG Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01352-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, A.; Cosma, C.; Sciacovelli, L.; Faggian, D.; Plebani, M. Analytical performances of a chemiluminescence immunoassay for SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG and antibody kinetics. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.F.; Chen, J.; Li Hu, J.; Long, Q.X.; Deng, H.J.; Liu, P.; Fan, K.; Liao, P.; Liu, B.Z.; Wu, G.C.; et al. A Peptide-Based Magnetic Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay for Serological Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Cavalera, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Calabria, D.; Rosati, S.; Simoni, P.; Colitti, B.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, M.; Anfossi, L. Dual lateral flow optical/chemiluminescence immunosensors for the rapid detection of salivary and serum IgA in patients with COVID-19 disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hong, M.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G. A highly sensitive chemiluminescent metalloimmunoassay for H1N1 influenza virus detection based on a silver nanoparticle label. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10563–10565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ge, L.; Yu, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, F. Highly sensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor based on hybridization chain reaction and amplification of gold nanoparticles for DNA detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kim, K.; Ma, K.; Lee, W.; Choi, J.-W.; Yun, C.-O.; Kim, D. Enhanced detection of virus particles by nanoisland-based localized surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Kumar, J.S.; Singh, V.V.; Biswas, U.; Sarkar, S.S.; Alam, S.I.; Dash, P.K.; Boopathi, M.; Ganesan, K.; Jain, R. Surface plasmon resonance sensing of Ebola virus: A biological threat. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4101–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, R.; Hargis, B.; Lu, H.; Li, Y. A SPR Aptasensor for Detection of Avian Influenza Virus H5N1. Sensors 2012, 12, 12506–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estmer Nilsson, C.; Abbas, S.; Bennemo, M.; Larsson, A.; Hämäläinen, M.D.; Frostell-Karlsson, Å. A novel assay for influenza virus quantification using surface plasmon resonance. Vaccine 2010, 28, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, D.; Jiménez, A.; Beauvais, J.; Dubowski, J.J. Real-time detection of influenza A virus using semiconductor nanophotonics. Light Sci. Appl. 2013, 2, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Seo, H.B.