Analysis of the Sequence Characteristics of Antifreeze Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
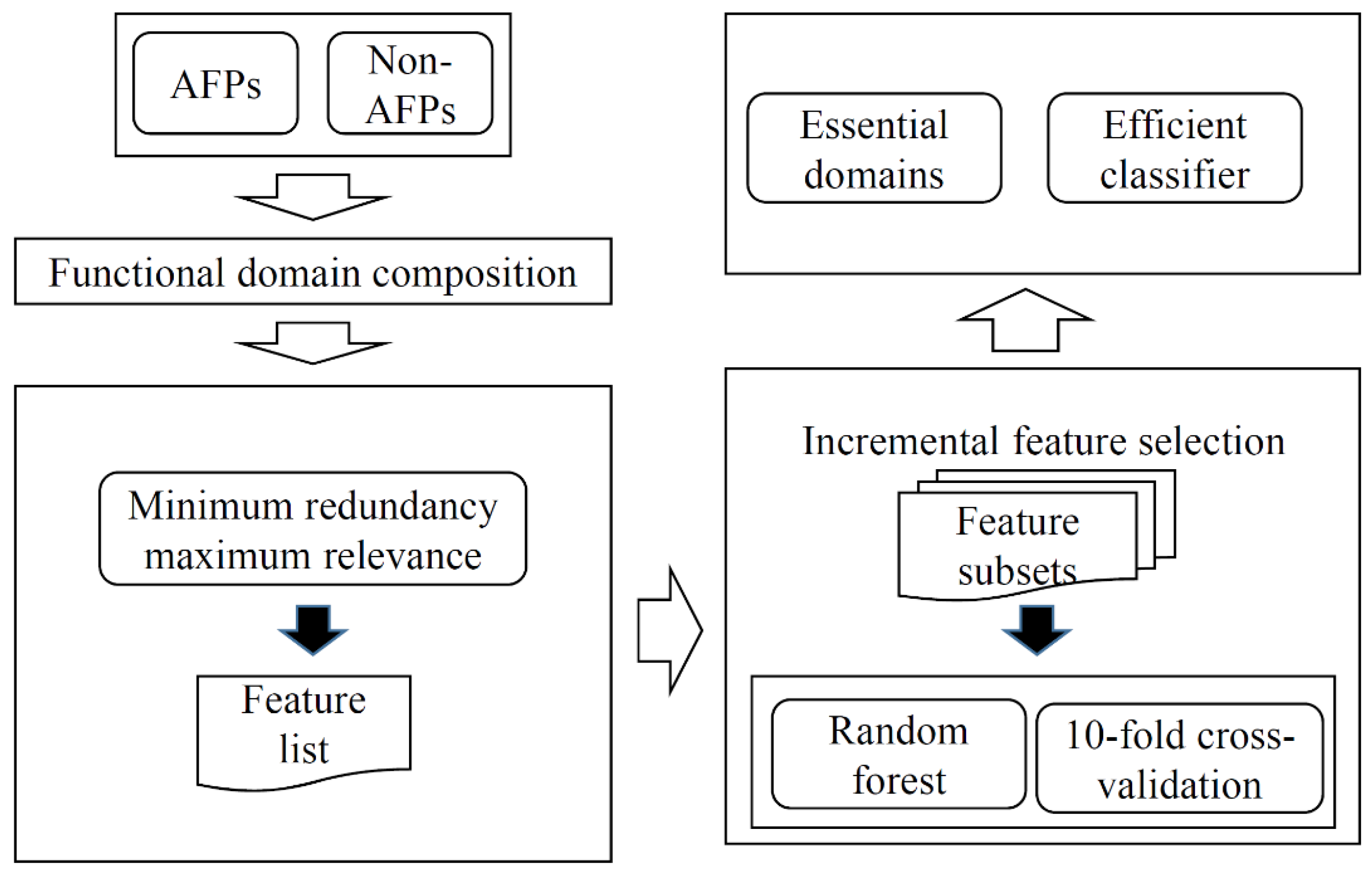
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AFPs and Their Sequence Features
2.2. Minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance Feature Selection
2.3. Incremental Feature Selection
2.4. Random Forest
2.5. Performance Evaluation
3. Results
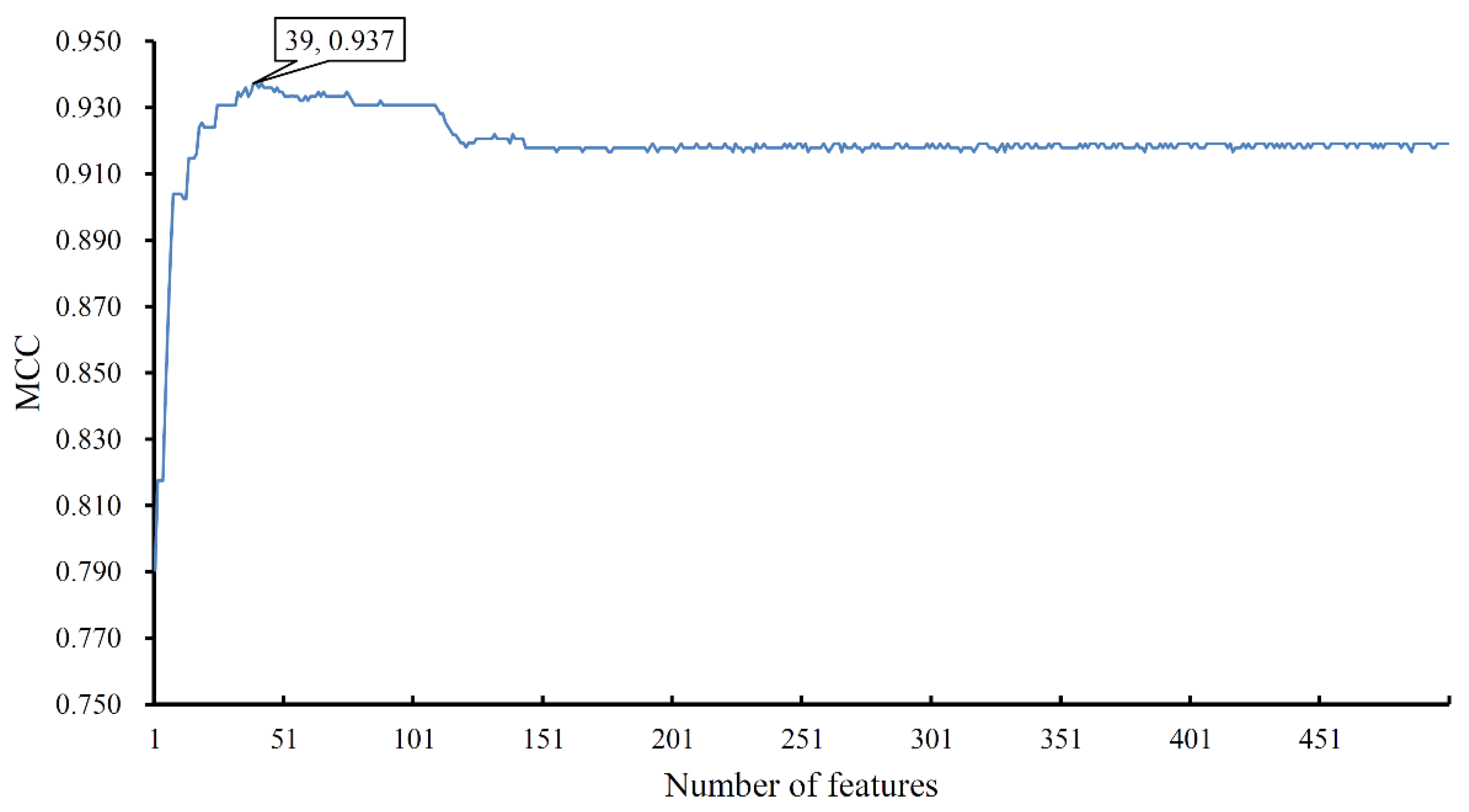
3.1. Results of mRMR Method
3.2. Results of IFS Method
3.3. Comparisons with Previous Methods
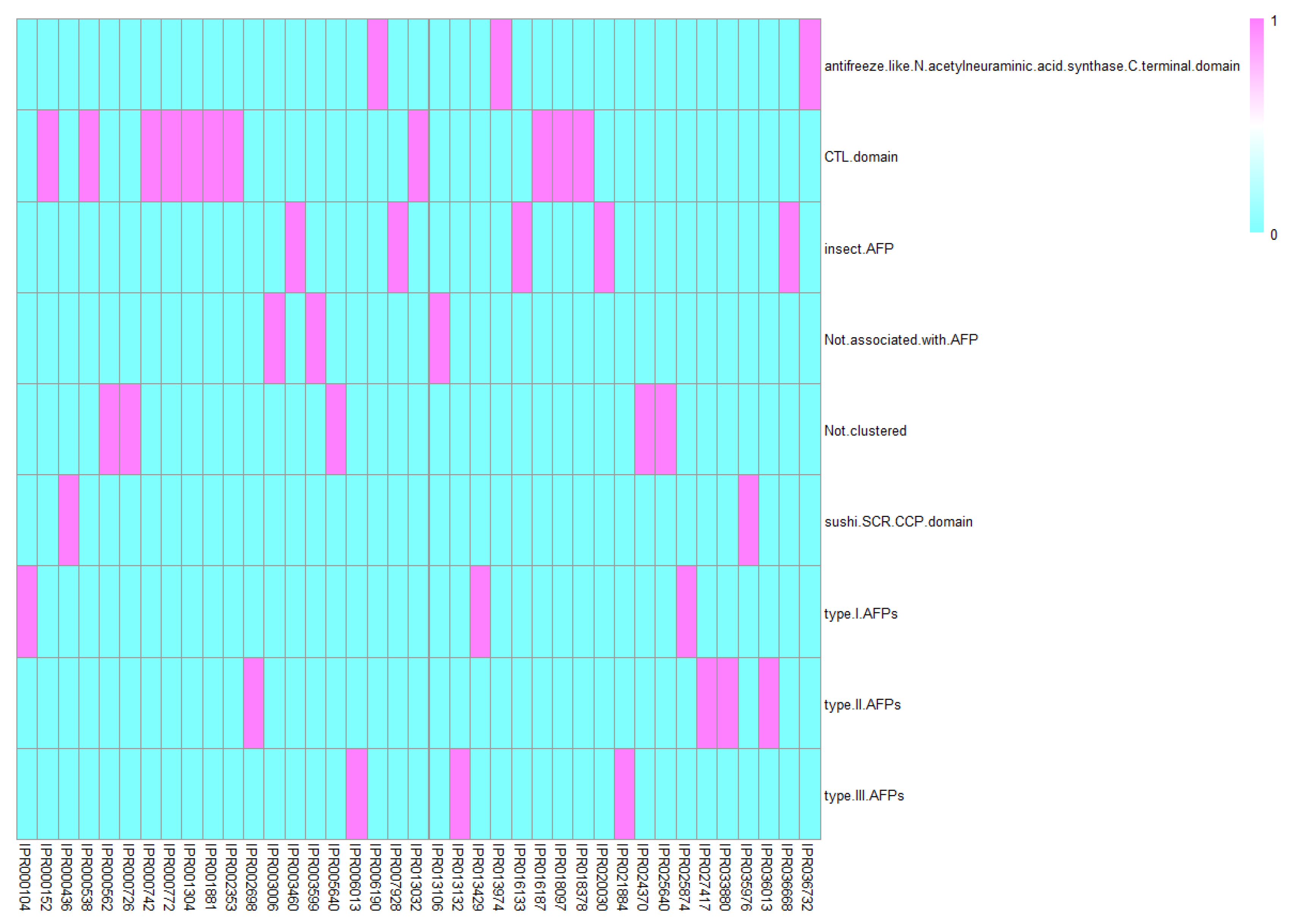
4. Discussion
4.1. CTL Domains
4.2. Sushi/SCR/CCP Domains
4.3. Antifreeze-Like/N-Acetylneuraminic Acid Synthase
4.4. Insect AFPs
4.5. AFP, Type I
4.6. AFP, Type II
4.7. AFP, Type III
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cziko, P.A.; DeVries, A.L.; Evans, C.W.; Cheng, C.H. Antifreeze protein-induced superheating of ice inside antarctic notothenioid fishes inhibits melting during summer warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14583–14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Wojnar, J.M.; Harris, P.W.; DeVries, A.L.; Evans, C.W.; Brimble, M.A. Chemical synthesis of a masked analogue of the fish antifreeze potentiating protein (afpp). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 4935–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chakrabartty, A.; Ananthanarayanan, V.S.; Hew, C.L. Structure-function relationships in a winter flounder antifreeze polypeptide. I. Stabilization of an alpha-helical antifreeze polypeptide by charged-group and hydrophobic interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 11307–11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Houston, M.E., Jr.; Hodges, R.S.; Kay, C.M.; Sykes, B.D.; Loewen, M.C.; Davies, P.L.; Sonnichsen, F.D. A diminished role for hydrogen bonds in antifreeze protein binding to ice. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 14652–14660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.G.; Park, C.J.; Kim, H.E.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, A.R.; Choi, S.R.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, J.H. Comparison of backbone dynamics of the type III antifreeze protein and antifreeze-like domain of human sialic acid synthase. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 61, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandaswamy, K.K.; Chou, K.C.; Martinetz, T.; Moller, S.; Suganthan, P.N.; Sridharan, S.; Pugalenthi, G. Afp-pred: A random forest approach for predicting antifreeze proteins from sequence-derived properties. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 270, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.W.; Ding, H.; Wang, D.H.; Han, S.G. Identifying antifreeze proteins based on key evolutionary information. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.A.; Lougheed, S.C.; Ewart, K.V.; Davies, P.L. Lateral transfer of a lectin-like antifreeze protein gene in fishes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, K.; Lotze, S.; Olijve, L.L.; DeVries, A.L.; Duman, J.G.; Voets, I.K.; Bakker, H.J. Investigation of the ice-binding site of an insect antifreeze protein using sum-frequency generation spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschan, B.; Morawetz, K.; Thoms, S. Dynamical mechanism of antifreeze proteins to prevent ice growth. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter. Phys. 2014, 90, 022711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, C.; Gao, R.; Zhang, L. An effective antifreeze protein predictor with ensemble classifiers and comprehensive sequence descriptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21191–21214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. Interproscan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.C.; Long, F.H.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information: Criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Li, H.; Zeng, T.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Identification of protein subcellular localization with network and functional embeddings. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 626500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Li, H.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Identifying transcriptomic signatures and rules for sars-cov-2 infection. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 627302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guo, F.; Zou, Q.; Ding, H. Mrmd2.0: A python tool for machine learning with feature ranking and reduction. Curr. Bioinform. 2020, 15, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.A.; Setiono, R. Incremental feature selection. Appl. Intell. 1998, 9, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In IJCAI’95: Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QB, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Ltd.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 1137–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Detecting the multiomics signatures of factor-specific inflammatory effects on airway smooth muscles. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 599970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-P.; Chen, L.; Guo, Z.-H. Iatc-nrakel: An efficient multi-label classifier for recognizing anatomical therapeutic chemical classes of drugs. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, L.; Dai, Q. IMPTCE-Hnetwork: A multi-label classifier for identifying metabolic pathway types of chemicals and enzymes with a heterogeneous network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 6683051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Pan, X.; Guo, W.