Principles of Treatment and Clinical-Evolutionary Peculiarities of Deep Cervical Spaces Suppurations—Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
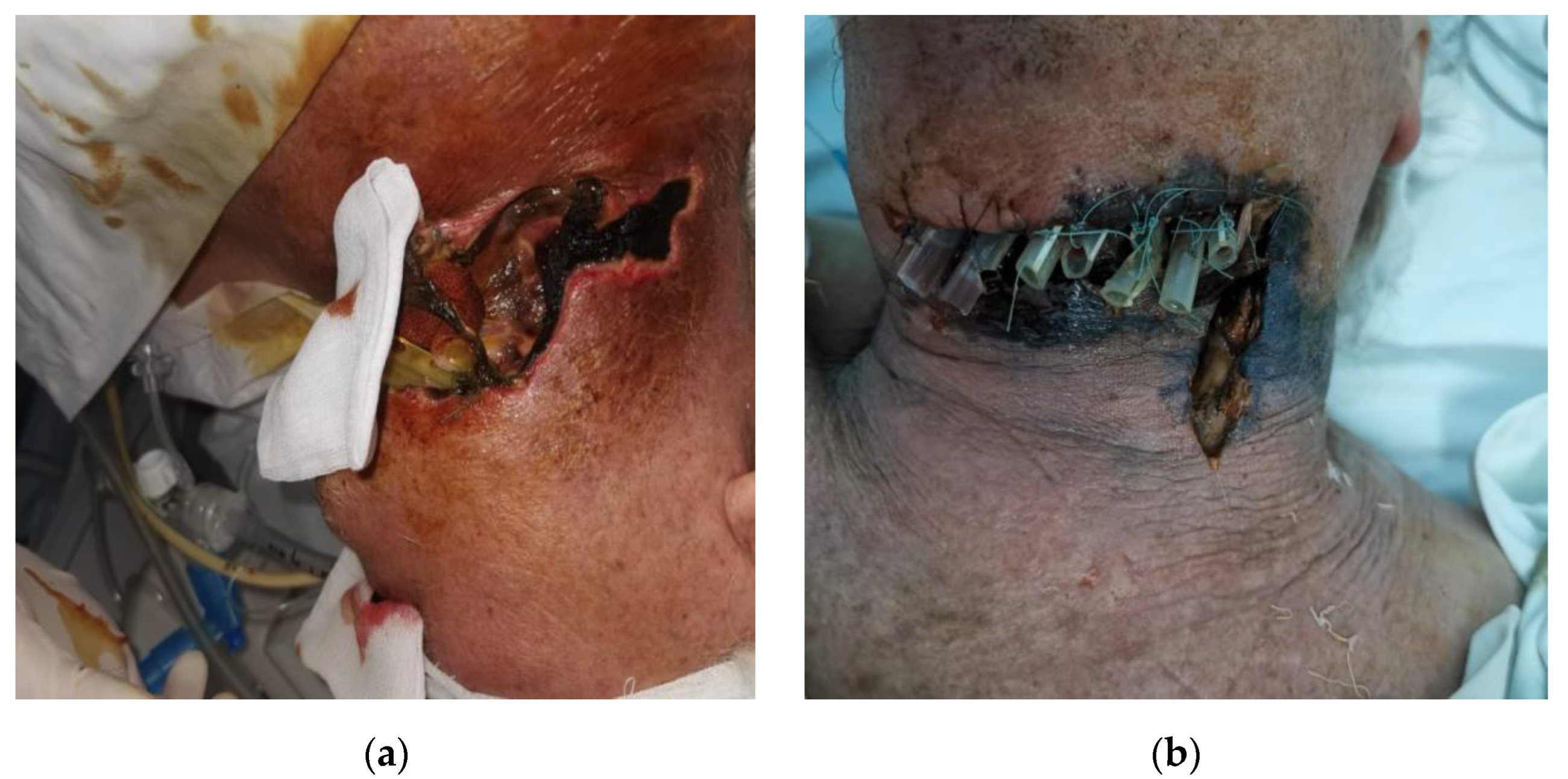
