Co-Prevalence of Virulence and Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Aeromonas spp. from Diseased Fishes with In Silico Insight on the Virulent Protein Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
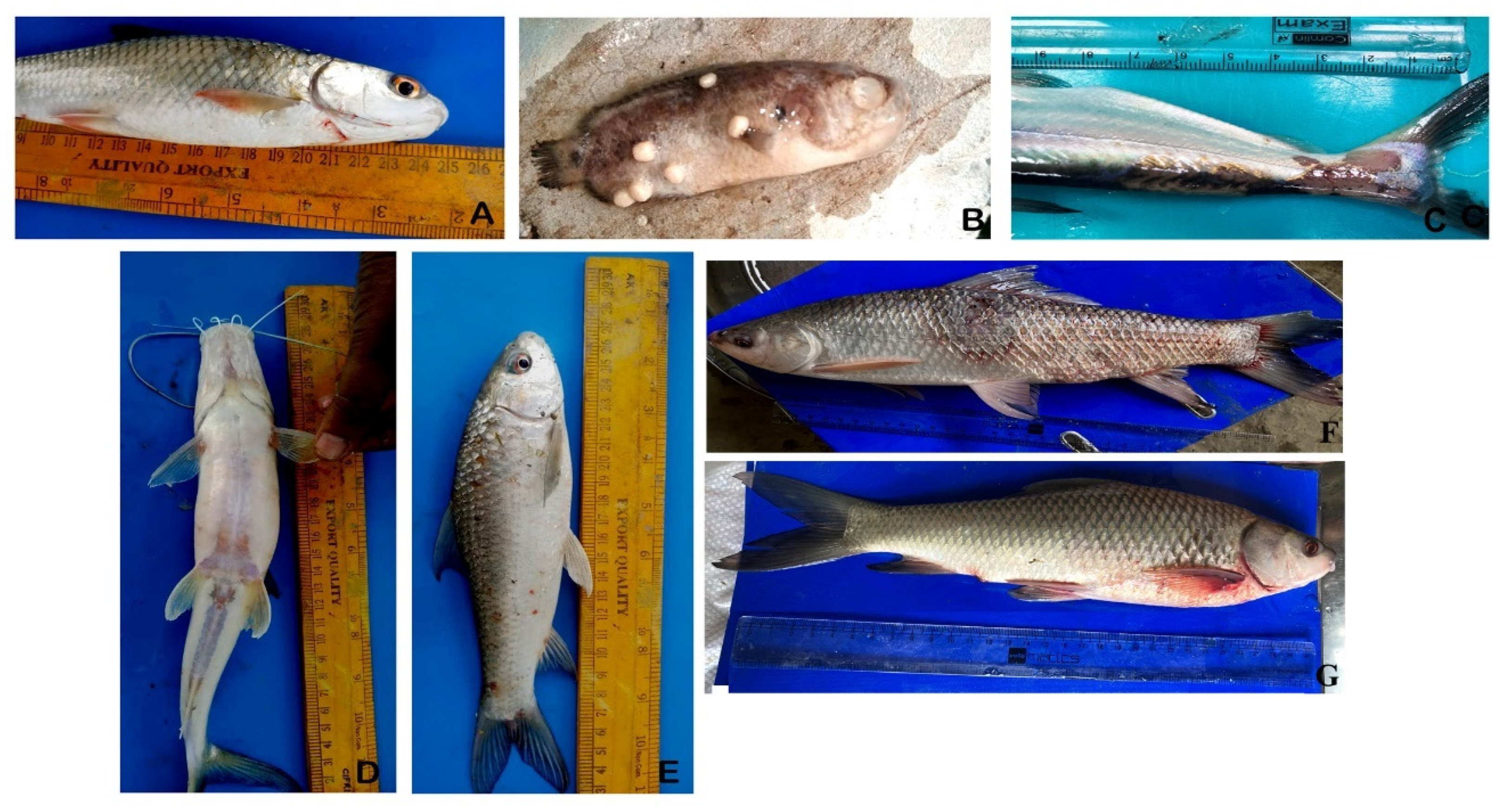
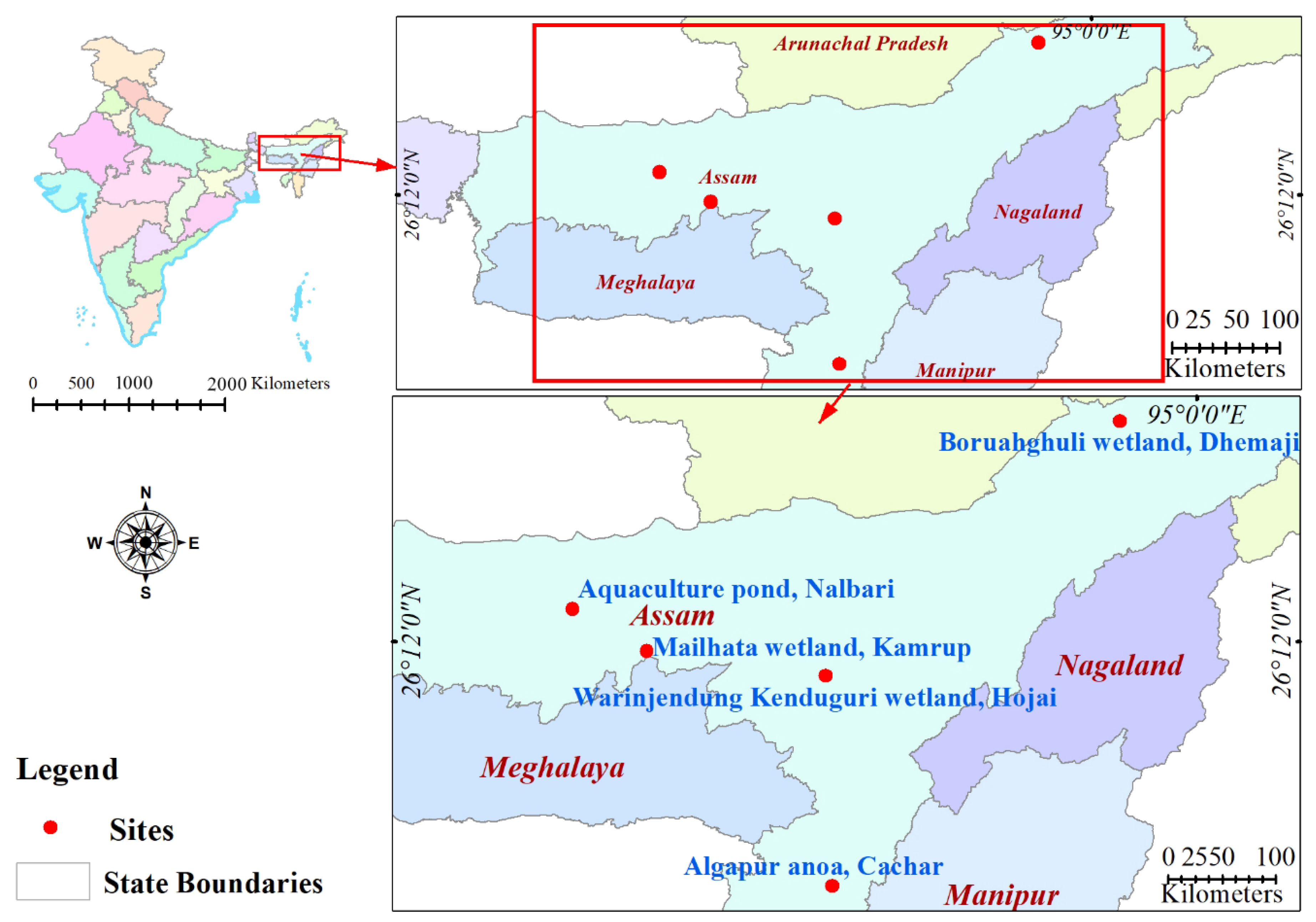
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Virulence Gene Detection by PCR
2.5. LD50 Determination
2.6. In Silico Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis of Virulence Genes
3. Results
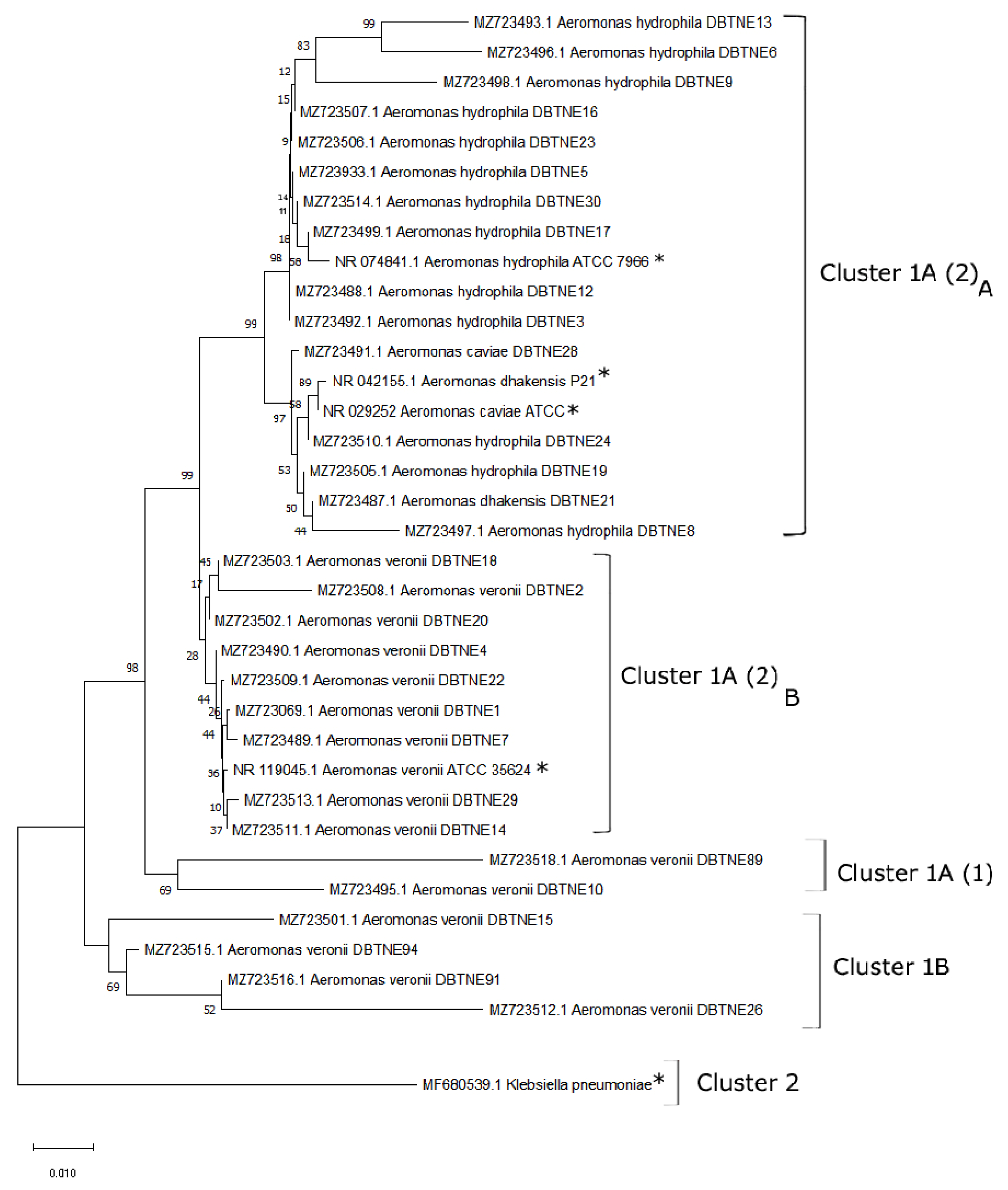
3.1. Aeromonas Isolation and Identification with Phylogenetic Studies
3.2. Prevalence of Virulence Genes
3.3. Antibiogram of the Confirmed Aeromonas Strains
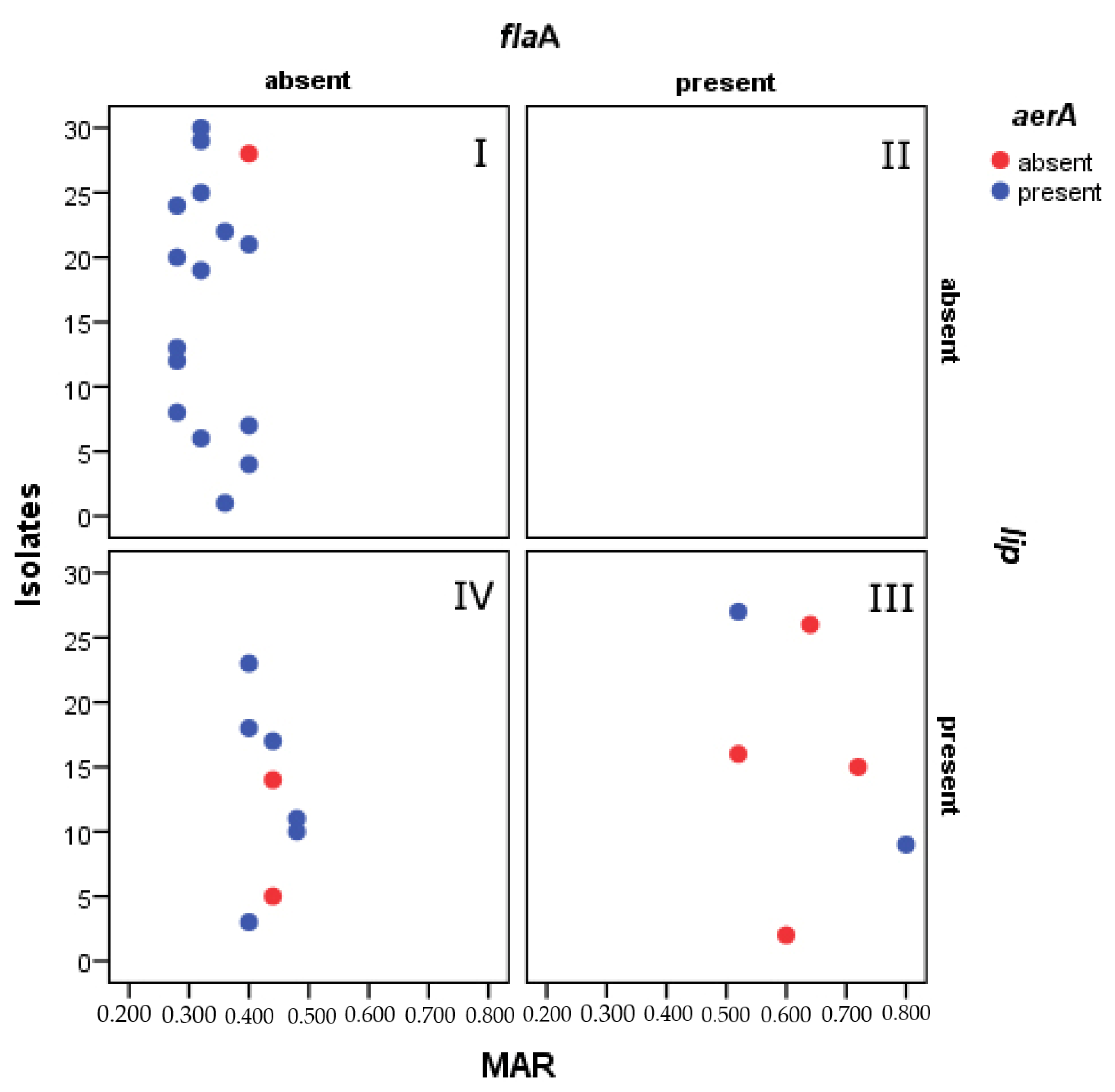
3.4. Association between Virulence Genes and Antibiotic Resistance
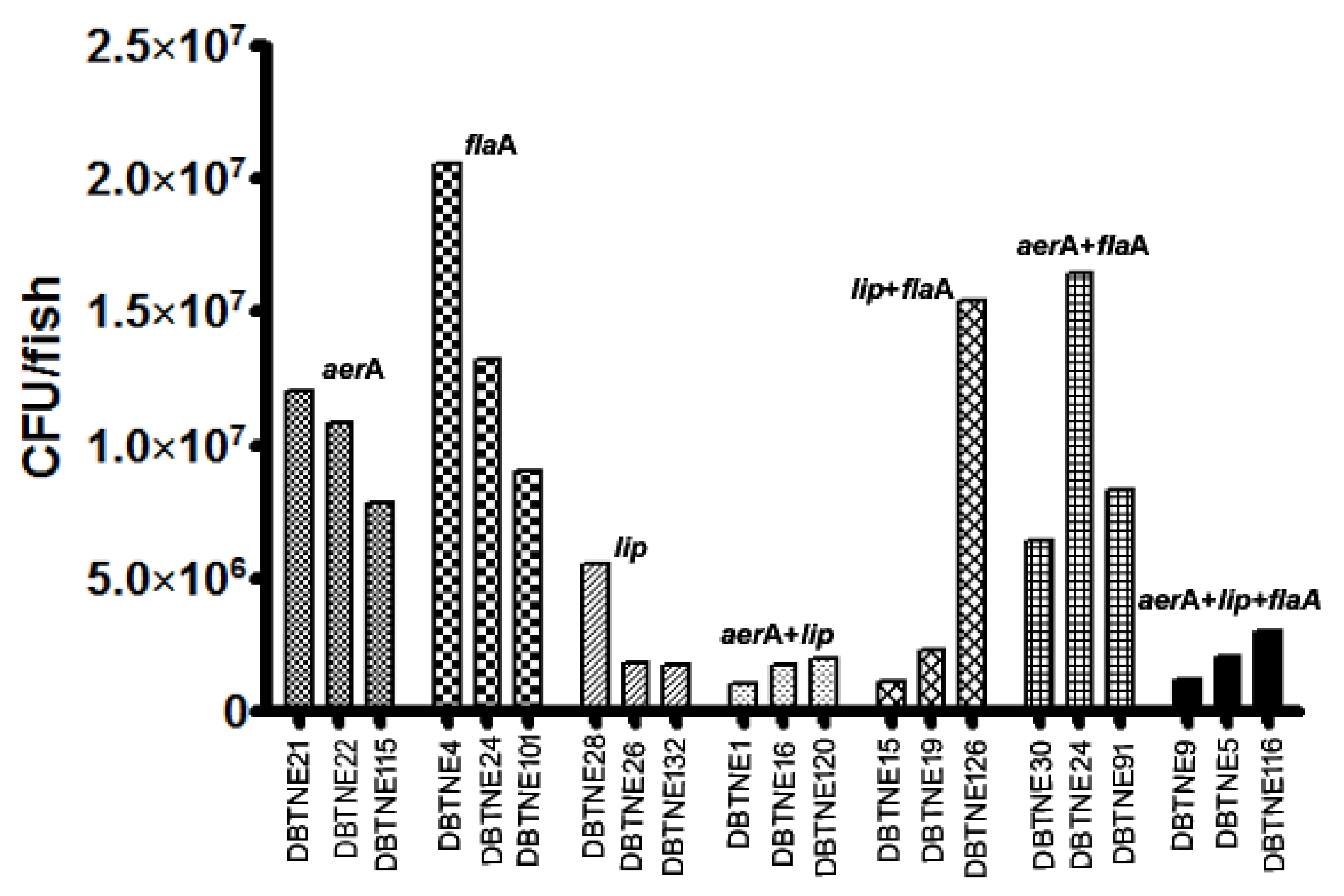
3.5. LD50 Determination
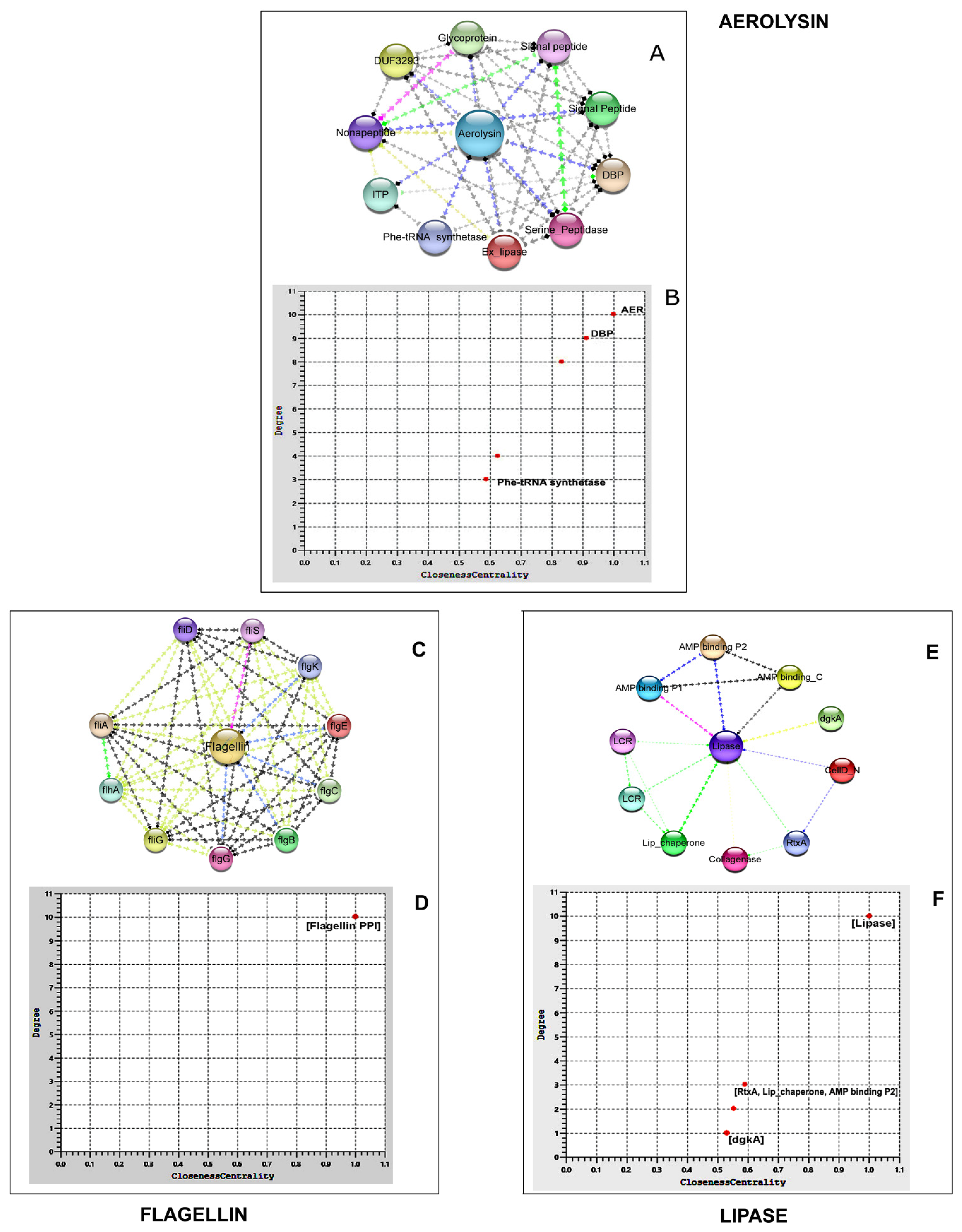
3.6. Protein Network Analysis of Virulence Genes
3.6.1. Aerolysin
3.6.2. Flagellin
3.6.3. Lipase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chutia, S.J.; Yashwanth, B.S.; Baruah, A.K.; Kashyap, A.; Chetia, B.R.; Nath, B.B.; Choudhury, A.; Rathlavath, S.; Borah, S.; Chripsin, C.L. Trends in Fish Production of Assam: An Analysis. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 3417–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.K.; Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Borah, S.; Das, P.; Debnath, D.; Yengkokpam, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Sharma, N.; Singh, N.S.; Pandit, A. Roadmap for Development of Open Water Fisheries in North-Eastern States; ICARCIFRI: Barrackpore, India, 2017; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, U.K.; Mishal, P.; Borah, S.; Karnatak, G.; Chandra, G.; Kumari, S.; Meena, D.K.; Debnath, D.; Yengkokpam, S.; Das, P. Status, Potential, Prospects, and Issues of Floodplain Wetland Fisheries in India: Synthesis and Review for Sustainable Management. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Das, K.K.; Borah, S.; Das, P.; Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Das, B.K. Impact of Fish Stock Enhancement on Fish Yield of Floodplain Wetlands in Different Agro-Climatic Zones of Assam, India. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2021, 24, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, S.; Sarkar, U.K.; Das, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Puthiyottil, M.; Pame, D.; Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Das, B.K. Managing Floodplain Wetlands through Culture-Based Fisheries (CBF) for Livelihood Security and Sustainable Development: A Study from a Biodiversity Hotspot Region of India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Borah, S.; Sharma, N.; Dewan, B.M.; Nath, K.D. Amblypharyngodon Mola: A Valuable Candidate Species for Species Enhancement in Floodplain Wetlands (Beels) of Assam, India. Fish. Chimes 2018, 38, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kabin, M.; Nirmal, T.; Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Shashi, B.; Amulya, K.; Simanku, B.; Abhijit, M.; Das, B.K. An Inventory on the Freshwater Fish Diversity of Two Tropical Flood Plain Wetlands of Brahmaputra Basin, Assam, India. J. Exp. Zool. 2019, 22, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, S.; Das, P.; Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Yadav, A.K.; Saud, B.J.; Das, B.K. A Report on the Occurrence of Bangana Dero (Hamilton, 1822) from Deepor Beel (Ramsar Site No. 1207), Brahmaputra Valley, Assam. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2020, 12, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Saud, B.J.; Borah, S.; Saikia, P.K.; Das, B.K. Status of Biodiversity and Limno-Chemistry of Deepor Beel, a Ramsar Site of International Importance: Conservation Needs and the Way Forward. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2021, 24, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, U.K.; Borah, B.C. Flood Plain Wetland Fisheries of India: With Special Reference to Impact of Climate Change. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharia, P.K.; Hussain, I.A.; Pokhrel, H.; Kalita, B.; Borah, G.; Yasmin, R. Prevalence of Motile Aeromonas Septicaemia (MAS) in Fish Culture Systems of the Central Brahmaputra Valley Zone of Assam, India. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękala-Safińska, A. Contemporary Threats of Bacterial Infections in Freshwater Fish. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camus, A.C.; Durborow, R.M.; Hemstreet, W.G.; Thune, R.L.; Hawke, J.P. Aeromonas Bacterial Infections-Motile Aeromonad Septicemia; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 1998; Volume 478. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, A.; Choudhury, H.; Dey, A.; Sarma, D. Isolation and Characterization of Two Virulent Aeromonads Associated with Haemorrhagic Septicaemia and Tail-Rot Disease in Farmed Climbing Perch Anabas Testudineus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Pathogenicity, and Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seshadri, R.; Joseph, S.W.; Chopra, A.K.; Sha, J.; Shaw, J.; Graf, J.; Haft, D.; Wu, M.; Ren, Q.; Rosovitz, M.J. Genome Sequence of Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966T: Jack of All Trades. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8272–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence Factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: In the Wake of Reclassification. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chopra, A.K.; Peterson, J.W.; Xu, X.J.; Coppenhaver, D.H.; Houston, C.W. Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of a Heat-Labile Cytotonic Enterotoxin from Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb. Pathog. 