Respiratory and Systemic Toxicity of Inhaled Artificial Asian Sand Dust in Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Artificial ASD
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Laboratory Blood Tests
2.5. Cytokine Analysis
2.6. Pathological Examination
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pigs Exposed to ASD Have a Predisposition to Systemic Inflammation and Organ Dysfunction
3.2. ASD Inhalation Provokes Systemic Hyperinflammatory Responses in Domestic Animals
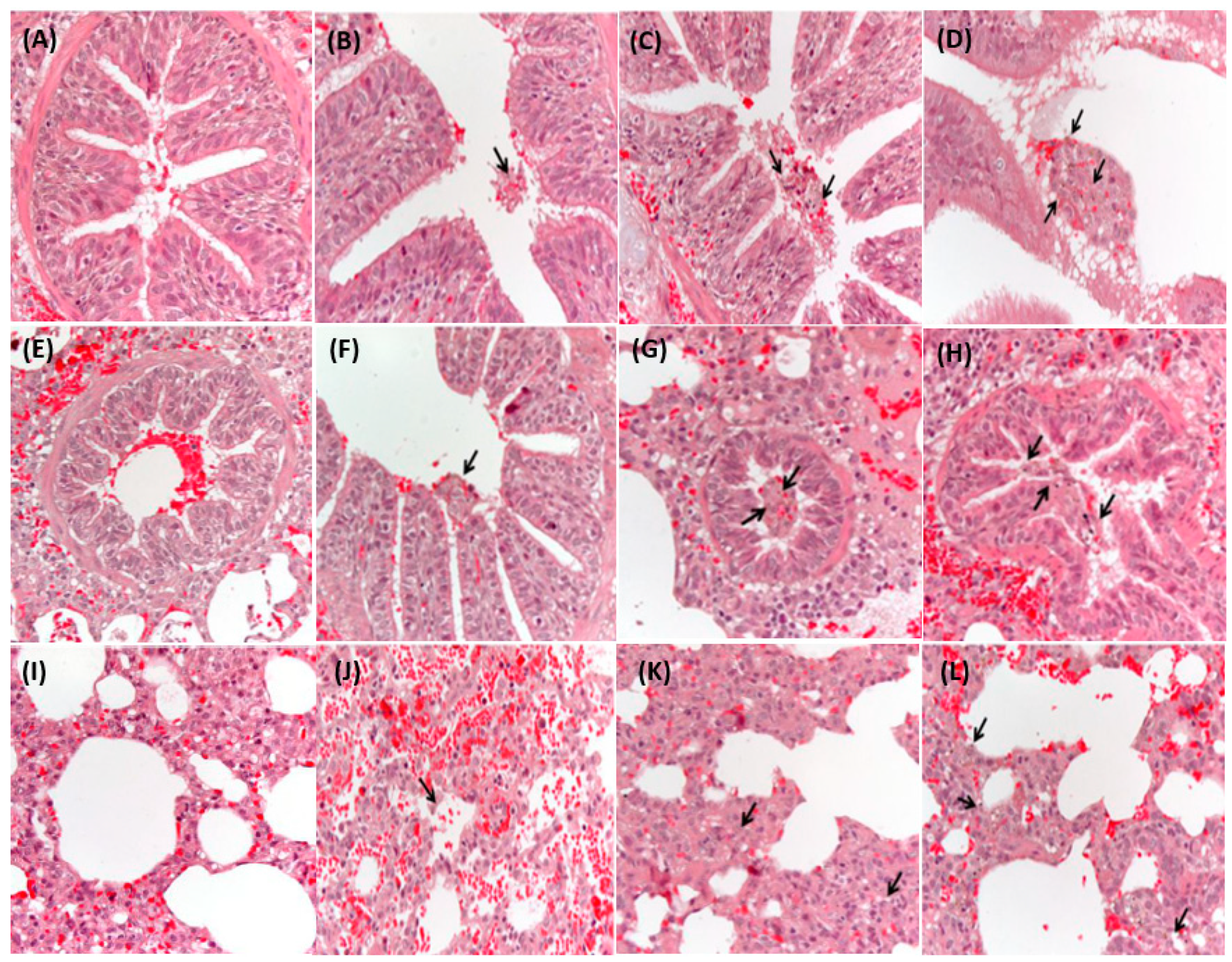
3.3. Experimental ASD Exposure Causes Toxicity in the Porcine Respiratory System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coulibaly, S.; Minami, H.; Abe, M.; Hasei, T.; Oro, T.; Funasaka, K.; Asakawa, D.; Watanabe, M.; Honda, N.; Wakabayashi, K.; et al. Long-range transport of mutagens and other air pollutants from mainland East Asia to western Japan. Genes Environ. 2015, 37, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. Cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudie, A.S. Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, E.J.; Kliebenstein, J.B.; Johnson, C.D.; Mabry, J.W.; Bush, E.J.; Seitzinger, A.H.; Green, A.L.; Zimmerman, J.J. Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome on swine production in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 227, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naota, M.; Mukaiyama, T.; Shimada, A.; Yoshida, A.; Okajima, M.; Morita, T.; Inoue, K.; Takano, H. Pathological study of acute pulmonary toxicity induced by intratracheally instilled Asian sand dust (Kosa). Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Lim, Y.H.; Kyung, S.Y.; An, C.H.; Lee, S.P.; Jeong, S.H.; Ju, Y.S. Effects of ambient particulate matter on peak expiratory flow rates and respiratory symptoms of asthmatics during Asian dust periods in Korea. Respirology 2005, 10, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Choi, B.; Yi, S.M.; Ko, G. Characterization of microbial community during Asian dust events in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, M.; Ueda, K.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Michikawa, T.; Onozuka, D. Health effects of Asian dust events: A review of the literature. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 2010, 65, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Cho, S.H.; Chun, Y.; Lagarde, F.; Pershagen, G. Effects of the Asian dust events on daily mortality in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Res. 2002, 90, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castranova, V.; Porter, D.; Millecchia, L.; Ma, J.Y.; Hubbs, A.F.; Teass, A. Effect of inhaled crystalline silica in a rat model: Time course of pulmonary reactions. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2002, 234, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, T.; Yoshida, S.; Hiyoshi, K.; Sadakane, K.; Takano, H.; Nishikawa, M.; Mori, I.; Yanagisawa, R.; Kawazato, H.; Yasuda, A.; et al. The effects of microbial materials adhered to Asian sand dust on allergic lung inflammation. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, M.J.; Pearson, G.R.; Lucke, V.M.; Lane, S.J.; Sparks, R.S. Lesions associated with mineral deposition in the lymph node and lung of the dog. Vet. Pathol. 