Prone Positioning May Improve the Treatment of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Secondary to ANCA Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
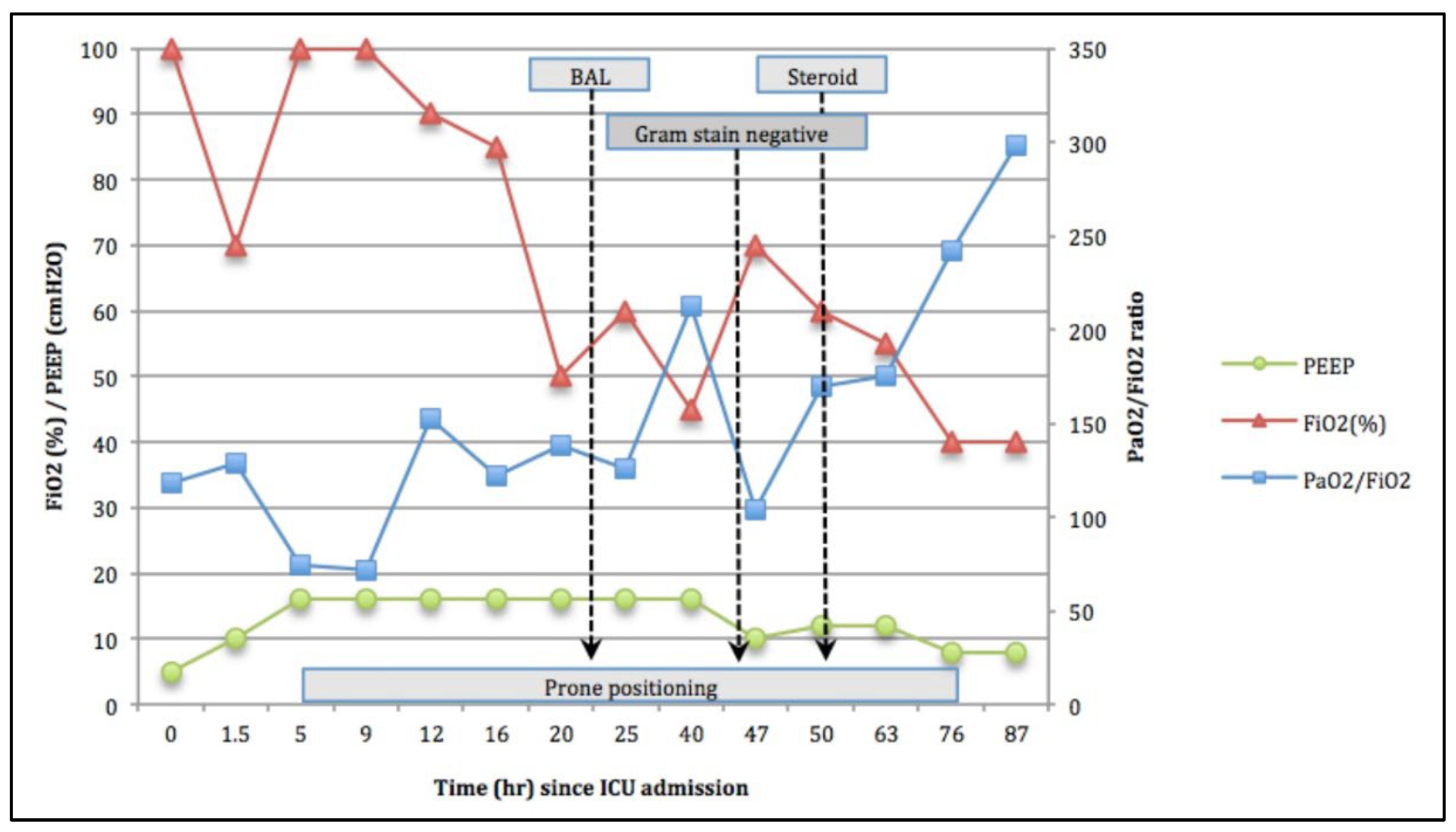
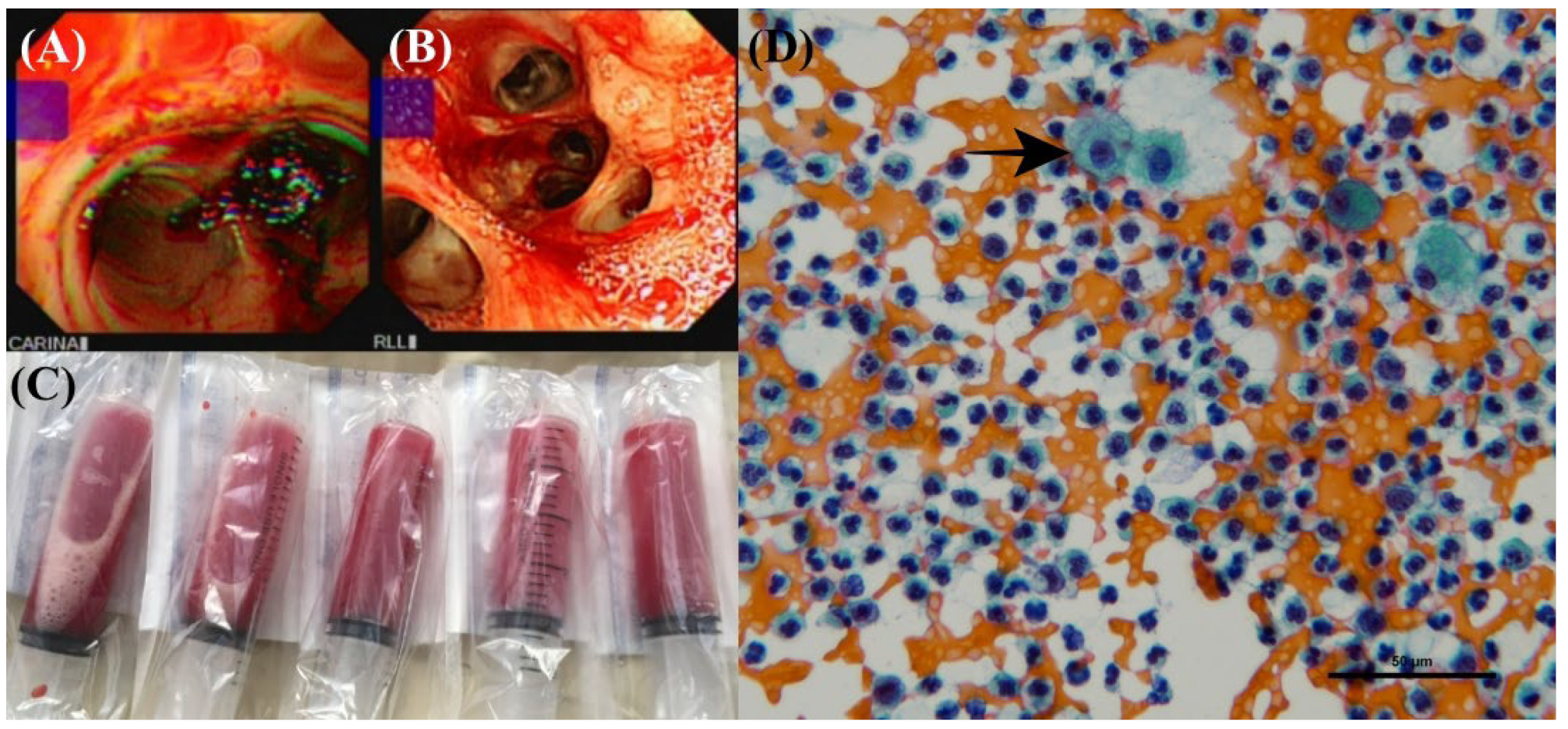
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; Van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharoon, S.; Brent, B.; Nita, M.; Abdo, T. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, a rare presentation of polymyositis. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, D.; Jefferson, J.A. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARDS Definition Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronbichler, A.; Lee, K.H.; Denicolo, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, H.; Ahn, D.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, M.; et al. Immunopathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, A.R.; Schwarz, M.I. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Chest 2010, 137, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Duan, X.; Shi, X.; Guo, N.; Liu, S. Predictors of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 762004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, C.; Appenrodt, B.; Hoff, C.; Ewig, S.; Klehr, H.U.; Sauerbruch, T.; Nickenig, G.; Tasci, S. Severe respiratory failure due to diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: Clinical characteristics and outcome of intensive care. J. Crit. Care 2010, 25, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.; Kuhn, J.; Gabrie, D.; Barrow, J.; Jennette, J.C.; Henke, D.C. Use of Activated Factor VII in Patients with Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: A 10 Years Institutional Experience. Lung 2015, 193, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zejnullahu, K.; Khatami, S.; Manesh, R.S. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Blood, Sweat and Tears. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 812–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Savage, R. Prone position as a life-saving measure for acute pulmonary haemorrhage in a young adult with cystic fibrosis. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2002, 30, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes-Bradley, C. Hypoxia from vasculitic pulmonary haemorrhage improved by prone position ventilation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2004, 92, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patel, J.J.; Lipchik, R.J. Systemic lupus-induced diffuse alveolar hemorrhage treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report and review of the literature. J. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 29, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, D.; Agerstrand, C.L.; Biscotti, M.; Burkart, K.M.; Bacchetta, M.; Brodie, D. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the management of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. ASAIO J. 2015, 61, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, G.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, S. ECMO Rescue Therapy in Diffuse Alveolar Haemorrhage: A Case Report with Review of Literature. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OD10–OD11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvino, P.; Monti, S.; Balduzzi, S.; Belliato, M.; Montecucco, C.; Caporali, R. The role of extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in the treatment of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage secondary to ANCA-associated vasculitis: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, M.C.; Sy, E.; Lequier, L.; Fan, E.; Kanji, H.D. Anticoagulation Practices during Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Respiratory Failure. A Systematic Review. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, B.; Stahl, K.; Schenk, H.; Schmidt, J.J.; Wiesner, O.; Welte, T.; Kuehn, C.; Bauersachs, J.; Hoeper, M.M.; David, S. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe ARDS due to Immune Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: A Retrospective Observational Study. Chest 2020, 157, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, D.; Slutsky, A.S.; Combes, A. Extracorporeal Life Support for Adults with Respiratory Failure and Related Indications: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer, S.; de Haro, C.; Peruga, P.; Oliva, J.C.; Artigas, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of complications and mortality of veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, S.; Friedrich, J.O.; Taccone, P.; Polli, F.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Latini, R.; Pesenti, A.; Guérin, C.; Mancebo, J.; Curley, M.; et al. Prone ventilation reduces mortality in patients with acute respiratory failure and severe hypoxemia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerole, E.; Peine, P.; Wittkopp, S.; Marini, J.J.; Albert, R.K. The pragmatics of prone positioning. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makdisi, G.; Wang, I.W. Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) review of a lifesaving technology. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, E166–E176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, D.; Ferguson, N.D.; Brochard, L.; Fan, E.; Mercat, A.; Combes, A.; Pellegrino, V.; Schmidt, M.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brodie, D. ECMO for ARDS: From salvage to standard of care? Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.K.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, W.N.