Limited-Position Set Model-Reference Adaptive Observer for Control of DFIGs without Mechanical Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
- High energy conversion efficiency due to the implementation of the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) technique.
- Changes of the wind speed does not affect the electrical utility.
- No capacitor bank is required.
- The price of the power electronics circuits is low due to the use of partial-scale back-to-back (BTB) power converter, i.e., of the generator power.
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Non-linear control system and no modulator is required.
- Constrains can by easily considered in the design of the FS-MPC.
- Multi-variable control problem can be easily handled by the FS-MPC.
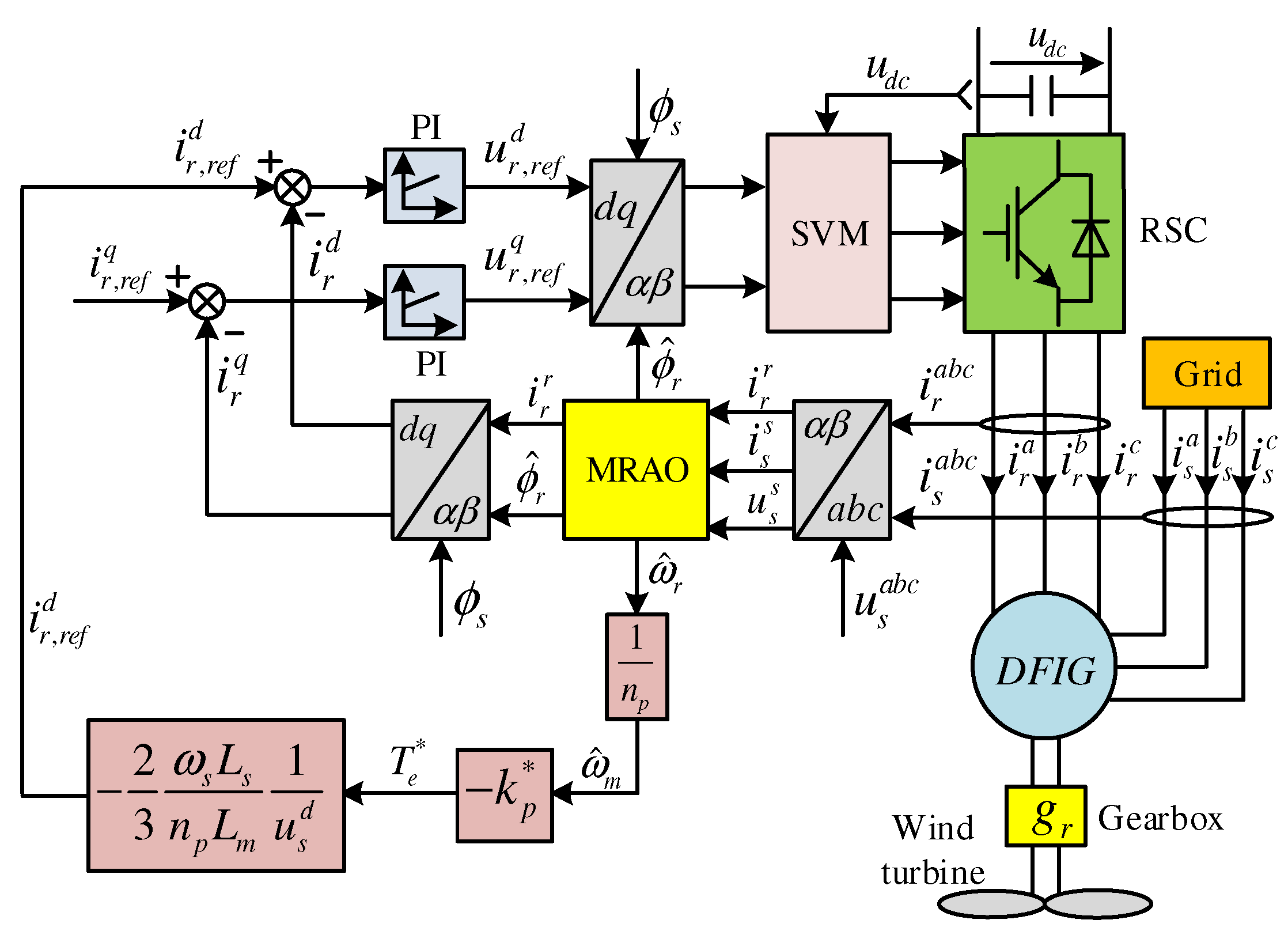
2. Modeling and Control of the DFIG
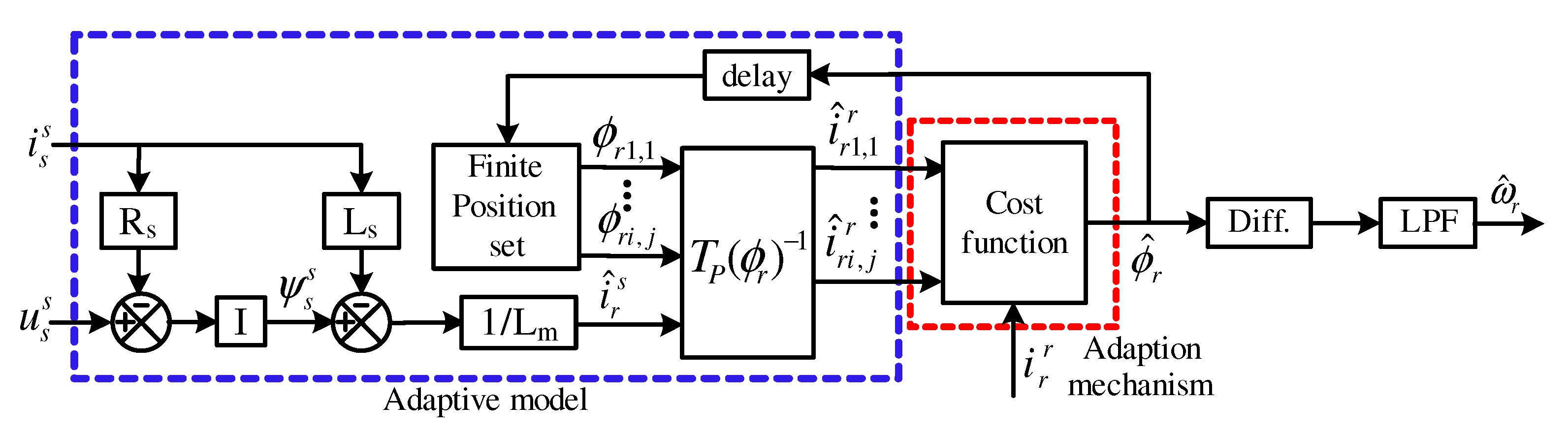
3. Traditional MRAO for DFIGs
4. Proposed Limited-Position Set MRAO for DFIGs
| Algorithm 1 Proposed LPS-MRAO for DFIGs |
| Step 1: Read the rotor and stator currents , and stator voltage . |
| Step 2: Compute . |
| Step 3: Estimate . |
| Step 4: |
| Initiate the angle and error |
| For |
| calculate . |
| For |
| compute . |
| compute . |
| evaluate the cost function . |
| if |
| end |
| end |
| set |
| end |
| Step 5: |
| Step 6: Return to Step 1. |
5. Description of the Test Bench
- DS3002 incremental encoder board to interface the measured speed/position of the rotor with the main board. Note: this measured speed/position of the rotor is only for comparison with the estimated ones.
- DS2004 analog to digital converter (A/D) board to interface the measured currents of the rotor and stator, measured voltages of the stator, and measured DC-link with the main board.
- DS5101 pulse-width-modulation board to interface the switching signals with the power converters.
