Electromagnetic Vibration Analysis and Mitigation of FSCW PM Machines with Auxiliary Teeth
Abstract
1. Introduction
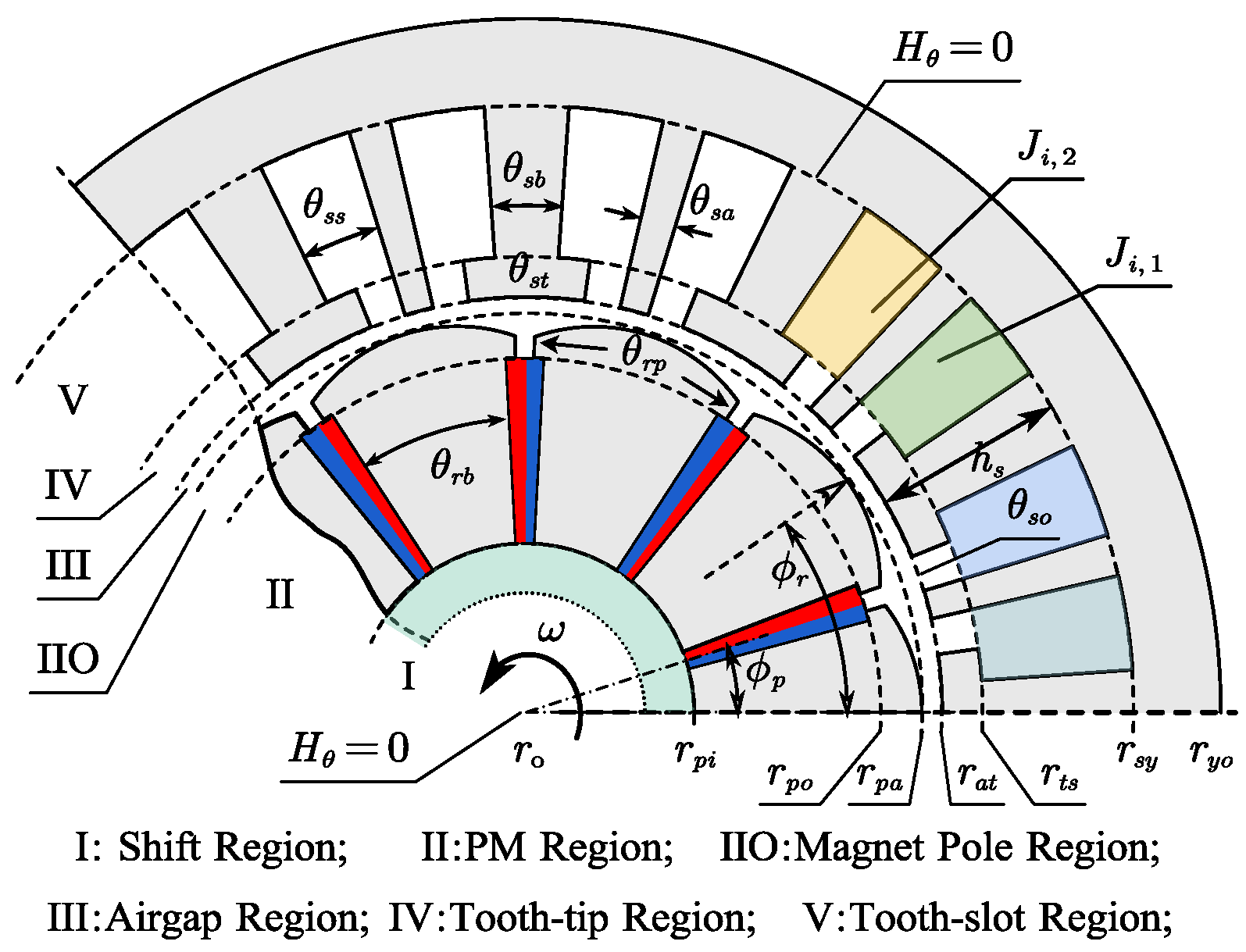
2. Equivalent Yoke Force Model
- The motor’s stator core and housing undergo small elastic deformation;
- The teeth are considered rigid bodies; under this assumption, forces acting on the teeth are transferred to the interface of teeth and yoke (no deformation-induced force loss);
- Bending moments can be equivalent to a pair of forces that have the same amplitude, opposite directions, and parallel non-collinear action lines.
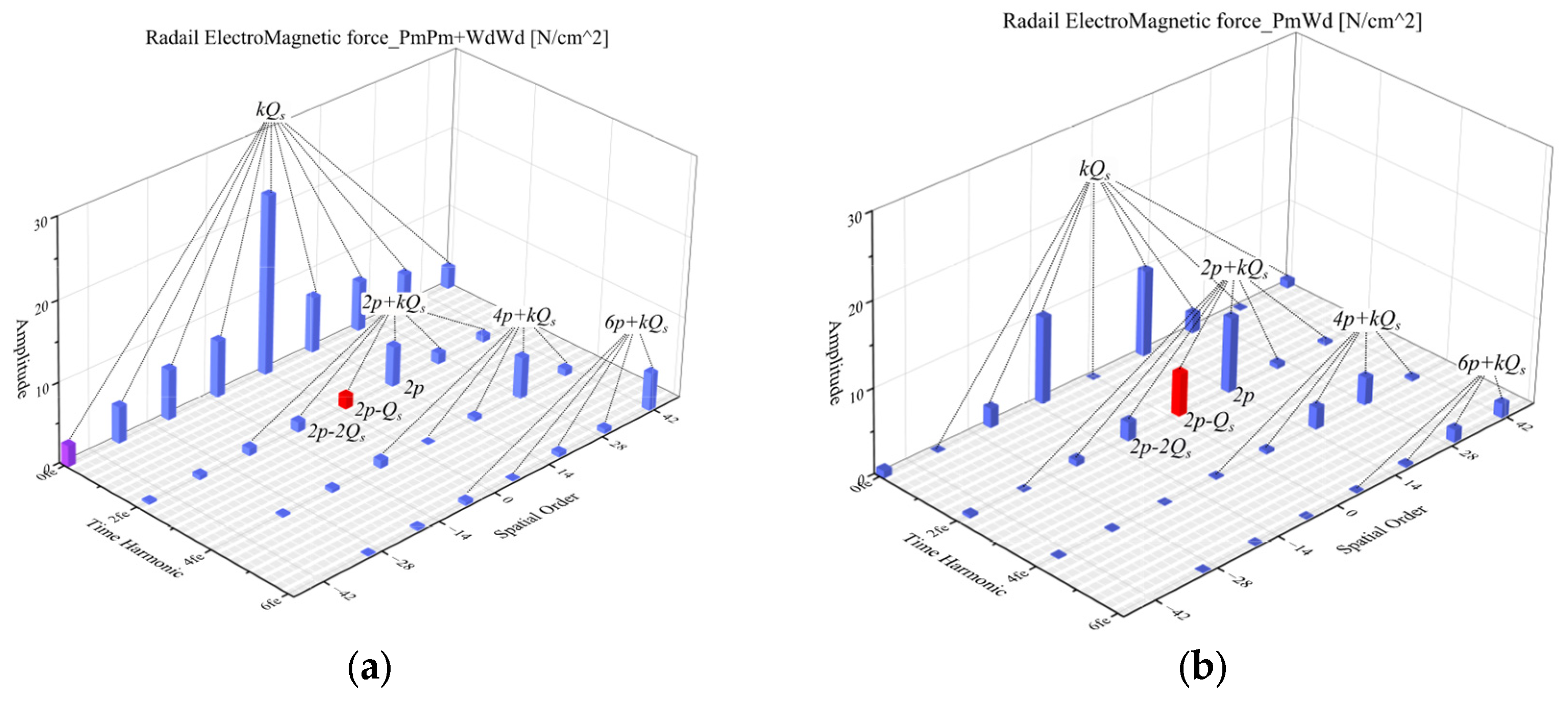
3. Electromagnetic Force Harmonics Analysis
3.1. Airgap Forces and Their Harmonics
- The interaction between PM’s pth-order field and armature’s slot harmonic component .
