Flexible Enantioselectivity of Tryptophanase Attributable to Benzene Ring in Heterocyclic Moiety of D-Tryptophan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of DAP and D-Tryptophan on L-Tryptophan Degradation Reaction
| DAP concn./M | k cat/s | Km/mM | k cat/Km/M∙s | Inhibition const./mM | Inhibition type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki | Ki' | |||||
| 0 | 0.40 | 0.3 | 1.3×103 | 21 | - | competitive |
| 0.6 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.9×103 | 25 | 128 | mixed |
| 1.2 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.8×103 | 30 | 90 | mixed |
| 1.9 | 0.11 | 0.2 | 0.6×103 | 38 | 56 | mixed |
| 3.1 | 0.07 | 0.2 | 0.4×103 | 49 | 49 | noncompetitive |
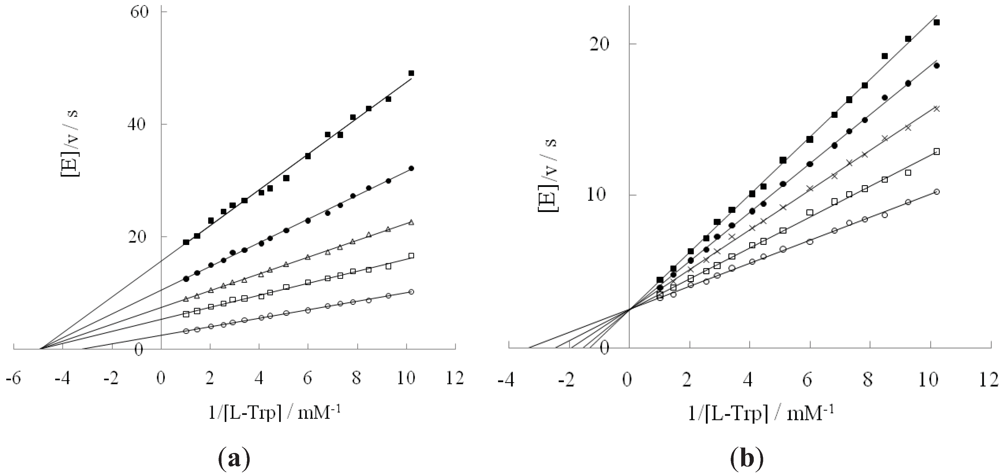
2.2. Inhibition Behavior of D-Tryptophan in the Presence of DAP
2.3. Inhibition Type of Two Tryptophan Analogues
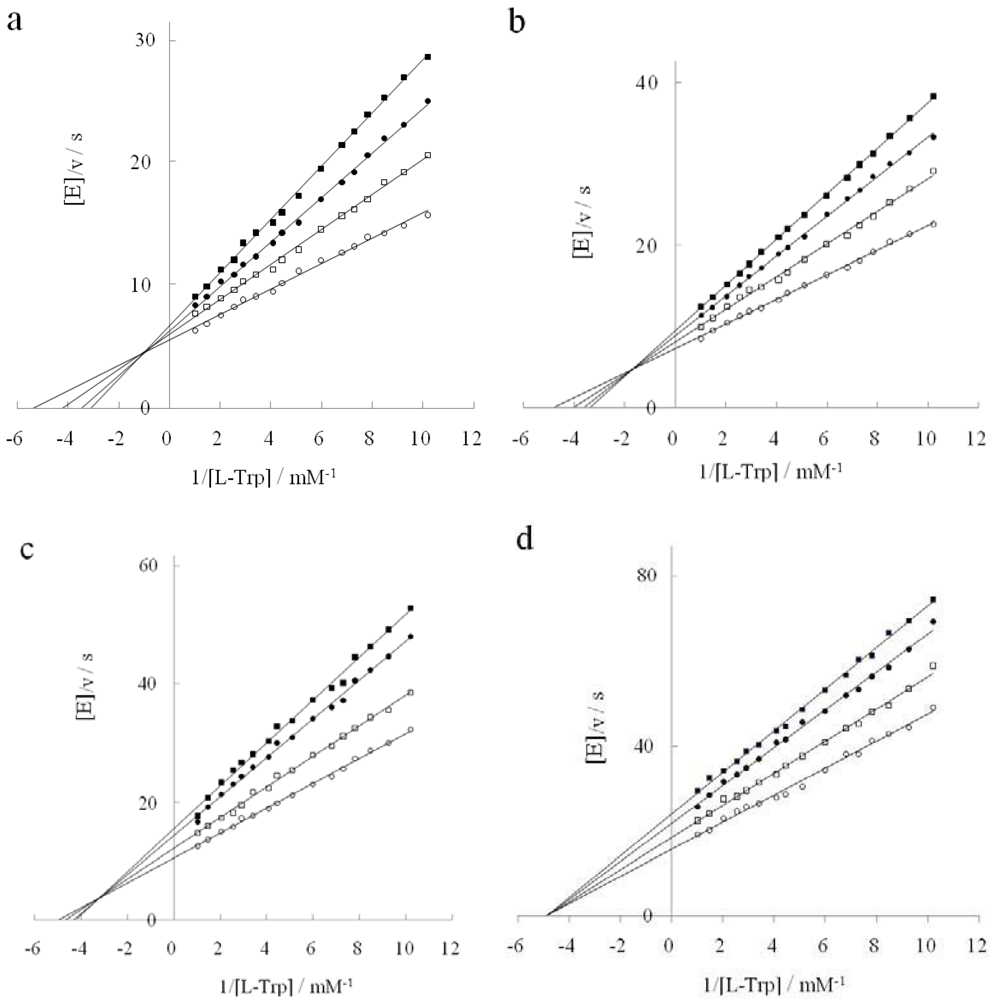

| inhibitor | substrate | DAP concn./M | Inhibition const./mM | Inhibition type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki | Ki' | ||||
| potassium pyruvate | L-Trp | 0 | 3 | - | competitive |
| indole pyruvate | L-Trp | 0 | 0.2 | - | competitive |
| L-Trp | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.3 | mixed | |
| L-Trp | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | noncompetitive | |
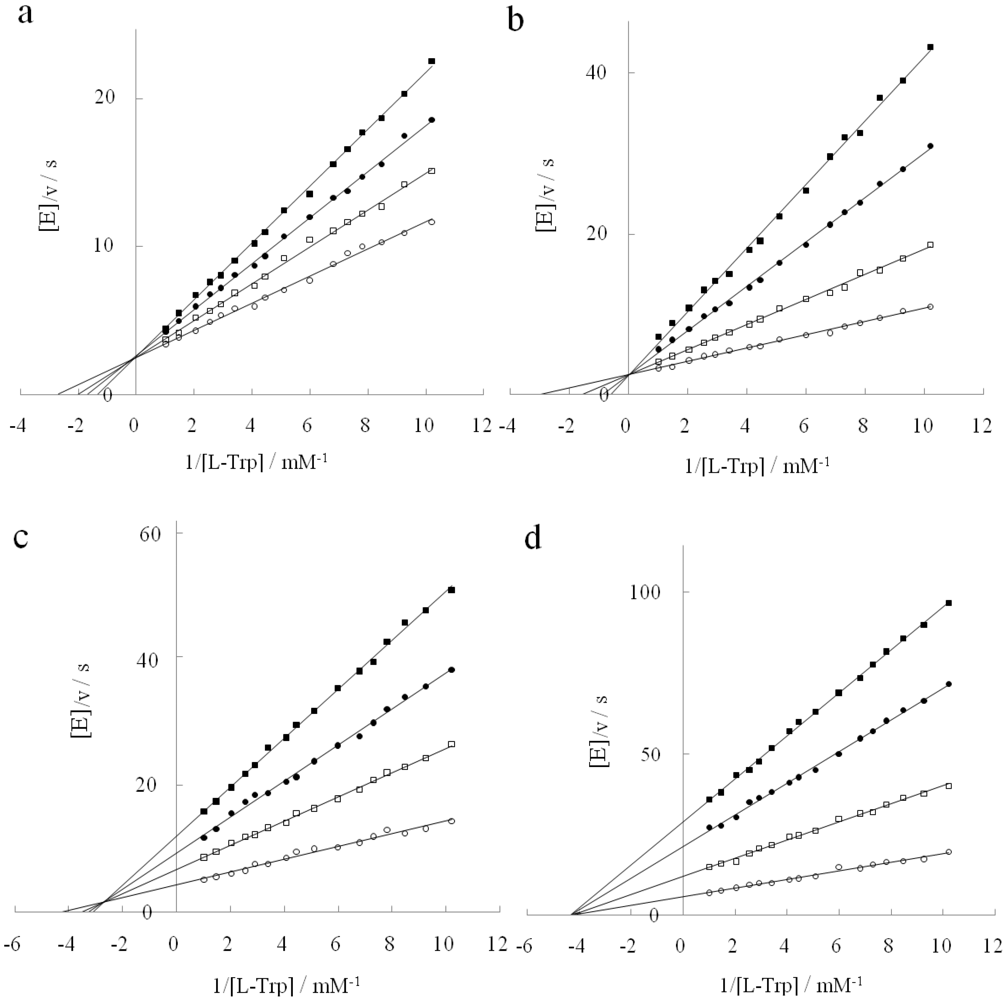
2.4. Inhibitory Action of D-Histidine with Pentagonal Heterocyclic Ring


2.5. Flexible Enantioselectivity of Tryptophanase
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Reaction Conditions
3.3. Kinetic Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Bonner, W.A. The origin and amplification of biomolecular chirality. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 1991, 21, 59–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.A.; Chyba, C.F. Racemization of meteoritic amino acids. Icarus 2000, 145, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, A.; Miller, S.L. How long did it take for life to begin and evolve to cyanobacteria? J. Mol. Evol. 1994, 39, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bada, J.L.; Miller, S.L. Racemization and the origin of optically active organic compounds in living organisms. Biosystems 1987, 20, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, M. Question 4: Basic questions about the origin of life: On chirobiogenesis. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2007, 37, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzarello, S.; Weber, A.L. Prebiotic amino acids as asymmetric catalysts. Science 2004, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.A. Chirality and life. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 1995, 25, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reist, M.; Carrupt, P.A.; Francotte, E.; Testa, B. Chiral inversion and hydrolysis of thalidomide: Mechanisms and catalysis by bases and serum albumin, and chiral stability of teratogenic metabolites. