Thermal Behavior Improvement in Induction Motors Using a Pulse-Width Phase Shift Triangle Modulation Technique in Multilevel H-Bridge Inverters
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Increased losses due to Joule effect (copper losses)—Current harmonics have frequencies higher than the fundamental (50 or 60 Hz). As a consequence, the total copper losses increase. In addition, these harmonics circulate through both the stator and rotor (in the form of eddy currents), aggravating the Joule losses in both parts.
- Additional losses in the iron (magnetic core)—The harmonic components of the voltage generate rapid variations in the magnetic flux in the motor core, increasing hysteresis losses, which depend on the frequency and magnetization cycle, and eddy current losses; these increase quadratically with frequency. Both mechanisms contribute to additional heat dissipation in the stator core and rotor [9].
- Skin effect—At higher harmonic frequencies, the current tends to concentrate at the periphery of the conductor, reducing the effective cross-section through which the current flows. This increases the apparent resistance of the conductor and, therefore, the resistive losses. This phenomenon is more noticeable in large motors but also has an impact on small motors under high distortion [10].
- Less effective ventilation due to pulsating torque—Some harmonics, especially those of low odd order (such as the fifth or seventh), produce pulsations in the electromagnetic torque that can cause vibrations, resonances, and unwanted changes in the speed of the motor fan (if coupled to the shaft). This reduces the efficiency of the motor’s cooling system, further raising its temperature [11].
- Localized thermal imbalance—The effect of harmonics is not uniform throughout the motor; certain areas, such as the turn heads or stator slots, can become hotter due to winding geometry and non-uniform loss distribution. This can accelerate insulation deterioration and lead to premature failure [12].
- Deterioration of the winding insulation—The high temperature degrades the dielectric material covering the stator conductors. It is estimated that for every 10 °C above the limit, the lifespan of the insulation is reduced by half (Montsinger’s rule). This can lead to short circuits between turns or phases, resulting in catastrophic electrical failures [13,14,15,16].
- Efficiency loss—At higher temperatures, copper resistance increases, which increases the I2R losses. This reduces the energy efficiency of the motor and increases the electrical consumption [17].
- Rotor damage—Although the rotor is more thermally robust, it also suffers from temperature increases. Mechanical deformation, uneven expansion, or weakening of the shaft may also occur [18].
