Impact of Acute Kidney Injury on the COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality in Octogenarian Patients: Insights from the COVOCA Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Variables (Outcome and Exposure)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
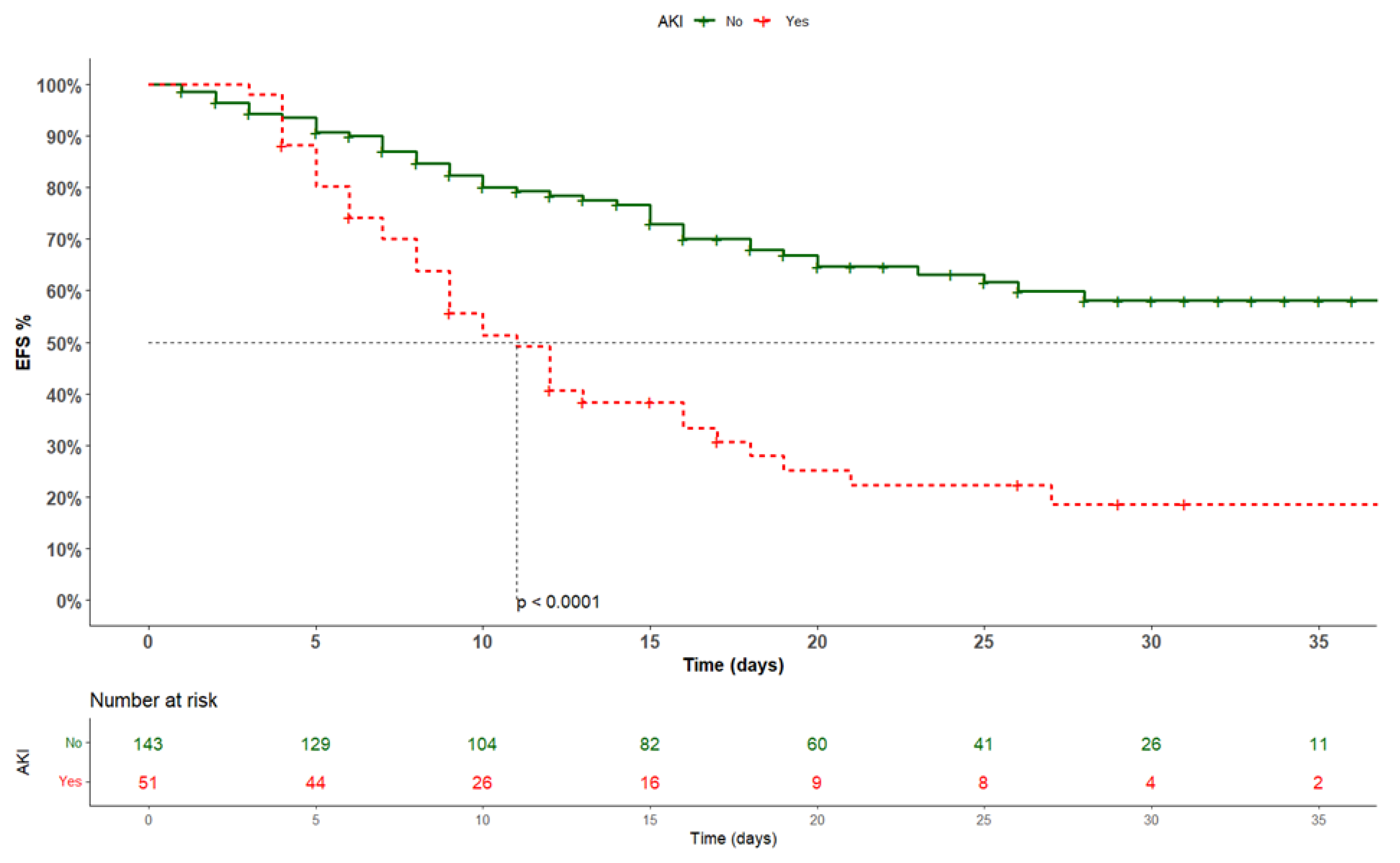
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Ahmad Farouk, I.; Lal, S.K. COVID-19: A Review on the Novel Coronavirus Disease Evolution, Transmission, Detection, Control and Prevention. Viruses 2021, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdenassi, L.; Franzini, M.; Ricevuti, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Galoforo, A.C.; Tirelli, U. Potential mechanisms by which the oxygen-ozone (O2-O3) therapy could contribute to the treatment against the coronavirus COVID-19. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 4059–4061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- Vianello, A.; De Vita, N.; Scotti, L.; Guarnieri, G.; Confalonieri, M.; Bonato, V.; Molena, B.; Maestrone, C.; Airoldi, G.; Olivieri, C.; et al. Clinical Outcomes in Patients Aged 80 Years or Older Receiving Non-Invasive Respiratory Support for Hypoxemic Acute Respiratory Failure Consequent to COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiero, R.; Pafundi, P.C.; Simeon, V.; Rinaldi, L.; Perrella, A.; Vetrano, E.; Caturano, A.; Alfano, M.; Beccia, D.; Nevola, R.; et al. Impact of chronic liver disease upon admission on COVID-19 in-hospital mortality: Findings from COVOCA study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila-Reniu, A.; Pellice, M.; Prieto-González, S.; Ventosa, H.; Ladino, A.; Naval, J.; Rodriguez-Nuñez, O.; César Milisenda, J.; Moreno-Lozano, P.J.; Soriano, A.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients aged over 80 years with COVID-19. Medicine 2021, 100, e24750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiero, R.; Simeon, V.; Loffredo, G.; Caturano, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Vetrano, E.; Medicamento, G.; Alfano, M.; Beccia, D.; Brin, C.; et al. Association between Renal Function at Admission and COVID-19 in-Hospital Mortality in Southern Italy: Findings from the Prospective Multicenter Italian COVOCA Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pang, Q.; Zhou, T.; Meng, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, A. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2170809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 Practice Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Cardiology: ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 2284–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; He, J.C. Mechanisms and treatment of COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Daoud, A.; Mohamed, M.M.; Salim, S.A.; Yessayan, L.; Baharani, J.; Murtazaf, A.; Rao, V.; Soliman, K.M. Survival rate in acute kidney injury superimposed COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J.S.; Ng, J.H.; Ross, D.W.; Sharma, P.; Shah, H.H.; Barnett, R.L.; Hazzan, A.D.; Fishbane, S.; Jhaveri, K.D. Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, R.; Li, K.; Zheng, L.; Yang, J. Risk factors and prognosis for COVID-19-induced acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchepalina, A.; Chebotareva, N.; Akulkina, L.; Brovko, M.; Sholomova, V.; Androsova, T.; Korotchaeva, Y.; Kalmykova, D.; Tanaschuk, E.; Taranova, M.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Risk Factors and Serum Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.; Chaudhary, K.; Saha, A.; Chauhan, K.; Vaid, A.; Zhao, S.; Paranjpe, I.; Somani, S.; Richter, F.; Miotto, R.; et al. AKI in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrone, T.; Magrone, M.; Jirillo, E. Focus on Receptors for Coronaviruses with Special Reference to Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2 as a Potential Drug Target—A Perspective. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 807–811. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadian, E.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Razi Soofiyani, S.; Abediazar, S.; Shoja, M.M.; Ardalan, M.; Zununi Vahed, S. COVID-19 and kidney injury: Pathophysiology and molecular mechanisms. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puelles, V.G.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Sperhake, J.P.; Wong, M.N.; Allweiss, L.; Chilla, S.; Heinemann, A.; Wanner, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Multiorgan and renal tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 383, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.Y.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.C.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Human Kidney is a Target for Novel Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, B.; Mao, J. The pathogenesis and treatment of the ‘Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, D.; Sessa, G.; Salvatore, T.; Sasso, F.C.; Giugliano, D.; Lefebvre, P.J.; Torella, R. The involvement of the opioid system in human obesity: A study in normal weight relatives of obese people. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caturano, A.; Acierno, C.; Nevola, R.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Salvatore, T.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Sasso, F.C. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Impact. Processes 2021, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caturano, A.; D’Angelo, M.; Mormone, A.; Russo, V.; Mollica, M.P.; Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Vetrano, E.; Marfella, R.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: Impacts from Pathogenesis to Lifestyle Modifications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6651–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.; Radhakrishnan, Y.; Sedor, J.; Vachharajani, T.; Vachharajani, V.T.; Augustine, J.; Demirjian, S.; Thomas, G. COVID-19 and the kidney. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 619–631. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanein, M.; Thomas, G.; Taliercio, J. Management of acute kidney injury in COVID-19. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Rinaldi, L.; Coviello, F.