Camptocormia as a Novel Phenotype in a Heterozygous POLG2 Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
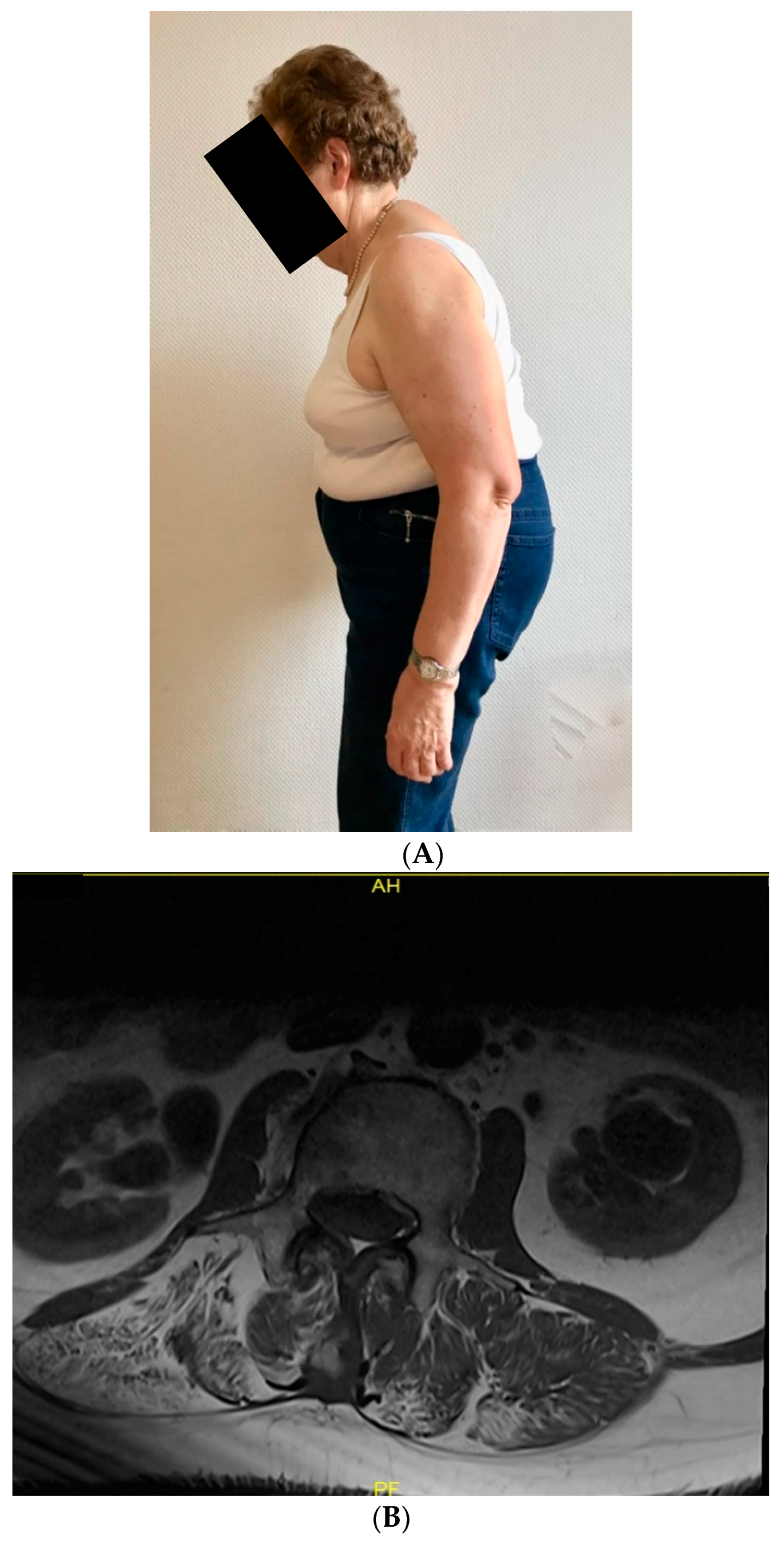
2.1. Clinical Description
2.2. Muscle Histopathology
2.3. Activities of Respiratory Chain Complexes
2.4. Next Generation Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings and Muscle Biopsy
3.2. Activities of Respiratory Chain Complexes
3.3. Genetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, D.; Schubert, K.; Joshi, P.R.; Baty, K.; Blakely, E.L.; Zierz, S.; Taylor, R.W.; Deschauer, M. A novel m.7539C>T point mutation in the mt-tRNA(Asp) gene associated with multisystemic mitochondrial disease. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2015, 25, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hattab, A.W.; Scaglia, F. Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes: Review and updates of genetic basis, manifestations, and therapeutic options. Neurotherapeutics 2013, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Pozzo, P.; Cardaioli, E.; Rubegni, A.; Gallus, G.N.; Malandrini, A.; Rufa, A.; Battisti, C.; Carluccio, M.A.; Rocchi, R.; Giannini, F.; et al. Novel POLG mutations and variable clinical phenotypes in 13 Italian patients. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, W.C. Defects of mitochondrial DNA replication. J. Child. Neurol. 2014, 29, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, H.; Faust, P.L.; Iglesias, A.D.; Lagana, S.M.; Wou, K.; Hirano, M.; Di Mauro, S.; Mansukani, M.M.; Hoff, K.E.; Nagy, P.L.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies a homozygous POLG2 missense variant in an infant with fulminant hepatic failure and mitochondrial DNA depletion. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.D.; Tennant, S.; Powell, H.; Pyle, A.; Blakely, E.L.; He, L.; Hudson, G.; Roberts, M.; du Plessiset, D.; Gow, D.; et al. Novel POLG1 mutations associated with neuromuscular and liver phenotypes in adults and children. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goethem, G.; Dermaut, B.; Löfgren, A.; Martin, J.-J.; van Broeckhoven, C. Mutation of POLG is associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia characterized by mtDNA deletions. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.C.; Czermin, B.; Muller-Ziermann, S.; Bulst, S.; Stewart, J.D.; Hudson, G.; Schneiderat, P.; Abicht, A.; Holinski-Feder, E.; Lochmüller, H.; et al. Late-onset ptosis and myopathy in a patient with a heterozygous insertion in POLG2. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, M.J.; Clark, S.; Man, C.Y.W.; Hudson, G.; Durham, S.E.; Taylor, R.W.; Nightingale, S.; Turnbull, D.M.; Copeland, W.C.; Chinnery, P.F. Mutant POLG2 disrupts DNA polymerase gamma subunits and causes progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Am. J. Hum. Gene 2006, 78, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maldergem, L.; Besse, A.; De Paepe, B.; Blakely, E.L.; Appadurai, V.; Humble, M.M.; Piard, J.; Craig, K.; He, L.; Hella, P.; et al. POLG2 deficiency causes adult-onset syndromic sensory neuropathy, ataxia and parkinsonism. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.J.; Longley, M.J.; Li, F.-Y.; Kasiviswanathan, R.; Wong, L.