Automation of Lung Ultrasound Interpretation via Deep Learning for the Classification of Normal versus Abnormal Lung Parenchyma: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset Curation and Labelling
2.1.1. Local Data
2.1.2. External Data
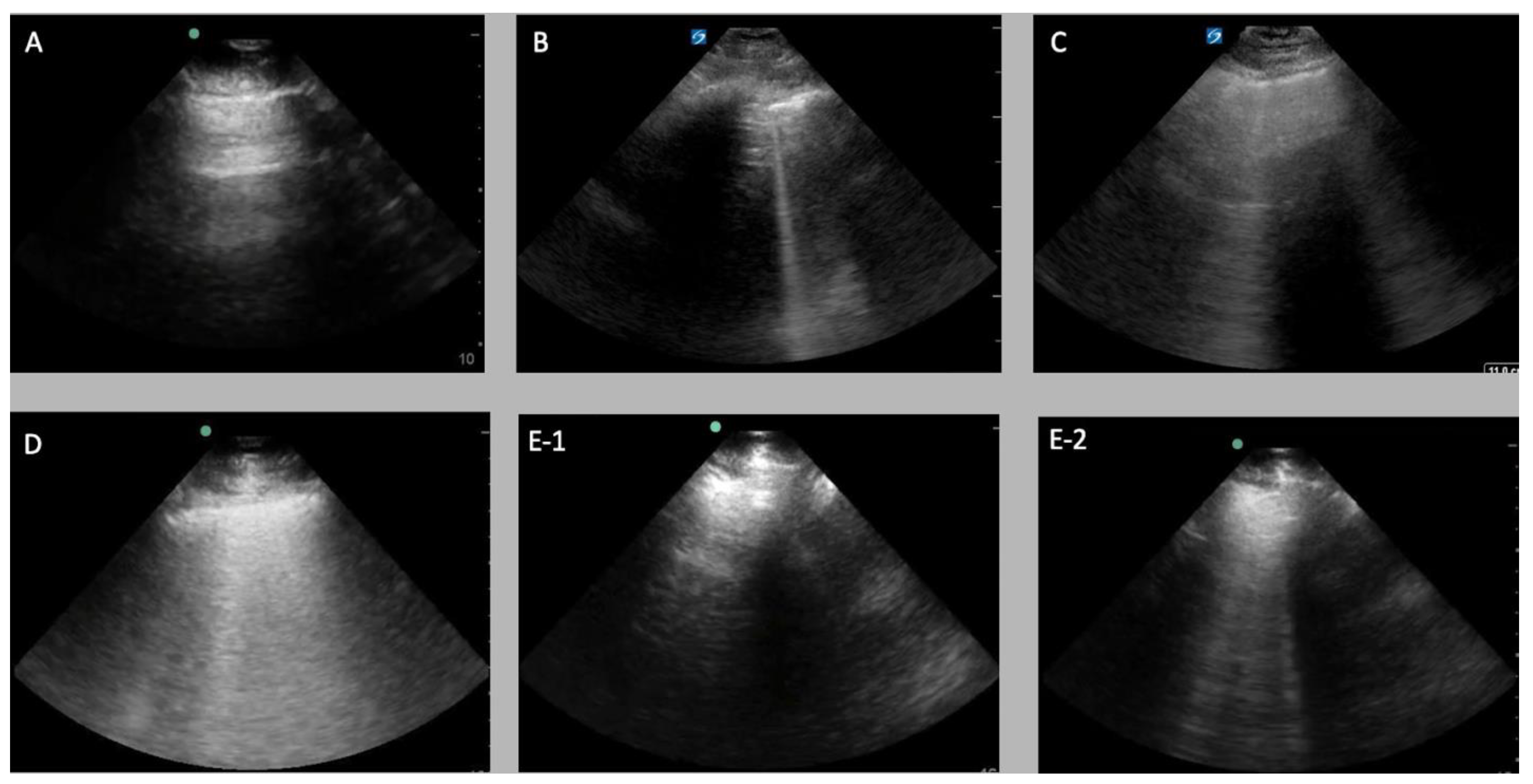
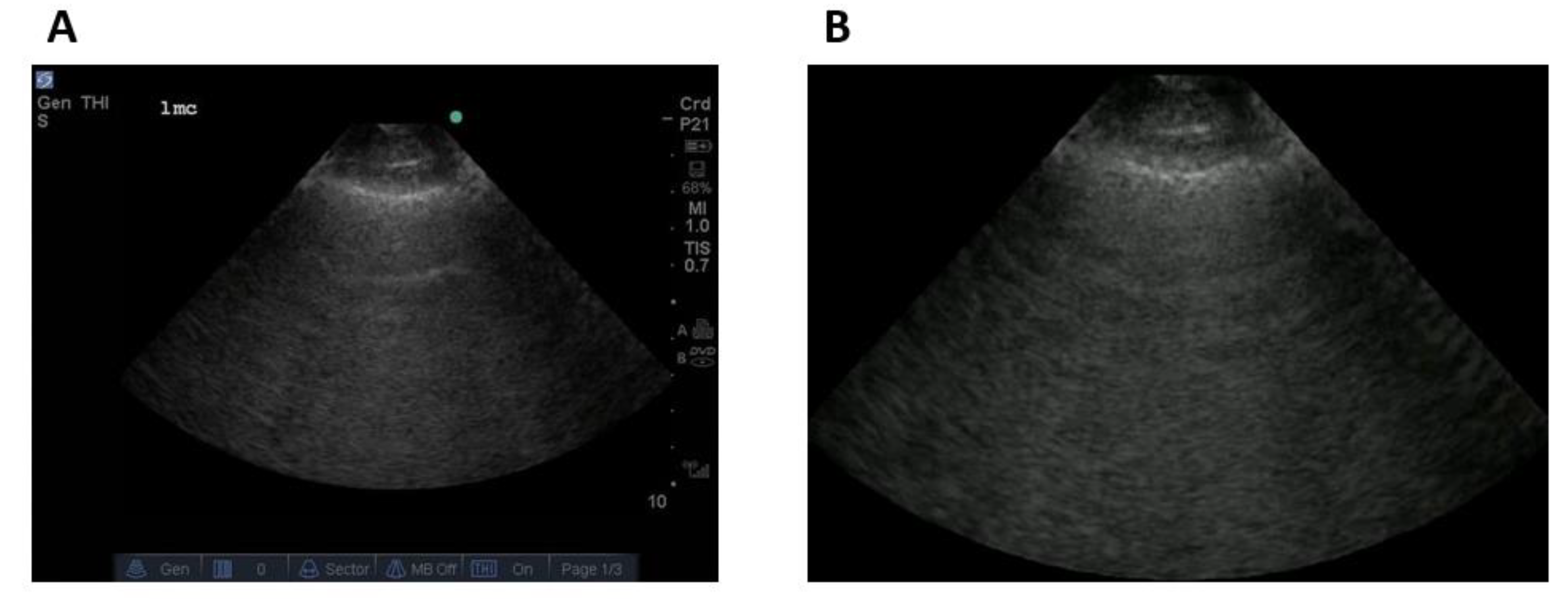
2.1.3. Data Labelling
2.2. Experimental Setup
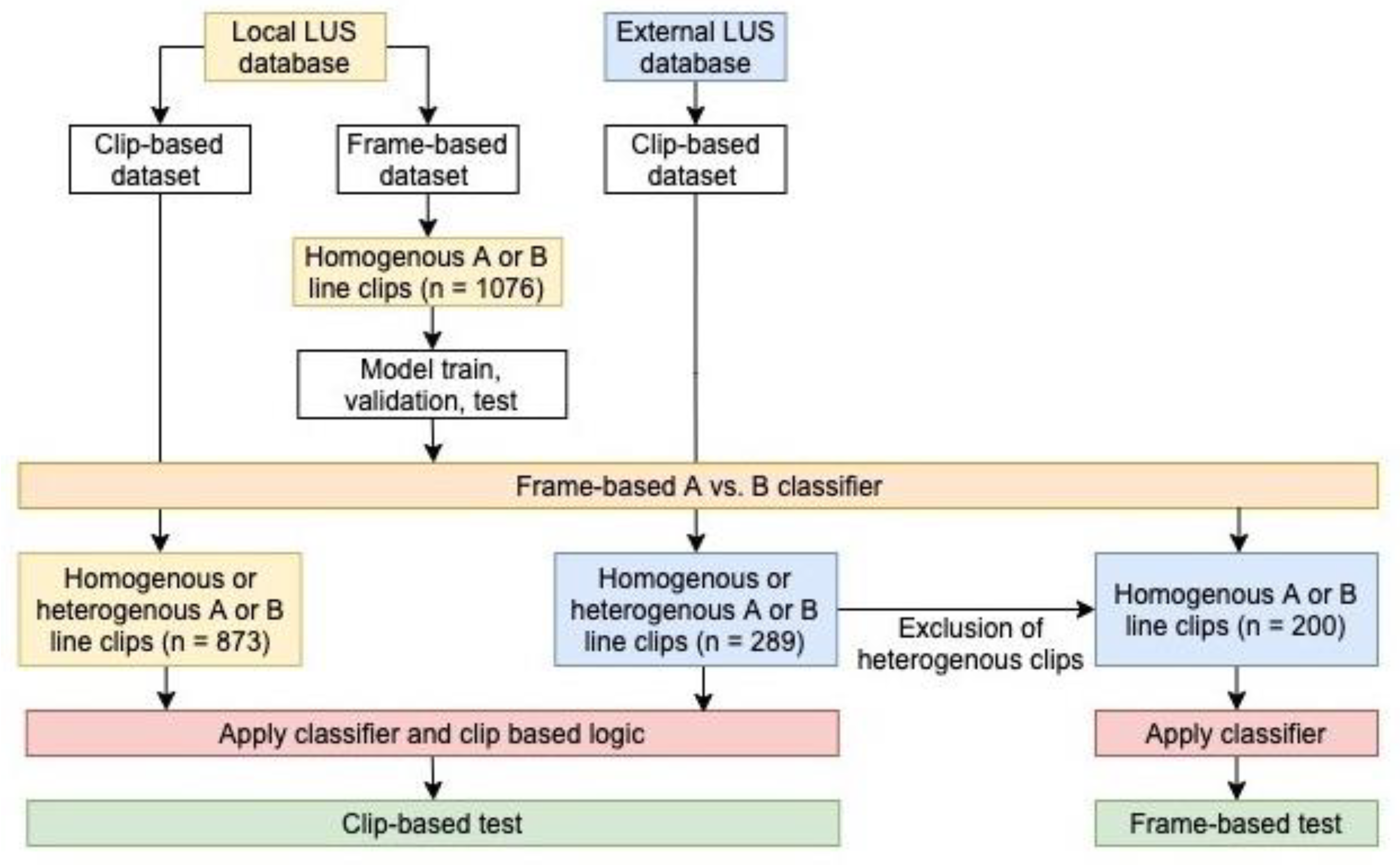
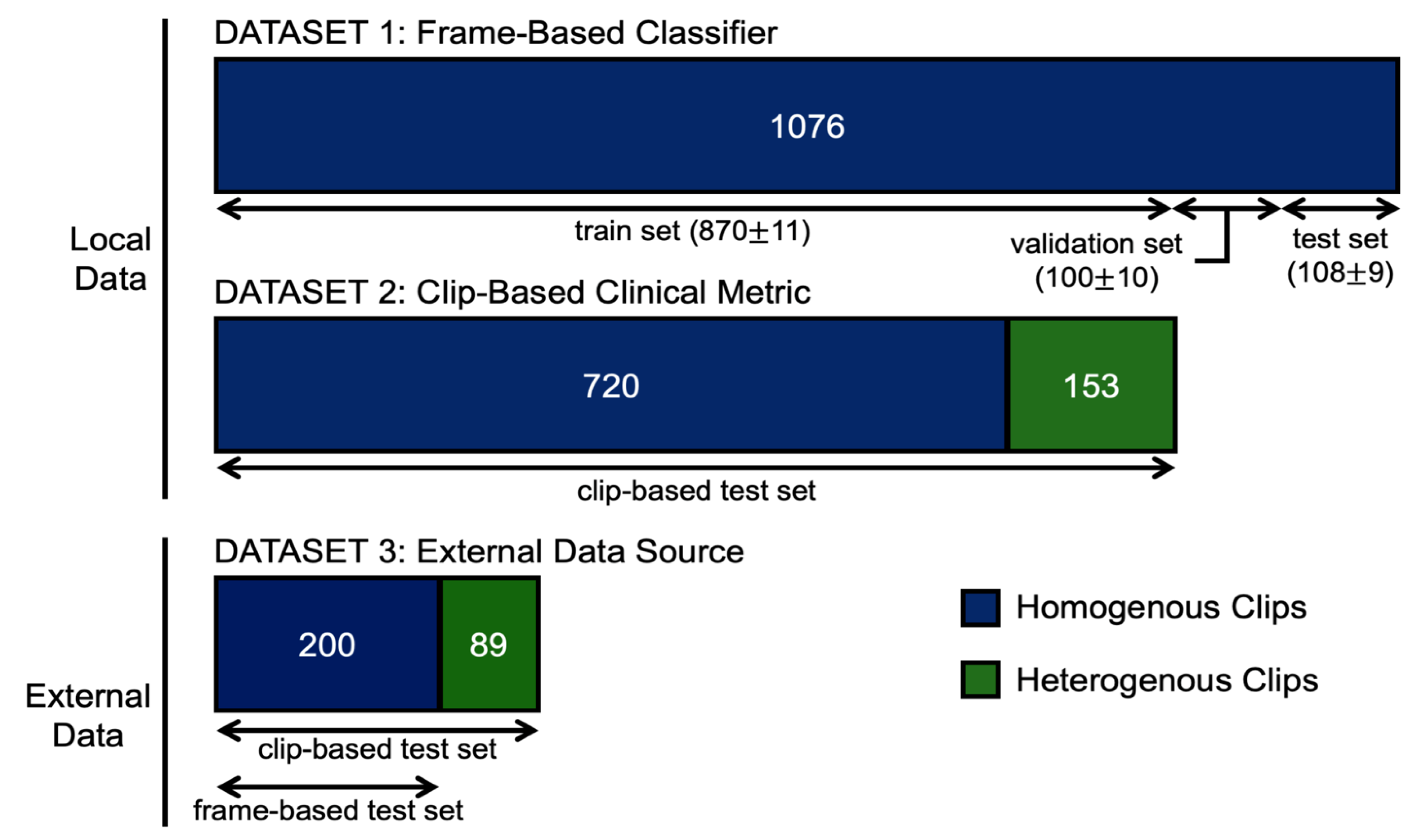
2.2.1. Frame-Based Data
2.2.2. Clip-Based Inference Data
2.2.3. Dataset Split
2.2.4. Data Preprocessing
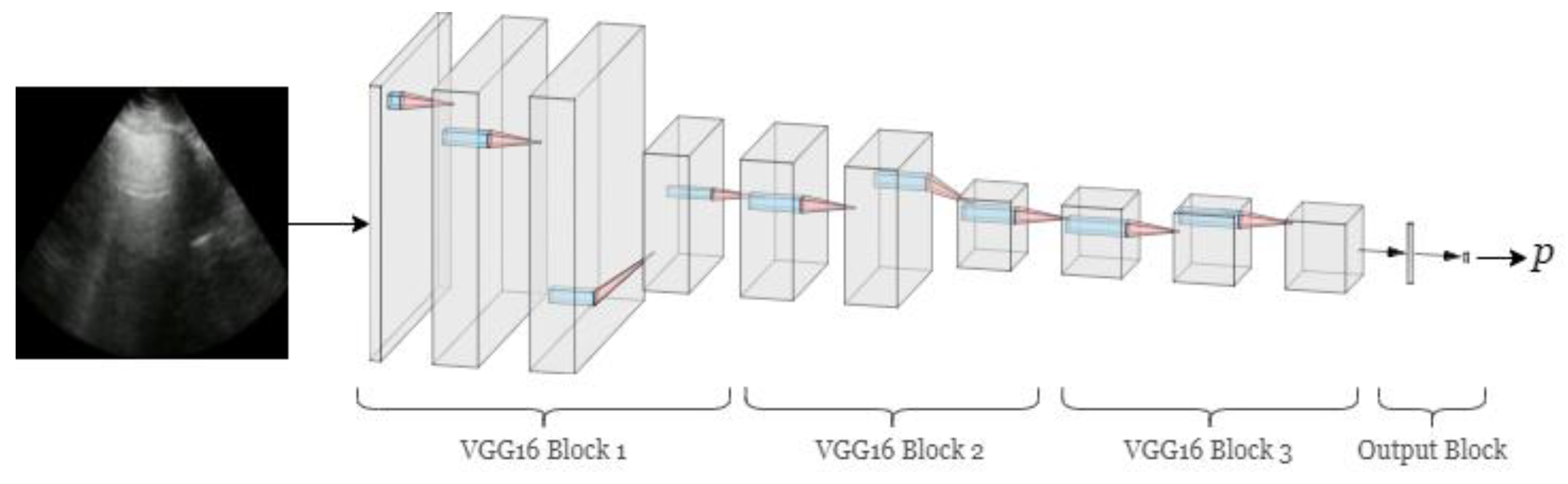
2.3. Frame-Based Deep Learning Classifier
Model Architecture
2.4. Clip-Based Clinical Metric
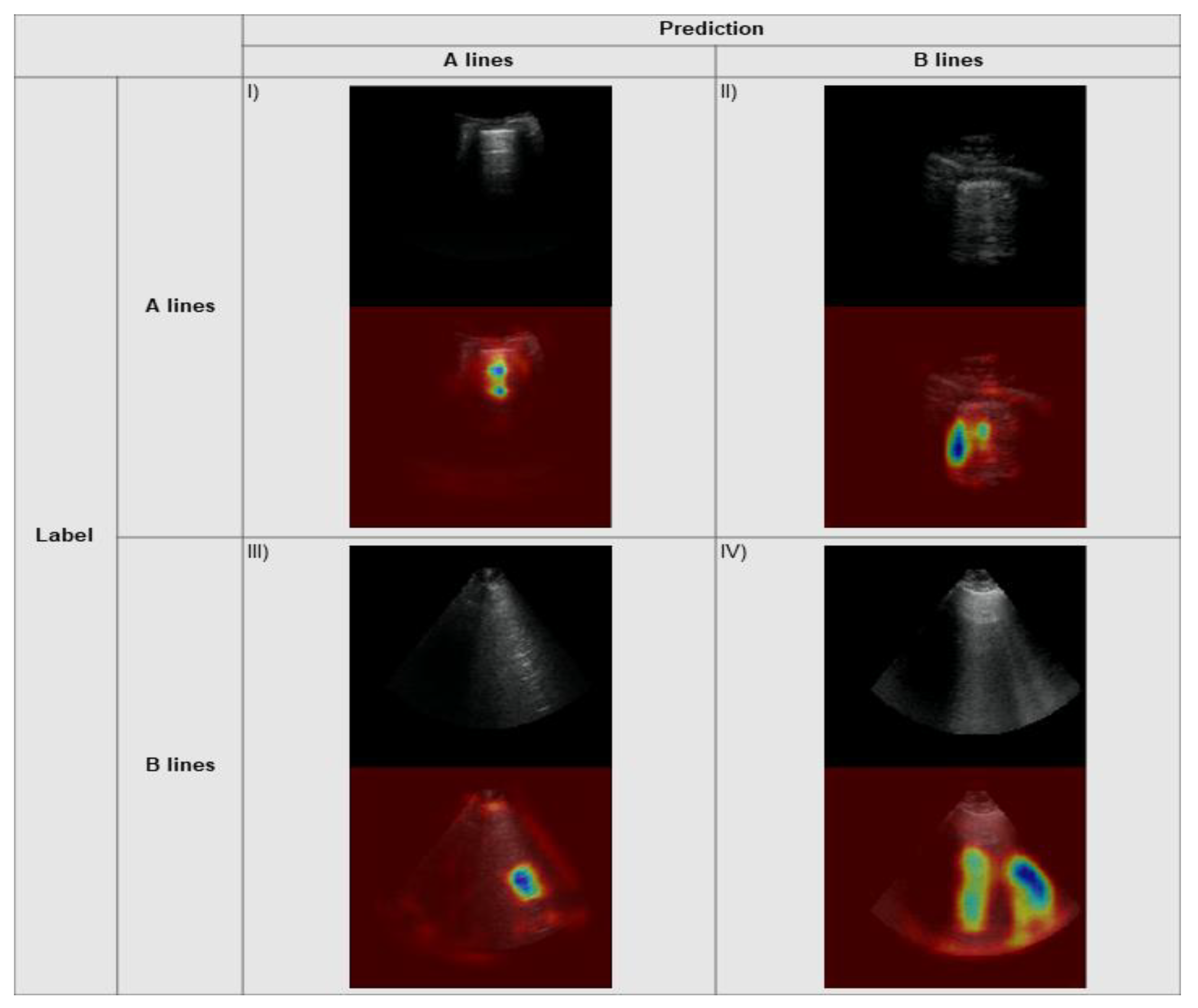
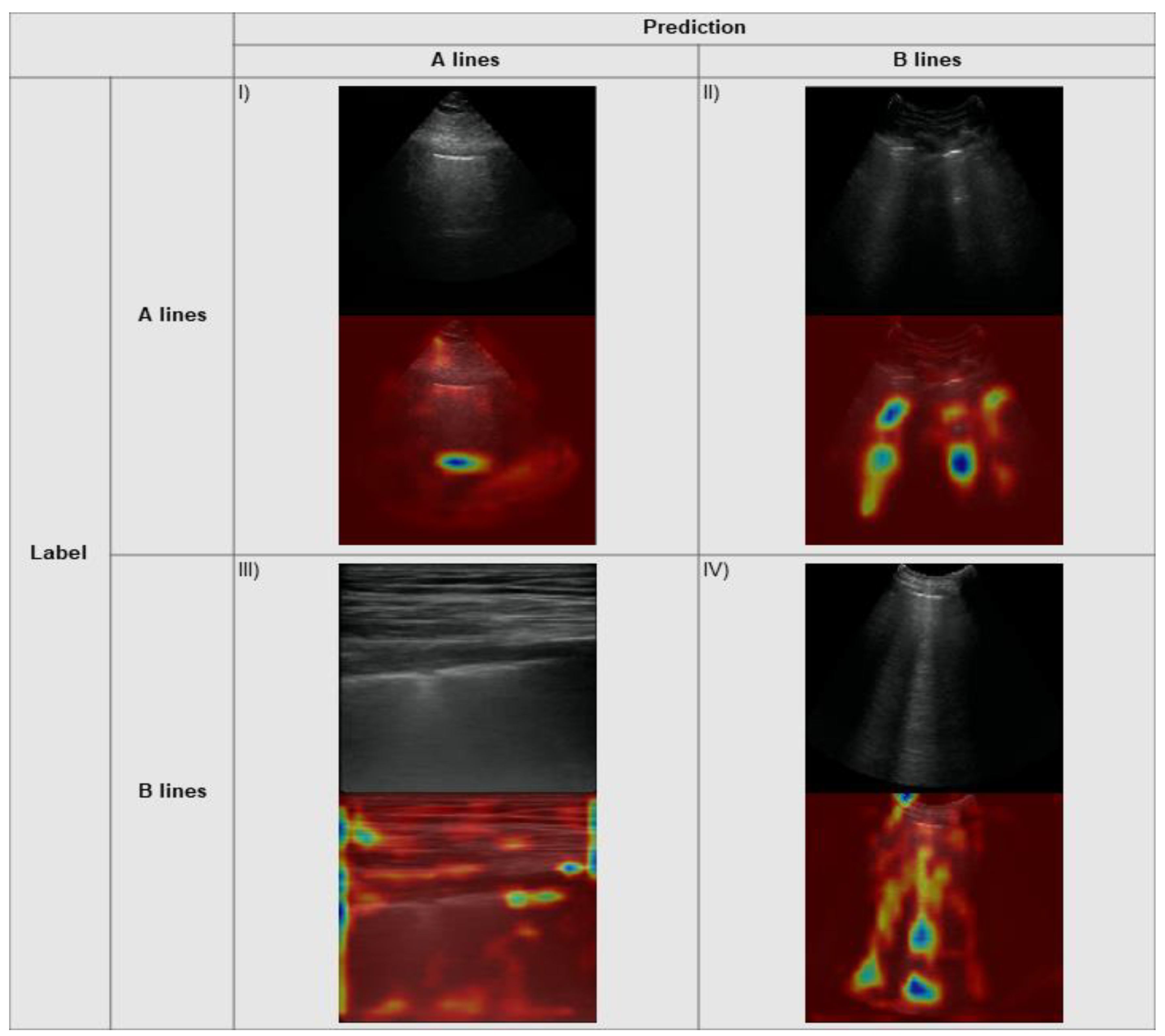
2.5. Explainability
3. Results
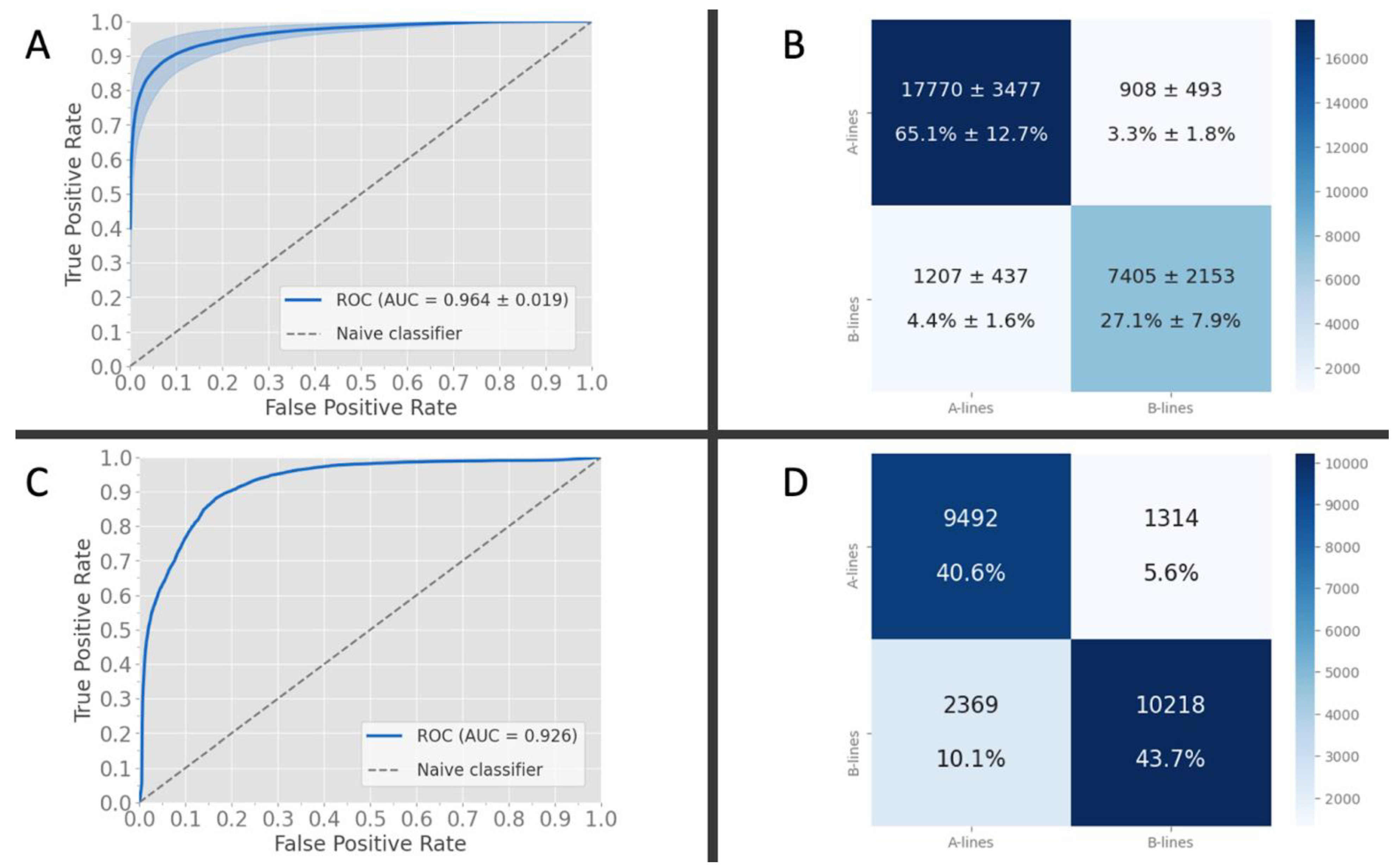
3.1. Frame-Based Performance and K-Fold Cross-Validation
3.2. Frame-Based Performance on External Data
3.3. Explainability
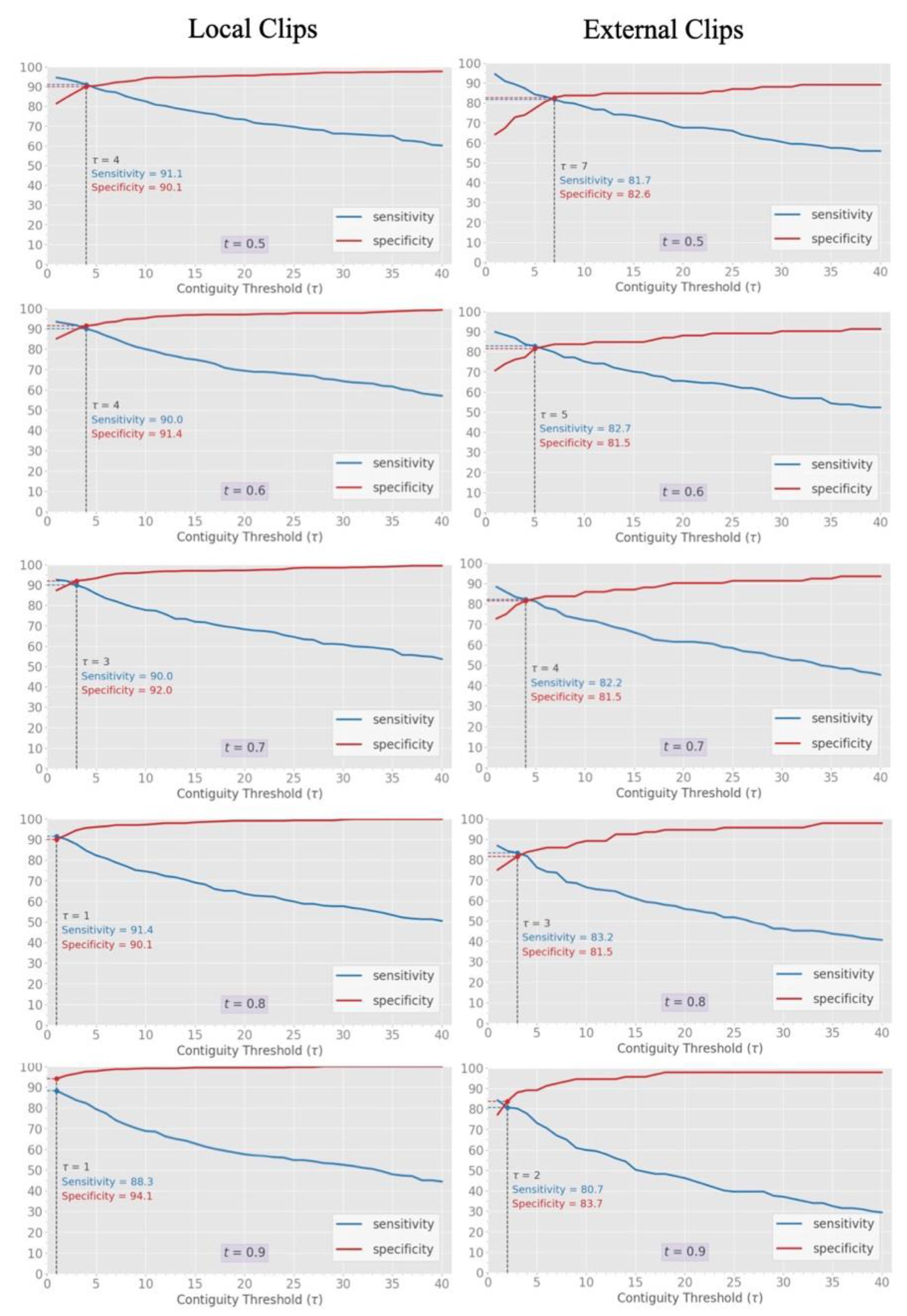
3.4. Clip-Based Clinical Metric
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiumello, D.; Umbrello, M.; Sferrazza Papa, G.F.; Angileri, A.; Gurgitano, M.; Formenti, P.; Coppola, S.; Froio, S.; Cammaroto, A.; Carrafiello, G. Global and Regional Diagnostic Accuracy of Lung Ultrasound Compared to CT in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazerian, P.; Volpicelli, G.; Vanni, S.; Gigli, C.; Betti, L.; Bartolucci, M.; Zanobetti, M.; Ermini, F.R.; Iannello, C.; Grifoni, S. Accuracy of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of consolidations when compared to chest computed tomography. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haak, S.L.; Renken, I.J.; Jager, L.C.; Lameijer, H.; van der Kolk, B.B.Y. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care lung ultrasound in COVID-19. Emerg. Med. J. 2021, 38, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mezière, G.A. Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure the BLUE protocol. Chest 2008, 134, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sargsyan, A.E.; Hamilton, D.R.; Jones, J.A.; Melton, S.; Whitson, P.A.