- Bearing and lubrication failures—Excessive heat can degrade lubricating grease, causing premature bearing wear. This leads to vibration, noise, and mechanical failure. This decreases the thermal performance of the housing [19].
2. Simplified Thermal–Electrical Modeling of an Induction Machine
3. Phase Shift Triangle Modulator-PWM Technique
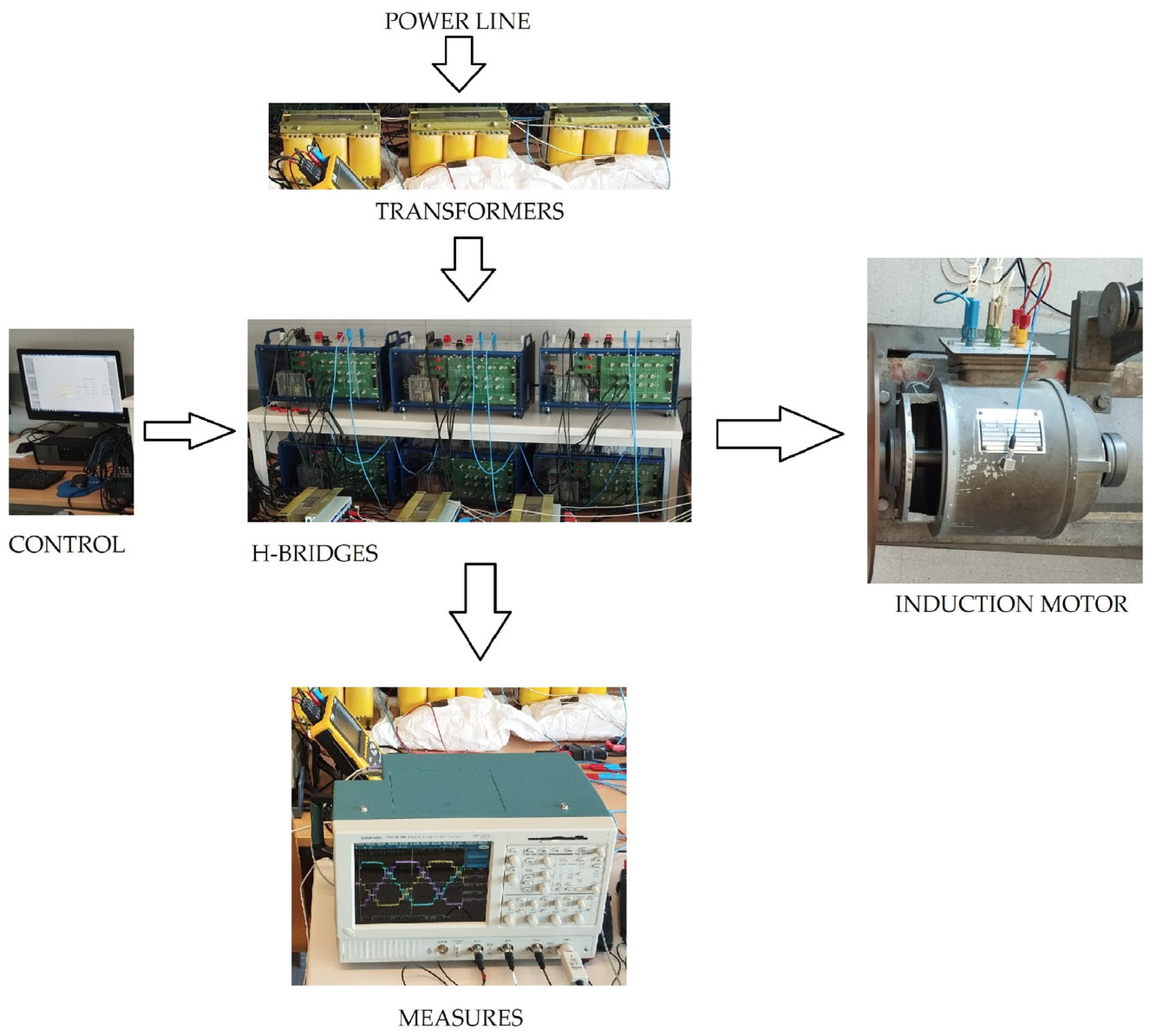
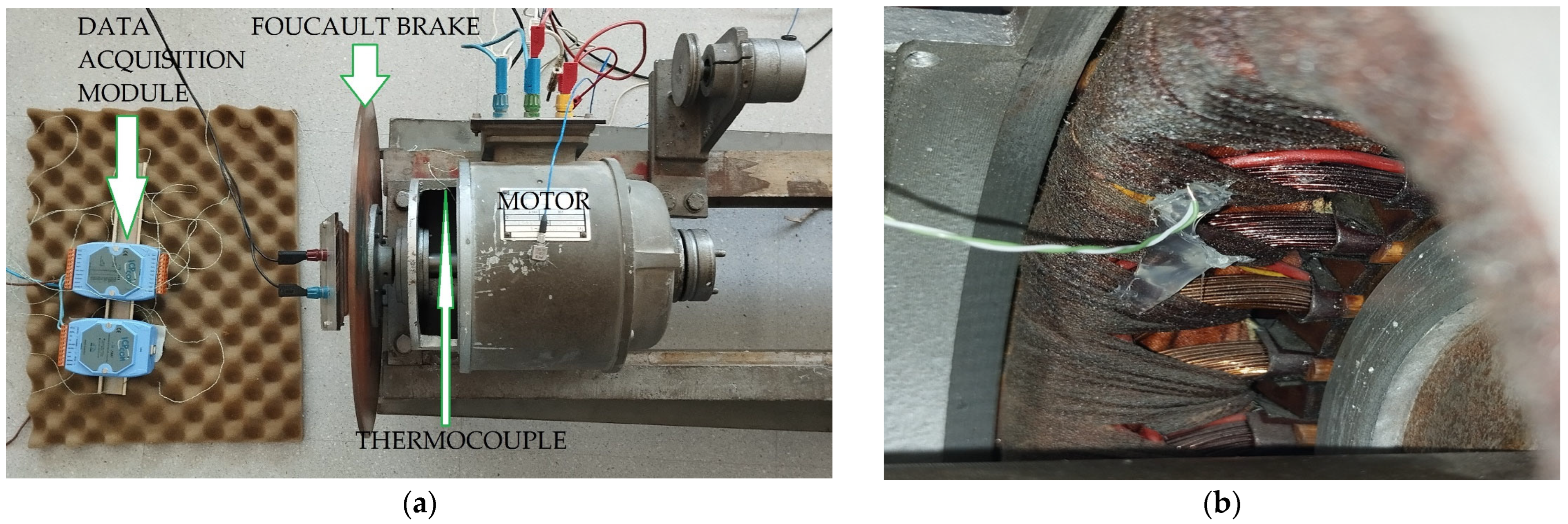
4. Experimental Model of the Multilevel H-Bridge Inverter
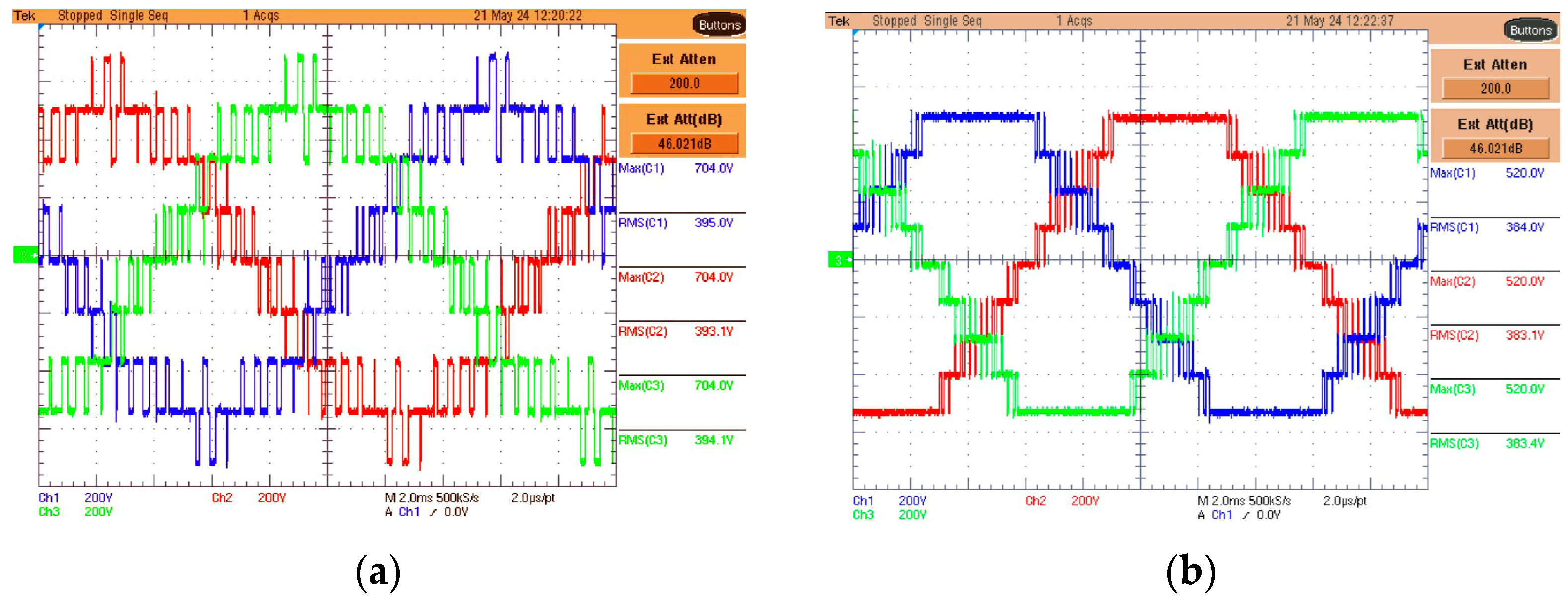
5. Experimental Results
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tabora, J.M.; Tostes, M.E.d.L.; de Matos, E.O.; Soares, T.M.; Bezerra, U.H. Voltage harmonic impacts on electric motors: A comparison between IE2, IE3 and IE4 induction motor classes. Energies 2020, 13, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEMA MG 1—“Motors and Generators” National Electrical Manufacturers Association 1300 North 17th Street, Suite 1752, Rosslyn, VA 22209. Available online: https://www.weg.net (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Umesh, H.; Rashmi, K. Causes and Effect of Inverter Harmonics. In Current Perspective to Physical Science Research 6; Dong, S.-H., Ed.; BP International: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2024; pp. 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleiu, H.G.; Maier, V.; Pavel, S.G.; Birou, I.; Pică, C.S.; Dărab, P.C. Harmonics consequences on drive systems with induction motor. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaciński, P.; Pepliński, M.; Muc, A.; Hallmann, D.; Klimczak, P. Induction motors under voltage fluctuations and power quality standards. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 39, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs Ewald, F. Are harmonic recommendations according to IEEE-519 and CEI/IEC 555 too restrictive? In Proceedings of the Frontiers of Power Conference; Engineering Energy Laboratory, Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 4 October 2002; pp. 1–18. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290494727 (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Mirza, A.Y.; Bazzi, A.; Nguyen, H.H.; Cao, Y. Motor stator insulation stress due to multilevel inverter voltage output levels and power quality. Energies 2022, 15, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Fernández, D.; Guerrero, J.M.; Díaz, I.; Briz, F. Insulation Condition Assessment in Inverter-Fed Motors Using the High-Frequency Common Mode Current: A Case Study. Energies 2024, 17, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, C.; Vandevelde, L.; Desmet, J. Harmonic Effects on Induction and Line Start Permanent Magnet Machines. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264195127 (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Fatima, A.; Kumar, R.; Li, Z.; Byczynski, G.; Kar, N.C. Modelling of Inductances Considering Bar Harmonics and Temperature to Accurately Predict Output Torque of an Induction Motor. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 156561–156571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, B.I.; Datskovskii, L.K.; Kuz’min, I.K.; Shevyrev, Y.V. Electric drives of mining installations. Russ. Electr. Eng. 2017, 88, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donolo, P.; Bossio, G.; De Angelo, C.; García, G.; Donolo, M. Voltage unbalance and harmonic distortion effects on induction motor power, torque and vibrations. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 140, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De abreu, J.P.G.; Emanuel, A.E. Induction motor thermal aging caused by voltage distortion and imbalance: Loss of useful life and its estimated cost. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Technical Conference, New Orleans, LO, USA, 13–17 May 2001; Conference Record (Cat. No. 01CH37226). IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husach, S. Python-based Induction Motors Monitoring and Lifetime Estimation System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Modern Electrical and Energy Systems (MEES); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu-Zagar, C.; Notingher, P.; Navrapescu, V.; Mares, G.; Rusu-Zagar, G.; Setnescu, T.; Setnescu, R. Method for estimating the lifetime of electric motors insulation. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest, Romania, 23–25 May 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxiri, A.C.P.; Bento, F.; Fonseca, D.S.B.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Thermal analysis of an induction motor subjected to inter-turn short-circuit failures in the stator windings. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), Sochi, Russia, 25–29 March 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.K. A research survey of induction motor operation with non-sinusoidal supply wave forms. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2005, 75, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelfi, H.; Hamdani, S.; Hamouda, S.; Baghdouche, K.K.; Ammari, Z.; Attab, A. Analysis of Harmonic and Noise Influence on Temporal Envelope Estimation for Detecting Broken Rotor Bars in Asynchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Automatic Control (ICEEAC), Setif, Algeria, 12–14 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; De Gaetano, D.; Chen, X.; Jewell, G.W.; Hu, Y. A review of modeling and mitigation techniques for bearing currents in electrical machines with variable-frequency drives. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 125279–125297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN50160; Voltage Characteristics of Electricity Supplied by Public Distribution Networks. DIN: German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2025.
