MRI-Based Machine Learning for Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ethics Statement
3.2. Patient Selection
3.3. Treatments
3.4. Evaluation of Response
3.5. Imaging Acquisition
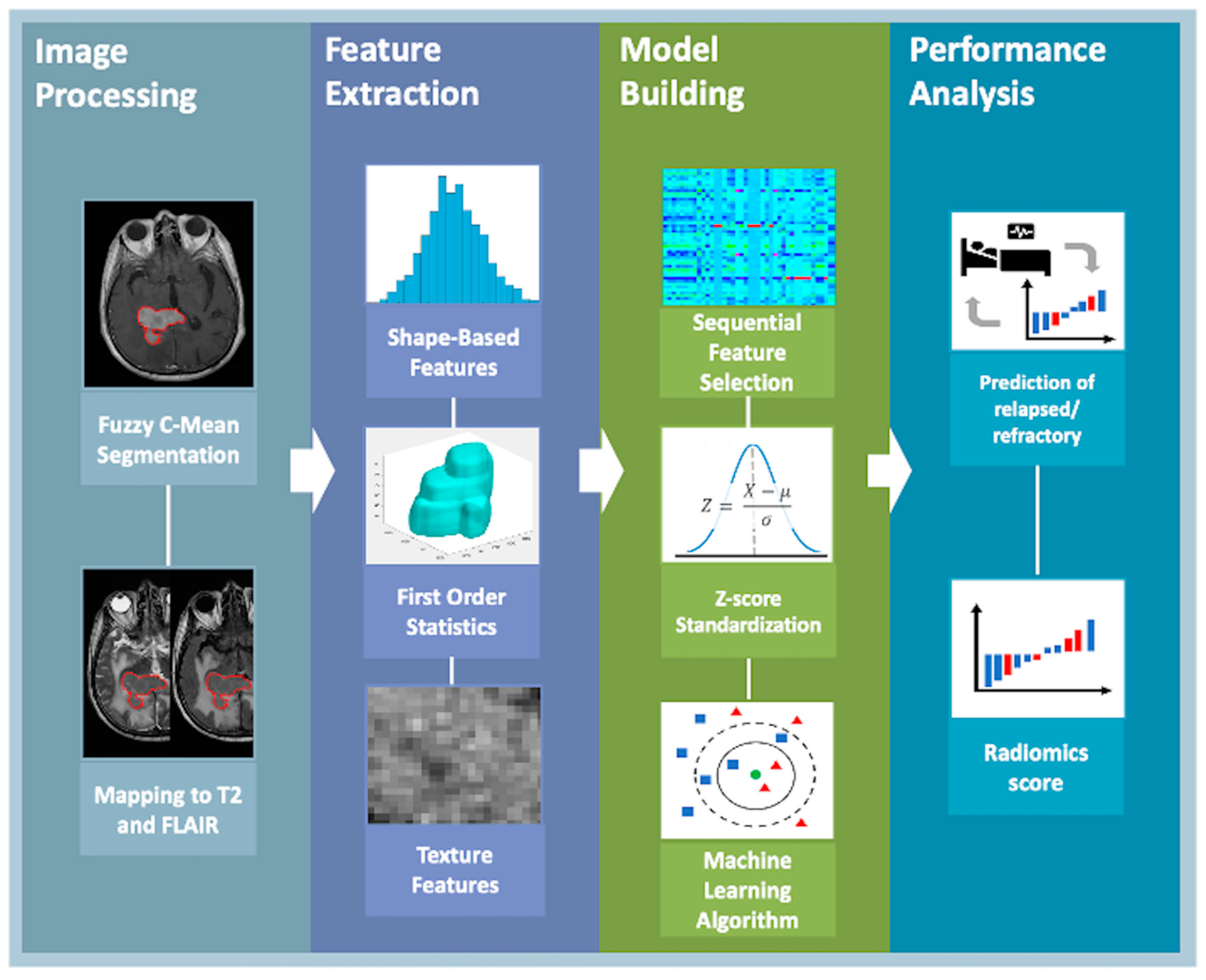
3.6. Tumor Segmentation and Quantitative Feature Extraction
3.7. Measurement of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
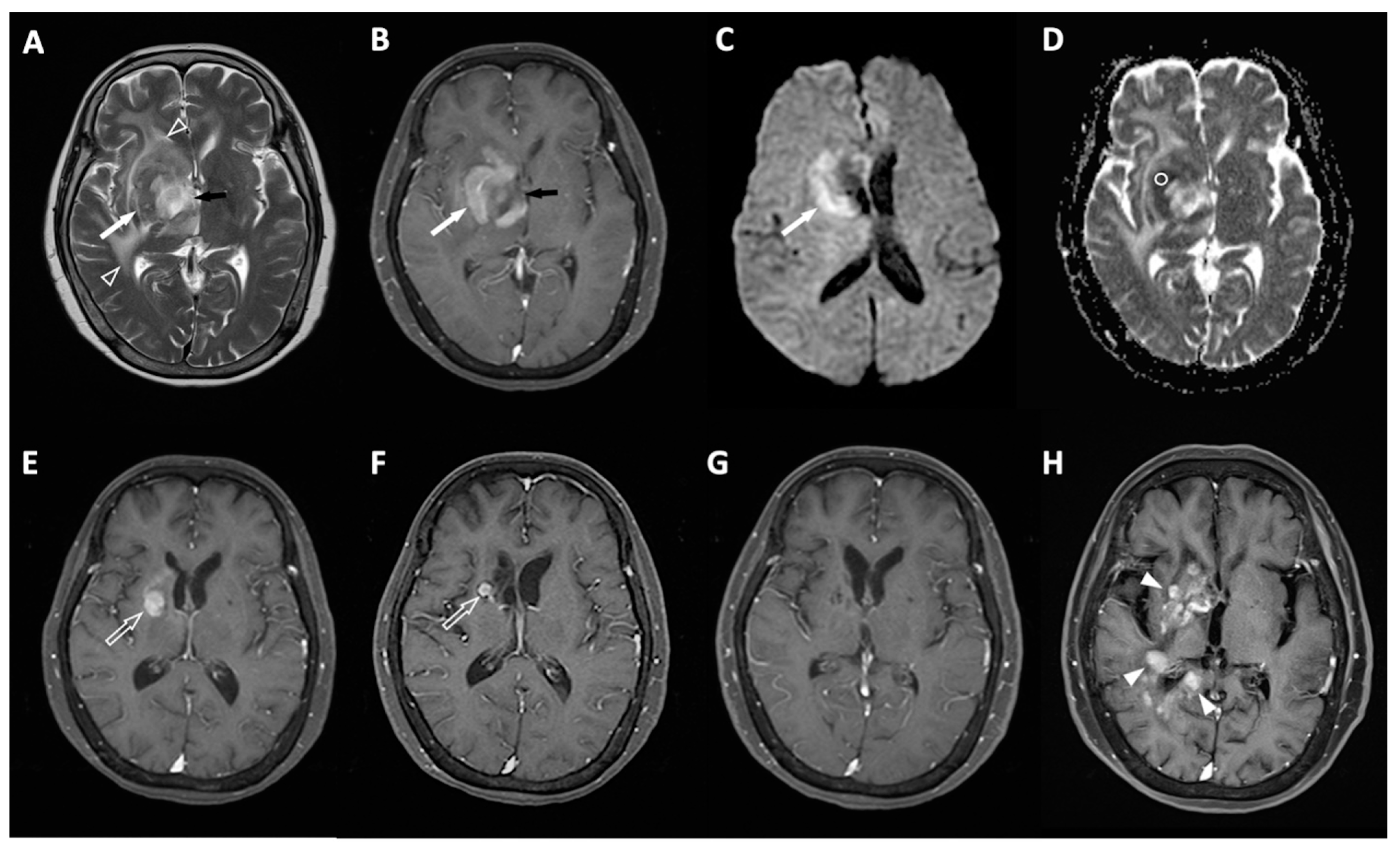
4.1. Clinical Information and MRI Results
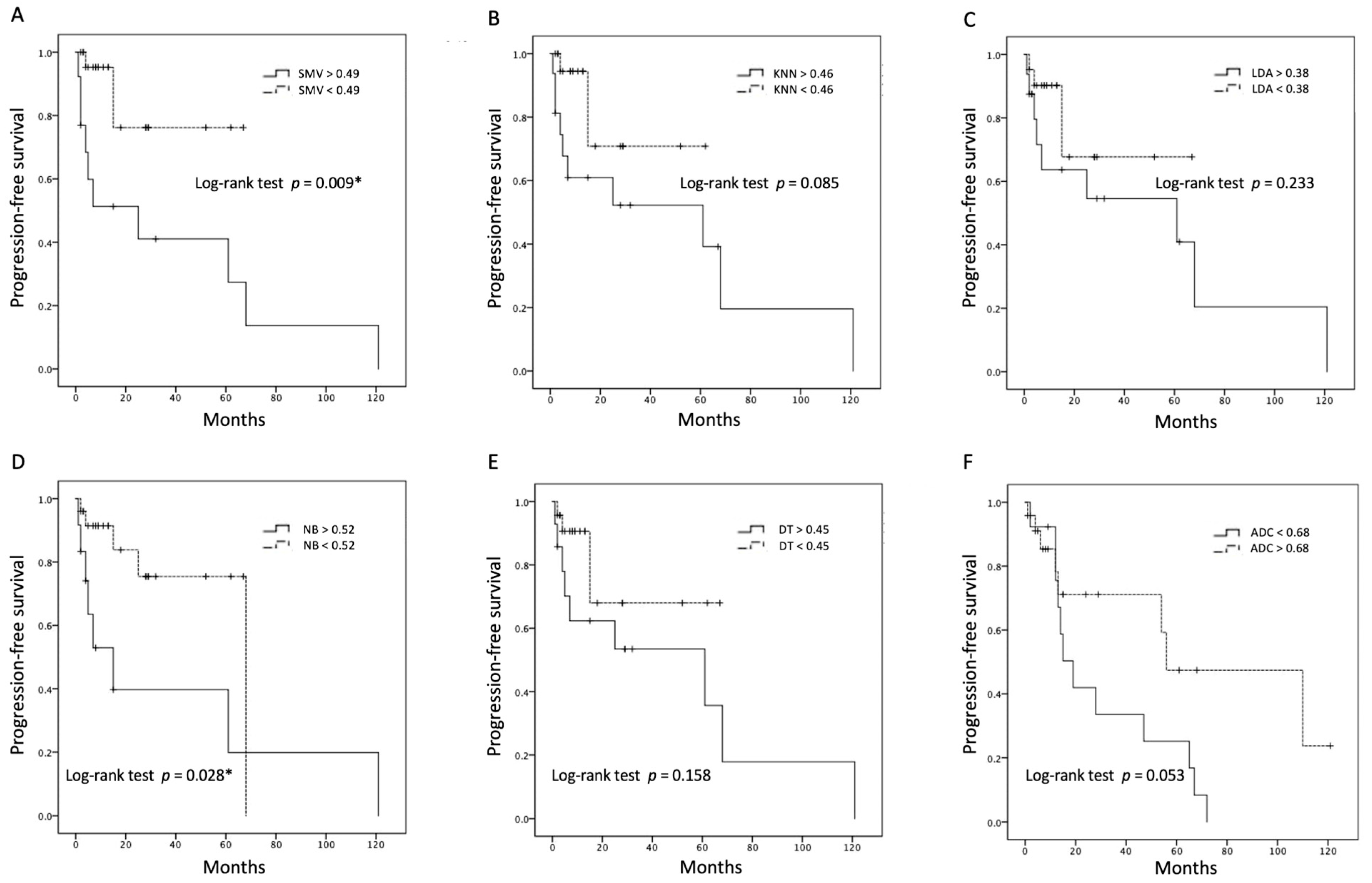
4.2. Performance of ML Algorithms and Survival Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villano, J.L.; Koshy, M.; Shaikh, H.; Dolecek, T.A.; McCarthy, B.J. Age, gender, and racial differences in incidence and survival in primary CNS lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Bentink, S.; Basso, K.; Lim, W.K.; Klapper, W.; Schaller, C.; Reifenberger, G.; Rubenstein, J.; Wiestler, O.D.; et al. Gene expression profiling suggests primary central nervous system lymphomas to be derived from a late germinal center B cell. Leukemia 2008, 22, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Samant, R.; Jay, M.; Chaudry, H.; Fan, X.Y.; MacDonald, D.; Bence-Bruckler, I.; Nair, V. Whole brain radiotherapy improves survival outcomes in primary CNS lymphoma patients ineligible for systemic therapy. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 5363–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.G.; Abrey, L.E. Therapeutic challenges in primary CNS lymphoma. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; DeAngelis, L.M. Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfel, A.; Schlegel, U.; Herrlinger, U.; Dreyling, M.; Schmidt, C.; von Baumgarten, L.; Pezzutto, A.; Grobosch, T.; Kebir, S.; Thiel, E.; et al. Phase II Trial of Temsirolimus for Relapsed/Refractory Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabouret, E.; Houillier, C.; Martin-Duverneuil, N.; Blonski, M.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Houot, R.; Larrieu, D.; Soubeyran, P.; Gressin, R.; et al. Patterns of response and relapse in primary CNS lymphomas after first-line chemotherapy: Imaging analysis of the ANOCEF-GOELAMS prospective randomized trial. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyadi, R.; Handoko, H.; Zairinal, R.A.; Prihartono, J. The Role of Pretherapeutic Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Derived Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Immunocompetent Patients with Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.C.; Yeh, L.R.; Hung, K.C.; Lim, S.W.; Cheng, C.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, J.H.; Ko, C.C. Pretreatment diffusion-weighted imaging for prediction of relapsed and refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1227607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, B.; Durmaz, E.; Ateş, E.; Kılıçkesmez, Ö. Radiomics with artificial intelligence: A practical guide for beginners. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Cho, H.H.; Kim, S.T.; Park, H.; Nam, D.; Kong, D.S. Radiomics features to distinguish glioblastoma from primary central nervous system lymphoma on multi-parametric MRI. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, A.; Ou, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, X. Comparison of Radiomics-Based Machine-Learning Classifiers in Diagnosis of Glioblastoma From Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, O.M.; Nalawade, S.S.; Xi, Y.; Wagner, B.; Mazal, A.; Ahlers, S.; Rizvi, S.M.; Awan, F.T.; Kumar, K.A.; Desai, N.B. A Radiomic Machine Learning Model to Predict Treatment Response to Methotrexate and Survival Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL). Blood 2020, 136, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destito, M.; Marzullo, A.; Leone, R.; Zaffino, P.; Steffanoni, S.; Erbella, F.; Calimeri, F.; Anzalone, N.; De Momi, E.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; et al. Radiomics-Based Machine Learning Model for Predicting Overall and Progression-Free Survival in Rare Cancer: A Case Study for Primary CNS Lymphoma Patients. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenning, K.H.; Gesperger, J.; Furtner, J.; Nemc, A.; Roetzer-Pejrimovsky, T.; Choi, S.-W.; Mitter, C.; Leber, S.L.; Hofmanninger, J.; Klughammer, J.; et al. Radiomic features define risk and are linked to DNA methylation attributes in primary CNS lymphoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Z.; Marzullo, A.; Destito, M.; Spadea, M.F.; Leone, R.; Anzalone, N.; Steffanoni, S.; Erbella, F.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Ferrigno, G.; et al. Deep learning-based overall survival prediction model in patients with rare cancer: A case study for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2023, 18, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhuo, H.; Wei, X.; Ma, X. Contrast-Enhanced MRI Texture Parameters as Potential Prognostic Factors for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Patients Receiving High-Dose Methotrexate-Based Chemotherapy. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 5481491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrey, L.E.; Batchelor, T.T.; Ferreri, A.J.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Pulczynski, E.J.; Zucca, E.; Smith, J.R.; Korfel, A.; Soussain, C.; DeAngelis, L.M.; et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize baseline evaluation and response criteria for primary CNS lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5034–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Pfistner, B.; Juweid, M.E.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Specht, L.; Horning, S.J.; Coiffier, B.; Fisher, R.I.; Hagenbeek, A.; Zucca, E.; et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Chen, J.H.; Yu, H.J.; Chu, Y.; Nalcioglu, O.; Su, M.Y. Quantitative analysis of lesion morphology and texture features for diagnostic prediction in breast MRI. Acad. Radiol. 2008, 15, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Chang, E. Support vector machine active learning for image retrieval. In Proceedings of the Ninth ACM international Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 30 September–5 October 2001; pp. 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, B.P.; Decker, P.A.; Tieu, C.; Cerhan, J.R. The changing incidence of primary central nervous system lymphoma is driven primarily by the changing incidence in young and middle-aged men and differs from time trends in systemic diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataille, B.; Delwail, V.; Menet, E.; Vandermarcq, P.; Ingrand, P.; Wager, M.; Guy, G.; Lapierre, F. Primary intracerebral malignant lymphoma: Report of 248 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 92, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, S.; Mauguen, A.; Yildirim, O.; Hatzoglou, V.; Francis, J.H.; Schaff, L.R.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Schöder, H.; Grommes, C. Prognostic value of [18F]FDG PET/CT in patients with CNS lymphoma receiving ibrutinib-based therapies. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3940–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhani, A.R.; Liu, G.; Koh, D.M.; Chenevert, T.L.; Thoeny, H.C.; Takahara, T.; Dzik-Jurasz, A.; Ross, B.D.; Van Cauteren, M.; Collins, D.; et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: Consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.W.; Cho, H.J.; Bae, J.H.; Sohn, S.K.; Moon, J.H. Apparent diffusion coefficient as a valuable quantitative parameter for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma. Blood Res. 2020, 55, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowski, K.; Kucharski, D.; Machura, B.; Adamski, S.; Gutierrez Becker, B.; Krason, A.; Zarudzki, L.; Tessier, J.; Nalepa, J. Detecting liver cirrhosis in computed tomography scans using clinically-inspired and radiomic features. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.S. Reproducibility and Generalizability in Radiomics Modeling: Possible Strategies in Radiologic and Statistical Perspectives. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiri, I.; Abdollahi, H.; Shaysteh, S.; Mahdavi, S.R. Test-retest reproducibility and robustness analysis of recurrent glioblastoma MRI radiomics texture features. Iran. J. Radiol. 2017, 5, e48035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell-Hay, R.N.; Ahearn, T.S.; Murray, A.D.; Waiter, G.D. Investigation of the Inter- and Intrascanner Reproducibility and Repeatability of Radiomics Features in T1-Weighted Brain MRI. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2022, 56, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeßler, B.; Weiss, K.; Pinto Dos Santos, D. Robustness and Reproducibility of Radiomics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Phantom Study. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Specific Methods | Strengths | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Destito et al. [15] |
|
|
|
| Nenning et al. [16] |
|
|
|
| She et al. [17] |
|
|
|
| Ali et al. [14] |
|
|
|
| Chen et al. [18] |
|
|
|
| Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) | Non-R/R | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 20 | 26 | |
| Sex | 0.139 | ||
| Male | 6 (30%) | 14 (53.8%) | |
| Female | 14 (70%) | 12 (46.2%) | |
| Age (y) | 62 (54.5, 69.5) | 66.5 (57, 76) | 0.287 |
| Response to first-line chemotherapy | 0.069 | ||
| Complete response (CR) | 8 (40%) | 19 (73.1%) | |
| Partial response (PR)/Stable disease (SD) | 7 (35%) | 5 (19.2%) | |
| Progressive disease (PD) | 5 (25%) | 2 (7.7%) | |
| Tumor location | 0.449 | ||
| Cerebral cortex | 11 (55%) | 18 (69.2%) | |
| Basal ganglia/thalamus/corpus callosum | 7 (35%) | 5 (19.2%) | |