-J.; Copeland, W.C. Biochemical analysis of human POLG2 variants associated with mitochondrial disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3052–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; Hassan, A. Camptocormia: Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment response. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2018, 8, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakiyama, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Higuchi, I.; Inamori, Y.; Sangatsuda, Y.; Michizono, K.; Watanabe, O.; Hatakeyama, H.; Goto, Y.; Arimura, K.; et al. A new phenotype of mitochondrial disease characterized by familial late-onset predominant axial myopathy and encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcey, V.; Hachulla, E.; Michon-Pasturel, U.; Queyrel, V.; Hatron, P.Y.; Boutry, N.; Lemaitre, V.; Vanhille, P.; Serratrice, J.; Disdier, P.; et al. Camptocormia: A sign of axial myopathy. Report of 7 cases. Rev. Med. Interne. 2002, 23, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Puerta, J.A.; Peris, P.; Grau, J.M.; Martinez, M.A.; Guañabens, N. Camptocormia as a clinical manifestation of mitochondrial myopathy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poullin, P.; Daumen-Legre, V.; Serratrice, G. Camptocormia in the elderly patient: Myopathy or muscular dystonia? Rev. Rhum. Ed. Fr. 1993, 60, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Schabitz, W.R.; Glatz, K.; Schuhan, C.; Sommer, C.; Berger, C.; Schwaninger, M.; Hartmann, M.; Hilmar Goebel, H.; Meinck, H.M. Severe forward flexion of the trunk in Parkinson’s disease: Focal myopathy of the paraspinal muscles mimicking camptocormia. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serratrice, G.; Pouget, J.; Pellissier, J.F. Bent spine syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1996, 60, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, J.; Lehmann, D.; Hardy, S.A.; Falkous, G.; Knowles, C.V.Y.; Jones, R.L.; Kunz, W.S.; Taylor, R.W.; Kornblum, C. Camptocormia and shuffling gait due to a novel MT-TV mutation: Diagnostic pitfalls. Neurol. Genet. 2017, 3, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellerich, F.N.; Deschauer, M.; Chen, Y.; Müller, T.; Neudecker, S.; Zierz, S. Mitochondrial respiratory rates and activities of respiratory chain complexes correlate linearly with heteroplasmy of deleted mtDNA without threshold and independently of deletion size. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1556, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- megSAP—A Medical Genetics Sequence Analysis Pipeline. Available online: https://github.com/imgag/megSAP (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Sturm, M.; Schroeder, C.; Bauer, P. SeqPurge: Highly-sensitive adapter trimming for paired-end NGS data. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assemblycontigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997 [q-bio.GN]. [Google Scholar]
