Dendritic Cells and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
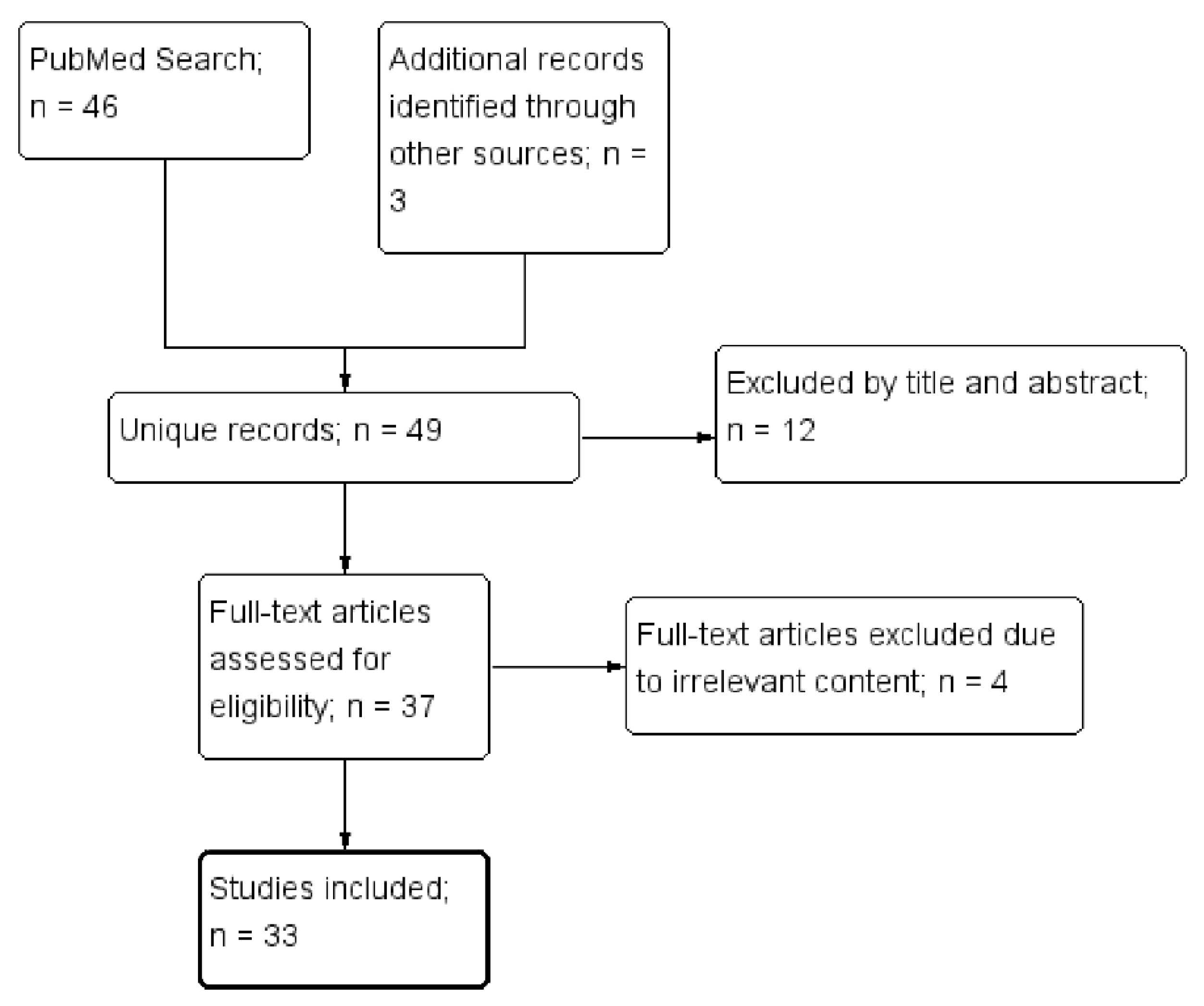
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Background
3.1.1. The Pathogenesis of APS
3.1.2. Dendritic Cells
3.1.3. Dendritic Cells and Arterial Thrombosis
3.1.4. Dendritic Cells and Venous Thrombosis
3.1.5. Dendritic Cells and Pregnancy
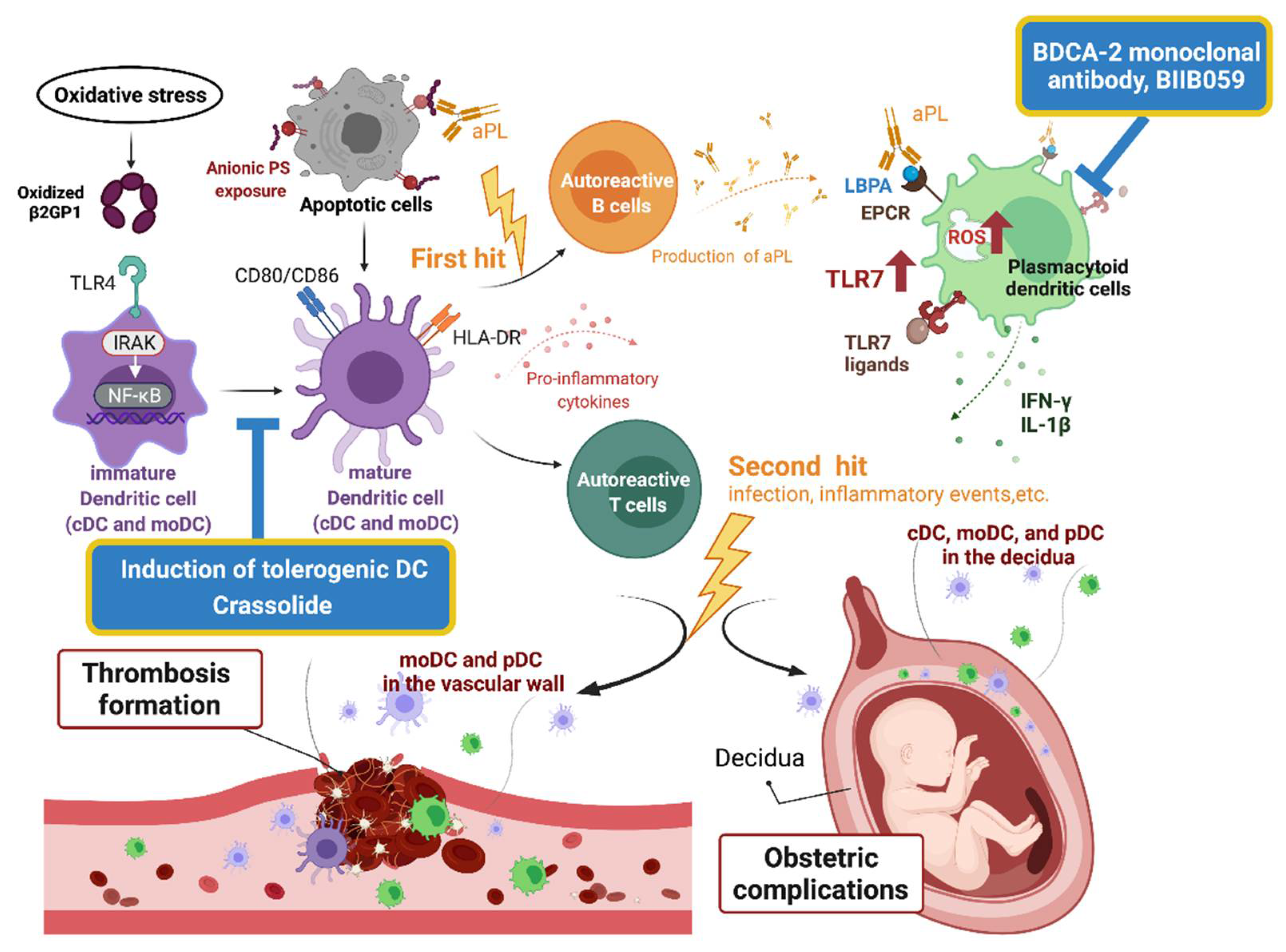
3.2. DC in the Pathogenesis of APS
3.2.1. B2GPI and Dendritic Cells
3.2.2. Dendritic Cells and Generation of APS
3.2.3. Conventional Dendritic Cells and Propagation of APS
3.2.4. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and APS
3.3. Dendritic Cells-Based Therapy for APS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannakopoulos, B.; Krilis, S.A. The pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, M. Beta2-glycoprotein I: Antiphospholipid syndrome and T-cell reactivity. Thromb. Res. 2004, 114, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Raimondo, M.G.; Meroni, P.L. Management of Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 44, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus, G.R.; Rodrigues, G.; de Jesus, N.R.; Levy, R.A. Pregnancy morbidity in antiphospholipid syndrome: What is the impact of treatment? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthman, I.; Noureldine, M.H.A.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Khamashta, M. Management of antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, B.; Krilis, S.A. How I treat the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2009, 114, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hunt, B.J.; Khamashta, M.A. A systematic review of secondary thromboprophylaxis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 57, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, I.; Abbattista, M.; Bucciarelli, P.; Tripodi, A.; Artoni, A.; Gianniello, F.; Novembrino, C.; Peyvandi, F. Recurrent thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies treated with vitamin K antagonists or rivaroxaban. Haematologica 2018, 103, e315–e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.; Radin, M.; Sciascia, S. Current insights in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 29, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, C.A.; Camoin-Jau, L.; Mege, J.L.; Raoult, D. Can hydroxychloroquine be protective against COVID-19-associated thrombotic events? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.R.; Liu, M.F. Rituximab usage in systemic lupus erythematosus-associated antiphospholipid syndrome: A single-center experience. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Teng, J.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Su, Y.; Shi, H.; et al. Rituximab in thrombotic primary antiphospholipid syndrome: A pilot study from a single centre in China. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, A.; Yazirli, B.; Erkan, D. Belimumab in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2017, 26, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, F.; Miossec, P. Altered dendritic cell functions in autoimmune diseases: Distinct and overlapping profiles. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P.L.; Borghi, M.O.; Raschi, E.; Tedesco, F. Pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome: Understanding the antibodies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, M.; Bigley, V. Human dendritic cell subsets: An update. Immunology 2018, 154, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulendran, B.; Smith, J.L.; Caspary, G.; Brasel, K.; Pettit, D.; Maraskovsky, E.; Maliszewski, C.R. Distinct dendritic cell subsets differentially regulate the class of immune response in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchereau, J.; Briere, F.; Caux, C.; Davoust, J.; Lebecque, S.; Liu, Y.J.; Pulendran, B.; Palucka, K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 767–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, A.T.; Wu, X.; Albring, J.C.; Murphy, K.M. Re(de)fining the dendritic cell lineage. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Hemmi, H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 85, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijt, L.S.; Vos, N.; Willart, M.; Kleinjan, A.; Coyle, A.J.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N. Essential role of dendritic cell CD80/CD86 costimulation in the induction, but not reactivation, of TH2 effector responses in a mouse model of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalod, M.; Chelbi, R.; Malissen, B.; Lawrence, T. Dendritic cell maturation: Functional specialization through signaling specificity and transcriptional programming. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.-I.; Liu, K.; Smith, C.; Bonito, A.J.; Steinman, R.M. The Linkage of Innate to Adaptive Immunity via Maturing Dendritic Cells In Vivo Requires CD40 Ligation in Addition to Antigen Presentation and CD80/86 Costimulation. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, N. Dendritic cells: A conductor of T cell differentiation. Allergol. Int. 2007, 56, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terhune, J.; Berk, E.; Czerniecki, B.J. Dendritic Cell-Induced Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation for Cancer Therapy. Vaccines 2013, 1, 527–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, M.B. Induction of CD4(+) Regulatory and Polarized Effector/helper T Cells by Dendritic Cells. Immune Netw. 2016, 16, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, P.A.; Oriss, T.B. Crossregulation between Th1 and Th2 cells. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 18, 275–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agalioti, T.; Villablanca, E.J.; Huber, S.; Gagliani, N. TH17 cell plasticity: The role of dendritic cells and molecular mechanisms. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 87, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabelitz, D.; Wesch, D.; Oberg, H.H. Regulation of regulatory T cells: Role of dendritic cells and toll-like receptors. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 26, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M. Dendritic Cells in Immunity and Tolerance—Do They Display Opposite Functions? Immunity 2003, 19, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M.; Hawiger, D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 685–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinajero, M.G.; Gotlieb, A.I. Recent Developments in Vascular Adventitial Pathobiology: The Dynamic Adventitia as a Complex Regulator of Vascular Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Lochno, M.; Traeg, F.; Cicha, I.; Reiss, C.; Stumpf, C.; Raaz, D.; Anger, T.; Amann, K.; Probst, T.; et al. Emergence of dendritic cells in rupture-prone regions of vulnerable carotid plaques. Atherosclerosis 2004, 176, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessner, A.; Sato, K.; Chaikof, E.L.; Colmegna, I.