1996, 33, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Shimada, A.; Nemoto, M.; Morita, T.; Adilbish, A.; Bayasgalan, M.O. Adverse effects of inhaled sand dust particles on the respiratory organs of sheep and goats exposed to severe sand storms in Mongolia. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2014, 52, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C. Impact of chronic and acute inflammation on extra- and intracellular iron homeostasis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1581S–1587S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.N. Anemia of Inflammation. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2010, 2010, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, M. Application of acute phase proteins as biomarkers in modern veterinary science. Ind. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. Res. 2014, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, S.L.; Weinberg, A.D.; English, M.; Huston, G. IL-4 directs the development of Th2-like helper effectors. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3796–3806. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, K.; Robinson, D.; Zonin, F.; Hartley, S.B.; Macatonia, S.E.; Somoza, C.; Hunter, C.A.; Murphy, K.M.; O’Garra, A. IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha are required for IL-12-induced development of Th1 cells producing high levels of IFN-gamma in BALB/c but not C57BL/6 mice. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman, F.D.; Holmes, J.; Katona, I.M.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Beckmann, M.P.; Park, L.S.; Schooley, K.A.; Coffman, R.L.; Mosmann, T.R.; Paul, W.E. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1990, 8, 303–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, W.E. Interleukin-4: A prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood 1991, 77, 1859–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ban, Y.; Wei, F.; Ma, X. Regulation of Interleukin-12 Production in Antigen-Presenting Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 941, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.G.; Dee, S.A. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Theriogenology 2006, 66, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurai, J.; Watanabe, M.; Sano, H.; Hantan, D.; Tohda, Y.; Shimizu, E. Effects of asian dust particles on the early-stage antigen-induced immune response of asthma in Nc/Nga mice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Murayama, R.; Tsuji, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Koike, E.; Yoshida, S.; Ichinose, T.; Takano, H. Effects of Asian sand dust particles on the respiratory and immune system. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 34, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, T.; Yamagami, S.; Fujishima, H.; Noma, H.; Kamei, Y.; Goto, M.; Kondo, A.; Matsubara, M. Sensitization to Asian dust and allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Blood Indices | Before Exposure of Artificial ASD | After Exposure of Artificial ASD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h | 12 h | 24 h | 72 h | ||
| N = 16 | N = 12 | N = 9 | N = 6 | N = 3 | |