| Cerebellum | 2 (10%) | 3 (11.5%) | |
| Ocular involvement | 3 (15%) | 2 (7.7%) | 0.640 |
| Enhancement | 0.855 | ||
| Homogeneous | 9 (45%) | 11 (42.3%) | |
| Heterogeneous | 11 (55%) | 15 (57.7%) | |
| Necrosis | 7 (35%) | 10 (38.5%) | 0.809 |
| Hemorrhagic change | 4 (20%) | 8 (30.8%) | 0.467 |
| Peritumoral edema | 19 (95%) | 24 (92.3%) | 1 |
| Leptomeningeal seeding | 3 (15%) | 2 (7.7%) | 0.640 |
| Multiple lesions | 11 (55%) | 11 (42.3%) | 0.393 |
| Maximal tumor diameter (cm) | 3.9 (3.1, 4.8) | 3.2 (2.3, 4.2) | 0.245 |
| High DWI signal | 18 (90%) | 21 (80.8%) | 0.446 |
| ADC value (×10−3 mm2/s) | 0.67 (0.62, 0.72) | 0.75 (0.66, 0.83) | 0.017 * |
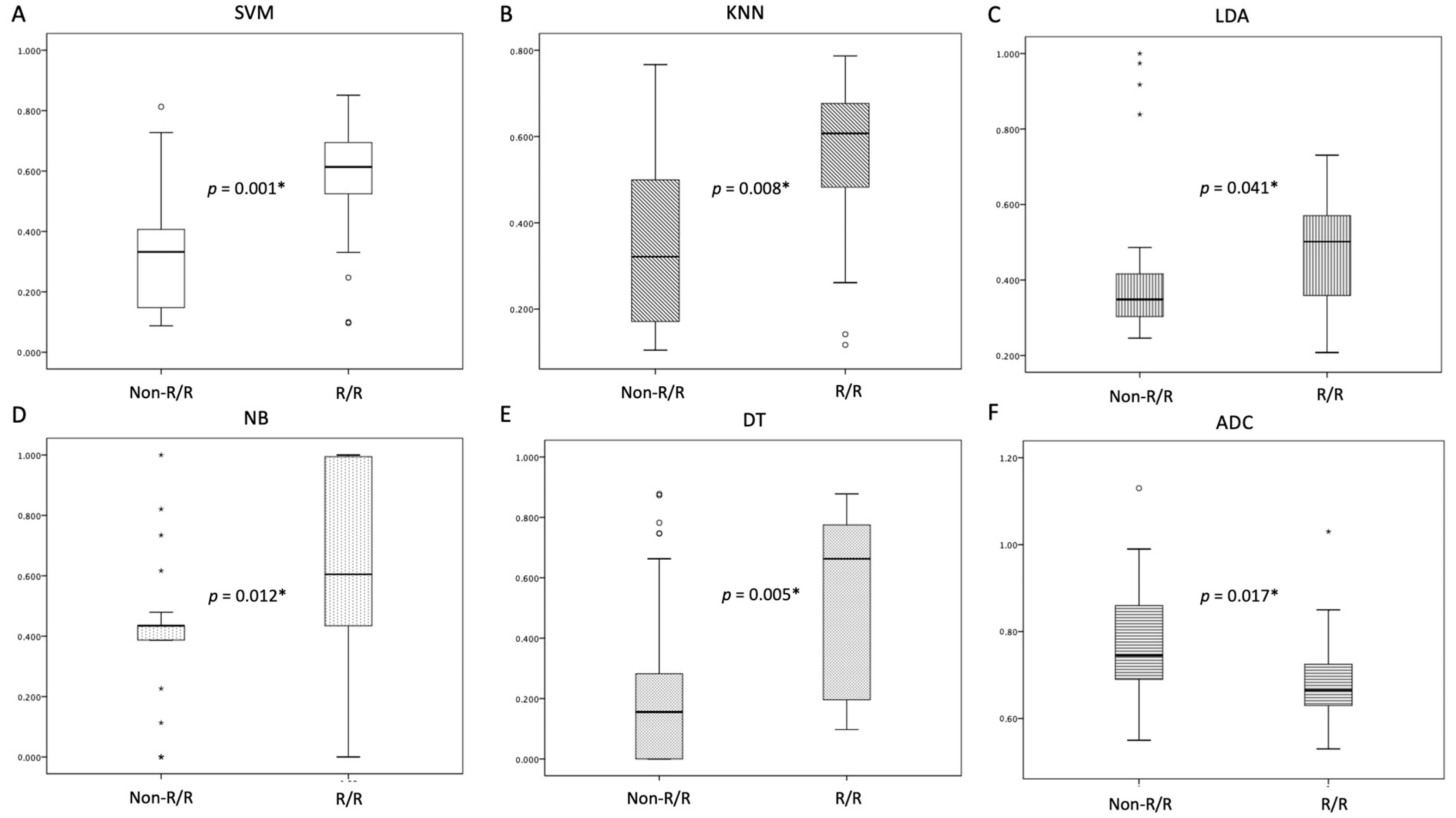
| SVM score | 0.61 (0.52, 0.71) | 0.33 (0.20, 0.47) | 0.001 * |
| KNN score | 0.61 (0.51, 0.71) | 0.32 (0.15, 0.49) | 0.008 * |
| LDA score | 0.50 (0.39, 0.62) | 0.35 (0.28, 0.42) | 0.041 * |
| NB score | 0.61 (0.32, 0.89) | 0.44 (0.39, 0.48) | 0.010 * |
| DT score | 0.66 (0.37, 0.96) | 0.16 (0.13, 0.34) | 0.005 * |
| LDH (units/L) | 204 (181, 227) | 225 (158, 292) | 0.194 |
| Ki-67 (%) | 85 (79, 92) | 85 (76, 95) | 0.758 |
| Recurrence site | |||
| CNS | 19 (95%) | ||
| Isolated systemic | 0 | ||
| Both CNS and systemic | 1 (5%) | ||
| Death | 12 (60%) | 8 (30.8%) | 0.047 * |
| Follow-up time (months) | 31.1 (17, 45.2) | 22.6 (6.1, 39.1) | 0.198 |
| Accuracy | Precision | AUC | Cut-Off Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
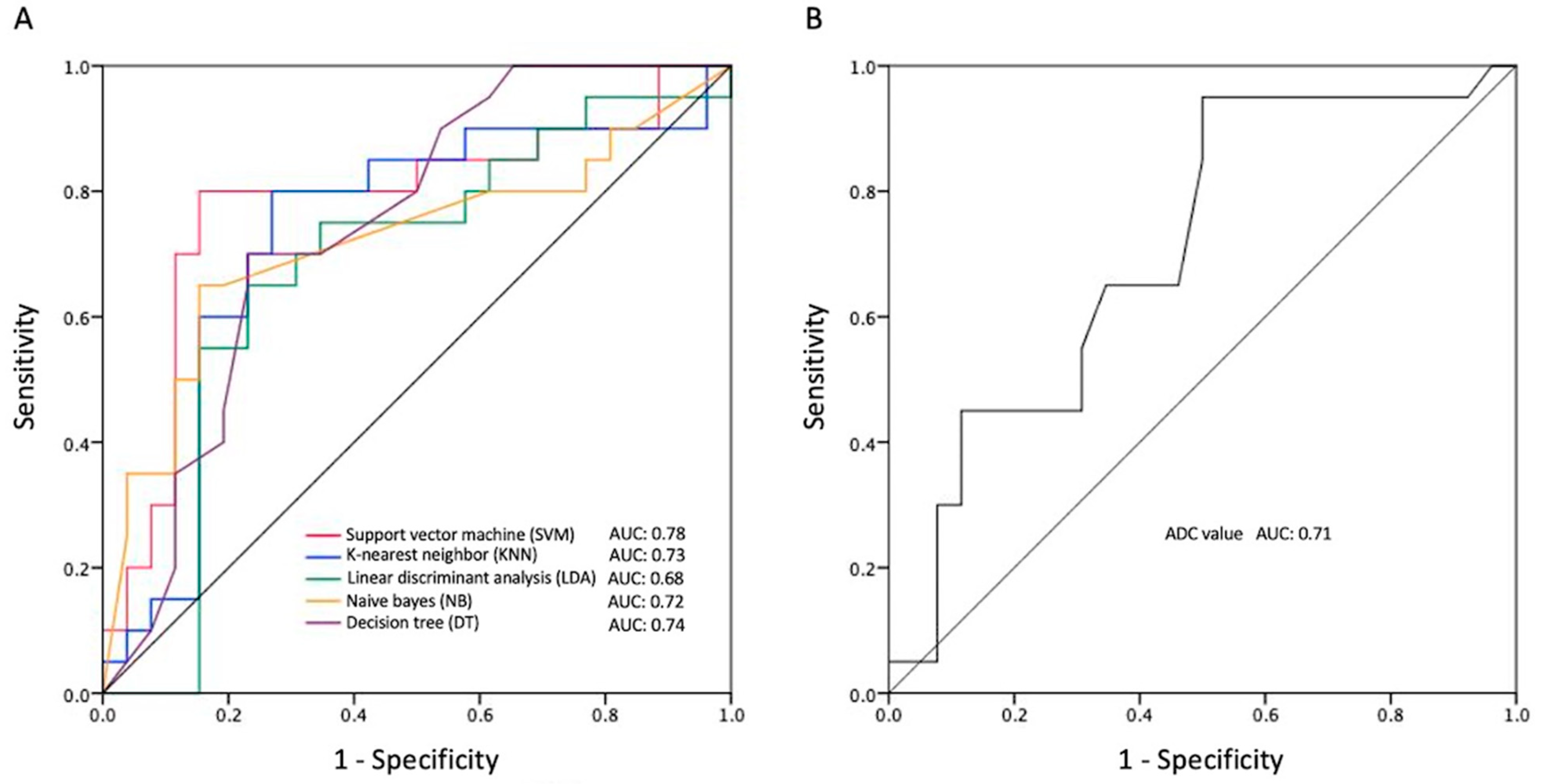
| SVM score | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.78 (0.63, 0.93) | 0.49 | 0.001 * |