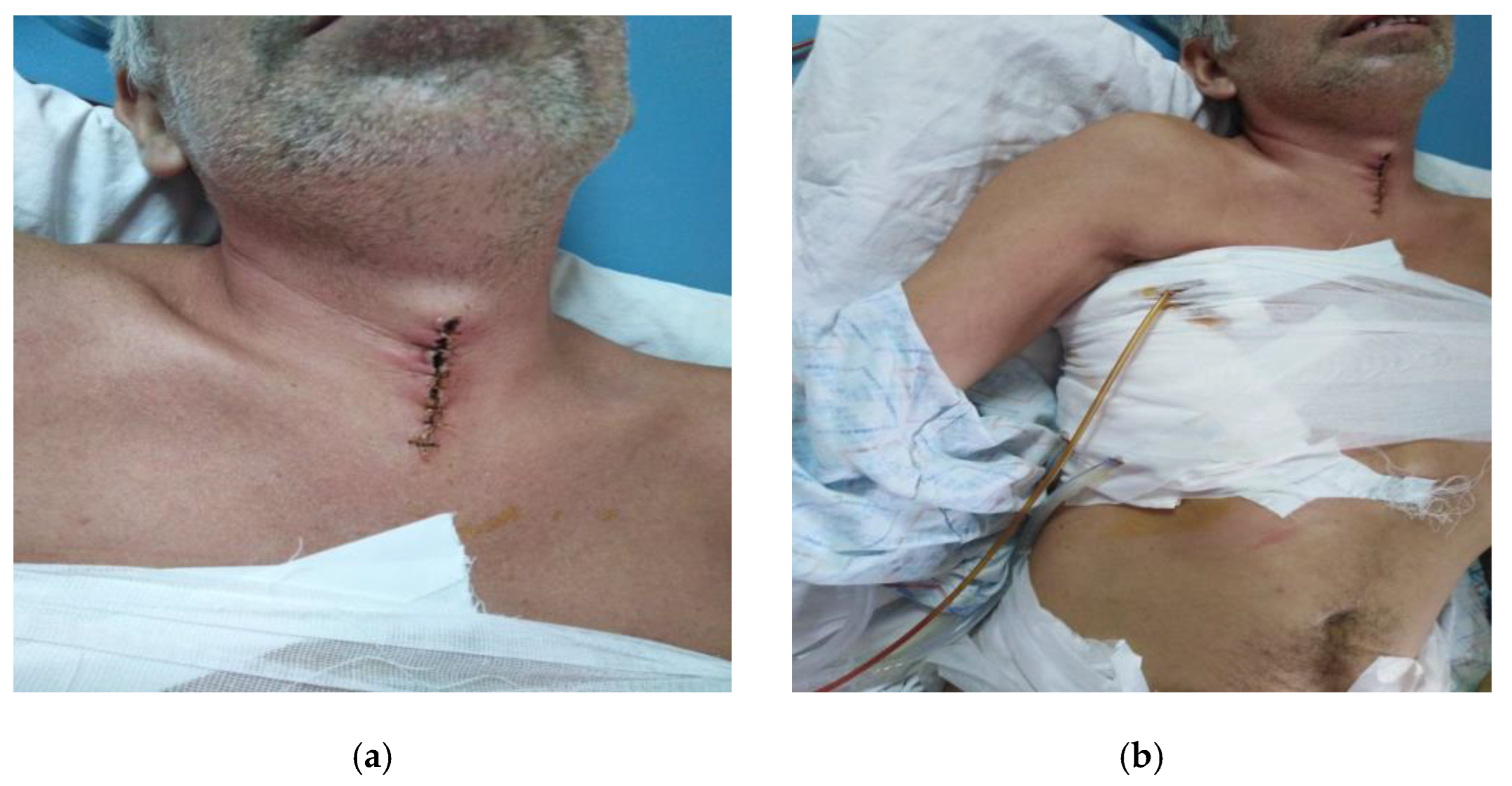
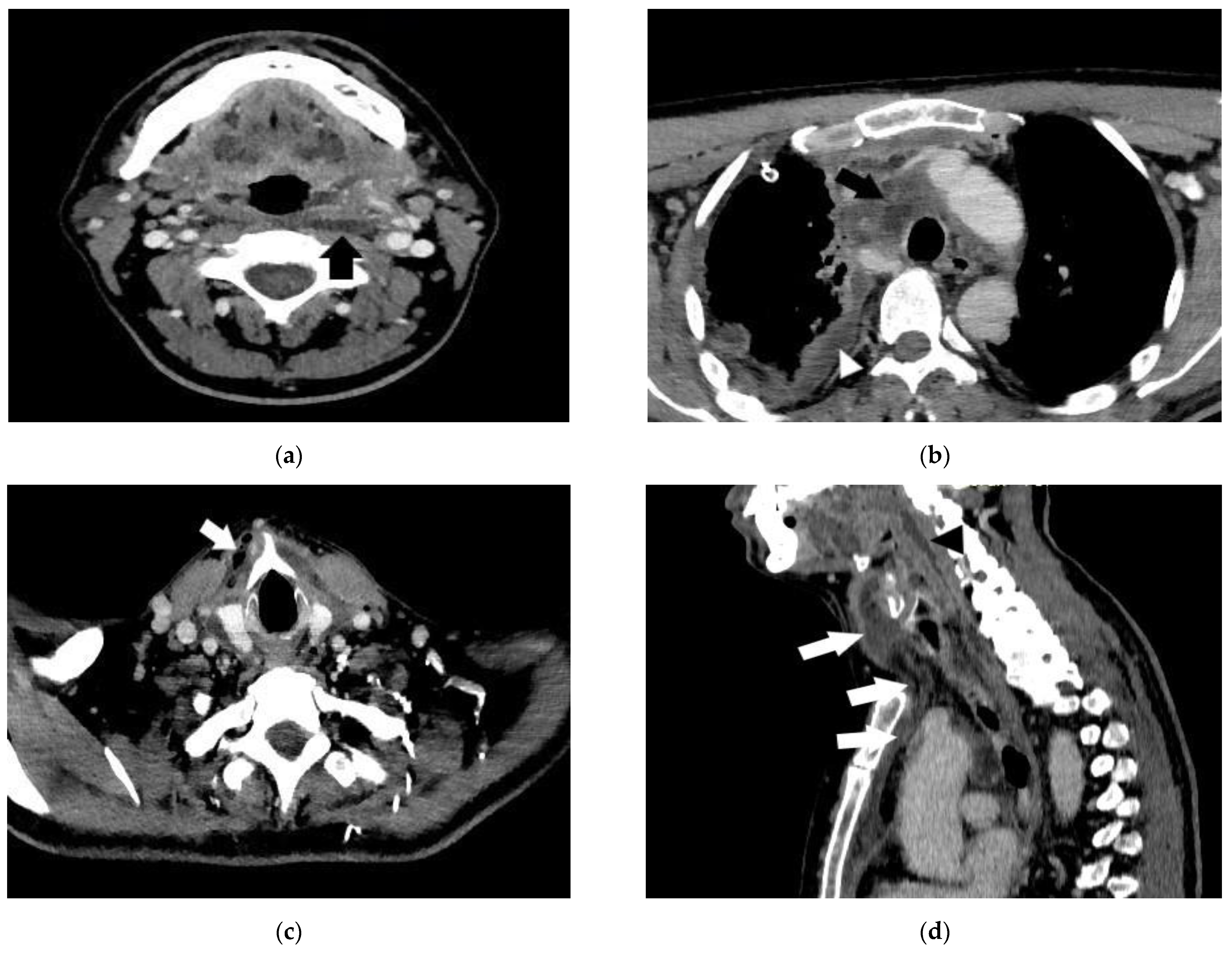
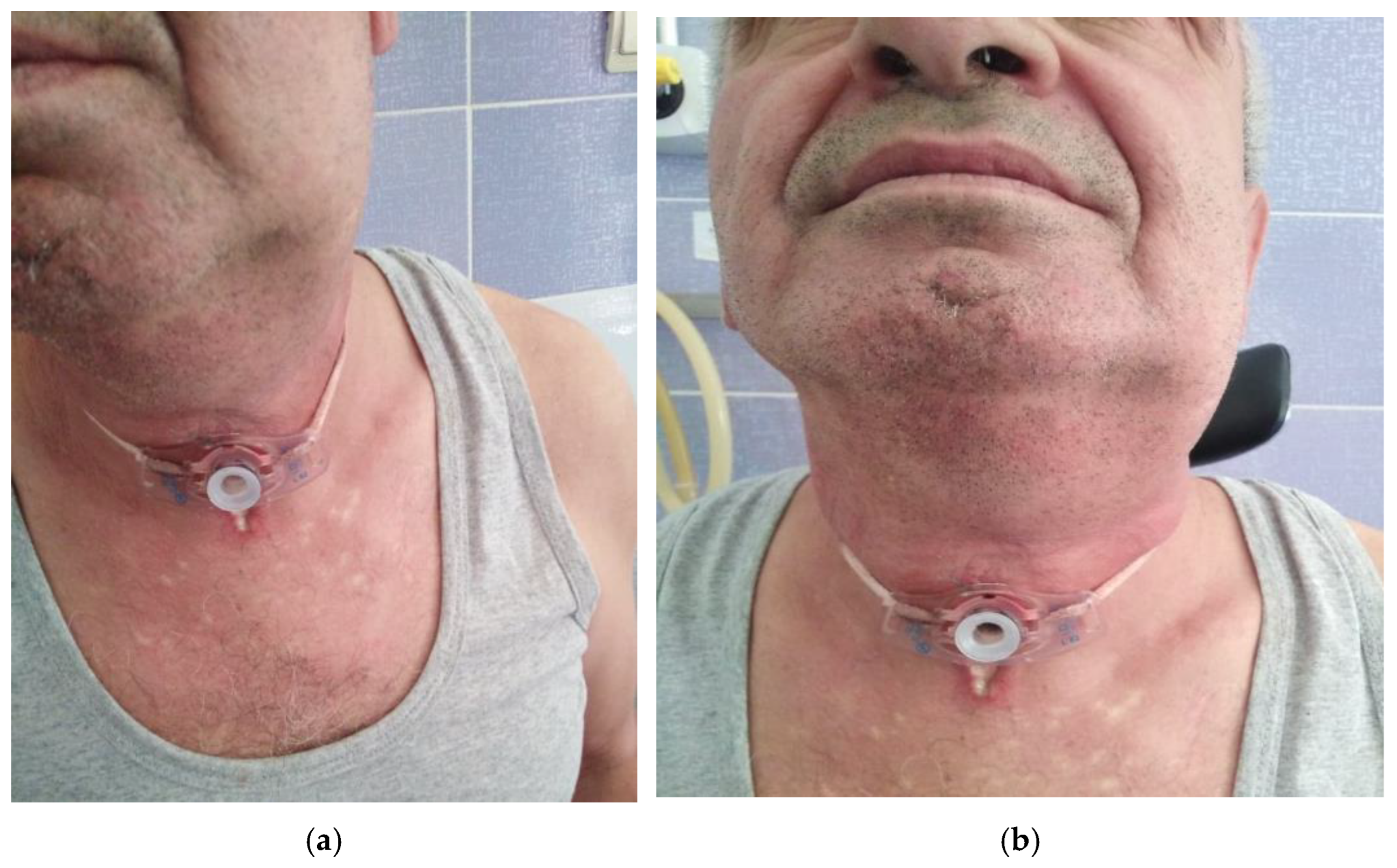
