Hybrid Brushless Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine with Dual-Mode Operation for Washing Machine Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
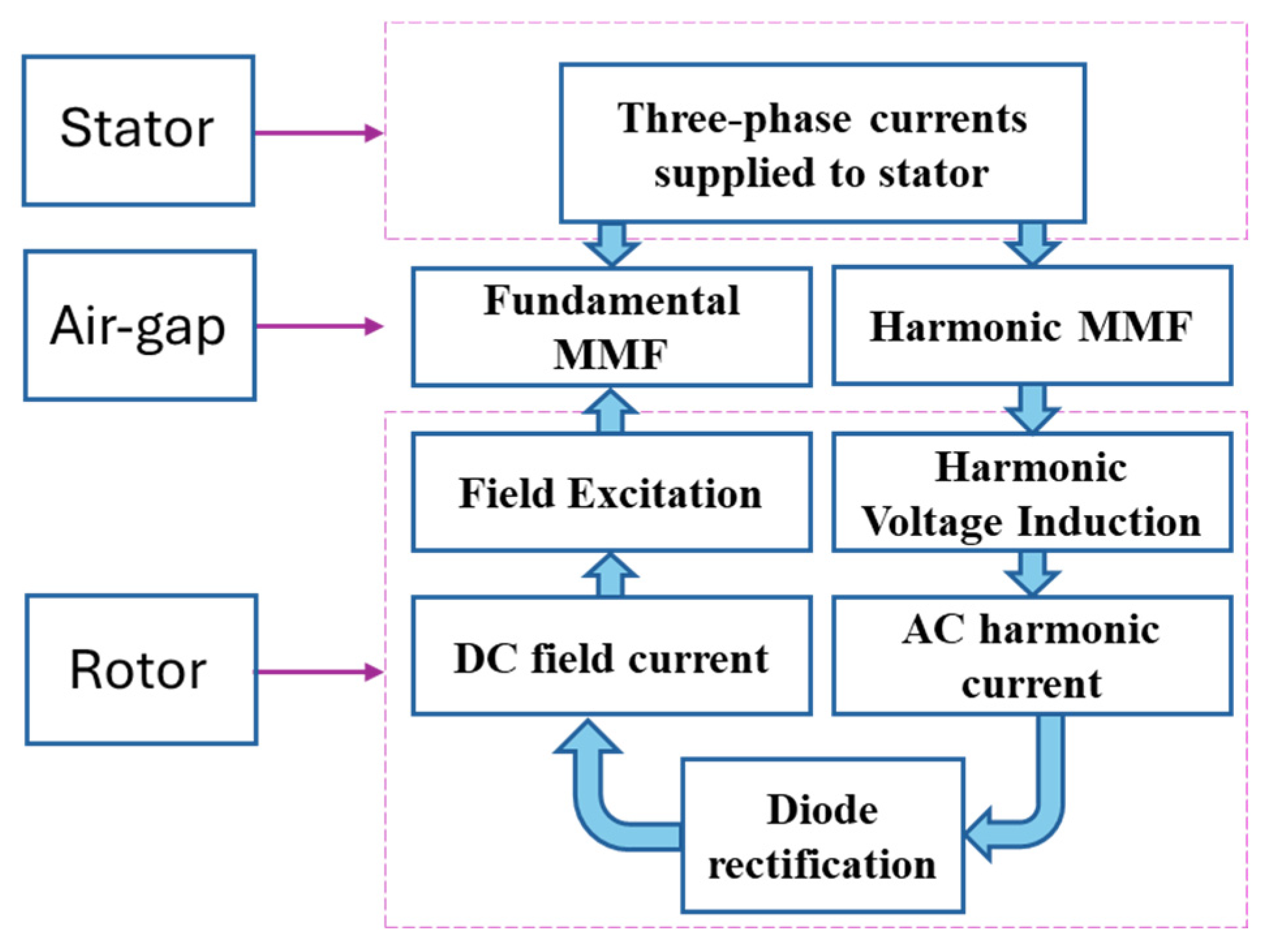
2. The Latest Brushless Technology