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Pathogen-sensing plasmacytoid dendritic cells stimulate cytotoxic T-cell function in the atherosclerotic plaque through interferon-alpha. Circulation 2006, 114, 2482–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Weber, J.; Cicha, I.; Stumpf, C.; Klein, M.; Raithel, D.; Daniel, W.G.; Garlichs, C.D. Decrease in circulating myeloid dendritic cell precursors in coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Schaller, T.; Cicha, I.; Altendorf, R.; Stumpf, C.; Klinghammer, L.; Ludwig, J.; Daniel, W.G.; Garlichs, C.D. Predictive value of the decrease in circulating dendritic cell precursors in stable coronary artery disease. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, B.; Mangin, P.H.; Eckly, A.; Heim, V.; Cazenave, J.P.; Lanza, F.; Hanau, D.; Gachet, C. Immature myeloid dendritic cells capture and remove activated platelets from preformed aggregates. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, K.E.; Zhu, S.N.; Chen, M.; Nurmohamed, S.; Jongstra-Bilen, J.; Cybulsky, M.I. Resident intimal dendritic cells accumulate lipid and contribute to the initiation of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Y.I.; Choi, S.H.; Wiesner, P.; Fang, L.; Harkewicz, R.; Hartvigsen, K.; Boullier, A.; Gonen, A.; Diehl, C.J.; Que, X.; et al. Oxidation-specific epitopes are danger-associated molecular patterns recognized by pattern recognition receptors of innate immunity. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, C.; Pang, H.; Uchida, Y.; Libby, P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Lichtman, A.H. B7-1/B7-2 costimulation regulates plaque antigen-specific T-cell responses and atherogenesis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Circulation 2004, 109, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, P.; Gijbels, M.J.; Zernecke, A.; Eijgelaar, W.; Vergouwe, M.N.; van der Made, I.; Vanderlocht, J.; Beckers, L.; Buurman, W.A.; Daemen, M.J.; et al. Myeloid type I interferon signaling promotes atherosclerosis by stimulating macrophage recruitment to lesions. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, S.M.; Bobryshev, Y.V.; Inder, S.J.; Lord, R.S.; Ashwell, K.W. Dendritic cells in venous pathologies. Angiology 1999, 50, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Tsuda, H.; Sakai, M.; Hori, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Futatani, T.; Miyawaki, T.; Saito, S. Predominance of Th2-promoting dendritic cells in early human pregnancy decidua. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.; Kyurkchiev, D.; Altankova, I.; Dimitrov, J.; Binakova, E.; Kyurkchiev, S. CD83 monocyte-derived dendritic cells are present in human decidua and progesterone induces their differentiation in vitro. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2005, 53, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmochwal-Kolarz, D.; Rolinski, J.; Tabarkiewicz, J.; Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B.; Buczkowski, J.; Wojas, K.; Oleszczuk, J. Myeloid and lymphoid dendritic cells in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 132, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrentraut, S.; Sauss, K.; Neumeister, R.; Luley, L.; Oettel, A.; Fettke, F.; Costa, S.D.; Langwisch, S.; Zenclussen, A.C.; Schumacher, A. Human Miscarriage Is Associated with Dysregulations in Peripheral Blood-Derived Myeloid Dendritic Cell Subsets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.M.; Herasimtschuk, A.A.; Boasso, A.; Benlahrech, A.; Fuchs, D.; Imami, N.; Johnson, M.R. Changes in T Cell and Dendritic Cell Phenotype from Mid to Late Pregnancy Are Indicative of a Shift from Immune Tolerance to Immune Activation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.R.; Guo, P.F.; Piao, H.L.; Wang, S.C.; Sun, C.; Jin, L.P.