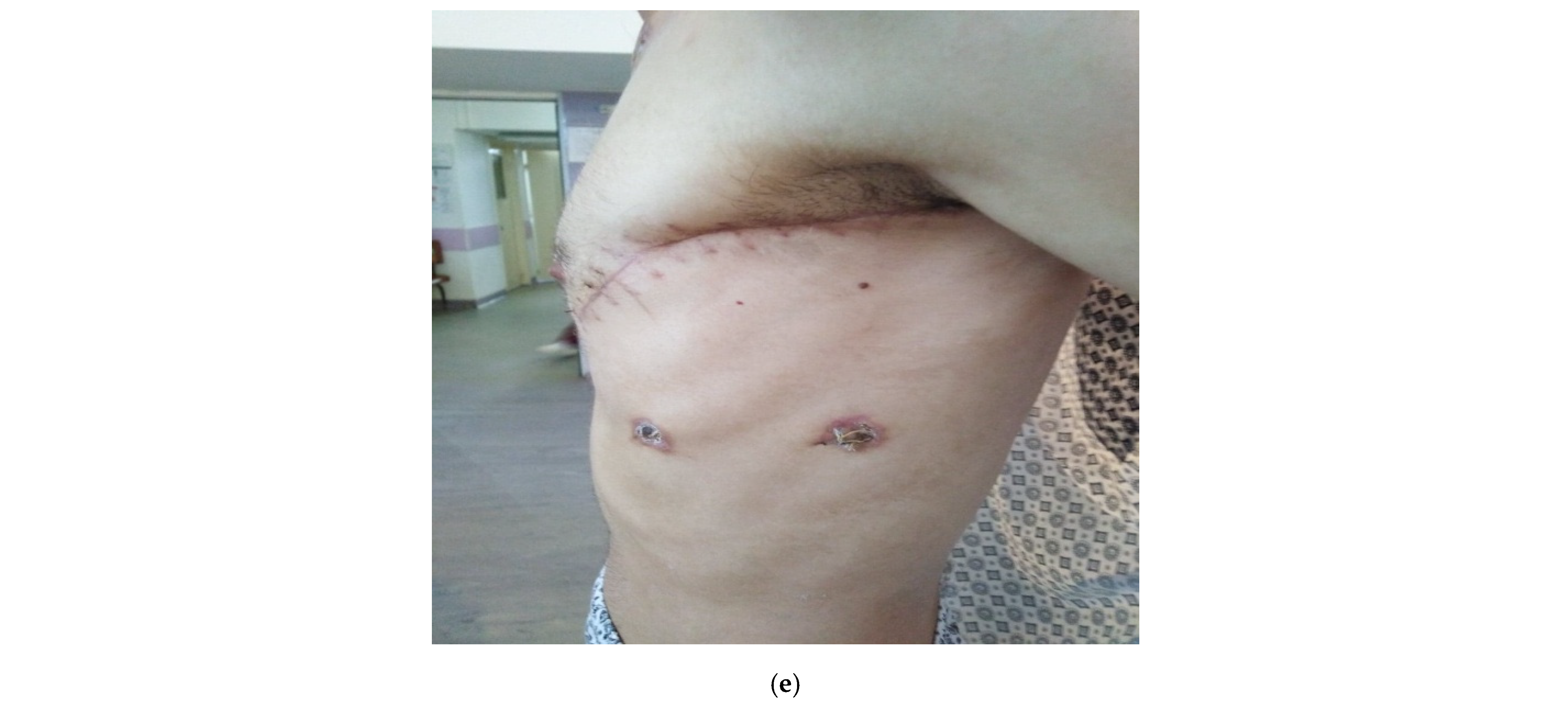
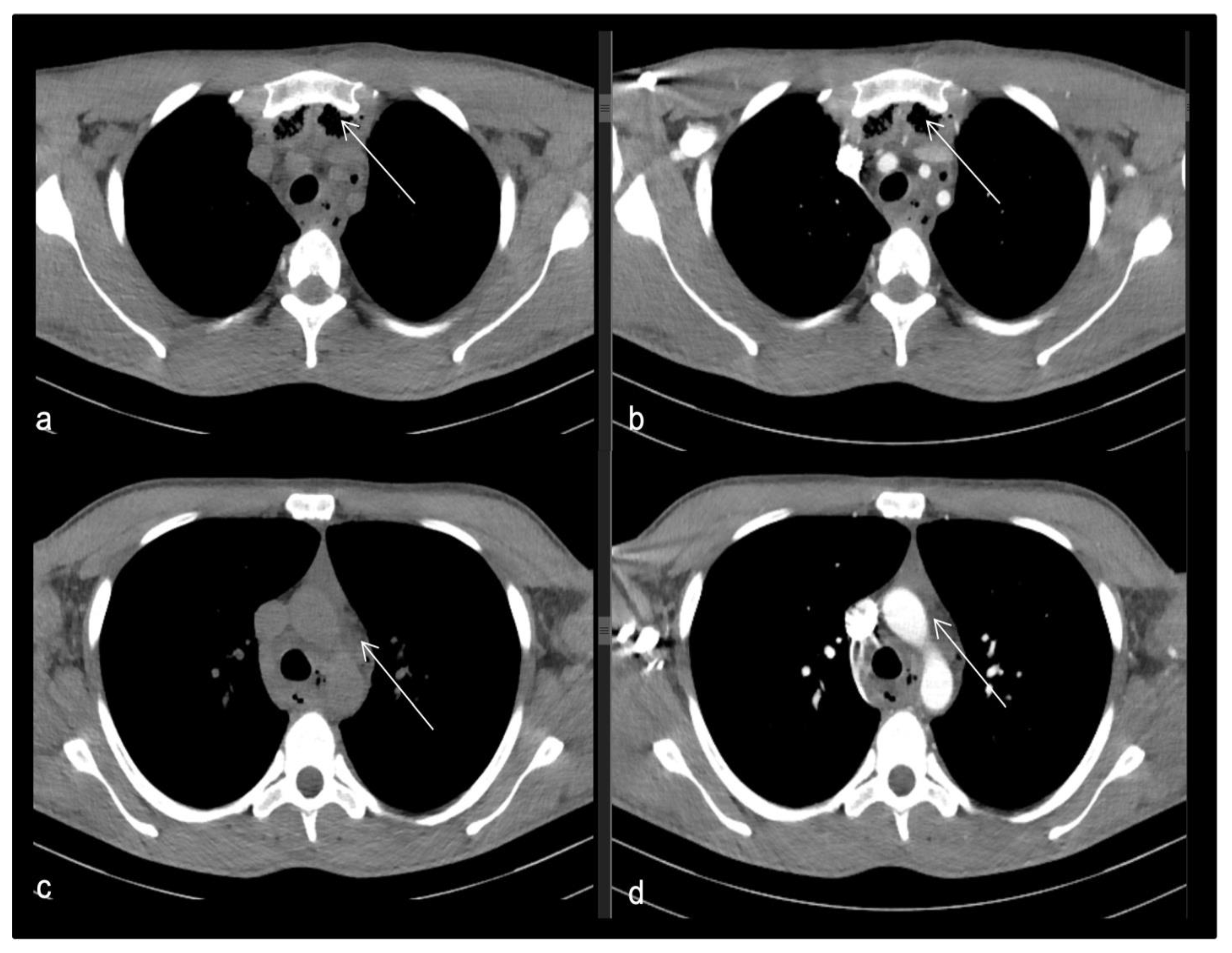
- Case 1.