and Its Applications
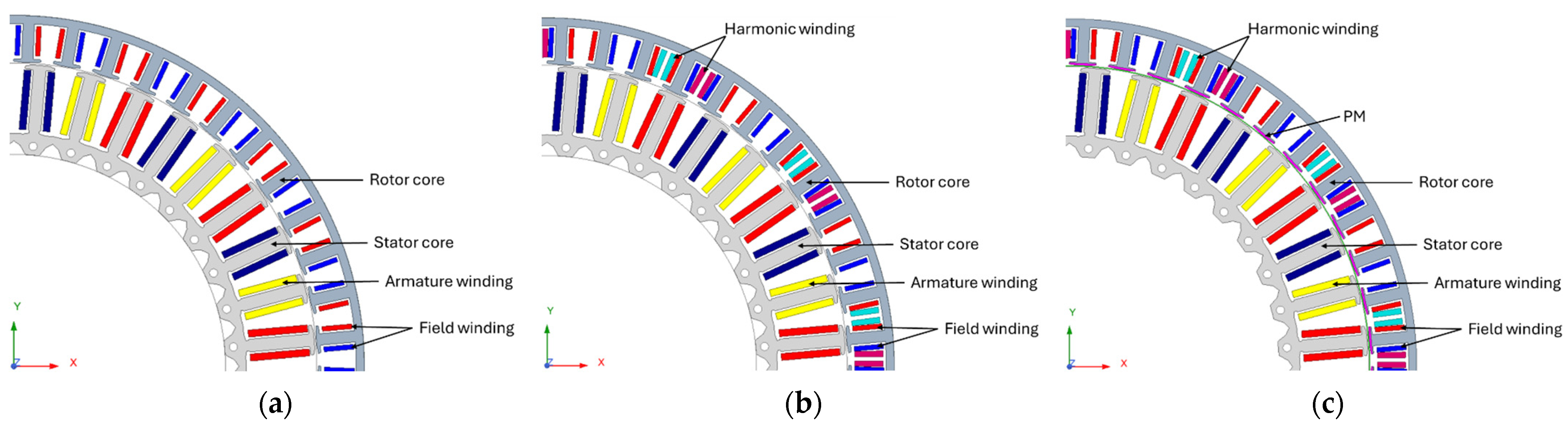
2.1. The Latest Brushless Technology
2.2. Dual Speed Applications