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, S.K.; Song, C.S.; Gu, M.B. Highly sensitive sandwich-type SPR based detection of whole H5Nx viruses using a pair of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, N.A.S.; Fen, Y.W.; Abdullah, J.; Mustapha Kamil, Y.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Mahdi, M.A. Sensitive Detection of Dengue Virus Type 2 E-Proteins Signals Using Self-Assembled Monolayers/Reduced Graphene Oxide-PAMAM Dendrimer Thin Film-SPR Optical Sensor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Lee, G.-Y.; Ko, H.; Chang, Y.W.; Kang, M.-J.; Pyun, J.-C. Development of SPR biosensor for the detection of human hepatitis B virus using plasma-treated parylene-N film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, C.Z. One-step conjugation chemistry of DNA with highly scattered silver nanoparticles for sandwich detection of DNA. Analyst 2012, 137, 3434–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhan, L. Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor for sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus in buffer, blood serum and plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Song, J.; Xu, R.; Liu, D.; Dong, B.; Xu, L.; Song, H. Zinc oxide inverse opal electrodes modified by glucose oxidase for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, H.; Vučković, J. Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, B.; Tang, H. Bioinspired sensor chip for detection of miRNA-21 based on photonic crystals assisted cyclic enzymatic amplification method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, F.; Rashidi, M.-R.; Pakchin, P.S.; Ahmadi-Kandjani, S.; Nikniazi, A. Photonic crystal based biosensors: Emerging inverse opals for biomarker detection. Talanta 2021, 221, 121615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griol, A.; Peransi, S.; Rodrigo, M.; Hurtado, J.; Bellieres, L.; Ivanova, T.; Zurita, D.; Sánchez, C.; Recuero, S.; Hernández, A.; et al. Design and Development of Photonic Biosensors for Swine Viral Diseases Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha Kamil, Y.; Abu Bakar, M.H.; Mustapa, M.A.; Yaacob, M.H.; Abidin, N.H.Z.; Syahir, A.; Lee, H.J.; Mahdi, M.A. Label-free Dengue E protein detection using a functionalized tapered optical fiber sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Che, C.