Review on Melt Electrowriting Modelling and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
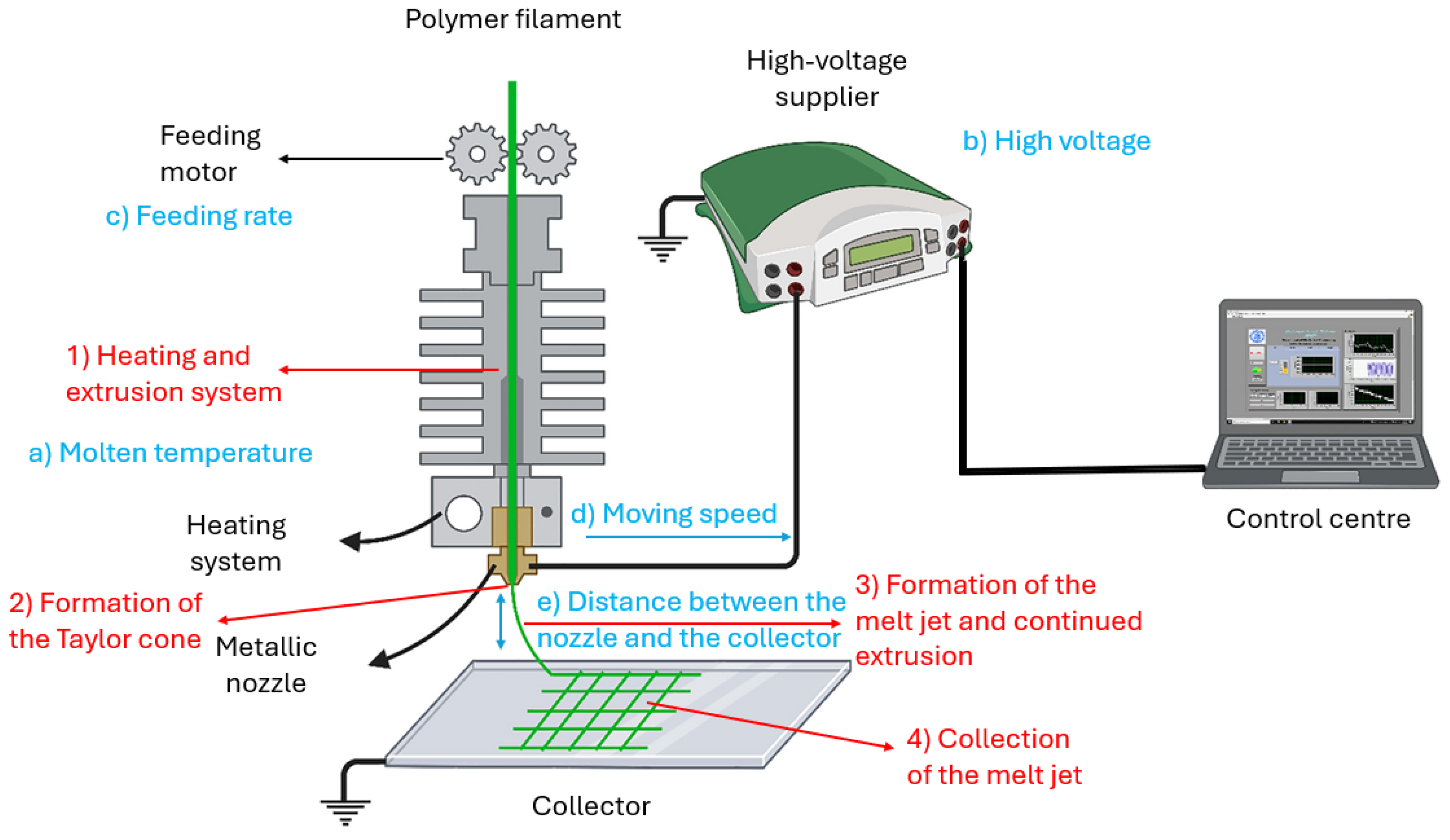
2. Modelling
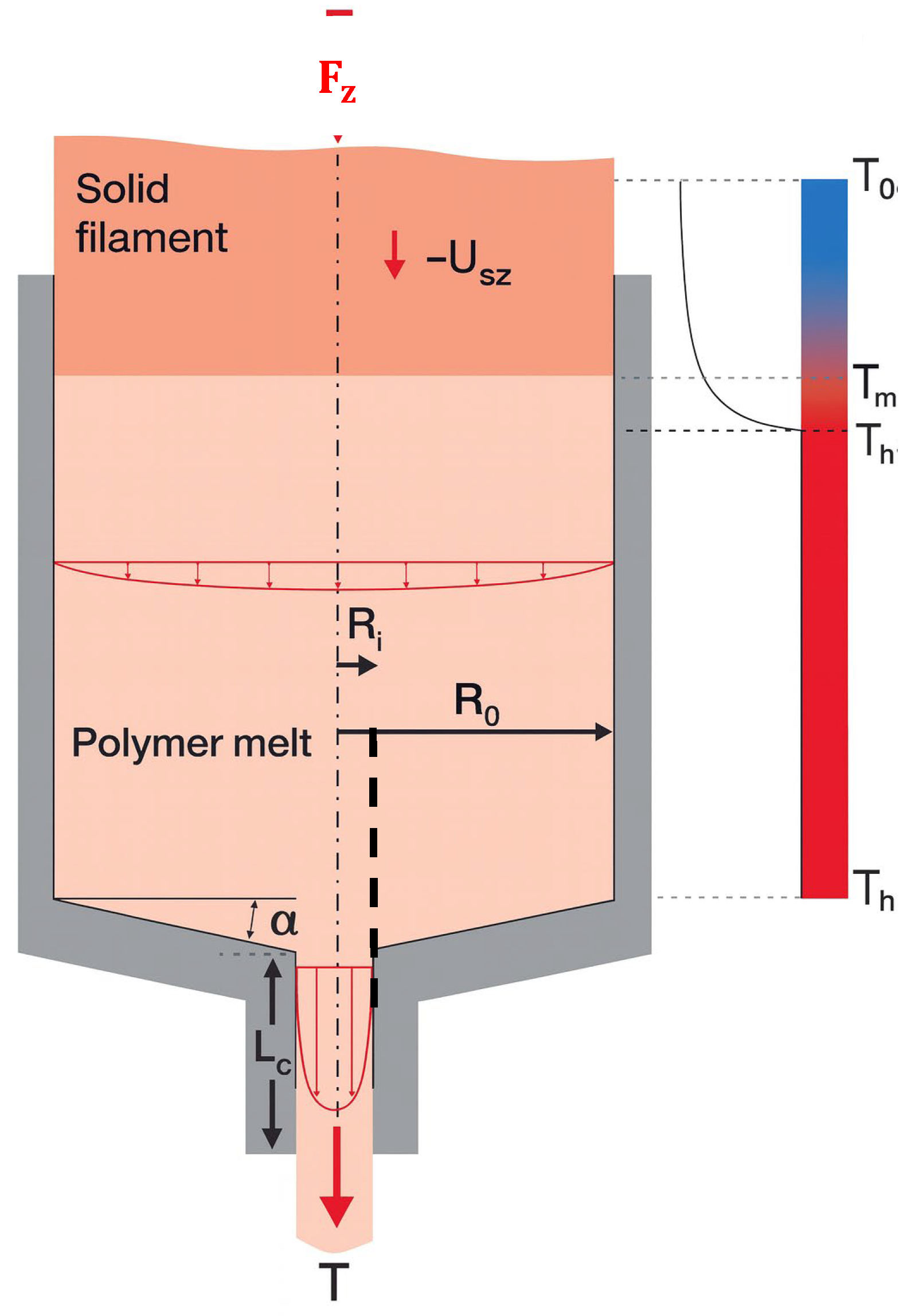
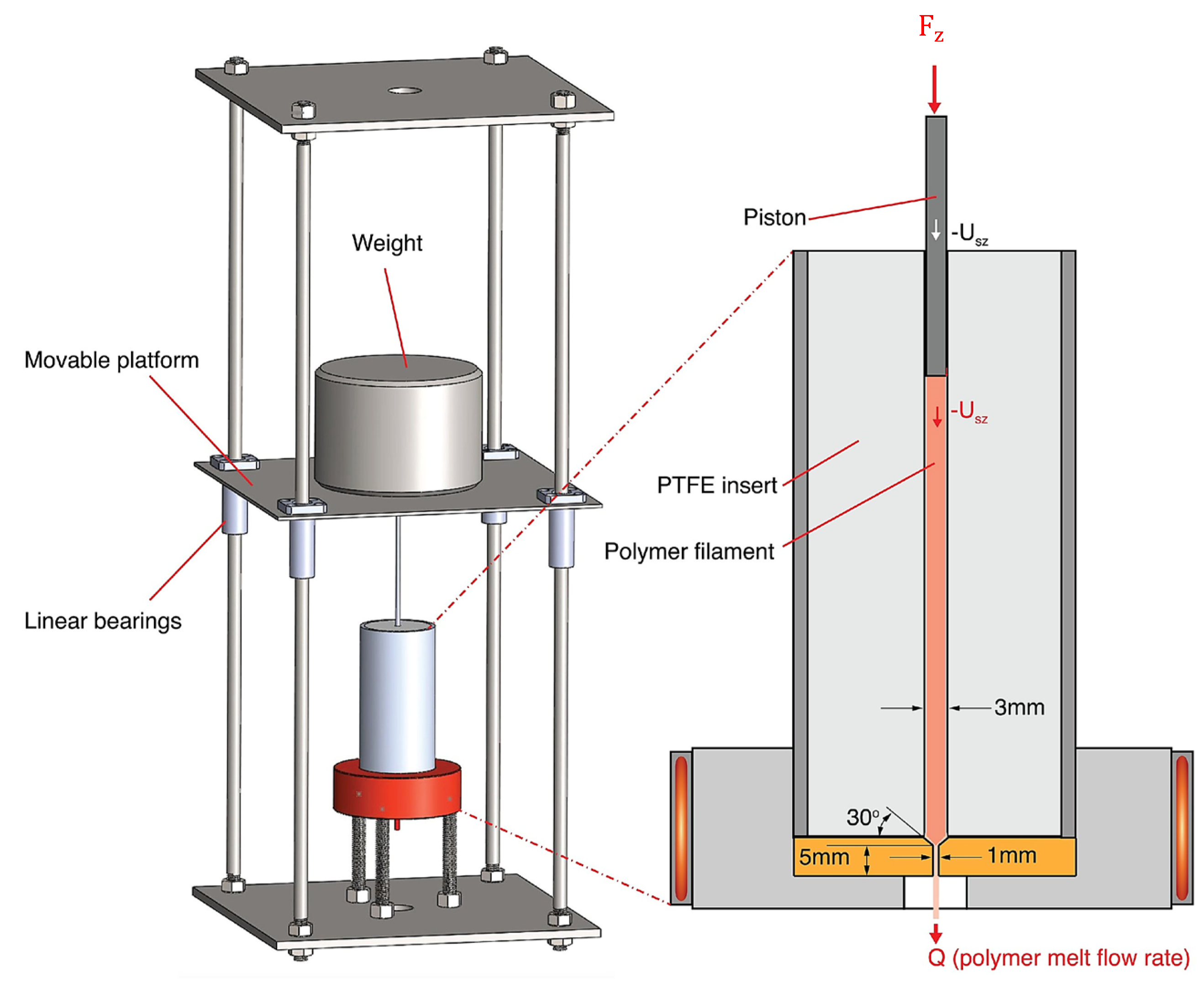
2.1. Heating and Extrusion System
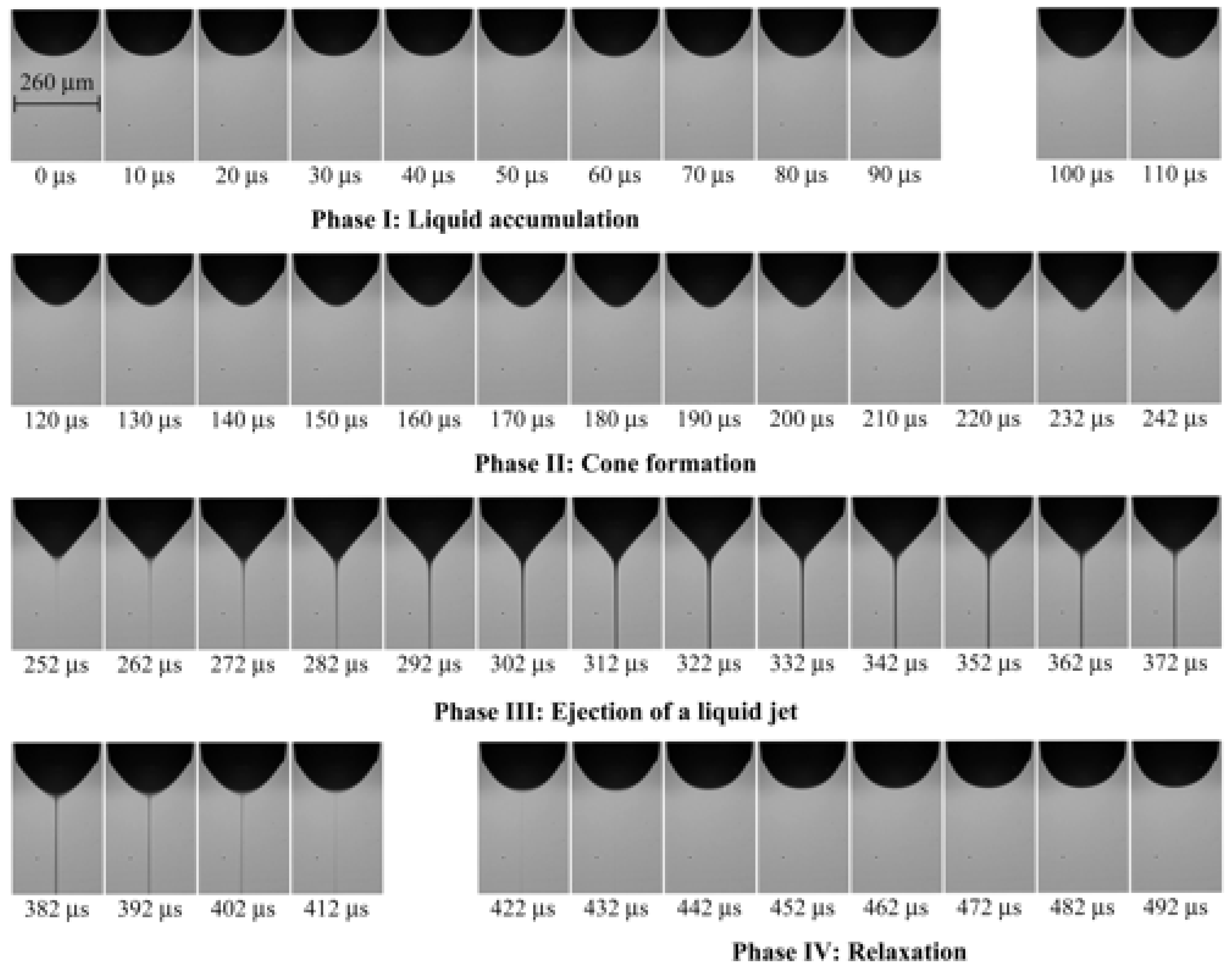
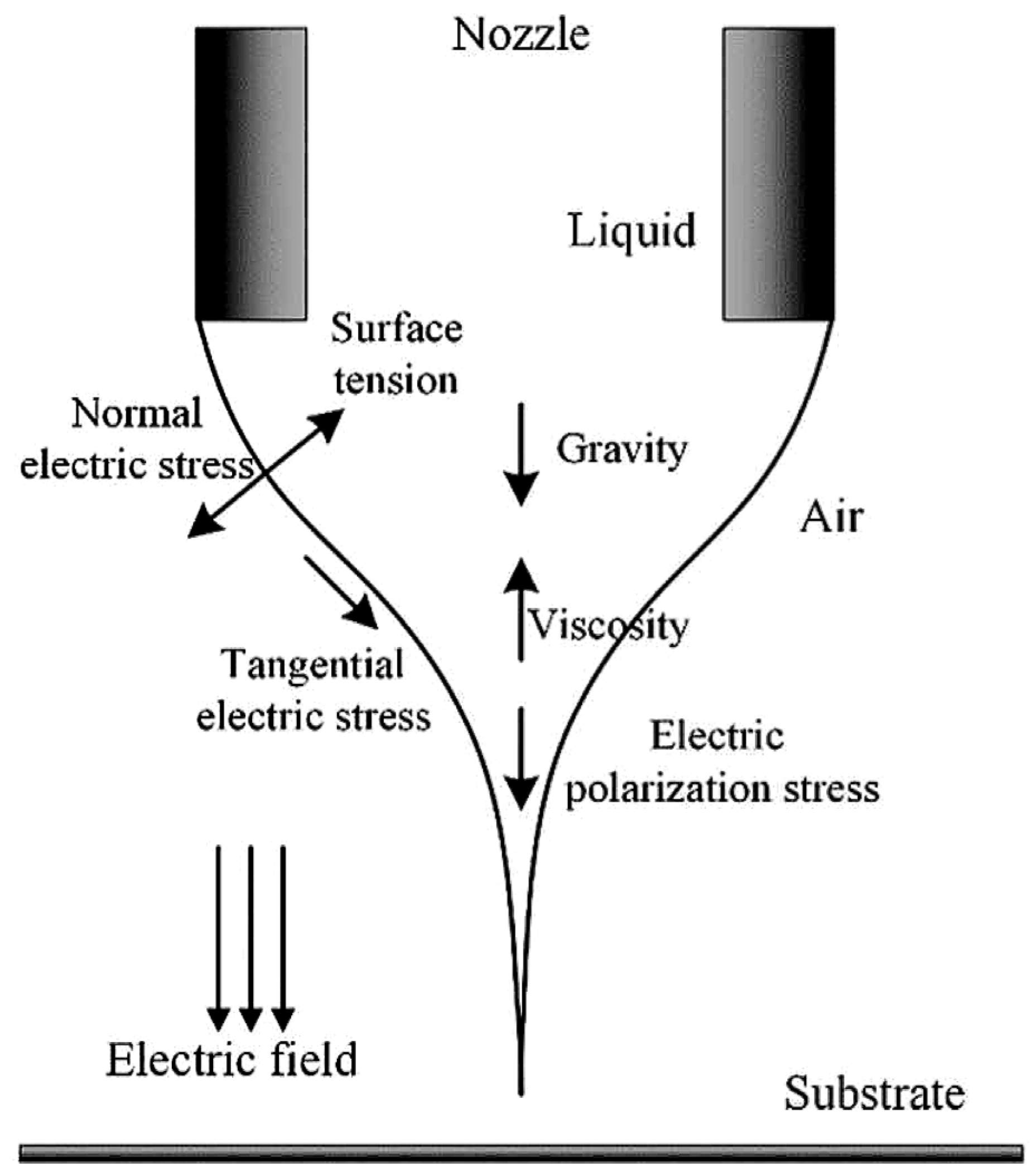
2.2. Formation of the Taylor Cone
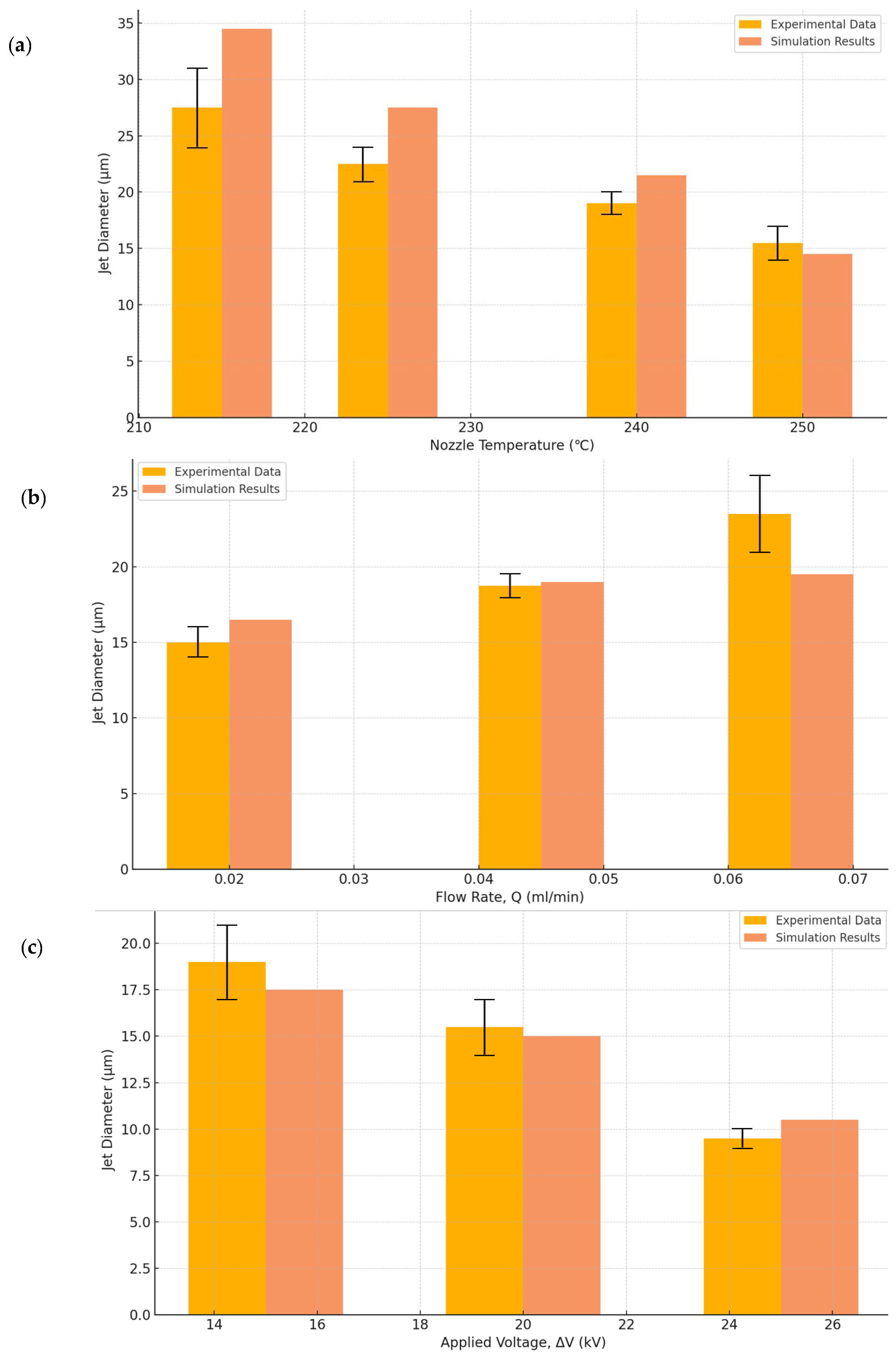
2.3. Melt Jet Formation and Continuous Extrusion
2.4. Collection of the Melt Jet
3. MEW Applications
3.1. Energy Storage
3.2. Filtration and Separation
3.3. Microfluidics
3.4. Biomedical Scaffold
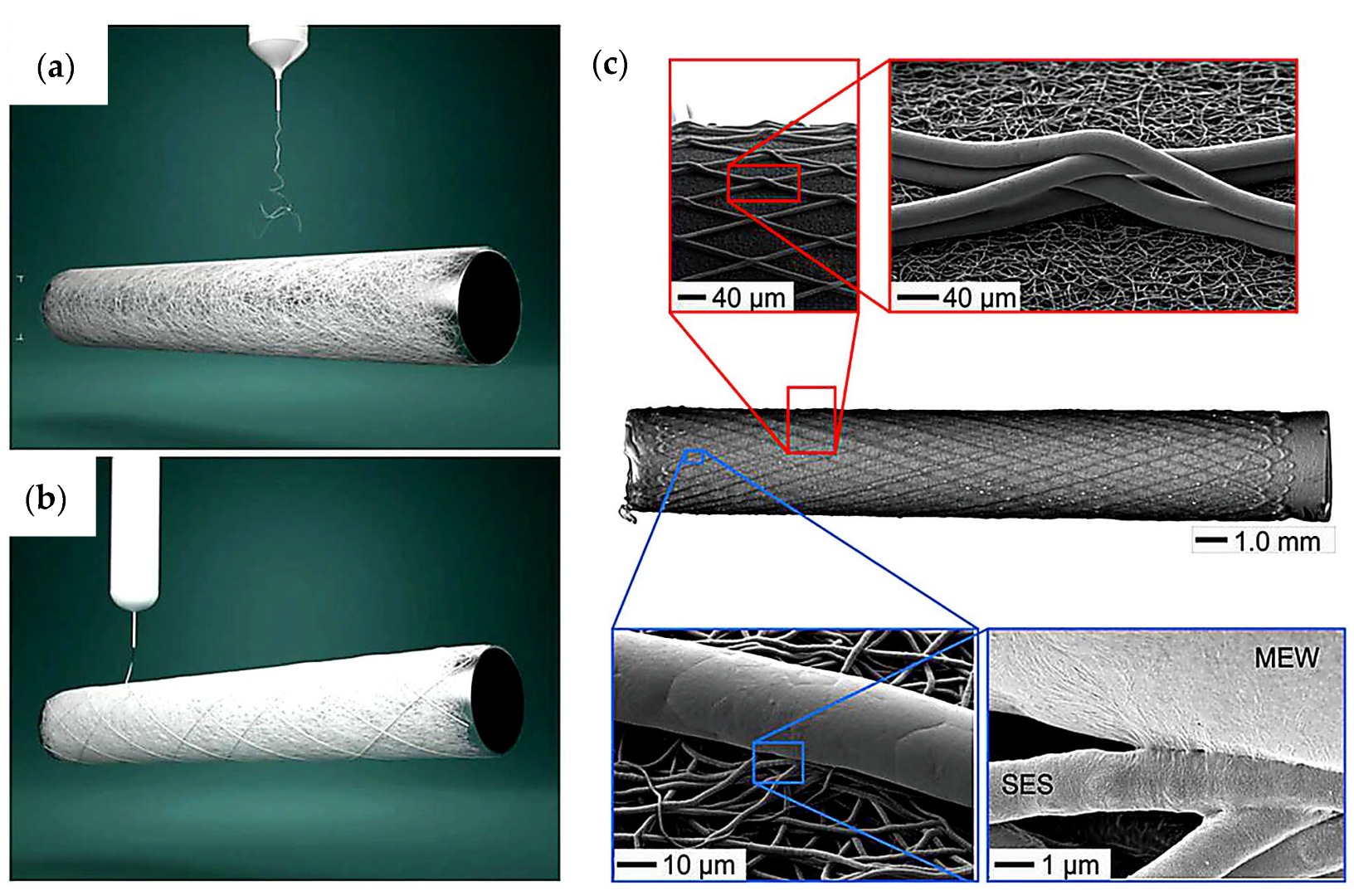
3.4.1. MEW Scaffold Developments
3.4.2. Hybrid Scaffold
3.5. Drug Delivery
| Year | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Curcumin-loaded melt-electrospun PCL fibres with smoother surfaces and higher drug content | [81] |
| 2017 | PLA/starch/PCL/triclosan scaffolds with 3% nHAp to improve degradability, hydrophilicity, and antibacterial activity | [82] |
| 2019 | Fibrous membranes (fabricated by MEW) with varying ratios of PCL, PEG, and ciprofloxacin for wound dressing applications | [83] |
| 2020 | Portable melt electrospinning device designed to create PCL/Fe3O4 fibre membranes for magnetic hyperthermia therapy | [84] |
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges and Technological Limitations
4.1.1. System Design
4.1.2. Material Limitation
4.1.3. Scalability Constraints
4.1.4. Environmental Sensitivity
4.1.5. Sustainability Considerations
4.2. Future Direction
4.2.1. Hybrid Manufacturing
4.2.2. Material Innovation
4.2.3. Improved Precision and Customisation
4.2.4. Scale-Up
4.2.5. Environmental Control
4.2.6. Sustainable Manufacturing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Wen, P. Metal vaporization and its influence during laser powder bed fusion process. Mater. Des. 2022, 215, 110505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieminski, P. Chapter 7—Introduction to fused deposition modelling. In Additive Manufacturing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 217–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumakala, P.K.; Santo, J.; Thomas, A. A critical review on the fused deposition modelling of thermoplastic polymer composites. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2020, 201, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollet, A.; Stack, T. On electricity communicated by sparks. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1753, 45, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, J.F. Improved Methods of and Apparatus for Electrically Separating the Relatively Volatile Liquid Component from the Component of Relatively Fixed Substances of Composite Fluids. United Kingdom Patent 6385, 19 May 1900. [Google Scholar]
