Spectrum Bias and Individual Strengths of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests—A Population-Based Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. “Wetlab”-Methods
2.2.1. Independence of Testing
2.2.2. SARS-CoV-2 in-House SRBD-ELISA
2.2.3. Roche SARS-CoV-2 ELECSYS S Antibody Test
2.2.4. Roche SARS-CoV-2 ELECSYS N Antibody Test
2.2.5. YHLO SARS CoV-2 Test
2.2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Test
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Dichotomized Data on Serostatus
2.3.2. Raw Data on Seropositivity
2.3.3. Illustration of Spectrum Bias
2.3.4. Software and Tools
3. Results
3.1. Agreement between Dichotomized Serological Tests
3.2. Relationship between Dichotomized Serological Tests and Neutralization
3.3. Illustration of the Effect of Spectrum Bias on Diagnostic Performance Measure
3.4. Relationship between Serostatus Predicted by Latent Class Modelling and Neutralization Results
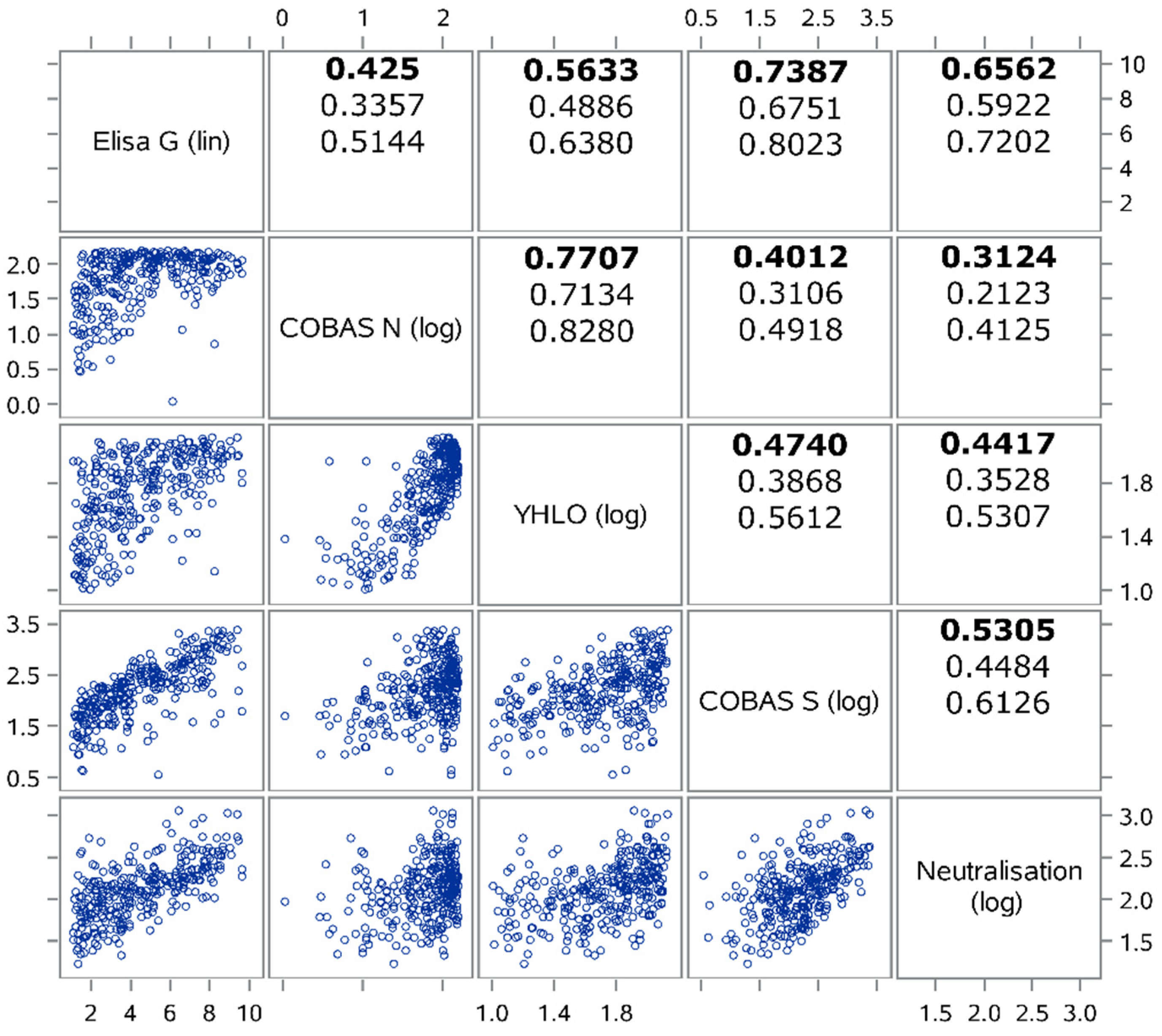
3.5. Correlation of Quantitative Serological Test Results and Neutralization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peterhoff, D.; Glück, V.; Vogel, M.; Schuster, P.; Schütz, A.; Neubert, P.; Albert, V.; Frisch, S.; Kiessling, M.; Pervan, P.; et al. A highly specific and sensitive serological assay detects SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels in COVID-19 patients that correlate with neutralization. Infection 2021, 49, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England Evaluation of Roche Elecsys AntiSARS-CoV-2 Serology Assay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. 2020. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/891598/Evaluation_of_Roche_Elecsys_anti_SARS_CoV_2_PHE_200610_v8.1_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Šimánek, V.; Pecen, L.; Krátká, Z.; Fürst, T.; Řezáčková, H.; Topolčan, O.; Fajfrlík, K.; Sedláček, D.; Šín, R.; Pazdiora, P.; et al. Five Commercial Immunoassays for SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Determination and Their Comparison and Correlation with the Virus Neutralization Test. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, P.I.; Braliou, G.G.; Dimou, N.L.; Nikolopoulos, G.; Bagos, P.G. Antibody Tests in Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, M.; Pervan, P.; Glück, V.; Zeman, F.; Koller, M.; Burkhardt, R.; Glück, T.; Wenzel, J.J.; Schmidt, B.; Gessner, A.; et al. Evaluation of a Broad Panel of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests for Diagnostic Use. JCM 2021, 10, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, D.F.; Feinstein, A.R. Problems of Spectrum and Bias in Evaluating the Efficacy of Diagnostic Tests. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 299, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, H.; Gefeller, O. Variation of sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios and predictive values with disease prevalence. Stat. Med. 1997, 16, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehring, C.; Perrier, A.; Morabia, A. Spectrum bias: A quantitative and graphical analysis of the variability of medical diagnostic test performance. Statist. Med. 2004, 23, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Bekele, Y.; Berzofsky, J.A. Potential SARS-CoV-2 Immune Correlates of Protection in Infection and Vaccine Immunization. Pathogens 2021, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Peterhoff, D.; Beileke, S.; Günther, F.; Berr, M.; Einhauser, S.; Schütz, A.; Niller, H.H.; Steininger, P.; Knöll, A.; et al. Estimates and Determinants of SARS-Cov-2 Seroprevalence and Infection Fatality Ratio Using Latent Class Analysis: The Population-Based Tirschenreuth Study in the Hardest-Hit German County in Spring 2020. Viruses 2021, 13, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.W.; et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalton, G.; Flores-Cervantes, I. Weighting methods. J. Off. Stat. 2003, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- COVID-19 Datenhub. Available online: https://npgeo-corona-npgeo-de.hub.arcgis.com/ (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2-S. Available online: https://www.roche.de/diagnostik-produkte/produktkatalog/tests-parameter/elecsys-anti-sars-cov-2-s (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.roche.de/diagnostik-produkte/produktkatalog/tests-parameter/elecsys-anti-sars-cov-2 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Michailidis, E.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Mendoza, P.; Rutkowska, M.; Bednarski, E.; Gaebler, C.; et al. Measuring SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity using pseudotyped and chimeric viruses. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20201181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepler, L.; Rössler, A.; Falch, A.; Volland, A.; Borena, W.; von Laer, D.; Kimpel, J. Comparison of Four SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays. Vaccines 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.D.; Walter, S.D. A reappraisal of the kappa coefficient. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollset, S.E. Confidence intervals for a binomial proportion. Statist. Med. 1993, 12, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarsfeld, P.F. The logical and mathematical foundation of latent structure analysis. In Studies in Social Psychology in World War II: Vol. 4. Measurement and Prediction; Stouffer, S.A., Guttman, L., Suchman, E.A., Lazarsfeld, P.F., Star, S.A., Clausen, J.A., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1950; Chapter 10; pp. 362–412. [Google Scholar]
- van Smeden, M.; Naaktgeboren, C.A.; Reitsma, J.B.; Moons, K.G.M.; de Groot, J.A.H. Latent Class Models in Diagnostic Studies When There is No Reference Standard--A Systematic Review. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanza, S.T.; Collins, L.M.; Lemmon, D.R.; Schafer, J.L. PROC LCA: A SAS Procedure for Latent Class Analysis. Struct. Equ. Modeling 2007, 14, 671–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, V.; Denolly, S.; Vogrig, M.; Boson, B.; Siret, E.; Rigaill, J.; Pillet, S.; Grattard, F.; Gonzalo, S.; Verhoeven, P.; et al. A longitudinal study of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients reveals a high correlation between neutralizing antibodies and COVID-19 severity. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubina, R.; Dziedzic, A. Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimeglio, C.; Loubes, J.-M.; Miedougé, M.; Herin, F.; Soulat, J.-M.; Izopet, J. The real seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in France and its consequences for virus dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.H.; Lin, H.-M.; Baine, I.; Wajnberg, A.; Gumprecht, J.P.; Rahman, F.; Rodriguez, D.; Tandon, P.; Bassily-Marcus, A.; Bander, J.; et al. Convalescent plasma treatment of severe COVID-19: A propensity score–matched control study. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, D.; Mayora-Neto, M.; Nadesalingham, A.; Wells, D.A.; Carnell, G.W.; Ohlendorf, L.; Ferarri, M.; Palmer, P.; Chan, A.C.Y.; Smith, P.; et al. Neutralisation hierarchy of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern using standardised, quantitative neutralisation assays reveals a correlation with disease severity; towards deciphering protective antibody thresholds. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Olivares, J.; Wells, D.A.; Ferrari, M.; Chan, A.; Smith, P.; Nadesalingam, A.; Paloniemi, M.; Carnell, G.; Ohlendorf, L.; Cantoni, D.; et al. Towards Internationally standardised humoral Immune Correlates of Protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschug, A.; Schwanbeck, J.; Hahn, A.; Hillebrecht, A.; Blaschke, S.; Mese, K.; Groß, U.; Dierks, S.; Frickmann, H.; Zautner, A.E. Comparison of Five Serological Assays for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche Diagnostics. Roche Diagnostics Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137605 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Resman Rus, K.; Korva, M.; Knap, N.; Avšič Županc, T.; Poljak, M. Performance of the rapid high-throughput automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassay targeting total antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain in comparison to the neutralization assay. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 139, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muench, P.; Jochum, S.; Wenderoth, V.; Ofenloch-Haehnle, B.; Hombach, M.; Strobl, M.; Sadlowski, H.; Sachse, C.; Torriani, G.; Eckerle, I.; et al. Development and Validation of the Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunoassay as a Highly Specific Tool for Determining Past Exposure to SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Shin, S.; Nam, M.; Hong, Y.J.; Roh, E.Y.; Park, K.U.; Song, E.Y. Performance evaluation of three automated quantitative immunoassays and their correlation with a surrogate virus neutralization test in coronavirus disease 19 patients and pre-pandemic controls. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favresse, J.; Eucher, C.; Elsen, M.; Gillot, C.; Van Eeckhoudt, S.; Dogné, J.-M.; Douxfils, J. Persistence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Depends on the Analytical Kit: A Report for Up to 10 Months after Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Manufacturer | Principle | Target | Abbreviation | Antigen | Time after PCR | Sensitivity | Specificity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in house ELISA | ELISA | IgG; (IgA; IgM) | ELISA_G ELISA_A ELISA_M | Spike-RBD | >10 d | 96% 92% 98% | 99.3% | Peterhoff et al. 2021 [1] |
