Radiological Risk to Human and Non-Human Biota Due to Radioactivity in Coastal Sand and Marine Sediments, Gulf of Oman
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
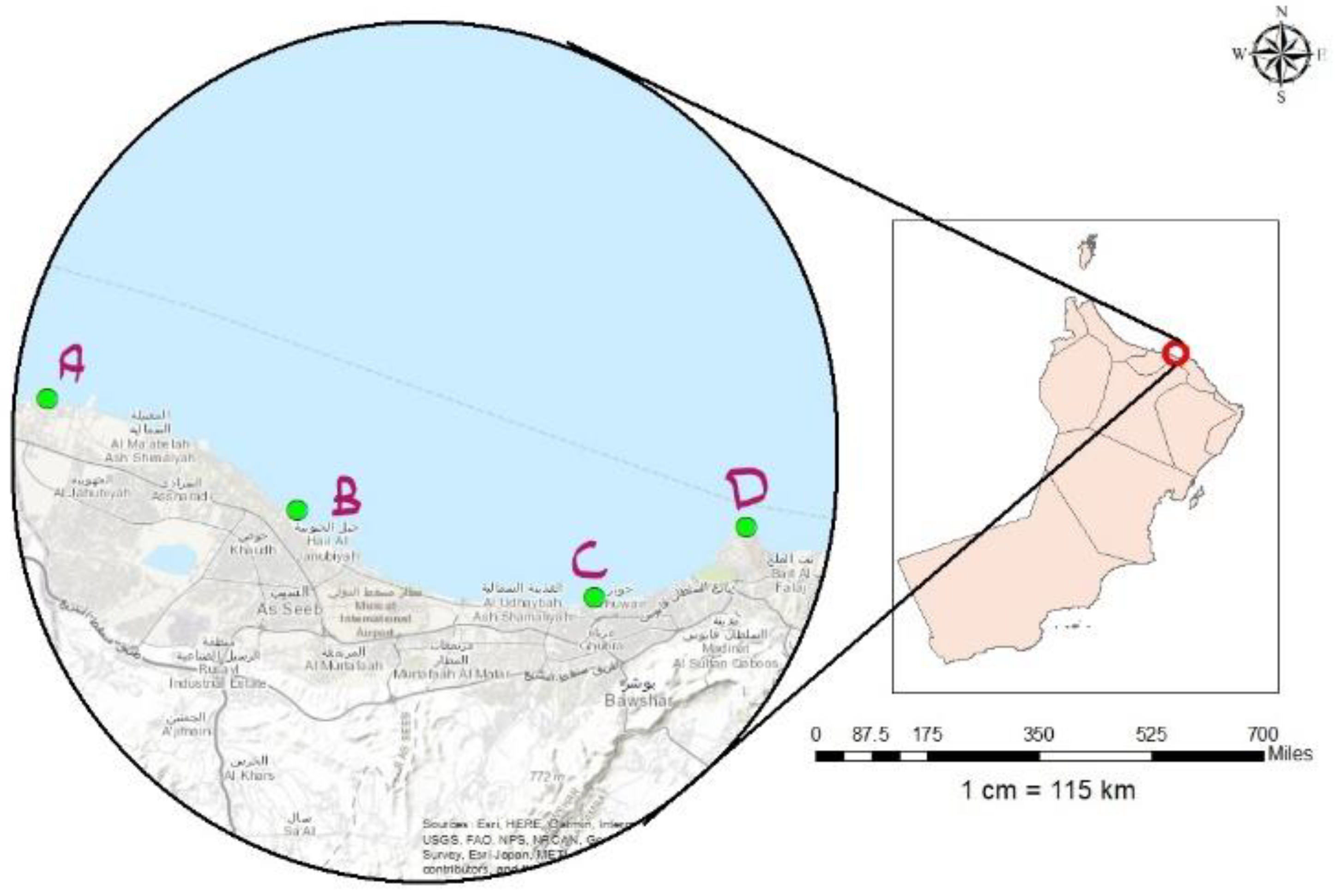
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Radioactivity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
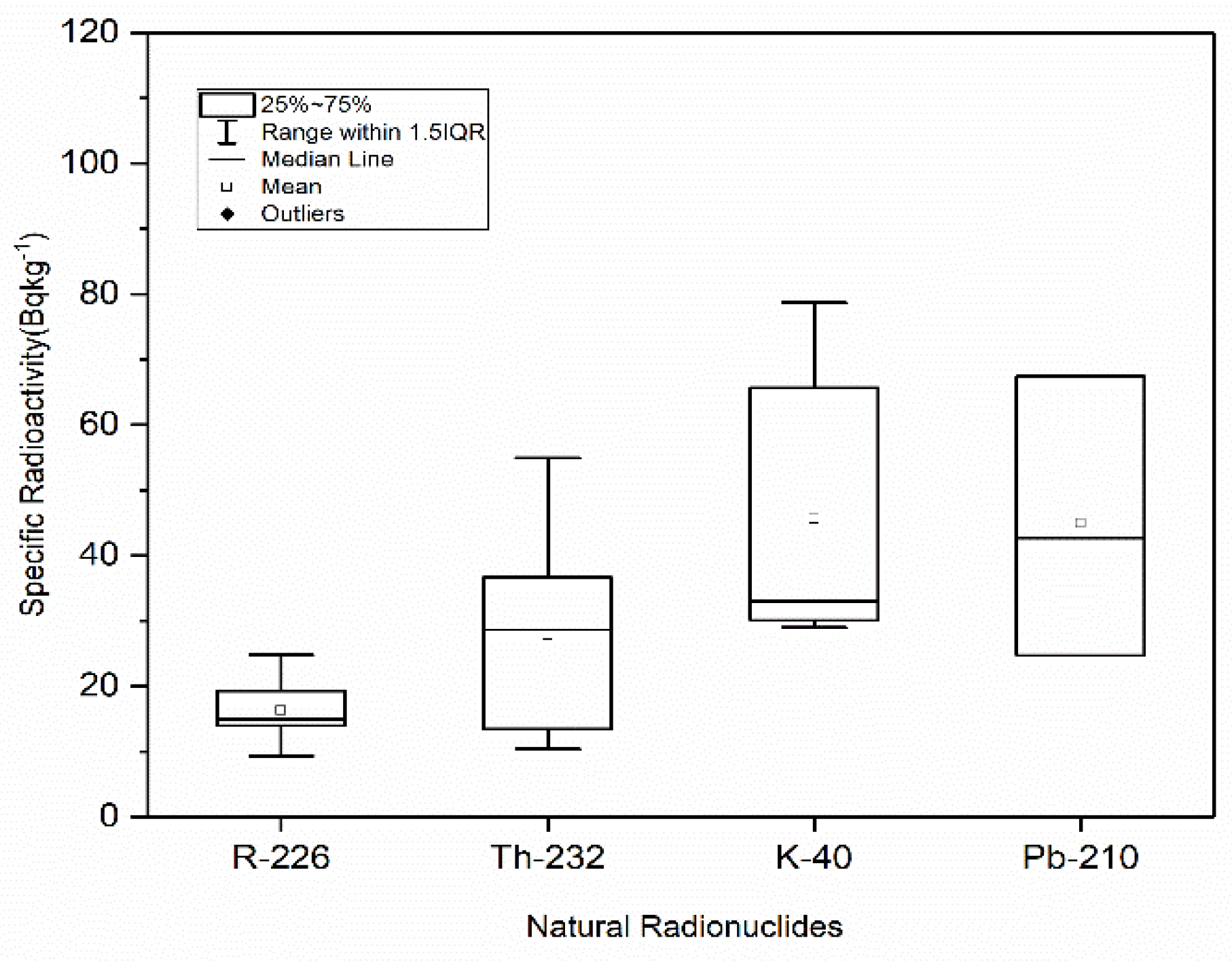
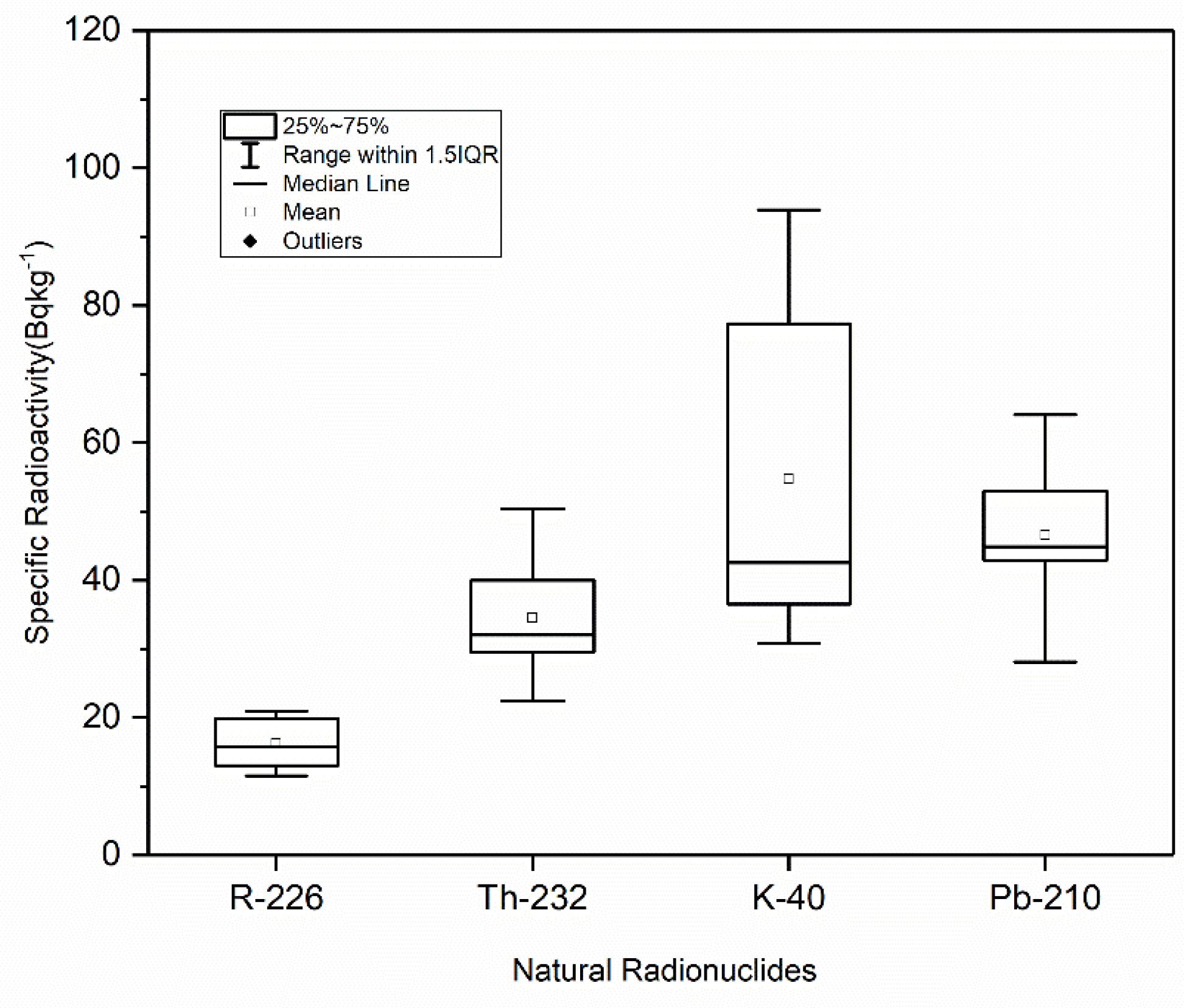
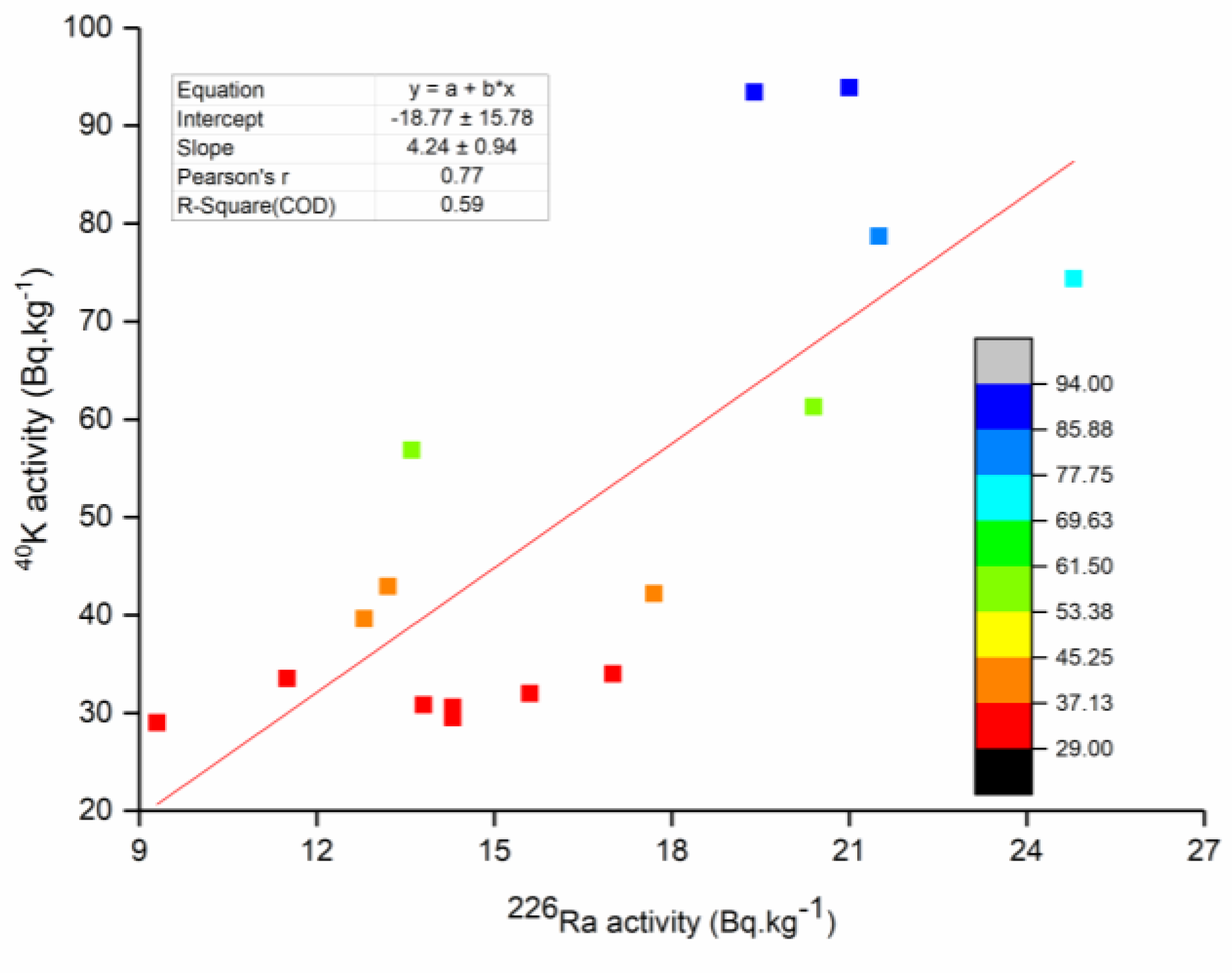
3.1. Radioactivity Contents in Marine Sediment
3.2. Assessing Radiological Hazards
3.2.1. Radium-Equivalent Activity
3.2.2. External Hazard Index (Hex)
3.3. External Absorbed Dose Rates
3.4. Excess Lifetime Cancer Risk (ELCR)
3.5. Annual Gonadal Dose Equivalent (AGDE)
3.6. Radiological Risk to Non-Human Biota
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yii, M.W.; Zaharudin, A.; Abdul-Kadir, I. Distribution of naturally occurring radionuclides activity concentration in East Malaysian marine sediment. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionization Radiation; Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes B: Exposures from Natural Radiation Sources; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Pálsson, S.E.; Skuterud, L.; Fesenko, S.; Golikov, V. Radionuclide transfer in arctic ecosystems. In Quantification of Radionuclide Transfers in Terrestrial and Freshwater Environments for Radiological Assessments; IAEATECDOC-1616; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2009; pp. 381–396. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Extent of Environmental Contamination by Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material (NORM) and Technological Options for Mitigation; IAEA Technical Reports Series No. 419; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, J. Environmental Protection: The Concept and Use of Reference Animals and Plants. Annals of the ICRP; ICRP Publication 108; ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP); ICRP Publication 103; Ann. ICRP 37; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA. Radiation Protection and Safety of Radiation Sources: International Basic Safety Standards; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adreani, T.E.; Mattar, E.; Alsafi, K.; Sulieman, A.; Suliman, I.I. Natural radioactivity and radiological risk parameters in local and imported building materials used in Sudan. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 7563–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaradawi, I.; Abdel-Moati, M.; Al-Yafei, M.A.A.; Al-Ansari, E.; Al-Maslamani, I.; Holm, E.; Al-Shaikh, I.; Mauring, A.; Pinto, P.V.; Abdulmalik, D.; et al. Radioactivity levels in the marine environment along the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of Qatar. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.; Aba, A.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M.; Ismaeel, A.; Al-Shammari, H.; Alboloushi, A.; Mietelski, J.W.; Al-Ghadban, A.; Al-Ghunaim, A.; et al. Radioactivity in the Kuwait marine environment—Baseline measurements and review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.R.; Mostajaboddavati, M.; Kamali, M.; Abdi, M.R.; Mortazavi, M.S. 235U, 238U, 232Th, 40K and 137Cs activity concentrations in marine sediments along the northern coast of Oman Sea using high-resolution gamma-ray spectrometry. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1956–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Trabulsy, H.A.; Khater, A.E.M.; Habbani, F.I. Radioactivity levels and radiological hazard indices at the Saudi coastline of the Gulf of Aqaba. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2011, 80, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zamel, A.Z.; Bou-Rabee, F.; Olszewski, M.; Bem, H. Natural radionuclides and 137Cs activity concentration in the bottom sediment cores from Kuwait Bay. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2005, 266, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.H. Radioactivity of 238U, 232Th, 40 K, and 137Cs and assessment of depleted uranium in soil of the Musandam Peninsula, Sultanate of Oman. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2012, 36, 236–248. [Google Scholar]
- ISO; IEC; BIPM OIML. Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Quantifying Uncertainty in Nuclear Analytical Measurements; IAEA-TECDOC-1401; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pappa, F.K.; Tsabaris, C.; Ioannidou, A.; Patiris, D.L.; Kaberi, H.; Pashalidis, I.; Eleftheriou, G.; Androulakaki, E.G.; Vlastou, R. Radioactivity and metal concentrations in marine sediments associated with mining activities in Ierissos Gulf, North Aegean Sea, Greece. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 116, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriou, G.; Tsabaris, C.; Kapsimalis, V.; Patiris, D.L.; Androulakaki, E.G.; Pappa, F.K.; Kokkoris, M.; Vlastou, R. Radionuclides and heavy metals concentrations at the seabed of NW Piraeus, Greece. In Proceedings of the 22nd Conference of the Hellenic Nuclear Physics Society, Athens, Greece, 30 May–1 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Du, J.; Bi, Q. Natural radioactivity assessment of surface sediments in the Yangtze Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanfi, M.Y.; Masoud, M.S.; Ambrosino, F.; Mostafa, M.Y. Natural radiological characterization at the Gabal El Seila region (Egypt). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2021, 31, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretka, J.; Mathew, P.J. Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrials wastes and by-products. Health Phys. 1985, 48, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.I. The relative radioactivity of building materials. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1971, 32, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEA-OECD. Exposure to Radiation from the Natural Radioactivity in Building Materials: Report by a Group of Exports of the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency; NEA-OECD: Paris, France, 1979; pp. 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Tariq, S.; Din, K.U.; Manzoor, S.; Calligaris, C.; Waheed, A. Evaluation of excessive lifetime cancer risk due to natural radioactivity in the rivers sediments of Northern Pakistan. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Alfonso, B.; Avila, R.; Beresford, N.A.; Copplestone, D.; Pröhl, G.; Ulanovsky, A. The ERICA tool. J. Environ. Radioact. 2008, 99, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, D.A.; Sam, A.K.; Hassona, R.K. Distribution of 226Ra–210Pb–210Po in marine biota and surface sediments of the Red Sea, Sudan. J. Environ. Radioact. 2008, 99, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugandhi, S.; Joshi, V.M.; Ravi, P.M. Studies on natural and anthropogenic radionuclides in sediment and biota of Mumbai Harbour Bay. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 300, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botwe, B.O.; Schirone, A.; Delbono, I.; Barsanti, M.; Delfanti, R.; Kelderman, P.; Nyarko, E.; Lens, P.N. Radioactivity concentrations and their radiological significance in sediments of the Tema Harbour (Greater Accra, Ghana). J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2017, 10, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Code | Weight (kg) | Activity Concentrations (Bqkg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226Ra | 232Th | 40K | 210Pb | 137Cs | ||
| Beach Sand | ||||||
| S01 | 1421 | 21.5 ± 1.4 | 28.0 ± 2.8 | 78.7 ± 4.8 | ** | 0.11 |
| S02 | 1371 | 24.8 ± 1.2 | 54.9 ± 3.1 | 74.4 ± 3.2 | 42.7 ± 19.4 | 0.05 |
| S05 | 1592 | 14.3 ± 1.0 | 29.3 ± 2.2 | 29.5 ± 2.0 | (125.5 ± 12.2) | 0.04 |
| S06 | 1568 | 14.3 ± 1.0 | 10.4 ± 1.1 | 30.6 ± 2.1 | 24.7 ± 11.4 | 0.07 |
| S09 | 1501 | 13.6 ± 0.9 | 43.3 ± 3.3 | 56.9 ± 3.7 | 67.4 ± 13.5 | 0.19 |
| S10 | 1414 | 9.3 ± 0.7 | 30.0 ± 2.6 | 29.0 ± 2.1 | ** | 0.13 |