| KNN score | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.73 (0.57, 0.89) | 0.46 | 0.008 * |
| LDA score | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.68 (0.51, 0.84) | 0.38 | 0.041 * |
| NB score | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.72 (0.56, 0.88) | 0.52 | 0.012 * |
| DT score | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.74 (0.60, 0.89) | 0.45 | 0.005 * |
| ADC value | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.71 (0.55, 0.86) | 0.68 | 0.017 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Hung, K.-C.; Yang, C.-C.; Lim, S.-W.; Yeh, L.-R.; Chen, J.-H.; Su, M.-Y. MRI-Based Machine Learning for Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Life 2024, 14, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101290
Ko C-C, Liu Y-L, Hung K-C, Yang C-C, Lim S-W, Yeh L-R, Chen J-H, Su M-Y. MRI-Based Machine Learning for Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Life. 2024; 14(10):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101290
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Ching-Chung, Yan-Lin Liu, Kuo-Chuan Hung, Cheng-Chun Yang, Sher-Wei Lim, Lee-Ren Yeh, Jeon-Hor Chen, and Min-Ying Su. 2024. "MRI-Based Machine Learning for Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma" Life 14, no. 10: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101290
APA StyleKo, C.-C., Liu, Y.-L., Hung, K.-C., Yang, C.-C., Lim, S.-W., Yeh, L.-R., Chen, J.-H., & Su, M.-Y. (2024). MRI-Based Machine Learning for Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Life, 14(10), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101290






