Prognostic and Clinical Significance of PD-L1, EGFR and Androgen Receptor (AR) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
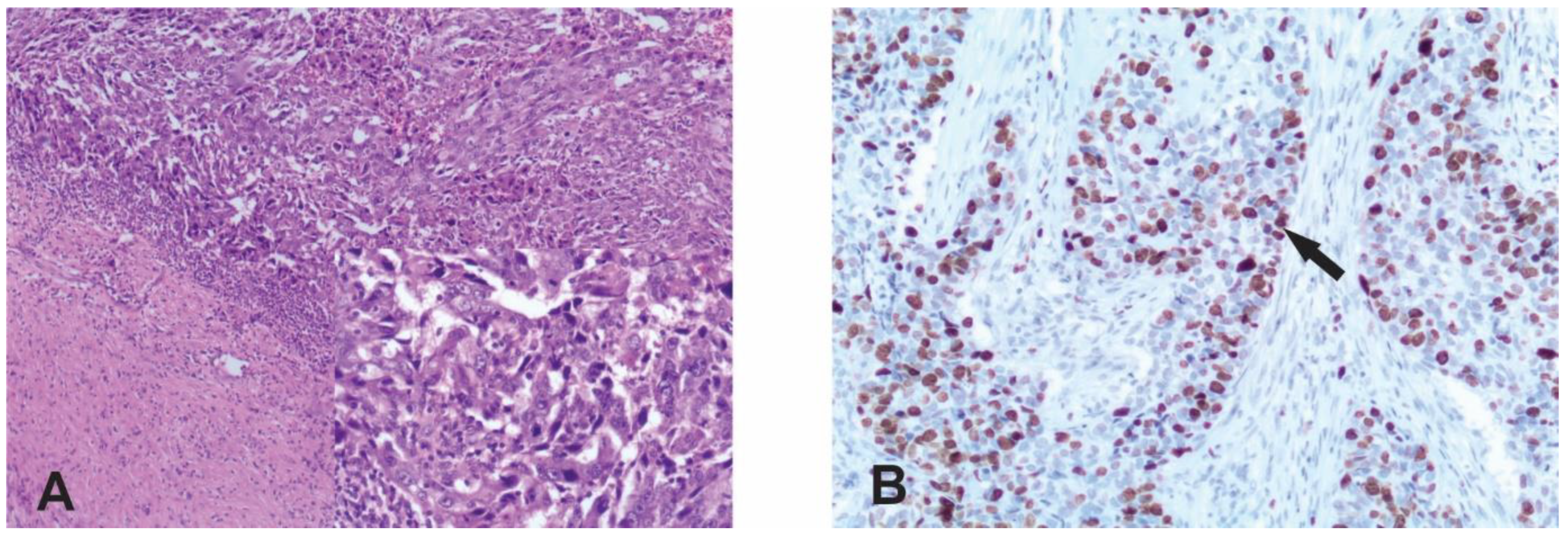
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Evaluation of Staining
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
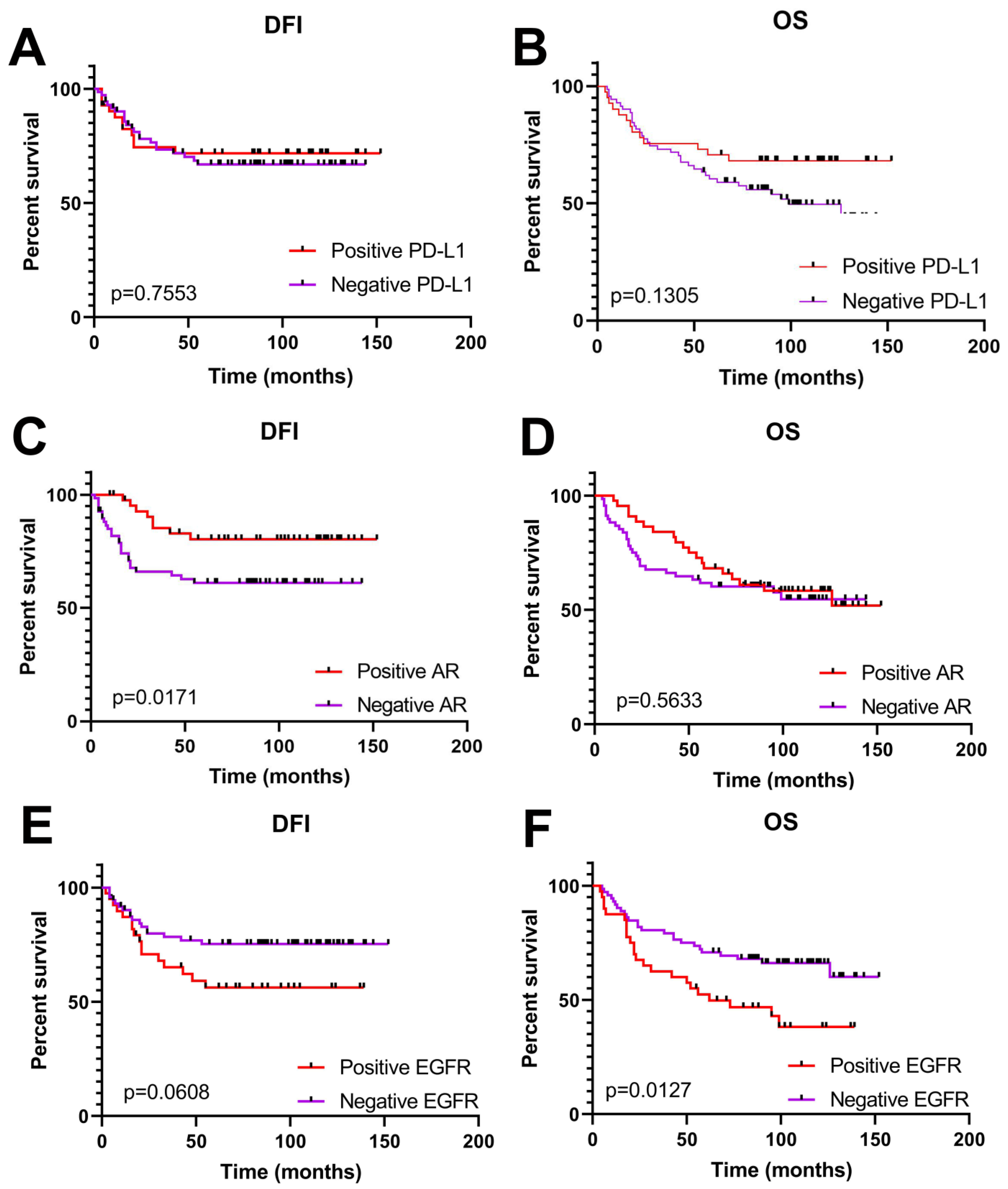
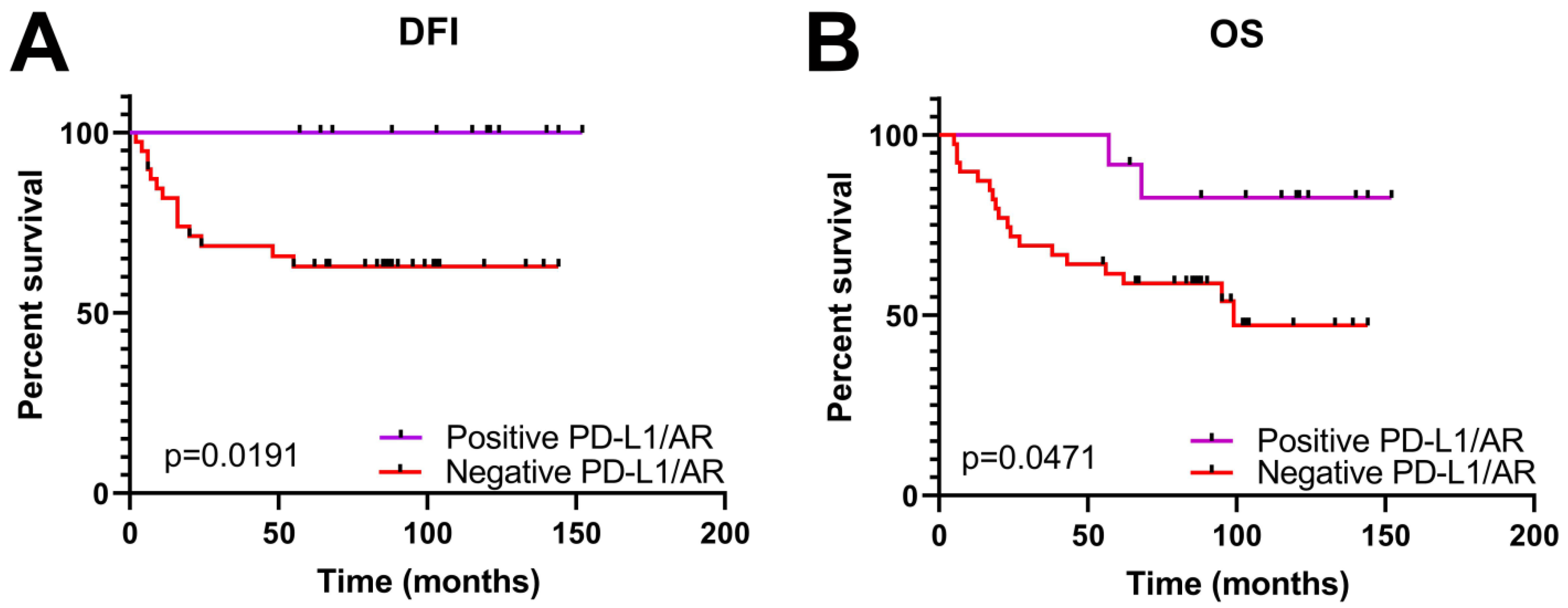
Clinical Significance of PD-L1, AR and EGFR Expression in TNBC Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagami, P.; Carey, L.A. Triple negative breast cancer: Pitfalls and progress. npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennecke, H.; Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Cheang, M.C.; Voduc, D.; Speers, C.H.; Nielsen, T.O.; Gelmon, K. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeljković, M.; Damjanović, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera Juarez, M.; Tolosa Ortega, P.; Sanchez de Torre, A.; Ciruelos Gil, E. Biology of the Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Immunohistochemical, RNA, and DNA Features. Breast Care 2020, 15, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, P.; Fei, X.; Zong, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, O.; He, J.-R.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of Ki-67 in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31079–31087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thike, A.A.; Chong, L.Y.Z.; Cheok, P.Y.; Li, H.H.; Yip, G.W.C.; Bay, B.H.; Tse, G.M.K.; Iqbal, J.; Tan, P.H. Loss of androgen receptor expression predicts early recurrence in triple-negative and basallike breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampurwala, M.; Wisinski, K.B.; O’Regan, R. Role of the androgen receptor in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 14, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Qiu, F. Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumuskaya, B.; Alper, M.; Hucumenoglu, S.; Altundag, K.; Uner, A.; Guler, G. EGFR expression and gene copy number in triple-negative breast carcinoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2010, 203, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 2004, 25, 276–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignon, J.C.; Koopmansch, B.; Nolens, G.; Delacroix, L.; Waltregny, D.; Winkler, R. Androgen Receptor Controls EGFR and ERBB2 Gene Expression at Different Levels in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2941–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, S.S.; Saliminejad, K.; Sotoudeh, M.; Soleimanifard, N.; Kouchaki, S.; Yazdanbod, M.