- Stator permeance modulation of 2p-order forces (from PM/winding self/interaction effects) generating lower-order components.
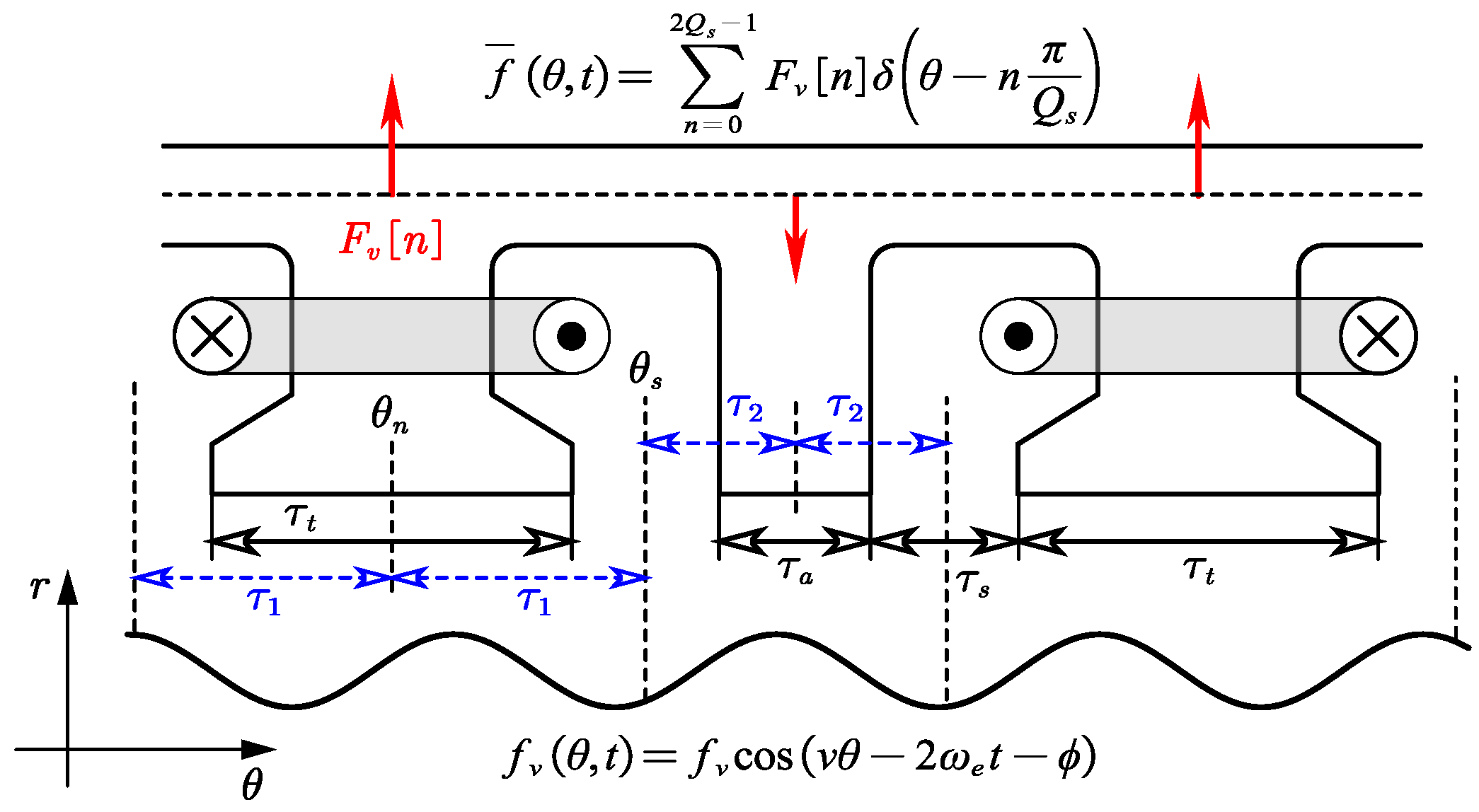
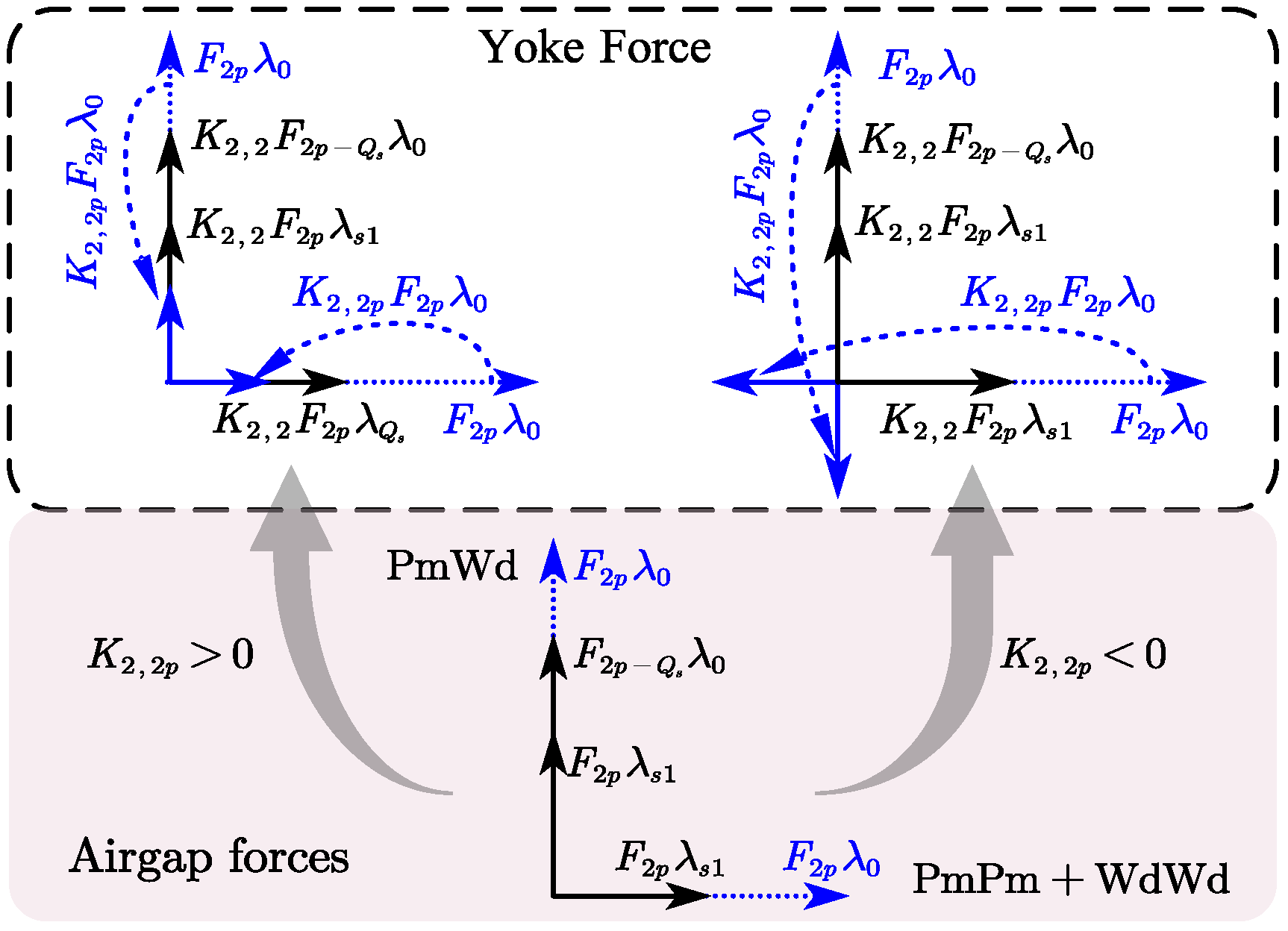
3.2. Yoke Forces and Tooth Modulation Coefficients
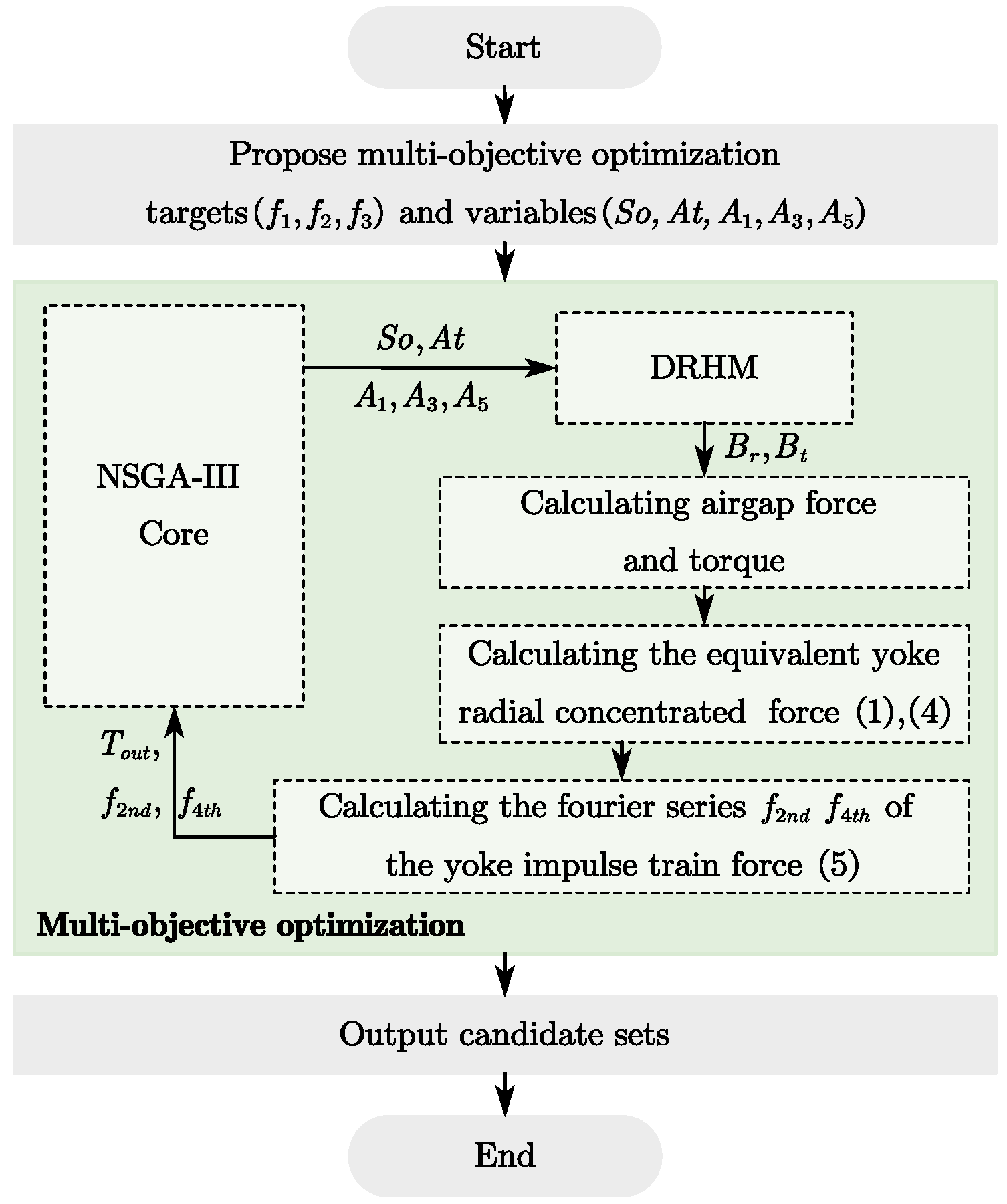
4. Auxiliary Teeth Impact Analysis and Vibration Optimization
4.1. Influence of Auxiliary Teeth on Winding MMF and Stator Permeance
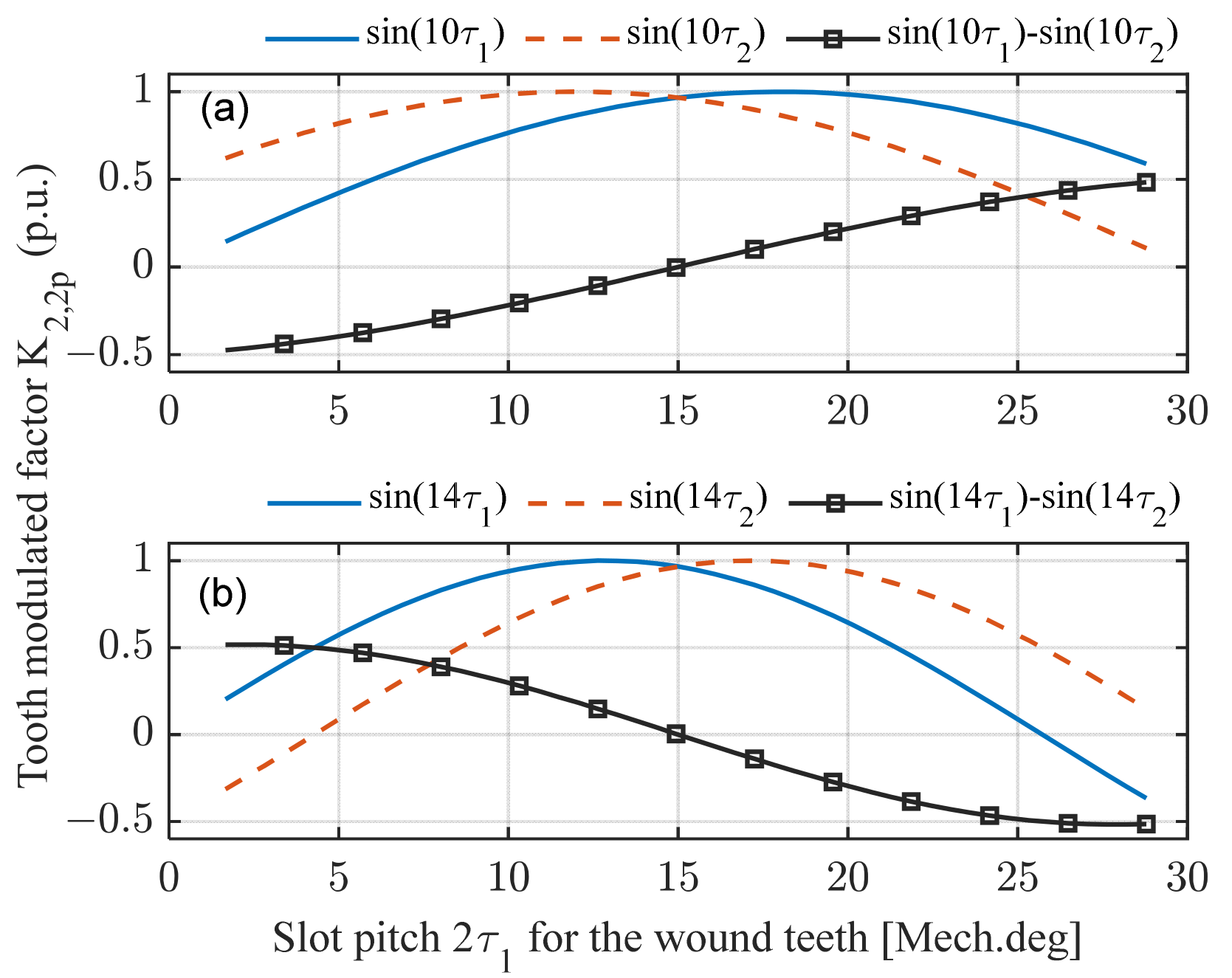
4.2. Influence of Auxiliary Teeth on Tooth Modulation Effect
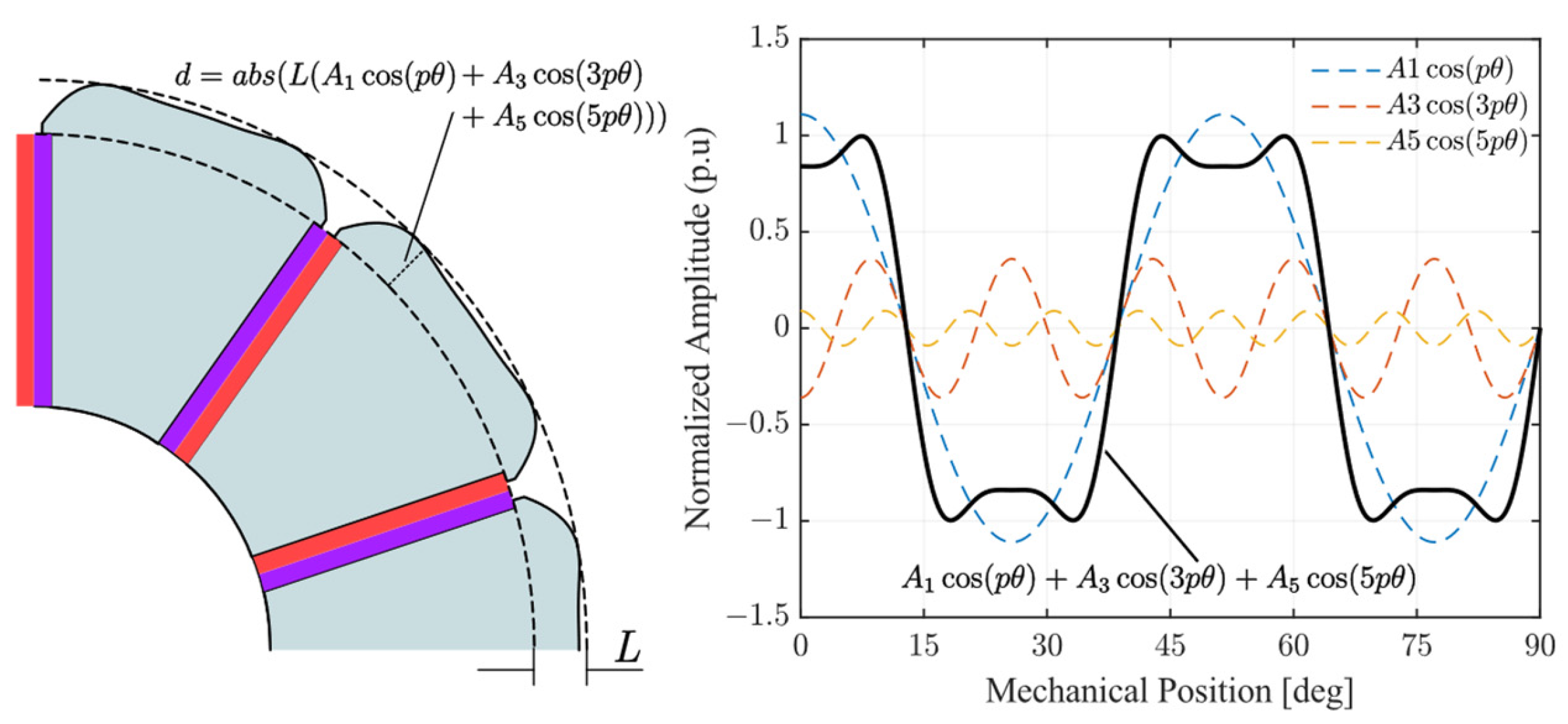
4.3. Vibration Mitigation Method
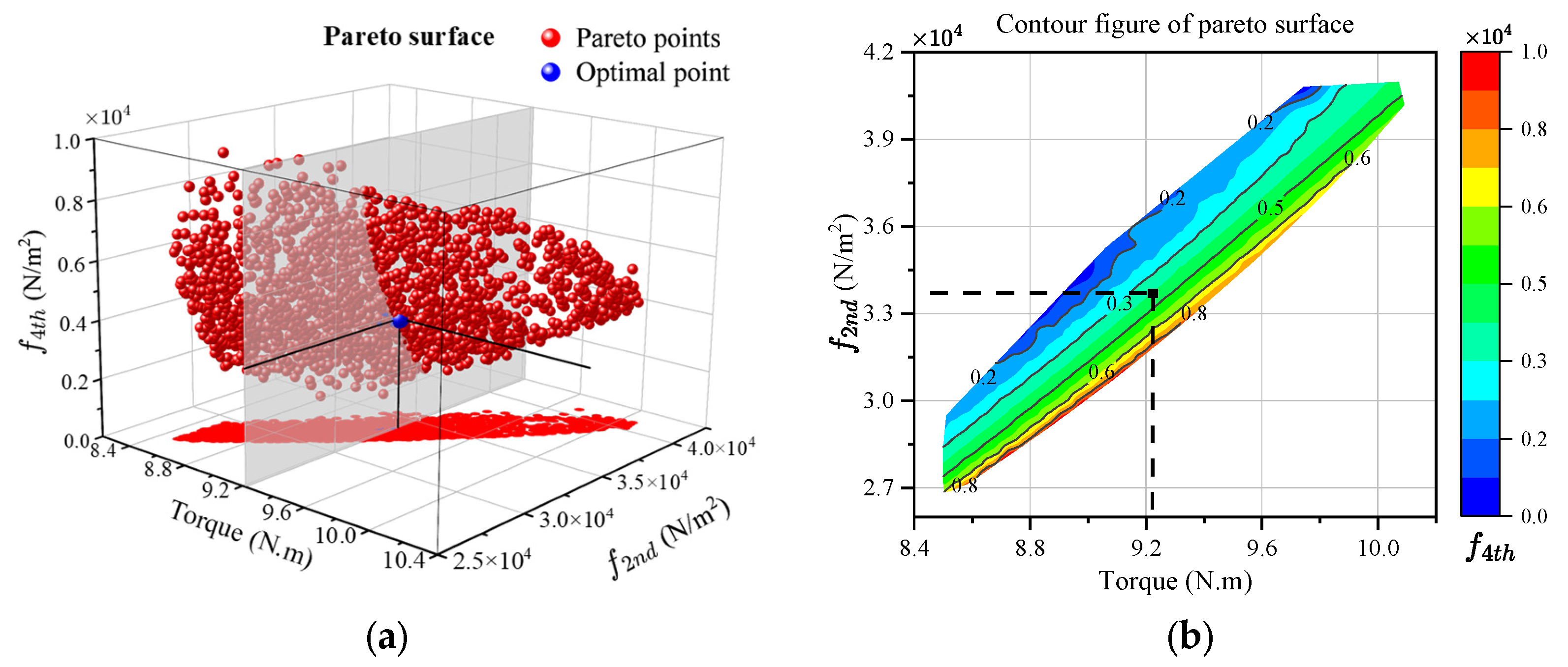
5. Optimal Design Verification Via Finite Element Analysis
5.1. Comparison of Electromagnetic Performance
5.2. Comparison of Electromagnetic Force and Vibration Response
6. Conclusions
- For configurations, the tooth modulation coefficient , where 2p-order airgap forces enhance second-order electromagnetic vibrations;
- In machines, , resulting in 2p-order forces suppressing second-order vibrations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Radial airgap force density []. | Pole pairs | ||
| Tangential airgap force density []. | Slot number | ||
| Radial force density on yoke []. | Position of the nth tooth. | ||
| Radius of airgap central circle [m]. | Slot pitch of the tooth. | ||
| Radius of yoke central circle [m]. | Slot pitch of wound teeth. | ||
| Radial concentrated forces [N/m]. | Slot pitch of auxiliary teeth. | ||
