HPV and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Brief Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation
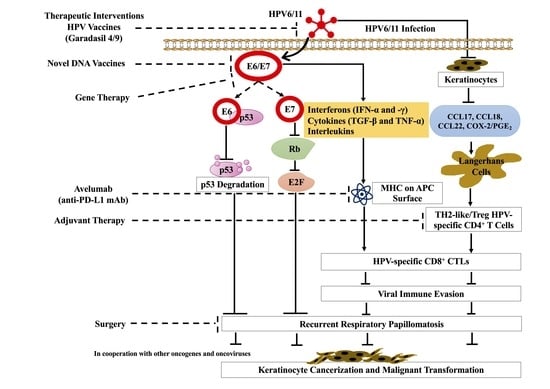
3. Immune Response
4. Malignant Transformation
5. Treatment of RRP
5.1. Surgery
5.2. Adjuvant Therapies
5.3. HPV Vaccines
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AoRRP | Adult-onset RRP |
| APC | Antigen-presenting cell |
| CCL | Chemokines |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CXCL | Chemokine ligand |
| DHE | Di-hematoporphyrin ether |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| HPV | Human papillomavirus |
| HSV-1 | Herpes simplex virus-1 |
| I3C | Indole-3-Carbinol |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factors |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL | Interleukin |
| iLCs | Immature Langerhans cells |
| INF | Interferon |
| IRF | Interferons regulatory factors |
| JoRRP | juvenile-onset |
| MMR | Measles-mumps-rubella |
| KTP | Potassium titanium phosphate |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| RRP | Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| TH2 | T helper type 2 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| Treg | Regulatory T cells |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Langer, C.; Wittekindt, C.; Wolf, G. Laryngeal Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: Current Aspects on Diagnosis and Therapy. Laryngorhinootologie 2019, 98, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkay, C.S.; Bluher, A.E. Update on Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 52, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, H.R.; von Ranke, F.M.; Escuissato, D.L.; Araujo Neto, C.A.; Zanetti, G.; Hochhegger, B.; Souza, C.A.; Marchiori, E. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A state-of-the-art review. Respir. Med. 2017, 126, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seedat, R.Y. Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Diagnosis and Management—A Developing Country Review. Pediatric Health Med. Ther. 2020, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- San Giorgi, M.R.; van den Heuvel, E.R.; Tjon Pian Gi, R.E.; Brunings, J.W.; Chirila, M.; Friedrich, G.; Golusinski, W.; Graupp, M.; Horcasitas Pous, R.A.; Ilmarinen, T.; et al. Age of onset of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A distribution analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2016, 41, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, I.; Montomoli, E. Epidemiology and prevention of Human Papillomavirus. Ann. Ig. 2018, 30, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, B.; Marangoni, B.; Boccardo, E. Human papillomavirus and genome instability: From productive infection to cancer. Clinics 2018, 73, e539s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.A.; Laimins, L.A. Human papillomavirus oncoproteins: Pathways to transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.-E.A. E5 and E6/E7 of high-risk HPVs cooperate to enhance cancer progression through EMT initiation. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Moustafa, A.-E.; Al-Awadhi, R.; Missaoui, N.; Adam, I.; Durusoy, R.; Ghabreau, L.; Akil, N.; Ahmed, H.G.; Yasmeen, A.; Alsbeih, G. Human papillomaviruses-related cancers. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Moustafa, A.-E.; Al-Antary, N.; Aboulkassim, T.; Akil, N.; Batist, G.; Yasmeen, A. Co-prevalence of Epstein–Barr virus and high-risk human papillomaviruses in Syrian women with breast cancer. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessis, T.D.; Connolly, D.C.; Hedrick, L.; Cho, K.R. Expression of HPV16 E6 or E7 increases integration of foreign DNA. Oncogene 1996, 13, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Bodelon, C.; Untereiner, M.E.; Machiela, M.J.; Vinokurova, S.; Wentzensen, N. Genomic characterization of viral integration sites in HPV-related cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakislova, N.; Saco, A.; Sierra, A.; Del Pino, M.; Ordi, J. Role of Human Papillomavirus in Vulvar Cancer. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunade, K.S. Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. J. Obstet Gynaecol. 2020, 40, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, R.; Reddy, V.; Einarsdottir, H.; Longo, W.E. Anorectal human papillomavirus: Current concepts. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2014, 87, 537–547. [Google Scholar]
- Morbini, P.; Alberizzi, P.; Ferrario, G.; Capello, G.; De Silvestri, A.; Pedrazzoli, P.; Tinelli, C.; Benazzo, M. The evolving landscape of human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma at a single institution in Northern Italy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2019, 39, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, E.-M.; Fauquet, C.; Broker, T.R.; Bernard, H.-U.; zur Hausen, H. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology 2004, 324, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, H.-U. The clinical importance of the nomenclature, evolution and taxonomy of human papillomaviruses. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, G.I.; Jaramillo, R.; Cuello, G.; Quintero, K.; Baena, A.; O’Byrne, A.; Reyes, A.J.; Santamaria, C.; Cuello, H.; Arrunategui, A.; et al. Human papillomavirus genotype detection in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) in Colombia. Head Neck 2013, 35, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilboudo, M.; Zohoncon, T.M.; Traore, I.M.A.; Traore, E.M.A.; Kande, A.; Obiri-Yeboah, D.; Djigma, F.W.; Gyebre, Y.M.C.; Simpore, J. Implication of low risk human papillomaviruses, HPV6 and HPV11 in laryngeal papillomatosis in Burkina Faso. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welschmeyer, A.; Berke, G.S. An updated review of the epidemiological factors associated with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2021, 6, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.T.; Longworth, M.S.; Laimins, L.A. Roles of the E6 and E7 proteins in the life cycle of low-risk human papillomavirus type 11. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2620–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lépine, C.; Voron, T.; Berrebi, D.; Mandavit, M.; Nervo, M.; Outh-Gauer, S.; Péré, H.; Tournier, L.; Teissier, N.; Tartour, E.; et al. Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Aggressiveness: In Situ Study of the Level of Transcription of HPV E6 and E7. Cancers 2020, 12, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; MacIntyre, D.A.; Marchesi, J.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Bennett, P.R.; Kyrgiou, M. The vaginal microbiota, human papillomavirus infection and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: What do we know and where are we going next? Microbiome 2016, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toh, Z.; Kosasih, J.; Russell, F.M.; Garland, S.M.; Mulholland, E.K.; Licciardi, P.V. Recombinant human papillomavirus nonavalent vaccine in the prevention of cancers caused by human papillomavirus. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1951–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.M.; Park, J.S.; Norwitz, E.R.; Koo, J.N.; Oh, I.H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.W.; Song, Y.S. Risk of vertical transmission of human papillomavirus throughout pregnancy: A prospective study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatesan, N.N.; Pine, H.S.; Underbrink, M.P. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 45, 671–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, A.C.; Mariz, F.C.; Silva, M.A.; Jesus, A.L. Human papillomavirus vertical transmission: Review of current data. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zgura, A.F.; Bratila, E.; Vladareanu, S. Transplacental Transmission of Human Papillomavirus. Maedica 2015, 10, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen, S.; Rintala, M.; Sarkola, M.; Willberg, J.; Rautava, J.; Koskimaa, H.; Paaso, A.; Syrjänen, K.; Grénman, S.; Louvanto, K. Oral Human Papillomavirus Infection in Children during the First 6 Years of Life, Finland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzistamatiou, K.; Sotiriadis, A.; Agorastos, T. Effect of mode of delivery on vertical human papillomavirus transmission—A meta-analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 36, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.V.; Stern, W.F.; Shah, F.K.; Bishai, D.; Kashima, H.K. Risk factors for juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1998, 17, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, H.K.; Shah, F.; Lyles, A.; Glackin, R.; Muhammad, N.; Turner, L.; Van Zandt, S.; Whitt, S.; Shah, K. A comparison of risk factors in juvenile-onset and adult-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 1992, 102, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S.; Wiatrak, B. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zouridis, A.; Kalampokas, T.; Panoulis, K.; Salakos, N.; Deligeoroglou, E. Intrauterine HPV transmission: A systematic review of the literature. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 298, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, E.M.; Sandstrom, R.E.; zur Hausen, H.; Buck, C.E. Presence of papillomavirus sequences in condylomatous lesions of the mamillae and in invasive carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R1–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, I.H.; Ryu, H.M.; Cho, A.R.; Kang, Y.S.; Hong, S.R.; Kim, S.S.; Seong, S.J.; Shin, S.M.; et al. Rate of vertical transmission of human papillomavirus from mothers to infants: Relationship between infection rate and mode of delivery. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seedat, R.Y.; Schall, R. Age of diagnosis, incidence and prevalence of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis-A South African perspective. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, H.; Mounts, P.; Leventhal, B.; Hruban, R.H. Sites of predilection in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1993, 102, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.; Shamil, E.; Aymat-Torrente, A.; Gibbins, N.; Harris, S. Management of laryngeal papillomatosis using coblation: Another option of surgical intervention. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.; Katundu, D.; Chussi, D.; Shija, P. Prevalence, clinical presentations, associated risk factors and recurrence of laryngeal papillomatosis among inpatients attended at a Tertiary Hospital in Northern zone Tanzania. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2018, 30, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knör, M.; Tziridis, K.; Agaimy, A.; Zenk, J.; Wendler, O. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Prevalence in Nasal and Antrochoanal Polyps and Association with Clinical Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seedat, R.Y. The incidence and prevalence of juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in the Free State province of South Africa and Lesotho. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 2113–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulwafu, W.; Ensink, R.; Kuper, H.; Fagan, J. Survey of ENT services in sub-Saharan Africa: Little progress between 2009 and 2015. Glob Health Action 2017, 10, 1289736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peer, S.; Vial, I.; Numanoglu, A.; Fagan, J.J. What is the availability of services for paediatric ENT surgery and paediatric surgery in Africa? Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2018, 135, S79–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, M.J.; Thorsen, P.; Lindeberg, H.; Ahdieh-Grant, L.; Shah, K.V. Clinical course of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in Danish children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawlor, C.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bottero, S.; Boudewyns, A.; Campisi, P.; Carter, J.; Cheng, A.; Cocciaglia, A.; DeAlarcon, A.; Derkay, C.; et al. International Pediatric Otolaryngology Group (IPOG): Juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis consensus recommendations. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 128, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiori, E.; Araujo Neto, C.; Meirelles, G.S.; Irion, K.L.; Zanetti, G.; Missrie, I.; Sato, J. Laryngotracheobronchial papillomatosis: Findings on computed tomography scans of the chest. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2008, 34, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusconi, M.; Grasso, M.; Greco, A.; Gallo, A.; Campo, F.; Remacle, M.; Turchetta, R.; Pagliuca, G.; De Vincentiis, M. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis by HPV: Review of the literature and update on the use of cidofovir. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Ağgünlü, L.; Erbaş, G. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with lung involvement. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 15, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Wang, H.C.; Wu, M.T.; Lu, J.Y. Virtual bronchoscopy for diagnosis of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2006, 105, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauz, P.S.; Zago, M.; Kurth, R.; Pawlita, M.; Holderried, M.; Thiericke, J.; Iftner, A.; Stubenrauch, F.; Sotlar, K.; Iftner, T. A case of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with malignant transformation, HPV11 DNAemia, high L1 antibody titre and a fatal papillary endocardial lesion. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marchiori, E.; Pozes, A.S.; Souza Junior, A.S.; Escuissato, D.L.; Irion, K.L.; Araujo Neto, C.; Barillo, J.L.; Souza, C.A.; Zanetti, G. Diffuse abnormalities of the trachea: Computed tomography findings. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2008, 34, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taliercio, S.; Cespedes, M.; Born, H.; Ruiz, R.; Roof, S.; Amin, M.R.; Branski, R.C. Adult-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A review of disease pathogenesis and implications for patient counseling. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, A.L.; Steinberg, B.M.; Winkler, B. Laryngeal papillomatosis: Clinical, histopathologic and molecular studies. Laryngoscope 1987, 97, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrak, B.J. Overview of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 11, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, P.; Hawkes, M.; Simpson, K.; Canadian Juvenile Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Working Group. The epidemiology of juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis derived from a population level national database. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tuong, Z.K.; Frazer, I.H. Papillomavirus Immune Evasion Strategies Target the Infected Cell and the Local Immune System. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guess, J.C.; McCance, D.J. Decreased migration of Langerhans precursor-like cells in response to human keratinocytes expressing human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7 is related to reduced macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha production. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14852–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiser, J.; Hurst, J.; Voges, M.; Krauss, P.; Münch, P.; Iftner, T.; Stubenrauch, F. High-risk human papillomaviruses repress constitutive kappa interferon transcription via E6 to prevent pathogen recognition receptor and antiviral-gene expression. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11372–11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Cho, M.C.