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Ghavamzadeh, A.; Malekzadeh, R.; Chahardouli, B.; et al. The Correlation between EGFR and Androgen Receptor Pathways: A Novel Potential Prognostic Marker in Gastric Cancer. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicki, T.S.; HuLieskovan, S.; Ribas, A. Mechanisms of resistance to PD1 and PDL1 blockade. Cancer J. 2018, 24, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Gatti-Mays, M.E.; Kalinsky, K.; Korde, L.A.; Sharon, E.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Mittendorf, E.A. Current landscape of immunotherapy in breast cancer: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhani, S.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Schnitt Tan, P.H.; van de Vijver, M.J. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Elston, C.W.; Ellis, I.O. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 1991, 19, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobin, L.H.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed.; International Union Against Cancer Wiley–Blackwell: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Allred, D.C.; Harvey, J.M.; Berardo, M.; Clark, G.M. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dias, K.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; Hallett, R.M.; Wu, Y.; Hassell, J.; Pond, G.R.; Levine, M.; Whelan, T.; Bane, A.L. Claudin-Low Breast Cancer; Clinical & Pathological Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168669. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, M.E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; Dowsett, M.; Allred, D.C.; Hagerty, K.L.; Badve, S.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Francis, G.; Goldstein, N.S.; Hayes, M.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Guideline Recommendation for Immunohistochemical Testing of Estrogen and Progesterone receptors in Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Dowsett, M.; McShane, L.M.; Allison, K.H.; Allred, D.C.; Bartlett, J.M.; Bilous, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.; et al. Recommendations for Human Epidermal Growth Factor receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologist Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3997–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HerceptTest™. For Determination of HER2 Protein Overexpression. In Catalog Products and Services; DAKO: Jena, Germany, 2007; pp. 