Low-Rate Characterization of a Mechanical Inerter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling
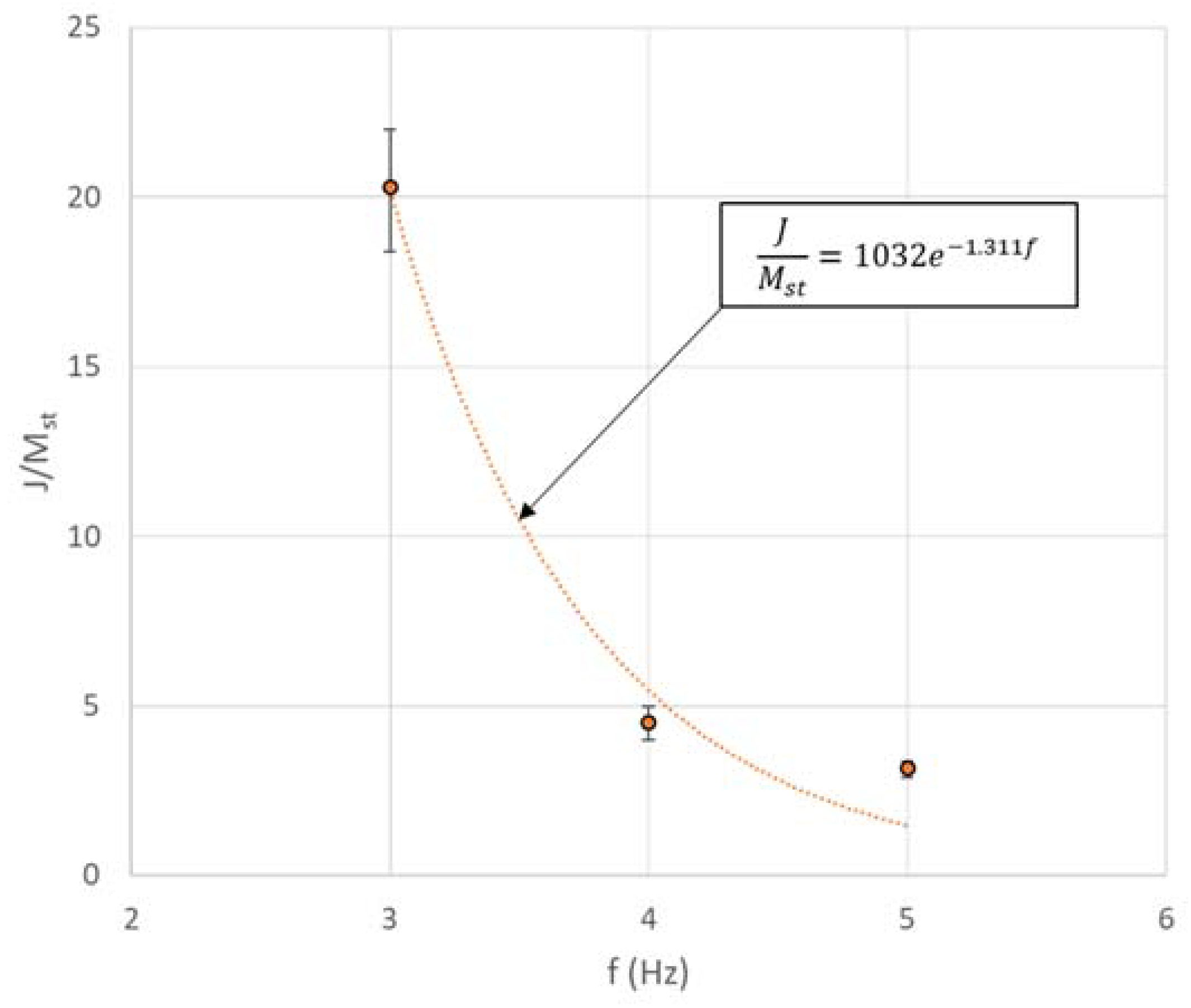
2.1. Analytical Expressions for Specific Inertance
2.2. Parametric Study
3. Experimental Methods
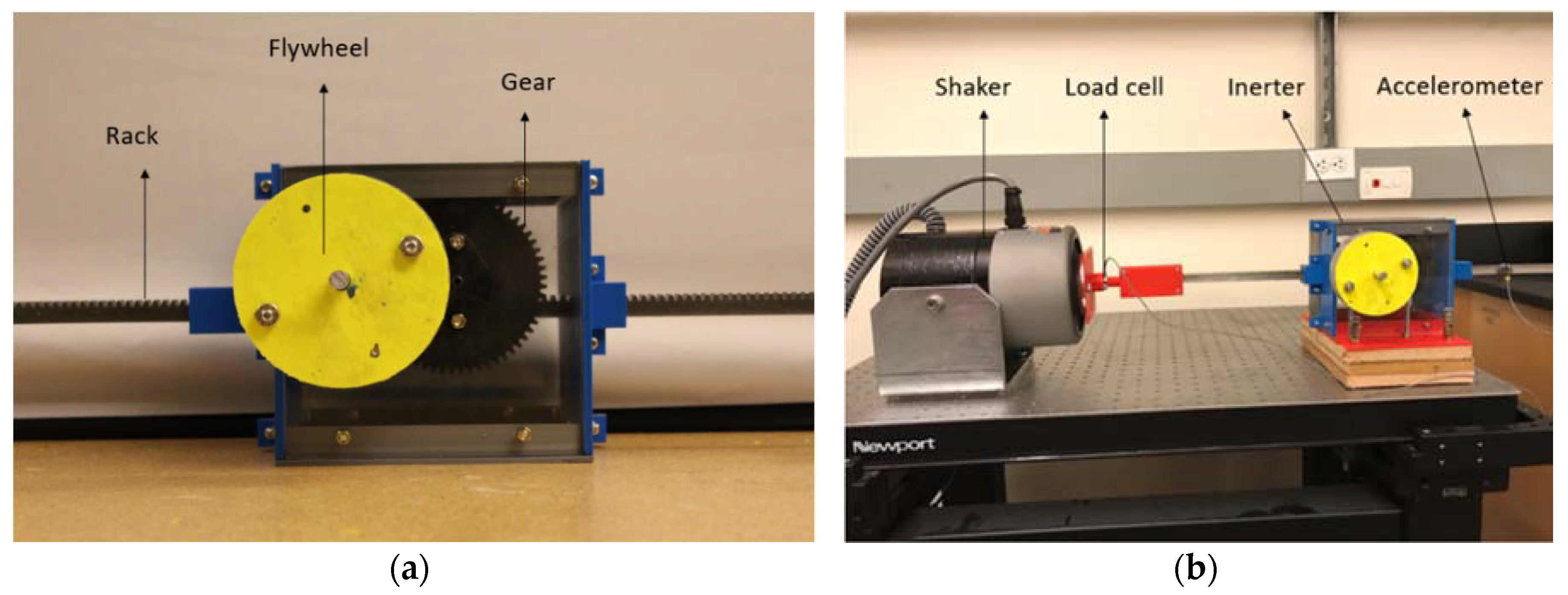
3.1. Test Article Fabrication
3.2. Experimental Setup and Procedures
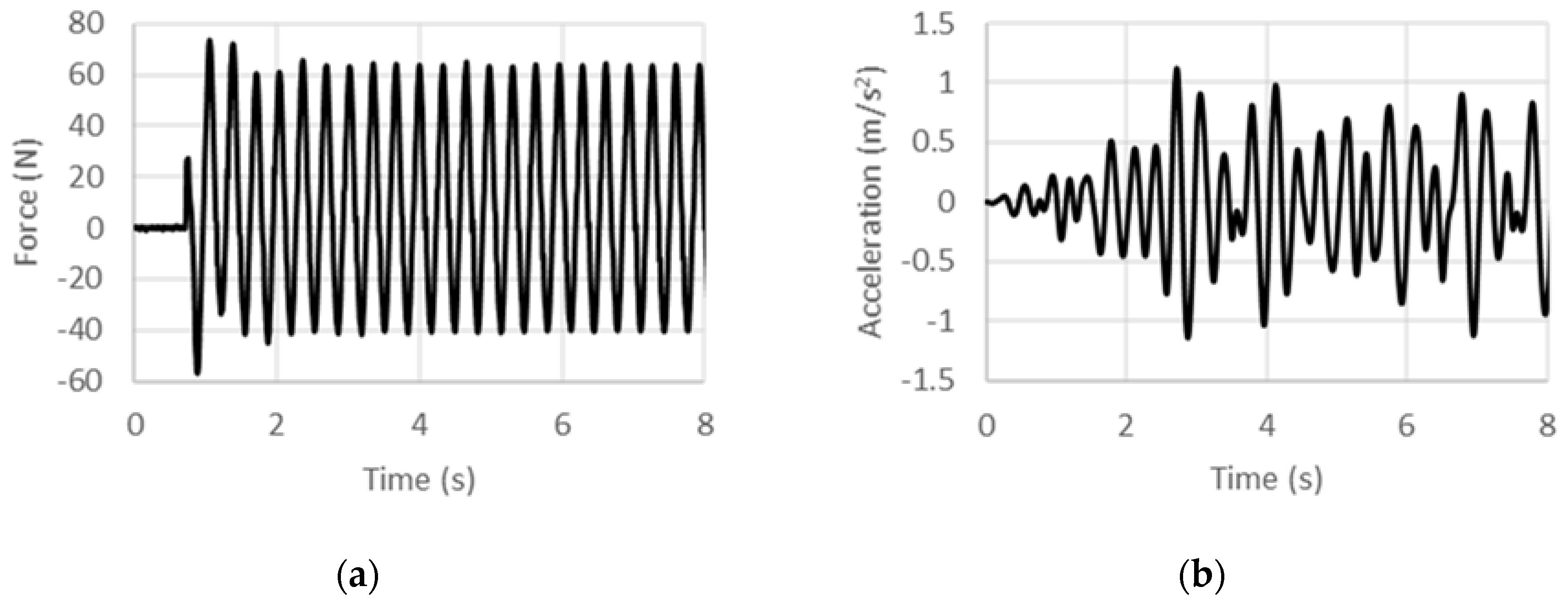
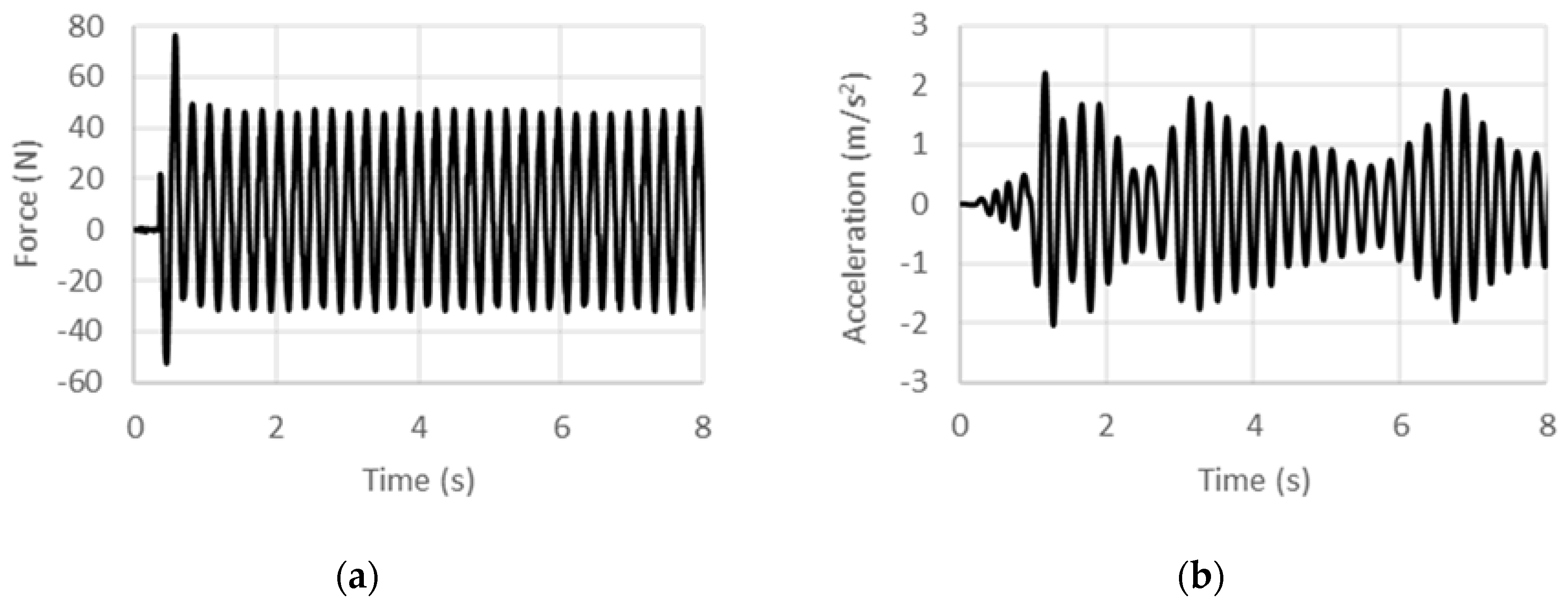
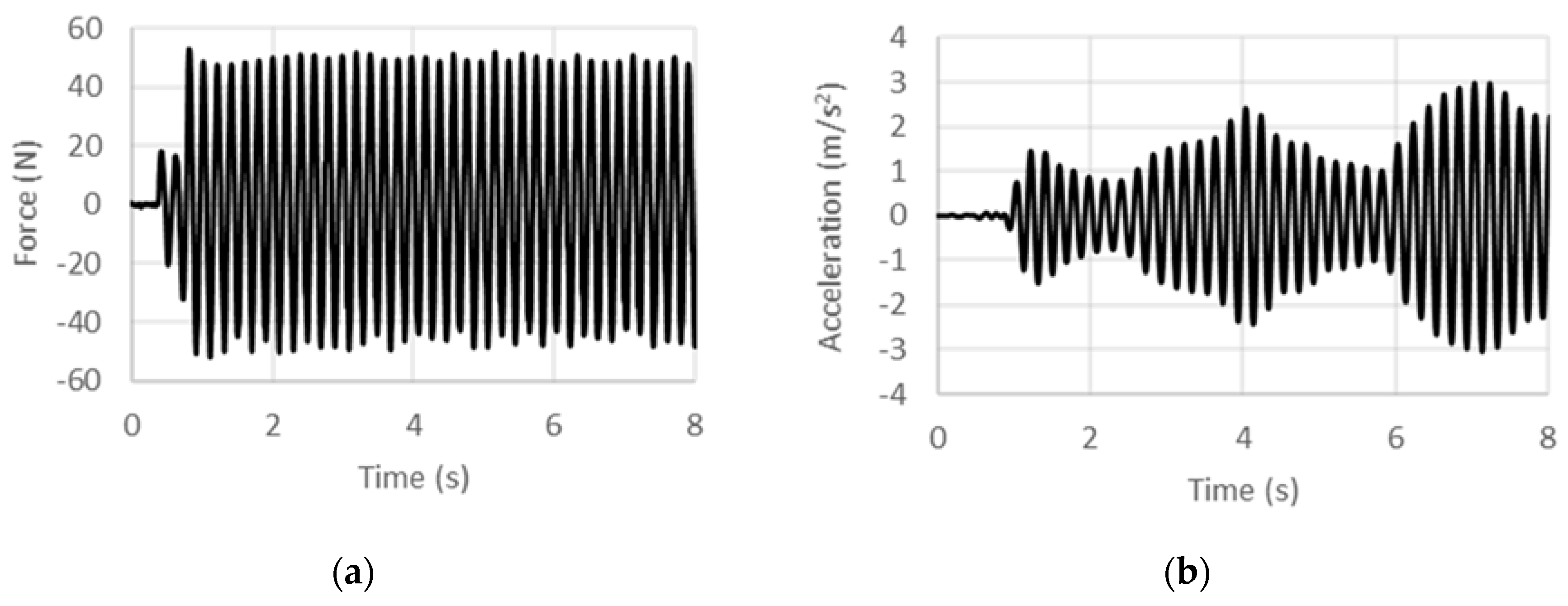
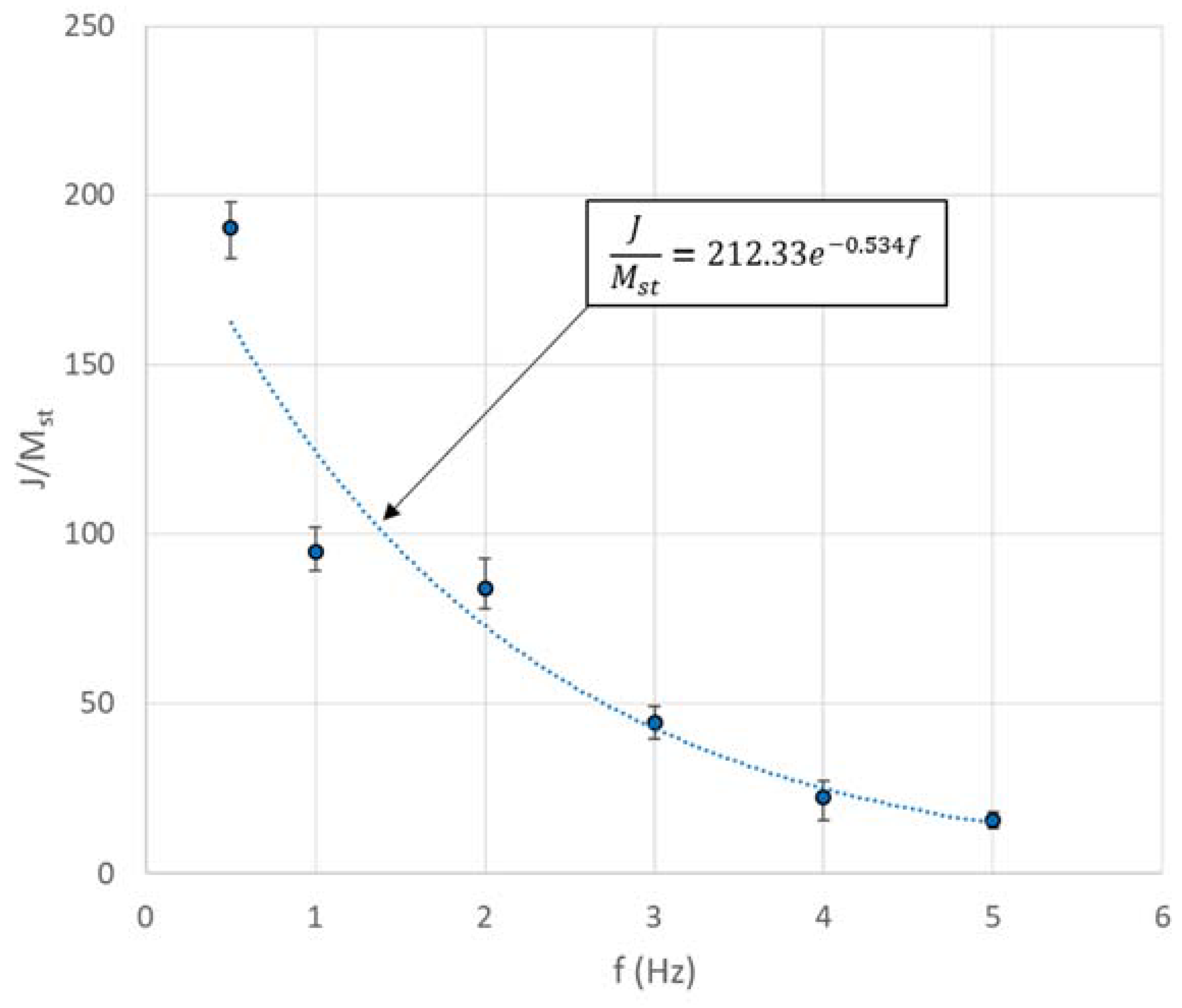
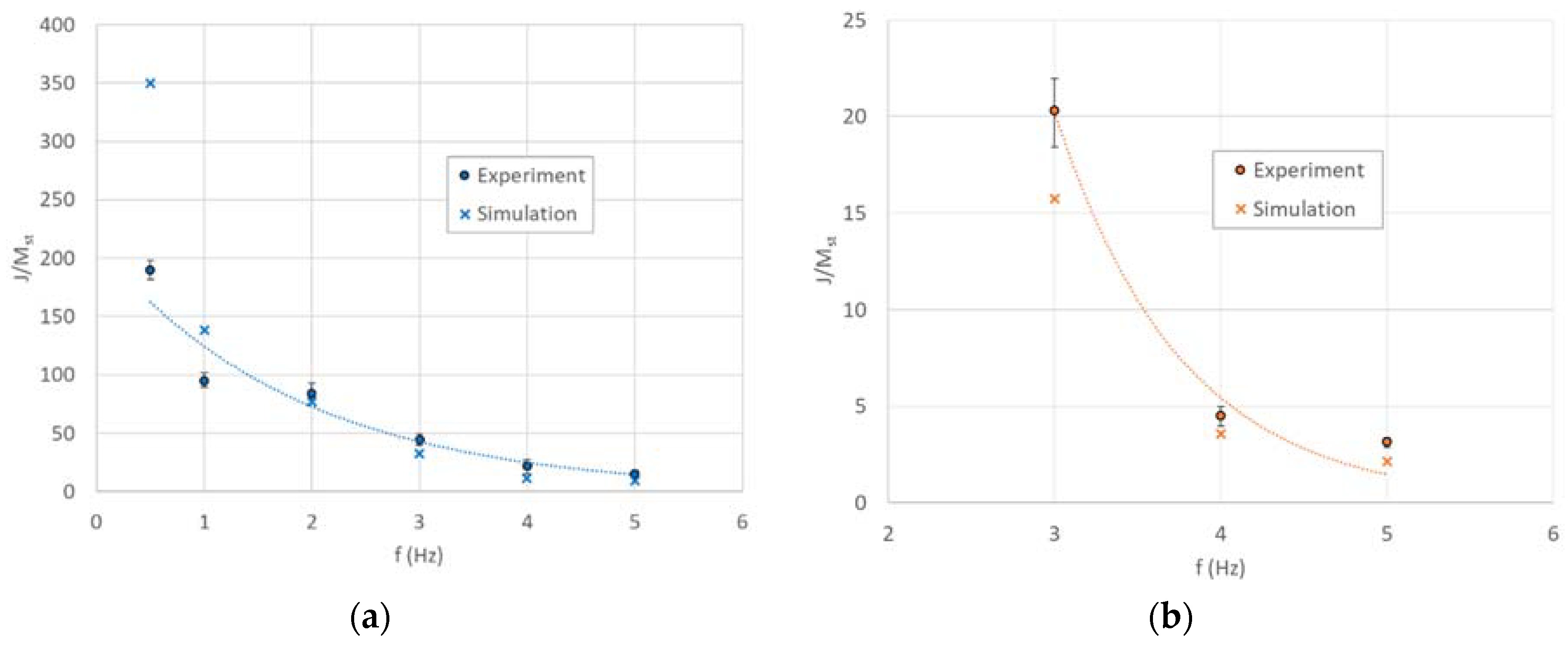
4. Results and Discussions
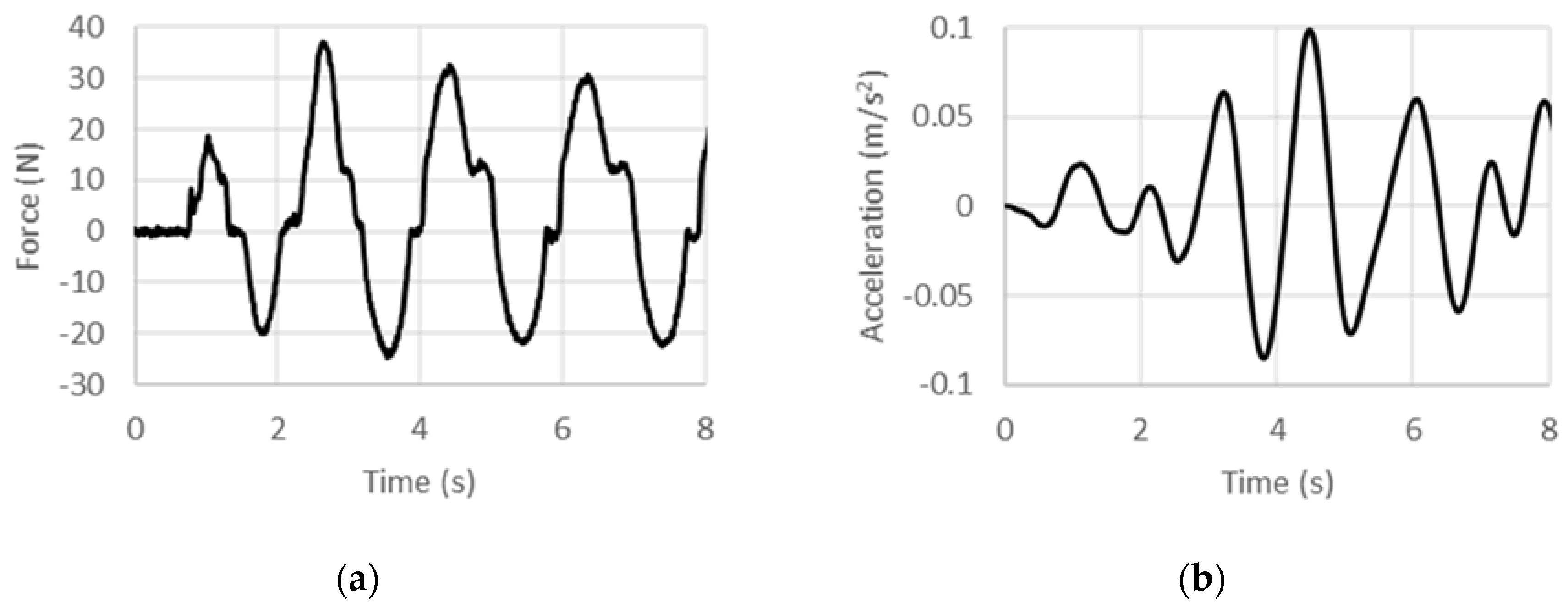
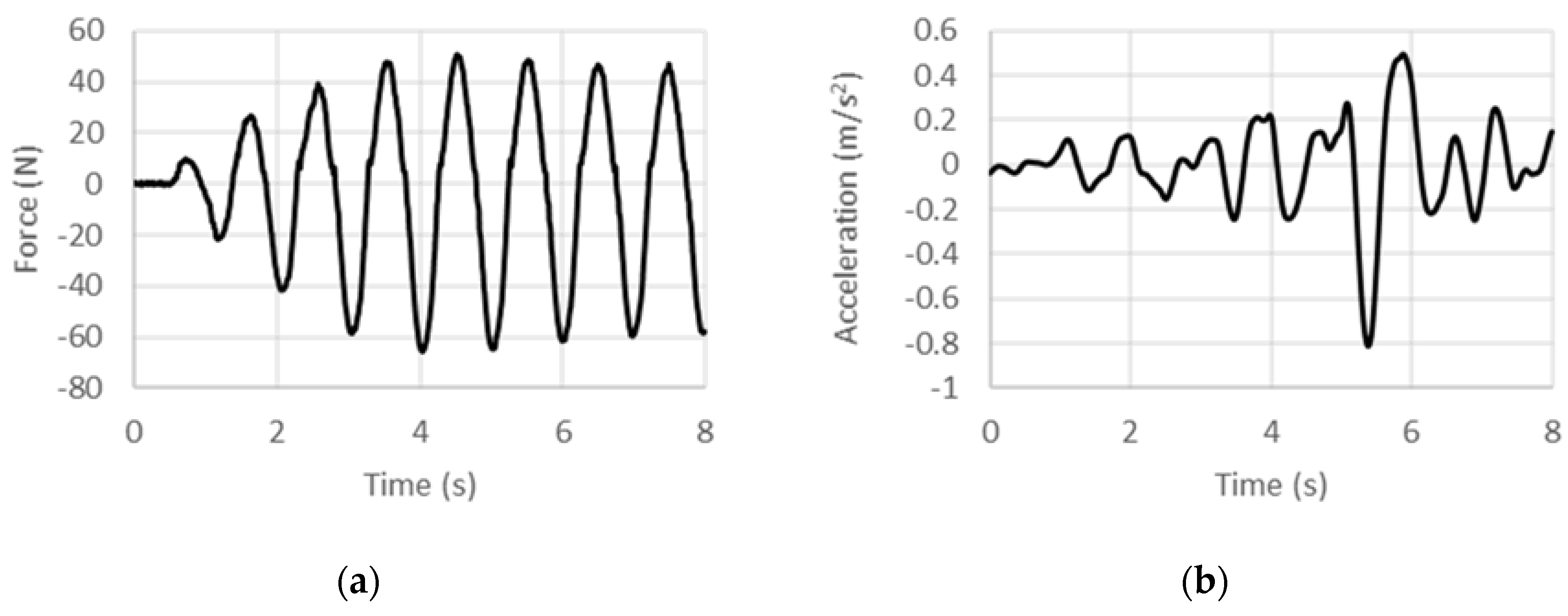
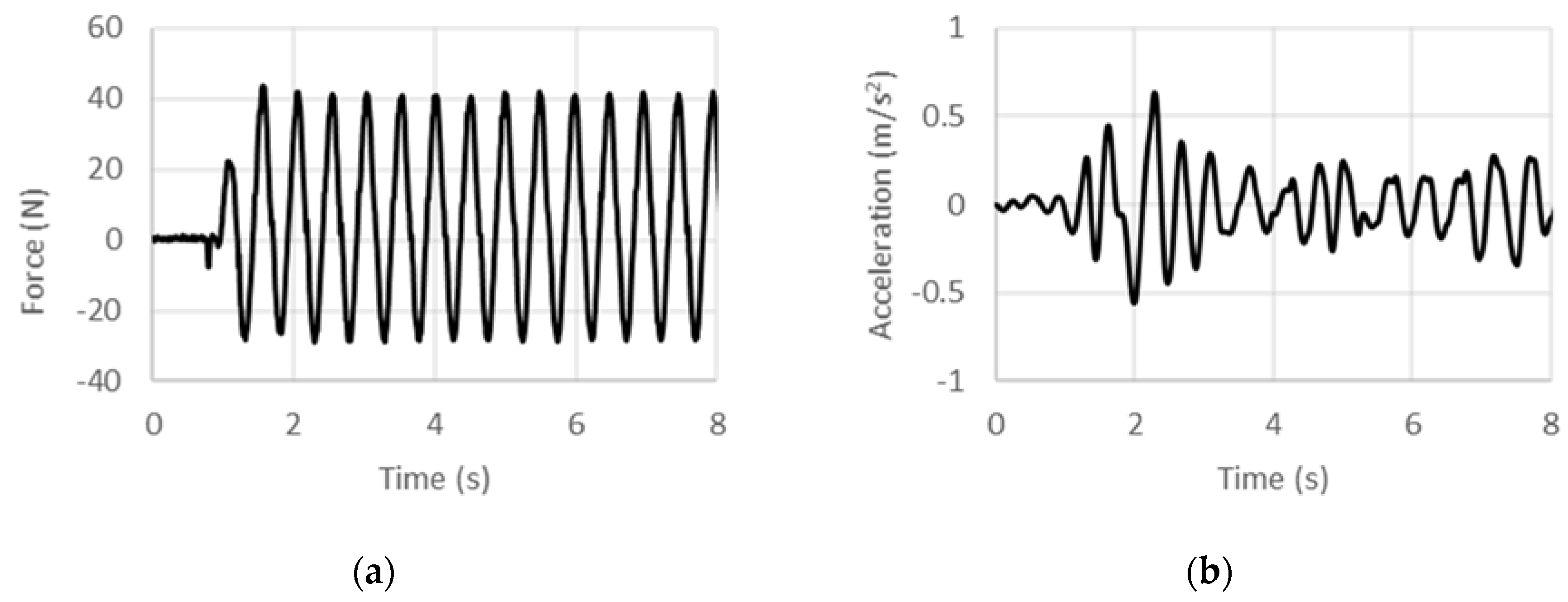
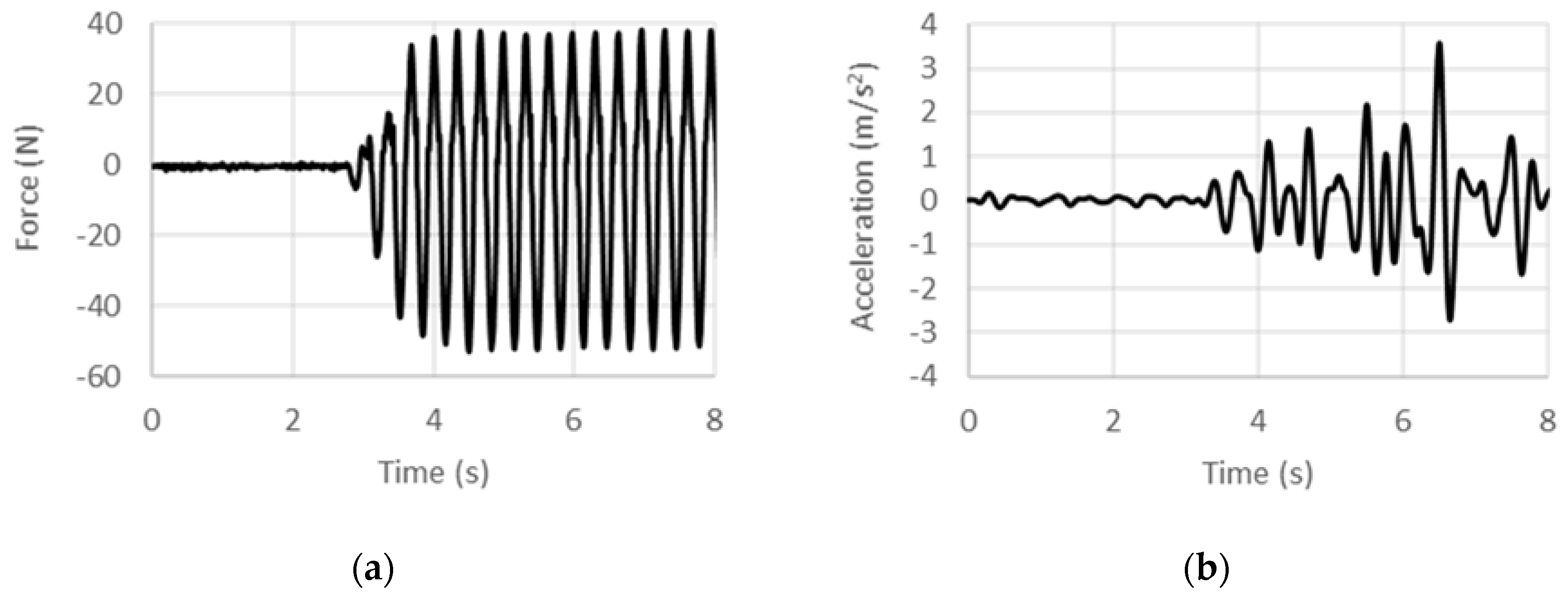
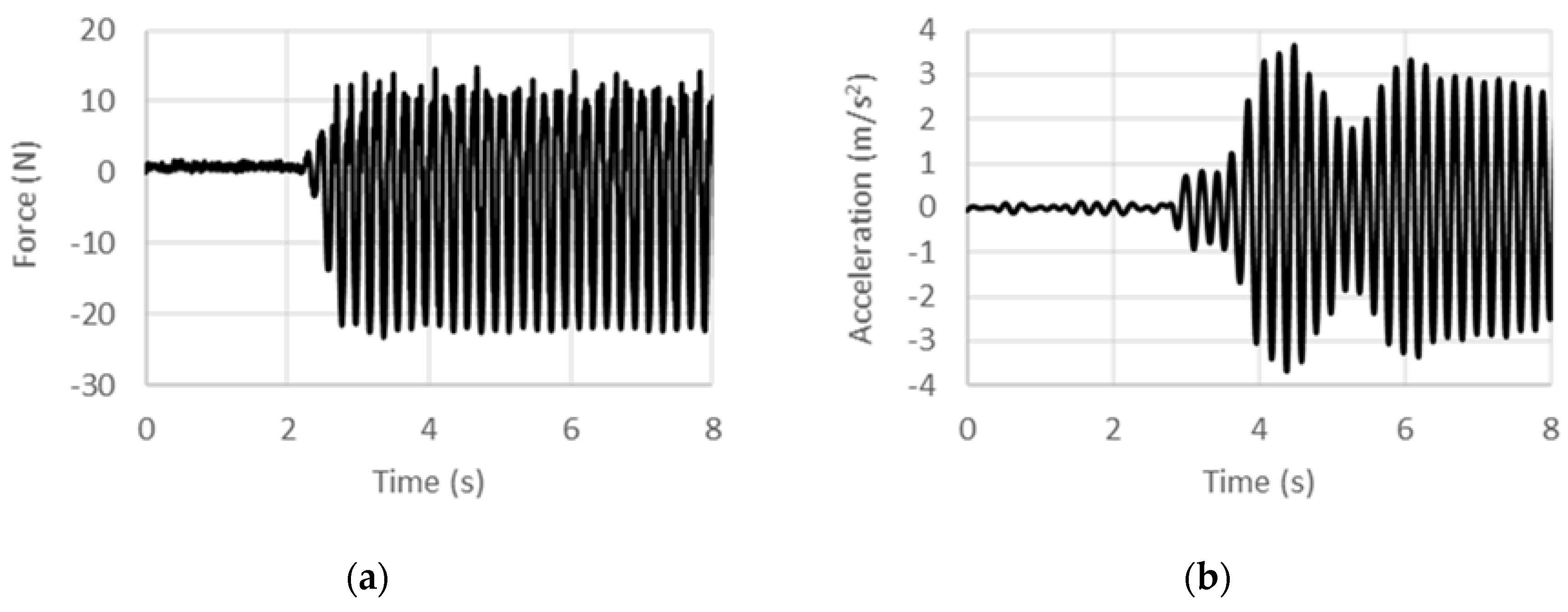
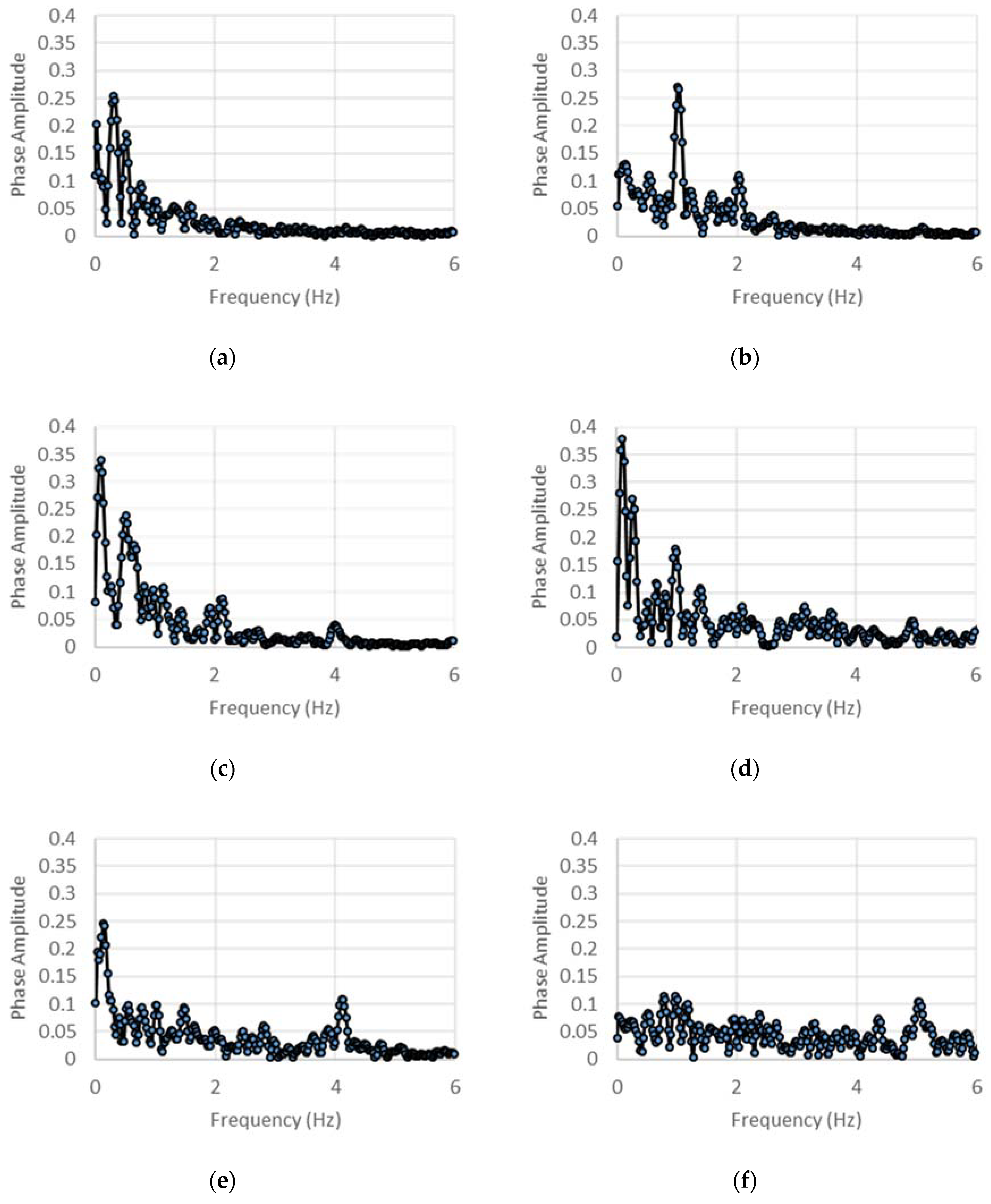
4.1. Displacement-Controlled Sinusoidal Excitation
4.2. Acceleration-Controlled Sinusoidal Excitation
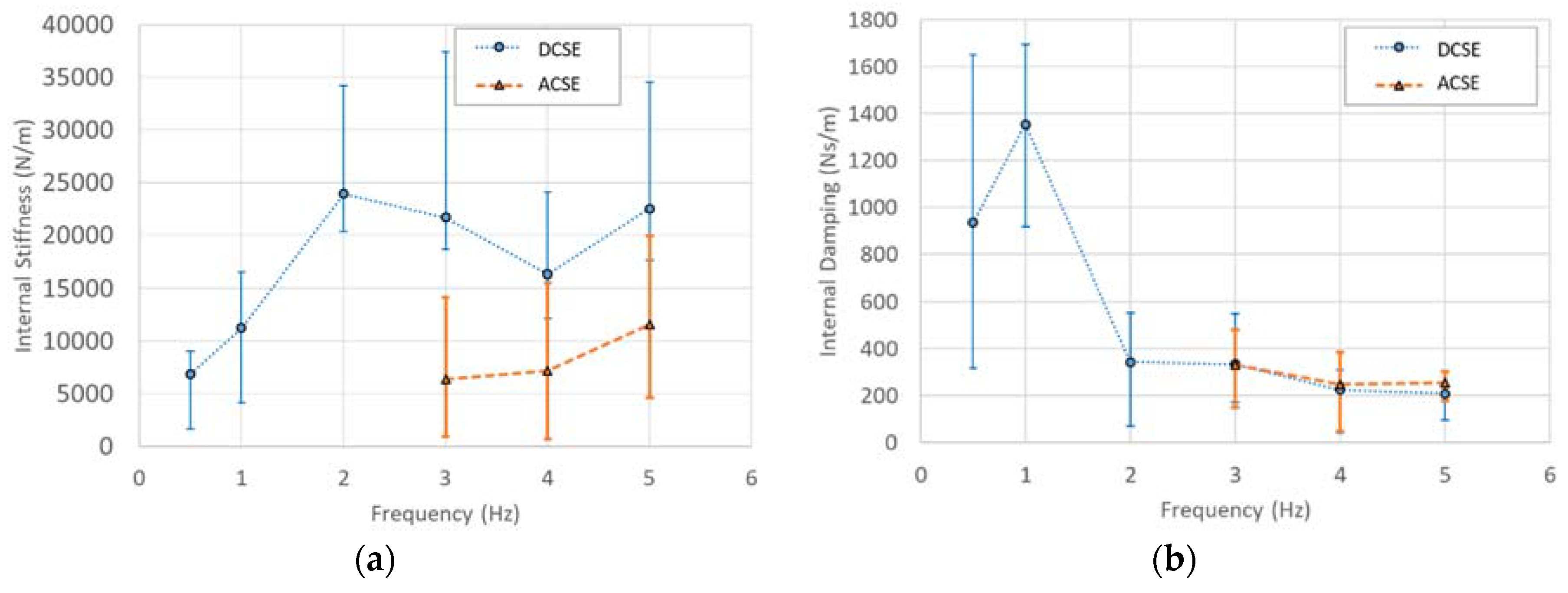
4.3. Estimation of Internal Stiffness and Damping
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firestone, F.A. A new analogy between mechanical and electrical systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1933, 4, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C. Synthesis of mechanical networks: The inerter. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 2002, 47, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Wang, F.C. Performance benefits in passive vehicle suspensions employing inerters. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2004, 42, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Yu, C.H.; Chang, M.L.; Hsu, M. The performance improvements of train suspension systems with inerters. In Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–15 December 2006; pp. 1472–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.C.; Su, W.J. Impact of inerter nonlinearities on vehicle suspension control. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2008, 46, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, D.; Yang, J. Improved design of dynamic vibration absorber by using the inerter and its application in vehicle suspension. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 361, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, C.; Smith, M.C. Laboratory experimental testing of inerters. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2005 and 2005 European Control Conference, Seville, Spain, 12–15 December 2005; pp. 3351–3356. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.C.; Hong, M.F.; Lin, T.C. Designing and testing a hydraulic inerter. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.J.; Smith, M.C.; Glover, A.R.; Papageorgiou, C.; Gartner, B.; Houghton, N.E. Design and modelling of a fluid inerter. Int. J. Control 2013, 86, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, S.S.; Limebeer, D.J.N.; Sharp, R.S.; Smith, M.C. Steering compensation for high-performance motorcycles. In Proceedings of the 43rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Paradise Island, Bahamas, 14–17 December 2004; pp. 749–754. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.Z.Q.; Papageorgiou, C.; Scheibe, F.; Wang, F.C.; Smith, M.C. The missing mechanical circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2009, 9, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, M.Z.Q. Optimal control for semi-active suspension with inerter. In Proceedings of the 31st Chinese Control Conference, Hefei, China, 25–27 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.Z.Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, G. Performance Benefits of Using Inerter in Semi Active Suspensions. IEEE. Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Z.Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, G. Semi-active suspension with semi-active inerter and semi-active damper. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress the International Federation of Automatic Control, Cape Town, South Africa, 24–29 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Ahmadian, M.; Guo, K.H. On the benefits of semi-active suspensions with inerters. Shock Vib. 2012, 19, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Z.Q.; Hu, Y.; Du, B. Suspension Performance with One Damper and One Inerter. In Proceedings of the 24th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Taiyuan, China, 23–25 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, A.; Mammadov, M.; Sultan, I.; Hajilarov, E. Optimization of improved suspension system with inerter device of the quarter-car model in vibration analysis. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2011, 81, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Hasegawa, H. Advanced Passive Suspension with Inerter Devices and optimization design for vehicle oscillation. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.Z.Q.; Huang, L. Frequency Response of a Suspension System with Inerter and Play. In Proceedings of the 21st International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Beijing, China, 13–17 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.Z.Q. Performance Optimization for Passive Suspensions with One Damper One Inerter and Three Springs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Analysis of vibration transfer characteristics of vehicle suspension system employing inerter. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2017, 55, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M.Z.Q.; Tian, Y. Nonlinearities in Landing Gear Model Incorporating Inerter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, D.; Yuance, L.; Chen, M.Z.Q. Application of Inerter to Aircraft Landing Gear Suspension. In Proceedings of the 34th Chinese Control Conference, Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, M.Z.Q. Performance evaluation for inerter-based dynamic vibration absorbers. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 99, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, L.; Giaralis, A. Optimal design of a novel tuned mass-damper-inerter (TMDI) passive vibration control configuration for stochastically support-excited structural systems. Probabil. Eng. Mech. 2014, 38, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeski, P.; Pavlovskaia, E.; Kapitaniak, T.; Perlikowski, P. The application of inerter in tuned mass absorber. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 2015, 70, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-C.; Chen, C.-W.; Liao, M.-K.; Hong, M.-F. Performance analyses of building suspension control with inerters. In Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, New Orleans, LA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; pp. 3786–3791. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.-C.; Hong, M.-F.; Chen, C.-W. Building suspensions with inerters. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2010, 224, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, I.F.; Neild, S.A.; Wagg, D.J. Using an inerter-based device for structural vibration suppression. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1129–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami, A.; Cigada, A.; Karimi, H.R.; Zappa, E. Vibration Protection of a Famous Statue against Ambient and Earthquake Excitation Using a Tuned Inerter–Damper. Machines 2017, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, J.L.; Valiente-Blanco, I.; Cristache, C. Z-Damper: A New Paradigm for Attenuation of Vibrations. Machines 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lam, J.; Cheung, K.C. Investigation on Semi-Active Control of Vehicle Suspension using Adaptive Inerter. In Proceedings of the 21st International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Beijing, China, 13–17 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski, P.; Lazarek, M.; Perlikowski, P. Experimental study of the novel tuned mass damper with inerter which enables changes of inertance. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 404, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.D.J.; Wagg, D.J. A fluid inerter with variable inertance properties. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Structural Control, Sheffield, England, 11–13 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Suciu, B.; Tsuji, Y. Theoretical Investigation on the Dynamic Characteristics of One Degree of Freedom Vibration System Equipped with Inerter of Variable Inertance. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeski, P.; Perlikowski, P. Effects of play and inerter nonlinearities on the performance of tuned mass damper. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 88, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, X.F. Performance Investigation of Vehicle Suspension System with Nonlinear Ball-Screw Inerter. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2008, 17, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Buelga, A.; Lazar, I.F.; Jiang, J.Z.; Neild, S.A.; Inman, D.J. Assessing the Effect of Nonlinearities on the Performance of a Tuned Inerter Damper. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Gao, Q.; Nie, J. The Mem-Inerter: A New Mechanical Element with Memory. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
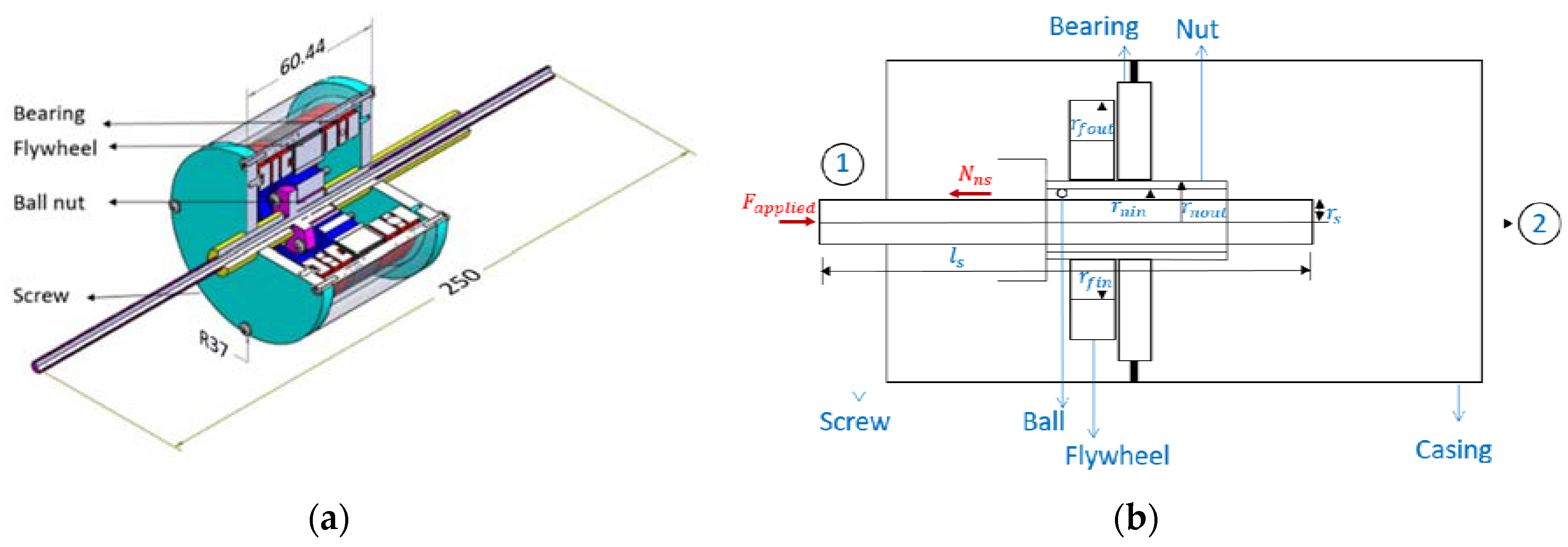
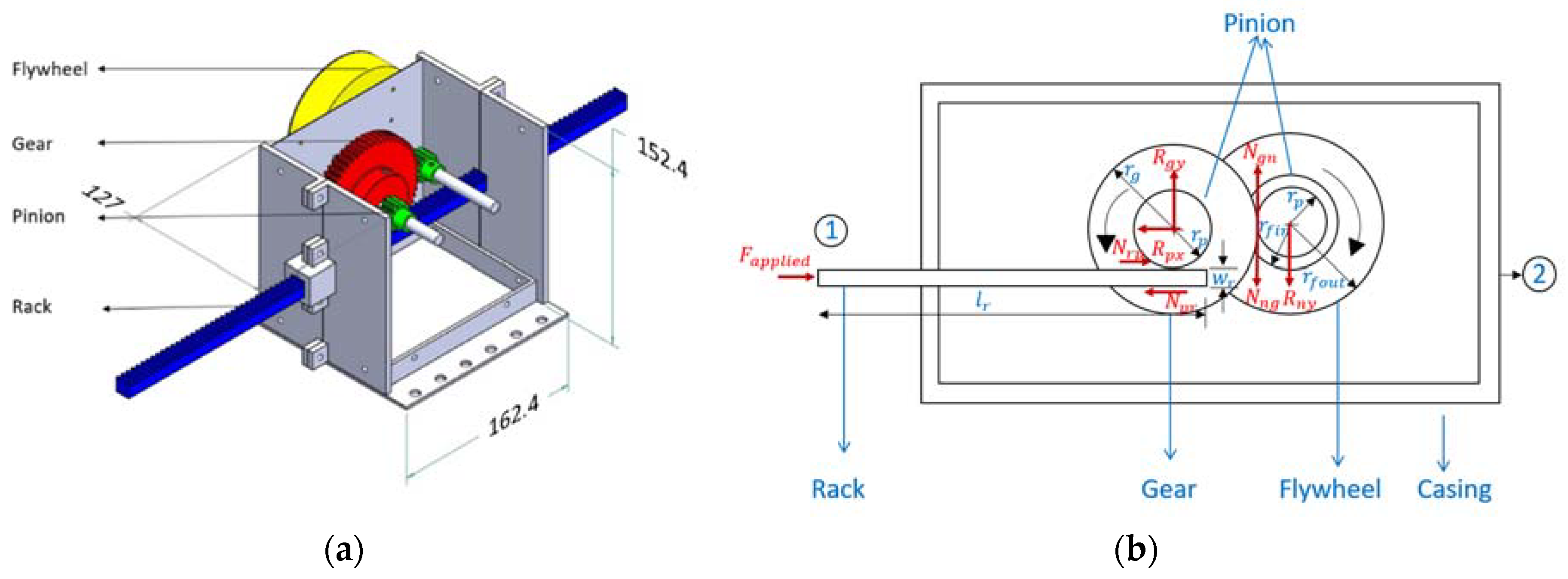
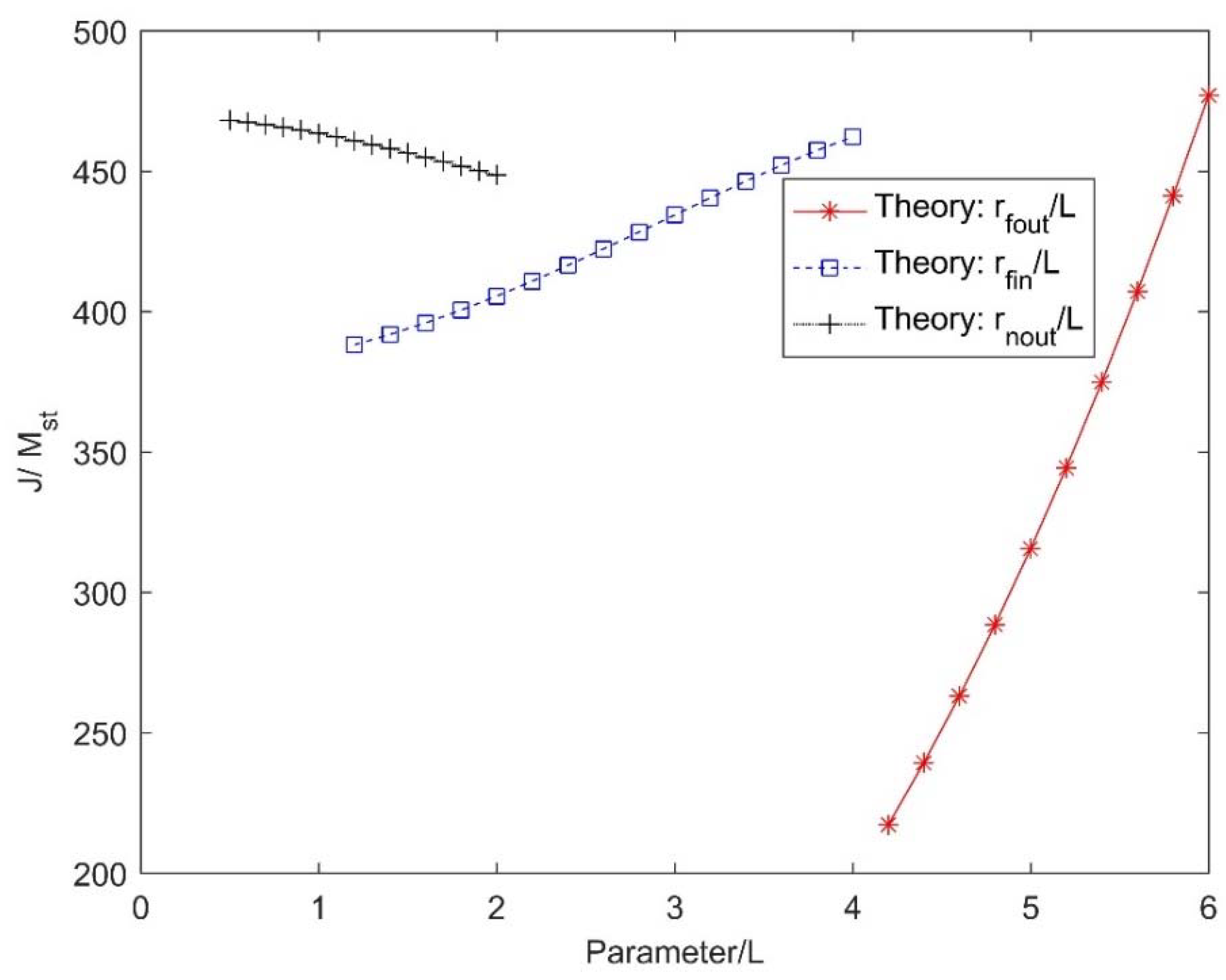
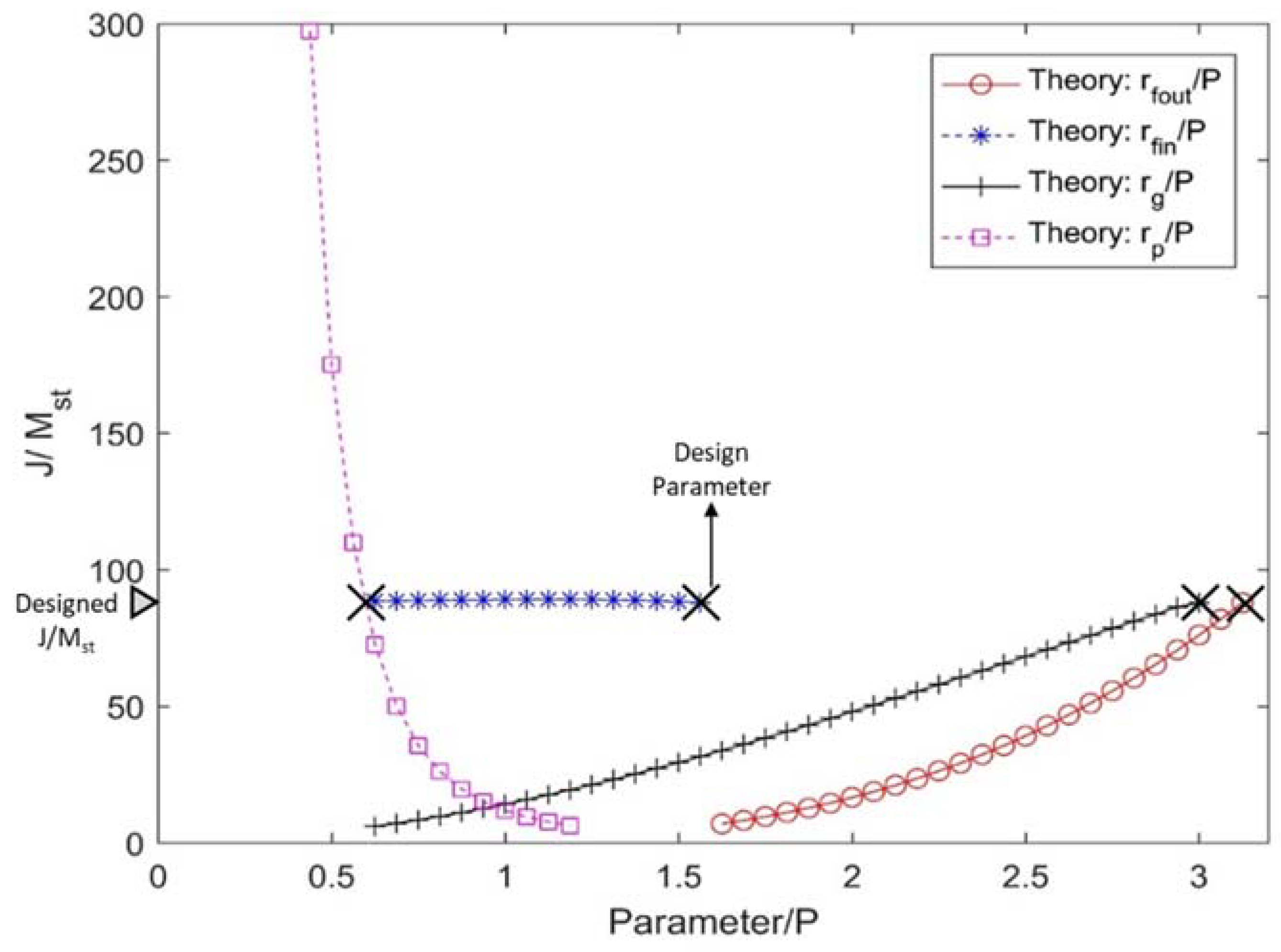



| Component | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Nut | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Thickness | 17 mm | |
| Outer radius | 5.5 mm | |
| Inner radius | 2 mm | |
| Flywheel | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Thickness | 13 mm | |
| Outer radius | 30 mm | |
| Inner radius | 20 mm | |
| Ball-Screw | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Length | 250 mm | |
| Radius | 2 mm | |
| Lead | 5 mm | |
| Casing | Mass | 0.2 kg |
| Bearing | Mass | 0.174 kg |
| Component | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gear | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Thickness | 13 mm | |
| Outer radius | 47.6 mm | |
| Inner radius | 6.4 mm | |
| Pitch | 16 mm | |
| Flywheel | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Thickness | 25.4 mm | |
| Outer radius | 50.8 mm | |
| Inner radius | 25.4 mm | |