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Cunningham, B.T. Single-step, wash-free digital immunoassay for rapid quantitative analysis of serological antibody against SARS-CoV-2 by photonic resonator absorption microscopy. Talanta 2021, 225, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Yadav, A.R.; Lifson, M.A.; Baker, J.E.; Fauchet, P.M.; Miller, B.L. Selective virus detection in complex sample matrices with photonic crystal optical cavities. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippa, M.; Castagna, R.; Brandi, S.; Fusco, G.; Monini, M.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J.; Zyss, J.; Petti, L. Octupolar Plasmonic Nanosensor Based on Ordered Arrays of Triangular Au Nanopillars for Selective Rotavirus Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 4837–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
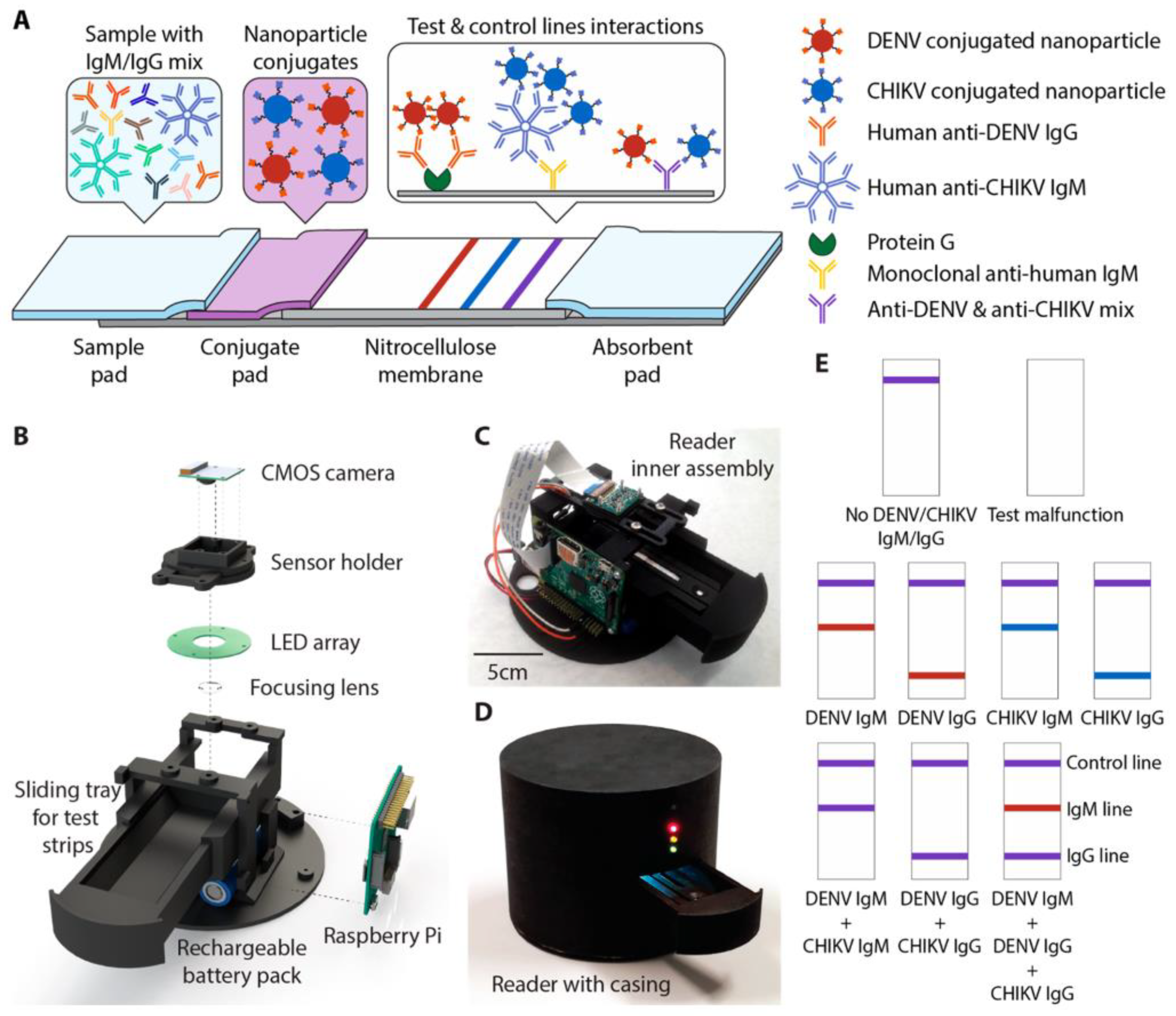
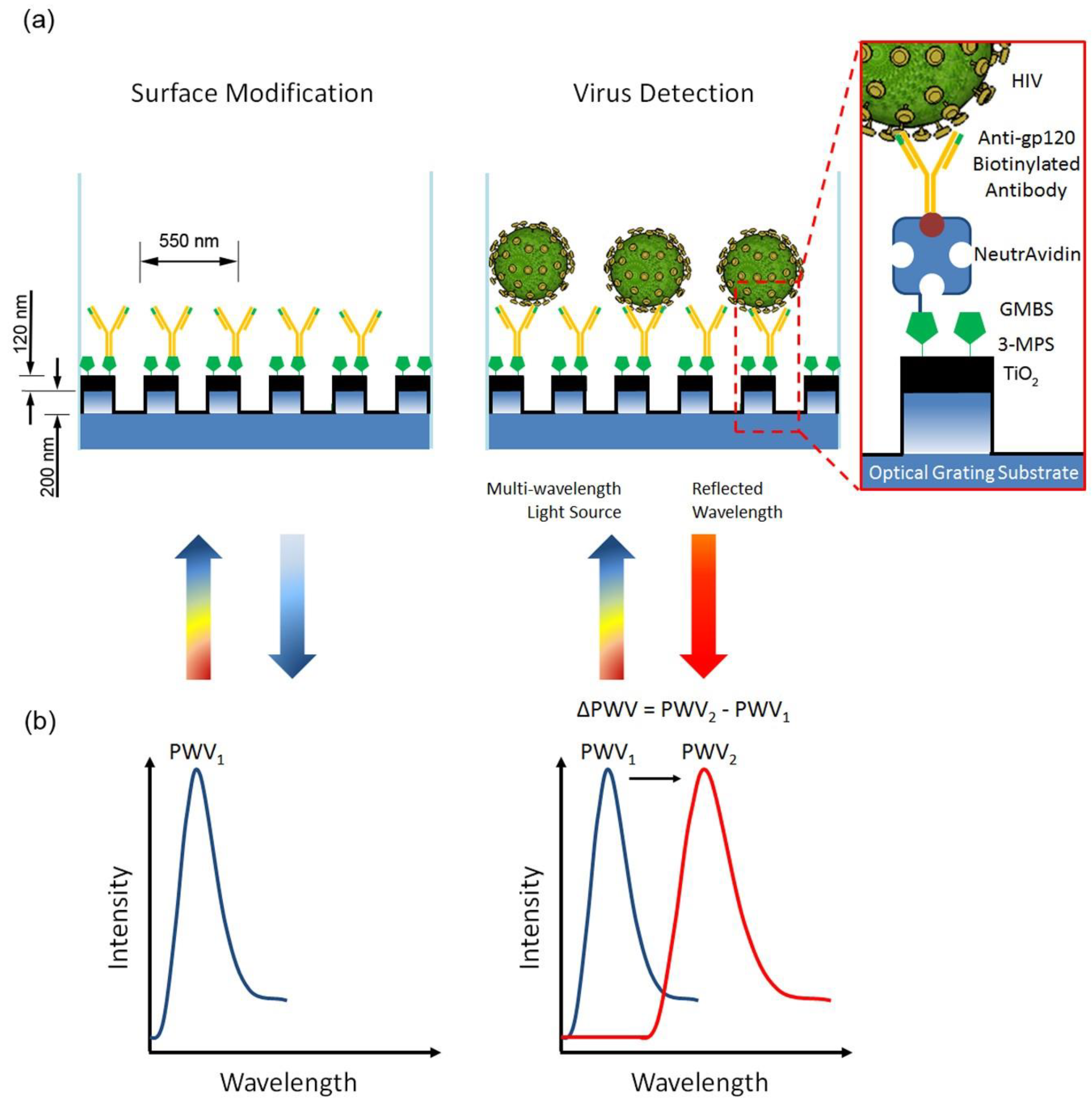
| S. No. | Antigen/Analyte | Bio-Element/Detection Strategy | Nanomaterial | Detection/ Linearity Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | DENV | PNA sequences | GNPs | 0.00 to 12.0 μM | 0.12 μM | [149] |
| 2. | DENV and CHIKV IgG and IgM | Lateral-flow test strip | Red and blue Latex nanoparticles | - | - | [141] |
| 3. | New Caledonia/H1N1/1999 influenza virus | Peroxidase-like activity | AuNP films | 10 pg mL−1–10 µg mL−1 | 50.50 pg mL−1 | [156] |
| 4. | Influenza A virus (H3N2) | Peroxidaselike activity | AuNP films | up to 10.0 pg mL−1 | 4.5 pg mL−1 | [156] |
| 5. | Influenza A virus (H3N2) | M149 antibody (Label-free fluorescence-based detection) | Ab-Polydiacetylene (PDA) Conjugate coated with Polyvinylidene (PVDF) Difluoride Membrane | 30 µg mL−1 | [163] | |
| 6. | Influenza H1N1 virus | Anti-influenza A HA-Ab (Ab-E) and HRP-tagged anti-influenza A HA-Ab (HRP-Ab) | Au immunostrip | 0 to 10,000 PFU mL−1 | 1.34 PFU mL−1 (PBS) 2.27 PFU mL−1 (Saliva) | [164] |
| 7. | Avian influenza virus | Fluorescence Reflection | AuNPs and ZnO nanorods | 8.0 × 105 to 2.7 × 103 EID50/mL | 2.7 × 104 EID50/mL (naked eye) 8.0 × 103 EID50/mL (smartphone device) | [157] |