| WBC (K/μL) | 19.24 ± 6.70 | 22.25 ± 6.31 | 21.06 ± 4.28 | 19.14 ± 4.52 | 33.95 ± 11.41 |
| NEU (K/μL) | 6.70 ± 3.75 | 6.51 ± 2.23 | 6.87 ± 3.09 | 5.80 ± 1.87 | 11.36 ± 2.62 |
| LYM (K/μL) † | 6.57 ± 3.26 | 9.35 ± 2.98 | 9.12 ± 2.28 | 8.72 ± 2.50 | 10.11 ± 3.76 |
| MONO (K/μL) † | 2.01 ± 0.79 | 1.84 ± 0.72 | 2.31 ± 0.97 | 1.71 ± 0.78 | 4.63 a ± 2.22 |
| EOS (K/μL) | 3.78 ± 2.47 | 3.75 ± 2.45 | 2.71 ± 1.35 | 2.85 ± 1.20 | 7.04 ± 3.20 |
| BASO (K/μL) † | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.12 ± 0.08 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.63 ± 0.51 |
| RBC (M/μL) | 6.17 ± 0.08 | 13.73 ± 3.87 | 11.38 ± 2.51 | 10.22 ± 1.71 | 13.22 ± 4.71 |
| Hb (g/μL) | 16.33 ± 4.69 | 14.35 ± 3.46 | 9.38 ± 3.25 | 11.02 ± 1.68 | 13.20 ± 2.76 |
| MCV (fL/μL) | 51.03 ± 5.27 | 55.59 ± 1.77 | 49.00 ± 2.69 | 49.53 ± 2.55 | 61.10 ± 1.31 |
| ALB(g/dL) † | 3.43 ± 0.26 | 3.15 ± 0.52 | 3.66 ± 0.91 | 3.37 ± 0.91 | 1.91 b ± 0.10 |
| pCO2 (mgHg) † | 59.67 ± 8.82 | 68.15 ± 11.37 | 70.78 ± 6.53 | 73.00 ± 5.22 | 79.00 ± 19.97 |
| HCO3− (mEq/L) | 28.65 ± 5.35 | 31.17 ± 3.97 | 30.06 ± 4.07 | 31.42 ± 5.23 | 27.07 ± 6.05 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 8.85 ± 3.92 | 8.79 ± 2.66 | 8.35 ± 4.38 | 10.43 ± 3.24 | 11.40 ± 2.61 |
| Na+ (mEq/L) | 145.53 ± 3.44 | 145.62 ± 4.15 | 143.67 ± 2.25 | 145.00 ± 4.29 | 144.67 ± 1.53 |
| K+ (mEq/L) | 6.13 ± 1.35 | 6.63 ± 1.29 | 6.57 ± 1.40 | 5.53 ± 0.81 | 9.53 ± 0.68 |
| Airway | Before Exposure of Artificial ASD | After Exposure of Artificial ASD | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h | 12 h | 24 h | 72 h | |||||||
| N = 16 | N = 12 | N = 9 | N = 6 | N = 3 | ||||||
| Lt | Rt | Lt | Rt | Lt | Rt | Lt | Rt | Lt | Rt | |
| Bronchus | 0% (0/19) | 0% (0/14) | 40.0% (12/30) | 46.4% (13/28) | 42.4% (14/33) | 33.3% (10/30) | 20.8% (5/24) | 25.6% (7/27) | 20% (5/25) | 19.4% (6/31) |
| Bronchioles | 0% (0/37) | 0% (0/37) | 77.5% (62/80) | 72.4% (55/76) | 63.2% (36/57) | 56.7% (34/60) | 52.8% (28/53) | 51.0% (25/49) | 36.2% (21/58) | 29.6% (16/54) |
| Alveolus | 0% (0/120) | 0% (0/120) | 65.8% (158/240) | 60.9% (140/230) | 60.0% (96/160) | 56.8% (84/148) | 45.0% (81/180) | 39.4% (71/180) | 33.9% (81/180) | 22.8% (41/180) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Kim, S.-D.; Shin, T.-H.; Bae, C.-S.; Ahn, T.; Shin, S.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, C.-M.; Suh, G.-H. Respiratory and Systemic Toxicity of Inhaled Artificial Asian Sand Dust in Pigs. Life 2021, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010025
Kim K, Kim S-D, Shin T-H, Bae C-S, Ahn T, Shin S-S, Kim H-J, Lee C-M, Suh G-H. Respiratory and Systemic Toxicity of Inhaled Artificial Asian Sand Dust in Pigs. Life. 2021; 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Keon, Seon-Deuk Kim, Tae-Hoon Shin, Chun-Sik Bae, Taeho Ahn, Sung-Shik Shin, Ha-Jung Kim, Chang-Min Lee, and Guk-Hyun Suh. 2021. "Respiratory and Systemic Toxicity of Inhaled Artificial Asian Sand Dust in Pigs" Life 11, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010025
APA StyleKim, K., Kim, S.-D., Shin, T.-H., Bae, C.-S., Ahn, T., Shin, S.-S., Kim, H.-J., Lee, C.-M., & Suh, G.-H. (2021). Respiratory and Systemic Toxicity of Inhaled Artificial Asian Sand Dust in Pigs. Life, 11(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010025