- Dugan, R.C.; McGranaghan, M.F.; Santoso, S.; Beaty, H.W. Electrical Power Systems Quality, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rata, G.; Rata, M.; Graur, I.; Milici, D.L. Induction Motor Speed Estimator Using Rotor Slot Harmonics. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2009, 9, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleiu, H.G.; Miron, A.; Pavel, S.G.; Cziker, A.C.; Niste, D.F.; Darab, P.C. Impact of Voltage Unbalance and Harmonics on Induction Motor Efficiency. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference and Exposition on Electric and Power Engineering (EPEi), Iasi, Romania, 17–19 October 2024; pp. 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, V.; Abarzadeh, M.; Corzine, K.A.; Enslin, J.H.; Sadigh, A.K.; Rodriguez, J.; Blaabjerg, F.; Maqsood, A. Fundamental Circuit Topology of Duo-Active-Neutral-Point-Clamped and Duo-Neutral-Point-Piloted Multilevel Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 1224–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Bernet, S.; Steimer, P.K.; Lizama, I.E. A survey on neutral-point-clamped inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, I.; Kondo, T.; Kodama, T. Experiment of five-level BTB-system with common flying capacitors. In Proceedings of the 8th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines, and Drives, PEMD, Glasgow, UK, 19–21 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Malinowski, M.; Gopakumar, K.; Rodriguez, J.; Perez, M.A. A survey on cascaded multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Franquelo, L.G. Multilevel converters: Control and modulation techniques for their operation and industrial applications. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.W.; Hassan, J.; Minambres-Marcos, V.; Al-Salloomee, A.G.S.; Roncero-Clemente, C. Traditional and Hybrid Topologies for Single-Three-Phase Transformerless Multilevel Inverters. Electronics 2024, 13, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Bajaj, M.; Dash, T.; Kamel, S.; Jurado, F. Multilevel Inverter: A Survey on Classical and Advanced Topologies, Control Schemes, Applications to Power System and Future Prospects. Energies 2021, 14, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Y.; Ma, J.; Lu, Q.; Qiu, L.; Fang, Y. Temperature Analysis of Secondary Plate of Linear Induction Motor on Maglev Train Under Periodic Running Condition and Its Optimization. Machines 2025, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szamel, L.; Oloo, J. Monitoring of Stator Winding Insulation Degradation through Estimation of Stator Winding Temperature and Leakage Current. Machines 2024, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, Ł.; Magdziarz, A.; Rasolomampionona, D.D.; Łukaszewski, P.; Sapuła, Ł.; Szreder, R. The