Position Estimation of a Two-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor at Standstill
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Position Estimation Method at Standstill
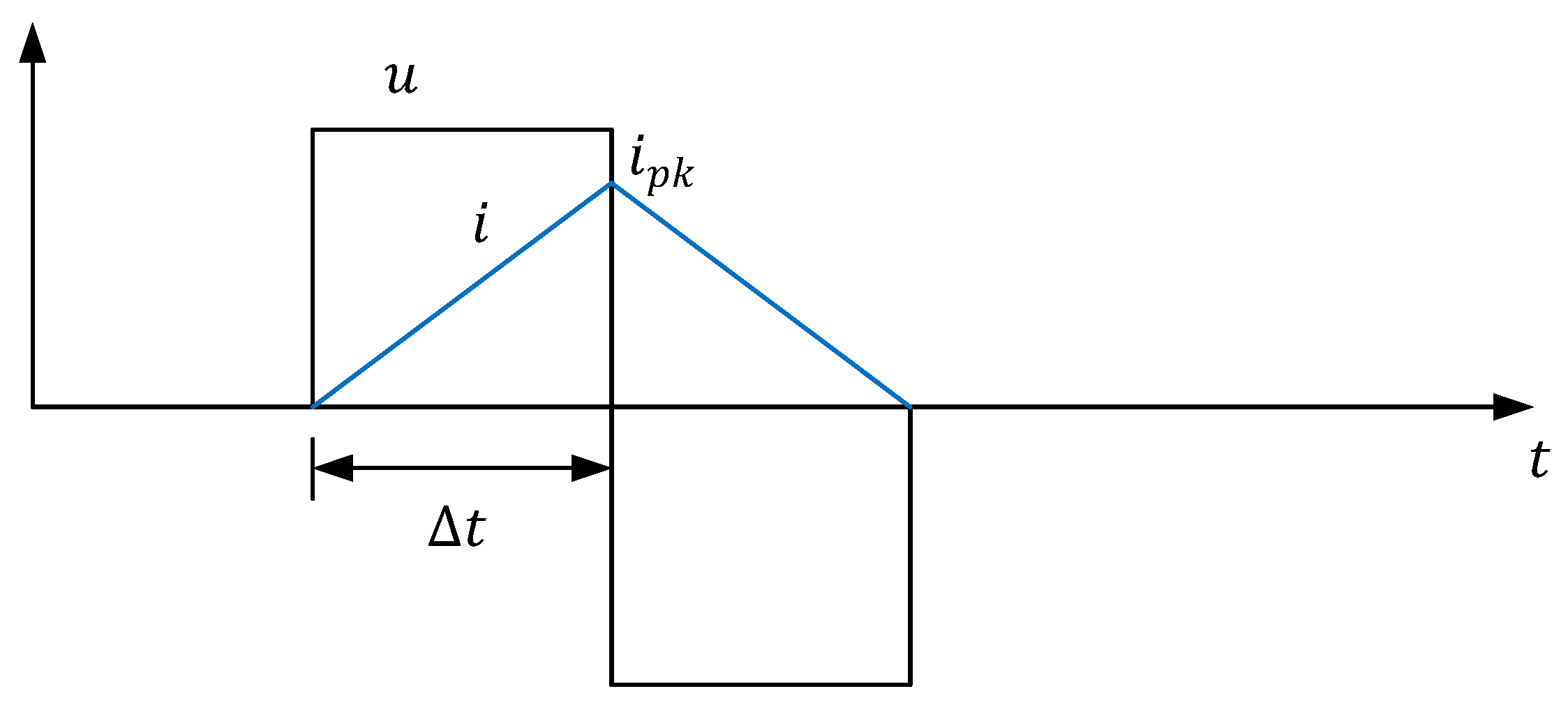
2.1. Principle of the Pulse Injection Method
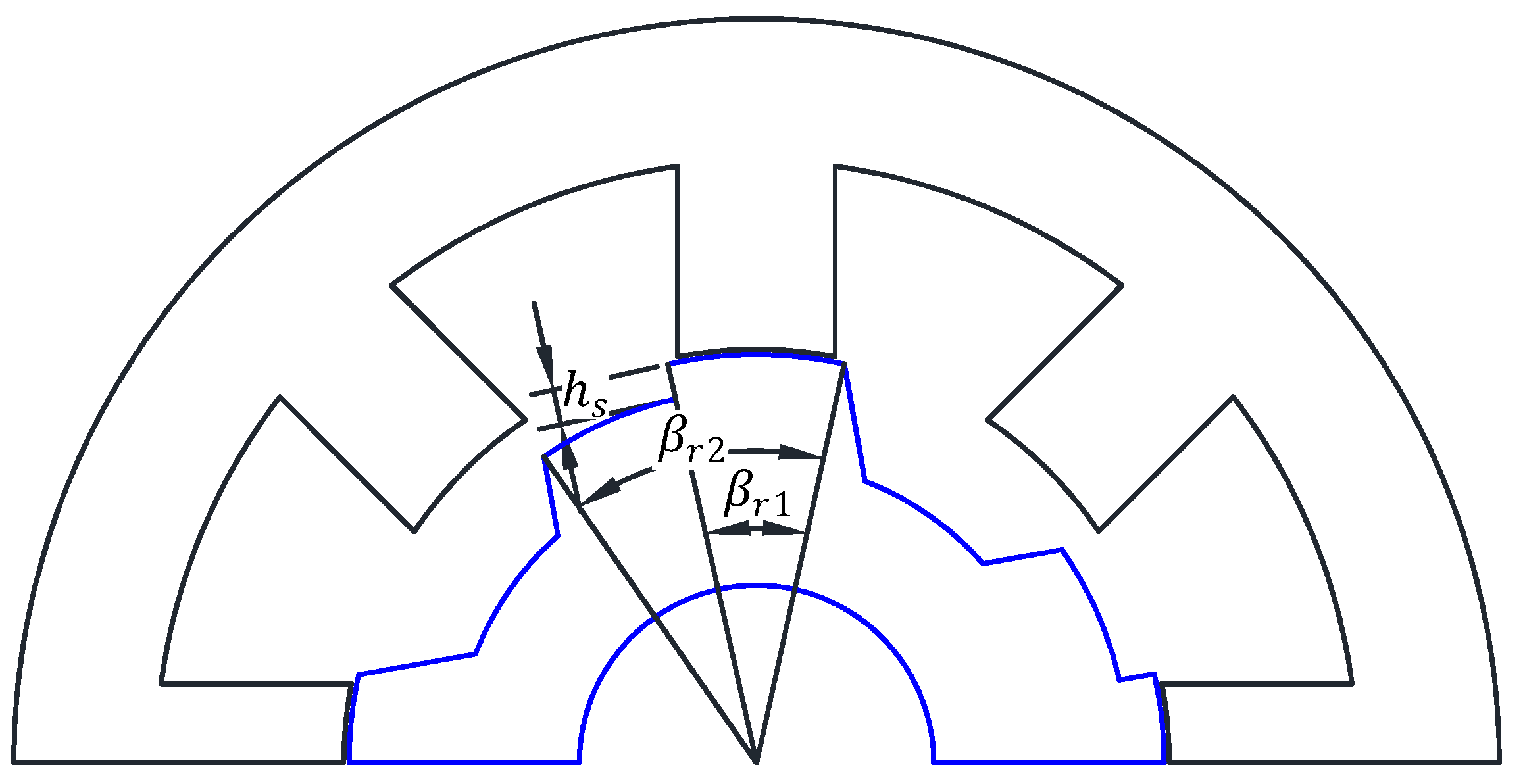
2.2. Inductance Model of a Two-Phase SRM with a Stepped Rotor
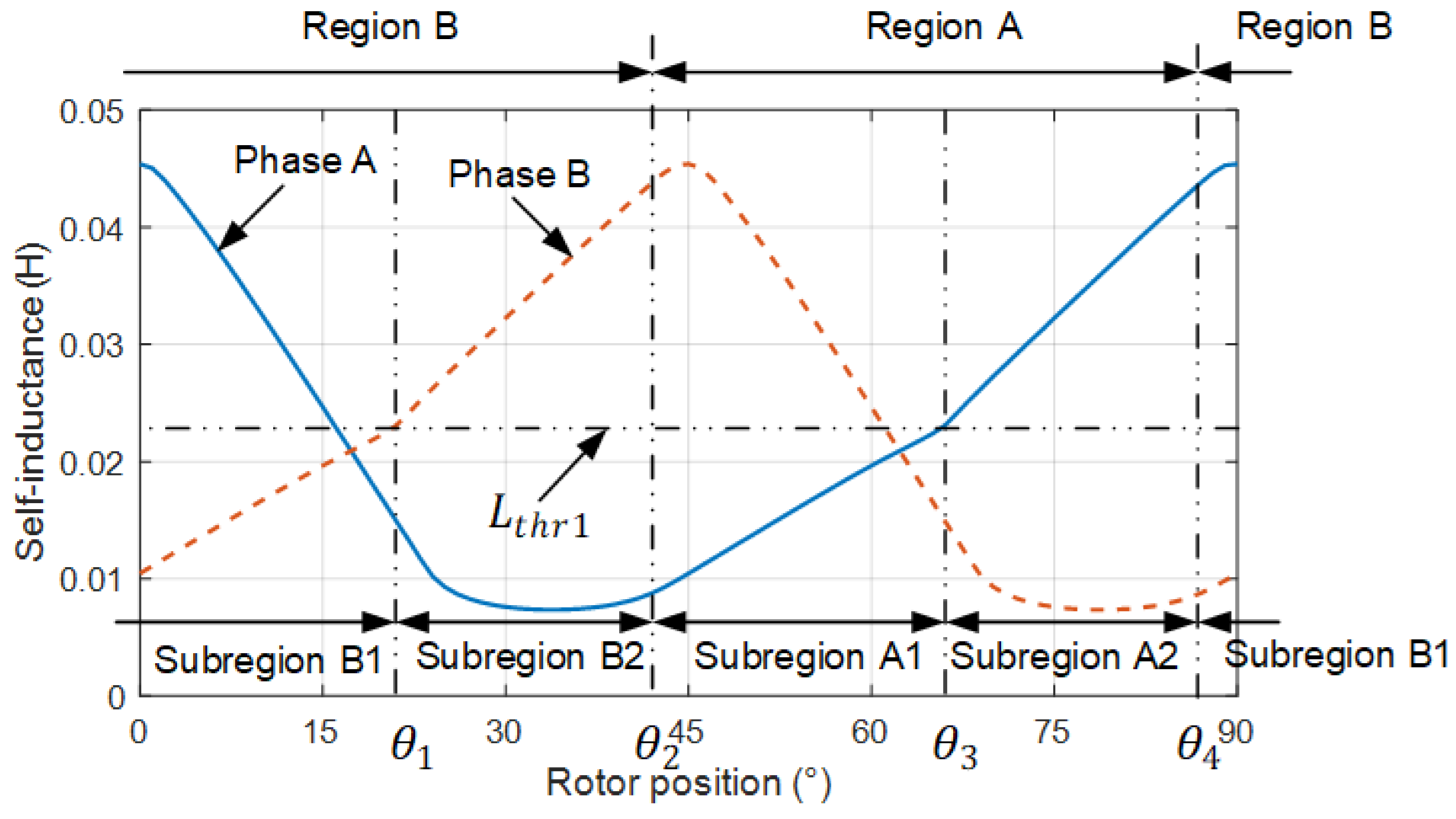
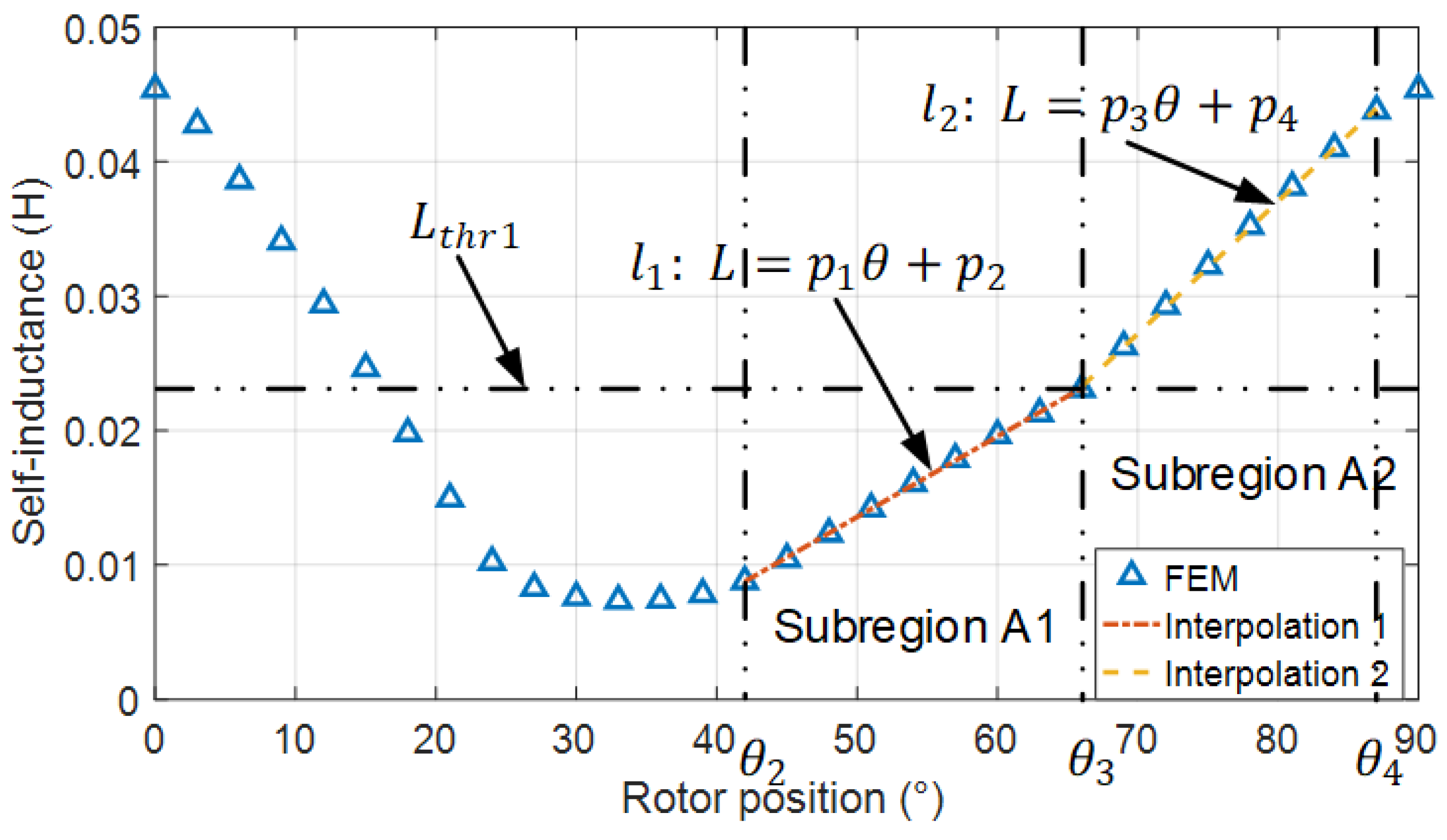
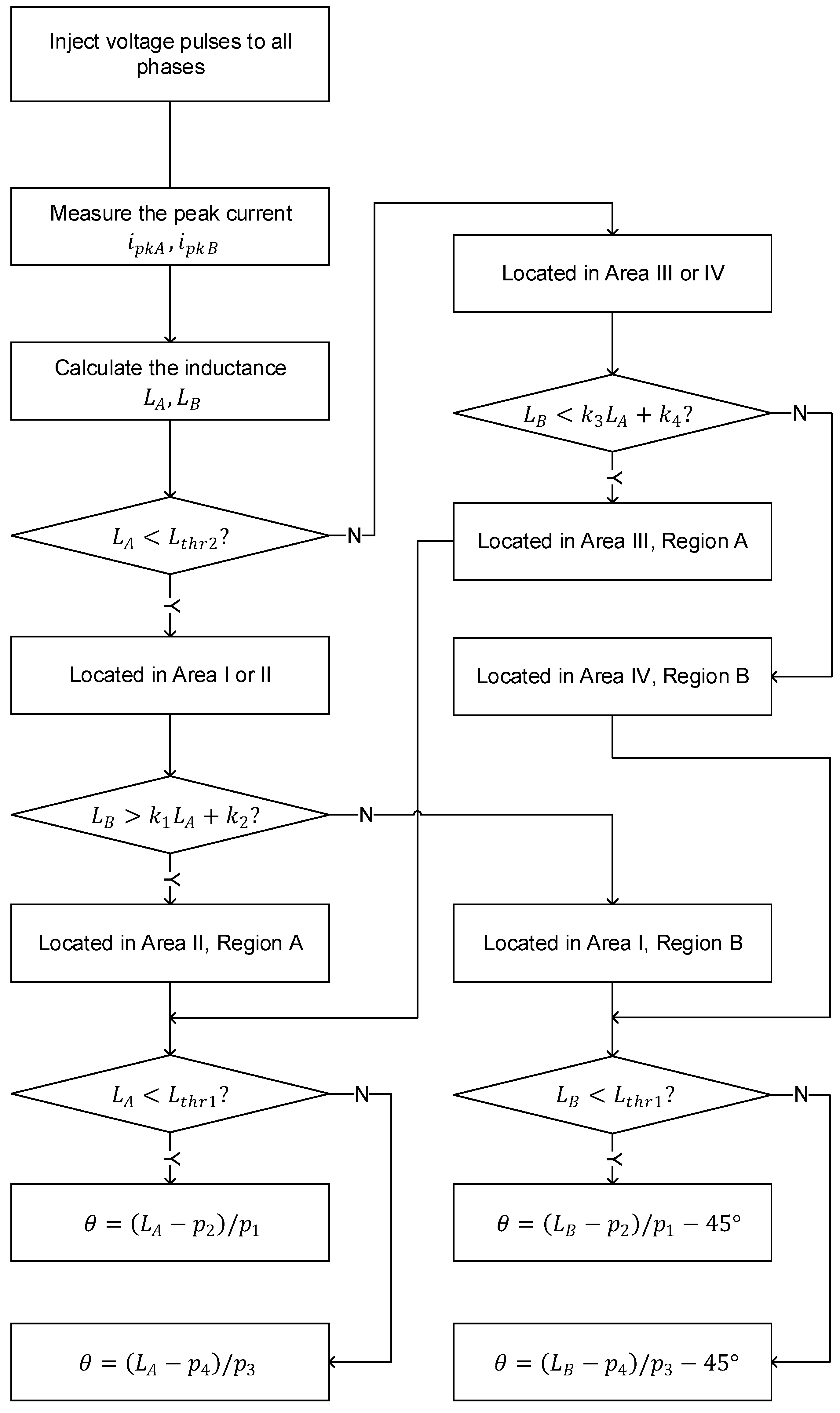
2.3. Region Judgement and Position Estimation
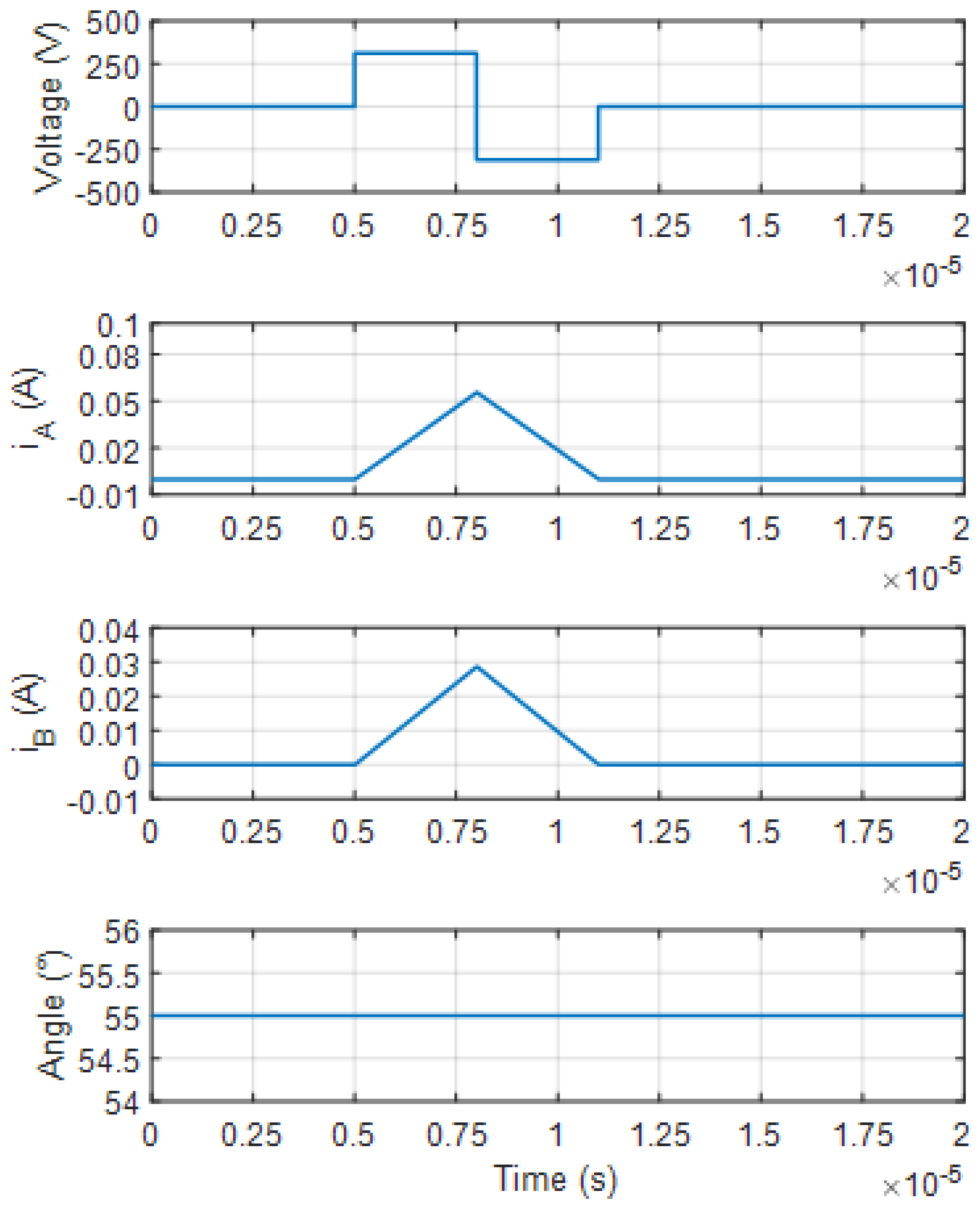
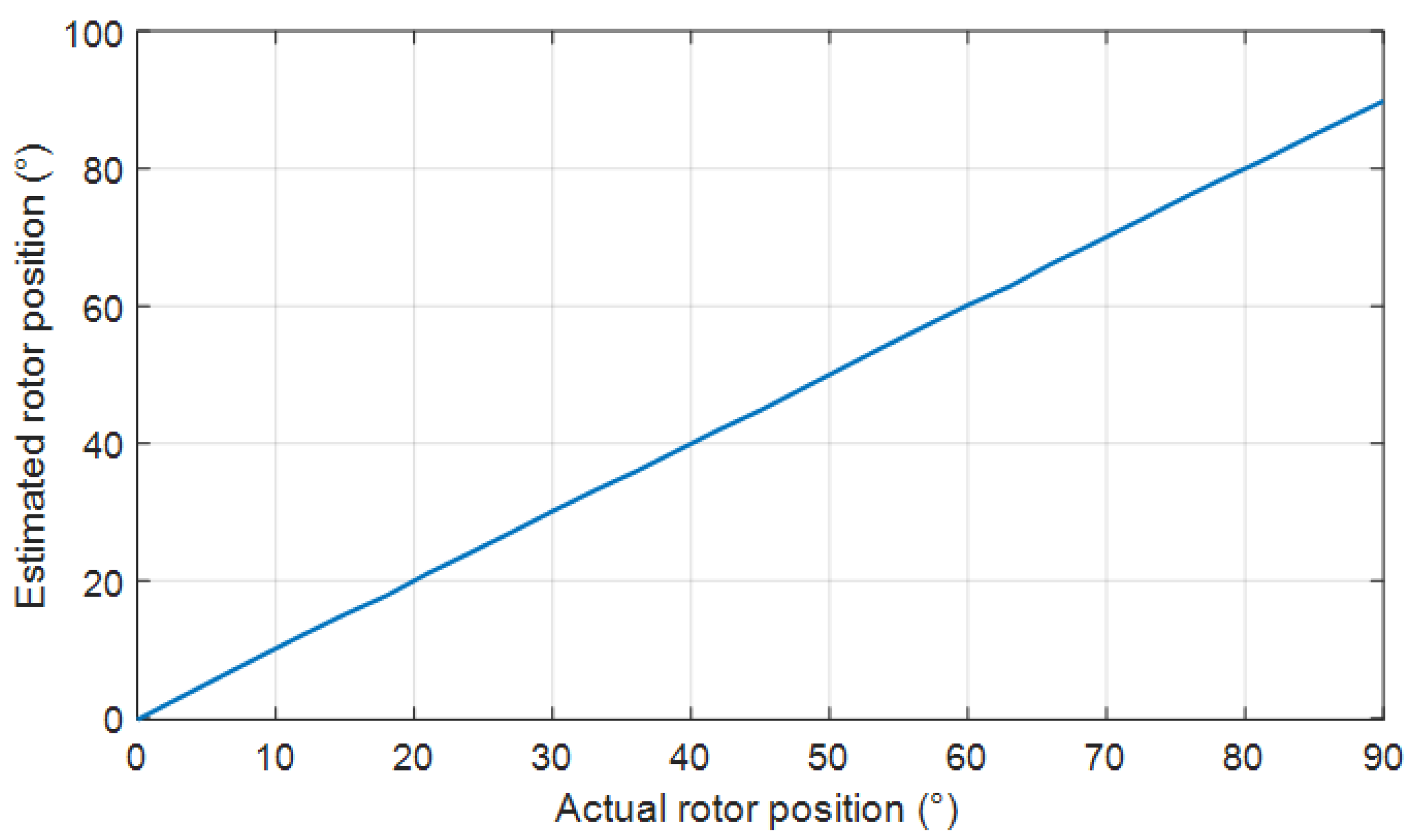
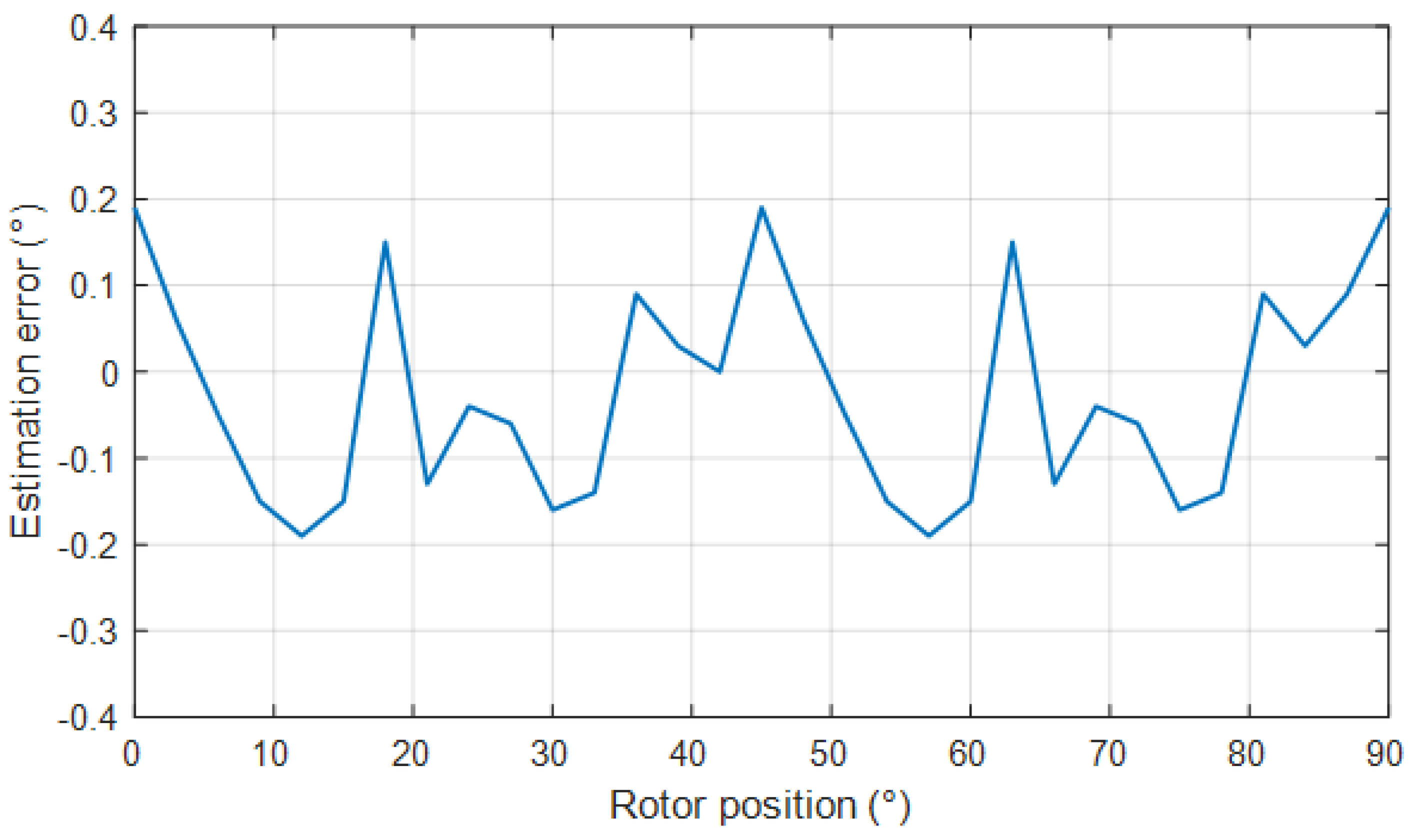