- Case 2.
- Case 3.
- Case 4.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kauffmann, P.; Cordesmeyer, R.; Tröltzsch, M.; Sömmer, C.; Laskawi, R. Deep neck infections: A single-center analysis of 63 cases. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2017, 22, e536–e541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuqamam, M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Kondamudi, N.P. Deep Neck Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, K.; Hu, H.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J. Anatomical Proposal for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Targeting the Platysma Muscle for Treating Platysmal Band and Jawline Lifting: A Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, G.; Condino, S.; Stecco, A.; Soldani, P.; Belmonte, M.M.; Gesi, M. Is the cervical fascia an anatomical proteus? Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2015, 37, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigl, G.; Hammer, G.P.; Litz, R.; Kachlik, D. The intercarotid or alar fascia, other cervical fascias, and their adjacent spaces—A plea for clarification of cervical fascia and spaces terminology. J. Anat. 2020, 237, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.W. Deep Neck Space Infections in Adults. 2019. Available online: https://www.medilib.ir/uptodate/show/3415 (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Tong, X.; Liu, H. Imaging Anatomy of Cervical Space. In Radiology of Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases; Li, H., Xia, S., Lyu, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 2, pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S. Anatomy of the fasciae and fascial spaces of the maxillofacial and the anterior neck regions. Anat. Sci. Int. 2018, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, P.; Lasrado, S. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Deep Cervical Neck Fascia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 25 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, Z.; Farahani, F.; Seif-Rabiee, M. Clinical and epidemiological profile of deep neck space infections: A retrospective study in Hamadan, Western Iran, during 2008–2013. JOHE 2017, 6, 40–46. Available online: http://johe.rums.ac.ir/article-1-241-en.html (accessed on 2 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bucur, A.; Navarro Vila, C.; Lowry, J.; Acero, J. Compendiu de Chirurgie Oro-Maxilo-Faciala; Editura Academiei Române: Bucuresti, Romania, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 241–291. [Google Scholar]
- Maharaj, S.; Mungul, S.; Ahmed, S. Deep neck space infections: Changing trends in pediatric versus adult patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniko, M.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Bonkowsky, V.; Bradley, P.; Iurato, S. European Manual of Medicine, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Velhonoja, J.; Lääveri, M.; Soukka, T.; Irjala, H.; Kinnunen, I. Deep neck space infections: An upward trend and changing characteristics. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.D.; Russell, M.S. Urgent infections of the head and neck. Med.Clin.N.Am. 2018, 102, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageţan, M.; Ivan, I. Flegmonul submandibular şi laterocervical ca urmare a unei patologii periapicale. AMT 2012, 17, 133–134. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, T.P.; Hazboun, I.M.; Fernandes, F.L.; Bento, L.R.; Zappelini, C.E.; Chone, C.T.; Crespo, A.N. Deep neck abscesses: Study of 101 cases. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekharian, A.; Roozbahany, N.A.; Vaezeafshar, R.; Narimani, N. Deep neck infections: A retrospective review of 112 cases. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 266, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Liu, T.C.; Chen, P.R.; Tseng, F.Y.; Yeh, T.H.; Chen, Y.S. Deep neck infection: Analysis of 185 cases. Head Neck 2004, 26, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochner, R.E.; Gangar, M.; Belamarich, P.F. A clinical approach to tonsillitis, tonsillar hypertrophy, and peritonsillar and retropharyngeal abscesses. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 38, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernotico, L.; Picca, D.; Calculli, L.; Proto, F.; Valentini, N.; Covelli, V. The management in emergency of a septic complication from tonsillar abscess: Cervico mediastinal gangrene—A case report. Int. J. Sci. Res. Public 2018, 12, 1–15. Available online: http://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-1214.php?rp=P363507 (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Brănișteanu, D.E.; Pintilie, A.; Dimitriu, A.; Cerbu, A.; Ciobanu, D.; Oanţă, A.; Tatu, A.L. Clinical, laboratory and therapeutic profile of lichen planus. Med.-Surg. J. 2017, 121, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tușaliu, M.; Tiță, I.; Tuas, D.; Zarei, R.; Vulpe, M.; Onisâi, E.; Bucur, C.; Diaconu, E. Supuraţiile cervicale profunde–management terapeutic atipic. ORL.ro 2021, 51, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Pricop, R.; Cristea, V.C.; Gheorghe, I.; Tatu, A.L.; Mihaescu, G.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mas spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) reveals the anaerobic Slakia exigua as unique etiology of a dental abscess. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2017, 7, 1995–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mosoiu, A.R.; Musteata, O.M.; Grigore, R.; Bertesteanu, Ș.V.G.; Oancea, A.L.A. Deep neck space infection—Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges: Two case reports. Arch. Balk. Med. Union 2019, 54, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Nath, G.; Mishra, A. Clinico-Pathological Profile of Deep Neck Space Infection: A Prospective Study. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 69, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Haq, N.M.; Harahsheh, A.; Asmar, B.I. Retropharyngeal abscess in children: The emerging role of group A beta hemolytic streptococcus. SMJ 2006, 99, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, A.W. Submandibular Space Infections (Ludwig’s Angina). Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/deep-neck-space-infections-in-adults (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Hansen, B.W.; Ryndin, S.; Mullen, K.M. Infections of Deep Neck Spaces. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2020, 41, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetricean, S.; Osman, V.; Osman, V.; Gritco, E. Flegmoane cervicale postamigdalectomie. Cazuri clinice. ORL. Ro 2020, 47, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, E.; Nguyen, X.; Brooks, M.A. Descending necrotising mediastinitis: Two case reports and review af the literature. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2010, 19, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanti, L.A.; Lubis, F.M.; Bahar, E.; Ghanie, A. Factors associated with the length of stay of deep neck abscess patients. Oto Rhino Laryngol. Indones. 2022, 52, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.A.; Perera, T.B. Necrotizing Fasciitis. Updated 29 May 2022. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rebegea, L.; Ilie, A.M.; Neagu, A.; Firescu, D.; Constantin, G.B.; Bîrlă, R.; Bacinschi, X.; Şerban, C. Cutaneous and Inguinal Lymph Nodes Metastases Disseminated from an Endometrial Serous Carcinoma—Case Report and Literature Review. Chirurgia 2021, 116, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejzlik, J.; Celakovsky, P.; Tucek, L.; Kotulek, M.; Vrbacky, A.; Matousek, P.; Stanikova, L.; Hoskova, T.; Paz, A.; Mittu, P.; et al. Univariate and multivariate models for the prediction of life-threatening complications in 586 cases of deep neck space infections: Retrospective multi-institutional study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.Y.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Lin, C.H. Necrotizing fasciitis of the entire head and neck: Literature review and case report. Biomed J. 2020, 43, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hasegawa, J.; Yano, H.; Kakuta, R.; Ozawa, D.; Nomura, K.; Katori, Y. Clinical and bacteriological influence of diabetes mellitus on deep neck infection: Systematic review and metaanalysis. Head Neck 2015, 37, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriem, R.; Hassan, N.; Abdelaziz, R.; Nabila, S. The Bacteriological Profile of Otorhinolaryngological Infections. Am. J. Lab. Med. 2019, 4, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, I. Recovery of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in sinus fungal ball. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanopol, I.A.; Baroiu, L.; Constantin, G.B.; Danila, D.M.; Anghel, L.; Nechifor, A.; Tatu, A.L. Diagnostic and Management of Undescended Ovary—A Preoperative Dilemma: A Case-Based Systematic Review. Int. J. Womens Health 2022, 14, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Stellin, M.; Muzzi, E.; Mantovani, M.; Fuson, R.; Lupato, V.; Trabalzini, F.; Da Mosto, M.C. Deep neck infections: A study of 365 cases highlighting recommendations for management and treatment. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2012, 269, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebegea, L.F.; Firescu, D.; Anghel, R.M.; Gales, L.; Ilie, A.M.; Dumitru, M.E.; Crăescu, M.; Niculeț, E.; Tatu, A.L.; Stuparu Crețu, M.; et al. Clinical, histological and therapeutical aspects in the management of uterine and extrauterine stromal sarcomas. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mărginean, E.; Egor, S.; Venter, C.; Pantiș, A.; Vălenaș, O.; Sorban, I.; Domuța, M.; Bălălău, C.; Scaunasu, R.V.; Popescu. Management of deep space infections of the neck. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2018, 5, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Fasolka, B.; Treacy, C. Necrotizing fasciitis: A comprehensive review. Nursing 2020, 50, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, N.; McCoubrey, G. Necrotizing fasciitis: A plastic surgeon’s perspective. Surgery 2019, 37, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculeț, E.; Chioncel, V.; Elisei, A.M.; Miulescu, M.; Buzia, O.; Nwabudike, L.C.; Crăescu, M.; Draganescu, M.; Bujoreanu, F.; Marinescu, E.; et al. Multifactorial expression of IL-6 with update on COVID-19 and the therapeutic strategies of its blockade (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawa, R.S.; Anillo, S.; Huntoon, K.; Baumann, H.; Kulaylat, M. Interleukin-6 in Surgery, Trauma, and Critical Care Part II: Clinical Implications. J. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 26, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Rüddel, I.; Hessam, S.; Bechara, F.G.; Stockfleth, E.; Schmitz, L. Altered epigenetic pathways and cell cycle dysregulation in healthy appearing skin of patients with koebnerized squamous cell carcinomas following skin surgery. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazenberg, H.M.J.L.; Dubbink, J.H.; Sesay, I.; Versteege, T.; Bangura, H.; Hoevenaars, L.K.; Falama, A.M.; Koudijs, H.M.; Roemers, R.; Bache, E.B.; et al. Complicated Odontogenic Infections at 2 District Hospitals in Tonkolili District, Sierra Leone: Protocol for a Prospective Observational Cohort Study (DELAY). JMIR Res. Protocol. 2021, 10, e33677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Age Groups | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| 18–20 years | 3 (2.8) |