| Pinion | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Thickness | 13 mm | |
| Outer radius | 9.5 mm | |
| Inner radius | 6.4 mm | |
| Pitch | 16 mm | |
| Rack | Density | 7890 kg/m3 |
| Length | 500 mm | |
| Width | 12.7 mm | |
| Pitch | 16 mm | |
| Casing | Mass | 0.3 kg |
| S. No | Component | Material | Density (kg/m3) | Key Parameter | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rack | Steel | 7890 | lr (length) | COTS |
| 2 | Pinion(s) | Steel | 7890 | rp (radius) | COTS |
| 3 | Gear | Steel | 7890 | rg (radius) | COTS |
| 4 | Flywheel | Aluminum | 2800 | rf (radius) | COTS |
| 5 | Casing | PLA/Acrylic | 1250 | mc (mass) | 3D printed |
| 6 | Hub | PLA | 1250 | - | 3D printed |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madhamshetty, K.; Manimala, J.M. Low-Rate Characterization of a Mechanical Inerter. Machines 2018, 6, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines6030032
Madhamshetty K, Manimala JM. Low-Rate Characterization of a Mechanical Inerter. Machines. 2018; 6(3):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines6030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadhamshetty, Karthik, and James M. Manimala. 2018. "Low-Rate Characterization of a Mechanical Inerter" Machines 6, no. 3: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines6030032
APA StyleMadhamshetty, K., & Manimala, J. M. (2018). Low-Rate Characterization of a Mechanical Inerter. Machines, 6(3), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines6030032