| S13 | 1038 | 15.6 ± 1.0 | 13.2 ± 1.3 | 32.0 ± 2.1 | ** | 0.07 |
| S14 | 1376 | 17.0 ± 1.1 | 13.6 ± 1.3 | 34.0 ± 2.3 | ** | 0.15 |
| Average | 16.30 | 27.84 | 45.64 | 44.9 | 0.10 | |
| Marine sediments | ||||||
| S03 | 1363 | 21.0 ±1.0 | 50.4 ± 3.0 | 93.9 ± 3.8 | 44.9 ± 1.9 | 0.05 |
| S04 | 1425 | 19.4 ± 1.4 | 47.3 ± 3.8 | 93.4 ± 5.7 | ** | 0.07 |
| S07 | 1532 | 12.8 ± 0.8 | 31.6 ± 1.2 | 39.6 ± 2.3 | (158.9 ± 12.9) | 0.07 |
| S08 | 1750 | 11.5 ± 0.8 | 31.0 ± 2.4 | 33.5 ± 2.6 | 42.9 ± 12.5 | 0.09 |
| S11 | 1496 | 13.8 ± 0.8 | 22.4 ± 2.2 | 30.8 ± 2.8 | 53.0 ± 11.4 | 0.13 |
| S12 | 1421 | 13.2 ± 1.0 | 28.0 ± 1.8 | 42.9 ± 2.0 | ** | 0.08 |
| S15 | 1332 | 17.7 ± 1.4 | 32.6 ± 2.6 | 42.2 ± 3.9 | 65.1 ± 14.2 | 0.09 |
| S16 | 1423 | 20.4 ± 1.2 | 32.5 ± 1.6 | 61.3 ± 2.7 | 28.1 ± 13.3 | 0.08 |
| Average | 16.2 | 34.5 | 54.7 | 46.8 | 0.08 | |
| Location | 226Ra | 232Th | 40K | 210Pb | 137Cs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World | 35 | 30 | 400 | ** | ** | [2] |
| Qatar | 4.2–19.5 | 1.0–6.0 | 11–188 | ** | 0.18–0.66 | [9] |
| Kuwait | 17.3–20.5 | 15–16.4 | 353–445 | 23.6–44.3 | 1.0–3.1 | [10] |
| Iran | 11.8–22.7 | 10.7–25 | 223–535 | ** | 0.14–2.8 | [11] |
| Saudi Arabia | 4.4–19.3 | 5.3–58.9 | 324.6–1133 | ** | 0.6–8.7 | [12] |
| Kuwait | 18.6–21.4 | 14.0–17.1 | 351.2–404.0 | ** | 1.5–2.9 | [13] |
| Greece | 18–86 | 20–31 | 368–610 | 47–105 | 0.7–3.8 | [17] |
| China | 13.7–52. | 26.1–71.9 | 392–898 | ** | ** | [19] |
| Egypt | 38.51 | ** | 33.35 | 659.18 | ** | [20] |
| Oman | 16.2 (16.3) | 34.5 (27.8) | 54.7 (45.6) | 46.8 (44.9) | 0.1 (0.1) | This stud |