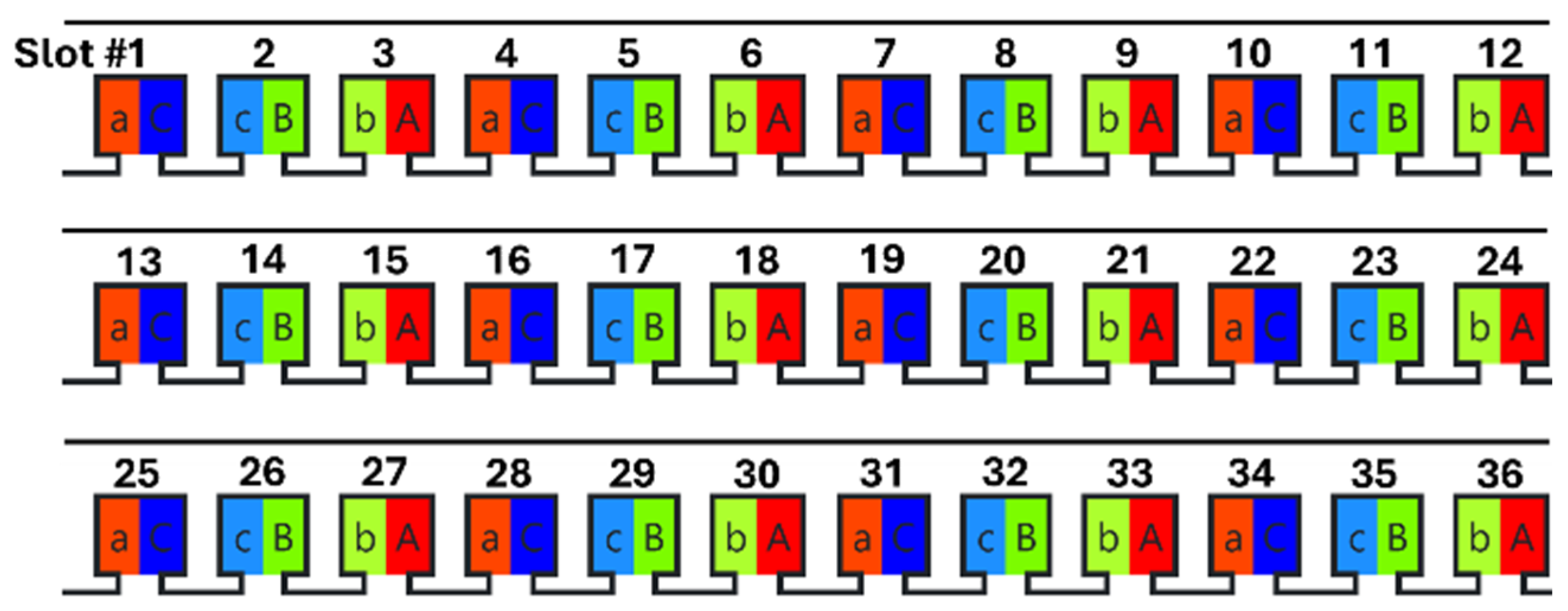
3. Simulation Results
4. Machine Performance Analysis
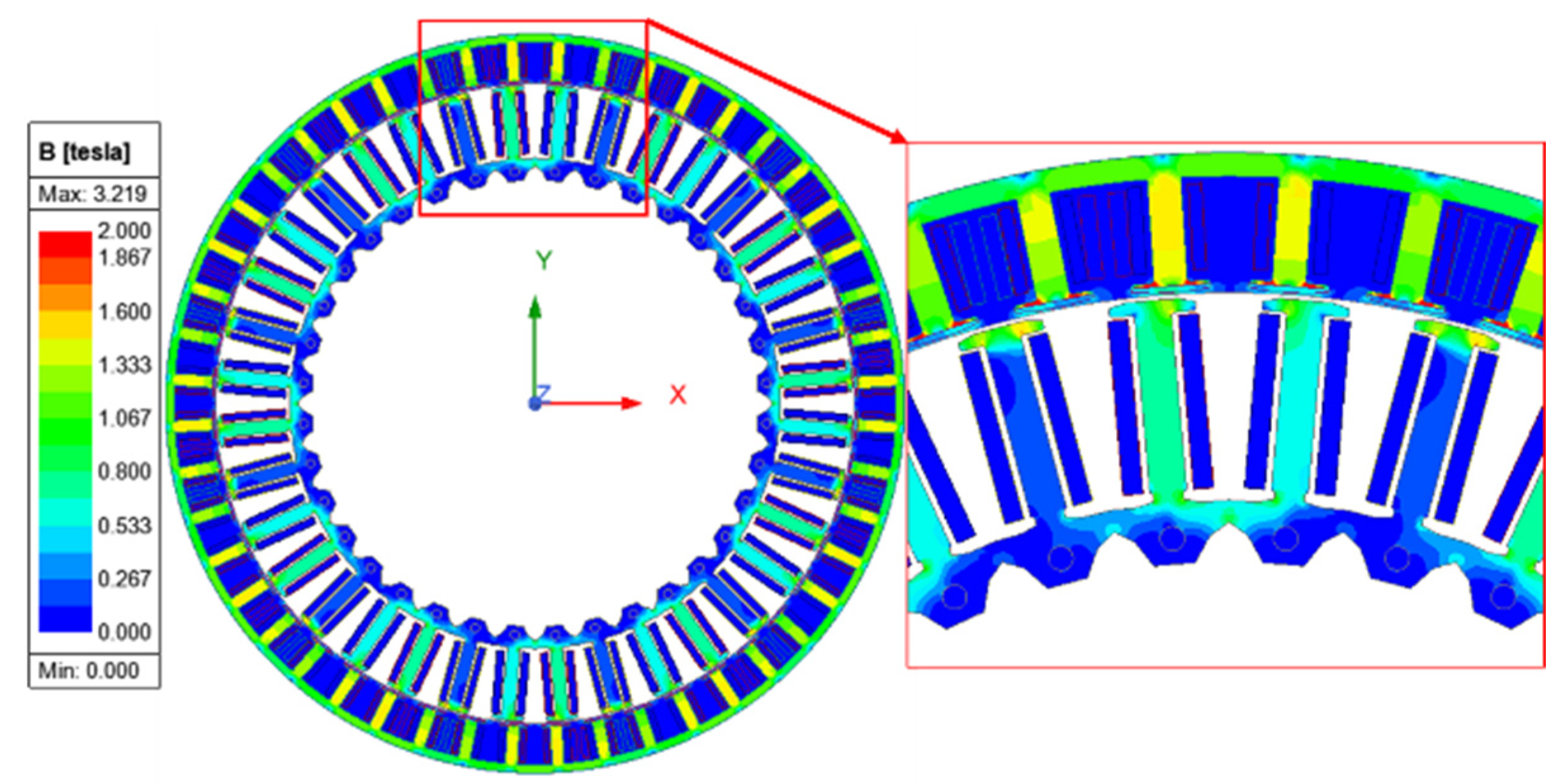
