The Alteration of Intestinal Microbiota Profile and Immune Response in Epinephelus coioides during Pathogen Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Challenge of Juvenile Grouper
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.4. Genomic DNA Extraction and Gene Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
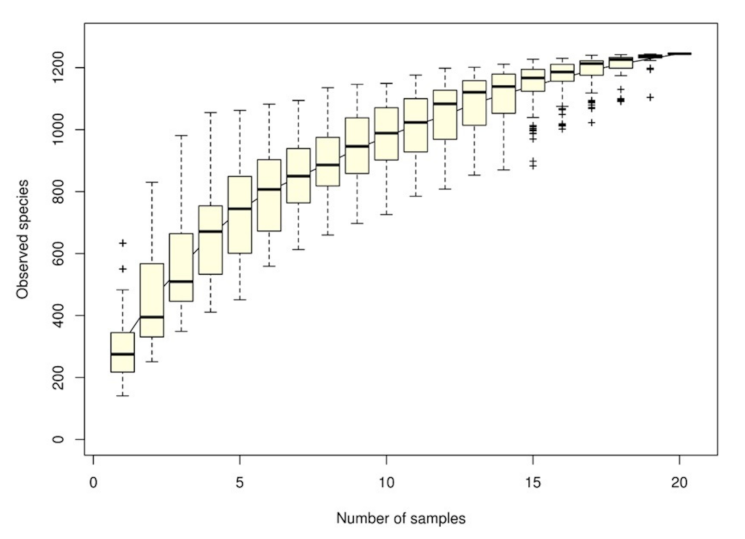
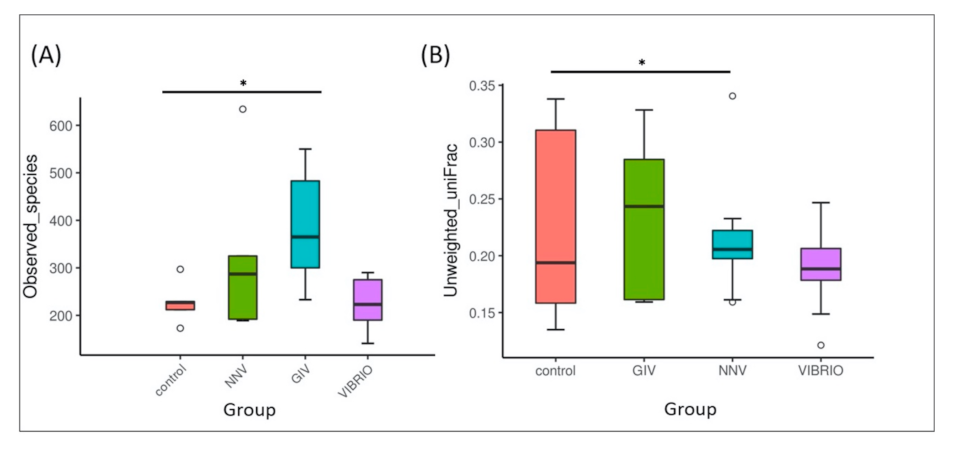
3.1. The Intestinal Microbiota Richness and Diversity Associated with Grouper Disease
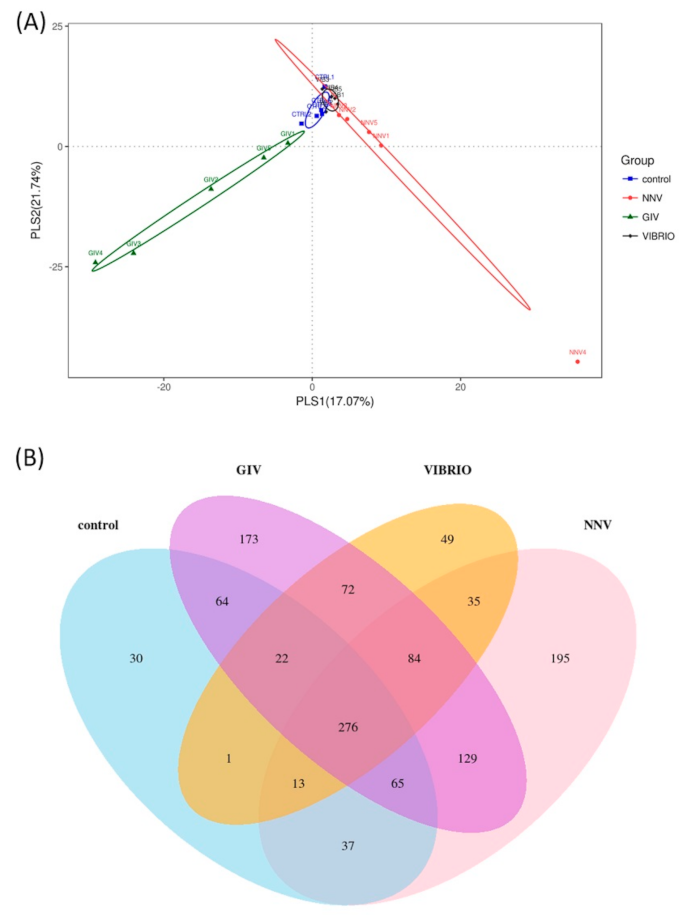
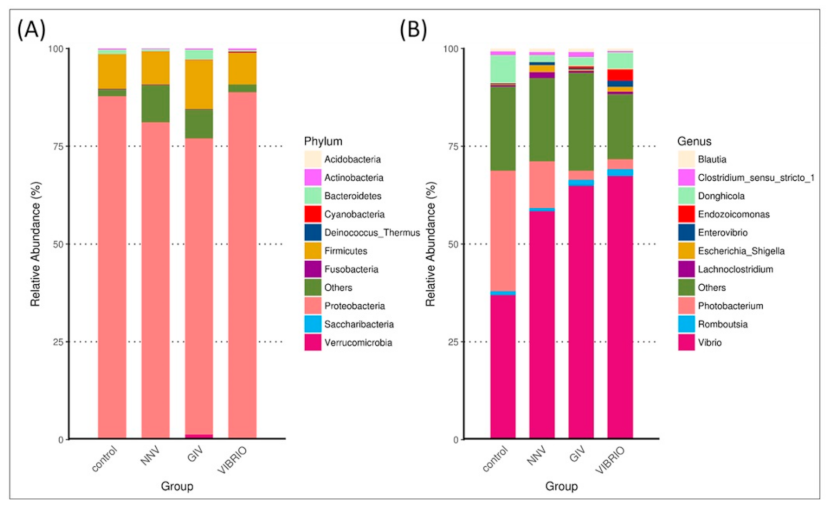
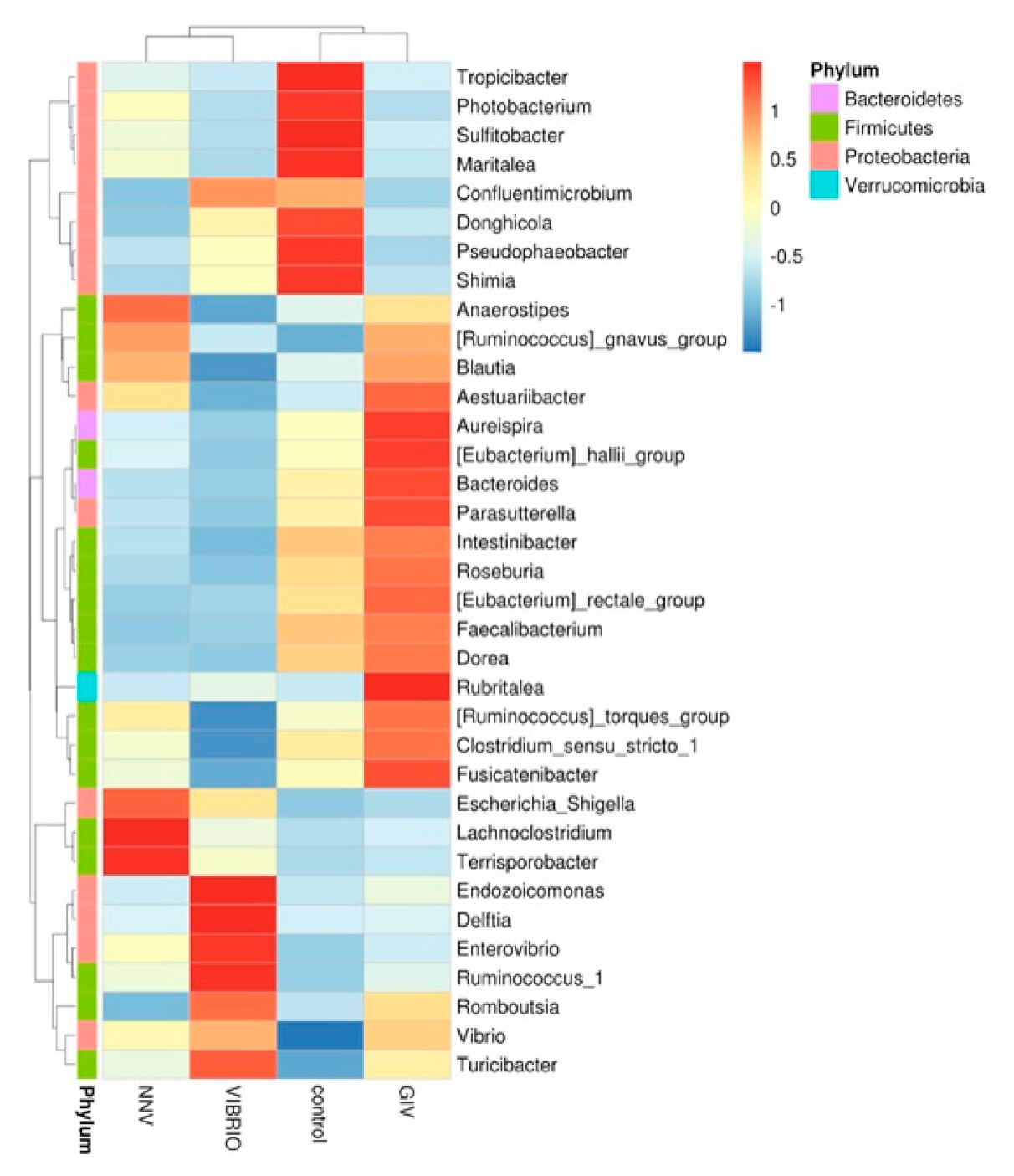
3.2. The Intestinal Flora Community Composition of Uninfected and Diseased Grouper
3.3. Interaction between Disease and Intestinal Microbiomes
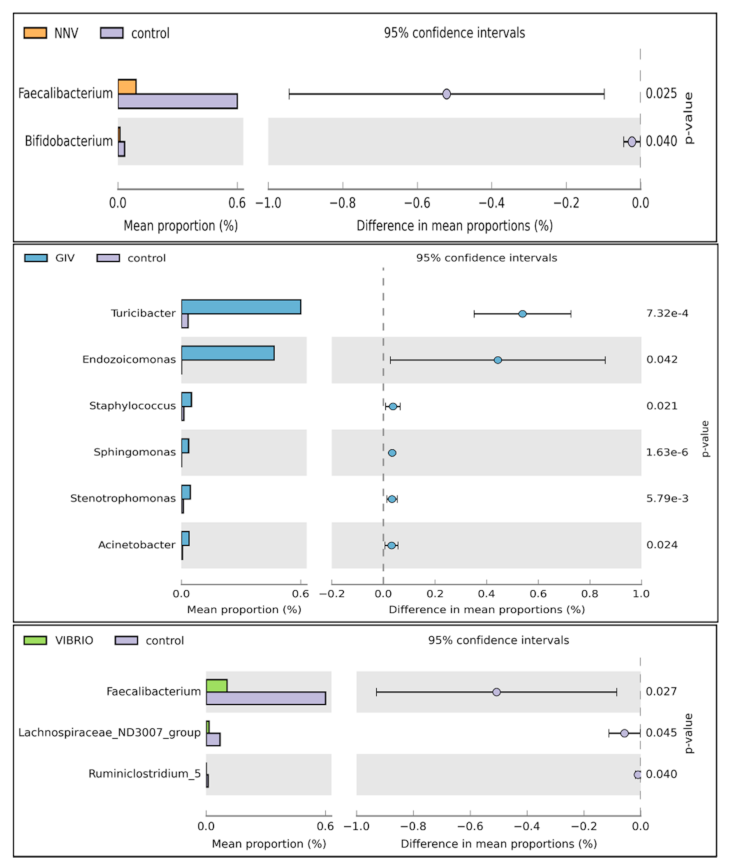
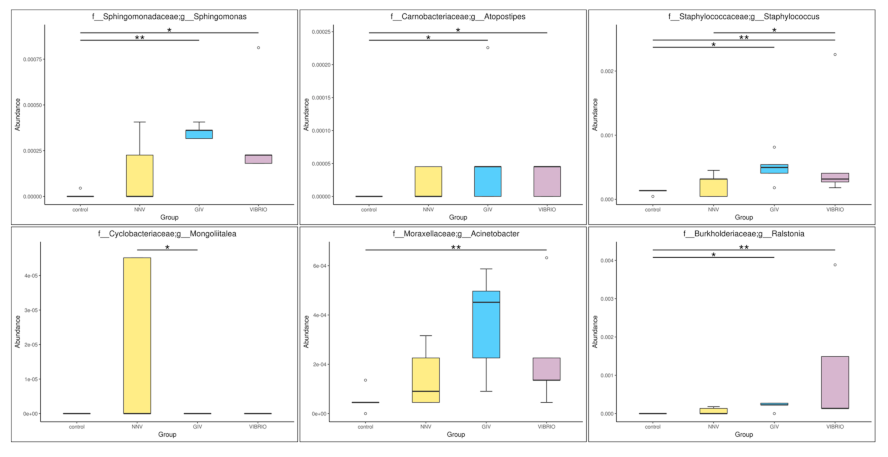
3.4. Differential Abundance Analysis and Statistical Analysis
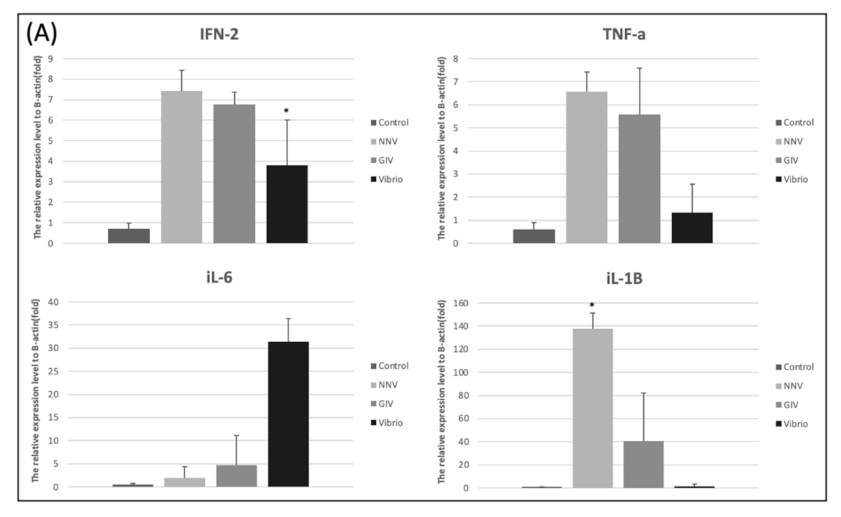
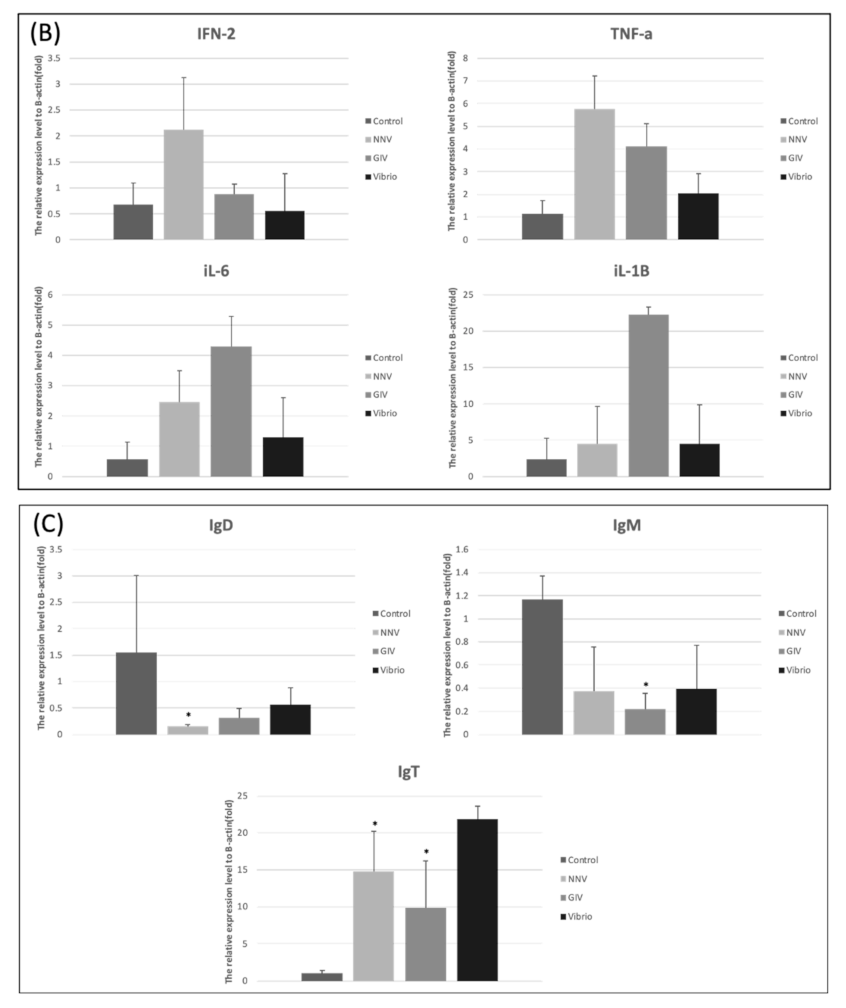
3.5. Pathogenic Infection Up-Regulates the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Gene Expression in E. coioides Intestine and Head Kidney
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, K.H.; Kim, H.J. Current status and future directions of fish vaccines employing virus-like particles. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Jian, J.; Lu, Y.; Cai, S.; Wang, B.; Tang, J.; Pang, H.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Z.-H. Draft genome sequence of the fish pathogen Vibrio harveyi strain ZJ0603. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6644–6645. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Ma, H.; Su, Y.; Wen, W.; Feng, J.; Guo, Z.-X.; Qiu, L. Susceptibility of farmed juvenile giant grouper Epinephelus lanceolatus to a newly isolated grouper iridovirus (genus Ranavirus). Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, B.; Kwang, J.; Moody, N. Betanodavirus infections of teleost fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Thompson, K.D. Understanding the interaction between Betanodavirus and its host for the development of prophylactic measures for viral encephalopathy and retinopathy. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 53, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, S.; Olveira, J.G.; Vázquez-Salgado, L.; Dopazo, C.P.; Bandín, I. Betanodavirus infection in primary neuron cultures from sole. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Cheng, C.F.; Chiou, P.P.; Liou, C.J.; Yiu, J.C.; Lai, Y.S. Identification and characterization of a late gene encoded by grouper iridovirus 2L (GIV-2L). J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Wu, M.S.; Huang, Y.J.; Lin, P.W.; Shih, C.J.; Lin, F.P.; Chang, C.Y. Iridovirus CARD protein inhibits apoptosis through intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.B.; Chen, C.Y.; Lai, Y.