- Boland, E.D.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Pawlowski, K.J.; Bowlin, G.L. Tailoring tissue engineering scaffolds using electrostatic processing techniques: A study of poly(glycolic acid) electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Part. A 2001, 38, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: Characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.; Murugesan, S.; Pushparaj, V.; Nalamasu, O.; Ajayan, P.M.; Linhardty, R.J. Preparation of biopolymer fibers by electrospinning from room temperature ionic liquids. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewner, S.; Heene, S.; Baroth, T.; Heymann, H.; Cholewa, F.; Blume, H.; Blume, C. Recent advances in melt electro writing for tissue engineering for 3D printing of microporous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 896719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P.D. Melt electrowriting with additive manufacturing principles. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 2, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Direct writing by way of melt electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2011, 21, 5651–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, M.; Seifi, S.; Akbari, A.; Mohammadi, K.; Shamloo, A.; Movahhedy, M.R. Melt electrowriting of PLA, PCL, and composite PLA/PCL scaffolds for tissue engineering application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichholz, K.F.; Gonçalves, I.; Barceló, X.; Federici, A.S.; Hoey, D.A.; Kelly, D.J. How to design, develop and build a fully-integrated melt electrowriting 3D printer. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 58, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM52900-15; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Terminology. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Altıparmak, S.C.; Yardley, V.A.; Shi, Z.; Lin, J. Extrusion-based additive manufacturing technologies: State of the art and future perspectives. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 83, 607–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıparmak, S.C.; Daminabo, S.I.C. Suitability analysis for extrusion-based additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. Front. 2024, 3, 200106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, A. Fused Deposition of Ceramics: A Comprehensive Experimental, Analytical and Computational Study of Material Behaviour, Fabrication Process and Equipment Design. Ph.D. Thesis, Drexel University Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/7a42ce9237bce7b25bee6dc952e70efb/1?pq-origsite=gscholarandcbl=18750anddiss=y (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Ramanath, H.S.; Chua, C.K.; Leong, K.F. Melt flow behaviour of poly-ε-caprolactone in fused deposition modelling. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón, M.D.; Gibson, I.; Benítez, A.N. Process and material behaviour modelling for a new design of micro-additive fused deposition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 2717–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, Z.; Alemán, M.E.; Benítez, A.N.; Monzon, M.D. Theoretical-experimental evaluation of different biomaterials for parts obtaining by fused deposition modelling. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2016, 89, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaqour, B.; Abuabiah, M.; Abdel-Fattah, S. Gaining a better understanding of the extrusion process in fused filament fabrication 3D printing: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, A.; Guceri, S.; Bertoldi, M. Liquefier dynamics in fused deposition. ASME J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2004, 126, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, T.A.; Puentes, J.; Kattinger, J. Fused filament fabrication melting model. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Disintegration of water drops in an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1964, 280, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Electrically driven jets. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marginean, I.; Parvin, L.; Heffernan, L.; Vertes, A. Flexing the electrified meniscus: The birth of jet in electrosprays. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4202–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, J.; Taylor, G.I. Electrohydrodynamics: A review of the role of interfacial shear stresses. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 1969, 1, 111–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zeng, L. Simulation and validation of droplet generation process for revealing three design constraints in electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Micromachines 2019, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gañán-Calvo, A.; Dávila, J.; Barrero, A. Current and droplet size in the electrospraying of liquids. Scaling laws. J. Aerosol Sci. 1997, 28, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, A.; Gañán-Calvo, A.; Dávila, J.; Palacios, A.; Gómez-González, E. The role of the electrical conductivity and viscosity on the motions inside taylor cones. J. Electrost. 1999, 47, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Farouk, B.; Ko, F. Numerical modeling of an electrostatically driven liquid meniscus in the cone–jet mode. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastow, O.; Balachandran, W. Numerical simulation of electrohydrodynamic (EHD) atomization. J. Electrost. 2006, 64, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Oleshuk, R.D.; Cann, N.M. Characterization of microstructured fibre emitters: In pursuit of improved nano electrospray ionization performance. Analyst 2012, 137, 4150–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin, K. Singh and Arunkumar Subramanian. Phase-field simulations of electrohydrodynamic jetting for printing nano-to-microscopic constructs. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25022–25028. Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/ra/d0ra04214e#!divAbstract (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Cândido, S.; Páscoa, J.C. A three-dimensional numerical investigation of taylor cone jets instabilities using VOF method. In Proceedings of the ASME 2023 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, New York, NY, USA, 29 October–2 November 2023; Volume 9: Fluids Engineering. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Non-Newtonian Fluid. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-Newtonian_fluid (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Spivak, A.; Dzenis, Y.; Reneker, D. A model of steady state jet in the electrospinning process. Mech. Res. Commun. 