3. Simulation Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, C.; Hsieh, M.; Li, Y.; Tsai, M. Impact of Electrical Steel Punching Process on the Performance of Switched Reluctance Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8113304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Ahn, J.S.; Lee, J. The characteristic analysis of switched reluctance motor considering DC-link Voltage ripple on hard and soft chopping modes. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 4096–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shang, F.; Brown, I.P.; Krishnamurthy, M. Comparative Study of Interior Permanent Magnet, Induction, and Switched Reluctance Motor Drives for EV and HEV Applications. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, C.A.; Lobo, N.S.; Krishnan, R. Sensorless Control of Single Switch-Based Switched Reluctance Motor Drive Using Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.J.; Takahashi, M.; Watanabe, T.; Ichinokura, O. A new sensorless drive method of Switched Reluctance Motors based on motor’s magnetic characteristics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2831–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugrul, N.; Cheok, A.D. Indirect angle estimation in switched reluctance motor drive using fuzzy logic based motor model. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2000, 15, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Fahimi, B. Elimination of position sensors in switched reluctance motor drives: State of the art and future trends. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.; Yuan, X.; Gao, J.; Zheng, J. Initial Rotor Position Detection for Sensorless Interior PMSM With Square-Wave Voltage Injection. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8112104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champa, P.; Somsiri, P.; Wipasuramonton, P.; Nakmahachalasint, P. Initial Rotor Position Estimation for Sensorless Brushless DC Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, E.; Husain, T.; Sozer, Y.; Husain, I. A Pulse-Injection-Based Sensorless Position Estimation Method for a Switched Reluctance Machine Over a Wide Speed Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3867–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.U.; Kongprawechnon, W.; Chayopitak, N. Eliminating