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Colantuoni, S.; Medicamento, G.; et al. Dysregulated Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Risk Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in Diabetes. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Simeon, V.; Rinaldi, L.; Perrella, A.; Vetrano, E.; Caturano, A.; Alfano, M.; Beccia, D.; Nevola, R.; et al. Lack of effect on in-hospital mortality of drugs used during COVID-19 pandemic: Findings of the retrospective multicenter COVOCA study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, J.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Salehi-Pourmehr, H.; Gharekhani, A.; Ziaee, M. Nephrotoxicity of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 Patients. Tabriz Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liang, Y. Potential risk of the kidney vulnerable to novel coronavirus 2019 infection. Am. J. Physiology. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 318, F1136–F1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheruiyot, I.; Henry, B.; Lippi, G.; Kipkorir, V.; Ngure, B.; Munguti, J.; Misiani, M. Acute Kidney Injury is Associated with Worse Prognosis In COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020029. [Google Scholar]
- Uhler, C.; Shivashankar, G.V. Mechano-genomic regulation of coronaviruses and its interplay with ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhler, C.; Shivashankar, G.V. Regulation of genome organization and gene expression by nuclear mechanotransduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Thomas, P.G.; Randolph, A.G. Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, R.; Zeng, L.; Liang, H.; Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Distinct Disease Severity Between Children and Older Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Impacts of ACE2 Expression, Distribution, and Lung Progenitor Cells. Clin Infect Dis. 2021, 73, e4154–e4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, R.; Chen, D. Prevalence and Impact of Acute Renal Impairment on COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Reed, A.B.; Ponzo, S.; Yassaee, A.; Aral, M.; Plans, D.; Labrique, A.; Mohan, D. Population Risk Factors for Severe Disease and Mortality in COVID-19: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalić, A.; Davidović, M.; Kos, I.; Vrljičak, K.; Lamot, L. Hematuria as an Early Sign of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Case Report of a Boy With Multiple Comorbidities and Review of Literature. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 760070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Overall (n = 194) | Non-AKI Development (n = 143) | AKI Development (n = 51) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median [IQR] | 83.0 [82.0–87.0] | 83.0 [81.3–87.0] | 84.0 [82.0–87.0] | 0.562 |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| M | 100 (51.5) | 70 (49.0) | 30 (58.8) | 0.207 |
| F | 94 (48.5) | 73 (51.0) | 21 (41.2) | |
| Duration of hospitalization, median [IQR] | 15.0 [8.0–25.0] | 16.0 [9.0–25.0] | 10.0 [6.0–16.8] | 0.007 |
| Days before hospitalization, median [IQR] | 6.0 [3.0–9.0] | 5.0 [3.0–8.0] | 7.0 [1.3–12.8] | 0.688 |
| Body temp (°C), median [IQR] | 36.3 [36.0–37.0] | 36.3 [36.0–37.0] | 36.3 [36.0–37.1] | 0.956 |