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, K.A.; Ko, K.K.; Choe, Y.K.; Park, S.N.; Hoshino, T.; Kim, S.; et al. Both E6 and E7 oncoproteins of human papillomavirus 16 inhibit IL-18-induced IFN-gamma production in human peripheral blood mononuclear and NK cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Meyers, C.; Backendorf, C.; Ludigs, K.; Offringa, R.; van Ommen, G.J.; Melief, C.J.; van der Burg, S.H.; Boer, J.M. Human papillomavirus deregulates the response of a cellular network comprising of chemotactic and proinflammatory genes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kang, J.W.; Cho, M.; Cho, C.W.; Lee, S.; Choe, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Choi, I.; Park, S.N.; Kim, S.; et al. Down modulation of IL-18 expression by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncogene via binding to IL-18. FEBS Lett. 2001, 501, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.M.; McCance, D.J. Down regulation of the interleukin-8 promoter by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 through effects on CREB binding protein/p300 and P/CAF. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8710–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeVoti, J.; Hatam, L.; Lucs, A.; Afzal, A.; Abramson, A.; Steinberg, B.; Bonagura, V. Decreased Langerhans cell responses to IL-36γ: Altered innate immunity in patients with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, M.; Purwar, R.; Hartmann, C.; Gutzmer, R.; Werfel, T. Human keratinocytes respond to interleukin-18: Implication for the course of chronic inflammatory skin diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, K.H.; Doble, R.; Wasson, C.W.; Haider, M.; Blair, G.E.; Wittmann, M.; Macdonald, A.; Imperiale, M.J. Human Papillomavirus E7 Oncoprotein Increases Production of the Anti-Inflammatory Interleukin-18 Binding Protein in Keratinocytes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4173–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonsson, A.; Payne, E.; Hengst, K.; McMillan, N.A. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein binds human interferon regulatory factor-9 via a novel PEST domain required for transformation. J. Interferon. Cytokine Res. 2006, 26, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordano, P.; Gillan, V.; Bratlie, S.; Bouvard, V.; Banks, L.; Tommasino, M.; Campo, M.S. The E6E7 oncoproteins of cutaneous human papillomavirus type 38 interfere with the interferon pathway. Virology 2008, 377, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byg, L.M.; Vidlund, J.; Vasiljevic, N.; Clausen, D.; Forslund, O.; Norrild, B. NF-κB signalling is attenuated by the E7 protein from cutaneous human papillomaviruses. Virus. Res. 2012, 169, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermark, E.R.; Deluca, K.A.; Gardner, C.R.; Marker, D.F.; Schreiner, C.N.; Strickland, D.A.; Wilton, K.M.; Mondal, S.; Woodworth, C.D. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E 7 proteins alter NF-kB in cultured cervical epithelial cells and inhibition of NF-kB promotes cell growth and immortalization. Virology 2012, 425, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietenpol, J.A.; Stein, R.W.; Moran, E.; Yaciuk, P.; Schlegel, R.; Lyons, R.M.; Pittelkow, M.R.; Münger, K.; Howley, P.M.; Moses, H.L. TGF-beta 1 inhibition of c-myc transcription and growth in keratinocytes is abrogated by viral transforming proteins with pRB binding domains. Cell 1990, 61, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münger, K.; Basile, J.R.; Duensing, S.; Eichten, A.; Gonzalez, S.L.; Grace, M.; Zacny, V.L. Biological activities and molecular targets of the human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7888–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnard, P.; McMillan, N.A. The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein abrogates signaling mediated by interferon-alpha. Virology 1999, 259, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Hwang, E.S.; Namkoong, S.E.; Um, S.J. Inactivation of interferon regulatory factor-1 tumor suppressor protein by HPV E7 oncoprotein. Implication for the E7-mediated immune evasion mechanism in cervical carcinogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6764–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, A.; Papendick, U.; Gissmann, L.; De Villiers, E.M. Interferon treatment of human genital papillomavirus infection: Importance of viral type. Int. J. Cancer 1987, 40, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israr, M.; DeVoti, J.A.; Lam, F.; Abramson, A.L.; Steinberg, B.M.; Bonagura, V.R. Altered Monocyte and Langerhans Cell Innate Immunity in Patients With Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. Th1 and Th2 in human diseases. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 80, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonagura, V.R.; Hatam, L.J.; Rosenthal, D.W.; de Voti, J.A.; Lam, F.; Steinberg, B.M.; Abramson, A.L. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A complex defect in immune responsiveness to human papillomavirus-6 and -11. APMIS 2010, 118, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D.W.; DeVoti, J.A.; Steinberg, B.M.; Abramson, A.L.; Bonagura, V.R. T(H)2-like chemokine patterns correlate with disease severity in patients with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVoti, J.A.; Rosenthal, D.W.; Wu, R.; Abramson, A.L.; Steinberg, B.M.; Bonagura, V.R. Immune dysregulation and tumor-associated gene changes in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A paired microarray analysis. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadas, R.A.; Li, X.; Shubitowski, D.M.; Samineni, S.; Wills-Karp, M.; Ewart, S.L. IL-1 Receptor antagonist as a positional candidate gene in a murine model of allergic asthma. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Bishop, J.A.; Roden, R.B.S.; Allen, C.T.; Best, S.R.A. The PD-1 and PD-L1 pathway in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, E27–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancic, R.; Iqbal, H.; deSilva, B.; Pan, Q.; Matrka, L. Immunological tolerance of low-risk HPV in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Drake, C.G.; Wollner, I.; Powderly, J.D.; Picus, J.; Sharfman, W.H.; Stankevich, E.; Pons, A.; Salay, T.M.; McMiller, T.L.; et al. Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: Safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3167–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, C.; Hamilton, J.; Birzgalis, A.R.; Farrington, W.T. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis—The Manchester experience, 1974–1992. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1994, 108, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.R.; Hill, D.A.; Humphrey, P.A.; Pfeifer, J.D.; El-Mofty, S.K. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with pulmonary involvement: Emerging common pattern of clinical features and human papillomavirus serotype association. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, P.L.; Schnadig, V.J.; Weiss, R.L.; Hughes, T.K.; Tyring, S.K. Malignant transformation of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis associated with integrated human papillomavirus type 11 DNA and mutation of p53. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, D.; El Haddad, B. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lungs arising in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Respir. Med. CME 2010, 3, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanazawa, T.; Fukushima, N.; Imayoshi, S.; Nagatomo, T.; Kawada, K.; Nishino, H.; Misawa, K.; Ichimura, K. Rare case of malignant transformation of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis associated with human papillomavirus type 6 infection and p53 overexpression. Springerplus 2013, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reidy, P.M.; Dedo, H.H.; Rabah, R.; Field, J.B.; Mathog, R.H.; Gregoire, L.; Lancaster, W.D. Integration of human papillomavirus type 11 in recurrent respiratory papilloma-associated cancer. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoulis, V.; Rassidakis, G.; Karameris, A.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Barbatis, C.; Kittas, C. Expression of p53 protein in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and dysplasia: Possible correlation with human papillomavirus infection and clinicopathological findings. Virchows. Arch. 1994, 425, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabah, R.; Lancaster, W.D.; Thomas, R.; Gregoire, L. Human papillomavirus-11-associated recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is more aggressive than human papillomavirus-6-associated disease. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2001, 4, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerein, V.; Rastorguev, E.; Gerein, J.; Jecker, P.; Pfister, H. Use of interferon-alpha in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: 20-year follow-up. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2005, 114, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.E.; Wiatrak, B.J.; McClatchey, K.D.; Koopmann, C.F.; Thomas, G.R.; Bradford, C.R.; Carey, T.E. High-risk human papillomavirus types and squamous cell carcinoma in patients with respiratory papillomas. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 120, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Coffino, P. High-risk human papillomavirus E6 protein has two distinct binding sites within p53, of which only one determines degradation. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4509–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heck, D.V.; Yee, C.L.; Howley, P.M.; Münger, K. Efficiency of binding the retinoblastoma protein correlates with the transforming capacity of the E7 oncoproteins of the human papillomaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4442–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, W.; Roman, A. The E7 proteins of low- and high-risk human papillomaviruses share the ability to target the pRB family member p130 for degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korzeniewski, N.; Spardy, N.; Duensing, A.; Duensing, S. Genomic instability and cancer: Lessons learned from human papillomaviruses. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McBride, A.A.; Warburton, A. The role of integration in oncogenic progression of HPV-associated cancers. PLoS Pathog 2017, 13, e1006211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Moustafa, A.E.; Foulkes, W.D.; Wong, A.; Jallal, H.; Batist, G.; Yu, Q.; Herlyn, M.; Sicinski, P.