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1998, 11, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, W.A.; Snell, E.E. Catalytic properties of tryptophanase, a multifunctional pyridoxal phosphate enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1964, 51, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Nakamura, I. Degradation of D-tryptophan by tryptophanase under high salt concentration. Viva Orig. 1992, 20, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, A.; Ozaki, H.; Saito, T.; Fujii, N. Tryptophanase-catalyzed L-tryptophan synthesis from D-serine in the presence of diammonium hydrogen phosphate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimada, A.; Ozaki, H.; Saito, T.; Fujii, N. Reaction pathway of tryptophanase-catalyzed L-tryptophan synthesis from D-serine. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3289–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulikova, V.V.; Zakomirdina, L.N.; Bazhulina, N.P.; Dementieva, I.S.; Faleev, N.G.; Gollnick, P.D.; Demidkina, T.V. Role of arginine 226 in the mechanism of tryptophan indole-lyase from Proteus vulgaris. Biochemistry 2003, 68, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A. Activity on D-tryptophan Attributable to Slight Conformational Change of Tryptophanase in Highly Concentrated Ammonium Phosphate Solution. In Enzymes Involved in the Metabolism of D-Amino Acids: Practical Methods and Protocols; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 4, pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, K.R. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase: A model for the cooperativity kinetics induced by d- and l-phenylalanine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1981, 211, 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, A.; Nakamura, I. Degradation of D-tryptophan by tryptophanase under high salt concentration. Viva Orig. 1992, 20, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, R. Diastereoisomerism, contact points, and chiral selectivity: A four-site saga. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 414, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, E.E. Tryptophanase: Structure, catalytic activities, and mechanism of action. Adv. Enxymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1975, 42, 287–333. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, A.; Kogure, H.; Shishido, H.; Nakamura, I. Reaction pathway of tryptophanase degrading D-tryptophan. Amino Acids 1997, 12, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgár, L. The catalytic triad of serine peptidases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2161–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidkina, T.V. ; Antson, A.A.; Faleev, N.G.; Phillips, R.S.; Zakomirdina, L.N. Spatial structure and mechanism of tyrosine phenol-lyase and tryptophan indole-lyase. Mol. Biol. (Moskow.) 