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Denkert, C.; Loibl, S.; Müller, B.M.; Eidtmann, H.; Schmitt, W.D.; Eiermann, W.; Gerber, B.; Tesch, H.; Hilfrich, J.; Huober, J.; et al. Ki67 levels as predictive and prognostic parameters in pretherapeutic breast cancer core biopsies: A translational investigation in the neoadjuvant GeparTrio trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGhan, L.J.; McCullough, A.E.; Protheroe, C.A.; Dueck, A.C.; Lee, J.J.; Nunez-Nateras, R.; Castle, E.P.; Gray, R.J.; Wasif, N.; Goetz, M.P.; et al. Androgen receptor-positive triple negative breast cancer: A unique breast cancer subtype. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dako Agilent Tehnologies. PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx Interpretation Manual—Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC); DAKO Agilend: Jena, Germany, 2020; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Keir, M.E.; Liang, S.C.; Guleria, I.; Latchman, Y.E.; Qipo, A.; Albacker, L.A.; Koulmanda, M.; Freeman, G.J.; Sayegh, M.H.; Sharpe, A.H. Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanowska, O.; Kuczkiewicz-Siemion, O.; Debowska, M.; Olszewski, W.P.; Jagiełło-Gruszfeld, A.; Tysarowski, A.; Prochorec-Sobieszek, M. PD-L1-Positive High-Grade Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Respond Better to Standard Neoadjuvant Treatment—A Retrospective Study of PD-L1 Expression in Relation to Different Clinicopathological Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, F.; Lin, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Huang, X.; Sun, Q. Prognostic Value of PD-L1 in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Breast J. 2017, 23, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatier, R.; Finetti, P.; Mamessier, E.; Adelaide, J.; Chaffanet, M.; Ali, H.; Viens, P.; Caldas, C.; Birnbaum, D.; Bertucci, F. Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5449–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astvatsaturyan, K.; Yue, Y.; Walts, A.E.; Bose, S. Androgen receptor positive triple negative breast cancer: Clinicopathologic, prognostic, and predictive features. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackbart, H.; Cui, X.; Lee, J.S. Androgen receptor in breast cancer and its clinical implication. Transl. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrava, A.L.; Kyaw, P.S.P.; Newman, J.; Pringle, J.; Westhuyzen, J.; La Hera Fuentes, G.; Shakespeare, T.P.; Sakalkale, R.; Aherne, N.J. Androgen Receptor Status in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Does It Correlate with Clinicopathological Characteristics? Breast Cancer; Dove Med Press: Macclesfield, UK, 2023; Volume 11, pp. 359–371. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, N.; Garber, J.E.; Hacker, M.R.; Torous, V.; Freeman, G.J.; Poles, E.; Rodig, S.; Alexander, B.; Lee, L.; Collins, L.C.; et al. Prevalence and predictors of androgen receptor and programmed death-ligand 1 in BRCA1-associated and sporadic triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhan, Y.; Luo, J.; Ning, Y.; Fan, S. Clinical implications of the interaction between PD-1/PD-L1 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in progression and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer. 2022, 13, 3434–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prvanović, M.; Nedeljković, М.; Tanić, N.; Tomić, T.; Terzić, T.; Milovanović, Z.; Maksimović, Z.; Tanić, N. Role of PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Life 2021, 11, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | np (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | |
| <50 | 99 (79.2) |
| ≥50 | 26 (20.8) |
| Tumor type | |
| Ductal | 79 (63.2) |
| Lobular | 16 (12.8) |
| Mixed (ductal/lobular) | 11 (8.8) |
| Other * | 19 (15.2) |
| Tumor size (cm) | |
| ≤2 | 38 (30.4) |
| 2 -5 | 76 (60.8) |
| ≥5 | 11 (8.8) |
| Tumor grade | |
| G2 | 58 (46.4) |
| G3 | 67 (53.6) |
| Nuclear grade | |
| NG1 | 5 (4) |
| NG2 | 51 (40.8) |
| NG3 | 69 (55.2) |
| Lymph node status | |
| Negative | 79 (63.2) |
| Positive | 45 (36) |
| Unknown | 1 (0.8) |
| Locoregional reccurance | |
| No | 112 (89.6) |
| Yes | 13 (10.4) |
| Distant metastases | |
| No | 96 (76.8) |
| Yes | 29 (23.2) |
| PD-L1 | AR | EGFR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| np (%) | np (%) | np (%) | |||||||