| Roche ELECSYS COBAS | ECLIA | total Ig | COBAS_S | Spike | ≥14 d | 99.5% | 99.8% | IFU * [14] |
| Roche ELECSYS COBAS | ECLIA | total Ig | COBAS_N | Nucleoprotein | ≥14 d | 98.81% | 99.98% | IFU * [15] |
| YHLO Biotech | ECLIA | total Ig | YHLO | Nucleo-protein & Spike | not specified | 97.3% | 96.3% | Wagner et al. 2021 [10] |
| Kappa 95% KI | COBAS_S | COBAS_N | ELISA_G | ELISA_A | ELISA_M | ELISA_ GAM | YHLO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COBAS_ S | |||||||
| COBAS_N | 0.9646 0.9467; 0.9825 | ||||||
| ELISA_ G | 0.9116 0.8836; 0.9396 | 0.9163 0.8889; 0.9437 | |||||
| ELISA_ A | 0.1916 0.1395; 0.2438 | 0.2097 0.1560; 0.2634 | 0.2114 0.1559; 0.2669 | ||||
| ELISA_ M | 0.1140 0.0768; 0.1513 | 0.1208 0.0818; 0.1598 | 0.1235 0.0826; 0.1644 | 0.1617 0.0716; 0.2519 | |||
| ELISA_ GAM | 0.8488 0.8129; 0.8847 | 0.8579 0.8230; 0.8928 | 0.9262 0.9006; 0.9519 | 0.3216 0.2707; 0.3725 | 0.1298 0.0928; 0.1668 | ||
| YHLO | 0.8853 0.8537; 0.9170 | 0.9146 0.8868; 0.9423 | 0.8741 0.8405; 0.9076 | 0.2402 0.1823; 0.2981 | 0.1225 0.0794; 0.1657 | 0.8116 0.7719; 0.8513 |
| Neutralization | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Cohort | Kappa | 95% CI | Sensitivity | 95%-CI | Specificity | 95% CI | Youden- Index J | PPV | 95%-CI | NPV | 95%-CI |
| COBAS _S | all | 0.9719 | 0.9560; 0.9879 | 0.9719 | 0.9496; 0.9845 | 0.9971 | 0.9871; 0.9994 | 0.9690 | 0.9691 | 0.9009; 0.9909 | 0.9974 | 0.9906; 0.9993 |
| Spectrum | 0.9961 | 0.9886; 1.0000 | 0.9954 | 0.9737; 0.9992 | 0.9997 | 0.9900; 1.0000 | 0.9951 | 0.9968 | 0.9261; 0.9999 | 0.9996 | 0.9924; 1.0000 | |
| COBAS _N | all | 0.9418 | 0.9190; 0.9646 | 0.9386 | 0.9093, 0.9589 | 0.9966 | 0.9862; 0.9991 | 0.9352 | 0.9628 | 0.8904; 0.9880 | 0.9943 | 0.9861; 0.9976 |
| Spectrum | 0.9986 | 0.9942; 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9820; 1.0000 | 0.9990 | 0.9888; 0.9999 | 0.9990 | 0.9894 | 0.9143; 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 0.9932; 1.0000 | |
| YHLO | all | 0.8619 | 0.8275; 0.8963 | 0.8526 | 0.8127, 0.8852 | 0.9944 | 0.9830; 0.9982 | 0.8470 | 0.9345 | 0.8487; 0.9732 | 0.9863 | 0.7189; 0.9924 |
| Spectrum | 0.9614 | 0.9383; 0.9845 | 0.9587 | 0.9225; 0.9784 | 0.9952 | 0.9824; 0.9987 | 0.9539 | 0.9493 | 0.8546; 0.9835 | 0.9961 | 0.9866; 0.9989 | |
| ELISA _G | all | 0.8915 | 0.8607; 0.9222 | 0.8917 | 0.8558; 0.9195 | 0.9894 | 0.9758; 0.9954 | 0.8811 | 0.8875 | 0.7953; 0.9412 | 0.9898 | 0.9800; 0.9949 |
| Spectrum | 0.9734 | 0.9543; 0.9926 | 0.9817 | 0.9530; 0.9930 | 0.9914 | 0.9767; 0.9969 | 0.9731 | 0.9145 | 0.8129; 0.9634 | 0.9983 | 0.9900; 0.9997 | |
| ELISA _GAM | all | 0.8736 | 0.8406; 0.9066 | 0.9224 | 0.8905; 0.9456 | 0.9500 | 0.9269; 0.9661 | 0.8724 | 0.6336 | 0.5391; 0.7189 | 0.9924 | 0.9832; 0.9966 |