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, R.; et al. Embryonic trophoblasts induce decidual regulatory T cell differentiation and maternal-fetal tolerance through thymic stromal lymphopoietin instructing dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, G.; Mugione, A.; Sanchez, A.M.; Vigano, P.; Candiani, M.; Somigliana, E.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Panina-Bordignon, P.; Gregori, S. HLA-G expressing DC-10 and CD4(+) T cells accumulate in human decidua during pregnancy. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, Y.M.; Cheng, X.Y.; Zhu, T.F.; Chen, Z.F.; Yao, H.; Su, L.X. Dendritic cells derived from preeclampsia patients influence Th1/Th17 cell differentiation in vitro. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5303–5309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.T.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, Y.H. Cardiolipin interacts with beta-2-glycoprotein I and forms an open conformation-Mechanisms analyzed using hydrogen/deuterium exchange. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, K.M.J.; Ortel, T.L.; Pengo, V.; de Laat, B. Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Laboratory criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Chang, Y.K.; Lin, S.C.; Su, J.H.; Chao, Y.H.; Tang, K.T. Crassolide Suppresses Dendritic Cell Maturation and Attenuates Experimental Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Molecules 2021, 26, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radway-Bright, E.L.; Inanc, M.; Isenberg, D.A. Animal models of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buttari, B.; Profumo, E.; Mattei, V.; Siracusano, A.; Ortona, E.; Margutti, P.; Salvati, B.; Sorice, M.; Rigano, R. Oxidized beta2-glycoprotein I induces human dendritic cell maturation and promotes a T helper type 1 response. Blood 2005, 106, 3880–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; He, C.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Xie, H.; Cheng, S. Effects of TLR4 on beta2-glycoprotein I-induced bone marrow-derived dendritic cells maturation. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 290, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, J.; Kaneshige, R.; Motoki, Y.; Ieko, M. Increased oxidative stress may be a risk factor for thromboembolic complications in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2020, 196, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.T.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Chao, Y.H.; Li, J.P.; Lan, J.L.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, D.Y. Apoptosis in patients with primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondanza, A.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Zimmermann, V.S.; Balestrieri, G.; Tincani, A.; Sabbadini, M.G.; Manfredi, A.A. Requirement for dendritic cells in the establishment of anti-phospholipid antibodies. Autoimmunity 2007, 40, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; van Loo, G.; Waelput, W.; De Prijck, S.; Muskens, F.; Sze, M.; van Praet, J.; Branco-Madeira, F.; Janssens, S.; Reizis, B.; et al. The ubiquitin-editing protein A20 prevents dendritic cell activation, recognition of apoptotic cells, and systemic autoimmunity. Immunity 2011, 35, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Miwa, M.; Miwa, K.; Hanayama, R.; Nagase, H.; Nagata, S.; Tanaka, M. Masking of phosphatidylserine inhibits apoptotic cell engulfment and induces autoantibody production in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwana, M.; Matsuura, E.; Kobayashi, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Kaburaki, J.; Ikeda, Y.; Kawakami, Y. Binding of beta 