Dominating Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension May Change Over Time—Diagnostic and Therapeutic Considerations in a Patient with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Rheumatoid Arthritis with Lung Involvement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
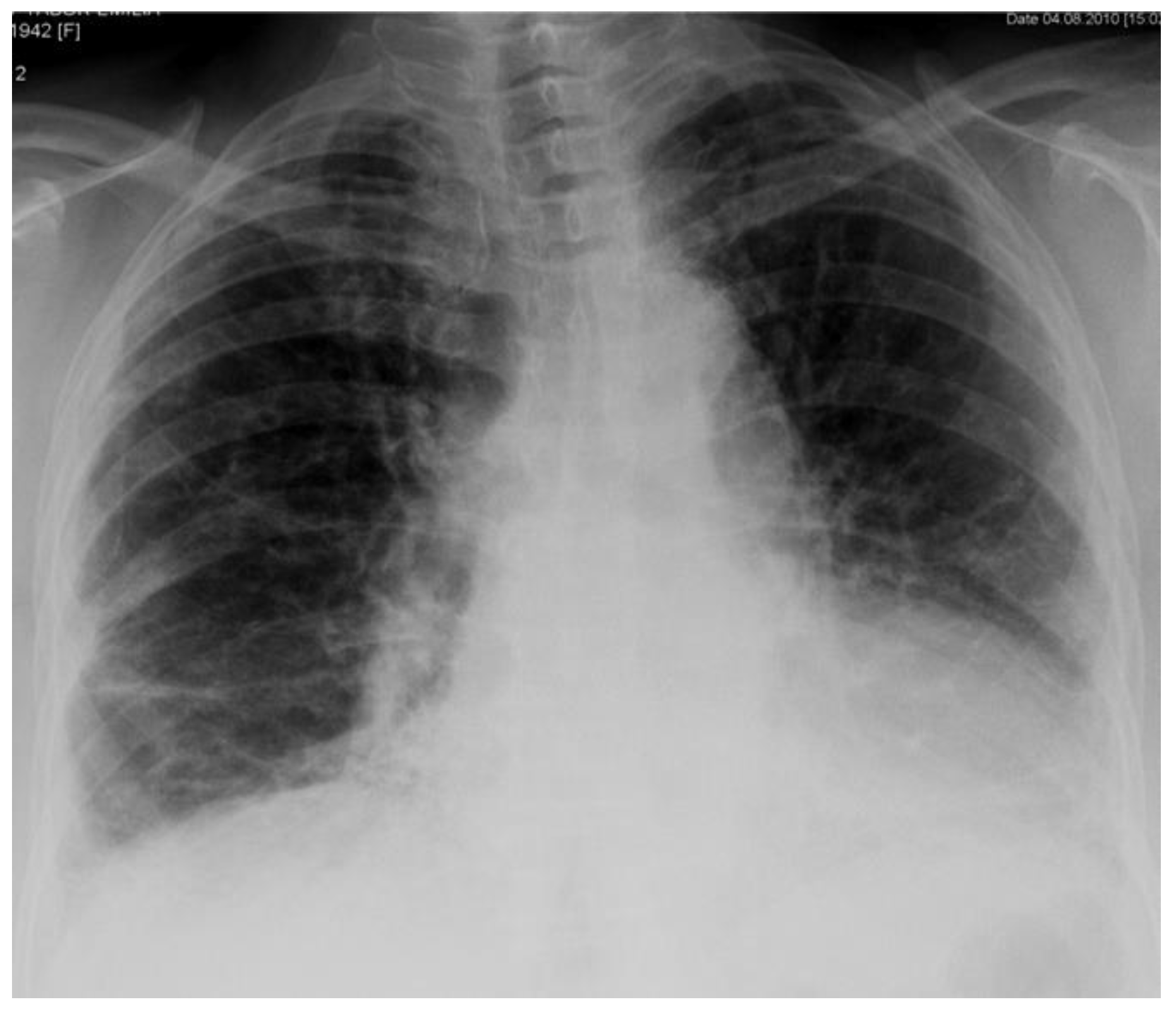
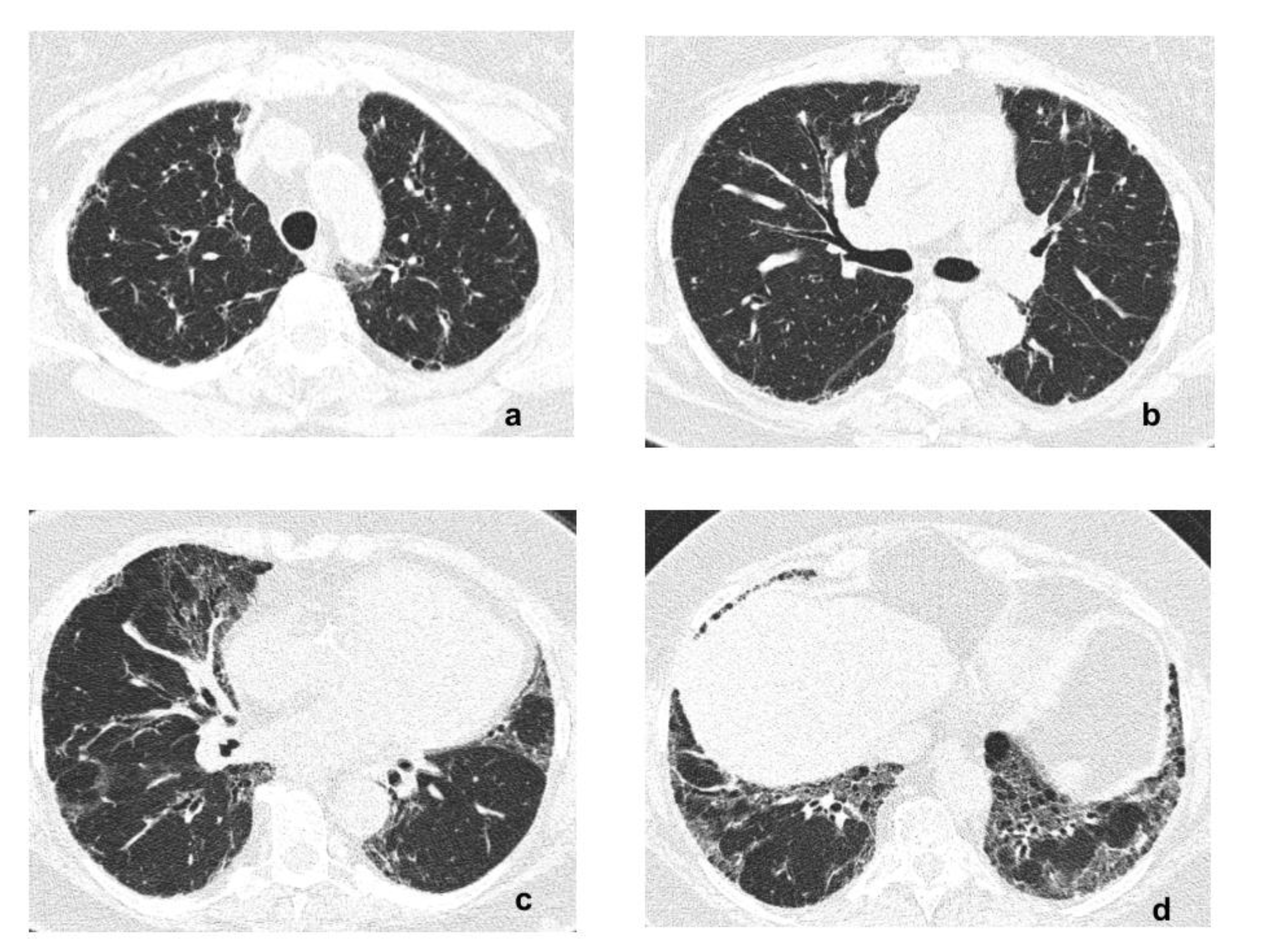
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gazoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, H.; Coglan, J.G. Pulmonary hypertension associated with connective tissue disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweik, R.A.; Rounds, S.; Erzurum, S.C.; Archer, S.; Fagan, K.; Hassoun, P.M.; Hill, N.S.; Humbert, M.; Kawut, S.M.; Krowka, M.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society statement: Pulmonary hypertension phenotypes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olschewski, H. The challenge to decide between pulmonary hypertension due to chronic lung disease and PAH with chronic lung disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Barbera, J.A.; Gaine, S.P.; Harari, S.; Martinez, F.J.; Olschewski, H.; Olsson, K.M.; Peacock, A.J.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Provencher, S.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung disease and hypoxia. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, A.; Cosgrove, G.P. Interstitial lung abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis are common and important. Chest 2014, 146, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathai, S.C.; Danoff, S.K. Management of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. Brit. Med. J. 2016, 352, h6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancio, N.; Pavone, M.; Torrisi, S.E.; Vanchieri, A.; Sambataro, D.; Palmucci, S.; Vanchieri, C.; Di Marco, F.; Sambataro, G. Contribution of pulmonary function tests (PFTs) to the diagnosis and follow up of connective tissue diseases. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2019, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, M.; Collins, B.F.; Ho, L.A.; Rhagu, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matson, S.; Lee, J.; Eickelberg, O. Two sides of the same coin? A review of the similarities and differences between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, G.C.; Doyle, T.J.; Sparks, J.A. Interstitial lung disease throughout the rheumatoid arthritis disease course. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, T.J.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Batra, K.; Frits, M.L.; Iannaccone, C.K.; Hatabu, H.; Nishino, M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Asherman, D.P.; Washko, G.R.; et al. Functional impact of a spectrum of interstitial lung abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Chest 2014, 146, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopeć, G.; Kurzyna, M.; Mroczek, E.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Mularek-Kubzdela, T.; Skoczylas, I.; Kuśmierczyk, B.; Pruszczyk, P.; Błaszczak, P.; Lewicka, E.; et al. Characterization of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: Data from Polish Registry of Pulmonary Hypertension (BNP-PL). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panagiotidou, E.; Sourla, E.; Kotoulas, S.X.; Akritidou, S.; Bikos, V.; Bagalas, V.; Stanopoulos, I.; Pitsiou, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated pulmonary hypertension: Clinical challenges reflecting the diversity of pathophysiology. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 20, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, N.S.; Desai, S.R.; Veeraraghavan, S.; Hansell, D.M.; Copley, S.J.; Maher, T.M.; Corte, T.J.; Sander, C.R.; Ratoff, J.; Devaraj, A.; et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: A simple staging system. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.H.; Wallace, W.D.; Nouraie, S.M.; Chan, S.Y.; Risbano, M.G. Lower DLCO% identifies exercise pulmonary hypertension in patients with parenchymal lung disease referred for dyspnoea. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhamad, E.H.; Cal, J.G.; Alrajhi, N.N.; Alharbi, W.M. Predictors of mortality in interstitial lung disease-associated pulmonary hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Kanwar, M.K.; Raina, A.; Scott, J.V.; Zhao, C.L.; Selej, M.; Elliot, G.; Farber, H.W. Development and validation of an abridged version of the REVEAL 2.0 risk score calculator, REVEAL Lite 2, for use in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2021, 159, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvelot, L.; Gamondes, D.; Berthiller, J.; Nieves, A.; Renard, S.; Catella-Chatron, J.; Ahmad, K.; Bertoletti, L.; Camara, B.; Gomez, E.; et al. Hemodynamic response to treatment and outcome in pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease versus pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. Arth. Rheum. 