Incorporation of an Allogenic Cortical Bone Graft Following Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in a Patient with Hallux Rigidus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Shark Screw® Specific Data
2.2. Surgical Techniques
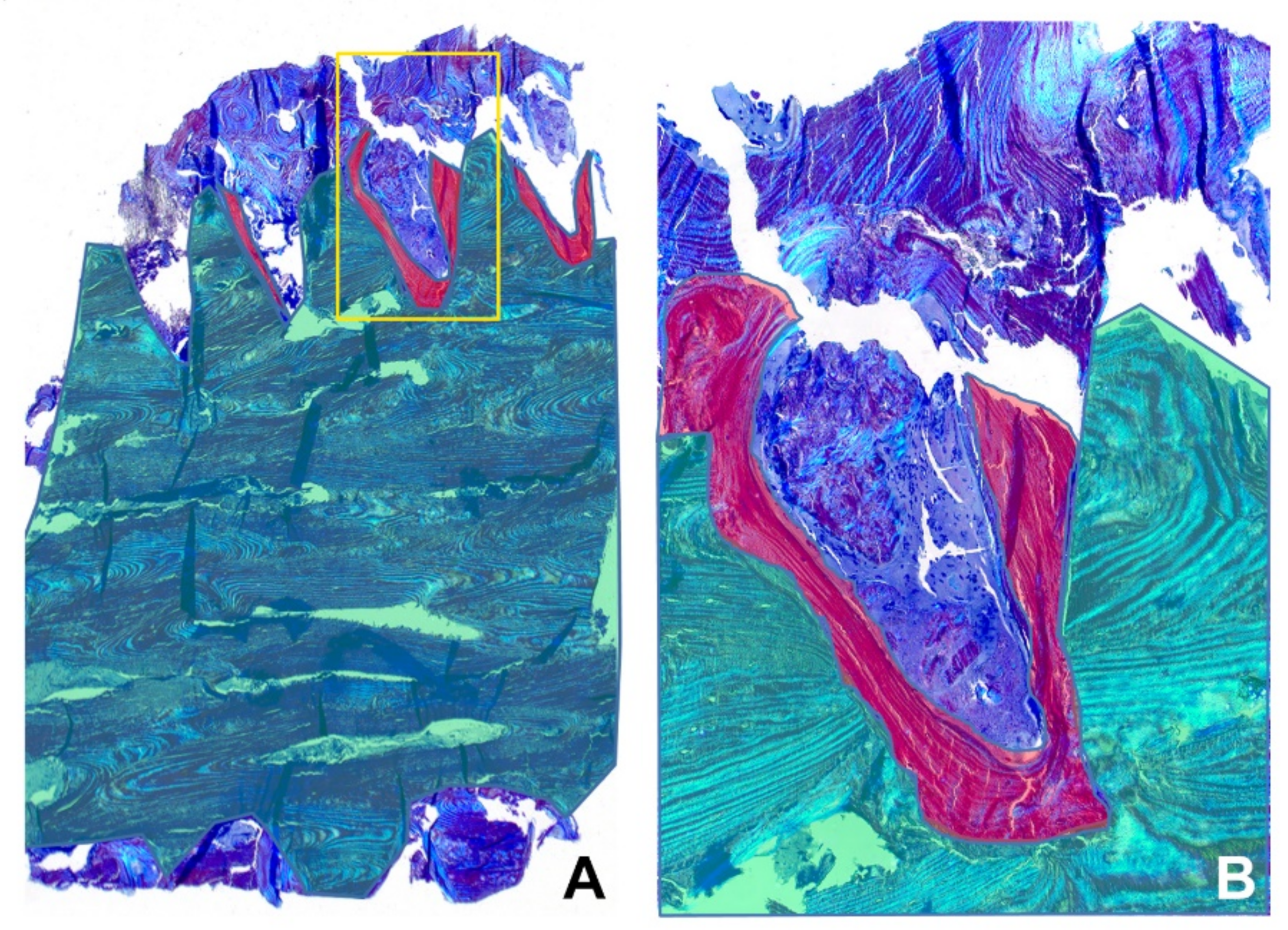
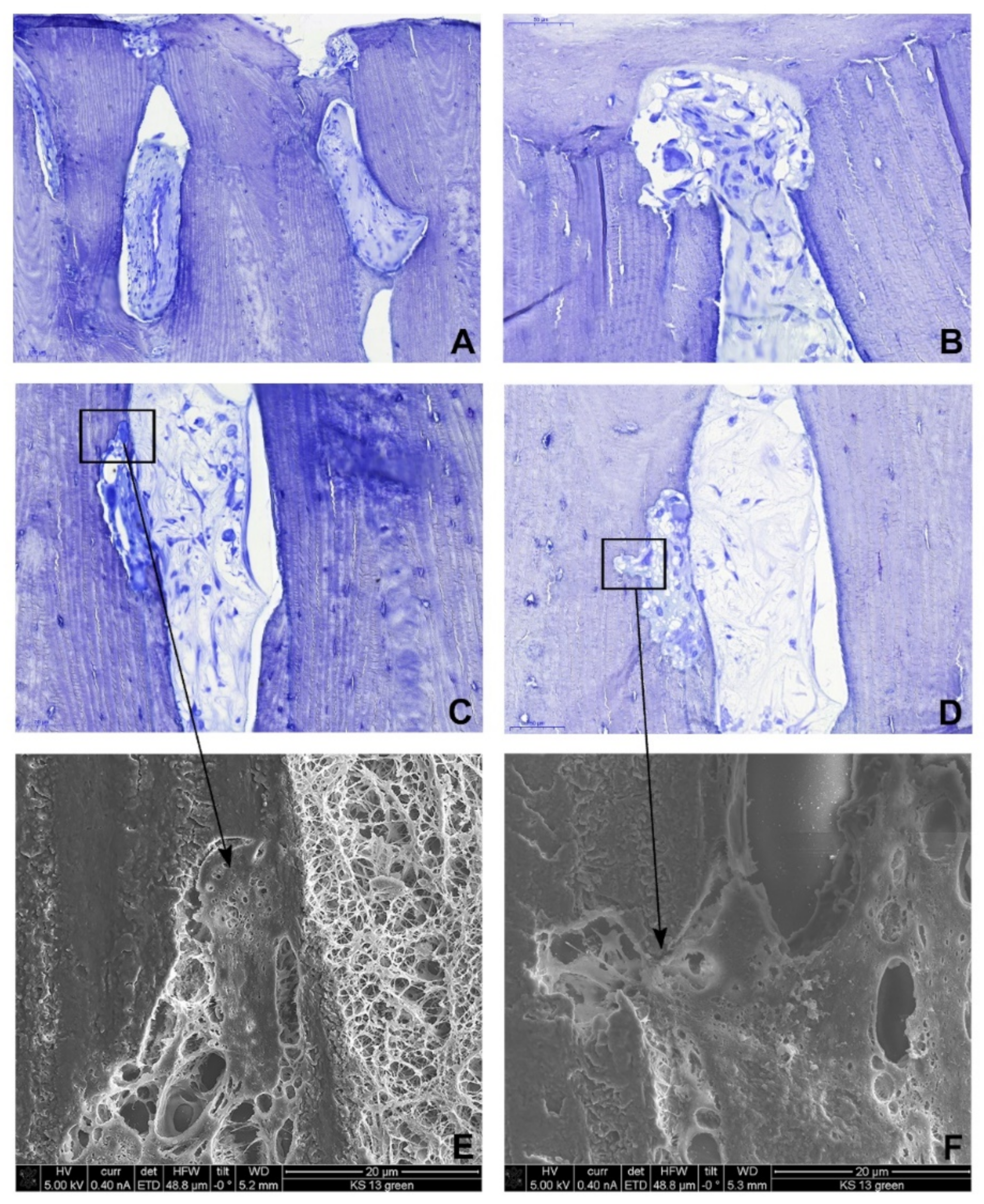
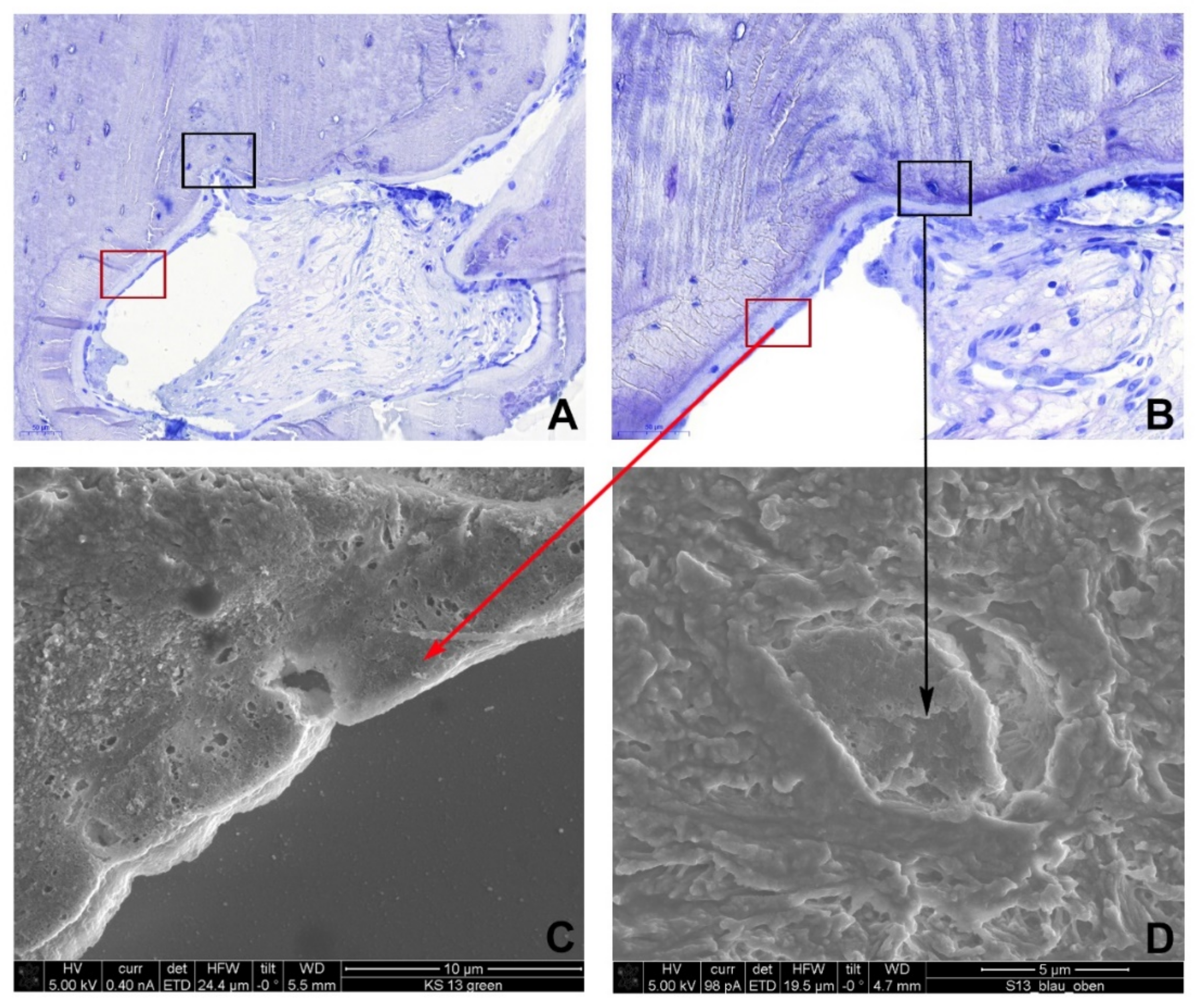
2.3. Light Microscopy
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
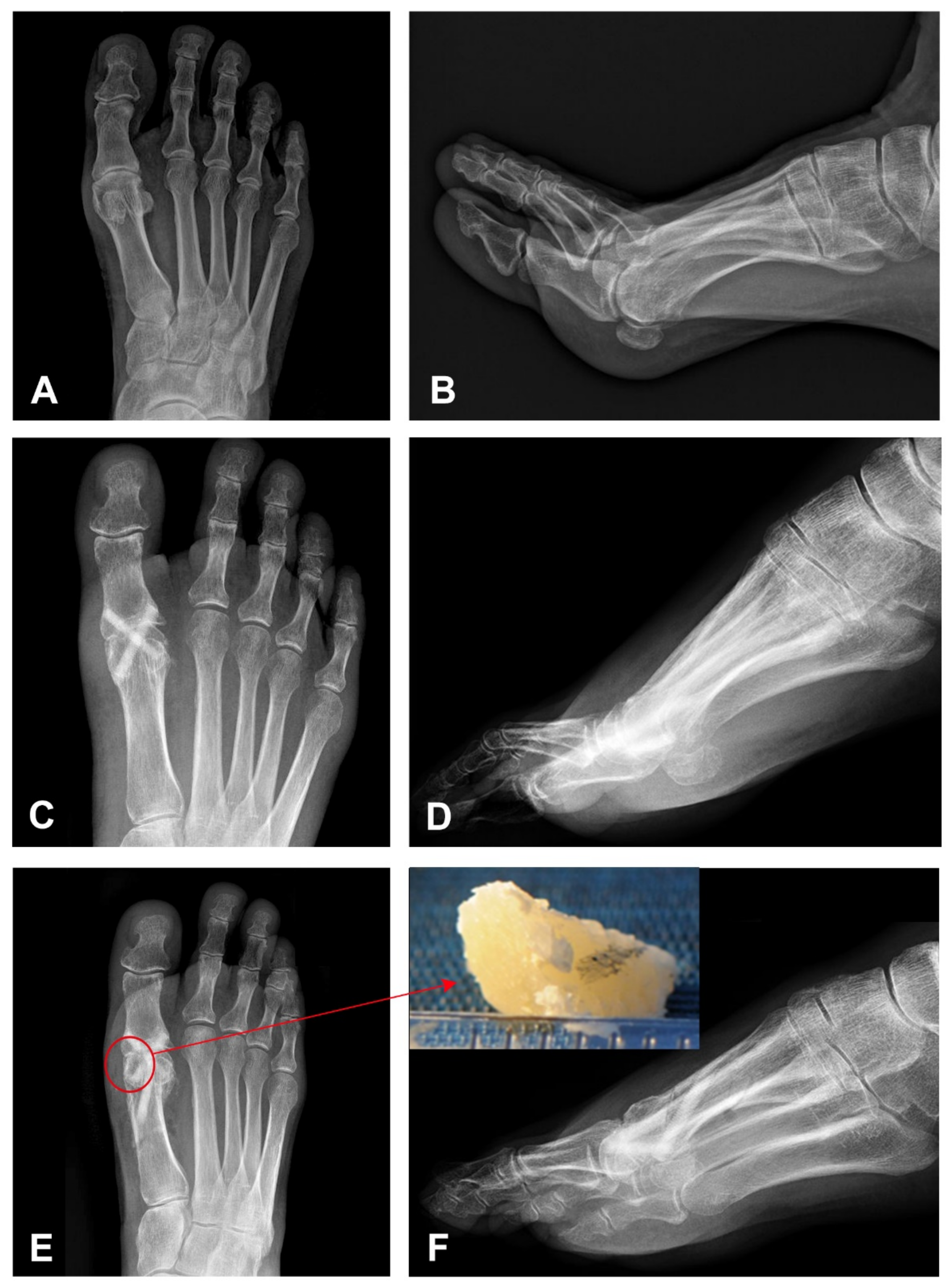
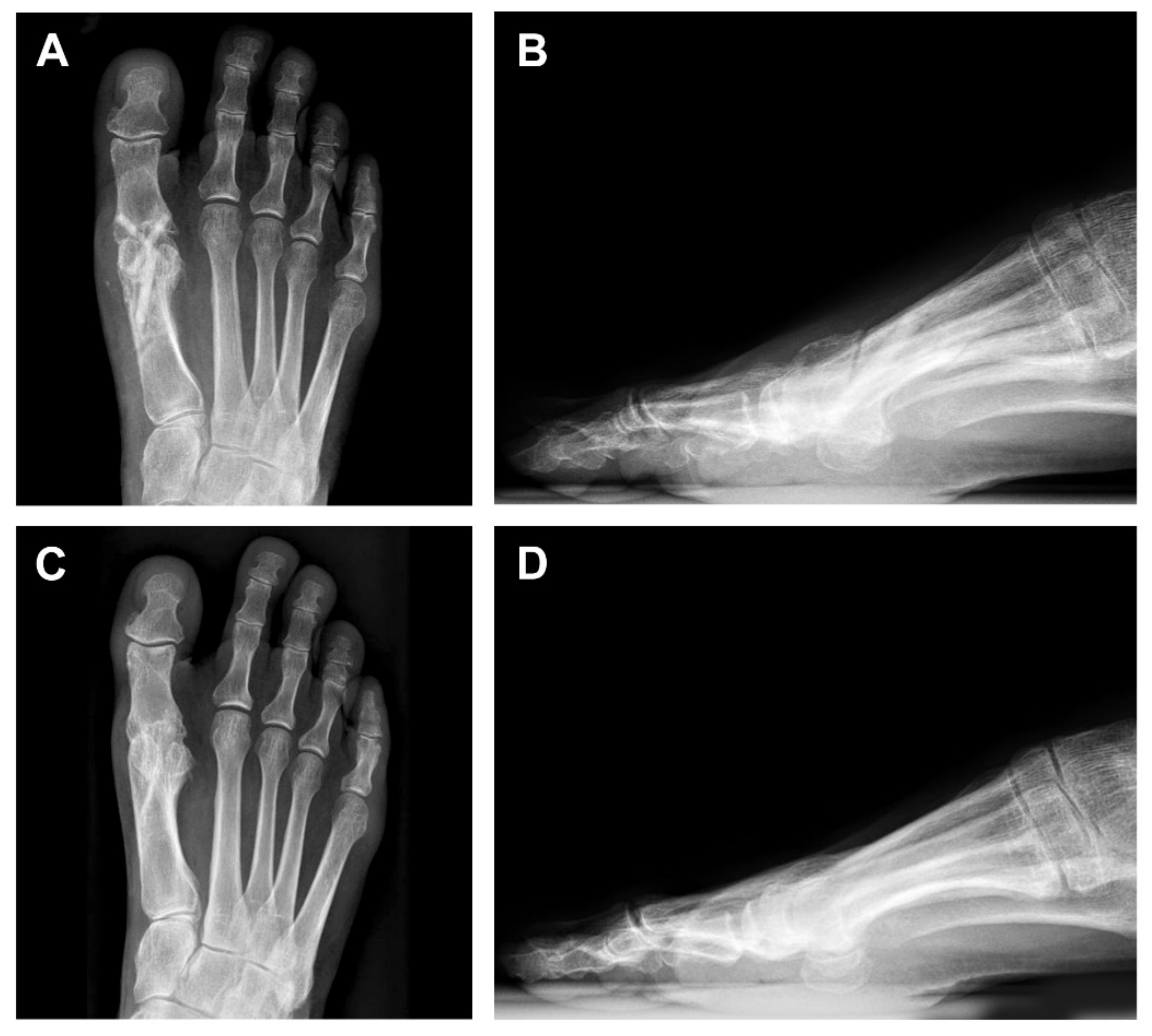
3. Case Presentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuhrmann, R.A. First metatarsophalangeal arthrodesis for hallux rigidus. Foot Ankle Clin. 2011, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peace, R.A.; Hamilton, G.A. End-stage hallux rigidus: Cheilectomy, implant, or arthrodesis? Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2012, 29, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perler, A.D.; Nwosu, V.; Christie, D.; Higgins, K. End-stage Osteoarthritis of the Great toe/hallux Rigidus: A Review of the Alternatives to Arthrodesis: Implant Versus Osteotomies and Arthroplasty Techniques. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2013, 30, 351–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsell, R.; Einhorn, T.A. The biology of fracture healing. Injury 2011, 42, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendra, V.; Darowish, M. Basic Science of Bone Healing. Hand. Clin. 2013, 29, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, P.; Marrs, J.; Gaviria, L.; Silliman, D.T.; Decker, J.F.; Brown Baer, P.; Guda, T. Quantifying Vascular Changes Surrounding Bone Regeneration in a Porcine Mandibular Defect Using Computed Tomography. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2019, 25, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enneking, W.F.; Mindell, E.R. Observations on massive retrieved human allografts. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1991, 73, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enneking, W.F.; Campanacci, D.A. Retrieved human allografts. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolainen, P.; Vuorio, E.; Aro, H.T. Gene Expression at Graft-Host Interfaces of Cortical Bone Allografts and Autografts. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993, 297, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, H.; Moreno, J.; Ripalda, P.; Forriol, F. Radiological and histological analysis of cortical allografts: An experimental study in sheep femora. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2004, 124, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastl, K.; Schimetta, W. The application of an allogeneic bone screw for osteosynthesis in hand and foot surgery: A case series. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2021. Ahead of Print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, E.; Röser, K.; Hahn, M.; Welkerling, H.; Delling, G. Enzyme and immunohistochemistry on undecalcified bone and bone marrow biopsies after embedding in plastic: A new embedding method for routine application. Virchows Archiv. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1992, 420, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, S.; Schilero, C.; Chiang, S.; Pham, P. Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Three Classification Systems for Hallux Rigidus. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankenson, K.D.; Dishowitz, M.; Gray, C.; Schenker, M. Angiogenesis in bone regeneration. Injury 2011, 42, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrek, T.; Johansson, C. Osteoinduction, osteoconduction and osteointegration. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, S96–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böstman, O.M.; Pihlajamäki, H.K. Adverse tissue reactions to bioabsorbable fixation devices. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2000, 371, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.K.; Roy, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Kundu, B.; De, D.K.; Basu, D. Orthopaedic applications of bone graft & graft substitutes: A review. Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 132, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Tuchman, A.; Brodke, D.S.; Youssef, J.A.; Meisel, H.J.; Dettori, J.R.; Park, J.B.; Yoon, S.T.; Wang, J.C. Autograft versus Allograft for Cervical Spinal Fusion: A Systematic Review. Glob. Spine J. 2017, 7, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, N.; Jupiter, D.C. Bone graft substitute: Allograft and xenograft. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2015, 32, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, P.; Li, D.J.; Auston, D.A.; Mir, H.S.; Yoon, R.S.; Koval, K.J. Autograft, Allograft, and Bone Graft Substitutes: Clinical Evidence and Indications for Use in the Setting of Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibovic, P.; de Groot, K. Osteoinductive biomaterials—Properties and relevance in bone repair. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, M.; Bünger, C. Factors stimulating bone formation. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, S102–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brcic, I.; Pastl, K.; Plank, H.; Igrec, J.; Schanda, J.E.; Pastl, E.; Werner, M. Incorporation of an Allogenic Cortical Bone Graft Following Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in a Patient with Hallux Rigidus. Life 2021, 11, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060473
Brcic I, Pastl K, Plank H, Igrec J, Schanda JE, Pastl E, Werner M. Incorporation of an Allogenic Cortical Bone Graft Following Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in a Patient with Hallux Rigidus. Life. 2021; 11(6):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060473
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrcic, Iva, Klaus Pastl, Harald Plank, Jasminka Igrec, Jakob E. Schanda, Eva Pastl, and Mathias Werner. 2021. "Incorporation of an Allogenic Cortical Bone Graft Following Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in a Patient with Hallux Rigidus" Life 11, no. 6: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060473
APA StyleBrcic, I., Pastl, K., Plank, H., Igrec, J., Schanda, J. E., Pastl, E., & Werner, M. (2021). Incorporation of an Allogenic Cortical Bone Graft Following Arthrodesis of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in a Patient with Hallux Rigidus. Life, 11(6), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060473