starting hesitation for reliable operation of switched reluctance motor without machine parameters for light electric vehicle applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-D.; Cao, G.-Z.; Qian, Q.-Q. A Novel Initial Mover Position Estimation Method for Planar Switched Reluctance Motors with Bipolar Square-Wave Voltage Injection. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Symposium on Linear Drives for Industry Applications (LDIA), Wuhan, China, 1–3 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X. A Reliable Sensorless Starting Scheme for SRM With Lowered Pulse Injection Current Influences. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1003209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanokvate, T.; Seubsuang, K.; Prapon, J.; Pakasit, S.; Chiba, A.; Tadashi, F. An Improvement on Position Estimation and Start up Operation for Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Trakrancharoungsook, K.; Kittiratsatcha, S. Position Estimation Technique of a Switched Reluctance Motor at Standstill. In Proceedings of the 2007 Power Conversion Conference—Nagoya, Nagoya, Japan, 2–5 April 2007; pp. 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Salmasi, F.R.; Ehsani, M. Sensorless control of SRM at standstill. In Proceedings of the APEC 2001. Sixteenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2001; Volume 2, pp. 850–856. [Google Scholar]
- Hieu, P.T.; Lee, D.; Ahn, J. Design of a high speed 4/2 switched reluctance motor for blender application. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Harbin, China, 7–10 August 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of stator poles | 8 |
| Number of rotor poles | 4 |
| Stator outer radius | 53 mm |
| Stator yoke thickness | 6.5 mm |
| Rotor outer radius | 21 mm |
| Rotor yoke thickness | 7 mm |
| Shaft radius | 10 mm |
| Stack length | 55.5 mm |
| 1st airgap | 0.3 mm |
| 2nd airgap | 0.4 mm |
| Stator pole arc | 23° |
| Rotor pole arc | 25° |
| Major pole arc of the rotor | 48° |
| Number of turns per pole | 72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Jung, I.; Lee, Y. Position Estimation of a Two-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor at Standstill. Machines 2021, 9, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120359
Fan J, Jung I, Lee Y. Position Estimation of a Two-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor at Standstill. Machines. 2021; 9(12):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120359
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jiayi, Insu Jung, and Yongkeun Lee. 2021. "Position Estimation of a Two-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor at Standstill" Machines 9, no. 12: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120359
APA StyleFan, J., Jung, I., & Lee, Y. (2021). Position Estimation of a Two-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor at Standstill. Machines, 9(12), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120359




