Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Parasitic Lice in Tibetan Yaks, Pigs and Sheep
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
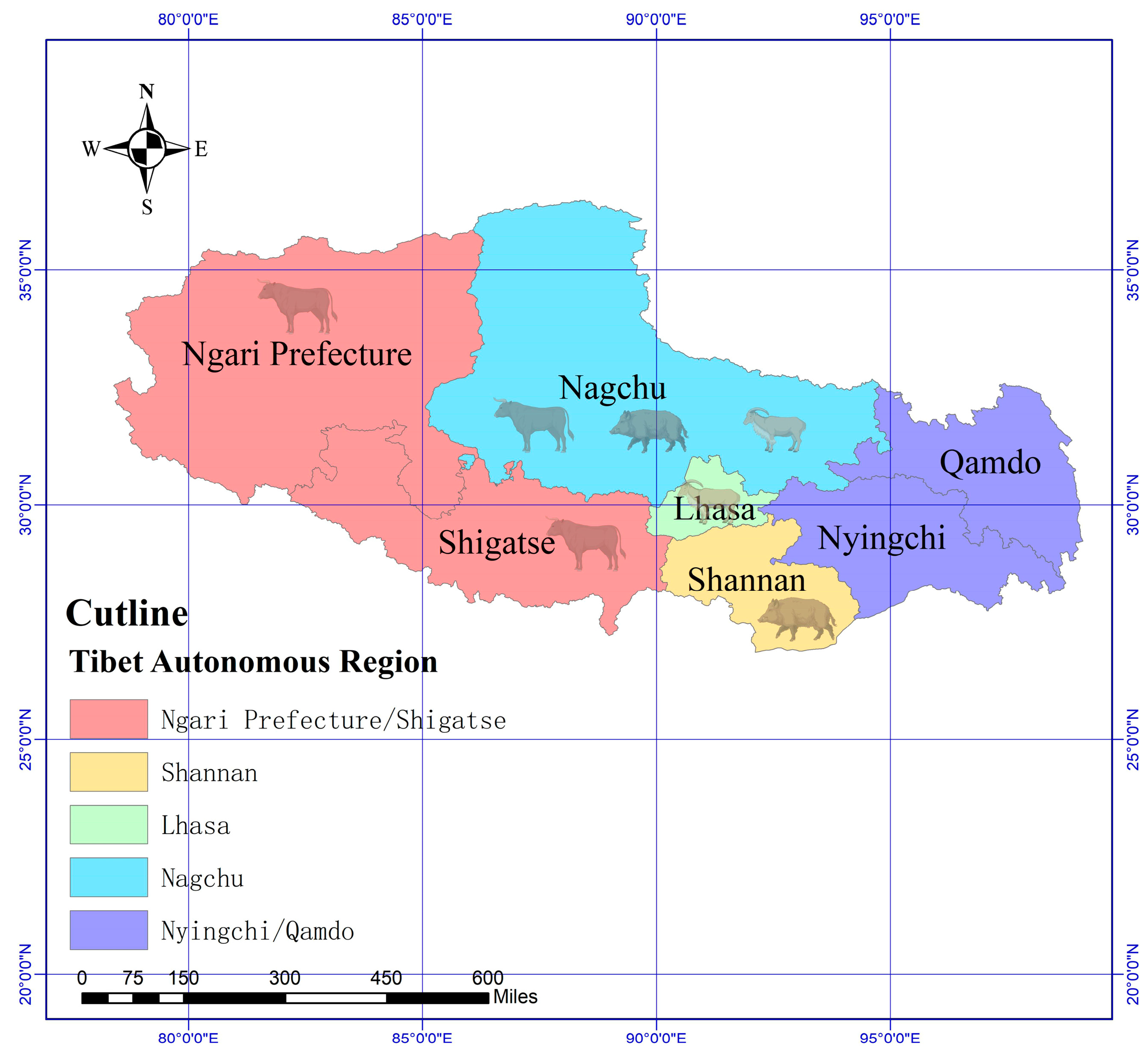
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Lice Examination and Morphological Identification
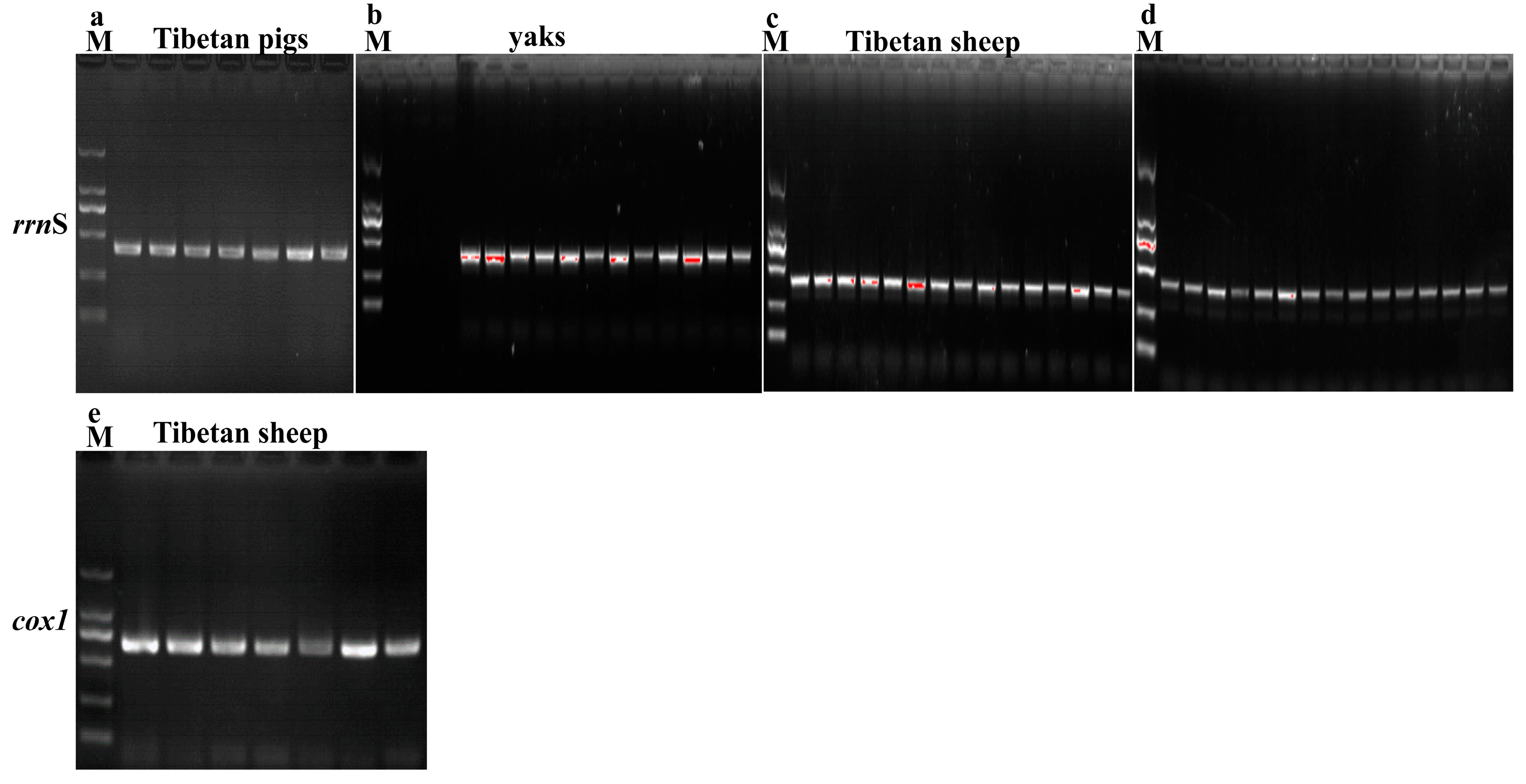
2.3. DNA Extraction and rrnS and cox1 Genes Amplification
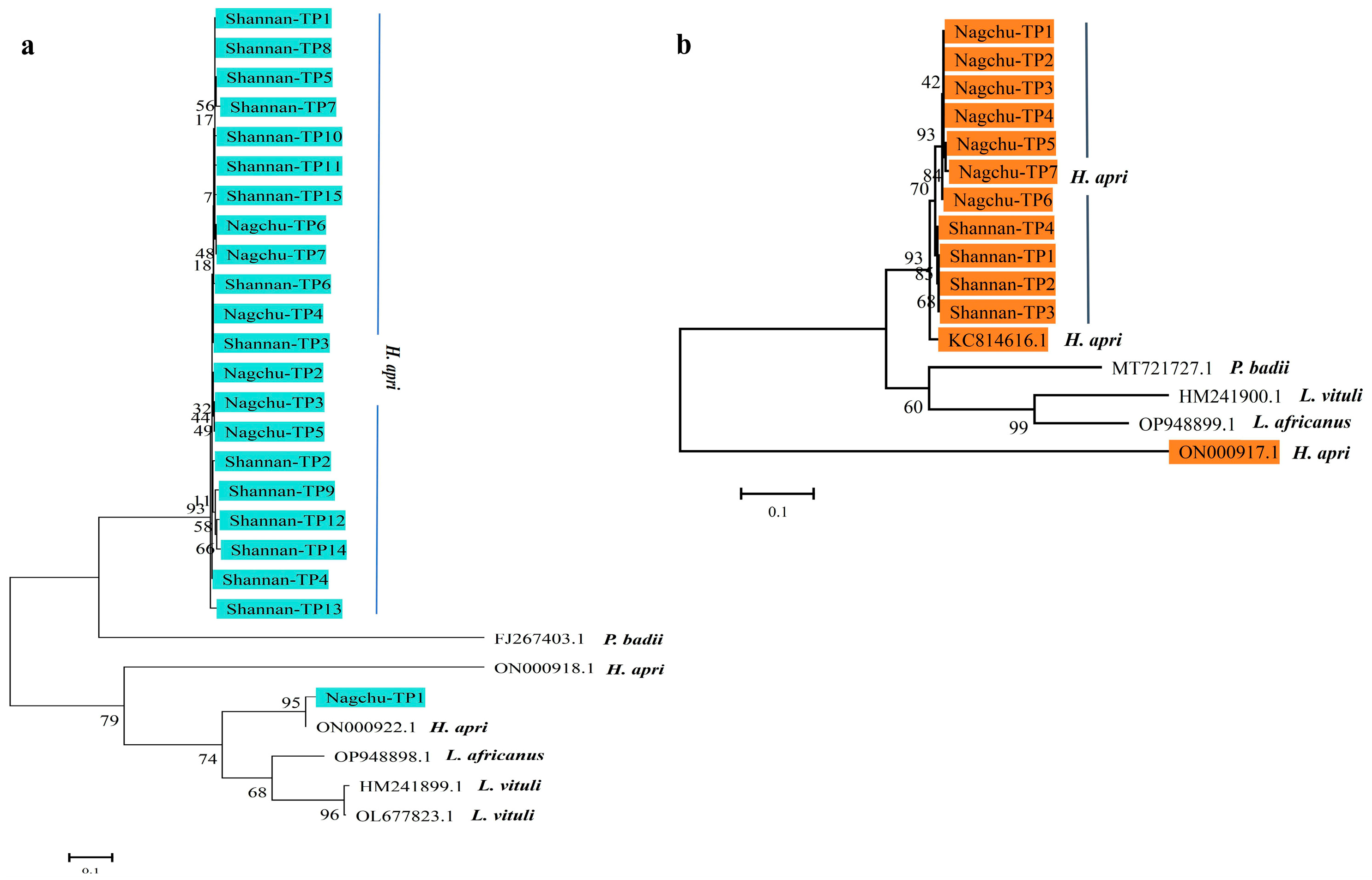
2.4. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Prevalence of Lice in Yaks, Tibetan Sheep and Tibetan Pigs
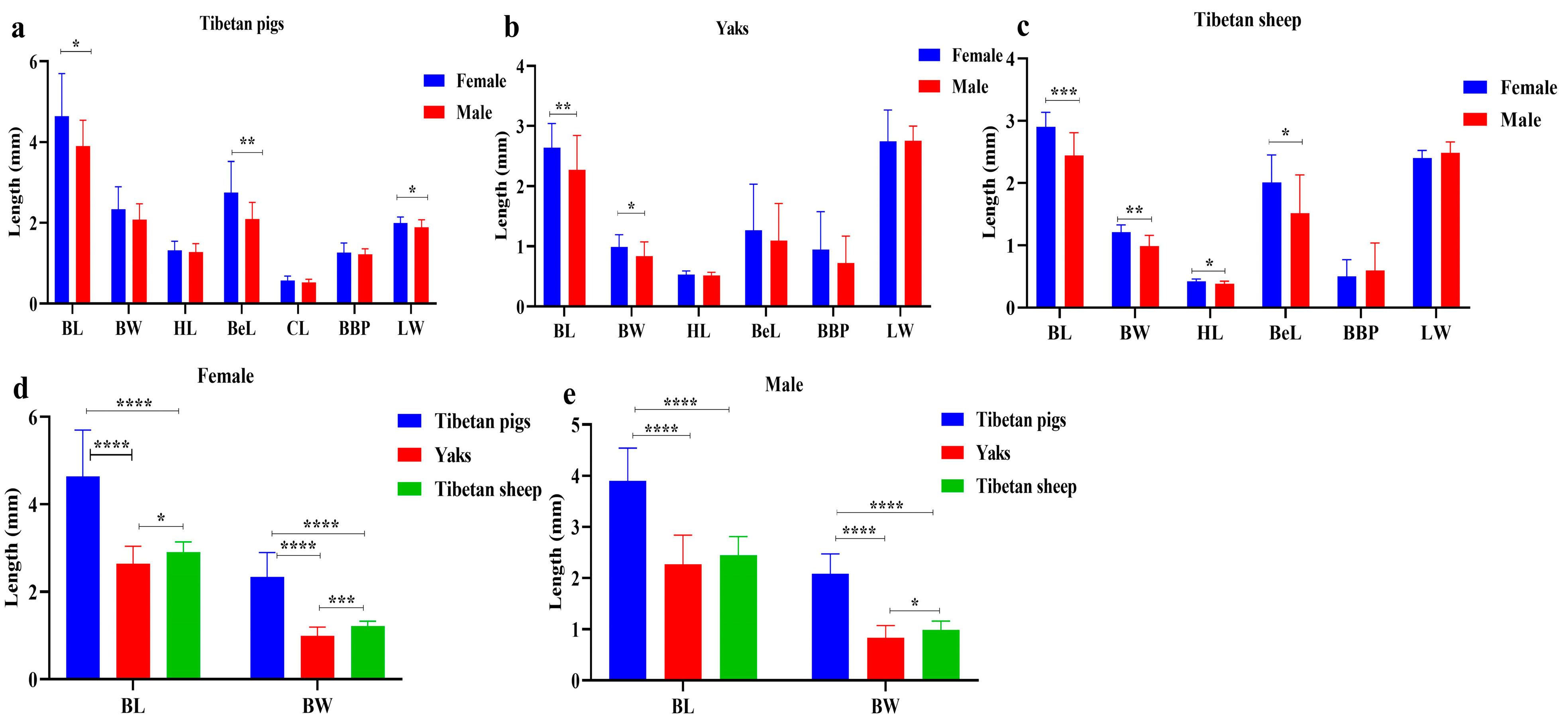
3.2. Molecular Characterization of Lice in Yaks, Tibetan Sheep and Tibetan Pigs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Gao, J.; Shahzad, M.; Han, Z.; Nabi, F.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, J. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in yaks (Bos grunniens) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Saeed, N.M.; Ding, J.; Dong, H.; Kulyar, M.F.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Mehmood, K.; Ali, M.M.; Irshad, I.; Zeng, J.; et al. Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Cryptosporidium sp., Giardia duodenalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Blastocystis sp. Infection in Free-ranged Yaks and Tibetan Pigs on the Plateau. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Z.; Luo, H.; Mehmood, K.; Shahzad, M.; Lan, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J. Epidemiological investigation and risk factors of Echinococcus granulosus in yaks (Bos grunniens), Tibetan pigs and Tibetans on Qinghai Tibetan plateau. Acta Trop. 2017, 173, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Xu, C.; Saleem, M.U.; Babar, W.; Idrees, A.; Li, K. Epidemiological Investigation of Cryptosporidium Infection in Yaks in Chamdo, China. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 2, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Ma, S.K.; Peng, W.; Fang, Y.G.; Duo, H.R.; Fu, H.Y.; Jia, G.X. Genetic diversity and population structure of Tibetan sheep breeds determined by whole genome resequencing. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, P.; Li, F.; Chang, S.; Yan, T.; Zheng, H.; Hou, F. Shift of Feeding Strategies from Grazing to Different Forage Feeds Reshapes the Rumen Microbiota to Improve the Ability of Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries) to Adapt to the Cold Season. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, 02816-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, T.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Lang, X.; Ma, Y. Whole genome sequencing revealed genetic diversity, population structure, and selective signature of Panou Tibetan sheep. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Luo, H.; Zhang, H.; Lan, Y.; Han, Z.; Shahzad, M.; Wang, X.; Qiu, G.; Huang, S.; Jiang, W.; et al. First report of Metastrongylus pudendotectus by the genetic characterization of mitochondria genome of cox1 in pigs from Tibet, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 223, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Q.; Idrees, A.; Almutairi, M.H.; Dong, H. A Comparative Analysis and Verification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs could Provide New Insights for the Treatment of Endometritis in Yaks. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 3, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhaxi, Y.; Liu, M.; Idrees, A.; Li, K. Revealing the Fungi Microbiome Difference of Suffolk Cross with Tibetan Sheep on Plateau. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 4, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRosa, A.A.; Pullins, A.; Tena, J.K.; Holzmer, S.; Packianathan, R. Effectiveness of a fixed-dose combination injectable (0.2 mg/kg doramectin + 6.0 mg/kg levamisole hydrochloride) against Rhipicephalus microplus and sucking lice infesting cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 323, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promrangsee, C.; Khositharattanakool, P.; Somwang, P.; Sunantaraporn, S.; Phumee, A.; Preativatanyou, K.; Tawatsin, A.; Brownell, N.; Siriyasatien, P. The Prevalence of Bartonella Bacteria in Cattle Lice Collected from Three Provinces of Thailand. Insects 2019, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisi, L.; Leite, R.C.; Martins, J.R.D.S.; Barros, A.T.M.D.; Andreotti, R.; Cançado, P.H.D.; León, A.A.P.D.; Pereira, J.B.; Villela, H.S. Reassessment of the potential economic impact of cattle parasites in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014, 23, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, A.F.; Reeve, I.; Kahn, L.P.; Thompson, L.J.; Horton, B.J.; Walkden-Brown, S.W. Prevalence of sheep lice and trends in control practices across Australia—Australian sheep parasite control surveys from 2003 to 2019. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2022, 27, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Bashir, R.; Mahmood, M.; Afzal, M.S.; Simsek, S.; Awan, U.A.; Khan, M.R.; Ahmed, H.; Cao, J. Epidemiology of Ectoparasites (Ticks, Lice, and Mites) in the Livestock of Pakistan: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 780738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, D. Life history parameters of the cattle long-nosed sucking louse, Linognathus vituli. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2014, 28, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, J.F.; Jenkins, C.; Bogema, D.; Emery, D. Mechanical transfer of Theileria orientalis: Possible roles of biting arthropods, colostrum and husbandry practices in disease transmission. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Fernández De Mera, I.G.; Meli, M.L.; Elek, V.; Hajtós, I.; Répási, A.; Gönczi, E.; Tánczos, B.; Farkas, R.; et al. Survey on blood-sucking lice (Phthiraptera: Anoplura) of ruminants and pigs with molecular detection of Anaplasma and Rickettsia spp. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 174, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanov Nizamov, N. Identification of ectoparasitic insects among domestic goats in Bulgaria. Vet. World 2023, 16, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, Y.; Yacob, H.T.; Ashenafi, H. Ectoparasites of small ruminants in three selected agro-ecological sites of Tigray Region, Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, J.; Krüger, A.; Rakotondranary, S.J.; Ratovonamana, R.Y.; Poppert, S.; Ganzhorn, J.U.; Tappe, D. Molecular detection of Rickettsia spp., Borrelia spp., Bartonella spp. and Yersinia pestis in ectoparasites of endemic and domestic animals in southwest Madagascar. Acta Trop. 2020, 205, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Fu, Y.-T.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Tang, W.-Q.; Liu, G.-H. Comparative analyses of the fragmented mitochondrial genomes of wild pig louse Haematopinus apri from China and Japan. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 18, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, N.; Muzaffar, S.B.; Al-Sabi, M.N.S.; Hamdan, L.; Aldarwich, A.; Iliashevich, D.; Mohteshamuddin, K.; Sparagano, O.A.; Willingham, A.L. The first record of ostrich feather louse (Struthiolipeurus struthionis) collected from farmed ostriches (Struthio camelus) in the United Arab Emirates. Vet. World 2024, 17, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.J.; Sweet, A.D. Prevalence and diversity of parasitic bird lice (Insecta: Psocodea) in northeast Arkansas. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 22, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Mu, D.; Tian, Z.; Li, D.