1996, 21, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghenghesh, K.S.; Ahmed, S.F.; Cappuccinelli, P.; Klena, J.D. Genospecies and Virulence Factors of Aeromonas Species in Different Sources in a North African Country. Libyan J. Med. 2014, 9, 25497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granum, P.E.; O’Sullivan, K.; Tomás, J.M.; Ørmen, Ø. Possible Virulence Factors of Aeromonas spp. from Food and Water. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. Evolving Concepts Regarding the Genus Aeromonas: An Expanding Panorama of Species, Disease Presentations, and Unanswered Questions. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marra, A. Targeting Virulence for Antibacterial Chemotherapy. Drugs R D 2006, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics: Enzymatic Degradation and Modification. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1451–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, M.J.; Guedes-Novais, S.; Alves, A.; Rema, P.; Tacão, M.; Correia, A.; Martínez-Murcia, A. Resistencia a Antibióticosb-Lactámicos En Aeromonas hydrophila Aislados de Truchas Arco Iris (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Int. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Mudryk, Z.J.; Perliński, P. Abundance and Antibiotic Resistance of Aeromonas Isolated from the Water of Three Carp Ponds. Vet. Res. Commun. 2020, 44, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wamala, S.P.; Mugimba, K.K.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, Ø.; Mdegela, R.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Sørum, H. Occurrence and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Fish Bacteria Isolated from Oreochromis niloticus (Nile Tilapia) and Clarias gariepinus (African Catfish) in Uganda. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preena, P.G.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Rejish Kumar, V.J.; Bright Singh, I.S. Unravelling the Menace: Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance in Aquaculture. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guz, L.; Kozinska, A. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Aeromonas hydrophila and A. Sobria Isolated from Farmed Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2004, 48, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ghenghesh, K.S.; El-Mohammady, H.; Levin, S.Y.; Zorgani, A.; Tawil, K. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Aeromonas Species Isolated from Libya. Libyan J. Med. 2013, 8, 21320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, W.H. Antimicrobial Use in Aquaculture and Antimicrobial Resistance; Report of a Joint FAO/OIE/WHO Expert Consultation on Antimicrobial Use in Aquaculture and An-Timicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sørum, H. Antimicrobial drug resistance in fish pathogens. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria of Animal Origin; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 213–238. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Shih, D.Y.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Yang, S.-S. Molecular Characterization of Class 1 Integrons and Antimicrobial Resistance in Aeromonas Strains from Foodborne Outbreak-Suspect Samples and Environmental Sources in Taiwan. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 59, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekedar, H.C.; Arick, M.A.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Thrash, A.; Blom, J.; Lawrence, M.L.; Abdelhamed, H. Identification of Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants in Aeromonas veronii Strain MS-17-88 Recovered from Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Popowska, M. Insight into the Mobilome of Aeromonas Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miñana-Galbis, D.; Farfán, M.; Lorén, J.G.; Fusté, M.C. Biochemical Identification and Numerical Taxonomy of Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Environmental and Clinical Samples in Spain. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Martínez-Murcia, A. Phylogenetic Analyses of the Genus Aeromonas Based on Housekeeping Gene Sequencing and Its Influence on Systematics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wayne, P.A. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PE, USA, 2011; pp. 100–121. [Google Scholar]
- Shyamapada, M. Bacteriological Profiling of Commercially Available Eye Cosmetics and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern. Transl. Biomed. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Ahmad, A. Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Phenotyping of Aeromonas Species Isolated from Aquatic Sources. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P. The STRING Database in 2021: Customizable Protein–Protein Networks, and Functional Characterization of User-Uploaded Gene/Measurement Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-Year Retrospective Review of Global Aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Lin, L. Characterization of virulence properties of Aeromonas veronii isolated from diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foysal, M.J.; Momtaz, F.; Ali, M.H.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Chaklader, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Prodhan, M.S.H.; Cole, A. Molecular Characterization and Interactome Analysis of Aerolysin (Aer) Gene from Fish Pathogen Aeromonas veronii: The Pathogenicity Inferred from Sequence Divergence and Linked to Histidine Kinase (CheA). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Raza, S.H.A.