A Case of Interstitial Lung Disease-Related Pulmonary Hypertension Successfully Treated with Inhaled Iloprost
Abstract
1. Introduction
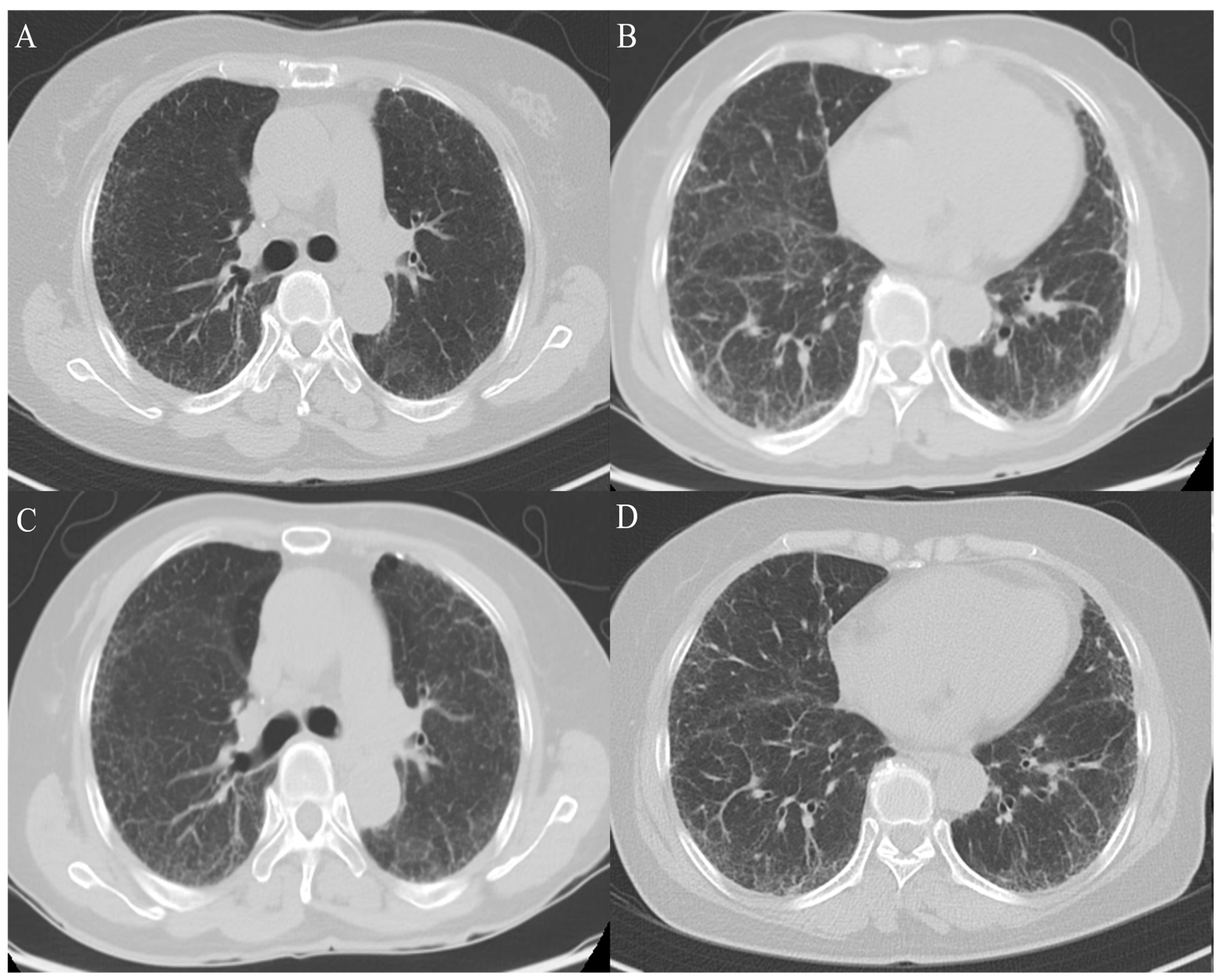
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassoun, P.M. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2361–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, J.; Nathan, S.D. Pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease: Screening, diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2021, 27, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.S.; Shlobin, O.A. The Trouble with Group 3 Pulmonary Hypertension in Interstitial Lung Disease: Dilemmas in Diagnosis and the Conundrum of Treatment. Chest 2020, 158, 1651–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, J.; Hudzik, B.; Niedziela, J.; Rozentryt, P.; Zembala, M.; Gasior, M. Role of Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Serum Concentration in the Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with End-Stage Lung Diseases Referred for Lung Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 2044–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger, J.R. Group III Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Lung Disease: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatments. Cardiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Barbera, J.A.; Gaine, S.P.; Harari, S.; Martinez, F.J.; Olschewski, H.; Olsson, K.M.; Peacock, A.J.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Provencher, S.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung disease and hypoxia. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxman, A.; Restrepo-Jaramillo, R.; Thenappan, T.; Ravichandran, A.; Engel, P.; Bajwa, A.; Allen, R.; Feldman, J.; Argula, R.; Smith, P.; et al. Inhaled Treprostinil in Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, C.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Barnett, S.D.; Ahmad, S.; Shorr, A.F. Prevalence and outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2006, 129, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffenach, G.; Hong, J.; Vaillancourt, M.; Medzikovic, L.; Eghbali, M. Pulmonary hypertension secondary to pulmonary fibrosis: Clinical data, histopathology and molecular insights. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacprzak, A.; Tomkowski, W.; Szturmowicz, M. Pulmonary Hypertension in the Course of Interstitial Lung Diseases-A Personalised Approach Is Needed to Identify a Dominant Cause and Provide an Effective Therapy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research, N.; Zisman, D.A.; Schwarz, M.; Anstrom, K.J.; Collard, H.R.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hunninghake, G.W. A controlled trial of sildenafil in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Raghu, G.; Wells, A.U.; Behr, J.; Richeldi, L.; Schinzel, B.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; Martinez, F.J.; Investigators, I. Nintedanib plus Sildenafil in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Nathan, S.D.; Wuyts, W.A.; Mogulkoc Bishop, N.; Bouros, D.E.; Antoniou, K.; Guiot, J.; Kramer, M.R.; Kirchgaessler, K.U.; Bengus, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil added to pirfenidone in patients with advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and risk of pulmonary hypertension: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Egan, J.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Wells, A.U.; Collard, H.R.; et al. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with ambrisentan: A parallel, randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Behr, J.; Collard, H.R.; Cottin, V.; Hoeper, M.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Corte, T.J.; Keogh, A.M.; Leuchte, H.; Mogulkoc, N.; et al. Riociguat for idiopathic interstitial pneumonia-associated pulmonary hypertension (RISE-IIP): A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, B.J.; Silverstein, A.M.; Mottola, D.M.; Clapp, L.H. Binding and activity of the prostacyclin receptor (IP) agonists, treprostinil and iloprost, at human prostanoid receptors: Treprostinil is a potent DP1 and EP2 agonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxman, A.; Restrepo-Jaramillo, R.; Thenappan, T.; Engel, P.; Bajwa, A.; Ravichandran, A.; Feldman, J.; Hajari Case, A.; Argula, R.G.; Tapson, V.; et al. Long-term inhaled treprostinil for pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease: INCREASE open-label extension study. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2202414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria-Urbina, M.; Oliveira, R.K.F.; Agarwal, M.; Waxman, A.B. Inhaled Treprostinil in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Lung Disease. Lung 2018, 196, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olschewski, H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Walmrath, D.; Schermuly, R.; Temmesfeld-Wollbruck, B.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W. Inhaled prostacyclin and iloprost in severe pulmonary hypertension secondary to lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

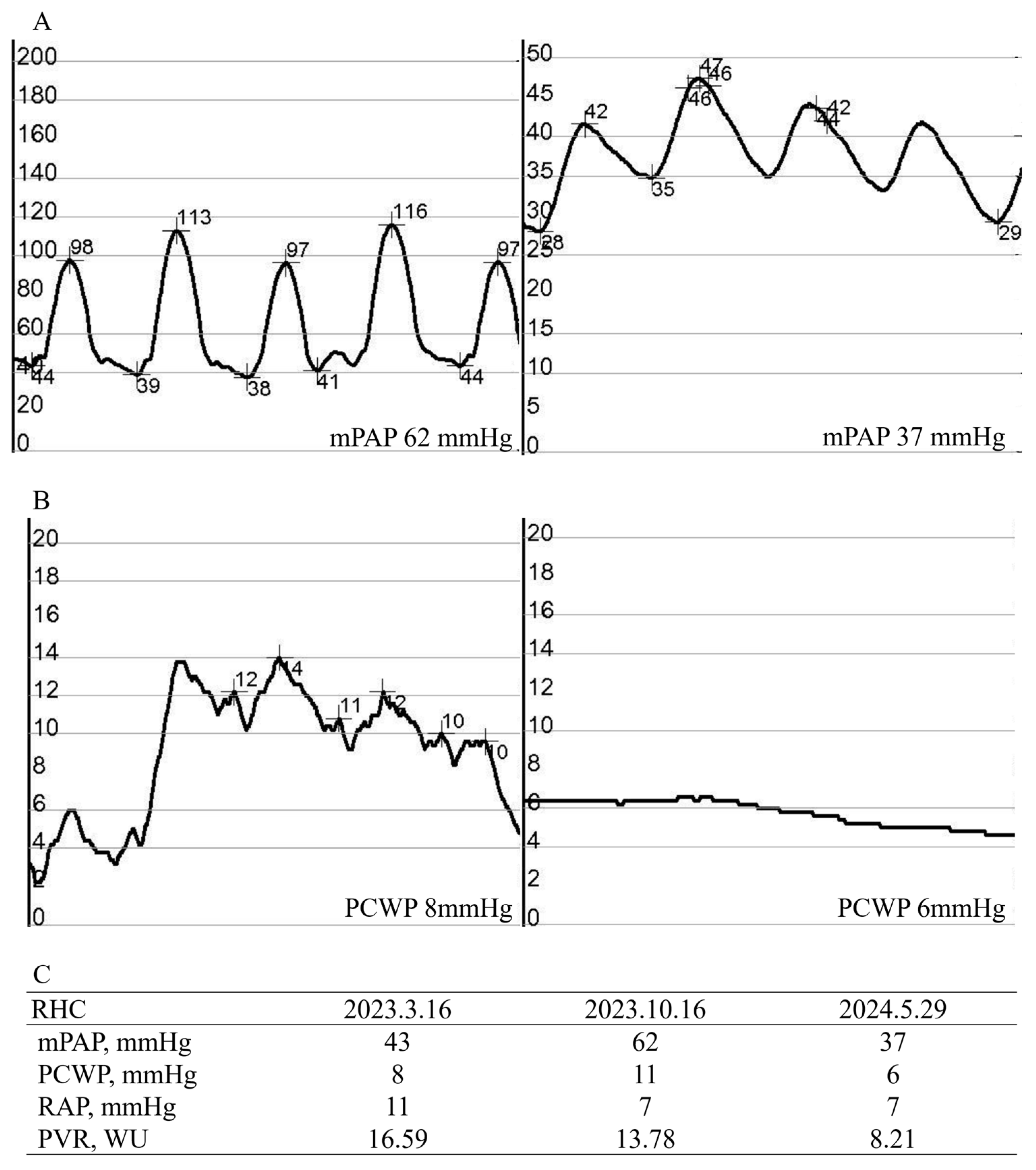
| March 2023 | July 2023 | October 2023 | January 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF, % | 61 | 56 | 58 | 62 |
| TAPSE, mm | 11 | 11.3 | 11.8 | 12.8 |
| TR Vmax, m/s | 4.2 | 3.81 | 4.25 | 3.44 |
| PG (RV–RA), mmHg | 70.6 | 58.1 | 72.3 | 47.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.H.; Jang, H.-J.; Lee, J.H. A Case of Interstitial Lung Disease-Related Pulmonary Hypertension Successfully Treated with Inhaled Iloprost. Life 2024, 14, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091068
Jang JH, Jang H-J, Lee JH. A Case of Interstitial Lung Disease-Related Pulmonary Hypertension Successfully Treated with Inhaled Iloprost. Life. 2024; 14(9):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091068
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Ji Hoon, Hang-Jea Jang, and Jae Ha Lee. 2024. "A Case of Interstitial Lung Disease-Related Pulmonary Hypertension Successfully Treated with Inhaled Iloprost" Life 14, no. 9: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091068
APA StyleJang, J. H., Jang, H.-J., & Lee, J. H. (2024). A Case of Interstitial Lung Disease-Related Pulmonary Hypertension Successfully Treated with Inhaled Iloprost. Life, 14(9), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14091068