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Guan, G.; Yin, H.; Li, F. Molecular Detection of Babesia gibsoni in Cats in China. Animals 2022, 12, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyonsenga, E.; Twizerimana, J.; Mwabonimana, M.F. Haematopinus suis Infestation in Pig Farms in Busogo Sector, Rwanda. J. Trop. Med. 2023, 2023, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballados-González, G.G.; Martínez-Hernández, J.M.; Martínez-Rodríguez, P.B.; Gamboa-Prieto, J.; González-Guzmán, S.; Paredes-Cervantes, V.; Grostieta, E.; Becker, I.; Aguilar-Domínguez, M.; Vieira, R.F.C.; et al. Molecular detection of hemotropic Mycoplasma and Bartonella species in lice from sheep and goats of Mexico. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2023, 44, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckiernan, F.; O’Connor, J.; Minchin, W.; O’Riordan, E.; Dillon, A.; Harrington, M.; Zintl, A. A pilot study on the prevalence of lice in Irish beef cattle and the first Irish report of deltamethrin tolerance in Bovicola bovis. Ir. Vet. J. 2021, 74, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insyari’ati, T.; Hamid, P.H.; Rahayu, E.T.; Sugar, D.L.; Rahma, N.N.; Kusumarini, S.; Kurnianto, H.; Wardhana, A.H. Ectoparasites Infestation to Small Ruminants and Practical Attitudes among Farmers toward Acaricides Treatment in Central Region of Java, Indonesia. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsa, B.; Socolovschi, C.; Parola, P.; Rolain, J.; Raoult, D. Molecular Detection of AcinetobacterSpecies in Lice and Keds of Domestic Animals in Oromia Regional State, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2012, 12, e52377. [Google Scholar]
- Rashmi, A.; Saxena, A.K. Population levels of phthirapteran ectoparasites on the goats in Rampur (U.P.). J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, D.B.; Ruiz, M.; Sanchez, J.P. First molecular detection of Mycoplasma suis in the pig louse Haematopinus suis (Phthiraptera: Anoplura) from Argentina. Acta Trop. 2019, 194, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, Y.; Dimri, U.