| Radionuclide | Statistics | 226Ra | 232Th | 40K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
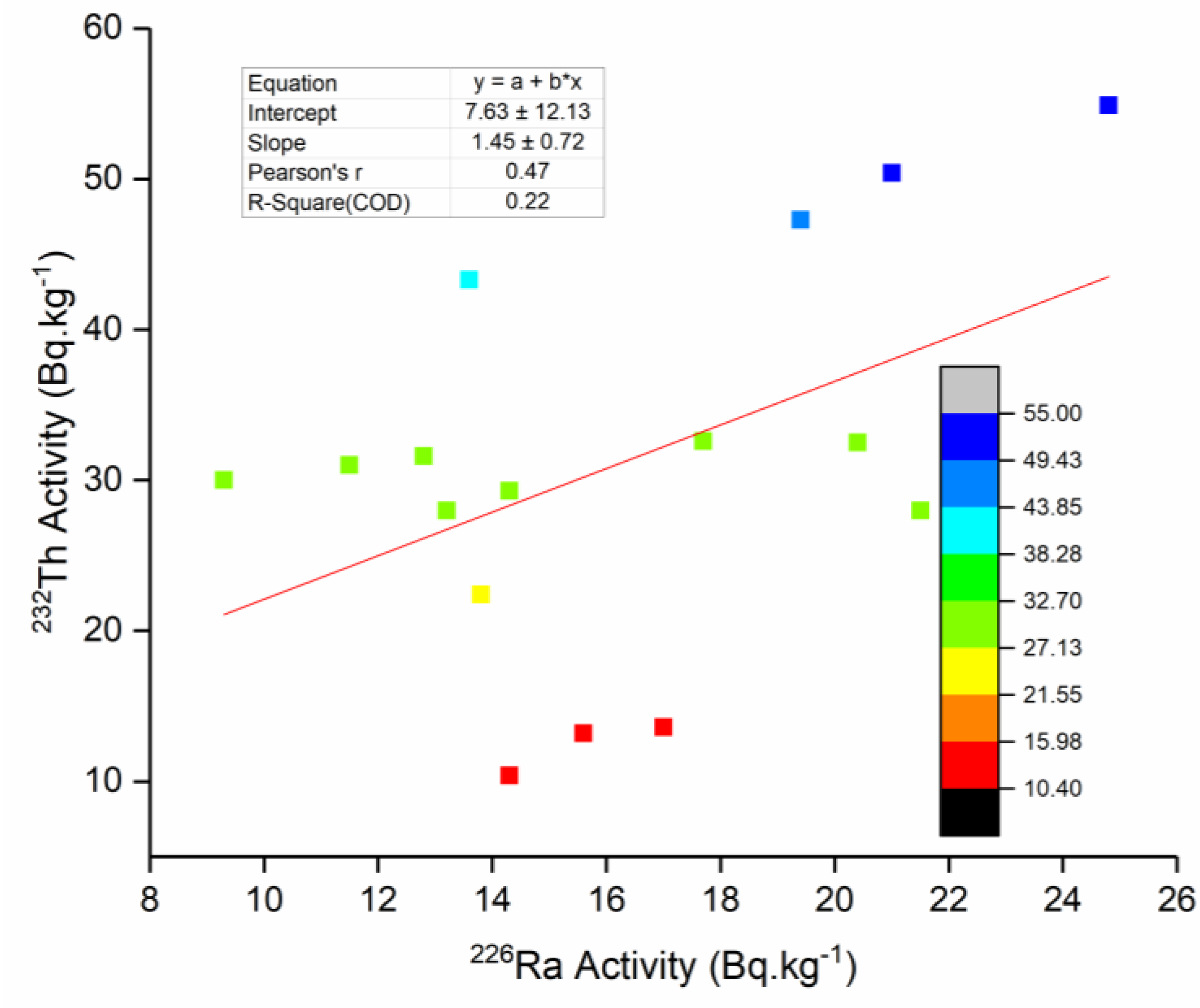
| 226Ra | Correlation coefficient | 1 | 0.47 | 0.77 |
| p-value | - | 0.07 | <0.001 | |
| 232Th | Correlation coefficient | 0.47 | 1 | 0.75 |
| p-value | 0.07 | - | <0.001 | |
| 40K | Correlation coefficient | 0.77 | 0.75 | - |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Sample Code | Raq (Bqkg−1) | Dose Rate (nGy.h−1) | (µSvy−1) | ELCR per 10−6 | AGD µGy.y−1 | Hex | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S01 | 67.6 ± 5.7 | 56.9 | 31.1 | 317.2 | 126 | 208.2 | 0.18 |
| S02 | 109.0 ± 4.6 | 89.2 | 50.2 | 498.9 | 203 | 329.5 | 0.30 |
| S05 | 58.5 ± 3.1 | 47.7 | 26.8 | 267.1 | 108 | 175.9 | 0.16 |
| S06 | 31.5 ± 2.6 | 27.0 | 14.3 | 150.2 | 58 | 97.3 | 0.09 |
| S09 | 79.5 ± 5.0 | 64.7 | 36.9 | 362.6 | 149 | 240.9 | 0.22 |
| S10 | 54.4 ± 3.4 | 43.9 | 25.1 | 246.0 | 101 | 163.2 | 0.15 |
| S13 | 36.9 ± 2.7 | 31.4 | 16.8 | 174.8 | 68 | 113.4 | 0.10 |
| S14 | 39.1 ± 2.9 | 33.3 | 17.7 | 185.2 | 72 | 120.1 | 0.11 |
| Average | 59.56 | 49.26 | 27.4 | 275.2 | 111 | 181.1 | 0.16 |
| Isotope | Activity in Sediment (Bqkg−1 d.w.) | Activity Concentration in Organism (Bq kg−1 f.w.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benthic Fish | Macroalgae | Mollusc-Bivalve | Pelagic Fish | Phytoplankton | Zooplankton | ||
| Ra-226 | 16.2 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 3.48 | 0.25 |
| Th-232 | 34.3 | 0.01 | 0.020 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 3.15 | 0.031 |