| 21–30 years | 15 (14.01) |
| 31–40 years | 17 (15.88) |
| 41–50 years | 13 (12.14) |
| 51–60 years | 28 (26.17) |
| 61–70 years | 18 (16.82) |
| 71–80 years | 13 (12.15) |
| >80 years | 0 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 48 (44.86) |
| Male | 59 (55.14) |
| Environment | |
| Rural | 74 (69.16) |
| Urban | 33 (30.84) |
| Comorbidities | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| History of suppurations | 47 (43.93) |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 38 (35.51) |
| Pulmonary diseases | 15 (14.02) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 25 (23.36) |
| Liver diseases | 12 (11.21) |
| Hematological diseases | 1 (0.93) |
| Dental infections | 15 (14.00) |
| Obesity | 8 (7.47) |
| Any pathology | 11 (10.28) |
| Other Factors Influencing Evolution and Complications | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Smoking | 60 (56.07) |
| Alcohol | 14 (13.08) |
| Starting Points of Suppurations | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Bacterial tonsillitis | 27 (25.23) |
| Odontogenic cause | 25 (23.36) |
| Lymphadenitis | 15 (14.01) |
| Tonsillo-pharyngitis | 8 (7.47) |
| Superinfected thyroid cyst | 6 (5.60) |
| Over infected sebaceous cyst | 5 (4.67) |
| Complicated otitis media | 3 (2.80) |
| Upper respiratory tract infections | 4 (3.74) |
| Sub-maxillitis | 3 (2.80) |
| Unidentified causes | 11 (10.28) |
| Signs and Symptoms | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Neck pain | 94 (87.85) |
| Neck swelling | 97 (90.65) |
| Dysphagia | 102 (95.32) |
| Odinophagia | 93 (86.91) |
| Toothache | 15 (14.01) |
| Trismus | 89 (83.17) |
| Limited neck mobility | 73 (68.22) |
| Dyspnea | 9 (8.41) |
| Fever | 19 (17.75) |
| Limphadenopathy | 32 (29.90) |
| Ear pain | 10 (9.34) |
| Airway obstruction | 4 (3.73) |
| Location | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Right side | 52 (48.59) |
| Left side | 47 (43.92) |
| Bilateral | 8 (7.47) |
| Peritonsillar space | 20 (18.69) |
| Submandibular space | 27 (25.23) |
| Para-pharyngeal space | 14 (13.08) |
| Buccal floor, sublingual space | 25 (23.36) |
| Retropharyngeal space | 4 (3.73) |
| Multispace | 17 (15.88) |
| Cultured Bacteria | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 30 (28.03) |
| Streptococcus Group G | 17 (15.88) |
| Streptococcus viridans | 14 (13.08) |
| Klebsiella | 9 (8.41) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 6 (5.60) |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 4 (3.73) |
| Fusobacterium necrophorum | 3 (2.80) |
| Negative culture | 24 (22.43) |
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (mm/h) | 100 | 108 | 92 | 105 | 112 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 796 | 850 | 959, 4 | 642 | 1037, 6 |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) (mg/L) | 28, 1 | 32, 5 | 15, 2 | 92, 1 | 1037, 6 |
| Procalcitonin (PCT) (ng/mL) | 1, 19 | 1, 20 | 1, 15 | 2, 18 | 2, 14 |
| Leukocyte (×103) | 16, 69 | 20, 31 | 19, 89 | 37, 45 | 25, 66 |
| Case Management | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Remedy under treatment | 11 (10.28) |
| Drainage with surgery | 80 (74.76) |
| Spontaneous fistula | 12 (11.21) |
| Deceased | 4 (3.73) |
| The Treatment Regime Applied | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Dual therapy | 25 (23.36) |
| Triple therapy | 62 (57.94) |
| More than 3 antibiotics | 10 (9.34) |
| Complications | No. of Patients (%) N = 107 |
|---|---|
| Upper airway obstruction | 4 (3.74) |
| Mediastinitis | 5 (4.67) |
| Necrotizing fasciitis | 3 (2.80) |
| Aspiration pneumonia | 6 (5.60) |
| Septic shock | 2 (1.87) |
| Death | 4 (3.74) |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 23 (21.95) |
| Correlation Matrix (Pearson): | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Upper Airway Obstruction | Mediastinitis | Necrotizing Fasciitis | Septic Shock | Aspiration Pneumonia | SARS-CoV-2 | Intensive Care | Deceased |
| Cardiovascular disease | 0.163 | −0.072 | 0.111 | −0.102 | 0.074 | −0.088 | −0.072 | −0.043 |
| Pulmonary diseases | 0.062 | −0.089 | 0.094 | 0.143 | −0.098 | 0.061 | 0.072 | 0.062 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.017 | 0.208 | 0.325 | 0.264 | 0.070 | 0.072 | 0.372 | 0.377 |
| Liver diseases | 0.086 | 0.202 | −0.060 | −0.049 | 0.171 | −0.108 | 0.197 | 0.086 |
| Hematological diseases | −0.019 | −0.022 | −0.016 | −0.013 | −0.024 | −0.049 | −0.048 | −0.019 |
| Dental infections | −0.083 | 0.156 | 0.088 | 0.136 | 0.012 | 0.046 | 0.189 | 0.056 |
| Obesity | −0.056 | −0.063 | −0.048 | −0.039 | −0.069 | 0.119 | −0.051 | −0.056 |
| Any pathology | −0.067 | −0.075 | −0.057 | −0.047 | −0.083 | −0.020 | −0.167 | −0.067 |