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Martin, D.; Dulchavsky, S.A. FAST at MACH 20: Clinical ultrasound aboard the International Space Station. J. Trauma 2005, 58, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsup, C.; Lipman, G.S.; Pomeranz, D.; Huang, R.-W.; Burns, P.; Juul, N.; Phillips, C.; Jurkiewicz, C.; Cheffers, M.; Evans, K.; et al. Interstitial pulmonary edema assessed by lung ultrasound on ascent to high altitude and slight association with acute mountain sickness: A prospective observational study. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2019, 20, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanyan, P.; Kerobyan, V.; Shankar-Aguilera, S.; Yousef, N.; De Luca, D. Introduction of point-of-care neonatal lung ultrasound in a developing country. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Pata, D.; Chiaretti, A. COVID-19 outbreak: Less stethoscope, more ultrasound. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisen, L.A.; Leung, S.; Gallagher, A.E.; Kvetan, V. Barriers to ultrasound training in critical care medicine fellowships: A survey of program directors. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 1978–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, J.; Montague, S.; Wallace, P.; Negishi, K.; Liteplo, A.; Ringrose, J.; Dversdal, R.; Buchanan, B.; Desy, J.; Ma, I.W.Y. Barriers to learning and using point-of-care ultrasound: A survey of practicing internists in six North American institutions. Ultrasound J. 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brady, A.K.; Spitzer, C.R.; Kelm, D.; Brosnahan, S.B.; Latifi, M.; Burkart, K.M. Pulmonary Critical Care Fellows’ Use of and Self-reported Barriers to Learning Bedside Ultrasound During Training: Results of a National Survey. Chest 2021, 160, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendram, R.; Souleymane, M.; Mahmood, N.; Kharal, M.; AlQahtani, M. Point-of-care diagnostic lung ultrasound is highly applicable to the practice of medicine in Saudi Arabia but the current skills gap limits its use. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2021, 16, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulshan, V.; Peng, L.; Coram, M.; Stumpe, M.C.; Wu, D.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Widner, K.; Madams, T.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 316, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gajjala, S.; Agrawal, P.; Tison, G.H.; Hallock, L.A.; Beussink-Nelson, L.; Lassen, M.H.; Fan, E.; Aras, M.A.; Jordan, C.; et al. Fully Automated Echocardiogram Interpretation in Clinical Practice. Circulation 2018, 138, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Distinguishes COVID-19 from Community Acquired Pneumonia on Chest CT. Radiology 2020, 296, E65–E71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Wu, M.-T.; Garcia-Castro, F.; Alberich-Bayarri, A.; Wu, F.-Z. Identifying pulmonary nodules or masses on chest radiography using deep learning: External validation and strategies to improve clinical practice. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, R.; Sounderajah, V.; Martin, G.; Ting, D.S.W.; Karthikesalingam, A.; King, D.; Ashrafian, H.; Darzi, A. Diagnostic accuracy of deep learning in medical imaging: A systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mento, F.; Perrone, T.; Fiengo, A.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L. Deep learning applied to lung ultrasound videos for scoring COVID-19 patients: A multicenter study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arntfield, R.; VanBerlo, B.; Alaifan, T.; Phelps, N.; White, M.; Chaudhary, R.; Ho, J.; Wu, D. Development of a convolutional neural network to differentiate among the etiology of similar appearing pathological B lines on lung ultrasound: A deep learning study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Menapace, W.; Oei, S.; Luijten, B.; Fini, E.; Saltori, C.; Huijben, I.; Chennakeshava, N.; Mento, F.; Sentelli, A.; et al. Deep learning for classification and localization of COVID-19 markers in point-of-care lung ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sloun, R.J.G.; Demi, L. Localizing B-lines in lung ultrasonography by weakly supervised deep learning, in-vivo results. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshavegh, R.; Hansen, K.L.; Moller-Sorensen, H.; Nielsen, M.B.; Jensen, J.A. Automatic Detection of B-Lines in In Vivo Lung Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2019, 66, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mezière, G.A.; Lagoueyte, J.-F.; Biderman, P.; Goldstein, I.; Gepner, A. A-lines and B-lines: Lung ultrasound as a bedside tool for predicting pulmonary artery occlusion pressure in the critically ill. Chest 2009, 136, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Mézière, M.; Philippe, B.; Agnès, G.; Olivier, B. The Comet-tail Artifact An Ultrasound Sign of Alveolar-Interstitial Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivel, V.; Lesnewski, A.; Shamim, S.; Carbonatto, G.; Govindan, T. CLUE: COVID-19 lung ultrasound in emergency department. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2020, 32, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Mathis, G.; Blaivas, M.; Volpicelli, G.; Seibel, A.; Wastl, D.; Atkinson, N.S.S.; Cui, X.-W.; Fan, M.; Yi, D. Lung B-line artefacts and their use. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas-Lasarte, M.; Álvarez-García, J.; Fernández-Martínez, J.; Maestro, A.; López-López, L.; Solé-González, E.; Pirla, M.J.; Mesado, N.; Mirabet, S.; Fluvià, P.; et al. Lung ultrasound-guided treatment in ambulatory patients with heart failure: A randomized controlled clinical trial (LUS-HF study). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araiza-Garaygordobil, D.; Gopar-Nieto, R.; Martinez-Amezcua, P.; Cabello-López, A.; Alanis-Estrada, G.; Luna-Herbert, A.; González-Pacheco, H.; Paredes-Paucar, C.P.; Sierra-Lara, M.D.; Briseño-De la Cruz, J.L.; et al. A randomized controlled trial of lung ultrasound-guided therapy in heart failure (CLUSTER-HF study). Am. Heart J. 2020, 227, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta, I.; Mustafa, R.A.; Kansagara, D.; Fitterman, N.; Wilt, T.J.; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians; Batur, P.; Cooney, T.G.; Crandall, C.J.; et al. Appropriate Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Patients with Acute Dyspnea in Emergency Department or Inpatient Settings: A Clinical Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byra, M.; Styczynski, G.; Szmigielski, C.; Kalinowski, P.; Michałowski, Ł.; Paluszkiewicz, R.; Ziarkiewicz-Wróblewska, B.; Zieniewicz, K.; Sobieraj, P.; Nowicki, A. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for liver steatosis assessment in ultrasound images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Power, M.; Fell, G.; Wright, M. Principles for high-quality, high-value testing. Evid. Based Med. 2013, 18, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119536611. [Google Scholar]
- Longoni, C.; Bonezzi, A.; Morewedge, C.K. Resistance to Medical Artificial Intelligence. J. Consum. Res. 2019, 46, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Lavin, P.T.; Birch, M.; Shah, N.; Folk, J.C. Pivotal trial of an autonomous AI-based diagnostic system for detection of diabetic retinopathy in primary care offices. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDx Autonomous AI Diagnostics Launch in Retail Health Clinics. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/autonomous-ai-diagnostics-launch-in-retail-health-clinics-300961103.html (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Diagnostic Imaging Dataset Annual Statistical Release 2019/20; NHS: London, UK, 2020.
- Caption Health Secures NTAP Authorization from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services for AI-Guided Ultrasound Platform. Available online: https://captionhealth.com/press/caption-health-secures-ntap-authorization-from-centers-for-medicare-and-medicaid-services-for-ai-guided-ultrasound-platform/ (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; et al. Proposal for International Standardization of the Use of Lung Ultrasound for Patients With COVID-19: A Simple, Quantitative, Reproducible Method. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1413–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narang, A.; Bae, R.; Hong, H.; Thomas, Y.; Surette, S.; Cadieu, C.; Chaudhry, A.; Martin, R.P.; McCarthy, P.M.; Rubenson, D.S.; et al. Utility of a Deep-Learning Algorithm to Guide Novices to Acquire Echocardiograms for Limited Diagnostic Use. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, P. Wavebase—Ultrasound Unlocked. Available online: https://www.wavebase.ai/ (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Cristiana, B.; Grzegorz, T.; Seungsoo, K.; Katelyn, M.; Rachel, L.; Shaw, M.; McNamara, R.L.; Balasundar, R.; Moore, C.L. Automated Lung Ultrasound B-line Assessment Using a Deep Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemink, M.J.; Koszek, W.A.; Hardell, C.; Wu, J.; Fleischmann, D.; Harvey, H.; Folio, L.R.; Summers, R.M.; Rubin, D.L.; Lungren, M.P. Preparing Medical Imaging Data for Machine Learning. Radiology 2020, 295, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Full Page Reload. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/view-from-the-valley/artificial-intelligence/machine-learning/andrew-ng-xrays-the-ai-hype (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Winkler, J.K.; Fink, C.; Toberer, F.; Enk, A.; Deinlein, T.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Thomas, L.; Lallas, A.; Blum, A.; Stolz, W.; et al. Association Between Surgical Skin Markings in Dermoscopic Images and Diagnostic Performance of a Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network for Melanoma Recognition. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Local Data | External Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clip Label | A lines (normal class) | B lines (abnormal class) | A lines (normal class) | B lines (abnormal class) |
| Patients | 253 | 155 | 40 | 32 |
| Frames | 186,772 | 86,119 | 10,806 | 12,587 |
| # of clips | 723 | 353 | 92 | 108 |
| Average clips per patient | 2.86 | 2.28 | 2.3 | 3.375 |
| Female sex/total | 84/253 | 66/155 | 12/40 | 8/32 |
| Unknown gender | 19 | 7 | 6 | 8 |
| Mean age (STD) | 63.23 (17.17) | 66.76 (16.11) | 62.26 (16.72) | 66.5 (11.51) |
| Machine Vendors | Sonosite: 721 Mindray: 2 | Sonosite: 353 | Philips: 62 SonoSite: 30 | Philips: 37 SonoSite: 71 |