| Pb-210 | 46.80 | 5.80 | 0.18 | 1.11 | 5.80 | 84.3 | 2.99 |
| Cs-137 | 0.08 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.0010 |
| Organism | Background Dose Rates | Screening Value [µGy h−1] | Total Dose Rate per Organism [µGy h−1] | Risk Quotient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benthic fish | 0.58 | 10 | 0.067 | 0.007 |
| Macroalgae | 0.87 | 10 | 0.048 | 0.005 |
| Mollusc-bivalve | 2.0 | 10 | 0.036 | 0.004 |
| Pelagic fish | 0.42 | 10 | 0.059 | 0.006 |
| Phytoplankton | 0.38 | 10 | 0.564 | 0.056 |
| Zooplankton | 0.94 | 10 | 0.035 | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suliman, I.I.; Alsafi, K. Radiological Risk to Human and Non-Human Biota Due to Radioactivity in Coastal Sand and Marine Sediments, Gulf of Oman. Life 2021, 11, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060549
Suliman II, Alsafi K. Radiological Risk to Human and Non-Human Biota Due to Radioactivity in Coastal Sand and Marine Sediments, Gulf of Oman. Life. 2021; 11(6):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060549
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuliman, Ibrahim I., and Khalid Alsafi. 2021. "Radiological Risk to Human and Non-Human Biota Due to Radioactivity in Coastal Sand and Marine Sediments, Gulf of Oman" Life 11, no. 6: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060549
APA StyleSuliman, I. I., & Alsafi, K. (2021). Radiological Risk to Human and Non-Human Biota Due to Radioactivity in Coastal Sand and Marine Sediments, Gulf of Oman. Life, 11(6), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060549