| Correlation Matrix (Pearson): | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Cardiovascular Disease | Pulmonary Diseases | Diabetes Mellitus | Liver Diseases | Hematological Diseases | Dental Infections | Obesity | Any Pathology | Deceased |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1 | −0.243 | −0.198 | −0.140 | −0.072 | −0.202 | −0.062 | −0.251 | −0.043 |
| Pulmonary diseases | −0.243 | 1 | −0.146 | −0.144 | −0.039 | −0.094 | −0.115 | −0.137 | 0.062 |
| Diabetes mellitus | −0.198 | −0.146 | 1 | −0.042 | −0.051 | −0.028 | −0.149 | −0.177 | 0.377 |
| Liver diseases | −0.140 | −0.144 | −0.042 | 1 | −0.035 | −0.149 | −0.101 | −0.120 | 0.086 |
| Hematological diseases | −0.072 | −0.039 | −0.051 | −0.035 | 1 | −0.041 | −0.028 | −0.033 | −0.019 |
| Dental infections | −0.202 | −0.094 | −0.028 | −0.149 | −0.041 | 1 | −0.119 | −0.142 | 0.056 |
| Obesity | −0.062 | −0.115 | −0.149 | −0.101 | −0.028 | −0.119 | 1 | −0.096 | −0.056 |
| Any pathology | −0.251 | −0.137 | −0.177 | −0.120 | −0.033 | −0.142 | −0.096 | 1 | −0.067 |
| p-values (Pearson): | |||||||||
| Variables | Cardiovascular disease | Pulmonary diseases | Diabetes mellitus | Liver diseases | Hematological diseases | Dental infections | Obesity | Any pathology | Deceased |
| Cardiovascular disease | 0 | 0.012 | 0.041 | 0.150 | 0.461 | 0.037 | 0.523 | 0.009 | 0.658 |
| Pulmonary diseases | 0.012 | 0 | 0.134 | 0.140 | 0.688 | 0.336 | 0.239 | 0.160 | 0.524 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.041 | 0.134 | 0 | 0.669 | 0.603 | 0.774 | 0.126 | 0.068 | <0.0001 |
| Liver diseases | 0.150 | 0.140 | 0.669 | 0 | 0.724 | 0.126 | 0.300 | 0.217 | 0.378 |
| Hematological diseases | 0.461 | 0.688 | 0.603 | 0.724 | 0 | 0.677 | 0.778 | 0.737 | 0.845 |
| Dental infections | 0.037 | 0.336 | 0.774 | 0.126 | 0.677 | 0 | 0.221 | 0.145 | 0.570 |
| Obesity | 0.523 | 0.239 | 0.126 | 0.300 | 0.778 | 0.221 | 0 | 0.324 | 0.567 |
| Any pathology | 0.009 | 0.160 | 0.068 | 0.217 | 0.737 | 0.145 | 0.324 | 0 | 0.495 |
| Correlation Matrix (Pearson): | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Negative Culture | Dual Therapy | Triple Therapy | More than 3 Antibiotics |
| Staphylococcus aureus | −0.320 | 0.158 | −0.104 | −0.062 |
| Streptococcus Group G | −0.234 | −0.067 | 0.047 | 0.021 |
| Streptococcus viridans | −0.209 | −0.091 | 0.166 | −0.131 |
| Klebsiella | −0.163 | −0.172 | 0.150 | 0.008 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | −0.131 | 0.051 | 0.006 | −0.083 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | −0.106 | 0.003 | −0.167 | 0.258 |
| Fusobacterium necrophorum | −0.091 | −0.096 | −0.234 | 0.502 |
| p-values (Pearson): | ||||
| Variables | Negative culture | Dual therapy | Triple therapy | More than 3 Antibiotics |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0.001 | 0.103 | 0.288 | 0.529 |
| Streptococcus Group G | 0.015 | 0.490 | 0.629 | 0.828 |
| Streptococcus viridans | 0.031 | 0.353 | 0.088 | 0.178 |
| Klebsiella | 0.094 | 0.077 | 0.124 | 0.932 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 0.178 | 0.599 | 0.948 | 0.398 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 0.277 | 0.974 | 0.085 | 0.007 |
| Fusobacterium necrophorum | 0.349 | 0.324 | 0.015 | <0.0001 |
| Correlation Matrix (Pearson): | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Remedy under Treatment | Drainage with Surgery | Spontaneous Fistula |
| Peritonsillar space | −0.117 | 0.063 | 0.037 |
| Submandibular space | −0.057 | −0.068 | 0.147 |
| Para pharyngeal space | 0.163 | −0.138 | 0.014 |
| Buccal floor, sublingual space | 0.032 | 0.088 | −0.149 |
| Retropharyngeal space | 0.062 | −0.102 | 0.070 |
| Multispace | −0.028 | 0.092 | −0.093 |
| p-values (Pearson): | |||
| Variables | Remedy under treatment | Drainage with surgery | Spontaneous Fistula |
| Peritonsillar space | 0.229 | 0.518 | 0.703 |
| Submandibular space | 0.562 | 0.490 | 0.130 |
| Para pharyngeal space | 0.094 | 0.158 | 0.888 |
| Buccal floor, sublingual space | 0.747 | 0.366 | 0.126 |
| Retropharyngeal space | 0.524 | 0.298 | 0.476 |
| Multispace | 0.773 | 0.344 | 0.342 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jicman, D.; Sârbu, N.; Rebegea, L.-F.; Crăescu, M.; Niculeț, E.; Țuța, M.-D.; Nechita, A.; Nicolescu, A.C.; Tatu, A.L. Principles of Treatment and Clinical-Evolutionary Peculiarities of Deep Cervical Spaces Suppurations—Clinical Study. Life 2023, 13, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020535
Jicman D, Sârbu N, Rebegea L-F, Crăescu M, Niculeț E, Țuța M-D, Nechita A, Nicolescu AC, Tatu AL. Principles of Treatment and Clinical-Evolutionary Peculiarities of Deep Cervical Spaces Suppurations—Clinical Study. Life. 2023; 13(2):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020535
Chicago/Turabian StyleJicman (Stan), Daniela, Nicolae Sârbu, Laura-Florentina Rebegea, Mihaela Crăescu, Elena Niculeț, Maria-Daniela Țuța, Aurel Nechita, Alin Codruț Nicolescu, and Alin Laurențiu Tatu. 2023. "Principles of Treatment and Clinical-Evolutionary Peculiarities of Deep Cervical Spaces Suppurations—Clinical Study" Life 13, no. 2: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020535
APA StyleJicman, D., Sârbu, N., Rebegea, L.-F., Crăescu, M., Niculeț, E., Țuța, M.-D., Nechita, A., Nicolescu, A. C., & Tatu, A. L. (2023). Principles of Treatment and Clinical-Evolutionary Peculiarities of Deep Cervical Spaces Suppurations—Clinical Study. Life, 13(2), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020535