| 8. | Influenza A virus (H1N1) | Anti-hemagglutinin (HA) mAb | Au Nanozymes and Silica-shelled magnetic nanobeads (MagNBs) | 5.0 × 10−15–5.0 × 10−6 g mL−1 | 5.0 × 10−12 g mL−1 (human eyes) 44.2 × 10−15 g mL−1 (microplate reader) | [165] |
| 9. | NPs of influenza A and B virus | STA-RPA70A@biotin-HRP and aptamer | - | 0.1 pg mL−1 to 1 mg mL−1 | 0.30 pg mL−1 0.16 pg mL−1 | [166] |
| 10. | Hepatitis B virus | DNA sequences | Cupper nanoclusters | 12.0 × 109 to 12.0 × 1013 target molecules | 12 × 109 molecules | [158] |
| 11. | Hepatitis B virus | HBsAg | Magnetic nanoparticles | 0.10–20 ng mL−1 | 0.012 ng mL−1 | [159] |
| 12. | Hepatitis C virus | HCV oligonucleotides | AuNPs | 7.50 × 102 to 2.00 × 106 IU mL−1 | 100 IU mL−1 (0.4 IU µL−1) | [160] |
| 13. | SARS CoV-2 | Colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) | - | 625 to 2 × 105 DNA copies | 62.5 DNA copies | [161] |
| S. No. | Principle | Analyte | Real Sample | Detection Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fluorescence | Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA (FRET-based) | Human urine sample | 0.045–6.0 nmol L−1 | 0.015 nmol L−1 | [169] |
| 2. | Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) sandwich immunochromatographic assay (ICA) | Human Serum | 75.0 pg mL−1–4.80 ng mL−1 4.80 pg mL−1–75.0 ng mL−1 | 75 pg mL−1 | [170] | |
| 3. | Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) | Human Serum | 0.04–6.0 nmol L−1 | 8. 0 nmol L−1 | [171] | |
| 4. | Recombinant hemagglutinin (rHA) protein of the H5N1 influenza virus | Aqueous Buffer Human serum | 0.0–200.0 ng mL−1 | 2.0 ng mL−1 3.5 ng mL−1 | [172] | |
| 5. | Human immunodeficiency virus 1 double-stranded DNA sequence Sudan virus RNA sequence | - | - | 196 pM 73 pM | [175] | |
| 6. | SARS-CoV-2 virus specific genes | TE buffer | 0.01–1.0 pM | 160 fm | [176] | |
| 7. | Chemiluminescence | anti-DENV IgM antibodies | Serum | - | - | [177] |
| 8. | Avian influenza viruses (AIV) | Embryonated chicken eggs | 1.0 pM–1.0 nM | 5.0 pM | [178] | |
| 9. | Human T-lymphotropic viruses | Human Serum | 1.0 aM–1.0 nM | 0.50 aM | [180] | |
| 10. | Pseudorabies Virus | Swine | 1.0 × 101–1.0 × 108 amol | 100 amol | [181] | |
| 11. | Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) | Serum | 0.40–15.0 ng mL−1 | 0.30 ng mL−1 | [182] | |