2000, 27, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, M.M.; Shin, M.; Rutledge, G.; Brenner, M.P. Electrospinning and electrically forced jets. I. Stability theory. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 2201–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, M.M.; Shin, M.; Rutledge, G.; Brenner, M.P. Electrospinning and electrically forced jets. II. Applications. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.J. The stretching of an electrified non-Newtonian jet: A model for electrospinning. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 3912–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassopoulos, D.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. A generalized Giesekus constitutive model with retardation time and its association to the spurt effect. J. Non-Newton. Fluid. Mech. 1995, 57, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, C.P.; Joo, Y.L. Electrospinning of viscoelastic Boger fluids: Modelling and experiments. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 053102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Zhou, H.; Joo, Y.L. Modelling of non-isothermal polymer jets in melt electrospinning. J. Non-Newton. Fluid. Mech. 2008, 153, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Cho, D.; Joo, Y.L. Modelling of melt electrospinning for semi-crystalline polymers. Polymer 2010, 51, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Katayama, K.; Amano, T. Some aspects of nonisothermal crystallization of polymers. II. Consideration of the isokinetic condition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1973, 17, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadeo, N.; Morikawa, K.; Naraghi, M.; Green, M.J. Modelling of downstream heating in melt electrospinning of polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynevich, A.; Liashenko, I.; Dalton, P.D. Accurate prediction of melt electrowritten laydown patterns from simple geometrical considerations. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, F.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y.; Zaeri, A.; Zgeib, R.; Mansouri, M.; Chang, R.C. Analytical interpretation of microscale fiber deviation in designing for polymer melt electrohydrodynamic-based additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 58, 103035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, F.; Zaeri, A.; Zgeib, R.; Chang, R.C. A holistic model for melt electrowritten three-dimensional structured materials based on residual charge. Int. J. Bioprint. 2022, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.; Bhullar, S.K.; Mohtaram, N.K.; Willerth, S.M.; Jun, M.B.G. Using mathematical modelling to control topographical properties of poly(ε-caprolactone) melt electrospun scaffolds. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 065009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Zhou, H.; Cho, Y.; Audus, D.; Joo, Y.L. Structural properties and superhydrophobicity of electrospun polypropylene fibers from solution and melt. Polymer 2010, 51, 6005–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Padhye, R.; Arnold, L. Melt-electrospinning of polypropylene with conductive additives. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6387–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praeger, M.; Saleh, E.; Vaughan, A.; Stewart, W.J.; Loh, W.H. Fabrication of nanoscale glass fibers by electrospinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 063114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, T.F.; Wu, C.M.; Chou, M.H.; Guo, Z.L. Melt electrospun reduced tungsten oxide/polylactic acid fiber membranes as a photothermal material for light-driven interfacial water evaporation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28955–28962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Bubakir, M.M.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y. Water filtration properties of novel composite membranes combining solution electrospinning and needleless melt electrospinning methods. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xia, S.; Yao, P.; Gong, R.H.; Liu, Q.; Deng, B. Structure regulation and properties of melt-electrospinning composite filter materials. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, B.; Jafek, A.; Lambert, C.; Goenner, B.; Moghimifam, H.; Nze, U.; Kamarapu, S. A review of current methods in microfluidic device fabrication and future commercialization prospects. Inventions 2018, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, F.; Fang, F.; Yang, F.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, X. Fabrication of microfluidic channels based on melt-electrospinning direct writing. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2018, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, F.; Risch, P.; Arnold, K.; Sevim, S.; Puigmartí-Luis, J.; Quick, A.; Thiel, M.; Hrynevich, A.; Dalton, P.D.; Helmer, D.; et al. Fabrication of arbitrary three-dimensional suspended hollow microstructures in transparent fused silica glass. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, N.C.; Daley, R.; Forrestal, D.P.; Allenby, M.C.; Woodruff, M.A. Auxetic tubular scaffolds via melt electrowriting. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.S.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.M.; Dalton, P.D.; Dargaville, T.R. Semi-woven structures via dual nozzle melt electrowriting. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2200526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, M.; Maher, M.G.; Metz, C.H.; Hochleitner, G.; Groll, J.; Doevendans, P.A.; Ito, K.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Malda, J. Melt electrowriting allows tailored microstructural and mechanical design of scaffolds to advance functional human myocardial tissue formation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, M.; Feyen, D.; Flandes-Iparraguirre, M.; Hochleitner, G.; Groll, J.; Doevendans, P.A.F.; Vermonden, T.; Ito, K.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Malda, J. Melt electrospinning writing of poly-hydroxymethylglycolide-co-ε-caprolactone-based scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidy, N.T.; Wolf, F.; Bas, O.; Keijdener, H.