| Tangential concentrated forces [N/m]. | Auxiliary teeth width. | ||
| Bending moments on tooth shoulder. | Wound teeth width. | ||
| Bending moments on yoke. | Slot opening width. | ||
| Equivalent forces by . | m | Winding phases number. | |
| Equivalent radial forces by . | Airgap permeance. | ||
| -th order stator permeance. | Electrical angular velocity. | ||
| -th order rotor permeance. | Electrical frequency. |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Equation
Appendix A.2. Proof of Equation
Appendix A.3. Sign Derivation of Tooth Modulation Coefficient
References
- Hua, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.; Han, J. Comparative Study of High Torque Density Spoke-Type PM In-Wheel Motors for Special Vehicle Traction Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, G.; Lan, H. Vibration Contribution Analysis of Radial and Tangential Electromagnetic Force Harmonic of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 5207605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, H. Analysis and Design of Dual Three-Phase Fractional-Slot Permanent Magnet Motor with Low Space Harmonic. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Won, Y.-J.; Lim, M.-S. Analysis and Reduction of Radial Vibration of FSCW PMSM Considering the Phase of Radial, Tangential Forces and Tooth Modulation Effect. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 11, 2976–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Liu, G.; Lee, C.H.T. Design to Reduce Modulated Vibration in Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Windings PM Machines Considering Slot–Pole Combination. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, D.; Gu, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G.; Hu, C.; Sun, X.; Sun, P.; Zhu, B. Innovative approach to mitigating vibration and noise in an external rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor. J. Vib. Control. 2024, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Ji, J.; Zhu, S.; Kang, M. Star and Delta Hybrid Connection of a FSCW PM Machine for Low Space Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9266–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Gong, J.; Tong, T.; Xu, Y.; Semail, E.; Nguyen, N.-K.; Gillon, F. A Novel Five-Phase Fractional Slot Concentrated Winding with Low Space Harmonic Contents. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 8104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Gao, D.; Yu, K. Vibration Optimization of FSCW-IPM Motor Based on Iron-Core Modification for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 14834–14845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ji, N.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Mao, Y.; Liu, G. Unequal Teeth Design to Reduce Electromagnetic Vibration in Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Windings Permanent-Magnet Machine. J. Magn. 2019, 24, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, W.; Ji, N.; Zheng, J.; Luo, J. Reduction of Tooth Harmonic in Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Winding Permanent-Magnet Machines Using New Stator Design. J.Magn. 2018, 23, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, W.; Tang, H.; Ji, J. Auxiliary teeth design to reduce short-circuit current in permanent magnet generators. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2020, 4, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Yan, P. Modulation Effect of Slotted Structure on Vibration Response in Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Liu, G.; Mao, Y.; Liu, T. Investigation of Bread-Loaf Magnet on Vibration Performance in FSCW PMSM Considering Force Modulation Effect. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, S.; Ji, J.; Liu, G.; Mao, Y. Analysis and Reduction of Electromagnetic Vibration in Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Windings PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3357–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Ryu, J.-Y.; Lim, M.-S. Comparative Study of Vibration on 10-Pole 12-Slot and 14-Pole 12-Slot PMSM Considering Tooth Modulation Effect. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 4007–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Ryu, J.-Y.; Park, S.-H.; Cha, K.-S.; Won, Y.-J.; Park, C.-S.; Lim, M.-S. Investigation on Radial Vibration of FSCW PMSM According to Pole/Slot Combination Considering Phase of Radial, Tangential Force and Moment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Luk, P.C.