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, S.P.; Kuo, C.T. Energy Achievement Rate Is an Independent Factor Associated with Intensive Care Unit Mortality in High-Nutritional-Risk Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Requiring Prolonged Prone Positioning Therapy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, E.L.; Beitler, J.R.; Prisk, G.K.; Malhotra, A. Treatment of ARDS with Prone Positioning. Chest 2017, 151, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, A.; Bellani, G.; Winterton, D.; Di Pierro, M.; Soria, A.; Faverio, P.; Cairo, M.; Mori, S.; Messinesi, G.; Contro, E.; et al. Feasibility and physiological effects of prone positioning in non-intubated patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (PRON-COVID): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Veno-Venous ECMO (VV-ECMO) | Prone Positioning |
|---|---|---|
| Indications | Very severe ARDS; Bridge to lung transplantation; Primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. | Severe ARDS regardless of etiologies |
| Contraindications | Absolute Contraindications: Irreversible underlying process when the patient is not a candidate for lung transplantation; Cardiogenic failure and severe chronic pulmonary hypertension (mean pulmonary artery pressure >50 mmHg). Relative Contraindications: Contraindication for anticoagulation; Advanced age; Obesity. | Serious burns or open wounds on the ventral body surface; Spinal instability; Pelvic fractures; Life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias or hypotension. |
| Complications | Medical Complications: Bleeding (including intracranial hemorrhage, pulmonary and cannula bleeding); Pneumothorax; Deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism; Cannula infection. Mechanical Complications Oxygenator failure; Cannula failure. | Pressure ulcers Endotracheal tube obstruction |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.-J.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Wang, K.-L.; Fu, P.-K. Prone Positioning May Improve the Treatment of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Secondary to ANCA Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report. Life 2022, 12, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020235
Wu S-J, Hsu Y-C, Wang K-L, Fu P-K. Prone Positioning May Improve the Treatment of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Secondary to ANCA Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report. Life. 2022; 12(2):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shang-Ju, Yong-Chen Hsu, Kao-Lun Wang, and Pin-Kuei Fu. 2022. "Prone Positioning May Improve the Treatment of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Secondary to ANCA Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report" Life 12, no. 2: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020235
APA StyleWu, S.-J., Hsu, Y.-C., Wang, K.-L., & Fu, P.-K. (2022). Prone Positioning May Improve the Treatment of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Secondary to ANCA Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report. Life, 12(2), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020235