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. Cyclin D1 is essential for neoplastic transformation induced by both E6/E7 and E6/E7/ErbB-2 cooperation in normal cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5252–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Moustafa, A.E.; Foulkes, W.D.; Benlimame, N.; Wong, A.; Yen, L.; Bergeron, J.; Batist, G.; Alpert, L.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. E6/E7 proteins of HPV type 16 and ErbB-2 cooperate to induce neoplastic transformation of primary normal oral epithelial cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Moustafa, A.E.; Chen, D.; Ghabreau, L.; Akil, N. Association between human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus infections in human oral carcinogenesis. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pou, A.M.; Rimell, F.L.; Jordan, J.A.; Shoemaker, D.L.; Johnson, J.T.; Barua, P.; Post, J.C.; Ehrlich, G.D. Adult respiratory papillomatosis: Human papillomavirus type and viral coinfections as predictors of prognosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1995, 104, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimell, F.L.; Shoemaker, D.L.; Pou, A.M.; Jordan, J.A.; Post, J.C.; Ehrlich, G.D. Pediatric respiratory papillomatosis: Prognostic role of viral typing and cofactors. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehoux, M.; D’Abramo, C.M.; Archambault, J. Molecular mechanisms of human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis. Public Health Genom. 2009, 12, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriconi, A.; Cesta, M.C.; Cervellera, M.N.; Aramini, A.; Coniglio, S.; Colagioia, S.; Beccari, A.R.; Bizzarri, C.; Cavicchia, M.R.; Locati, M.; et al. Design of noncompetitive interleukin-8 inhibitors acting on CXCR1 and CXCR2. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3984–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, K.; Tb, S. Management of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: Current Status. Int. J. Phonosurgery Laryngol. 2011, 1, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancic, R.; Iqbal, H.; deSilva, B.; Pan, Q.; Matrka, L. Current and future management of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, K.; Shapshay, S.M.; McGilligan, J.A.; Wang, Z.; Rebeiz, E.E. A 585-nanometer pulsed dye laser treatment of laryngeal papillomas: Preliminary report. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikowitz, M.J.; Abramson, A.L.; Steinberg, B.M.; DeVoti, J.; Bonagura, V.R.; Mullooly, V.; Nouri, M.; Ronn, A.M.; Inglis, A.; McClay, J.; et al. Clinical trial of photodynamic therapy with meso-tetra (hydroxyphenyl) chlorin for respiratory papillomatosis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeitels, S.M.; Barbu, A.M.; Landau-Zemer, T.; Lopez-Guerra, G.; Burns, J.A.; Friedman, A.D.; Freeman, M.W.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Hillman, R.E. Local injection of bevacizumab (Avastin) and angiolytic KTP laser treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis of the vocal folds: A prospective study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2011, 120, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, G.B.; Gelber, R.D.; Trowbridge, A.L.; Grundfast, K.M.; Ruben, R.J.; Price, K.N. Treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with human leukocyte interferon. Results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, B.G.; Kashima, H.K.; Weck, P.W.; Mounts, P.; Whisnant, J.K.; Clark, K.L.; Cohen, S.; Dedo, H.H.; Donovan, D.J.; Fearon, B.W.; et al. Randomized surgical adjuvant trial of interferon alfa-n1 in recurrent papillomatosis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1988, 114, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, G.C. Mechanism of interferon action: Progress toward its understanding. Prog. Nucleic Acid. Res. Mol. Biol. 1982, 27, 105–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlennen, R.C.; Adams, G.L.; Lewis, C.M.; Faras, A.J.; Ostrow, R.S. Pilot trial of ribavirin for the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis. Head Neck 1993, 15, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, J.; Sreenivas, V.; Hemanth, V.; Nandakumar, R. Management of adult recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with oral acyclovir following micro laryngeal surgery: A case series. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 66, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, M.N.; Galt, L.; Bashirzadeh, F. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: The role of cidofovir. Respirol. Case Rep. 2018, 6, e00371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.; Coniglio, S.J.; Chan, A.; Symons, M.H.; Steinberg, B.M. Up-regulation of Rac1 by epidermal growth factor mediates COX-2 expression in recurrent respiratory papillomas. Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, Z. Celebrex (Celecoxib) Treatment of Laryngeal Papilloma. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT00592319 (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Borkowski, G.; Sommer, P.; Stark, T.; Sudhoff, H.; Luckhaupt, H. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999, 256, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harcourt, J.P.; Worley, G.; Leighton, S.E. Cimetidine treatment for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999, 51, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.; Brodsky, L. Extraesophageal acid reflux and recurrent respiratory papilloma in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 69, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essman, E.J.; Abramson, A. Estrogen binding sites on membranes from human laryngeal papilloma. Int. J. Cancer 1984, 33, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newfield, L.; Goldsmith, A.; Bradlow, H.L.; Auborn, K. Estrogen metabolism and human papillomavirus-induced tumors of the larynx: Chemo-prophylaxis with indole-3-carbinol. Anticancer Res. 1993, 13, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.; Hong, W.K.; Itri, L.M.; McDonald, G.; Strong, M.S. The use of cis-retinoic acid in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis of the larynx: A randomized pilot study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1988, 9, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 605, 33–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Bassat, H.; Rosenbaum-Mitrani, S.; Hartzstark, Z.; Shlomai, Z.; Kleinberger-Doron, N.; Gazit, A.; Plowman, G.; Levitzki, R.; Tsvieli, R.; Levitzki, A. Inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase and of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activation induce growth arrest, differentiation, and apoptosis of human papilloma virus 16-immortalized human keratinocytes. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3741–3750. [Google Scholar]
- Bostrom, B.; Sidman, J.; Marker, S.; Lander, T.; Drehner, D. Gefitinib therapy for life-threatening laryngeal papillomatosis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, A.; Glisinski, K.; Clarke, J.; Lind, R.N.; Buckley, C.E.; Shofer, S. Systemic Bevacizumab for Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Single Center Experience of Two Cases. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.R.; Mohr, M.; Zur, K.B. Systemic bevacizumab for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A national survey. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maturo, S.; Hartnick, C.J. Use of 532-nm pulsed potassium titanyl phosphate laser and adjuvant intralesional bevacizumab for aggressive respiratory papillomatosis in children: Initial experience. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zur, K.B.; Fox, E. Bevacizumab chemotherapy for management of pulmonary and laryngotracheal papillomatosis in a child. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makiyama, K.; Hirai, R.; Matsuzaki, H. Gardasil Vaccination for Recurrent Laryngeal Papillomatosis in Adult Men: First Report: Changes in HPV Antibody Titer. J. Voice 2017, 31, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, L.E.; Dunne, E.F.; Saraiya, M.; Chesson, H.W.; Curtis, C.R.; Gee, J.; Bocchini, J.A.; Unger, E.R. Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Morb. and Mortal. Wkly. Rep. Recomm. Rep. 2014, 63, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mauz, P.S.; Schäfer, F.A.; Iftner, T.; Gonser, P. HPV vaccination as preventive approach for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis—A 22-year retrospective clinical analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, T.; Philipsen, B.B.; Mehlum, C.S.; Dyrvig, A.K.; Wehberg, S.; Chirilǎ, M.; Godballe, C. Therapeutic Use of the Human Papillomavirus Vaccine on Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.P.; Kraynyak, K.A.; Sylvester, A.J.; Shen, X.; Amante, D.; Sakata, L.; Parker, L.; Yan, J.; Boyer, J.; Roh, C.; et al. Augmentation of cellular and humoral immune responses to HPV16 and HPV18 E6 and E7 antigens by VGX-3100. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 16025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, C.; Cohen, R.B.; Morrow, M.P.; Kraynyak, K.A.; Sylvester, A.J.; Cheung, J.; Dickerson, K.; Schulten, V.; Knoblock, D.; Gillespie, E.; et al. Immune Therapy Targeting E6/E7 Oncogenes of Human Paillomavirus Type 6 (HPV-6) Reduces or Eliminates the Need for Surgical Intervention in the Treatment of HPV-6 Associated Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Vaccines 2020, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, E.R.; Schnack, D.T.; Jørkov, A.S.; Raja, A.A.; Olsen, C.H.; Homøe, P. Long-term follow-up and outcome in patients with recurrent respiratory laryngeal papillomatosis. Dan. Med. J. 2017, 64, A5424. [Google Scholar]