laboratory analysis of the thermal processes occurring in low-voltage asynchronous electric motors. Energies 2021, 14, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.F.; Hidalgo, F.P.; Martinez, M.D. Realization of tests to determine the parameters of the thermal model of induction machine. Proc. IEE Electr. Power Appl. 2001, 148, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Larrubia, J.-R.; Perez-Hidalgo, F.M.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Meco-Gutierrez, M.J. Discontinuous Multilevel Pulse Width Modulation Technique for Grid Voltage Quality Improvement and Inverter Loss Reduction in Photovoltaic Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
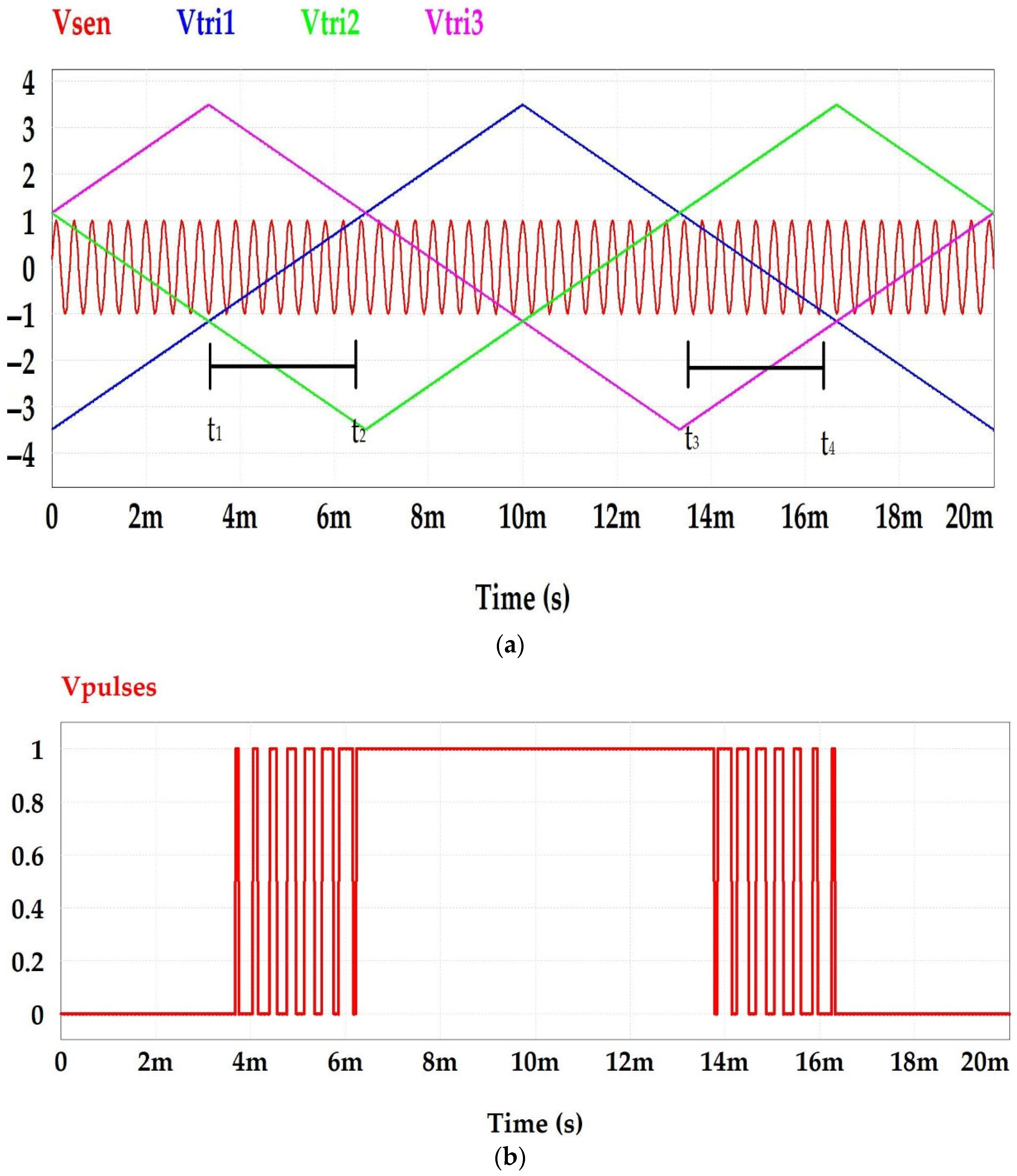
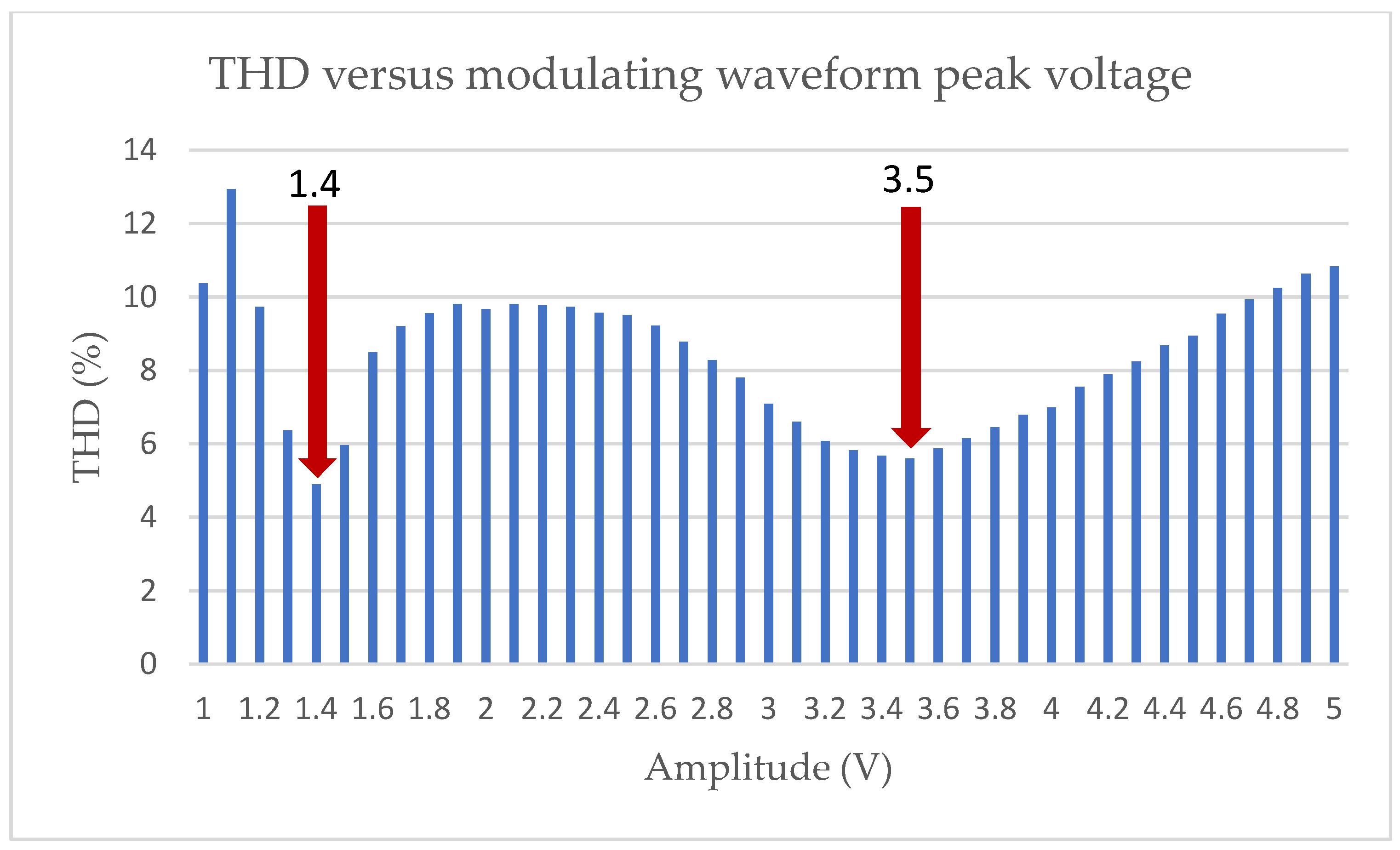
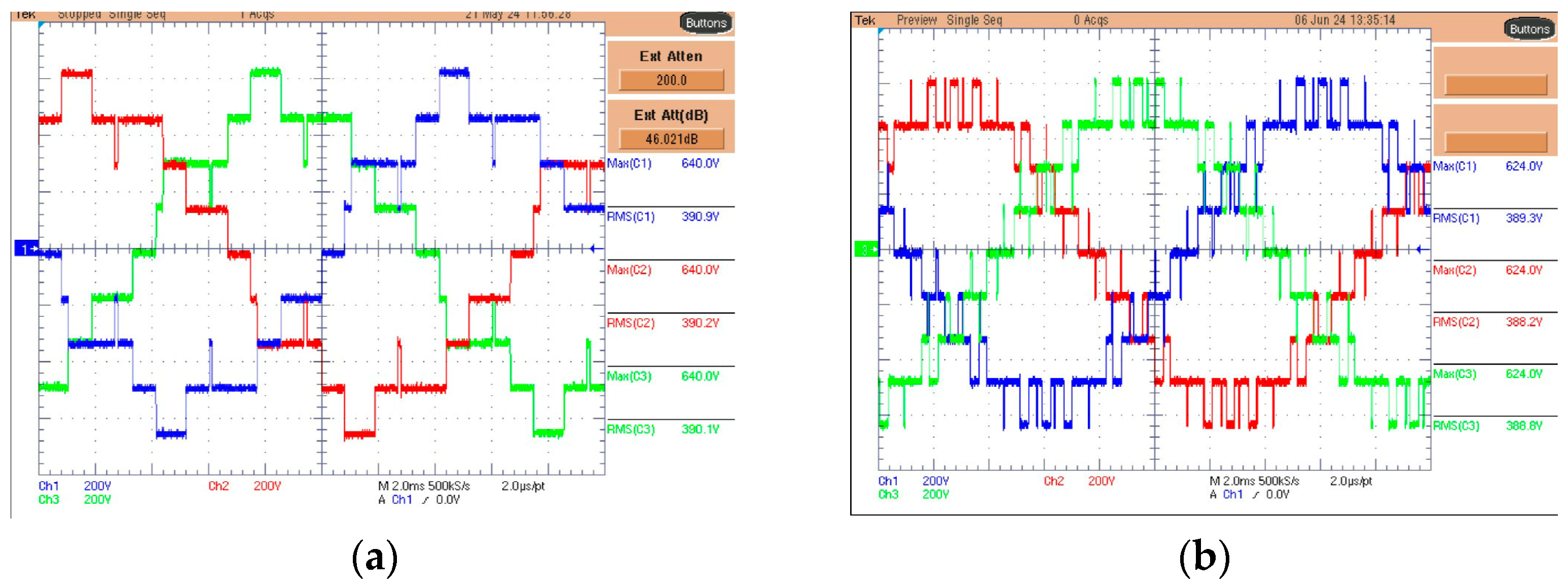
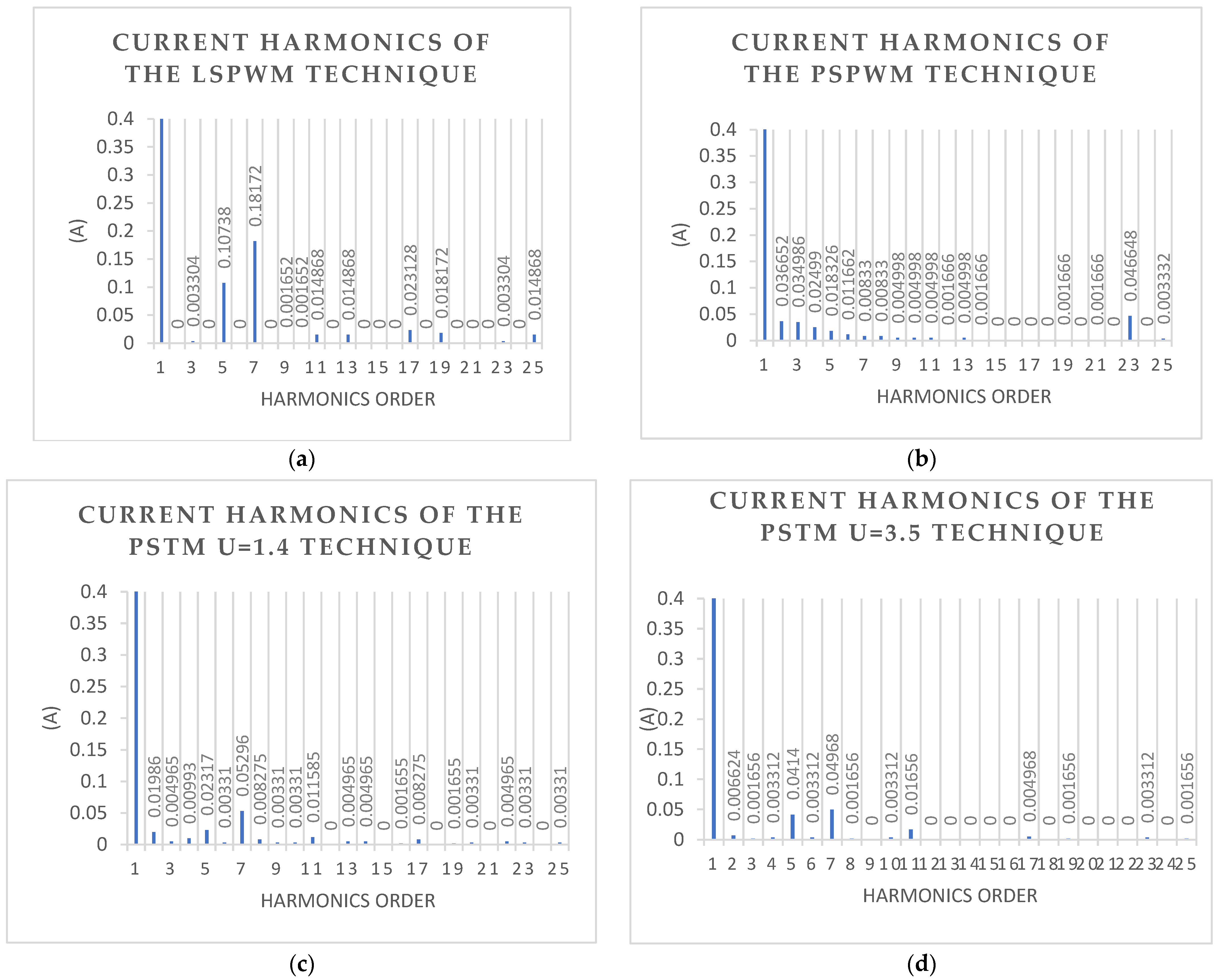
| Harm. | Standard EN50160 (%) | LS-PWM (%) | PS-PWM (%) | PSTM-PWM V = 1.4 (%) | PSTM-PWM V = 3.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 2 | 2.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.010 |
| 3 | 5.000 | 3.789 | 0.193 | 0.059 | 0.134 |
| 4 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.004 |
| 5 | 6.000 | 3.438 | 0.074 | 0.819 | 1.628 |
| 6 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 |
| 7 | 5.000 | 4.195 | 0.176 | 4.122 | 4.001 |
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.005 |
