Can Biological Drugs Diminish the Risk of Sarcopenia in Psoriatic Patients? A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and Clinical Relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournadre, A.; Vial, G.; Capel, F.; Soubrier, M.; Boirie, Y. Sarcopenia. Joint Bone Spine 2019, 86, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, L.A.; Koster, A.; Visser, M. Adiposity, Muscle Mass, and Muscle Strength in Relation to Functional Decline in Older Persons. Epidemiol. Rev. 2013, 35, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.P.; Teo, K.K.; Rangarajan, S.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Avezum, A., Jr.; Orlandini, A.; Seron, P.; Ahmed, S.H.; Rosengren, A.; Kelishadi, R.; et al. Prognostic Value of Grip Strength: Findings from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) Study. Lancet 2015, 386, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijnarends, D.M.; Meijers, J.M.M.; Halfens, R.J.G.; ter Borg, S.; Luiking, Y.C.; Verlaan, S.; Schoberer, D.; Cruz Jentoft, A.J.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Schols, J.M.G.A. Validity and Reliability of Tools to Measure Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Performance in Community-Dwelling Older People: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginster, J.-Y.; Cooper, C.; Rizzoli, R.; Kanis, J.A.; Appelboom, G.; Bautmans, I.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Boers, M.; Brandi, M.L.; Bruyère, O.; et al. Recommendations for the Conduct of Clinical Trials for Drugs to Treat or Prevent Sarcopenia. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 28, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A Symptom Score to Predict Persons with Sarcopenia at Risk for Poor Functional Outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, G.; Yilmaz, O.; Kiliç, C.; Oren, M.M.; Karan, M.A. Performance of SARC-F in Regard to Sarcopenia Definitions, Muscle Mass and Functional Measures. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, G.; Yilmaz, O.; Oren, M.M.; Karan, M.A.; Reginster, J.Y.; Bruyère, O.; Beaudart, C. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the SARC-F to Assess Sarcopenia: Methodological Report from European Union Geriatric Medicine Society Sarcopenia Special Interest Group. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasadzka, E.; Pieczyńska, A.; Trzmiel, T.; Pawlaczyk, M. Polish Translation and Validation of the SARC-F Tool for the Assessment of Sarcopenia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Magasi, S.R.; Bubela, D.J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gershon, R.C. Grip and Knee Extension Muscle Strength Reflect a Common Construct among Adults. Muscle Nerve 2012, 46, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; McCloskey, E.; Bruyère, O.; Cesari, M.; Rolland, Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Araujo de Carvalho, I.; Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan, J.; Bautmans, I.; Bertière, M.-C.; et al. Sarcopenia in Daily Practice: Assessment and Management. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckinx, F.; Landi, F.; Cesari, M.; Fielding, R.A.; Visser, M.; Engelke, K.; Maggi, S.; Dennison, E.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Allepaerts, S.; et al. Pitfalls in the Measurement of Muscle Mass: A Need for a Reference Standard. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB). Available online: http://www.nia.nih.gov/research/labs/leps/short-physical-performance-battery-sppb (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The Timed “Up & Go”: A Test of Basic Functional Mobility for Frail Elderly Persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Simonsick, E.M.; Harris, T.B.; Penninx, B.W.; Brach, J.S.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Satterfield, S.