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, W.; Qian, A.; Wang, C.; Kang, Y.; Shan, X. Aeromonas veronii Infection in Commercial Freshwater Fish: A Potential Threat to Public Health. Animals 2020, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An Update on the Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shan, X.; Qian, A. Research Advances of Virulence Factors in Aeromonas Veronii. Chin. Vet. Sci. Zhongguo Shouyi Kexue 2018, 48, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Nhinh, D.T.; Le, D.V.; Van, K.V.; Huong Giang, N.T.; Dang, L.T.; Hoai, T.D. Prevalence, Virulence Gene Distribution and Alarming the Multidrug Resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila Associated with Disease Outbreaks in Freshwater Aquaculture. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, J.; Kozlova, E.V.; Chopra, A.K. Role of Various Enterotoxins in Aeromonas hydrophila-Induced Gastroenteritis: Generation of Enterotoxin Gene-Deficient Mutants and Evaluation of Their Enterotoxic Activity. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ottaviani, D.; Parlani, C.; Citterio, B.; Masini, L.; Leoni, F.; Canonico, C.; Sabatini, L.; Bruscolini, F.; Pianetti, A. Putative Virulence Properties of Aeromonas Strains Isolated from Food, Environmental and Clinical Sources in Italy: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 144, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.T.L.; Veneroni-Gouveia, G.; Costa, M.M. Molecular Characterization of Virulence Factors in Aeromonas hydrophila Obtained from Fish. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2012, 32, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, R.; Amoah, I.D.; Adegoke, A.A.; Singh, G.; Kumari, S.; Swalaha, F.M.; Bux, F.; Stenström, T.A. Identification, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Profiling of Aeromonas and Pseudomonas Species from Wastewater and Surface Water. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartor, Y.H.; EL-Naenaeey, E.-S.Y.; Abdallah, H.M.; Samir, M.; Yassen, M.M.; Abdelwahab, A.M. Virulotyping and Genetic Diversity of Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus) in Aquaculture Farms in Egypt. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, A.; Neogi, S.B.; Bashar, T.; Sultana, M.; Johura, F.-T.; Islam, S.; Hasan, N.A.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R.R.; Alam, M. Dynamics, Diversity, and Virulence of Aeromonas Spp. in Homestead Pond Water in Coastal Bangladesh. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, S.; Wilhelms, M.; Tomás, J.M. Role of Aeromonas hydrophila Flagella Glycosylation in Adhesion to Hep-2 Cells, Biofilm Formation and Immune Stimulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21935–21946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pena, N.; Dranow, D.M.; Hu, Y.; Escamilla, Y.; Bullard, J.M. Characterization and Structure Determination of Prolyl-tRNA Synthetase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Development as a Screening Platform. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. [13] Evolutionary Families of Metallopeptidases. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 248, pp. 183–228. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Toma, C.; Nakasone, N.; Iwanaga, M. Aerolysin Is Activated by Metalloprotease in Aeromonas veronii Biovar Sobria. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adekoya, O.A.; Sylte, I. The Thermolysin Family (M4) of Enzymes: Therapeutic and Biotechnological Potential. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 73, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamazares, E.; MacLeod-Carey, D.; Miranda, F.P.; Mena-Ulecia, K. Theoretical Evaluation of Novel Thermolysin Inhibitors from Bacillus thermoproteolyticus. Possible Antibacterial Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergleit, M.; Vasquez, A.A.; Miller, C.J.; Sun, J.; Kato, I. Oral and Intestinal Bacterial Exotoxins: Potential Linked to Carcinogenesis. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 171, 131–193. [Google Scholar]
- El Khattabi, M.; Van Gelder, P.; Bitter, W.; Tommassen, J. Role of the Lipase-Specific Foldase of Burkholderia Glumae as a Steric Chaperone. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26885–26891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, Y.; van der Ploeg, J.R.; Kozuki, T.; Shirai, Y.; Saito, N.; Kawada-Matsuo, M.; Takeshita, T.; Yamashita, Y. Kinase Activity of the Dgk Gene Product Is Involved in the Virulence of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiology 2009, 155, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Xiao, X.; Liu, D.; Wu, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Liao, B.; He, H. Optimization of Collagenase Production by Pseudoalteromonas Sp. SJN2 and Application of Collagenases in the Preparation of Antioxidative Hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakane, F.; Imai, S.; Kai, M.; Yasuda, S.; Kanoh, H. Diacylglycerol Kinases as Emerging Potential Drug Targets for a Variety of Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, G.; Khajanchi, B.K.; Sierra, J.C.; Erova, T.E.; Sha, J.; Chopra, A.K. Actin Cross-Linking Domain of Aeromonas hydrophila Repeat in Toxin A (RtxA) Induces Host Cell Rounding and Apoptosis. Gene 2012, 506, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altarriba, M.; Merino, S.; Gavín, R.; Canals, R.; Rabaan, A.; Shaw, J.G.; Tomás, J.M. A Polar Flagella Operon (Flg) of Aeromonas hydrophila Contains Genes Required for Lateral Flagella Expression. Microb. Pathog. 2003, 34, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.K.; Ritchings, B.W.; Almira, E.C.; Lory, S.; Ramphal, R. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Flagellar Cap Protein, FliD, Is Responsible for Mucin Adhesion. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.Y.F.; Mayrhofer, G.; Heuzenroeder, M.W.; Atkinson, H.M.; Quinn, D.M.; Flower, R.L.P. Measurement of Virulence of Aeromonads Using a Suckling Mouse Model of Infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1996, 15, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratev, D.; Odeyemi, O.A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Different Food Sources: A Mini-Review. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, E.; Schwab, F.; Schroeren-Boersch, B.; Gastmeier, P. Dramatic Increase of Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant E. Coli in German Intensive Care Units: Secular Trends in Antibiotic Drug Use and Bacterial Resistance, 2001 to 2008. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, G.D. Mechanisms of Resistance to Antibiotics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.C.; Shaw, H.; Rhodes, V.; Hart, A. Review of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment and Its Relevance to Environmental Regulators. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayatgheib, N.; Calvez, S.; Fournel, C.; Pineau, L.; Pouliquen, H.; Moreau, E. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles and Resistance Genes in Genus Aeromonas spp. Isolated from the Environment and Rainbow Trout of Two Fish Farms in France. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schar, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Larsson, D.G.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Twenty-Year Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance from Aquaculture and Fisheries in Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sl No. | Biochemical Parameters | A 1 | A 2 | A 3 | A 4 | A 5 | A 6 | A 7 | A 8 | A 9 | A 10 | A 12 | A 13 | A 14 | A 15 | A 16 | A 17 | A 18 | A 19 | A 20 | A 21 | A 22 | A 23 | A 24 | A 26 | A 28 | A 29 | A 30 | A 89 | A 91 | A 94 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ONPG | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2 | Urease | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| 3 | Lysine utilization | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 4 | Nitrate reduction | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 5 | Ornithine utilization | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 6 | Malonate utilization | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 7 | VP | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 8 | Esculin hydrolysis | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 9 | Phenylalanine deamination | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 10 | Citrate utilization | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 11 | H2S production | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | + |
| 12 | Indole | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 13 | Methyl red | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 14 | Oxidase | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 15 | Arabinose | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 16 | Adonitol | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 17 | Xylose | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 18 | Rhamnose | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 