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Mela, P.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.M. Biologically inspired scaffolds for heart valve tissue engineering via melt electrowriting. Small 2019, 15, 1900873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochleitner, G.; Chen, F.; Blum, C.; Dalton, P.D.; Amsden, B.; Groll, J. Melt electrowriting below the critical translation speed to fabricate crimped elastomer scaffolds with non-linear extension behaviour mimicking that of ligaments and tendons. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, E.; Mros, S.; McConnell, M.; Cabral, J.D.; Ali, A. Melt-electrowriting with novel milk protein/PCL biomaterials for skin regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Boschetto, F.; Yagi, S.; Marin, E.; Adachi, T.; Chen, X.; Pezzotti, G.; Sakurai, S.; Yamane, H.; Xu, H. Design and manufacturing of 3D high-precision micro-fibrous poly(L-lactic acid) scaffold using melt electrowriting technique for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Des. 2021, 210, 110063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Miao, X.; Lan, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Cai, N.; Tang, Y. Fabrication and in vitro evaluation of PCL/gelatin hierarchical scaffolds based on melt electrospinning writing and solution electrospinning for bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, N.; Lee, R.S.B.; Ivanovski, S.; Love, R.M.; Hamlet, S. In vivo bone regeneration assessment of offset and gradient melt electrowritten (MEW) PCL scaffolds. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lian, M.; Sun, B.; Jia, B.; Wu, Q.; Qiao, Z.; Dai, K. Preparation of high precision multilayer scaffolds based on Melt Electro-Writing to repair cartilage injury. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10214–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarraga, J.H.; Locke, R.C.; Witherel, C.E.; Stoeckl, B.D.; Castilho, M.; Mauck, R.L.; Malda, J.; Levato, R.; Burdick, J.A. Fabrication of MSC-laden composites of hyaluronic acid hydrogels reinforced with MEW scaffolds for cartilage repair. Biofabrication 2021, 14, 014106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidy, N.T.; Shabab, T.; Bas, O.; Menne, M.; Henry, T.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Mela, P. Melt electrowriting of complex 3D anatomically relevant scaffolds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 550778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghrery, A.; Ferreira, J.A.; Araújo, S.; Clarkson, B.H.; Eckert, G.J.; Bhaduri, S.B.; Malda, J.; Bottino, M.C. A highly ordered, nanostructured fluorinated CaP-coated melt electrowritten scaffold for periodontal tissue regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, M.; Chen, M. An injectable high-conductive bimaterial scaffold for neural stimulation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2020, 195, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Shen, F.; Xia, H.; Min, Y.; Xie, K. Highly ordered 3D tissue engineering scaffolds as a versatile culture platform for nerve cells growth. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.; Melchels, F.P.; Jeon, J.E.; Van Bussel, E.M.; Kimpton, L.S.; Byrne, H.M.; Dhert, W.J.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Malda, J. Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungst, T.; Pennings, I.; Schmitz, M.; Rosenberg, J.W.P.; Groll, J.; Gawlitta, D. Heterotypic scaffold design orchestrates primary cell organization and phenotypes in cocultured small diameter vascular grafts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gu, J.; Meng, J.; Du, L.; Kumar, A.; Xu, H. Melt electrowriting reinforced composite membrane for controlled drug release. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 132, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keßler, L.; Mirzaei, Z.; Kade, J.C.; Luxenhofer, R. Highly porous and drug-loaded amorphous solid dispersion microfiber scaffolds of indomethacin prepared by melt electrowriting. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama-Odría, M.; Valle, L.J.; Puiggalí, J. Melt Electrospinning and Electrowriting for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Meng, Z. Melt electrospinning vs. solution electrospinning: A comparative study of drug-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) fibres. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davachi, S.M.; Shiroud, H.B.; Hejazi, I.; Seyfi, J.; Oliaei, E.; Farzaneh, A.; Rashedi, H. Interface modified polylactic acid/starch/poly ε-caprolactone antibacterial nanocomposite blends for medical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Deng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, L.; Ye, J.; Yin, C. Controlled release of antibiotics from poly-ε-caprolactone/polyethylene glycol wound dressing fabricated by direct-writing melt electrospinning. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Xiang, H.; Long, Y. In situ melt electrospun polycaprolactone/Fe3O4 nanofibers for magnetic hyperthermia. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afghah, F.; Dikyol, C.; Altunbek, M.; Koc, B. Biomimicry in bio-manufacturing: Developments in melt electrospinning writing technology towards hybrid biomanufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, B.L.; Kuba, S.; Hall, P.C.; McCosker, A.B.; Pickering, E.; Dalton, P.D.; Klein, T.J.; Woodruff, M.A.; Paxton, N.C. A melt electrowriting toolbox for automated G-code generation and toolpath correction of flat and tubular constructs. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
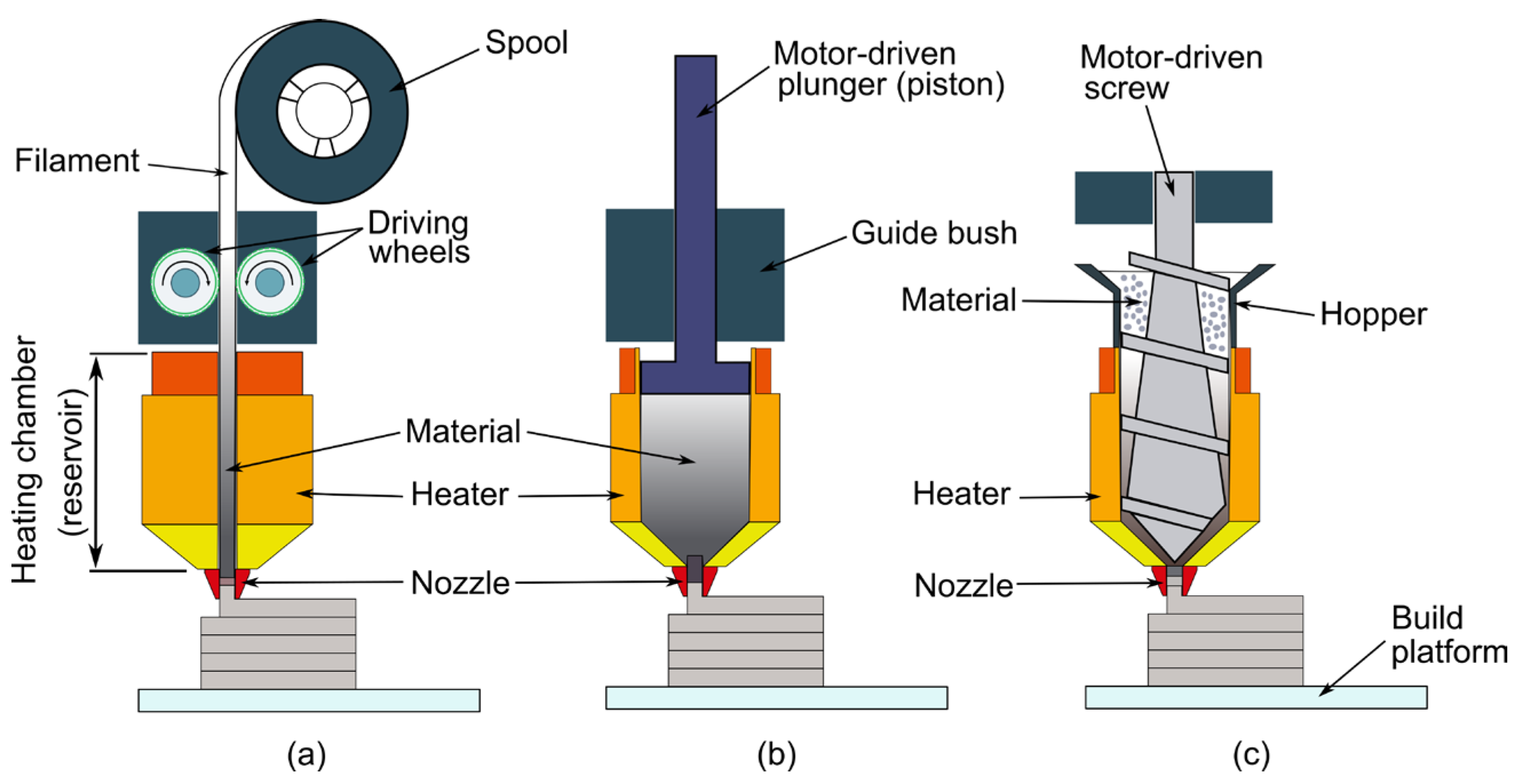




| Extrusion System | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Filament-based | Low cost and simple setup Compact print head Reliable on/off control | Limited to filament materials Inconsistent flow at extremes |
| Pressure-based | Supports wide material types Precise volume control | Pressure lag and poor on/off control Limited reservoir size Sensitive to air compression |
| Screw-assisted | Processes high-viscosity materials Uses pellets Stable, continuous extrusion | Complex/expensive system Heavy and bulky Cleaning challenges |
| Model Authors | Assumptions | Applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bellini et al. [17,22] |
|
|
|
