Factors Affecting Route Selection of Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy in Patients with Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A KASID Multicenter Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
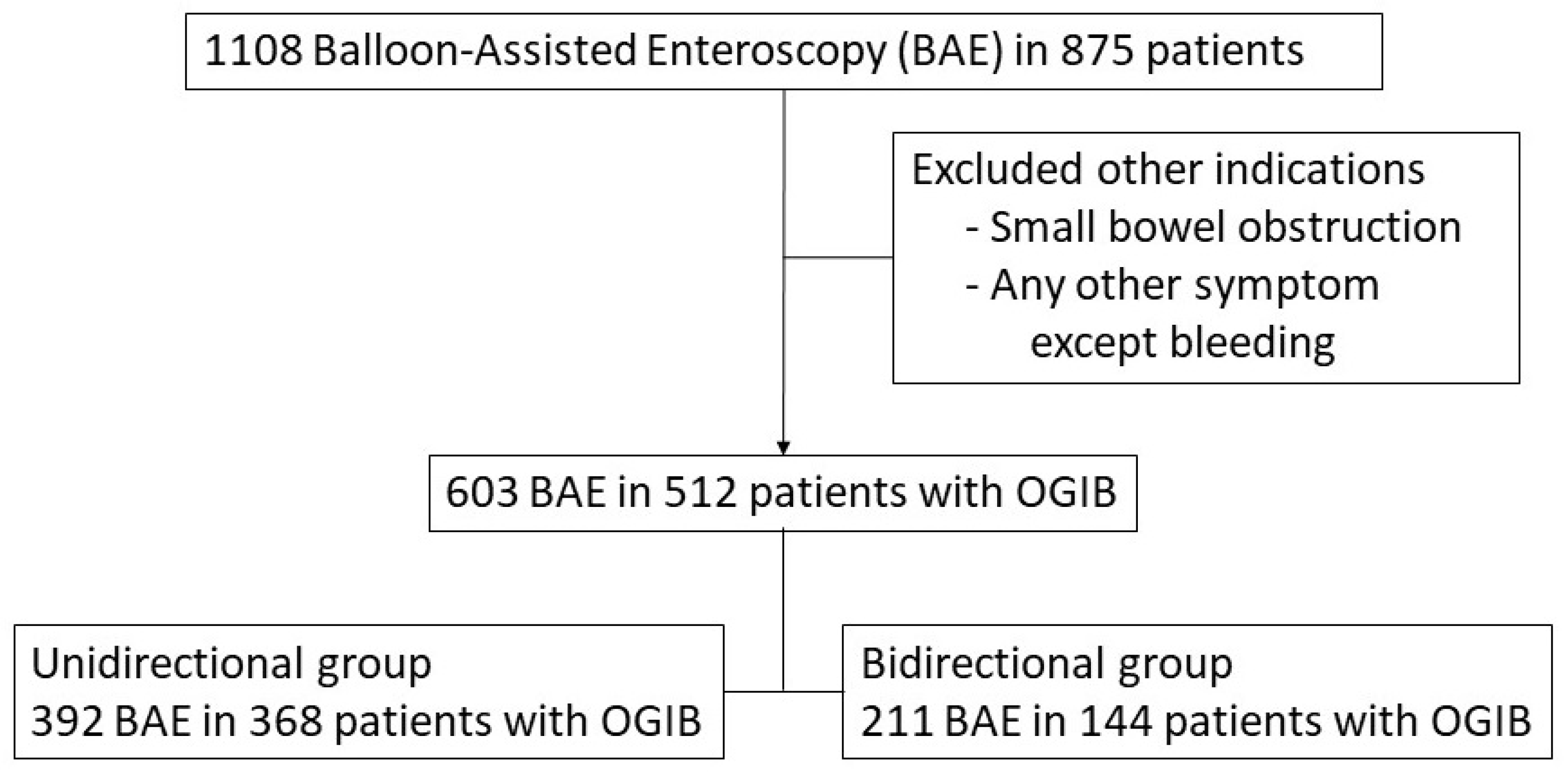
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. BAE
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Subjects
3.2. Diagnostic Modalities
3.3. Factors Associated with the Bidirectional Approach
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gralnek, I.M. Obscure-overt gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, L.B.; Fidler, J.L.; Cave, D.R.; Leighton, J.A. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Small Bowel Bleeding. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1265–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longstreth, G.F. Epidemiology and outcome of patients hospitalized with acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage: A population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pennazio, M.; Spada, C.; Eliakim, R.; Keuchel, M.; May, A.; Mulder, C.J.; Rondonotti, E.; Adler, S.N.; Albert, J.; Baltes, P.; et al. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy and device-assisted enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small-bowel disorders: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 352–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Ogata, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Ohmiya, N.; Ohtsuka, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yano, T.; Matsui, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Enteroscopy. Dig. Endosc. Off. J. Jpn. Gastroenterol. Endosc. Soc. 2017, 29, 519–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.N.; Moon, J.S.; Chang, D.K.; Do, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.H.; Jeon, S.R.; Kim, J.O.; Choi, M.G. Guideline for capsule endoscopy: Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin. Endosc. 2013, 46, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Sekine, Y.; Sato, Y.; Higashizawa, T.; Miyata, T.; Iino, S.; Ido, K.; Sugano, K. Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 53, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujikawa, T.; Saitoh, Y.; Andoh, A.; Imaeda, H.; Hata, K.; Minematsu, H.; Senoh, K.; Hayafuji, K.; Ogawa, A.; Nakahara, T.; et al. Novel single-balloon enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of the small intestine: Preliminary experiences. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerman, P.A.; Agrawal, D.; Cantero, D.; Pangtay, J. Spiral enteroscopy with the new DSB overtube: A novel technique for deep peroral small-bowel intubation. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Bamba, S.; Inatomi, O.; Takahashi, K.; Imai, T.; Murata, M.; Ohno, M.; Sasaki, M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Andoh, A. Prototype single-balloon enteroscopy with passive bending and high force transmission improves depth of insertion in the small intestine. Intest. Res. 2020, 18, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Liao, Z.; Jiang, Y.P.; Li, Z.S. Indications, detectability, positive findings, total enteroscopy, and complications of diagnostic double-balloon endoscopy: A systematic review of data over the first decade of use. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.A.; Stark, M.E. Initial experience with double-balloon enteroscopy at a U.S. center. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Nachbar, L.; Ell, C. Double-balloon enteroscopy (push-and-pull enteroscopy) of the small bowel: Feasibility and diagnostic and therapeutic yield in patients with suspected small bowel disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 62, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kita, H.; Sunada, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Sato, H.; Yano, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Sekine, Y.; Miyata, T.; Kuno, A.; et al. Clinical outcomes of double-balloon endoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of small-intestinal diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 2, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, L.; Lee Krinsky, M.; Anderson, M.A.; Appalaneni, V.; Banerjee, S.; Ben-Menachem, T.; Cash, B.D.; Decker, G.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Friis, C.; et al. The role of endoscopy in the management of obscure GI bleeding. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aniwan, S.; Viriyautsahakul, V.; Rerknimitr, R.; Angsuwatcharakon, P.; Kongkam, P.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Kullavanijaya, P. Urgent double balloon endoscopy provides higher yields than non-urgent double balloon endoscopy in overt obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Endosc. Int. Open 2014, 2, E90–E95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohmiya, N.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Tahara, T.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, M.; Hirooka, Y.; Goto, H.; Hirata, I. Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: Diagnosis and treatment. Dig. Endosc. Off. J. Jpn. Gastroenterol. Endosc. Soc. 2015, 27, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya, N. Management of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: Comparison of guidelines between Japan and other countries. Dig. Endosc. Off. J. Jpn. Gastroenterol. Endosc. Soc. 2020, 32, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Huang, L.Y.; Wu, C.R. Small intestinal vascular malformation bleeding: Diagnosis by double-balloon enteroscopy combined with abdominal contrast-enhanced CT examination. Abdom. Imaging 2012, 37, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakamura, M.; Ohmiya, N.; Shirai, O.; Takenaka, H.; Morishima, K.; Miyahara, R.; Ando, T.; Watanabe, O.; Kawashima, H.; Itoh, A.; et al. Route selection for double-balloon endoscopy, based on capsule transit time, in obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, G.; Delvaux, M.; Fassler, I. Outcome of capsule endoscopy in determining indication and route for push-and-pull enteroscopy. Endoscopy 2006, 38, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondonotti, E.; Pennazio, M.; Toth, E.; Menchen, P.; Riccioni, M.E.; De Palma, G.D.; Scotto, F.; De Looze, D.; Pachofsky, T.; Tacheci, I.; et al. Small-bowel neoplasms in patients undergoing video capsule endoscopy: A multicenter European study. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triester, S.L.; Leighton, J.A.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Fleischer, D.E.; Hara, A.K.; Heigh, R.I.; Shiff, A.D.; Sharma, V.K. A meta-analysis of the yield of capsule endoscopy compared to other diagnostic modalities in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighton, J.A.; Triester, S.L.; Sharma, V.K. Capsule endoscopy: A meta-analysis for use with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding and Crohn’s disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 16, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutter, M.; Dunston, D.; Ieyoub, J.; Hart, A.t.; Harper, J.; Burke, M.S. A retrospective analysis comparing small bowel follow-through with wireless capsule endoscopy in the evaluation of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2010, 33, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, A.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Jennings, S.G.; Maglinte, D.D.; McHenry, L.; Lappas, J.C.; Rex, D. Comparison of capsule endoscopy with enteroclysis in the investigation of small bowel disease. Abdom. Imaging 2009, 34, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Total (n = 603) | Unidirectional Group (n = 392) | Bidirectional Group (n = 211) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 52.2 ± 18.5 | 49.4 ± 18.1 | 0.731 | |
| Sex | 0.807 | |||
| Male | 379 (62.8) | 245 (62.5) | 134 (63.5) | |
| Female | 224 (37.2) | 147 (37.5) | 77 (36.5) | |
| OGIB | 0.024 | |||
| Overt | 528 (87.6) | 352 (89.8) | 176 (83.4) | |
| Occult | 75 (12.4) | 40 (10.2) | 35 (16.6) | |
| Medical History | ||||
| DM | 92 (15.3) | 65 (16.6) | 27 (12.8) | 0.218 |
| HTN | 162 (26.9) | 100 (25.5) | 62 (29.4) | 0.306 |
| LC | 28 (4.6) | 21 (5.4) | 7 (3.3) | 0.256 |
| ESRD | 22 (3.7) | 19 (4.9) | 3 (1.4) | 0.039 |
| Crohn’s disease | 19 (3.2) | 12 (3.1) | 7 (3.3) | 0.864 |
| Behcet disease | 6 (1.0) | 1 (0.3) | 5 (2.4) | 0.022 |
| Medication | ||||
| Aspirin | 99 (16.4) | 68 (17.4) | 31 (14.7) | 0.401 |
| Antiplatelet agent | 35 (5.8) | 26 (6.6) | 9 (4.3) | 0.236 |
| Anticoagulant | 21 (3.9) | 12 (3.1) | 9 (4.3) | 0.442 |
| Laboratory finding | ||||
| Hemoglobin(g/dL) | 9.2 ± 2.6 | 9.0 ± 2.4 | 0.463 | |
| Platelet | 231.6 ± 103.6 | 248.5 ± 99.8 | 0.059 | |
| BUN | 19.1 ± 16.4 | 16.3 ± 13.8 | 0.036 | |
| Creatinine | 1.2 ± 1.9 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 0.001 | |
| Protein | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 6.1 ± 1.0 | 0.004 | |
| Albumin | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.054 | |
| Initial | 0.134 | |||
| Insertion Route | ||||
| Oral approach | 359 (59.5) | 242 (61.7) | 117 (55.5) | |
| Anal approach | 244 (40.5) | 150 (38.3) | 94 (44.6) | |
| Final diagnosis | 0.848 | |||
| Tumorous | 67 (11.1) | 46 (11.7) | 21 (10.0) | |
| Non-tumorous | 515 (85.4) | 333 (85.0) | 182 (86.3) | |
| UGI | 17 (2.8) | 11 (2.8) | 6 (2.8) | |
| Colon | 4 (0.7) | 2 (0.5) | 2 (1.0) |