| 9 | 1.500 | 3.832 | 0.037 | 0.074 | 0.166 |
| 10 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
| 11 | 3.500 | 6.652 | 0.105 | 1.656 | 1.741 |
| 12 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 |
| 13 | 3.000 | 3.677 | 0.030 | 0.737 | 0.782 |
| 14 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.003 |
| 15 | 0.500 | 1.722 | 0.051 | 0.070 | 0.282 |
| 16 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| 17 | 2.000 | 4.126 | 0.196 | 1.347 | 1.562 |
| 18 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.000 |
| 19 | 1.500 | 0.160 | 0.161 | 0.108 | 0.337 |
| 20 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.001 |
| 21 | 0.500 | 4.876 | 5.017 | 0.048 | 0.434 |
| 22 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.002 |
| 23 | 1.500 | 1.715 | 11.772 | 1.007 | 1.290 |
| 24 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.000 |
| 25 | 1.500 | 4.761 | 0.090 | 0.412 | 0.627 |
| Fund. Value RMS | 250.51 | 243.95 | 221.32 | 295.57 | |
| THD25 (%) | 8 | 13.62 | 12.83 | 4.89 | 5.59 |
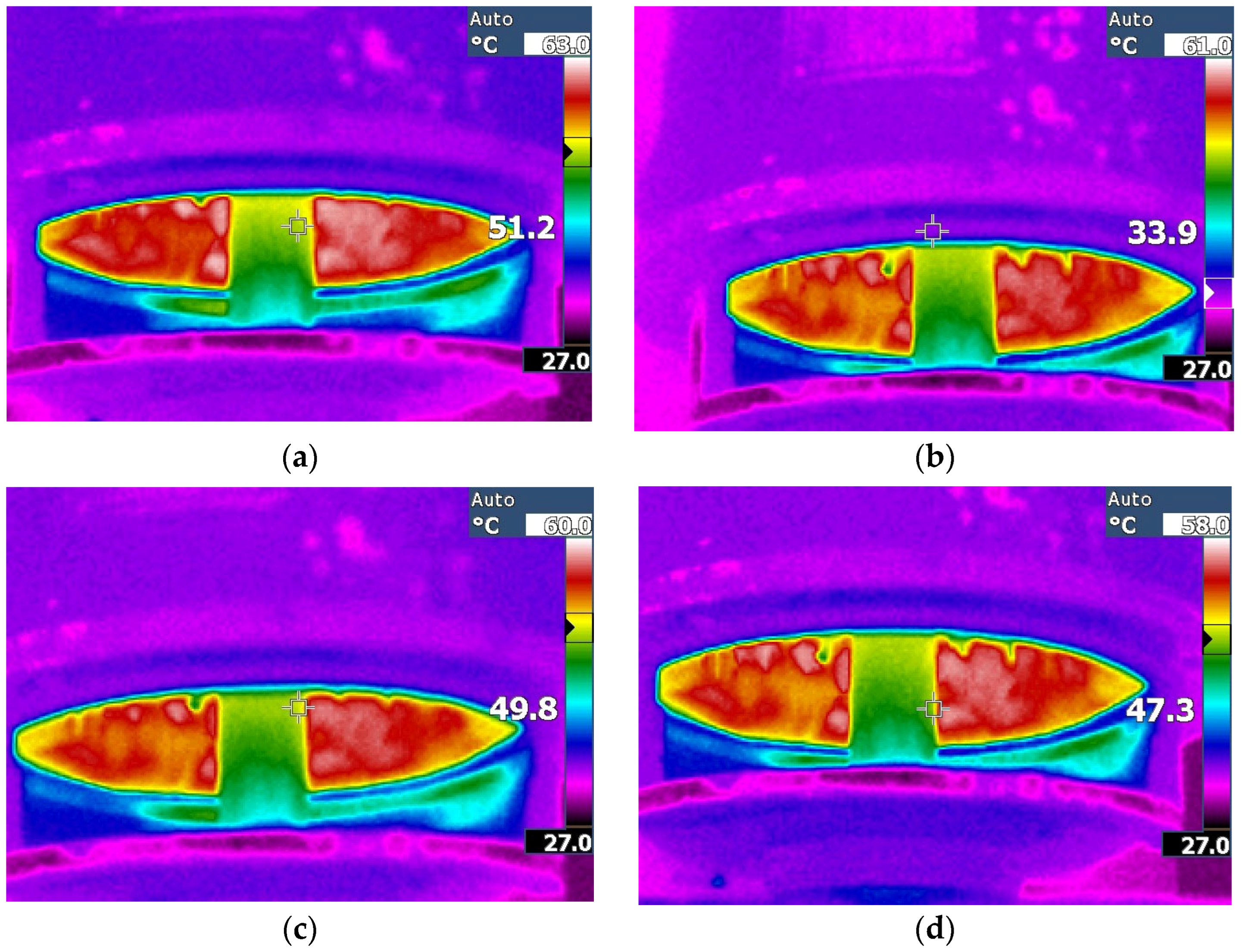
| Temperature (°C) | Pfe (W) | Pcu (W) | Rth (K/W) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSPWM | 63.2 | 30.58 | 54.91 | 0.446 |
| PSPWM | 61.1 | 29.11 | 53.94 | 0.434 |
| PSTM U = 1.4 | 60.3 | 27.95 | 53.62 | 0.432 |