| 12. | HBsAg | Serum | 0.12–30 ng mL−1 | 14.0 pg mL−1 | [183] | |
| 13. | H1N1 influenza virus | - | 1.0 × 10−12–1.0 × 10−6 g mL−1 | 1.0 × 10−13 g mL−1 | [189] | |
| 14. | Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) | Human Serum | 0.020–1.0 pM | 5.0 fM | [190] |
| S. No. | Antigen/Analyte | Bio-Element | Real Sample | Detection Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Avian Influenza Virus H5N1 | Aptamer | Poultry swab | 0.128 to 1.28 HAU | 0.128 HAU | [193] |
| 2. | Avian influenza virus subtype H6 | Monoclonal antibodies | Tracheal samples from chicken | 0.50–10 µg mL−1 | 5.14 × 105 EID50/0.1 mL | [158] |
| 3. | Influenza Virus | Antibodies/Protein | Serum | 0.50–10 µg mL−1 | <0.50 µg mL−1 | [194] |
| 4. | DENV protein | IgM Ab | - | 0.08 pM to 0.5 pM | 0.08 pM | [197] |
| 5. | Human hepatitis virus surface antigen (HBsAg) | Antibodies | - | 10 pg mL−1–1 µg mL−1 | 10 pg mL−1 | [198] |
| 6. | SARS-CoV | Goldbinding polypeptides (GBPs) | - | 0–10 µg mL−1 | 200 ng mL−1 | [18] |
| 7. | Hepatitis B | Monoclonal hepatitis B (HBsAb) | buffer, blood serum and plasma | 0.01–1.0 IU/mL | 0.01 IU/mL | [201] |
| 8. | HIV DNA | DNA | - | 0.30–2.0 nmol L−1 | ~195 pmol L−1 | [200] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Goud, K.Y.; Mohamed, M.A.; Kummari, S.; Tiwari, S.; Li, Z.; Narayan, R.; Stanciu, L.A.; Marty, J.L. Optical Biosensors for Diagnostics of Infectious Viral Disease: A Recent Update. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112083
Sharma A, Mishra RK, Goud KY, Mohamed MA, Kummari S, Tiwari S, Li Z, Narayan R, Stanciu LA, Marty JL. Optical Biosensors for Diagnostics of Infectious Viral Disease: A Recent Update. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Atul, Rupesh Kumar Mishra, K. Yugender Goud, Mona A. Mohamed, Shekher Kummari, Swapnil Tiwari, Zhanhong Li, Roger Narayan, Lia A. Stanciu, and Jean Louis Marty. 2021. "Optical Biosensors for Diagnostics of Infectious Viral Disease: A Recent Update" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112083
APA StyleSharma, A., Mishra, R. K., Goud, K. Y., Mohamed, M. A., Kummari, S., Tiwari, S., Li, Z., Narayan, R., Stanciu, L. A., & Marty, J. L. (2021). Optical Biosensors for Diagnostics of Infectious Viral Disease: A Recent Update. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112083