| Total (n = 603) N (%) | Unidirectional Group (n = 392) N (%) | Bidirectional Group (n = 211) N (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | <0.001 | |||
| No | 197 (32.7) | 99 (25.3) | 98 (46.5) | |
| Yes | 406 (67.3) | 293 (74.7) | 113 (53.6) | |
| Capsule | <0.001 | |||
| No | 407 (67.5) | 286 (73.0) | 121 (57.4) | |
| Yes | 196 (32.5) | 106 (27.0) | 90 (42.6) | |
| Barium study | 0.039 | |||
| (small bowel) | ||||
| No | 393 (65.2) | 267 (68.1) | 126 (59.7) | |
| Yes | 210 (34.8) | 125 (31.9) | 85 (40.3) | |
| Bleeding Scan | 0.747 | |||
| No | 459 (76.1) | 300 (76.5) | 159 (75.4) | |
| Yes | 144 (23.9) | 92 (23.5) | 52 (24.6) | |
| Angiography | 0.186 | |||
| No | 448 (74.3) | 298 (76.0) | 150 (71.1) | |
| Yes | 155 (25.7) | 94 (24.0) | 61 (28.9) | |
| Meckel scan | 0.878 | |||
| No | 553 (91.7) | 359 (91.6) | 194 (91.9) | |
| Yes | 50 (8.3) | 33 (8.4) | 17 (8.1) |
| Estimated Value | Standard Error | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.002 | 0.006 | 0.075 | 0.988–1.009 | 0.784 |
| Sex | 0.087 | 0.202 | 0.184 | 0.734–1.622 | 0.668 |
| OGIB (Occult) | 0.704 | 0.278 | 6.433 | 1.174–3.485 | 0.011 |
| CT | –0.923 | 0.203 | 20.590 | 0.267–0.592 | <0.001 |
| Capsule | 0.506 | 0.204 | 6.137 | 1.112–2.477 | 0.013 |
| Barium study (small bowel) | 0.405 | 0.203 | 3.983 | 1.007–2.230 | 0.046 |
| BUN | –0.008 | 0.007 | 1.310 | 0.977–1.006 | 0.252 |
| Albumin | 0.180 | 0.147 | 1.494 | 0.987–1.598 | 0.222 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, D.H.; Hwang, S.; Eun, C.S.; Jeon, S.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.R.; Yang, D.-H.; Jang, H.J.; Im, J.P.; Park, S.J.; et al. Factors Affecting Route Selection of Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy in Patients with Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A KASID Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101860
Baek DH, Hwang S, Eun CS, Jeon SR, Kim J, Kim ER, Yang D-H, Jang HJ, Im JP, Park SJ, et al. Factors Affecting Route Selection of Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy in Patients with Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A KASID Multicenter Study. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(10):1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101860
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Dong Hoon, Seonyeong Hwang, Chang Soo Eun, Seong Ran Jeon, Jinsu Kim, Eun Ran Kim, Dong-Hoon Yang, Hyun Joo Jang, Jong Pil Im, Soo Jung Park, and et al. 2021. "Factors Affecting Route Selection of Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy in Patients with Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A KASID Multicenter Study" Diagnostics 11, no. 10: 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101860
APA StyleBaek, D. H., Hwang, S., Eun, C. S., Jeon, S. R., Kim, J., Kim, E. R., Yang, D.-H., Jang, H. J., Im, J. P., Park, S. J., & Jung, S. H. (2021). Factors Affecting Route Selection of Balloon-Assisted Enteroscopy in Patients with Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A KASID Multicenter Study. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101860