- Yiu, Y.; Fayson, S.; Smith, H.; Matrka, L. Implementation of Routine HPV Vaccination in the Management of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2018, 128, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsenos, S.; Becker, H.D. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A rare chronic disease, difficult to treat, with potential to lung cancer transformation: Apropos of two cases and a brief literature review. Case Rep. Oncol. 2011, 4, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.T.; Lee, S.; Norberg, S.M.; Kovalovsky, D.; Ye, H.; Clavijo, P.E.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Schlegel, R.; Schlom, J.; Strauss, J.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of PD-L1 blockade in patients with aggressive recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brotherton, J. Human papillomavirus vaccination update. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 47, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S.; Smith, R.J.; McClay, J.; van Burik, J.A.; Wiatrak, B.J.; Arnold, J.; Berger, B.; Neefe, J.R. HspE7 treatment of pediatric recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: Final results of an open-label trial. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2005, 114, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Therapy | Treatment | Rationale | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Microdebridement | Removal of papilloma along with maintaining healthy respiratory tract tissue | [109,110] |
| Sharp dissection | |||
| CO2 laser surgery | |||
| Photodynamic Therapy | Di-hematoporphyrin ether (DHE) | Short-term immunologic viral clearance of antigens mediated by IL-10 and IFN-γ on presence of E6/E7 oncoproteins of HPV due to necrosis of infected tissue | [85,111,112] |
| M-tetra(hydroxyphenyl) chlorine | |||
| Photoangiolytic Laser | Potassium titanium phosphate [KTP] | Reduces the infected tissue by disrupting papilloma microcirculation | [111,113] |
| Adjuvant Therapies | Alpha-interferon | They block viral RNA or DNA replication by stimulating protein kinase and endonuclease | [114,115,116] |
| Antiviral Therapies | |||
| Ribavirin | Used to treat respiratory syncytial virus in infants. Used for treatment of aggressive laryngeal RRP | [117] | |
| Acyclovir | Treatment of RRP with co-existing viruses (HSV-1, EBV or cytomegalovirus) as it targets thymidine kinase presented by these viruses | [105,118] | |
| Cidofovir | An analog of cytosine, it reduces DNA transcription efficacy | [119] | |
| Celebrex (Ongoing Clinical Trials) | It is a COX-2 inhibitor and aims to provide a prolonged inhibitory effect on microvascular regrowth and COX-2 enzyme, thus preventing recurrence of RRP | [120,121] | |
| Ranitidine | Demonstrates immunomodulatory effects and reduces RRP recurrence | [122,123,124] | |
| Dietary Supplements | |||
| Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C) | Increases estrogen binding in RRP lesions. In mice, I3C reduced formation of papilloma lesion by 75% | [125,126] | |
| Retinoids, metabolites and Vitamin A | Excess and lack of vitamin A reduces squamous differentiation and induces hyperkeratinization | [127,128] | |
| Inhibitors | |||
| EGFR inhibitors (Gefitinib) | They inhibit epithelial growth and differentiation of HPV16-infected keratinocytes, thus reducing RRP growth. Used in RRP treatment in the presence of extensive tracheobronchial epithelial cells | [129,130] | |
| VEGF inhibitors | Inhibits VEGF activity and prevents receptor activation, thus increasing time between surgical intervention and reduces RRP severity | [131,132,133,134] | |
| Vaccines | HPV Vaccines | ||
| Cervarix | Targets HPVs-16 and -18 | [135,136,137,138] | |
| Gardasil | Targets HPVs-6, -11, -16 and -18 | ||
| Gardasil-9 | Targets HPVs-6, -11, -16, -18, -31, -33, -45, -52 and -58 | ||
| DNA Vaccines | |||
| INO-3016 | Targets the E6/E7 oncoproteins of HPV, creates a T-cell immunological response and reduces surgical intervention | [139,140] | |
| Bivalent Vaccine | Quadrivalent Vaccine | Nonavalent Vaccine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Name | Cervarix | Gardasil | Gardasil-9 |
| Type of Viral-Particle | HPV-16, -18 | HPV-6, -11, -16, -18 | HPV-6, -11, -16, -18, -31, -33, -45, -52 and -58 |
| Expression System | Baculovirus-insect cell | Yeast | Yeast |
| Adjuvant System | AS04 adjuvant system in sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate | Amorphous Aluminum Hydroxyphosphate Sulfate | Amorphous Alumi-num Hydroxyphosphate Sulfate |
| Recommended Dose | 20/20 μg | 20/40/40/20 μg | 30/40/60/40/20/20/20/20/20 μg |
| Scheduled Dose | 0, 1 and 6 months | 0, 2 and 6 months | 0, 2 and 6 months |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouda, A.M.; Elsabagh, A.A.; Elmakaty, I.M.; Gupta, I.; Vranic, S.; Al-Thawadi, H.; Al Moustafa, A.-E. HPV and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Brief Review. Life 2021, 11, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111279
Ouda AM, Elsabagh AA, Elmakaty IM, Gupta I, Vranic S, Al-Thawadi H, Al Moustafa A-E. HPV and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Brief Review. Life. 2021; 11(11):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111279
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuda, Amr Mohamed, Ahmed Adel Elsabagh, Ibrahim Mohamed Elmakaty, Ishita Gupta, Semir Vranic, Hamda Al-Thawadi, and Ala-Eddin Al Moustafa. 2021. "HPV and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Brief Review" Life 11, no. 11: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111279
APA StyleOuda, A. M., Elsabagh, A. A., Elmakaty, I. M., Gupta, I., Vranic, S., Al-Thawadi, H., & Al Moustafa, A.-E. (2021). HPV and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Brief Review. Life, 11(11), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111279