| History of fever, n (%) | 109 (56.2) | 81 (56.6) | 28 (54.9) | 0.830 |
| Respiratory rate (apm), median [IQR] | 20.0 [18.0–25.0] | 20.0 [16.8–25.0] | 22.0 [18.0–28.0] | 0.056 |
| Heart rate (bpm), median [IQR] | 80.0 [73.0–93.0] | 80.0 [73.0–90.0] | 85.5 [73.5–100.0] | 0.255 |
| Blood pressure (mmHg), median [IQR] | ||||
| Systolic | 135.0 [120.0–145.0] | 135.0 [120.0–145.0] | 130.0 [120.0–153.0] | 0.928 |
| Diastolic | 73.5 [69.0–80.0] | 70.0 [66.0–80.0] | 77.5 [70.0–80.0] | 0.217 |
| Diarrhea, n (%) | 15 (7.7) | 12 (8.4) | 3 (5.9) | 0.566 |
| Oxygen saturation %, median [IQR] | 93.0 [88.0–96.0] | 93.0 [89.0–96.0] | 94.0 [87.0–97.0] | 0.566 |
| GCS/15, n (%) | ||||
| Mild/non-impaired consciousness | 167 (86.1) | 128 (89.5) | 39 (76.5) | 0.021 |
| Moderate/Severe impaired consciousness | 27 (13.9) | 15 (10.5) | 12 (23.5) | |
| Oxygen therapy, n (%) | 99 (51.0) | 70 (48.9) | 29 (56.9) | 0.134 |
| Chronic cardiac disease, n (%) | 92 (49.5) | 63 (44.1) | 29 (56.9) | 0.053 |
| CKD, n (%) | 37 (18.8) | 23 (16.1) | 14 (27.5) | 0.097 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2, median [IQR] | 59.1 [34.7–75.7] | 63.0 [46.4–80.6] | 34.6 [20.4–57.7] | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 147 (75.8) | 108 (73.5) | 39 (83.0) | 0.187 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 50 (25.8) | 35 (23.8) | 15 (31.9) | 0.223 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 15 (7.7) | 14 (9.5) | 1 (2.1) | 0.099 |
| CLD, n (%) | 12 (6.2) | 10 (7.0) | 2 (3.9) | 0.436 |
| Chronic Respiratory Disease, n (%) | 51 (26.3) | 34 (23.8) | 17 (33.3) | 0.184 |
| Chronic neurological disorder, n (%) | 42 (21.6) | 32 (22.4) | 10 (19.6) | 0.681 |
| Malign, n (%) | 24 (12.4) | 16 (10.9) | 8 (17.0) | 0.267 |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 91 (53.1) | 53 (37.1) | 38 (74.5) | <0.001 |
| In-hospital Drugs | ||||
| Steroids, n (%) | 175 (90.2) | 131 (91.6) | 44 (86.3) | 0.209 |
| Monoclonal Abs, n (%) | 2 (1.0) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (2.0) | 0.445 |
| Antivirals, n (%) | 25 (12.9) | 21 (14.7) | 4 (7.8) | 0.212 |
| Antibiotics, n (%) | 166 (87.4) | 122 (85.3) | 44 (86.2) | 0.784 |
| NSAIDs, n (%) | 29 (14.9) | 24 (16.8) | 5 (9.8) | 0.244 |
| Anticoagulants, n (%) | 188 (96.9) | 137 (95.8) | 51 (100) | 0.138 |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 82 (42.3) | 45 (31.4) | 37 (72.5) | <0.001 |
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | ||
| Age | 1.01 | 0.96 | 1.06 | 0.637 | ||||
| Sex | ||||||||
| M (ref) | 1 | |||||||
| F | 0.86 | 0.56 | 1.30 | 0.464 | ||||
| Days before hospitalization | 1.03 | 0.92 | 1.14 | 0.650 | ||||
| Body temp (°C) | 1.11 | 0.86 | 1.12 | 0.429 | ||||
| History of fever | 0.93 | 0.61 | 1.41 | 0.724 | ||||
| Respiratory rate (apm) | 1.12 | 1.07 | 1.18 | <0.001 | 1.09 | 1.04 | 1.14 | <0.001 |
| Blood pressure (mmHg) | ||||||||
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.004 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.022 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.205 | ||||
| Diarrhea | 0.40 | 0.13 | 1.28 | 0.123 | ||||