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Added Value of Physical Performance Measures in Predicting Adverse Health-Related Events: Results from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Rolland, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Sieber, C.; Cooper, C.; Al-Daghri, N.; Araujo de Carvalho, I.; Bautmans, I.; Bernabei, R.; et al. Assessment of Muscle Function and Physical Performance in Daily Clinical Practice: A Position Paper Endorsed by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Liu, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.-Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Hsu, P.-S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, R.A.; Vellas, B.; Evans, W.J.; Bhasin, S.; Morley, J.E.; Newman, A.B.; Abellan van Kan, G.; Andrieu, S.; Bauer, J.; Breuille, D.; et al. Sarcopenia: An Undiagnosed Condition in Older Adults Current Consensus Definition: Prevalence, Etiology, and Consequences. International Working Group on Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH Sarcopenia Project: Rationale, Study Description, Conference Recommendations, and Final Estimates. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Morley, J.E.; von Haehling, S. Welcome to the ICD-10 Code for Sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Morley, J.E. Sarcopenia Is Recognized as an Independent Condition by an International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) Code. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, G.; Keshtkar, A.; Soltani, A.; Ahadi, Z.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R. Prevalence of Sarcopenia in the World: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis of General Population Studies. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2017, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, A.J.; Amog, K.; Phillips, S.; Parise, G.; McNicholas, P.D.; de Souza, R.J.; Thabane, L.; Raina, P. The Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults, an Exploration of Differences between Studies and within Definitions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethgen, O.; Beaudart, C.; Buckinx, F.; Bruyère, O.; Reginster, J.Y. The Future Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Europe: A Claim for Public Health Action. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2017, 100, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.S.Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Pham, V.K.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Lim, W.K.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia and Its Association with Falls and Fractures in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Zaaria, M.; Pasleau, F.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Bruyère, O. Health Outcomes of Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-V.; Hsu, T.-H.; Wu, W.-T.; Huang, K.-C.; Han, D.-S. Association Between Sarcopenia and Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1164.e7–1164.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-V.; Hsu, T.-H.; Wu, W.-T.; Huang, K.-C.; Han, D.-S. Is Sarcopenia Associated with Depression? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekoura, M.; Kastrinis, A.; Katsoulaki, M.; Billis, E.; Gliatis, J. Sarcopenia and Its Impact on Quality of Life. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 987, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, R.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Arnal, J.-F.; Bautmans, I.; Beaudart, C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Biver, E.; Boonen, S.; Brandi, M.-L.; Chines, A.; et al. Quality of Life in Sarcopenia and Frailty. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 93, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Youm, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Choi, W.; Chu, S.H.; Park, Y.-R.; Kim, H.C. Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass and Insulin Resistance in an Elderly Korean Population: The Korean Social Life, Health and Aging Project-Health Examination Cohort. Diabetes Metab. J. 2015, 39, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.B.F.; Nascimento, D.A.C.; Rodrigues, I.J.M.; Charone, C.C.O.; Lopes, G.L.; Lima, R.S.; Sá, A.A.; Carneiro, T.X.; Moraes, N.S. Association between Sarcopenia and Diabetes in Community Dwelling Elderly in the Amazon Region - Viver Mais Project. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 83, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Abe, K.; Fujita, M.; Okai, K.; Takahashi, A.; Ohira, H. Association between Sarcopenia and Osteoporosis in Chronic Liver Disease. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2018, 48, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhao, R.; Wan, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Shen, X.; Wu, X. Sarcopenia and Adverse Health-Related Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 7964–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic Obesity in Older Adults: Aetiology, Epidemiology and Treatment Strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xu, Y. Association of Sarcopenic Obesity with the Risk of All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Livshits, G. Sarcopenic Obesity or Obese Sarcopenia: A Cross Talk between Age-Associated Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation as a Main Mechanism of the Pathogenesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezameddin, R.; Itani, L.; Kreidieh, D.; El Masri, D.; Tannir, H.; El Ghoch, M. Understanding Sarcopenic Obesity in Terms of Definition and Health Consequences: A Clinical Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.J.; Park, Y.S. Relationship between Sarcopenic Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease Risk as Estimated by the Framingham Risk Score. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.M.; Wells, J.C.K.; Smith, S.R.; Stephan, B.C.M.; Siervo, M. Sarcopenic Obesity: A Critical Appraisal of the Current Evidence. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, S.R.; Feldman, S.R.; Exum, M.L.; Fleischer, A.B.; Reboussin, D.M. Psoriasis Causes as Much Disability as Other Major Medical Diseases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1999, 41, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, I.M.; Loring, B.; John, S.M. A Systematic Review of Worldwide Epidemiology of Psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2017, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Global Epidemiology of Psoriasis: A Systematic Review of Incidence and Prevalence. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurd, S.K.; Gelfand, J.M. The Prevalence of Previously Diagnosed and Undiagnosed Psoriasis in US Adults: Results from NHANES 2003-2004. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.; Korman, N.J.; Gordon, K.B.; Feldman, S.R.; Lebwohl, M.; Koo, J.Y.M.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Elmets, C.A.; Leonardi, C.L.; Beutner, K.R.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, L.C.; Helliwell, P.S. Psoriatic Arthritis: State of the Art Review. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan Menter, M. Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Overview. Suppl. Featur. Publ. 2016, 22, s216–s224. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, A.; Gottlieb, A.; Feldman, S.R.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Leonardi, C.L.; Gordon, K.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Koo, J.Y.M.; Elmets, C.A.; Korman, N.J.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 826–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, R.; Rutter, M.K.; Lunt, M.; Young, H.S.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Psoriasis and the Risk of Major Cardiovascular Events: Cohort Study Using the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Azfar, R.S.; Mehta, N.N. Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Risk: Strength in Numbers. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, E.J.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, J.; Grewal, S.; Langan, S.M.; Mehta, N.N.; Ogdie, A.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Gelfand, J.M. Psoriasis and Comorbid Diseases: Epidemiology. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.M.; Ellervik, C.; Yazdanyar, S.; Jemec, G.B.E. Meta-Analysis of Psoriasis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Associated Risk Factors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N. Pathogenesis and Clinical Features of Psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak-Stoma, A.; Pietrzak, A.