Towards Routine Implementation of Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Management: It Is Always Too Early, until Suddenly It Is Too Late
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
1.2. Beyond CTCs: The Clinical Use of Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA)
1.3. Clinical Translation, Cost-Effectiveness and Reimbursement
1.4. The Challenge of Clinically Translating Liquid Biopsies
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pre-Workshop Survey
2.2. Workshop Short Presentations
2.3. Workshop Polls
2.4. Break-Out Sessions
- Early detection of cancer, i.e., the use of blood tests for the early detection of (multiple) cancers. This could be the use of pan-cancer blood tests such as GRAIL, Cancer-Seek or PanSEER.
- MRD, i.e., the use of liquid biopsies following curative treatment to guide adjuvant therapy, such as to guide adjuvant systemic treatment in colorectal or breast cancer.
- Cancer treatment selection and monitoring, i.e., the use of liquid biopsies to select targeted treatment, monitor progressive disease and response to treatment.
2.5. Expert Elicitation of Current Level of Evidence
3. Results
4. Discussion
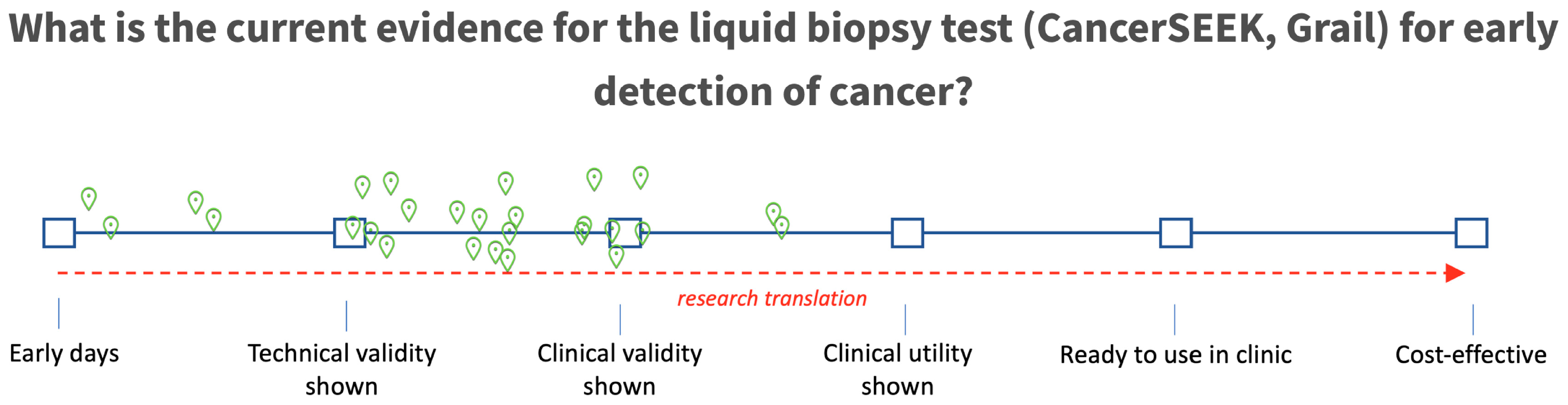
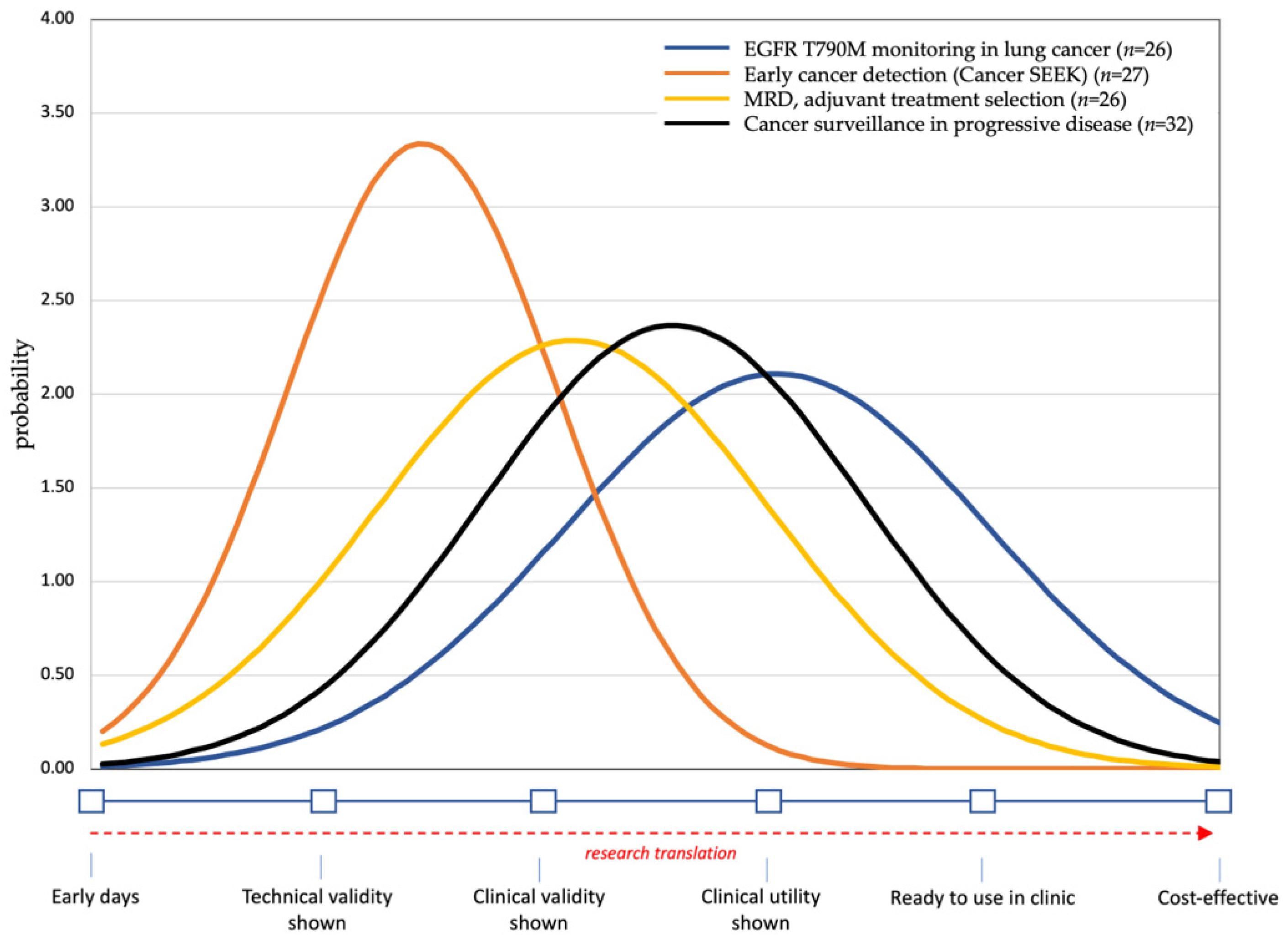
4.1. Early Detection
4.2. Clinical Utility of Liquid Biopsies for MRD, Treatment Selection and Monitoring
4.3. Turn-Around Time
4.4. Do We Need to Get the Test Right Before Routine Use?
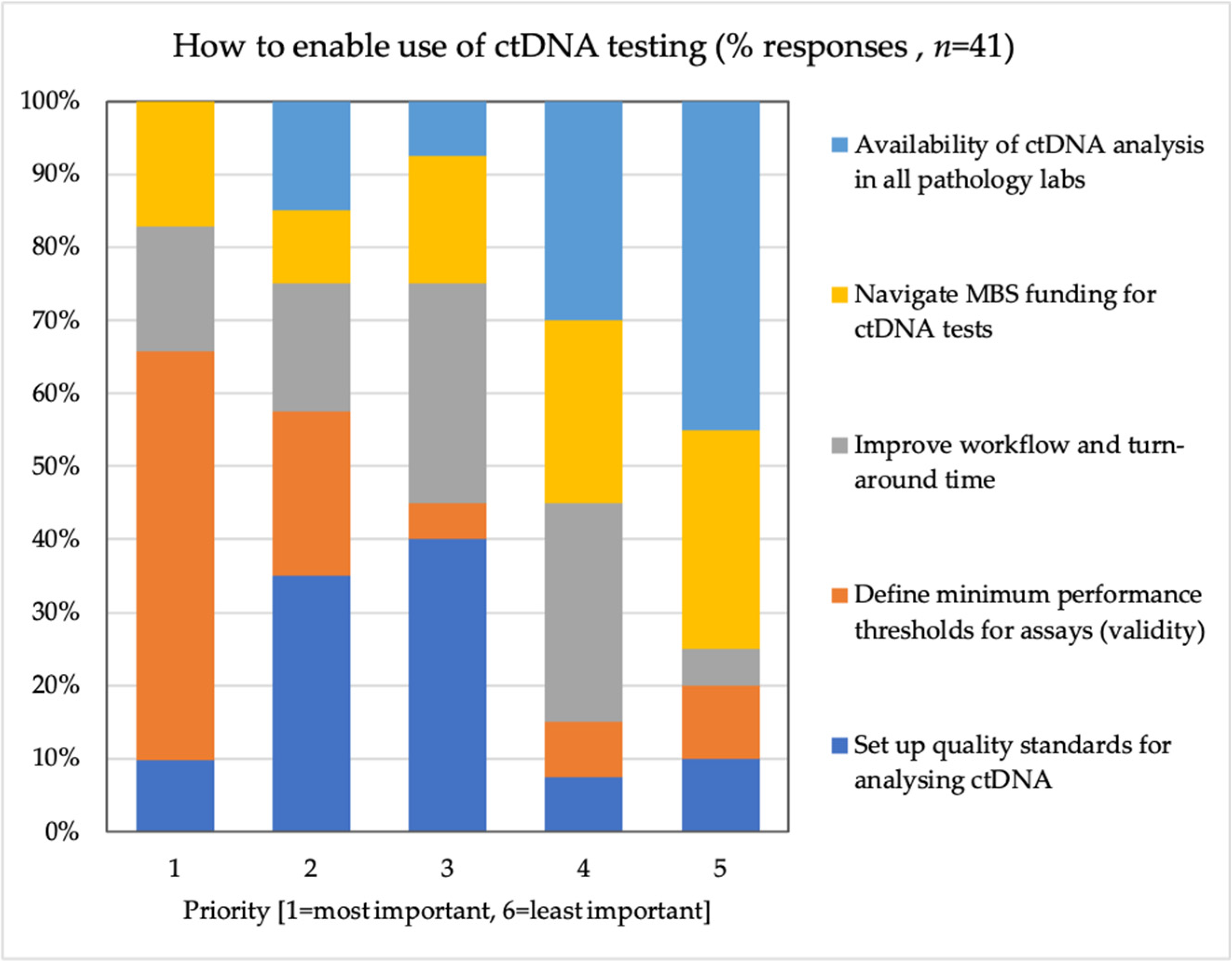
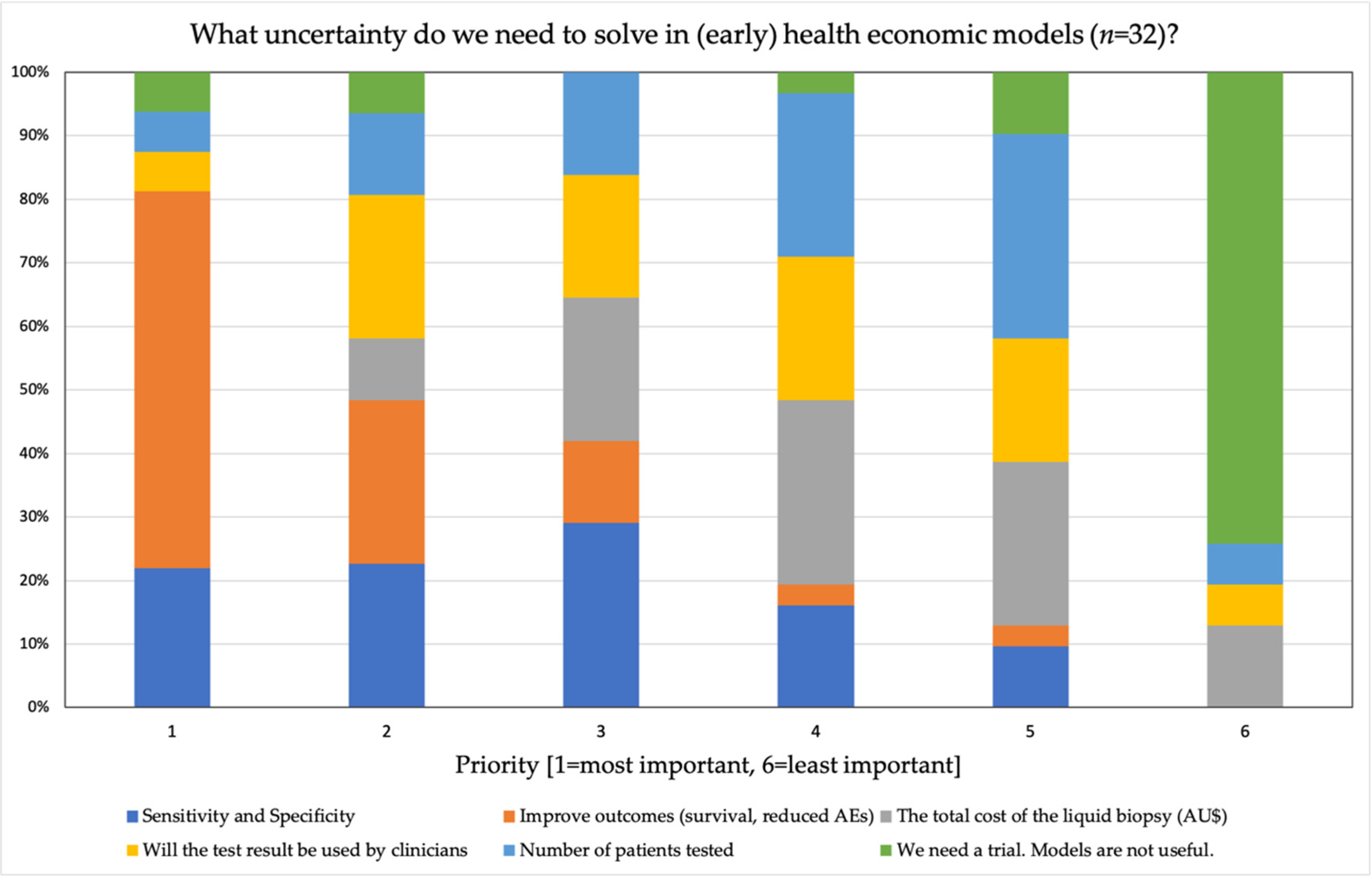
4.5. Reimbursing Liquid Biopsies and Evidence
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashworth, T.R. A Case of Cancer in Which Cells Similar to Those in the Tumors Were Seen in the Blood after Death. Australas. Med. J. 1869, 14, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Hayes, D.F.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: A novel prognostic factor for newly diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.C.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells Detected by the CellSearch System in Patients with Metastatic Breast Colorectal and Prostate Cancer. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 617421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.G.; Renehan, A.G.; Backen, A.; Gollins, S.; Chau, I.; Hasan, J.; Valle, J.W.; Morris, K.; Beech, J.; Ashcroft, L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration in a Phase II Trial of a Four-Drug Regimen in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2015, 14, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldkorn, A.; Ely, B.; Quinn, D.I.; Tangen, C.M.; Fink, L.M.; Xu, T.; Twardowski, P.; van Veldhuizen, P.J.; Agarwal, N.; Carducci, M.A.