2020, 73, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.A.; Thompson, A.A.R.; Billings, C.G.; Charalampopoulos, A.; Elliot, C.A.; Hamilton, N.; Hill, C.; Hurdman, J.; Rajaram, S.; Sabroe, I.; et al. Mild parenchymal lung disease and/or low diffusion capacity impacts survival and treatment response in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, I.; Gimeno, E.; Munoz, P.A.; Pizarro, S.; Gistau, C.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; Roca, J.; Barbera, J.A. Hemodynamic and gas exchange effects of sildenafil in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisman, D.A.; Schwarz, M.; Anstrom, K.J.; Collard, H.R.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hunninghake, G.W. A controlled trial of sildenafil in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 620–628. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.K.; Bach, D.S.; Hagan, P.G.; Yow, E.; Flaherty, K.R.; Toews, G.B.; Anstrom, K.J.; Martinez, F.J.; IPFnet Investigators. Sildenafil preserves exercise capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and right-sided ventricular dysfunction. Chest 2013, 143, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Behr, J.; Held, M.; Grunig, E.; Vizza, C.D.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Lange, T.J.; Claussen, M.; Grohe, C.; Klose, H.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic fibrosing idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brewis, M.J.; Church, A.C.; Johnson, M.K.; Peacock, A.J. Severe pulmonary hypertension in lung disease: Phenotypes and response to treatment. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, N.; Kumamaru, H.; Tamura, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Emoto, N.; Yamada, Y.; Nishiyama, O.; Tsujino, I.; Kuraishi, H.; Nishimura, Y.; et al. Multi-institutional prospective cohort study of patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with respiratory diseases. Circ. J. 2021, 85, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxman, A.; Restrepo-Jaramillo, R.; Thenappan, T.; Ravichandran, A.; Engel, P.; Bajwa, A.; Allen, R.; Feldman, J.; Argula, R.; Smith, P.; et al. Inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter/Year of Assessment | 2010 | 2012 | 2016 | 2018 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLC% pred. VC% pred. TLCO% pred. | 53 58 39 | 71 73 56 | 77 76 41 | 79 81 61 | 86 79 58 |