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Zalewska-Janowska, A.; Paszkowski, T.; Chodorowska, G. Cytokine Network in Psoriasis Revisited. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2011, 22, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, H.A. Effects of Weight Loss on Psoriasis: A Review of Clinical Trials. Cureus 2018, 10, e3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, J.; Heimbürger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Adipose Tissue and Its Relation to Inflammation: The Role of Adipokines. J. Ren. Nutr. 2005, 15, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-J.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Shi, G.; Fan, Y.-M. Leptin Levels in Patients with Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 38, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-J.; Shi, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Fan, Y.-M. Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shen, E.; Tang, S.; Tan, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Ding, H. Increased Serum Resistin Levels Correlate with Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamminga, E.A.; van der Lely, A.J.; Neumann, H.A.M.; Thio, H.B. Chronic Inflammation in Psoriasis and Obesity: Implications for Therapy. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Placek, W. Compounds of Psoriasis with Obesity and Overweight. Postepy Hig. Med. Doswiadczalnej Online 2017, 71, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowrońska, B.; Fichna, M.; Fichna, P. Rola Tkanki Tłuszczowej w Układzie Dokrewnym. Endokrynol. Otył. Zab. Przem. Mat 2005, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiang, H.; Tan, L.; Zhou, J.; Tang, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, M. Psoriasis Is Associated With Myosteatosis but Not Sarcopenia: A Case-Control Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 754932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.; Sequeira, J.; Meirinhos, T.; Ambrósio, C.; Barcelos, A. SARCOSPA - Sarcopenia in Spondyloarthritis Patients. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2014, 39, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, M.; Viggiani, M.T.; Anelli, M.G.; Fanizzi, R.; Lorusso, O.; Lopalco, G.; Cantarini, L.; Di Leo, A.; Lapadula, G.; Iannone, F. Sarcopenia in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Placek, W. Changes in Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women with Psoriatic Arthritis. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournadre, A.; Jaffeux, P.; Frayssac, T.; Fan, A.; Couderc, M.; Dubost, J.J.; Malochet-Guinamand, S.; Mathieu, S.; Tatar, Z.; Jourdy, J.C.; et al. SAT0682 Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, T.; Gullick, N.J.; Hutchinson, C.E.; Barber, T.M. Psoriatic Disease and Body Composition: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wan, C.S.; Ktoris, K.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Mortality in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gerontology 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Harhay, M.N. Sarcopenia and Mortality among a Population-based Sample of Community-dwelling Older Adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachettini, N.P.; Bielemann, R.M.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Menezes, A.M.B.; Tomasi, E.; Gonzalez, M.C. Sarcopenia as a Mortality Predictor in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Comparison of the Diagnostic Criteria of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.J.; Tizaoui, K.; Terrazzino, S.; Cargnin, S.; Lee, K.H.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Smith, L.; et al. Sarcopenia in Autoimmune and Rheumatic Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.; Massimino, E.; Riccardi, G.; Della Pepa, G. A Narrative Review on Sarcopenia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Associated Factors. Nutrients 2021, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, O.M.; de Sire, R.; Petito, V.; Testa, A.; Villani, G.; Scaldaferri, F.; Castiglione, F. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Sarcopenia: The Role of Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in the Development of Muscle Failure. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 694217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerpa-Cruz, S.; Castańeda-Ureńa, M.; Martínez-Bonilla, G.; González-Díaz, V.; Ruíz-González, F.J.; Pérez-Romero, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Ureńa, S. Sarcopenia in patients with autoimmune diseases. Rev. Médica MD 2016, 7.8, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Amevor, A.A.; Yodoshi, T.; Trout, A.T.; Dillman, J.R.; Singh, R.; Jarvis, R.; Fei, L.; Liu, C.; Taylor, A.; Miethke, A.; et al. Sarcopenia Is Highly Prevalent in Children with Autoimmune Liver Diseases and Is Linked to Visceral Fat and Parent-Perceived General Health. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenakker, K.G.M.; Ling, C.H.; Meskers, C.G.M.; de Craen, A.J.M.; Stijnen, T.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Maier, A.B. Patterns of Muscle Strength Loss with Age in the General Population and Patients with a Chronic Inflammatory State. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Pahor, M.; Taaffe, D.R.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Simonsick, E.M.; Newman, A.B.; Nevitt, M.; Harris, T.B. Relationship of Interleukin-6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha with Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength in Elderly Men and Women: The Health ABC Study. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, M326–M332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hall, G.; Steensberg, A.; Fischer, C.; Keller, C.; Møller, K.; Moseley, P.; Pedersen, B.K. Interleukin-6 Markedly Decreases Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover and Increases Nonmuscle Amino Acid Utilization in Healthy Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubenoff, R. Rheumatoid Cachexia: A Complication of Rheumatoid Arthritis Moves into the 21st Century. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meephansan, J.; Subpayasarn, U.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Pathogenic Role of Cytokines and Effect of Their Inhibition in Psoriasis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3252-3. [Google Scholar]
- Baliwag, J.; Barnes, D.H.; Johnston, A. Cytokines in Psoriasis. Cytokine 2015, 73, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arican, O.; Aral, M.; Sasmaz, S.; Ciragil, P. Serum Levels of TNF-Alpha, IFN-Gamma, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-18 in Patients with Active Psoriasis and Correlation with Disease Severity. Mediators Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreschi, K. Targeting Immune Checkpoints and Cytokines to Protect from Psoriasis Relapse. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Panguluri, S.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Dahiya, S.; Lundy, R.F.; Kumar, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Regulates Distinct Molecular Pathways and Gene Networks in Cultured Skeletal Muscle Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, L.A.; Pluijm, S.M.F.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Colbert, L.H.; Pahor, M.; Rubin, S.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; et al. Higher Inflammatory Marker Levels in Older Persons: Associations With 5-Year Change in Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2009, 64A, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.A.; Bowcock, A.M.; Krueger, J.G. Pathogenesis and Therapy of Psoriasis. Nature 2007, 445, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.H.; Yiu, Z.Z.N.; Bale, T.; Burden, A.D.; Coates, L.C.; Edwards, W.; MacMahon, E.; Mahil, S.K.; McGuire, A.; Murphy, R.; et al. British Association of Dermatologists Guidelines for Biologic Therapy for Psoriasis 2020: A Rapid Update. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Ganzetti, G.; Giuliodori, K.; Marra, M.; Bonfigli, A.; Testa, R.; Offidani, A. Serum Levels of Adipocytokines in Psoriasis Patients Receiving Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors: Results of a Retrospective Analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, R.; Schipani, C.; Mazzotta, A.; Esposito, M.; Di Renzo, L.; De Lorenzo, A.; Chimenti, S. Effect of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Therapies on Body Mass Index in Patients with Psoriasis. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florin, V.; Cottencin, A.C.; Delaporte, E.; Staumont-Sallé, D. Body Weight Increment in Patients Treated with Infliximab for Plaque Psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, e186–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsalos, O.; Dalton, B.; Leppanen, J.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Himmerich, H. Impact of TNF-α Inhibitors on Body Weight and BMI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. The Association between Psoriasis and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, T.; Christophers, E. Disease Concomitance in Psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 32, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, S.M.; Seminara, N.M.; Shin, D.B.; Troxel, A.B.; Kimmel, S.E.; Mehta, N.N.; Margolis, D.J.; Gelfand, J.M. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Psoriasis: A Population-Based Study in the United Kingdom. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzo, L.D.I.; Saraceno, R.; Schipani, C.; Rizzo, M.; Bianchi, A.; Noce, A.; Esposito, M.; Tiberti, S.; Chimenti, S.; DE Lorenzo, A. Prospective Assessment of Body Weight and Body Composition Changes in Patients with Psoriasis Receiving Anti-TNF-α Treatment. Dermatol. Ther. 2011, 24, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Bianchi, A.; Saraceno, R.; Calabrese, V.; Cornelius, C.; Iacopino, L.; Chimenti, S.; De Lorenzo, A. −174G/C IL-6 Gene Promoter Polymorphism Predicts Therapeutic Response to TNF-α Blockers. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2012, 22, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofoed, K.; Clemmensen, A.; Mikkelsen, U.R.; Simonsen, L.; Andersen, O.; Gniadecki, R. Effects of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy on Body Composition and Insulin Sensitivity in Patients with Psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martínez-Abundis, E.; Reynoso-von Drateln, C.; Hernández-Salazar, E.; González-Ortiz, M. Effect of Etanercept on Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity in a Randomized Trial with Psoriatic Patients at Risk for Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2007, 299, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Campanati, A.; Testa, R.; Sirolla, C.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Franceschi, C.; Marchegiani, F.; Offidani, A. Effect of Etanercept on Insulin Sensitivity in Nine Patients with Psoriasis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, K.; Sabat, R. Adipokines in Psoriasis: An Important Link between Skin Inflammation and Metabolic Alterations. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Boehncke, S.; Tobin, A.-M.; Kirby, B. The “Psoriatic March”: A Concept of How Severe Psoriasis May Drive Cardiovascular Comorbidity. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.; Catarino, C.; Santos-Silva, A. The Triad Psoriasis–Obesity–Adipokine Profile. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakou, A.; Patsatsi, A.; Sotiriadis, D.; Goulis, D.G. Serum Leptin, Resistin, and Adiponectin Concentrations in Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Dermatol. Basel Switz. 2017, 233, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Raimondo, A.; Lembo, S.; Fausti, F.; Dini, V.; Costanzo, A.; Monfrecola, G.; Balato, N.; Ayala, F.; Romanelli, M.; et al. Crosstalk between Skin Inflammation and Adipose Tissue-Derived Products: Pathogenic Evidence Linking Psoriasis to Increased Adiposity. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Ahern, T.; Sweeney, C.M.; Malara, A.; Tobin, A.