| Parameters | Negative | Positive | p value | Negative | Positive | p value | Negative | Positive | p value |
| 75 (60) | 50 (40) | 79 (63) | 46 (37) | 83 (66) | 42 (34) | ||||
| Tumor size | |||||||||
| ≤2 cm | 23 (30) | 15 (30) | 0.6417 | 21 (26) | 17 (37) | 0.4657 | 27 (33) | 11 (24) | 0.5844 |
| 2 -5 cm | 44 (59) | 32 (64) | 51 (65) | 25 (54) | 50 (60) | 26 (62) | |||
| >5 cm | 8 (11) | 3 (6) | 7 (9) | 4 (9) | 6 (7) | 5 (14) | |||
| Tumor grade | |||||||||
| G2 | 45 (60) | 13 (26) | 0.0002 | 31 (39) | 27 (59) | 0.0419 | 36 (43) | 22 (52) | 0.3505 |
| G3 | 30 (40) | 37 (74) | 48 (61) | 19 (41) | 47 (57) | 20 (48) | |||
| Nuclear grade | |||||||||
| NG1 | 4 (5) | 1 (2) | 0.0007 | 4 (5) | 1 (2) | 0.2425 | 2 (2) | 3 (7) | 0.3796 |
| NG2 | 40 (54) | 11 (22) | 28 (35) | 23 (50) | 33 (40) | 18 (43) | |||
| NG3 | 31 (41) | 38 (76) | 47 (60) | 22 (48) | 48 (58) | 21 (50) | |||
| Lymph node status | |||||||||
| Negative | 45 (60) | 34 (69) | 0.3416 | 51 (65) | 28 (61) | 0.6998 | 55 (67) | 24 (57) | 0.3255 |
| Positive | 30 (40) | 15 (31) | 27 (35) | 18 (39) | 27 (33) | 18 (43) | |||
| N stage | |||||||||
| N0 | 45 (60) | 34 (69) | 0.5684 | 51 (65) | 28 (61) | 0.4912 | 55 (67) | 24 (57) | 0.4946 |
| N1 | 24 (32) | 12 (25) | 23 (30) | 13 (28) | 21 (26) | 15 (36) | |||
| N2 and N3 | 6 (8) | 3 (6) | 4 (5) | 5 (11) | 6 (7) | 3 (7) | |||
| Metastases | |||||||||
| No | 57 (76) | 39 (78) | 0.8322 | 57 (72) | 39 (85) | 0.1273 | 69 (83) | 27 (64) | 0.0249 |
| Yes | 18 (24) | 11 (22) | 22 (28) | 7 (15) | 14 (17) | 15 (36) | |||
| Locoreg. reccurence | |||||||||
| No | 63 (84) | 49 (98) | 0.0146 | 69 (87) | 43 (93) | 0.368 | 75 (90) | 37 (88) | 0.7597 |
| Yes | 12 (16) | 1 (2) | 10 (13) | 3 (7) | 8 (10) | 5 (12) | |||
| Adjuvant radiotherapy | |||||||||
| No | 28 (37) | 16 (33) | 0.7008 | 27 (34) | 17 (38) | 0.8457 | 27 (34) | 17 (40) | 0.5524 |
| Yes | 46 (63) | 32 (67) | 50 (66) | 28 (62) | 53 (66) | 25 (60) | |||
| Ki67 | |||||||||
| ≤15% | 14 (19) | 2 (4) | 0.0148 | 1 (1) | 15 (32) | <0.0001 | 11 (13) | 5 (12) | 0.1831 |
| 16–30% | 8 (11) | 2 (4) | 4 (5) | 6 (14) | 4 (5) | 6 (14) | |||
| >30% | 53 (70) | 46 (92) | 74 (94) | 25 (54) | 68 (82) | 31 (74) | |||
| PD-L1/AR Expression | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| np (%) | |||
| Parameters | Negative | Positive | p value |
| 42 (76) | 13 (24) | ||
| Tumor size | |||
| ≤2 cm | 10 (24) | 4 (31) | 0.8344 |