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Huang, H.T. Histological, ultrastructural, and in situ hybridization study on enlarged cells in grouper Epinephelus hybrids infected by grouper iridovirus in Taiwan (TGIV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 58, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningqiu, L.; Junjie, B.; Shuqin, W.; Xiaozhe, F.; Haihua, L.; Xing, Y.; Cunbin, S. An outer membrane protein, OmpK, is an effective vaccine candidate for Vibrio harveyi in Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.K.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Amal, M.N.A.; Mohamad, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Annas, S.; Al-saari, N. Effects of skin abrasion in immersion challenge with Vibrio harveyi in Asian seabass Lates calcarifer fingerlings. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2020, 137, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. Molecular and functional characterisation of a mannose-binding lectin-like gene from Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 104, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jia, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yuanxing, Z. An attenuated Vibrio harveyi surface display of envelope protein VP28 to be protective against WSSV and vibriosis as an immunoactivator for Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becattini, S.; Taur, Y.; Pamer, E.G. Antibiotic-induced changes in the intestinal microbiota and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 458–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.S.; Kao, C.Y. Current understanding of the gut microbiota shaping mechanisms. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinane, C.M.; Cotter, P.D. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: Understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, X.; Xu, Y. Altered intestinal microbiota composition associated with enteritis in yellow seahorses Hippocampus kuda (Bleeker, 1852). Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Mora-Sánchez, B.; Vargas, A.; Balcázar, J.L. Changes in intestinal microbiota and disease resistance following dietary postbiotic supplementation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, C.; Ottem, K.F.; Brevik, Ø.J.; Davey, M.; Sørum, H.; Winther-Larsen, H.C. The environmental and host-associated bacterial microbiota of Arctic seawater-farmed Atlantic salmon with ulcerative disorders. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1645–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Xiong, J.B.; Ding, F.F.; Chen, J. Immune and gut bacterial successions of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) during Pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, V.E.; Bhatt, A.S. The human microbiome in hematopoiesis and hematologic disorders. Blood 2015, 126, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, J.T.X.; Chiou, P.P.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lin, J.H.J.; Wu, J.L.; Lu, M.W. The microbiota profile and transcriptome analysis of immune response during metamorphosis stages in orange spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, T.; Joe, J.T.X.; Lu, M.W. Cloning and expression of Malabar grouper (Epinephelus malabaricus) ADAR1 gene in response to immune stimulants and nervous necrosis virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 71, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, J.W.; Qu, S.Y.; Qi, X.Z.; Wang, G.X.; Ling, F. Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus velezensisK2 on growth, immunity and resistance to Vibrio harveyi infection of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × E. fuscoguttatus♀). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibb, W.; Luu, G.; Premachandra, H.K.A.; Lu, M.W.; Nguyen, N.H. Regional genetic diversity for NNV grouper viruses across the Indo-Asian region—Implications for selecting virus resistance in farmed groupers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.T.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, J.N.; Stine, O.C.; Bravo, H.C.; Pop, M. Differential abundance analysis for microbial marker-gene surveys. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLozupone, A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and qualitative beta diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, A.K.; Hemalatha, R.; Yadav, H.; Marotta, F.; Yamashiro, Y. Gut microbiota in health and disease: An overview focused on metabolic inflammation. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JZackular, P.; Rogers, M.A.; Ruffin, M.T.t.; Schloss, P.D. The human gut microbiome as a screening tool for colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, D.; Stentiford, G.D.; Wang, H.C.; Koskella, B.; Tyler, C.R. The pathobiome in animal and plant diseases. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; Sample, H.A.; Zorn, K.C.; Arevalo, S.; Yu, G.; Neuhaus, J.; Federman, S.; Stryke, D.; Briggs, B.; Langelier, C.; et al. Clinical metagenomic sequencing for aiagnosis of meningitis and encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, T.; Gilbert, J.; Meyer, F. Metagenomics—A guide from sampling to data analysis. Microb. Inform. Exp. 2012, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.W.; Ngou, F.H.; Chao, Y.-M.; Lai, Y.S.; Chen, N.-Y.; Lee, F.Y.; Chiou, P.P. Transcriptome characterization and gene expression of Epinephelus spp in endoplasmic reticulum stress-related pathway during betanodavirus infection in vitro. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Chiou, P.P.; Liou, C.J.; Lai, Y.S. Monoclonal antibody against a putative myristoylated membrane protein encoded by grouper iridovirus 59L gene. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 113, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Wang, T.Y.; Hsu, H.H.; Chen, P.P.; Lee, S.H.; Chen, Y.M.; Tsai, T.J.; Wang, C.-K.; Ku, H.-T.; Lee, G.-B.; et al. Nervous necrosis virus replicates following the embryo development and dual infection with iridovirus at juvenile stage in grouper. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Chen, C.W.; Liu, Y.C.; Huang, H.H.; Lin, C.H.; Tzeng, C.S.; Chang, C.Y. Transcriptional analysis of orange-spotted grouper reacting to experimental grouper iridovirus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Dong, C.F.; Weng, S.P.; He, J.G. The high prevalence of pathogenic Vibrio harveyi with multiple antibiotic resistance in scale drop and muscle necrosis disease of the hybrid grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (♀) × E. lanceolatus (♂), in China. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Qin, Y.; Sheng, X.; Xing, J.; Zhan, W. Generation, characterization and application of monoclonal antibodies against matrix protein of hirame novirhabdovirus (HIRRV) in flounder. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 128, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Chen, C.; Jia, L.; He, X.; Zhang, B. Comparison of the intestinal microbiota composition and function in healthy and diseased Yunlong Grouper. AMB Express 2019, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgay, E.; Steinum, T.M.; Eryalçın, K.M.; Yardımcı, R.E.; Karataş, S. The influence of diet on the microbiota of live-feed rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) used in commercial fish larviculture. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, S.; Prasad, A. Microflora in fish digestive tract plays significant role in digestion and metabolism. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2011, 22, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, F.; Wang, G.T.; Li, W.X.; Wu, S.G. Altered gut microbiota associated with intestinal disease in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Z.; Tu, X.; Zha, J.W.; Huang, A.G.; Wang, G.X.; Ling, F. Immunosuppression-induced alterations in fish gut microbiota may increase the susceptibility to pathogens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshukov, A.; Kashinskaya, E.; Simonov, E.; Hlunov, O.; Izvekova, G.; Andree, K.; Solovyev, M. Variations of the intestinal gut microbiota of farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), depending on the infection status of the fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Gooneratne, S.R.; Lai, R.; Zeng, C.; Zhan, F.; Wang, W. The gut microbiome and degradation enzyme activity of wild freshwater fishes influenced by their trophic levels. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Lu, X.L.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, B.H.; Liu, X.Y. Description of a sulfitobacter strain and its extracellular cyclodipeptides. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 393752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, A.; González, J.M.; Moran, M.A. Overview of the marine roseobacter lineage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5665–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Sawabe, T.; Zhukova, N.V.; Hayashi, K.; Kurilenko, V.V.; Alexeeva, Y.; Buljan, V.; Nicolau, D.V.; Mikhailov, V.V.; et al. Sulfitobacter delicatus sp. nov. and Sulfitobacter dubius sp. nov., respectively from a starfish (Stellaster equestris) and sea grass (Zostera marina). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jang, H.J.; Joung, Y.; Kang, I.; Cho, J.C. Sulfitobacter profundi sp. nov., isolated from deep seawater. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, J.M.; Kiene, R.P.; Moran, M.A. Transformation of sulfur compounds by an abundant lineage of marine bacteria in the alpha-subclass of the class Proteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3810–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsalimian, M.S.; Sepahy, A.A.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Kalantar, S.M.; Dabbagh, R. Isolation of Two Radiation Resistant and Desiccation Tolerant Bacteria, Modestobacter sp. A2 and Maritalea sp. B9, from Gandom Beryan Hill in the Lut Desert of Iran. Microbiology 2018, 87, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genard, B.; Larouche, O.; Nicolas, J.-L.; Miner, P.; Beaudin, M.-L.; Tremblay, R. Effect of the probiotic strain Phaeobacter gallaeciensis after bacterial challenge on the complete larval development of Pecten maximus. Aquat. Living Resour. 2014, 27, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yuan, T.; Piva, C.; Spinard, E.J.; Schuttert, C.W.; Rowley, D.C.; Nelson, D.R. The Probiotic Bacterium Phaeobacter inhibens Downregulates Virulence Factor Transcription in the Shellfish Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus by N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01545-18. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.R.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, M.; Yun, B.R.; Shin, K.S. Donghicola tyrosinivorans sp. nov., a tyrosine-degrading bacterium isolated from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 4140–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Cho, B.C. Shimia marina gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium of the Roseobacter clade isolated from biofilm in a coastal fish farm. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, E.G.; Nealson, K.H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol. Bull. 1976, 151, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, T.; Pujalte, M.J.; Ruvira, M.A.; Garay, E.; Macián, M.C.; Arahal, D.R. Tropicibacter multivorans sp. nov., an aerobic alphaproteobacterium isolated from surface seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangifesta, M.; Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Gaiani, F.; De’Angelis, N.; De’Angelis, G.L.; Van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M.; Turroni, F. Mucosal microbiota of intestinal polyps reveals putative biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.Q.; Li, T.; Nakatsu, G.; Chen, Y.-X.; Yau, T.O.; Chu, E.; Wong, S.H.; Szeto, C.H.; Ng, S.C.; Chan, F.K.; et al. A novel faecal Lachnoclostridium marker for the non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal adenoma and cancer. Gut 2019, 69, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.P.; Domingo, M.C.; Lévesque, S.; Yansouni, C.P. A case report of a deep surgical site infection with Terrisporobacter glycolicus/T. Mayombei and review of the literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Cascarano, M.C.; Schlapbach, R.; Katharios, P.; Vaughan, L.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B. Ca. Endozoicomonas cretensis: A novel fish pathogen characterized by genome plasticity. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andree, K.B.; Rodgers, C.J.; Furones, D.; Gisbert, E. Co-infection with Pseudomonas anguilliseptica and Delftia acidovorans in the European eel, Anguilla anguilla (L.): A case history of an illegally trafficked protected species. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davin-Regli, A.; Pagès, J.M. Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae; versatile bacterial pathogens confronting antibiotic treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, L.; Dvorska, L.; Lorencova, A.; Beran, V.; Pavlik, I. Fish: A potential source of bacterial pathogens for human beings. Vet. Med. 2004, 49, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, V.T.; Santiago, T.; Vijayan, K.; Alavandi, S.; Raj, V.S.; Rajan, J.; Sanjuktha, M.; Kalaimani, N. Involvement of Enterobacter cloacae in the mortality of the fish, Mugil cephalus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, M.T.; Kenny, D.J.; Cassilly, C.D.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J.; Clardy, J. Ruminococcus gnavus, a member of the human gut microbiome associated with Crohn’s disease, produces an inflammatory polysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12672–12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.D.; Lu, N.; Wang, Y.T.; Liu, H.N.; Dong, L.; Liu, T.T.; Shen, X.Z. Parasutterella, in association with irrit2 able bowel syndrome and intestinal chronic inflammation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engels, C.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Lacroix, C.; Schwab, C. The Common Gut Microbe Eubacterium hallii also Contributes to Intestinal Propionate Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigwedha, N.; Jia, L. Bifidobacterium in human GI tract: Screening, isolation, survival and growth kinetics in simulated gastrointestinal conditions. In Lactic Acid Bacteria—R & D for Food, Health and Livestock Purposes; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 281–308. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.M.; Zou, K.S.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X.D.; Li, Y.Y.; Gao, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X. Deep insights into gut microbiota in four carnivorous coral reef fishes from the South China Sea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, R.; Miquel, S.; Benevides, L.; Bridonneau, C.; Robert, V.; Hudault, S.; Chain, F.; Berteau, O.; Azevedo, V.; Chatel, J.M.; et al. Functional characterization of novel Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains isolated from healthy volunteers: A step forward in the use of F. prausnitzii as a next-generation probiotic. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1226. [Google Scholar]