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Counts Are Prognostic of Overall Survival in SWOG S0421: A Phase III Trial of Docetaxel With or Without Atrasentan for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Winer, E.P.; Jones, B.L.; Srkalovic, G.; Tejwani, S.; Schott, A.F.; O’Rourke, M.A.; Lew, D.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells and Response to Chemotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer: SWOG S0500. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3483–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.C.; Jacot, W.; Kiavue, N.; Dureau, S.; Kadi, A.; Brain, E.; Bachelot, T.; Bourgeois, H.; Gonçalves, A.; Ladoire, S.; et al. Efficacy of Circulating Tumor Cell Count–Driven vs Clinician-Driven First-line Therapy Choice in Hormone Receptor–Positive, ERBB2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, e205660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, E.; Viéitez, J.M.; España, A.G.; Calle, S.G.; Salvia, A.S.; Graña, B.; Garcia-Alfonso, P.; Rivera, F.; Aldana, G.A.Q.; Zoilo, J.J.R.; et al. FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFOX plus bevacizumab for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and ≥3 circulating tumour cells: The randomised phase III VISNÚ-1 trial. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, D.; Olmos, D.; Mateo, J.; Bianchini, D.; Seed, G.; Fleisher, M.; Danila, D.C.; Flohr, P.; Crespo, M.; Figueiredo, I.; et al. Decline in Circulating Tumor Cell Count and Treatment Outcome in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumanasuriya, S.; Omlin, A.; Armstron, A.; Attard, G.; Chi, K.N.; Bevan, C.L.; Shibakawa, A.; Jzerman, M.J.I.; Laere, B.; Lolkema, M.; et al. Consensus Statement on Circulating Biomarkers for Advanced Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 1, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, S.C.; Ho, C.L.; Wei, F.; Wong, D.T.; Su, W.C.; Lin, C.C. Liquid biopsy genotyping in lung cancer: Ready for clinical utility? Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18590–18608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabel, L.; Proudhon, C.; Gortais, H.; Loirat, D.; Coussy, F.; Pierga, J.Y.; Bidard, F.C. Circulating tumor cells: Clinical validity and utility. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 22, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elazezy, M.; Joosse, S.A. Techniques of using circulating tumor DNA as a liquid biopsy component in cancer management. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, E.; Haque, I.S.; Roberts, C.E.S.; Speicher, M.R. Current and future perspectives of liquid biopsies in genomics-driven oncology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devonshire, A.S.; Whale, A.S.; Gutteridge, A.; Jones, G.; Cowen, S.; Foy, C.A.; Hugget, J.F. Towards standardisation of cell-free DNA measurement in plasma: Controls for extraction efficiency, fragment size bias and quantification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6499–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, Z.C.; Butler, R.; Cheetham, M.; Dequeker, E.M.C.; Fairley, J.A.; Fenizia, F.; Hall, J.A.; Keppens, C.; Normanno, N.; Schuuring, E.; et al. IQN path ASBL report from the first European cfDNA consensus meeting: Expert opinion on the minimal requirements for clinical ctDNA testing. Virchows Arch. 2019, 474, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; Javed, A.A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.C.; Oxnard, G.R.; Klein, E.A.; Swanton, C.; Seiden, M.V.; Cummings, S.R.; Absalan, F.; Alexander, G.; Allen, B.; Aminiet, H.; et al. Sensitive and specific multi-cancer detection and localization using methylation signatures in cell-free DNA. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gole, J.; Gore, A.; He, Q.; Lu, M.; Min, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Non-invasive early detection of cancer four years before conventional diagnosis using a blood test. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merker, J.D.; Oxnard, G.R.; Compton, C.; Diehn, M.; Hurley, P.; Lazar, A.J.; Lindeman, N.; Lockwood, C.M.; Rai, A.J.; Schilsky, R.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Patients With Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists Joint Review. J Clin Oncol. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Delft, F.; Koffijberg, H.; Retèl, V.; Heuvel, M.V.D.; IJzerman, M.J. The Validity and Predictive Value of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Prediction of Response in the Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Kingston, B.; Kilburn, L.S.; Kernaghan, S.; Wardley, A.M.; Macpherson, I.R.; Baird, R.D.; Roylance, R.; Stephens, P.; Oikonomidou, O.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA analysis to direct therapy in advanced breast cancer (plasmaMATCH): A multicentre, multicohort, phase 2a, platform trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.P.; Overman, M.J.; Dasari, A.; Kazmi, S.M.A.; Mazard, T.; Vilar, E.; Morris, V.K.; Lee, M.S.; Herron, D.; Eng, C.; et al. Characterizing the patterns of clonal selection in circulating tumor DNA from patients with colorectal cancer refractory to anti-EGFR treatment. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parseghian, C.M.; Loree, J.M.; Morris, V.K.; Liu, X.; Clifton, K.K.; Napolitano, S.; Henry, J.T.; Pereira, A.A.; Vilar, E.; Johnson, B.; et al. Anti-EGFR-resistant clones decay exponentially after progression: Implications for anti-EGFR re-challenge. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbosh, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Wilson, G.A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; le Quesne, J.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature 2017, 545, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Christie, M.; Simons, K.; Lee, M.; Wong, R.; Kosmider, S.; Ananda, S.; McKendrick, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses as Markers of Recurrence Risk and Benefit of Adjuvant Therapy for Stage III Colon Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Lipton, L.; Cohen, J.; Tie, J.; Javed, A.A.; Li, L.; Goldstein, D.; Burge, M.; Cooray, P.; Nagrial, A.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA as a potential marker of adjuvant chemotherapy benefit following surgery for localized pancreatic cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillas, I.G.; Schiavon, G.; Weigelt, B.; Ng, C.; Hrebien, S.; Cutts, R.J.; Cheang, M.; Osin, P.; Nerurkar, A.; Kozarewa, I.; et al. Mutation tracking in circulating tumor DNA predicts relapse in early breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 302ra133. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, E.; Demtröder, K.B.; Sethi, H.; Shchegrova, S.; Salari, R.; Nordentoft, I.; Wu, H.T.; Knudsen, M.; Lamy, P.; Lindskrog, S.V.; et al. Early Detection of Metastatic Relapse and Monitoring of Therapeutic Efficacy by Ultra-Deep Sequencing of Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Patients With Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Saw, R.P.; Thompson, J.F.; Lo, S.; Spillane, A.J.; Shannon, K.F.; Stretch, J.R.; Howle, J.; Menzies, A.M.; Carlino, M.S.; et al. Pre-operative ctDNA predicts survival in high-risk stage III cutaneous melanoma patients. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Saw, R.P.; Thompson, J.F.; Lo, S.; Spillane, A.J.; Shannon, K.F.; Stretch, J.R.; Howle, J.; Menzies, A.M.; Carlino, M.S.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 346ra92. [Google Scholar]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Christie, M.; Simons, K.; Elsaleh, H.; Kosmider, S.; Wong, R.; Yip, D.; et al. Serial circulating tumour DNA analysis during multimodality treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer: A prospective biomarker study. Gut 2019, 68, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Sandhu, S.; Lee, R.J.; Li, J.; Callahan, J.; Ftouni, S.; Dhomen, N.; Middlehurst, P.; Wallace, A.; Raleigh, J.; et al. Prediction and monitoring of relapse in stage III melanoma using circulating tumor DNA. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghuis, A.M.S.; Koffijberg, H.; Prakash, J.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; IJzerman, M.J. Detecting Blood-Based Biomarkers in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review of Their Current Status and Clinical Utility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJzerman, M.J.; Berghuis, A.M.S.; de Bono, J.S.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Health economic impact of liquid biopsies in cancer management. Expert Rev. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 2018, 18, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessies, D.; Greuter, M.; van Rooijen, K. Performance of four platforms for KRAS mutation detection in plasma cell-free DNA: ddPCR, Idylla, COBAS z480 and BEAMing. Nat. Com. 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Plasma EGFR Mutation Tests for Adults with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Natl. Inst. Health Care Excell. 2018, Medtech Innovation Briefing. Available online: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/mib137 (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Calderón, D.S.; Pedraza, A.; Urrego, C.M.; Mejía, A.M.; Páez, A.L.M.; Perdomo, S. Analysis of the Cost-Effectiveness of Liquid Biopsy to Determine Treatment Change in Patients with Her2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer in Colombia. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2020, 12, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degeling, K.; Schivo, S.; Mehra, N.; Koffijberg, H.; Langerak, R.; de Bono, J.S.; Jzerman, M.J.I. Comparison of Timed Automata with Discrete Event Simulation for Modeling of Biomarker-Based Treatment Decisions: An Illustration for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Value Health 2017, 20, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, R.; So, J.B.Y.; Zhu, F.; Too, H.-P.; Yeoh, K.-G.; Yoong, J.S.-Y. Evaluating the Use of microRNA Blood Tests for Gastric Cancer Screening in a Stratified Population-Level Screening Program: An Early Model-Based Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Value Health 2020, 23, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, M.P.; Gray, S.W.; Phillips, K.A. Private Payer and Medicare Coverage for Circulating Tumor DNA Testing: A Historical Analysis of Coverage Policies From 2015 to 2019. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Corbacho, J.G.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid biopsies come of age: Towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescon, D.W.; Bratman, S.V.; Chan, S.M.; Siu, L.L. Circulating tumor DNA and liquid biopsy in oncology. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighl, N.B.; Rekhtman, N.; Biermann, W.A.; Huang, J.; Kenudson, M.M.; Ramalingam, S.S.; West, H.; Whitlock, S.; Somerfield, M.R. Molecular testing for selection of patients with lung cancer for epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3673–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, N.; Pradines, A.; Favre, G.; Mazières, J. Current and future applications of liquid biopsy in nonsmall cell lung cancer from early to advanced stages. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2020, 29, 190052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janni, W.J.; Rack, B.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Pierga, J.Y.; Taran, F.A.; Fehm, T.; Hall, C.; de Groot, M.R.; Bidard, F.C.; Friedl, T.W.P.; et al. Pooled Analysis of the Prognostic Relevance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Primary Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinami, T.; Kagara, N.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; Miyake, T.; Tanei, T.; Naoi, Y.; Shimoda, M.; Shimazu, K.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Detection of ct DNA with Personalized Molecular Barcode NGS and Its Clinical Significance in Patients with Early Breast Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Panabières, C.A. Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease-latest advances and implications for cure. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IJzerman, M.J.; Koffijberg, H.; Fenwick, E.; Krahn, M. Emerging Use of Early Health Technology Assessment in Medical Product Development: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Pharmacoeconomics 2017, 35, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towse, A.; Garrison, L.P. Economic incentives for evidence generation: Promoting an efficient path to personalized medicine. Value Health 2013, 16 (Suppl. 6), S39–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, S.D.; Sullivan, S.D. A new model for reimbursing genome-based cancer care. Oncologist 2014, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabé, R.; Hickson, N.; Wallace, A.; Blackhall, F.H. What do we need to make circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) a routine diagnostic test in lung cancer? Eur. J. Cancer. 2017, 81, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, E.; Holtorf, A.P.; Walton, S.