4.1. No-Load Performance
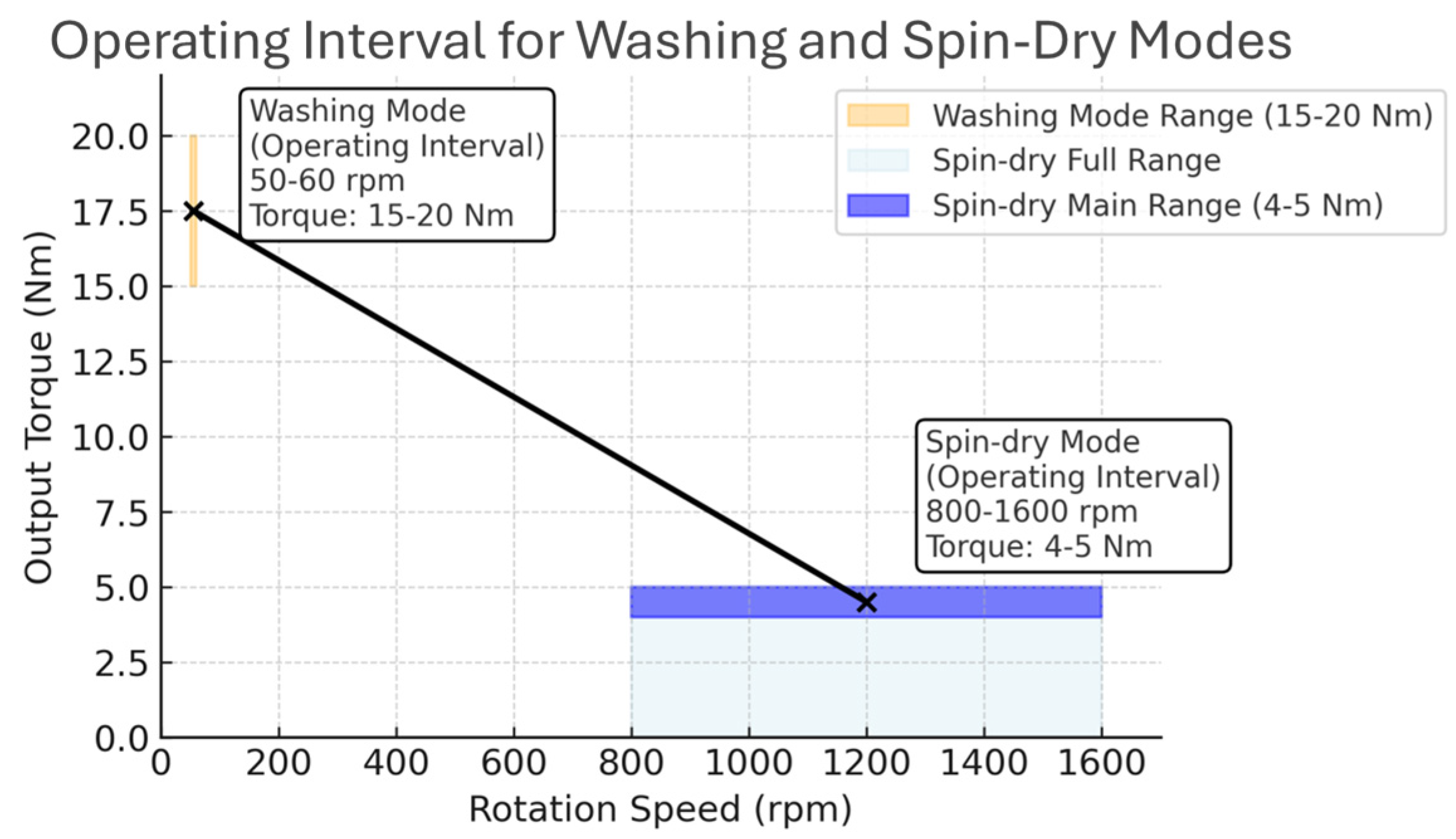
4.2. Washing Mode Performance