| Ramanath et al. [18] |
|
|
|
| Monzon et al. [19] |
|
|
|
| Ortega et al. [20] |
|
|
|
| Osswald et al. [15,21] |
|
|
|
| Model Authors | Assumptions | Applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taylor (1964, 1969) [24,25] |
|
|
|
| Melcher and Taylor (1969) [27] |
|
|
|
| Gañán-Calvo et al. (1997) [29] |
|
|
|
| Barrero et al. (1999) [30] |
|
|
|
| Yan et al. (2003) [31] |
|
|
|
| Lastow and Balachandran (2006) [32] |
|
|
|
| Wu et al. (2012) [33] |
|
|
|
| Pan et al. (2019) [28] |
|
|
|
| Sachin et al. (2020) [34] |
|
|
|
| Cândido and Páscoa (2023) [35] |
|
|
|
| Model Authors | Assumptions | Applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spivak and Dzenis [37] |
|
|
|
| Hohman et al. [38,39] |
|
|
|
| Feng et al. [40,41] |
|
|
|
| Carroll et al. [42] |
|
|
|
| Zhmayev et al. [43] |
|
|
|
| Zhmayev et al. [44] |
|
|
|
| Mayadeo et al. [46] |
|
|
|
| Model Authors | Assumptions | Applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hrynevich et al. (2020) [47] |
|
|
|
| Cao et al. (2022) [48,49] |
|
|
|
| Ko et al. (2014) [50] |
|
|
|
| Tissue | Scaffold Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Myocardial tissue | Hexagonal microstructure made by PCL | [62] |
| Rectangular or square pore scaffold made by PHMGCL | [63] | |
| Heart valve | Serpentine PCL architecture to mimic collagen fibres | [64] |
| Ligaments and tendons | Sinusoidal patterns of aligned, crimped collagen fibril imitation | [65] |
| Skin | PCL mixed with bioactive milk protein to promote cell growth and proliferation | [66] |
| Bone | PLA scaffolds with square pores | [67] |
| PCL and chaotic gelatin scaffolds with square holes made by mixing MEW | [68] | |
| Calcium phosphate-coated PCL scaffolds with square pores and fibre offset | [69] | |
| Cartilage | PLGA microspheres loaded with cells and PCL hybrid scaffolds with square pores | [70] |
| Reinforced hyaluronic acid scaffold MEW PCL structures with square pores | [71] | |
| Blood vessel | Tubular PCL scaffold with square pores with aortic root features | [72] |
| Periodontal tissue | PCL scaffolds with square pores with fluorinated calcium phosphate coating | [73] |
| Nerve tissue | Gold-coated PCL scaffold with square pores | [74] |
| PCL scaffold with square pores and different surface modifications | [75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ju, H.; Mirihanage, W.; Wang, W.; Kilic, Z.M. Review on Melt Electrowriting Modelling and Applications. Machines 2025, 13, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090763
Ju H, Mirihanage W, Wang W, Kilic ZM. Review on Melt Electrowriting Modelling and Applications. Machines. 2025; 13(9):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090763
Chicago/Turabian StyleJu, Hongli, Wajira Mirihanage, Weiguang Wang, and Zekai Murat Kilic. 2025. "Review on Melt Electrowriting Modelling and Applications" Machines 13, no. 9: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090763
APA StyleJu, H., Mirihanage, W., Wang, W., & Kilic, Z. M. (2025). Review on Melt Electrowriting Modelling and Applications. Machines, 13(9), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090763