| Transducers | Phased array: 596 Curved linear: 119 Linear: 8 | Phased array: 319 Curved linear: 30 Linear: 4 | Phased array: 46 Curved linear: 22 Linear: 24 | Phased array: 66 Curved linear: 23 Linear: 19 |
| Imaging Preset | Abdominal: 671 Lung: 33 Vascular: 4 Cardiac: 15 | Abdominal: 309 Lung: 20 Cardiac: 14 Obstetrical: 7 Other: 3 | Abdominal: 10 Lung: 35 Cardiac: 26 Nerve: 8 FAST: 7 Vascular: 6 | Abdominal: 11 Lung: 20 Cardiac: 55 Nerve:1 FAST: 4 Superficial: 3 Vascular: 14 |
| Location (by patient) | ICU: 166 ED: 82 Ward: 5 | ICU: 124 ED: 26 Ward: 5 | ICU: 21 ED: 14 Ward: 5 | ICU: 19 ED: 6 Ward: 7 |
| Depth (STD, cm) | 11.56 (3.48) | 12.50 (3.43) | 11.28 (4.64) | 11.13 (3.88) |
| Local Data | External Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clip Label | A lines (normal class) | B lines (abnormal class) | A lines (normal class) | B lines (abnormal class) |
| Patients | 156 | 120 | 40 | 49 |
| Clips | 523 | 350 | 92 | 197 |
| Average clips per patient | 2.35 | 1.92 | 2.30 | 4.02 |
| Heterogeneous | 153/873 | 89/289 | ||
| Female sex/total | 96/151 | 55/118 | 13/40 | 16/49 |
| Unknown gender | 5 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| Mean age (STD) | 59.92 (17.19) | 64.19 (16.84) | 62.51 (16.54) | 65.29 (13.65) |
| Machine Vendors | SonoSite: 516 Mindray: 4 Philips: 3 | SonoSite: 349 Philips: 1 | Philips: 62 Sonosite: 30 | Philips: 90 Sonosite: 107 |
| Transducers | Phased array: 448 Curved linear: 67 Linear: 8 | Phased array: 308 Curved linear: 33 Linear: 9 | Phased array: 46 Curved linear: 22 Linear: 24 | Phased array:127 Curved linear:43 Linear: 27 |
| Imaging preset | Abdominal: 463 Cardiac: 21 Lung: 33 MSK: 1 Vascular: 6 | Abdominal: 312 Cardiac: 11 Lung: 25 Vascular: 2 | Abdominal: 10 Cardiac: 26 FAST: 7 Lung: 35 Nerve: 8 Vascular: 6 | Abdominal: 25 Cardiac: 96 FAST: 7 Lung: 46 Nerve: 5 Superficial: 4 Vascular: 14 |
| Location (by patient) | ICU: 100 ED: 46 Ward: 10 | ICU: 88 ED: 24 Ward: 8 | ICU: 21 ED: 14 Ward: 5 | ICU: 28 ED: 13 Ward: 8 |
| Depth (STD, cm) | 11.77 (3.48) | 12.66 (3.47) | 11.28 (4.64) | 11.83 (4.02) |
| Class | Train | Validation | Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Clips | Frames | Patients | Clips | Frames | Patients | Clips | Frames | |