| Heart rate (bpm) | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 0.017 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.161 |
| Oxygen saturation | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.98 | <0.001 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.015 |
| GCS | 0.62 | 0.36 | 1.05 | 0.077 | ||||
| Oxygen therapy | 1.34 | 0.89 | 2.03 | 0.162 | ||||
| Chronic cardiac disease | 1.67 | 1.08 | 2.58 | 0.020 | 1.38 | 0.76 | 2.50 | 0.295 |
| Hypertension | 0.85 | 0.53 | 1.35 | 0.483 | ||||
| CKD | 1.38 | 0.84 | 2.26 | 0.203 | ||||
| Diabetes | 1.01 | 0.62 | 1.63 | 0.974 | ||||
| Smoking | 0.38 | 0.12 | 1.21 | 0.103 | ||||
| CLD | 0.51 | 0.16 | 1.60 | 0.248 | ||||
| Chronic respiratory disease | 1.22 | 0.77 | 1.93 | 0.388 | ||||
| Chronic neurological disorder | 0.87 | 0.52 | 1.43 | 0.574 | ||||
| Malign | 0.92 | 0.47 | 1.78 | 0.800 | ||||
| Steroids | 0.73 | 0.36 | 1.46 | 0.373 | ||||
| Antivirals | 0.51 | 0.24 | 1.10 | 0.087 | ||||
| Antibiotics | 1.07 | 0.69 | 1.68 | 0.757 | ||||
| NSAIDs | 0.42 | 0.19 | 0.93 | 0.031 | 0.79 | 0.24 | 2.60 | 0.704 |
| Diuretics | 1.84 | 1.19 | 2.82 | 0.006 | 0.79 | 0.42 | 1.49 | 0.470 |
| Anticoagulants | 0.39 | 0.14 | 1.07 | 0.068 | ||||
| AKI development | 2.60 | 1.70 | 3.97 | <0.001 | 3.96 | 1.87 | 8.41 | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.998 | 0.015 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.278 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caturano, A.; Galiero, R.; Vetrano, E.; Medicamento, G.; Alfano, M.; Beccia, D.; Brin, C.; Colantuoni, S.; Di Salvo, J.; Epifani, R.; et al. Impact of Acute Kidney Injury on the COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality in Octogenarian Patients: Insights from the COVOCA Study. Life 2024, 14, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010086
Caturano A, Galiero R, Vetrano E, Medicamento G, Alfano M, Beccia D, Brin C, Colantuoni S, Di Salvo J, Epifani R, et al. Impact of Acute Kidney Injury on the COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality in Octogenarian Patients: Insights from the COVOCA Study. Life. 2024; 14(1):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010086
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaturano, Alfredo, Raffaele Galiero, Erica Vetrano, Giulia Medicamento, Maria Alfano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Sara Colantuoni, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, and et al. 2024. "Impact of Acute Kidney Injury on the COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality in Octogenarian Patients: Insights from the COVOCA Study" Life 14, no. 1: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010086
APA StyleCaturano, A., Galiero, R., Vetrano, E., Medicamento, G., Alfano, M., Beccia, D., Brin, C., Colantuoni, S., Di Salvo, J., Epifani, R., Nevola, R., Marfella, R., Sardu, C., Coppola, C., Scarano, F., Maggi, P., Calabrese, C., De Lucia Sposito, P., Rescigno, C., ... Sasso, F. C., on behalf of COVOCA Study Group. (2024). Impact of Acute Kidney Injury on the COVID-19 In-Hospital Mortality in Octogenarian Patients: Insights from the COVOCA Study. Life, 14(1), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010086