| 2–5 | 27 (64) | 8 (62) | |
| >5 cm | 5 (12) | 1 (7) | |
| Tumor grade | |||
| G2 | 20 (48) | 2 (15) | 0.0533 |
| G3 | 22 (52) | 11 (85) | |
| Nuclear grade | |||
| NG1 | 3 (7) | 0 (0) | 0.0242 |
| NG2 | 18 (43) | 1 (7) | |
| NG3 | 21 (50) | 12 (93) | |
| Lymph nodes status | |||
| Negative | 28 (67) | 11 (85) | 0.3037 |
| Positive | 14 (33) | 2 (15) | |
| N stage | |||
| N0 | 28 (67) | 11 (85) | 0.2955 |
| N1 | 12 (28) | 1 (7) | |
| N2 and N3 | 2 (5) | 1 (7) | |
| Metastases | |||
| No | 31 (74) | 13 (100) | 0.0497 |
| Yes | 11 (26) | 0 (0) | |
| Locoreg. reccurence | |||
| No | 33 (79) | 13 (100) | 0.0961 |
| Yes | 9 (21) | 0 (0) | |
| Adjuvant radiotherapy | |||
| No | 15 (36) | 4 (33) | >0.9999 |
| Yes | 26 (64) | 8 (67) | |
| Ki67 | |||
| ≤15% | 0 (0) | 1 (7) | 0.1452 |
| 16–30% | 2 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| >30% | 40 (95) | 12 (93) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medić-Milijić, N.; Jovanić, I.; Nedeljković, M.; Marković, I.; Spurnić, I.; Milovanović, Z.; Ademović, N.; Tomić, T.; Tanić, N.; Tanić, N. Prognostic and Clinical Significance of PD-L1, EGFR and Androgen Receptor (AR) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Patients. Life 2024, 14, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060682
Medić-Milijić N, Jovanić I, Nedeljković M, Marković I, Spurnić I, Milovanović Z, Ademović N, Tomić T, Tanić N, Tanić N. Prognostic and Clinical Significance of PD-L1, EGFR and Androgen Receptor (AR) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Patients. Life. 2024; 14(6):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedić-Milijić, Nataša, Irena Jovanić, Milica Nedeljković, Ivan Marković, Igor Spurnić, Zorka Milovanović, Nejla Ademović, Tijana Tomić, Nasta Tanić, and Nikola Tanić. 2024. "Prognostic and Clinical Significance of PD-L1, EGFR and Androgen Receptor (AR) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Patients" Life 14, no. 6: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060682
APA StyleMedić-Milijić, N., Jovanić, I., Nedeljković, M., Marković, I., Spurnić, I., Milovanović, Z., Ademović, N., Tomić, T., Tanić, N., & Tanić, N. (2024). Prognostic and Clinical Significance of PD-L1, EGFR and Androgen Receptor (AR) Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Patients. Life, 14(6), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14060682