2009, 43, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaju, B.; Antson, A.A.; Phillips, R.S.; Demidkina, T.V.; Barbolina, M.V.; Gollnick, P.; Dodson, G.G.; Wilson, K.S. The crystal structure of Citrobacter freundii tyrosinephenol-lyase complexed with 3-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)propionicacid, together with site-directed mutagenesis and kineticanalysis, demonstrates that arginine 381 is required for substratespecificity. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 6502–6510. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.S.; Demidkina, T.V.; Faleev, N.G. Structureand mechanism of tryptophan indole-lyase andtyrosine phenol-lyase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1647, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Komoto, J.; Takata, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Pitot, H.C.; Takusagawa, F. Crystal structure of serine dehydratase from rat liver. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 12854–12865. [Google Scholar]
- Urusova, D.V.; Isupov, M.N.; Antonyuk, S.; Kachalova, G.S.; Obmolova, G.; Vagin, A.A.; Lebedev, A.A.; Burenkov, G.P.; Dauter, Z.; Bartunik, H.D.; Lamzin, V.S.; Melik-Adamyan, W.R.; Mueller, T.D.; Schnackerz, K.D. Crystal structure of D-serine dehydratase from Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1824, 422–432. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Phillips, R.S. Binding of phenol and analogues to alanine complexes of tyrosine phenol-lyase from Citrobacter freundii: Implications for the mechanisms of α, β-elimination and alanine racemization. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 11591–11599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimada, A.; Ozaki, H. Flexible Enantioselectivity of Tryptophanase Attributable to Benzene Ring in Heterocyclic Moiety of D-Tryptophan. Life 2012, 2, 215-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/life2020215
Shimada A, Ozaki H. Flexible Enantioselectivity of Tryptophanase Attributable to Benzene Ring in Heterocyclic Moiety of D-Tryptophan. Life. 2012; 2(2):215-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/life2020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimada, Akihiko, and Haruka Ozaki. 2012. "Flexible Enantioselectivity of Tryptophanase Attributable to Benzene Ring in Heterocyclic Moiety of D-Tryptophan" Life 2, no. 2: 215-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/life2020215
APA StyleShimada, A., & Ozaki, H. (2012). Flexible Enantioselectivity of Tryptophanase Attributable to Benzene Ring in Heterocyclic Moiety of D-Tryptophan. Life, 2(2), 215-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/life2020215