| A-Lines | 202.1 (2.85) | 575.4 (11.37) | 147,880.8 (2814.89) | 25.6 (2.07) | 75.3 (9.29) | 20,214 (2531.16) | 25.3 (2.98) | 72.3 (10.54) | 18,677.22 (3345.67) |
| B-Lines | 127.2 (3.48) | 294.4 (12.48) | 71,675.3 (3253.45) | 12.3 (1.57) | 24.2 (5.73) | 5831.8 (1579.64) | 15.5 (3.06) | 35.4 (9.85) | 8611.9 (2511.11) |
| Data Source | Metric | Accuracy | AUC | Precision | Recall/ Sensitivity | F1 Score | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Mean | 0.921 (SD 0.034) | 0.964 (SD 0.964) | 0.891 (SD 0.047) | 0.858 (SD 0.05) | 0.874 (SD 0.044) | 0.947 (SD 0.036) |
| External | Value | 0.843 | 0.926 | 0.886 | 0.812 | 0.847 | 0.878 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arntfield, R.; Wu, D.; Tschirhart, J.; VanBerlo, B.; Ford, A.; Ho, J.; McCauley, J.; Wu, B.; Deglint, J.; Chaudhary, R.; et al. Automation of Lung Ultrasound Interpretation via Deep Learning for the Classification of Normal versus Abnormal Lung Parenchyma: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112049
Arntfield R, Wu D, Tschirhart J, VanBerlo B, Ford A, Ho J, McCauley J, Wu B, Deglint J, Chaudhary R, et al. Automation of Lung Ultrasound Interpretation via Deep Learning for the Classification of Normal versus Abnormal Lung Parenchyma: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112049
Chicago/Turabian StyleArntfield, Robert, Derek Wu, Jared Tschirhart, Blake VanBerlo, Alex Ford, Jordan Ho, Joseph McCauley, Benjamin Wu, Jason Deglint, Rushil Chaudhary, and et al. 2021. "Automation of Lung Ultrasound Interpretation via Deep Learning for the Classification of Normal versus Abnormal Lung Parenchyma: A Multicenter Study" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112049
APA StyleArntfield, R., Wu, D., Tschirhart, J., VanBerlo, B., Ford, A., Ho, J., McCauley, J., Wu, B., Deglint, J., Chaudhary, R., Dave, C., VanBerlo, B., Basmaji, J., & Millington, S. (2021). Automation of Lung Ultrasound Interpretation via Deep Learning for the Classification of Normal versus Abnormal Lung Parenchyma: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112049