- Mose, L.E.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N.; Perou, C.M.; Parker, J.S. ABRA: Improved coding indel detection via assembly-based realignment. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2813–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907 [q-bio.GN]. [Google Scholar]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly (Austin) 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Clark, A.G.; Donnelly, P.; Eichler, E.E.; Flicek, P.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ngs-bits—Short-read sequencing tools for diagnostics: GSvar. Available online: https://github.com/imgag/ngs-bits (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Den Dunnen, J.T.; Dalgleish, R.; Maglott, D.R.; Hart, R.K.; Greenblatt, M.S.; McGowan-Jordan, J.; Roux, A.F.; Smith, T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Taschner, P.E. HGVS Recommendations for the Description of SequenceVariants: 2016 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 6, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, H.; Vogler, L.; Seibel, P. Ragged red or ragged blue fibers. Eur. Neurol. 1996, 36, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereau, M.; Anheim, M.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Magot, A.; Verny, C.; Goideau-Sevrain, M.; Barth, M.; Amati-Bonneau, P.; Allouche, S.; Ayrignac, X.; et al. The wide POLG-related spectrum: An. integrated view. J. Neurol Sci. 2016, 368, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zierz, C.M.; Joshi, P.R.; Zierz, S. Frequencies of myohistological mitochondrial changes in patients with mitochondrial DNA deletions and the common m.3243A>G point mutation. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanson, J.B.; Lannes, B.; Echaniz-Laguna, A. Is deltoid muscle biopsy useful in isolated camptocormia? A prospective study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, C.; Quarta, M.; Wei-LaPierre, L.; Michelucci, A.; Nori, A.; Reggiani, C.; Dirksen, R.T.; Protasi, F. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and cores in muscle from calsequestrin-1 knockout mice. Skelet. Muscle 2015, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungbluth, H. Central core disease. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewry, C.A.; Müller, C.; Davis, M.; Dwyer, J.S.; Dove, J.; Evans, G.; Schröder, R.; Fürst, D.; Helliwell, T.; Laing, N.; et al. The spectrum of pathology in central core disease. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2002, 12, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Respiratory Chain Complexes | Enzyme Activity (U/g Tissue) | |
|---|---|---|
| Patient | Controls (n = 20) Mean ± SD (Range) | |
| Complex I | 0.125 | 0.9 ± 0.6 (0.35–2.5) |
| Complexes II + III | 0.48 | 1.8 ± 0.8 (0.8–2.6) |
| Complex IV (COX) | 1.8 | 10.3 ± 1.5 (8.2–12.4) |
| Citrate synthase | 0.34 | 8.4 ± 2.7 (4.0–11.2) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehmann Urban, D.; Motlagh Scholle, L.; Alt, K.; Ludolph, A.C.; Rosenbohm, A. Camptocormia as a Novel Phenotype in a Heterozygous POLG2 Mutation. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020068
Lehmann Urban D, Motlagh Scholle L, Alt K, Ludolph AC, Rosenbohm A. Camptocormia as a Novel Phenotype in a Heterozygous POLG2 Mutation. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehmann Urban, Diana, Leila Motlagh Scholle, Kerstin Alt, Albert C. Ludolph, and Angela Rosenbohm. 2020. "Camptocormia as a Novel Phenotype in a Heterozygous POLG2 Mutation" Diagnostics 10, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020068
APA StyleLehmann Urban, D., Motlagh Scholle, L., Alt, K., Ludolph, A. C., & Rosenbohm, A. (2020). Camptocormia as a Novel Phenotype in a Heterozygous POLG2 Mutation. Diagnostics, 10(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020068