-K.; Fei, W. Analytical Study of Stator Tooth Modulation on Electromagnetic Radial Force in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11731–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pile, R.; Devillers, E.; Le Besnerais, J. Comparison of Main Magnetic Force Computation Methods for Noise and Vibration Assessment in Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, P.; Hajjaj, A.Z.; Mohammadpour, M.; Theodossiades, S. Analytical Multiphysics Methodology to Predict Vibroacoustics in PMSMs Combining Tangential Electromagnetic Excitation and Tooth Modulation Effects. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 5997–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Gui, L.; Cao, J. Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Tangential Force effect on Electromagnetic Vibration of PM Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, D.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Qu, R. Hybrid Model for Electromagnetic Vibration Synthesis of Electrical Machines Considering Tooth Modulation and Tangential Effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 7284–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Semi-Analytical Model for Spoke-Type PM Motor Nonlinear Magnetic Field Calculation with Irregular Magnetic Pole Shape. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2024, 60, 8204709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W. Fast Calculation of Electromagnetic Vibration of Surface-Mounted PMSM Considering Teeth Saturation and Tangential Electromagnetic Force. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



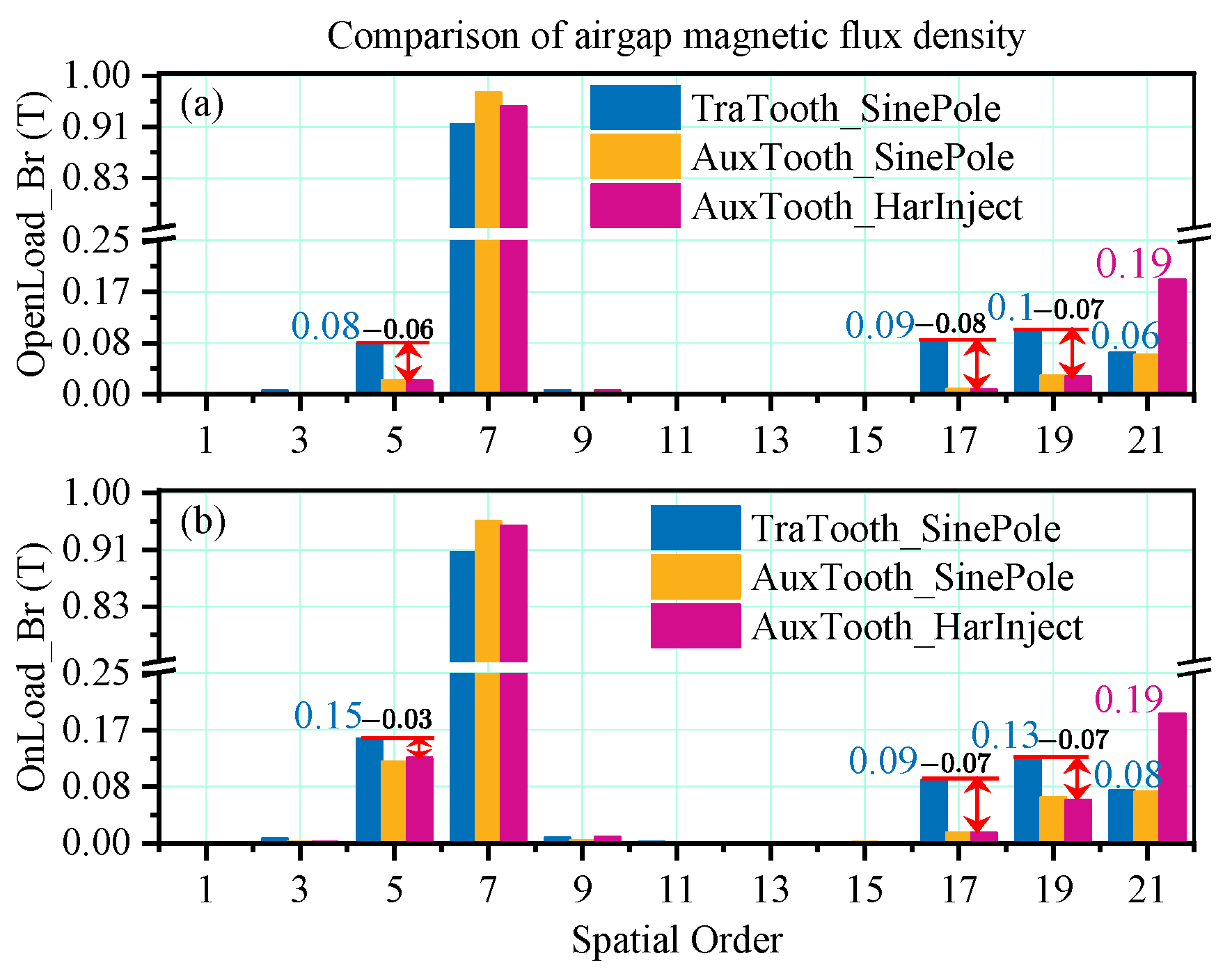
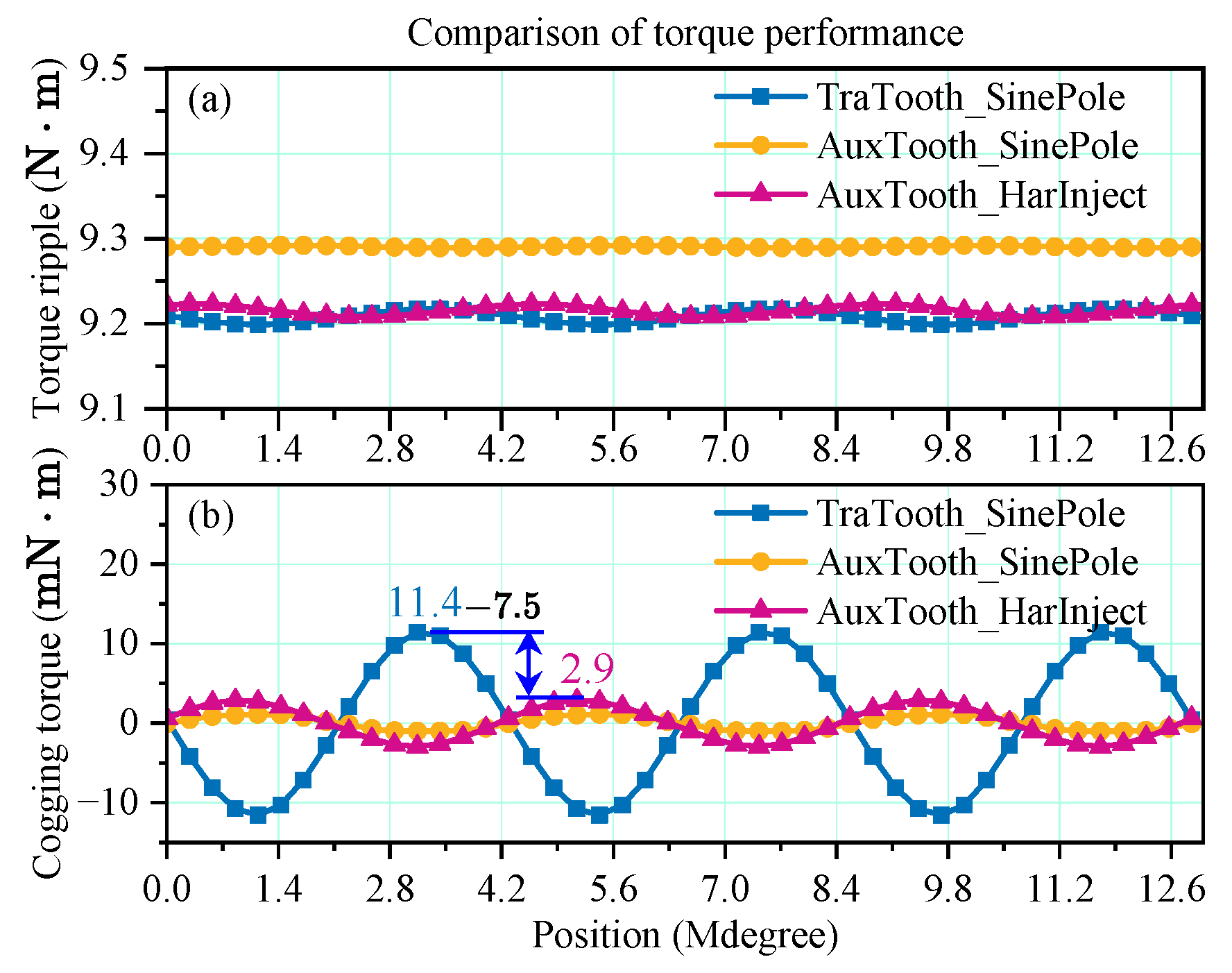
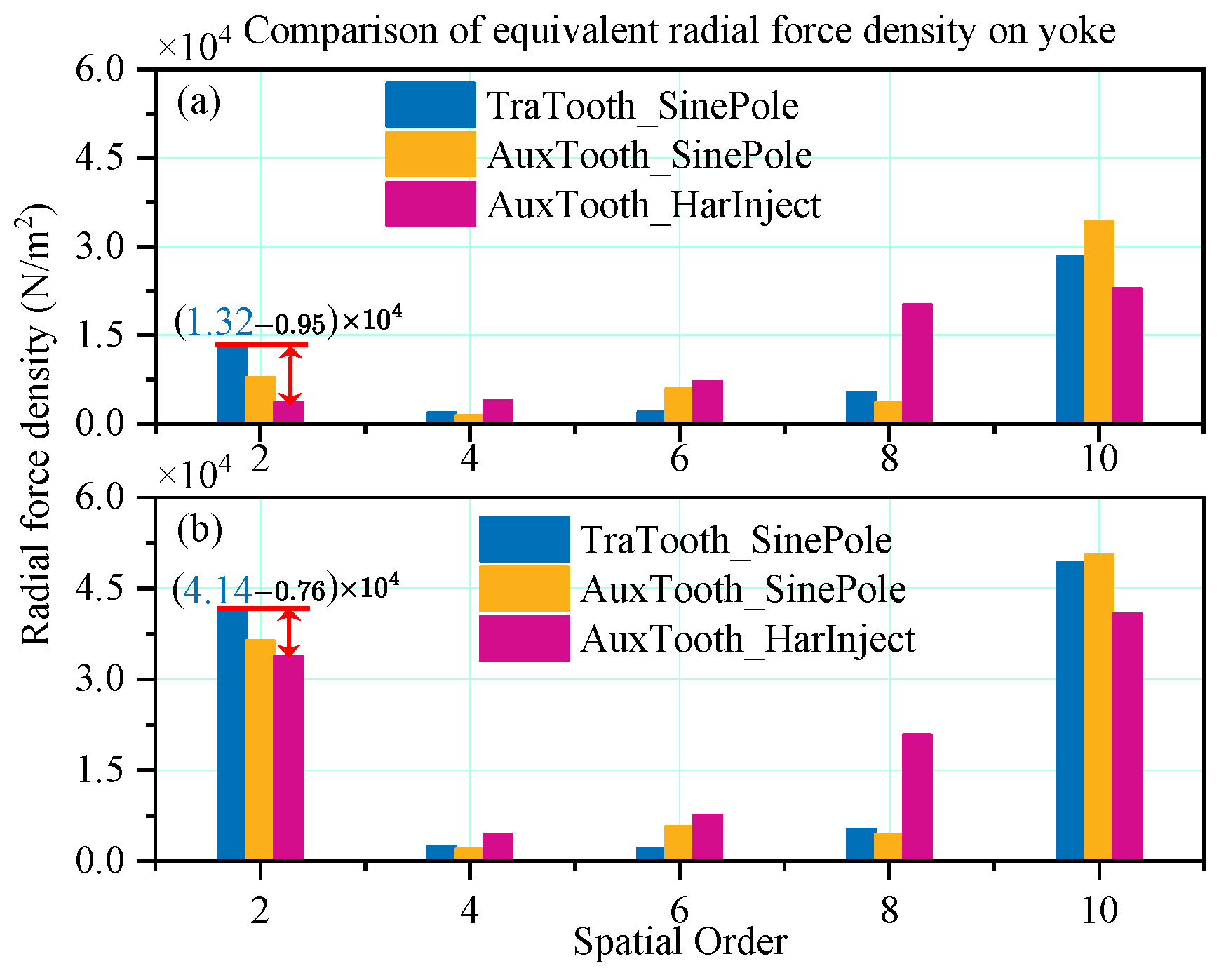
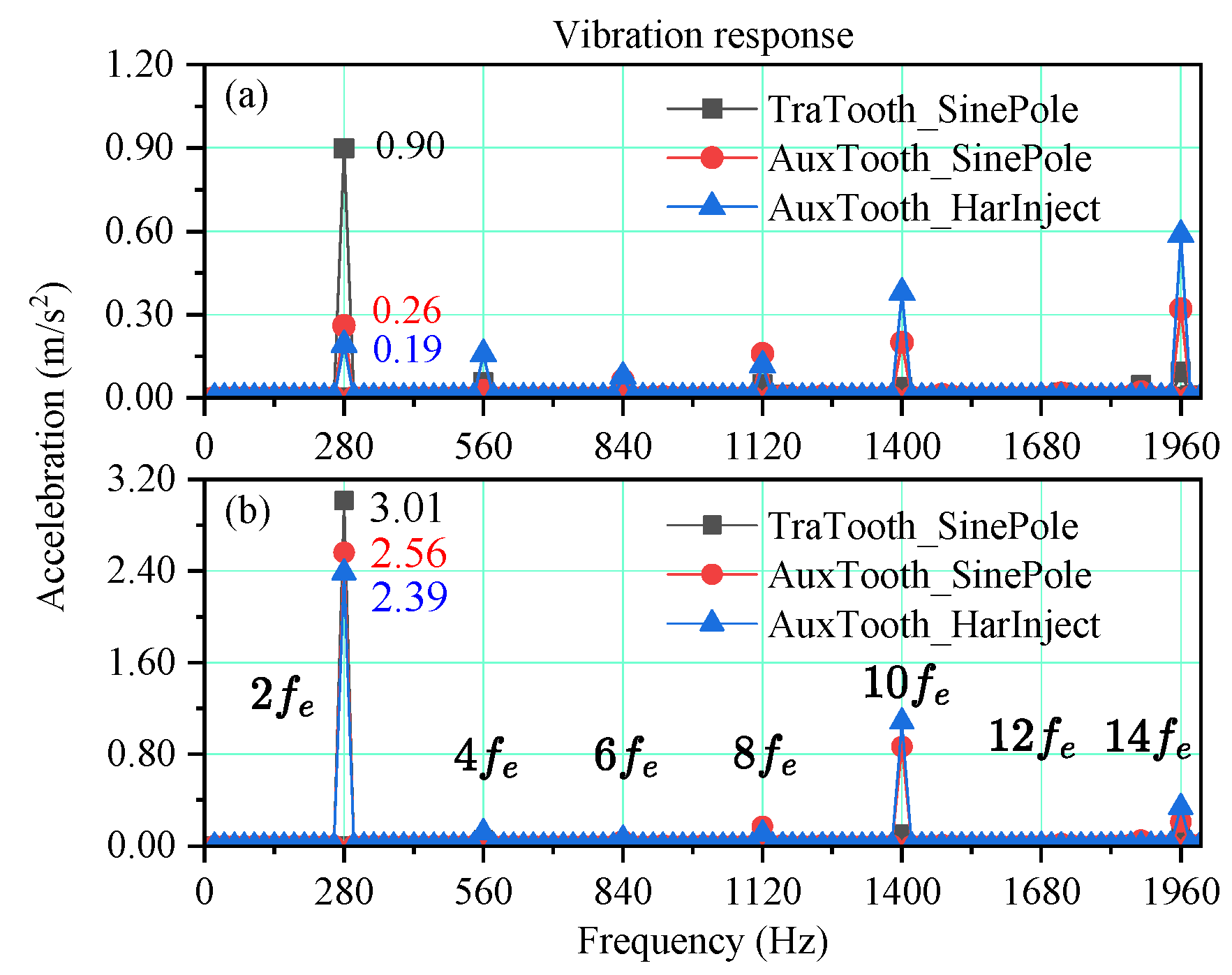

| Pm-Pm | Pm-Wd | Wd-Wd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial phase | ||||
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12s10p | −0.006 | −0.0033 | 0 | 0.0033 | 0.006 |
| Sign | |||||
| 12s14p | 0.0052 | 0.0032 | 0 | −0.0032 | −0.0052 |
| Sign | |||||
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | 62 | Tooth Height | 16 mm |
| (mm) | 56 | Tooth body width | mm |
| (mm) | 43 | Rotor Opening | 2 mm |
| (mm) | 40 | Rotor Insert (L) | 1.5 mm |
| (mm) | 39 | PM Insert | 1.5 mm |
| (mm) | 37.5 | PM Length | 15 mm |
| (mm) | 22.5 | PM Thickness | 2.5 mm |
| 1.395 | Axial Length | 80 mm |
| Parameters | TraTooth + SinePole | AuxTooth + SinePole | AuxTooth + HarInject | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slot open width (mm) | 5 | 2 | 2 | |
| Auxiliary teeth width (mm) | - | 2.5 | 2.5 | |
| Magnet poles inset (mm) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Magnet pole shape parameters | - | - | 1.079 | |
| - | - | −0.212 | ||
| - | - | 0.036 | ||
| Name | Parameters | Equivalent Stator | Housing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass density | 7372 | 2770 | |
| Young’s modulus | (GPa) | 194 | 71 |