19 | Melibiose | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| 20 | Cellobiose | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| 21 | Raffinose | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| 22 | Saccharose | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 23 | Trehalose | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 24 | Glucose | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 25 | Lactose | − | − | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Sl No. | Parameters | Aerolysin | Flagellin | Lipase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Number of nodes | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| 2 | Number of edges | 41 | 55 | 18 |
| 3 | Avg. Number of neighbours | 7.455 | 10.0 | 3.273 |
| 4 | Network diameter | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | Characteristic path length | 1.255 | 1 | 1.67 |
| 6 | Clustering coefficient | 0.872 | 1 | 0.804 |
| 7 | Network Density | 0.745 | 1 | 0.327 |
| 8 | Network heterogeneity | 0.264 | 0 | 0.6780 |
| 9 | Network centralization | 0.311 | 0 | 0.822 |
| PPI enrichment p-value | 1.94 × 10−12 | <1.0 × 10−16 | 0.0271 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborty, N.; Das, B.K.; Bera, A.K.; Borah, S.; Mohanty, D.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, J.; Koushlesh, S.K.; Chanu, T.N.; Panda, S.P.; et al. Co-Prevalence of Virulence and Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Aeromonas spp. from Diseased Fishes with In Silico Insight on the Virulent Protein Network. Life 2022, 12, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121979
Chakraborty N, Das BK, Bera AK, Borah S, Mohanty D, Yadav AK, Kumar J, Koushlesh SK, Chanu TN, Panda SP, et al. Co-Prevalence of Virulence and Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Aeromonas spp. from Diseased Fishes with In Silico Insight on the Virulent Protein Network. Life. 2022; 12(12):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121979
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborty, Nabanita, Basanta Kumar Das, Asit Kumar Bera, Simanku Borah, Debasmita Mohanty, Anil Kumar Yadav, Jeetendra Kumar, Satish Kumar Koushlesh, Thangjam Nirupada Chanu, Soumya Prasad Panda, and et al. 2022. "Co-Prevalence of Virulence and Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Aeromonas spp. from Diseased Fishes with In Silico Insight on the Virulent Protein Network" Life 12, no. 12: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121979
APA StyleChakraborty, N., Das, B. K., Bera, A. K., Borah, S., Mohanty, D., Yadav, A. K., Kumar, J., Koushlesh, S. K., Chanu, T. N., Panda, S. P., & Vallangi, R. (2022). Co-Prevalence of Virulence and Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Aeromonas spp. from Diseased Fishes with In Silico Insight on the Virulent Protein Network. Life, 12(12), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121979