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, H.; Biltaj, E.; Brixner, D.; Barr, C.; Oberg, J.; Shandhu, G.; et al. Being Precise About Precision Medicine: What Should Value Frameworks Incorporate to Address Precision Medicine? A Report of the Personalized Precision Medicine Special Interest Group. Value Health 2020, 23, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Pierga, J.Y.; Reuben, J.; Rademaker, A.; Davis, A.A.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nolé, F.; Criado, R.G.; Mavroudis, D.; et al. The clinical use of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) enumeration for staging of metastatic breast cancer (MBC): International expert consensus paper. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 134, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Morris, V.K.; Allegra, C.J.; Atreya, C.; Benson, A.B., III; Boland, P.; Chung, K.; Copur, M.S.; Corcoran, R.B.; Deming, D.A.; et al. ct DNA applications and integration in colorectal cancer: An NCI Colon and Rectal–Anal Task Forces whitepaper. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
IJzerman, M.J.; de Boer, J.; Azad, A.; Degeling, K.; Geoghegan, J.; Hewitt, C.; Hollande, F.; Lee, B.; To, Y.H.; Tothill, R.W.; et al. Towards Routine Implementation of Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Management: It Is Always Too Early, until Suddenly It Is Too Late. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010103
IJzerman MJ, de Boer J, Azad A, Degeling K, Geoghegan J, Hewitt C, Hollande F, Lee B, To YH, Tothill RW, et al. Towards Routine Implementation of Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Management: It Is Always Too Early, until Suddenly It Is Too Late. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010103
Chicago/Turabian StyleIJzerman, Maarten J., Jasper de Boer, Arun Azad, Koen Degeling, Joel Geoghegan, Chelsee Hewitt, Frédéric Hollande, Belinda Lee, Yat Ho To, Richard W. Tothill, and et al. 2021. "Towards Routine Implementation of Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Management: It Is Always Too Early, until Suddenly It Is Too Late" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010103
APA StyleIJzerman, M. J., de Boer, J., Azad, A., Degeling, K., Geoghegan, J., Hewitt, C., Hollande, F., Lee, B., To, Y. H., Tothill, R. W., Wright, G., Tie, J., & Dawson, S.-J. (2021). Towards Routine Implementation of Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Management: It Is Always Too Early, until Suddenly It Is Too Late. Diagnostics, 11(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010103