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Devi, G. A study on prevalence and factors associated with ectoparasitism in goats of two agro-climatic regions in India. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakew, B.T.; Kheravii, S.K.; Wu, S.; Eastwood, S.; Andrew, N.R.; Nicholas, A.H.; Walkden-Brown, S.W. Detection and distribution of haematophagous flies and lice on cattle farms and potential role in the transmission of Theileria orientalis. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 298, 109516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwell, D.D. Persistent activity of moxidectin pour-on and injectable against sucking and biting louse infestations of cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 104, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braae, U.C.; Ngowi, H.A.; Johansen, M.V. Smallholder pig production: Prevalence and risk factors of ectoparasites. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, Y.; Oguchi, K.; Murakami, M.; Moriyama, M.; Koga, R.; Fukatsu, T. Endosymbiotic bacteria of the boar louse Haematopinus apri (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Anoplura). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsul, V.S.; Okene, I.A.A.; Yahya, S.N.C.; Hamdan, R.H.; Lee, S.H.; Tan, L.P. Prevalence of Ectoparasitism on Small Ruminants in Kelantan, Malaysia. Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2020, 31, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-T.; Shao, R.; Suleman; Wang, W.; Wang, H.-M.; Liu, G.-H. The fragmented mitochondrial genomes of two Linognathus lice reveal active minichromosomal recombination and recombination hotspots. Iscience 2023, 26, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehounoud, C.B.; Fenollar, F.; Dahmani, M.; N’Guessan, J.D.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. Bacterial arthropod-borne diseases in West Africa. Acta Trop. 2017, 171, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target Gene | Name of Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Size of Target Band (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| cox1 | HACX1F | GCATATAATTATGGAGGAGAGAGGAA | 657 |