2-glycoprotein I to anionic phospholipids facilitates processing and presentation of a cryptic epitope that activates pathogenic autoreactive T cells. Blood 2005, 105, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaipl, U.S.; Beyer, T.D.; Baumann, I.; Voll, R.E.; Stach, C.M.; Heyder, P.; Kalden, J.R.; Manfredi, A.; Herrmann, M. Exposure of anionic phospholipids serves as anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive signal--implications for antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunobiology 2003, 207, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovere, P.; Manfredi, A.A.; Vallinoto, C.; Zimmermann, V.S.; Fascio, U.; Balestrieri, G.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Rugarli, C.; Tincani, A.; Sabbadini, M.G. Dendritic cells preferentially internalize apoptotic cells opsonized by anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies. J. Autoimmun. 1998, 11, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Asaduzzaman, A.; Noamani, B.; Fortin, P.R.; Gladman, D.D.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.B.; Wither, J. The baseline interferon signature predicts disease severity over the subsequent 5 years in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marketos, N.; Cinoku, I.; Rapti, A.; Mavragani, C.P. Type I interferon signature in Sjogren’s syndrome: Pathophysiological and clinical implications. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 118), 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Hoogen, L.L.; Fritsch-Stork, R.D.; Versnel, M.A.; Derksen, R.H.; van Roon, J.A.; Radstake, T.R. Monocyte type I interferon signature in antiphospholipid syndrome is related to proinflammatory monocyte subsets, hydroxychloroquine and statin use. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenn, R.C.; Yalavarthi, S.; Gandhi, A.A.; Kazzaz, N.M.; Nunez-Alvarez, C.; Hernandez-Ramirez, D.; Cabral, A.R.; McCune, W.J.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Knight, J.S. Endothelial progenitor dysfunction associates with a type I interferon signature in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, L.L.; Rossato, M.; Lopes, A.P.; Pandit, A.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Fritsch-Stork, R.D.E.; van Roon, J.A.G.; Radstake, T. microRNA downregulation in plasmacytoid dendritic cells in interferon-positive systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.; Prinz, N.; Lorenz, M.; Bauer, S.; Chapman, J.; Lackner, K.J.; von Landenberg, P. TLR7 and TLR8 ligands and antiphospholipid antibodies show synergistic effects on the induction of IL-1beta and caspase-1 in monocytes and dendritic cells. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, N.; Clemens, N.; Strand, D.; Putz, I.; Lorenz, M.; Daiber, A.; Stein, P.; Degreif, A.; Radsak, M.; Schild, H.; et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies induce translocation of TLR7 and TLR8 to the endosome in human monocytes and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood 2011, 118, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Calleja, N.; Hollerbach, A.; Royce, J.; Ritter, S.; Pedrosa, D.; Madhusudhan, T.; Teifel, S.; Meineck, M.; Hauser, F.; Canisius, A.; et al. Lipid presentation by the protein C receptor links coagulation with autoimmunity. Science 2021, 371, eabc0956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Rius, A.; Desai, A.; Yuen, D.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Voelcker, N.H. Inducing immune tolerance with dendritic cell-targeting nanomedicines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, A.; Willis, R.; Gonzalez, E.B.; Romay-Penabad, Z.; Shovman, O.