| PSTM U = 3.5 | 59.5 | 27.46 | 52.41 | 0.426 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez-Hidalgo, F.M.; Heredia-Larrubia, J.-R.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Meco-Gutierrez, M. Thermal Behavior Improvement in Induction Motors Using a Pulse-Width Phase Shift Triangle Modulation Technique in Multilevel H-Bridge Inverters. Machines 2025, 13, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080703
Perez-Hidalgo FM, Heredia-Larrubia J-R, Ruiz-Gonzalez A, Meco-Gutierrez M. Thermal Behavior Improvement in Induction Motors Using a Pulse-Width Phase Shift Triangle Modulation Technique in Multilevel H-Bridge Inverters. Machines. 2025; 13(8):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080703
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez-Hidalgo, Francisco M., Juan-Ramón Heredia-Larrubia, Antonio Ruiz-Gonzalez, and Mario Meco-Gutierrez. 2025. "Thermal Behavior Improvement in Induction Motors Using a Pulse-Width Phase Shift Triangle Modulation Technique in Multilevel H-Bridge Inverters" Machines 13, no. 8: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080703
APA StylePerez-Hidalgo, F. M., Heredia-Larrubia, J.-R., Ruiz-Gonzalez, A., & Meco-Gutierrez, M. (2025). Thermal Behavior Improvement in Induction Motors Using a Pulse-Width Phase Shift Triangle Modulation Technique in Multilevel H-Bridge Inverters. Machines, 13(8), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080703