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Niu, Z.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Investigating the gene expression profiles of cells in seven embryonic stages with machine learning algorithms. Genomics 2020, 112, 2524–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Y.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, L.; Feng, K.Y.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.D. Investigation and prediction of human interactome based on quantitative features. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Determining protein–protein functional associations by functional rules based on gene ontology and kegg pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Li, J.; Xing, Z.-H.; Yang, J.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Identify key sequence features to improve CRISPR sgRNA efficacy. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26582–26590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 832–844. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, K.M.; Witten, I.H. Stacking bagged and dagged models. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–18 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Casanova, R.; Saldana, S.; Chew, E.Y.; Danis, R.P.; Greven, C.M.; Ambrosius, W.T. Application of random forests methods to diabetic retinopathy classification analyses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.Y.; Zhu, L.; Fan, Y.X.; Yan, J.C. Predicting protein-rna interaction amino acids using random forest based on submodularity subset selection. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2014, 53, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Shen, H.B. Large-scale prediction of human protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequence based on latent topic features. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4992–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Lu, J. A similarity-based method for prediction of drug side effects with heterogeneous information. Math. Biosci. 2018, 306, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X. Prediction of drug side effects with a refined negative sample selection strategy. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 1573543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, L. Similarity-based machine learning model for predicting the metabolic pathways of compounds. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130687–130696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhong, Y.; Lin, W.; Zou, Q. Predicting disease-associated circular RNAs using deep forests combined with positive-unlabeled learning methods. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.Q.; Li, L.H.; Zou, Q. Incorporating distance-based top-n-gram and random forest to identify electron transport proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2931–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.W.; Ma, Z.Q.; Yin, M.H. Using support vector machine and evolutionary profiles to predict antifreeze protein sequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2196–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Pai, P.P. Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition improves sequence-based antifreeze protein prediction. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 356, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.E.; Gibson, M.I. Latent ice recrystallization inhibition activity in non antifreeze proteins: Ca2+-activated plant lectins and cation-activated antimicrobial peptides. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3411–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, L.A.; Li, J.; Davidson, W.S.; Davies, P.L. Smelt was the likely beneficiary of an antifreeze gene laterally transferred between fishes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makou, E.; Herbert, A.P.; Barlow, P.N. Creating functional sophistication from simple protein building blocks, exemplified by factor h and the regulators of complement activation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, S.; Ahorn, H.; Koehler, A.; Eisenhaber, F.; Rodi, H.P.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Park, J.E.; Rettig, W.J.; Lenter, M.C. Molecular cloning and characterization of endosialin, a c-type lectin-like cell surface receptor of tumor endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7408–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, T.; Ito, Y.; Abe, T.; Hayashi, F.; Guntert, P.; Inoue, M.; Kigawa, T.; Terada, T.; Shirouzu, M.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Solution structure of the antifreeze-like domain of human sialic acid synthase. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Lu, Y.; Cai, S.; Qiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and homology modeling of the first caudata amphibian antifreeze-like protein in axolotl (ambystoma mexicanum). Zoolog. Sci. 2013, 30, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, K.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Xu, Y.; Duman, J.G.; DeVries, A.; Gruebele, M.; Leitner, D.M.; Havenith, M. Long-range protein-water dynamics in hyperactive insect antifreeze proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, S.A.; Alavi, S.; Ripmeester, J.A.; Englezos, P. Why ice-binding type I antifreeze protein acts as a gas hydrate crystal inhibitor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 9984–9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.; Mao, Y.; Galdino, L.; Gunsen, Z. Effects of a type I antifreeze protein (afp) on the melting of frozen afp and afp+solute aqueous solutions studied by nmr microimaging experiment. J. Biol. Phys. 2013, 39, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorhannus, U. Evolution of type II antifreeze protein genes in teleost fish: A complex scenario involving lateral gene transfers and episodic directional selection. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2012, 8, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, C.; Poulsen, J.C.; Ramlov, H.; Lo Leggio, L. Purification, crystal structure determination and functional characterization of type III antifreeze proteins from the european eelpout zoarces viviparus. Cryobiology 2014, 69, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nishijima, K.; Tanaka, M.; Sakai, Y.; Koshimoto, C.; Morimoto, M.; Watanabe, T.; Fan, J.; Kitajima, S. Effects of type III antifreeze protein on sperm and embryo cryopreservation in rabbit. Cryobiology 2014, 69, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, D.F.; Campelo, I.S.; Silva, M.; Bhat, M.H.; Teixeira, D.I.A.; Melo, L.M.; Souza-Fabjan, J.M.G.; Mermillod, P.; Freitas, V.J.F. The use of antifreeze protein type III for vitrification of in vitro matured bovine oocytes. Cryobiology 2016, 73, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chao, L.; Yu, H.; Song, C.; Shen, Y.; Chen, H.; Deng, X. The protective role of antifreeze protein 3 on the structure and function of mature mouse oocytes in vitrification. Cryobiology 2014, 69, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | MCC | Sensitivity # | Specificity # | Accuracy # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our classifier | 0.937 | 0.890 | 1.000 | 0.995 |
| AFP-Pred [6] * | - | 0.847 | 0.840 | 0.843 |
| AFP-PSSM [38] * | - | 0.759 | 0.933 | 0.930 |
| AFP-PseAAC [39] * | - | 0.862 | 0.847 | 0.848 |
| AFP-Ensemble [11] * | - | 0.892 | 0.940 | 0.938 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-H.; Li, Z.; Lu, L.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Analysis of the Sequence Characteristics of Antifreeze Protein. Life 2021, 11, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060520
Zhang Y-H, Li Z, Lu L, Zeng T, Chen L, Li H, Huang T, Cai Y-D. Analysis of the Sequence Characteristics of Antifreeze Protein. Life. 2021; 11(6):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060520
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu-Hang, Zhandong Li, Lin Lu, Tao Zeng, Lei Chen, Hao Li, Tao Huang, and Yu-Dong Cai. 2021. "Analysis of the Sequence Characteristics of Antifreeze Protein" Life 11, no. 6: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060520
APA StyleZhang, Y.-H., Li, Z., Lu, L., Zeng, T., Chen, L., Li, H., Huang, T., & Cai, Y.-D. (2021). Analysis of the Sequence Characteristics of Antifreeze Protein. Life, 11(6), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060520