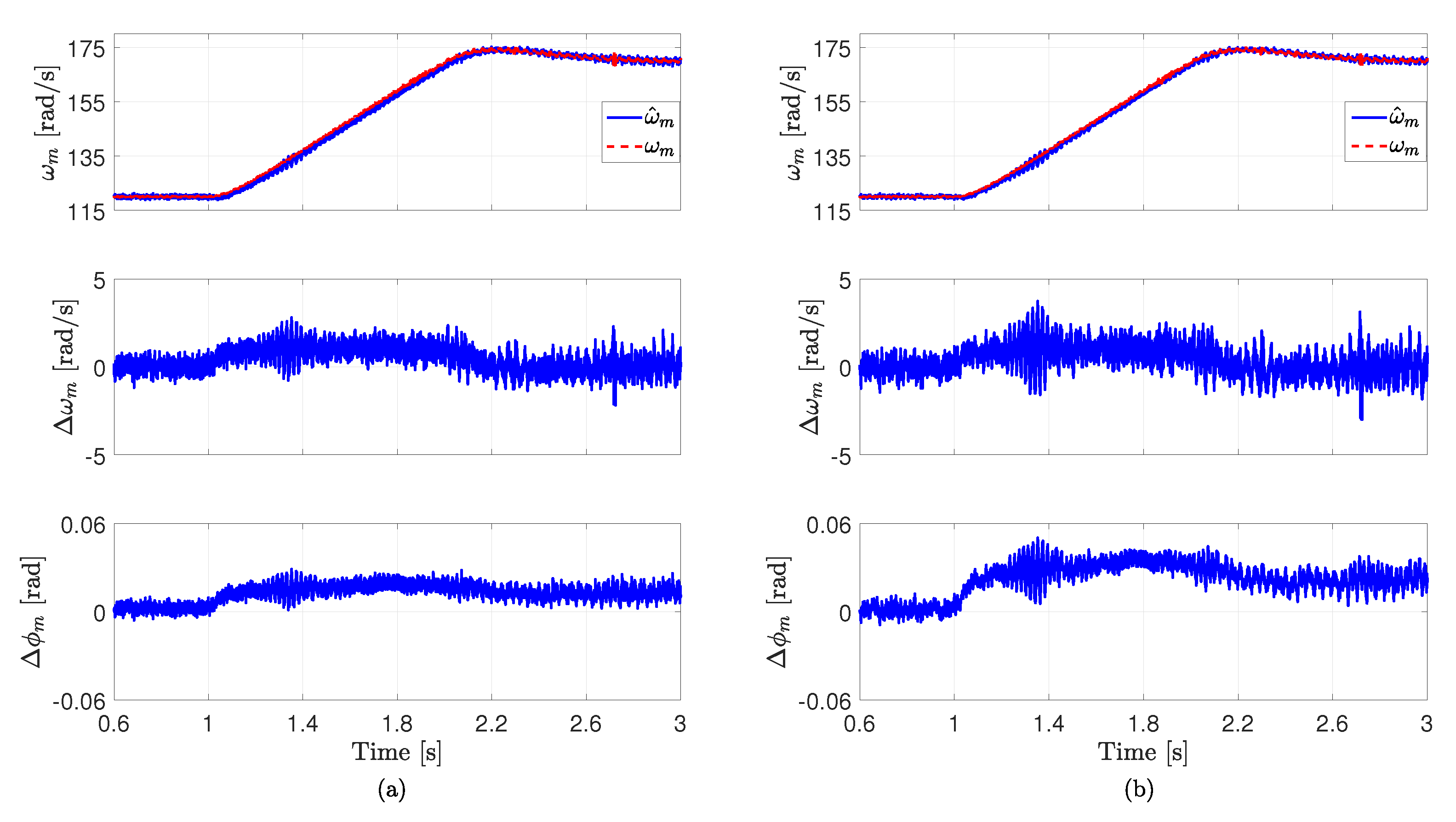
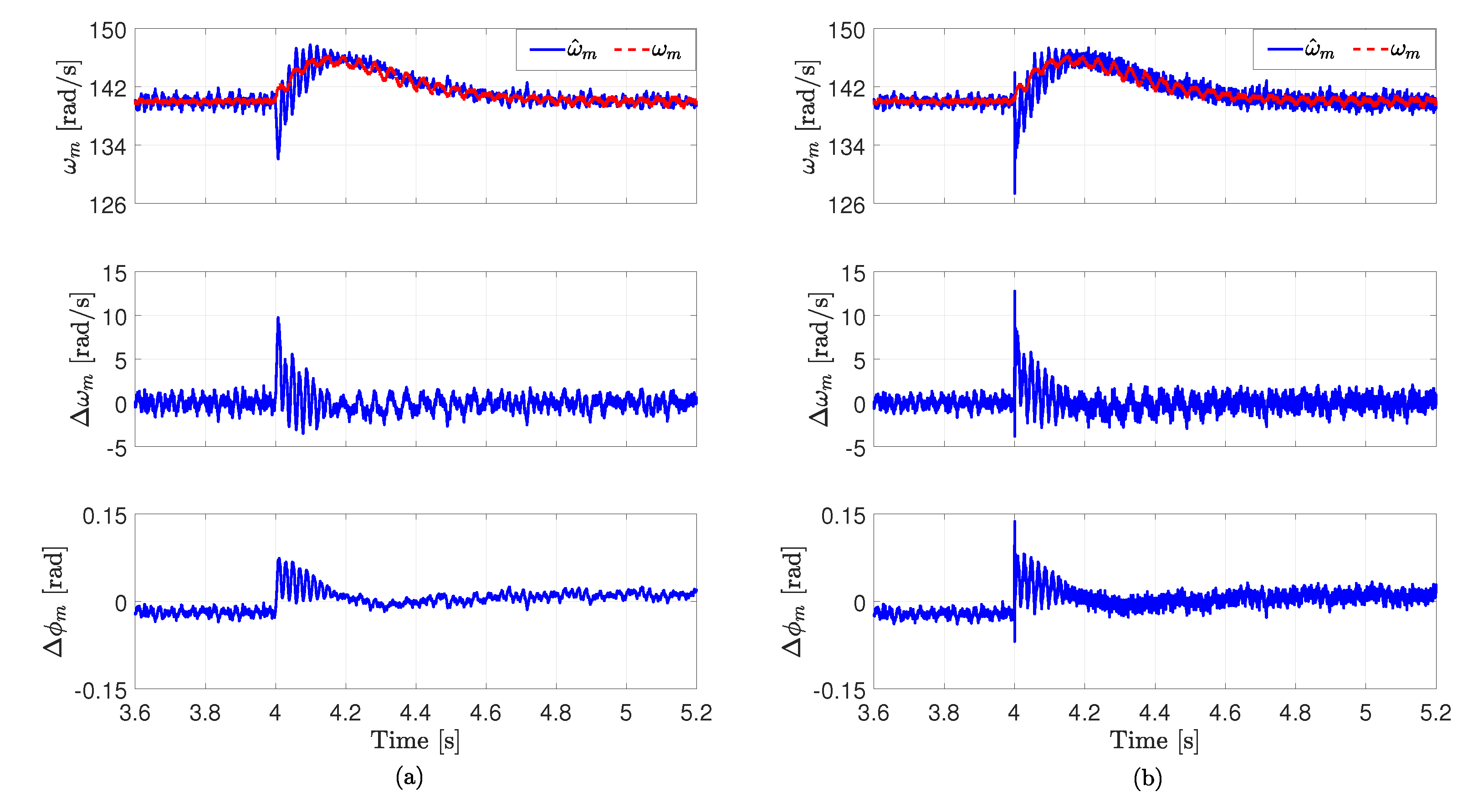
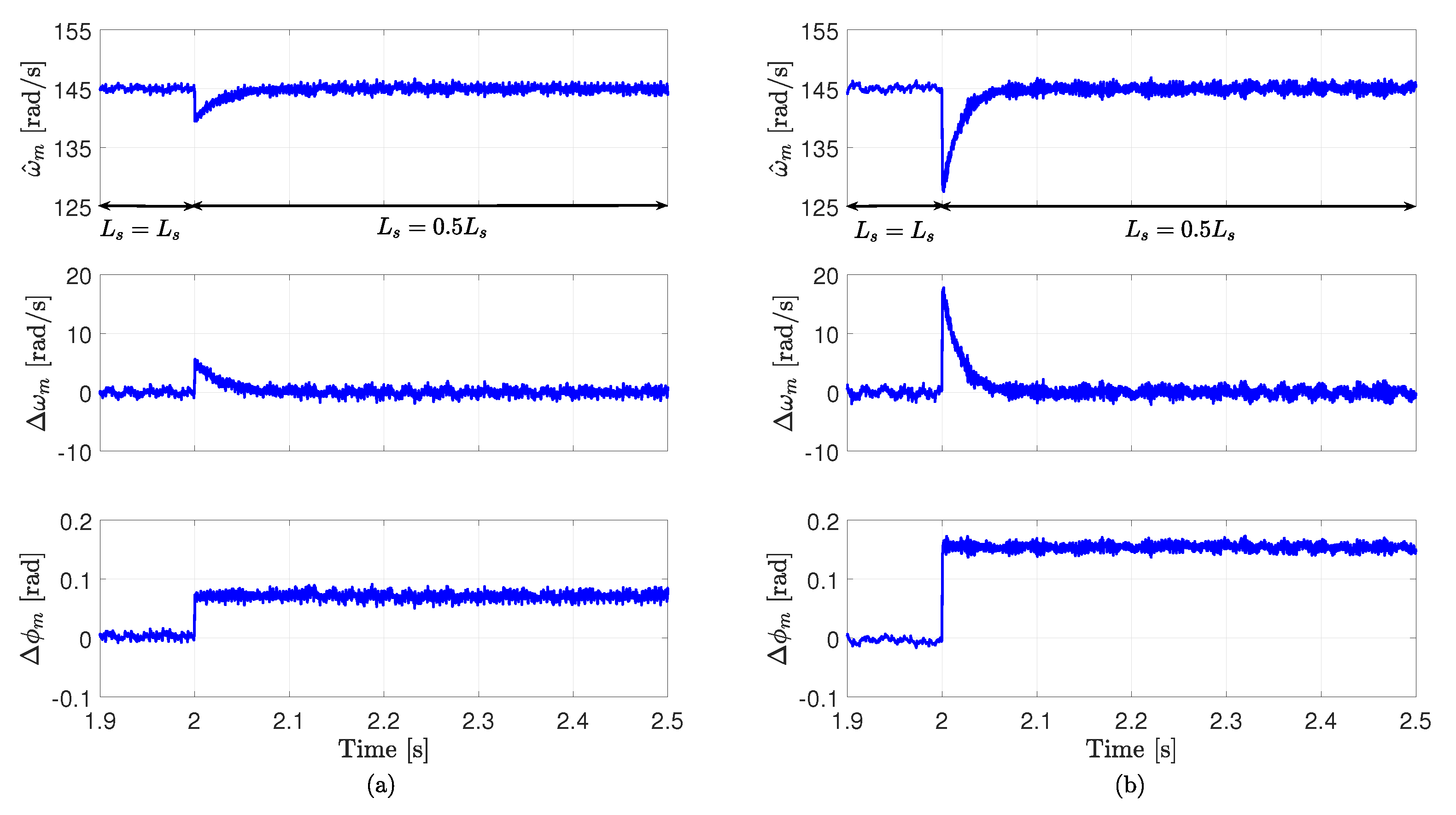
6. Experimental Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. What Is the Paris Agreement? Available online: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/what-is-the-paris-agreement (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- Li, H.; Chen, Z. Overview of different wind generator systems and their comparisons. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2008, 2, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder, H.; Ferreira, J.A.; Jensen, B.B.; Abrahamsen, A.B.; Atallah, K.; McMahon, R.A. Trends in Wind Turbine Generator Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaramasu, V.; Wu, B.; Sen, P.C.; Kouro, S.; Narimani, M. High-power wind energy conversion systems: State-of-the-art and emerging technologies. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 740–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, R.; Clare, J.; Asher, G. Doubly fed induction generator using back-to-back PWM converters and its application to variable-speed wind-energy generation. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 1996, 143, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, G.; López, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Marroyo, L.; Iwanski, G. Doubly Fed Induction Machine: Modeling and Control for Wind Energy Generation Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Giaourakis, D.G.; Safacas, A.N. Effect of Short-Circuit Faults in the Back-to-Back Power Electronic Converter and Rotor Terminals on the Operational Behavior of the Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Energy Conversion System. Machines 2015, 3, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, R.; Pena, R.; Alepuz, S.; Asher, G. Overview of Control Systems for the Operation of DFIGs in Wind Energy Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2776–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwinyiwiwa, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, B.; Ooi, B. Rotor Position Phase-Locked Loop for Decoupled P-Q Control of DFIG for Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, R.; Pena, R.; Proboste, J.; Asher, G.; Clare, J. MRAS observer for sensorless control of standalone doubly fed induction generators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, R.; Pena, R.; Clare, J.; Asher, G.; Proboste, J. MRAS observers for sensorless control of doubly-fed induction generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Encoderless Model Predictive Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generators in Variable-Speed Wind Turbine Systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 753, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Avila, N.F.; Chu, C.; Yeh, T. Model Reference Adaptive Back-Electromotive-Force Estimators for Sensorless Control of Grid-Connected DFIGs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Dal, M.; Kennel, R.; Rodriguez, J. Efficient Finite-Position-Set MRAS Observer for Encoder-less Control of DFIGs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Predictive Control of Electrical Drives and Power Electronics (PRECEDE), Quanzhou, China, 31 May–2 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Das, S.; Syam, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Review on model reference adaptive system for sensorless vector control of induction motor drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbukani, M.W.K.; Gule, N. Comparison of high-order and second-order sliding mode observer based estimators for speed sensorless control of rotor-tied DFIG systems. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Zhang, Z.; Kennel, R. Robust Predictive Control for Direct-Driven Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generators Without Mechanical Sensors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Simplified Model Predictive Current Control without Mechanical Sensors for Variable-Speed Wind Energy Conversion Systems. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Sensorless Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generators in Variable-Speed Wind Turbine Systems. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), Taormina, Italy, 16–18 June 2015; pp. 406–413. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, S.P.; Tate, J.E. Parameter estimation of doubly fed induction generator driven by wind turbine. In Proceedings of the IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 20–23 March 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapat, G.P.; Bhui, P.; Kumar, P.; Varma, S. Estimation based Maximum Power Point Control of DFIG based Wind Turbine Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES GTD Grand International Conference and Exposition Asia (GTD Asia), Bangkok, Thailand, 19–23 March 2019; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, S.; Verma, V.; Chakraborty, C.; Hori, Y. An Adaptive Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive with Artificial Neural Network for Stability Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 8, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadoue, S.M.; Giaouris, D.; Finch, J.W. MRAS Sensorless Vector Control of an Induction Motor Using New Sliding-Mode and Fuzzy-Logic Adaptation Mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, H.B.; Zaidi, N.; Jemli, M.; Boussak, M. Development and Experimental Evaluation of a Sensorless Speed Control of SPIM Using Adaptive Sliding Mode-MRAS Strategy. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Pontt, J.; Silva, C.A.; Correa, P.; Lezana, P.; Cortés, P.; Ammann, U. Predictive Current Control of a Voltage Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, S.; Leon, J.; Franquelo, L.; Rodriguez, J.; Young, H.; Marquez, A.; Zanchetta, P. Model Predictive Control: A Review of Its Applications in Power Electronics. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2014, 8, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R.; Rodriguez, J. Efficient Direct-Model Predictive Control with Discrete-Time Integral Action for PMSGs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Kennel, R. Efficient Direct Model Predictive Control for Doubly-Fed Induction Generators. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2017, 45, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Finite set model predictive control with on-line parameter estimation for active frond-end converters. Electr. Eng. 2018, 100, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R.; Shaltout, A.; Saleh, A. Advanced Strategy of Speed Predictive Control for Nonlinear Synchronous Reluctance Motors. Machines 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Improved Direct Model Predictive Control for Grid-Connected Power Converters. Energies 2020, 13, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbede, Y.B.; Gadoue, S.M.; Atkinson, D.J. Model Predictive MRAS Estimator for Sensorless Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3511–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Finite Position Set-Phase Locked Loop for Sensorless Control of Direct-Driven Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Model Reference Adaptive System with Finite-Set for Encoderless Control of PMSGs in Micro-Grid Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name of the Signal | Math. Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal power | ||
| Nominal line-line voltage of the stator | ||
| Voltage of the DC-link | ||
| Nominal mechanical angular speed | ||
| Stator resistance | ||
| Rotor resistance | ||
| Stator inductance | ||
| Rotor inductance | ||
| Mutual inductance | ||
| Pole pairs | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R. Limited-Position Set Model-Reference Adaptive Observer for Control of DFIGs without Mechanical Sensors. Machines 2020, 8, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040072
Abdelrahem M, Hackl CM, Kennel R. Limited-Position Set Model-Reference Adaptive Observer for Control of DFIGs without Mechanical Sensors. Machines. 2020; 8(4):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040072
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelrahem, Mohamed, Christoph M. Hackl, and Ralph Kennel. 2020. "Limited-Position Set Model-Reference Adaptive Observer for Control of DFIGs without Mechanical Sensors" Machines 8, no. 4: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040072
APA StyleAbdelrahem, M., Hackl, C. M., & Kennel, R. (2020). Limited-Position Set Model-Reference Adaptive Observer for Control of DFIGs without Mechanical Sensors. Machines, 8(4), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040072