-M.; O’Shea, D.; Kirby, B. Adipokines, Psoriasis, Systemic Inflammation, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, B.; Lynch, M. Adipokines and Psoriasis: The Obesity Link. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, S.; Paltser, G.; Chan, Y.; Tsui, H.; Engleman, E.; Winer, D.; Dosch, H.-M. Obesity Predisposes to Th17 Bias. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehimi, M.; Vidal, H.; Eljaafari, A. Pathogenic Role of IL-17-Producing Immune Cells in Obesity, and Related Inflammatory Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Stebut, E.; Boehncke, W.-H.; Ghoreschi, K.; Gori, T.; Kaya, Z.; Thaci, D.; Schäffler, A. IL-17A in Psoriasis and Beyond: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Implications. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piros, É.A.; Szabó, Á.; Rencz, F.; Brodszky, V.; Wikonkál, N.; Miheller, P.; Horváth, M.; Holló, P. Anti-Interleukin-17 Therapy of Severe Psoriatic Patients Results in an Improvement of Serum Lipid and Inflammatory Parameters ‘Levels, but Has No Effect on Body Composition Parameters. Life 2021, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, M.; D’Adamio, S.; Pastorino, R.; Andreoli, A.; Servoli, S.; Bianchi, L.; Talamonti, M. Effect of Anti IL-12/23 on Body Composition: Results of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Caucasian Psoriatic Patients. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Macchia, P.E.; Di Somma, C.; Napolitano, M.; Balato, A.; Falco, A.; Savanelli, M.C.; Balato, N.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Bioelectrical Phase Angle and Psoriasis: A Novel Association with Psoriasis Severity, Quality of Life and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical Phase Angle and Impedance Vector Analysis--Clinical Relevance and Applicability of Impedance Parameters. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, M.; Reber, H.; Kahaly, G.J. Bioimpedance Phase Angle Indicates Catabolism in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2015, 32, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Zocher, D.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Szramek, A.; Scheufele, R.; Smoliner, C.; Pirlich, M. Cutoff Percentiles of Bioelectrical Phase Angle Predict Functionality, Quality of Life, and Mortality in Patients with Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
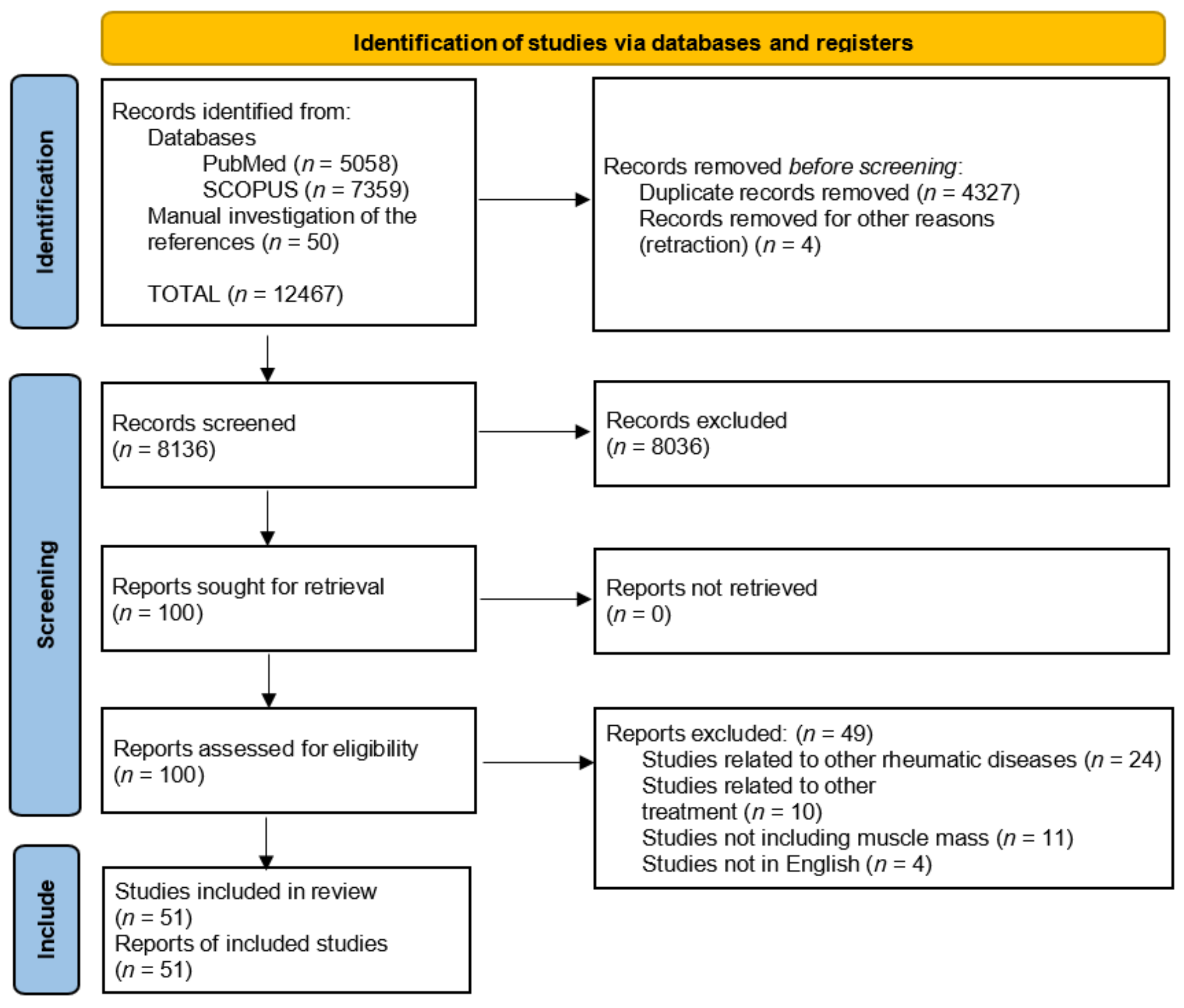
| Author | Country, Year | Study Design | Sarcopenia Prevalence | p Value | Participants | Sarcopenia Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aguiar et al. [71] | Portugal, 2014 | Cross-sectional | 61.7% | 0.001 | 60 M, Caucasian, 45.5 ± 13.4 yo | MMI (Lee’s equation) |
| Barone et al. [72] | Italy, 2018 | Cross-sectional | 20.0% | NS | 70 M/W, Caucasian, 51.6 ± 8.8 yo | MMI (BIA) + HS |
| Krajewska-Włodarczyk et al. [73] | Poland, 2017 | Cross-sectional | 13.7% 49.0% 43.1% | NS <0.001 - | 51 W, Caucasian, 65.6 ± 5.9 yo | ALM (BIA), SMI (BIA), SMI, TUG |
| Tournadre et al. [74] | France, 2017 | Cross-sectional | 9.1% 9.1% | 0.009 - | 148 W, 54.6 ± 11.0 yo | SMI (DXA), SMI + HS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piętowska, Z.; Nowicka, D.; Szepietowski, J. Can Biological Drugs Diminish the Risk of Sarcopenia in Psoriatic Patients? A Systematic Review. Life 2022, 12, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030435
Piętowska Z, Nowicka D, Szepietowski J. Can Biological Drugs Diminish the Risk of Sarcopenia in Psoriatic Patients? A Systematic Review. Life. 2022; 12(3):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030435
Chicago/Turabian StylePiętowska, Zuzanna, Danuta Nowicka, and Jacek Szepietowski. 2022. "Can Biological Drugs Diminish the Risk of Sarcopenia in Psoriatic Patients? A Systematic Review" Life 12, no. 3: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030435
APA StylePiętowska, Z., Nowicka, D., & Szepietowski, J. (2022). Can Biological Drugs Diminish the Risk of Sarcopenia in Psoriatic Patients? A Systematic Review. Life, 12(3), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030435