- Arboleya, S.; Watkins, C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Gut Bifidobacteria populations in human health and aging. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, C.; Fioramonti, J.; Francois, A.; Robinson, T.; Neant, F.; Matuchansky, C. Review article: Bifidobacteria as probiotic agents—Physiological effects and clinical benefits. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2005, 22, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, M.F.; Laursen, R.P.; Larnkjær, A.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Frøkiær, H.; Bahl, M.I.; Licht, T.R. Faecalibacterium gut colonization accelerated by presence older siblings. mSphere 2017, 2, e00448-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnoy, A.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Srisapoome, P. Acinetobacter strain KUO11TH, a unique organism related to Acinetobacter pittii and isolated from the skin mucus of healthy bighead catfish and its efficacy against several fish pathogens. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gil, B.; Fajer-Avila, E.; García-Vargas, F. Vibrios of the spotted rose snapper Lutjanus guttatus Steindachner, 1869 from northwestern Mexico. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.; Sutherland, R.; Thompson, F.; Swings, J. Pathogenicity of vibrios to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and Artemia nauplii. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musharrafieh, R.; Tacchi, L.; Trujeque, J.; LaPatra, S.; Salinas, I. Staphylococcus warneri, a resident skin commensal of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) with pathobiont characteristics. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.P.; Adley, C.C. Ralstonia spp emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Eur. J. Clin Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 33, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malick, R.C.; Bera, A.K.; Chowdhury, H.; Bhattacharya, M.; Abdulla, T.; Swain, H.S.; Baitha, R.; Kumar, V.; Das, B.K. Identification and pathogenicity study of emerging fish pathogens Acinetobacter junii and Acinetobacter pittii recovered from a disease outbreak in Labeo catla (Hamilton, 1822) and Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Valenciennes, 1844) of freshwater wetland in West Bengal, India. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Wamala, S.P.; Mugimba, K.K.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, Ø.; Mdegela, R.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Sørum, H. Occurrence and antibiotic susceptibility of fish bacteria isolated from Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia) and Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) in Uganda. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2018, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, I. The Mucosal Immune System of Teleost Fish. Biology 2015, 4, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neshani, A.; Zare, H.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; Khaledi, A.; Ghazvini, K. Epinecidin-1, a highly potent marine antimicrobial peptide with anticancer and immunomodulatory activities. BMC Pharm. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, T.; Balcázar, J.L.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Halaihel, N.; Vendrell, D.; Blas, I.D.; Múzquiz, J.L. Host-microbiota interactions within the fish intestinal ecosystem. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 355–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazuria, R.; Pérez, V.; Molina, E.; Juste, R.A.; Khafipour, E.; Elguezabal, N. Diet induced changes in the microbiota and cell composition of rabbit gut associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, Y.; García-Alcázar, A.; Esteban, M.Á.; Cuesta, A.; Chaves-Pozo, E. Antimicrobial response is increased in the testis of European sea bass, but not in gilthead seabream, upon nodavirus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehr, T.; Costa, M.M.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Martin, S.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J. Transforming growth factor-β1b: A second TGF-β1 paralogue in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) that has a lower constitutive expression but is more responsive to immune stimulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Wu, H.; Xiao, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Role of intestinal inflammation in predisposition of Edwardsiella tarda infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Cook, J.A.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Luttrell, L.M.; Wang, L.; Borg, K.; Halushka, P.V.; Fan, H. Increased expression of beta-arrestin 1 and 2 in murine models of rheumatoid arthritis: Isoform specific regulation of inflammation. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 49, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Pereiro, P.; Estensoro, I.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Gómez-Casado, E.; Novoa, B.; Mulero, V.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Differential modulation of IgT and IgM upon parasitic, bacterial, viral, and dietary challenges in a perciform fish. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, C. Effects of fish n-3 PUFAs on intestinal microbiota and immune system. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao Joe, J.T.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Wu, J.-L.; Lu, M.-W. The Alteration of Intestinal Microbiota Profile and Immune Response in Epinephelus coioides during Pathogen Infection. Life 2021, 11, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020099
Xiao Joe JT, Tseng Y-C, Wu J-L, Lu M-W. The Alteration of Intestinal Microbiota Profile and Immune Response in Epinephelus coioides during Pathogen Infection. Life. 2021; 11(2):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020099
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao Joe, Joan Tang, Yung-Che Tseng, Jen-Leih Wu, and Ming-Wei Lu. 2021. "The Alteration of Intestinal Microbiota Profile and Immune Response in Epinephelus coioides during Pathogen Infection" Life 11, no. 2: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020099
APA StyleXiao Joe, J. T., Tseng, Y.-C., Wu, J.-L., & Lu, M.-W. (2021). The Alteration of Intestinal Microbiota Profile and Immune Response in Epinephelus coioides during Pathogen Infection. Life, 11(2), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020099