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Blank, M.; Amital, H. Oral administration of Domain-I of beta-2glycoprotein-I induces immunological tolerance in experimental murine antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 99, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Aguilar, H.; Blank, M.; Jara, L.J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Tolerogenic dendritic cells in autoimmune diseases: Crucial players in induction and prevention of autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 10, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkens, C.M.; Isaacs, J.D. Tolerogenic dendritic cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: Where are we now? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 172, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandman-Goddard, G.; Pierangeli, S.S.; Gertel, S.; Blank, M. Tolerogenic dendritic cells specific for beta2-glycoprotein-I Domain-I, attenuate experimental antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 54, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Aguilar, H.; Blank, M.; Kivity, S.; Misgav, M.; Luboshitz, J.; Pierangeli, S.S.; Shoenfeld, Y. Tolerogenic dendritic cells inhibit antiphospholipid syndrome derived effector/memory CD4(+) T cell response to beta2GPI. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, A.; Otero, K.; Czerkowicz, J.M.; Kerns, H.M.; Shapiro, R.I.; Ranger, A.M.; Otipoby, K.L.; Taylor, F.R.; Cameron, T.O.; Viney, J.L.; et al. Anti-BDCA2 monoclonal antibody inhibits plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation through Fc-dependent and Fc-independent mechanisms. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Werth, V.P.; Merola, J.F.; Stevenson, L.; Reynolds, T.L.; Naik, H.; Wang, W.; Christmann, R.; Gardet, A.; Pellerin, A.; et al. Monoclonal antibody targeting BDCA2 ameliorates skin lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| DC Subsets | Immunophenotype | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional DC1 | BDCA-1 | Cross-presentation Activation of T helper 1 (Th1), CD8+ T, and natural killer cells |
| Conventional DC2 | BDCA-1, CD11b, CD11c | Cross-presentation Responding to lipopolysaccharide, flagellin, and fungal antigens Activation of Th1, Th2, Th17, and CD8+ T cells |
| Monocyte-derived DC | BDCA-1, CD11c, CD1a | Contributing to tissue inflammation Activation of Th1, Th17, and CD8+ T cells |
| Plasmacytoid DC | BDCA-2, BDCA-4, CD123 | Responding to viral antigens Production of type I and type III interferons |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, K.-T.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, T.-T.; Bracci, N.R.; Lin, C.-C. Dendritic Cells and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review. Life 2021, 11, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080801
Tang K-T, Chen H-H, Chen T-T, Bracci NR, Lin C-C. Dendritic Cells and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review. Life. 2021; 11(8):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080801
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Kuo-Tung, Hsin-Hua Chen, Tzu-Ting Chen, Nicole R. Bracci, and Chi-Chien Lin. 2021. "Dendritic Cells and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review" Life 11, no. 8: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080801
APA StyleTang, K.-T., Chen, H.-H., Chen, T.-T., Bracci, N. R., & Lin, C.-C. (2021). Dendritic Cells and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review. Life, 11(8), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080801