| Resting SaO2% | 92 | 95 | 94 | 94 | 93 |
| NT-proBNP pg/mL | 72 | 56 | 340 | 116 | 77 |
| 6MWT (meters, desaturation%) | 346 92–82 | 588 95–86 | 460 94–89 | 414 97–91 | 442 95–89 |
| PASP mmHg Act ms | 44 67 | 35 100 | 65 68 | 39 81 | na na |
| Parameter/Year of Assessment | 2016 | 2018 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|
| mPAP (mmHg) | 42 | 23 | 29 |
| mRAP (mmHg) | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| PCWP (mmHg) | 10 | 9 | 11 |
| CI (L/min/m2) | 3.22 | 2.73 | 3.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szturmowicz, M.; Franczuk, M.; Jędrych, M.E.; Wyrostkiewicz, D.; Oniszh, K.; Darocha, S.; Kasperowicz, K.; Kurzyna, M. Dominating Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension May Change Over Time—Diagnostic and Therapeutic Considerations in a Patient with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Rheumatoid Arthritis with Lung Involvement. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101931
Szturmowicz M, Franczuk M, Jędrych ME, Wyrostkiewicz D, Oniszh K, Darocha S, Kasperowicz K, Kurzyna M. Dominating Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension May Change Over Time—Diagnostic and Therapeutic Considerations in a Patient with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Rheumatoid Arthritis with Lung Involvement. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(10):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101931
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzturmowicz, Monika, Monika Franczuk, Małgorzata Ewa Jędrych, Dorota Wyrostkiewicz, Karina Oniszh, Szymon Darocha, Krzysztof Kasperowicz, and Marcin Kurzyna. 2021. "Dominating Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension May Change Over Time—Diagnostic and Therapeutic Considerations in a Patient with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Rheumatoid Arthritis with Lung Involvement" Diagnostics 11, no. 10: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101931
APA StyleSzturmowicz, M., Franczuk, M., Jędrych, M. E., Wyrostkiewicz, D., Oniszh, K., Darocha, S., Kasperowicz, K., & Kurzyna, M. (2021). Dominating Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension May Change Over Time—Diagnostic and Therapeutic Considerations in a Patient with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Rheumatoid Arthritis with Lung Involvement. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101931