| Spectrum | 0.9206 | 0.8884; 0.9528 | 0.9908 | 0.9664; 0.9975 | 0.9495 | 0.9236; 0.9669 | 0.9403 | 0.6478 | 0.5390; 0.7431 | 0.9991 | 0.9912; 0.9999 | |
| ELISA _M | all | 0.1092 | 0.0732; 0.1453 | 0.1043 | 0.0770; 0.1397 | 0.9930 | 0.9809; 0.9975 | 0.0973 | 0.5827 | 0.3287; 0.7994 | 0.9220 | 0.9020; 0.9383 |
| Spectrum | 0.1993 | 0.1380; 0.2605 | 0.1651 | 0.1209; 0.2214 | 0.9944 | 0.9812; 0.9984 | 0.1595 | 0.7343 | 0.4510; 0.9029 | 0.9270 | 0.9035; 0.9452 | |
| ELISA _A | all | 0.2315 | 0.1805; 0.2824 | 0.2445 | 0.2034; 0.2909 | 0.9667 | 0.9468; 0.9794 | 0.2112 | 0.4077 | 0.2756; 0.5545 | 0.9317 | 0.9123; 0.9471 |
| Spectrum | 0.3326 | 0.2595; 0.4058 | 0.3211 | 0.2615; 0.3871 | 0.9627 | 0.9395; 0.9773 | 0.2838 | 0.4466 | 0.3006; 0.6024 | 0.9380 | 0.9153; 0.9549 | |
| Neutralization | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Included in Model | Kappa | 95% CI | Sensitivity | 95% CI | Specificity | 95% CI | Youden -Index | 95% CI | |
| LCA 1 * | ELISA_G; COBAS_N; YHLO | 0.9220 | 0.8958; 0.9483 | 0.9152 | 0.8822; 0.9395 | 0.9976 | 0.9879; 0.9995 | 0.9128 | 0.8701; 0.9390 |
| LCA 2 | ELISA _GAM; COBAS_N; YHLO | 0.9244 | 0.8985; 0.9503 | 0.9178 | 0.8852; 0.9417 | 0.9976 | 0.9879; 0.9995 | 0.9154 | 0.8731; 0.9412 |
| LCA 3 | ELISA_G; COBAS_N; YHLO; COBAS_S | 0.9514 | 0.9305; 0.9722 | 0.9491 | 0.9216; 0.9672 | 0.9968 | 0.9866; 0.9993 | 0.9459 | 0.9082; 0.9665 |
| LCA 4 ** | ELISA _GAM; COBAS_N; YHLO; COBAS S | 0.9514 | 0.9305; 0.9722 | 0.9491 | 0.9216; 0.9672 | 0.9968 | 0.9866; 0.9993 | 0.9459 | 0.9082; 0.9665 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Einhauser, S.; Peterhoff, D.; Niller, H.H.; Beileke, S.; Günther, F.; Steininger, P.; Burkhardt, R.; Heid, I.M.; Pfahlberg, A.B.; Überla, K.; et al. Spectrum Bias and Individual Strengths of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests—A Population-Based Evaluation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101843
Einhauser S, Peterhoff D, Niller HH, Beileke S, Günther F, Steininger P, Burkhardt R, Heid IM, Pfahlberg AB, Überla K, et al. Spectrum Bias and Individual Strengths of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests—A Population-Based Evaluation. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(10):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101843
Chicago/Turabian StyleEinhauser, Sebastian, David Peterhoff, Hans Helmut Niller, Stephanie Beileke, Felix Günther, Philipp Steininger, Ralph Burkhardt, Iris M. Heid, Annette B. Pfahlberg, Klaus Überla, and et al. 2021. "Spectrum Bias and Individual Strengths of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests—A Population-Based Evaluation" Diagnostics 11, no. 10: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101843
APA StyleEinhauser, S., Peterhoff, D., Niller, H. H., Beileke, S., Günther, F., Steininger, P., Burkhardt, R., Heid, I. M., Pfahlberg, A. B., Überla, K., Gefeller, O., & Wagner, R. (2021). Spectrum Bias and Individual Strengths of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests—A Population-Based Evaluation. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101843