| (GPa) | 67.3 | 71 | |
| Shear modulus | (GPa) | 74.65 | 26.7 |
| (GPa) | 25.9 | 26.7 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.3 | 0.33 |
| Modal Order | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional teeth | 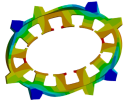 | 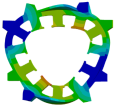 |  |
| Nature frequency | 2091 Hz | 3056 Hz | 4854 Hz |
| Auxiliary teeth | 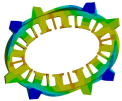 |  | 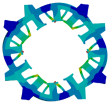 |
| Nature frequency | 2067 Hz | 3012 Hz | 4777 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Electromagnetic Vibration Analysis and Mitigation of FSCW PM Machines with Auxiliary Teeth. Machines 2025, 13, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090867
Zhang H, Wang W, Li X, Wang Z. Electromagnetic Vibration Analysis and Mitigation of FSCW PM Machines with Auxiliary Teeth. Machines. 2025; 13(9):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090867
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huang, Wei Wang, Xinmin Li, and Zhiqiang Wang. 2025. "Electromagnetic Vibration Analysis and Mitigation of FSCW PM Machines with Auxiliary Teeth" Machines 13, no. 9: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090867
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, W., Li, X., & Wang, Z. (2025). Electromagnetic Vibration Analysis and Mitigation of FSCW PM Machines with Auxiliary Teeth. Machines, 13(9), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090867