| HACX1R | ATGACCAAAAAACCAGAATAGATGCTGG | ||
| rrnS | HA12SF | GGTCCATGAAAACTAATAACATATGGCGGT | 452 |
| HA12R | CATTGTATATAGTAGGGTATCTAATCCTAG |
| Variable | Category | No. Examined | No. Positive | % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region a | Lhasa | 26 | 2 | 7.7% (0.9–25.1%) |
| Ngari | 20 | 3 | 15.0% (3.2–37.9%) | |
| Shigatse | 9 | 4 | 44.4% (13.7–78.8%) | |
| Shannan | 11 | 5 | 45.5% (16.7–76.6%) | |
| Nagchu | 123 | 83 | 67.5% (58.4–75.6%) | |
| Breed b | Domestic yak | 77 | 14 | 18.2% (10.3–28.6%) |
| Tibetan pig | 20 | 10 | 50.0% (27.2–72.8%) | |
| Tibetan sheep | 91 | 72 | 93.5% (85.5–97.9%) | |
| Wild yak | 1 | 1 | 100.0% (2.5–100.0%) | |
| Total | 189 | 97 | 51.3% (44.0–58.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Shi, B.; Nawaz, S.; Wu, Q.; Tang, W. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Parasitic Lice in Tibetan Yaks, Pigs and Sheep. Life 2025, 15, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030444
Luo W, Zhao X, Wang D, Shi B, Nawaz S, Wu Q, Tang W. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Parasitic Lice in Tibetan Yaks, Pigs and Sheep. Life. 2025; 15(3):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030444
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Wanmei, Xialing Zhao, Dengyun Wang, Bin Shi, Shah Nawaz, Qingxia Wu, and Wenqiang Tang. 2025. "Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Parasitic Lice in Tibetan Yaks, Pigs and Sheep" Life 15, no. 3: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030444
APA StyleLuo, W., Zhao, X., Wang, D., Shi, B., Nawaz, S., Wu, Q., & Tang, W. (2025). Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Parasitic Lice in Tibetan Yaks, Pigs and Sheep. Life, 15(3), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030444