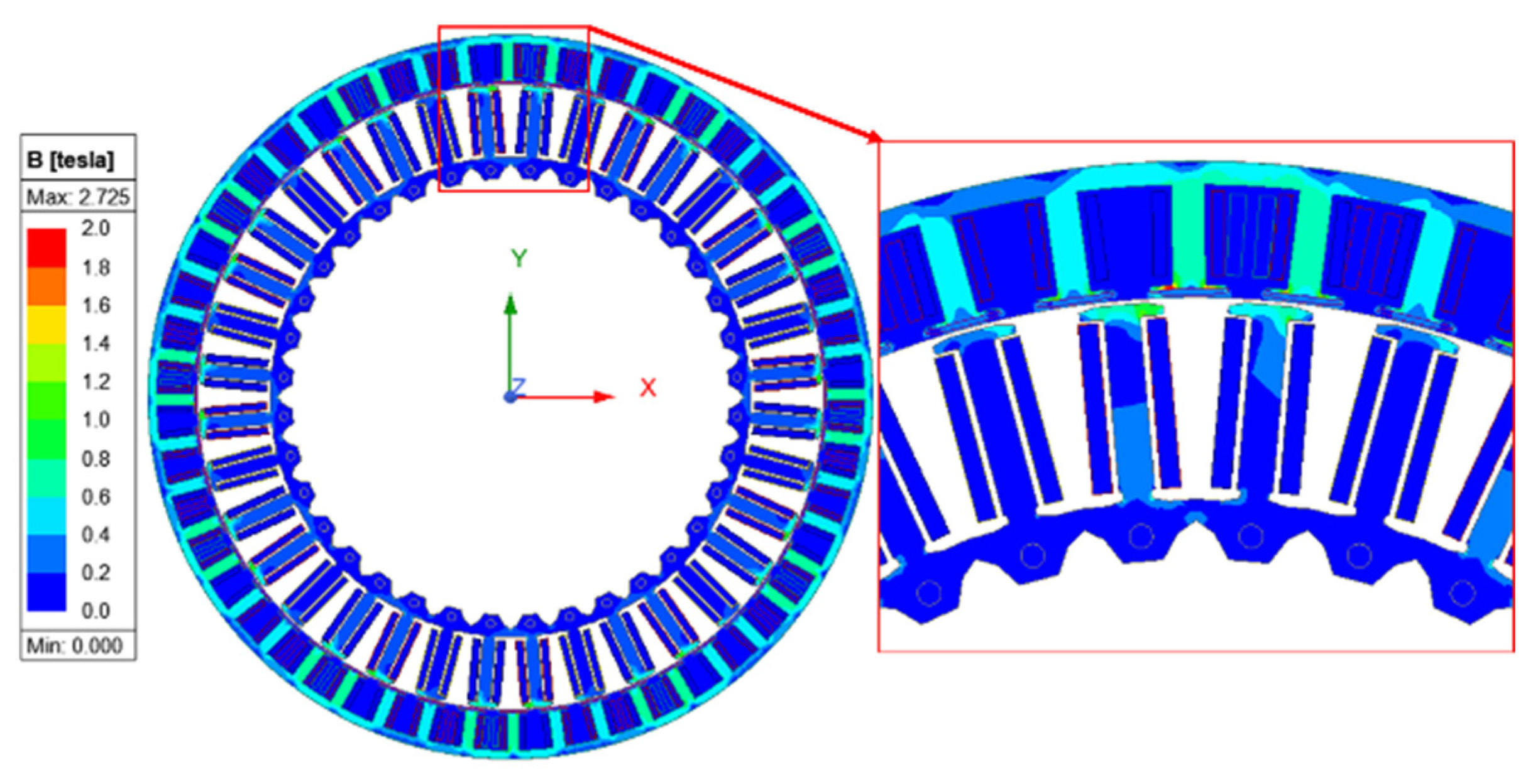
4.3. Dry-Mode Performance
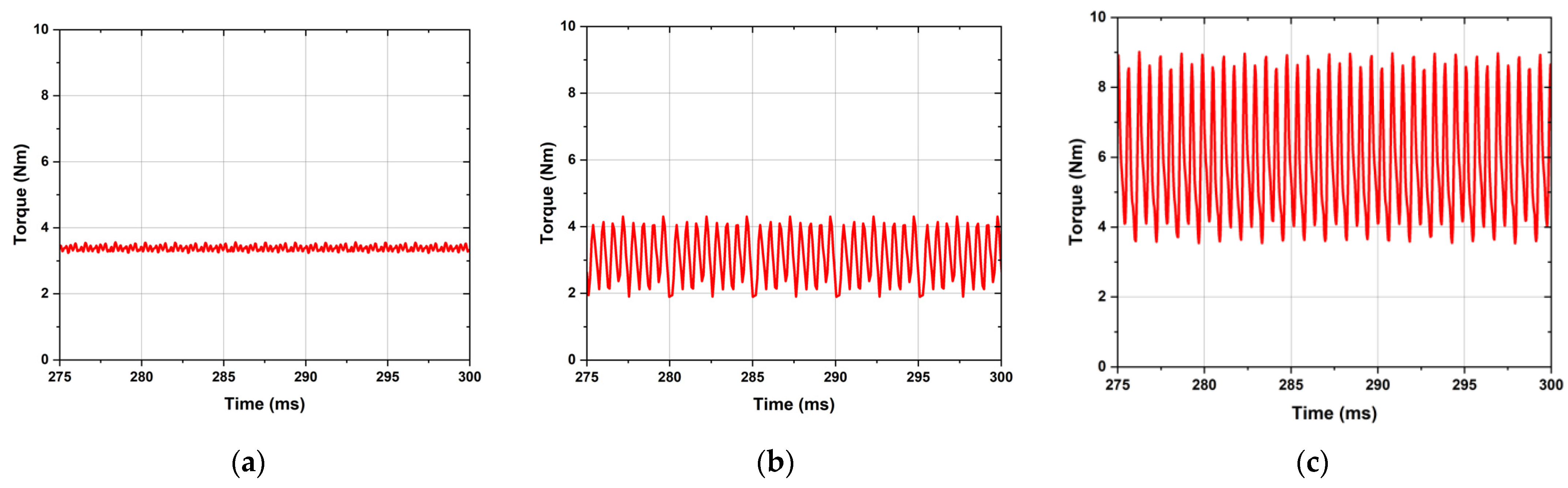
4.4. Performance Comparison
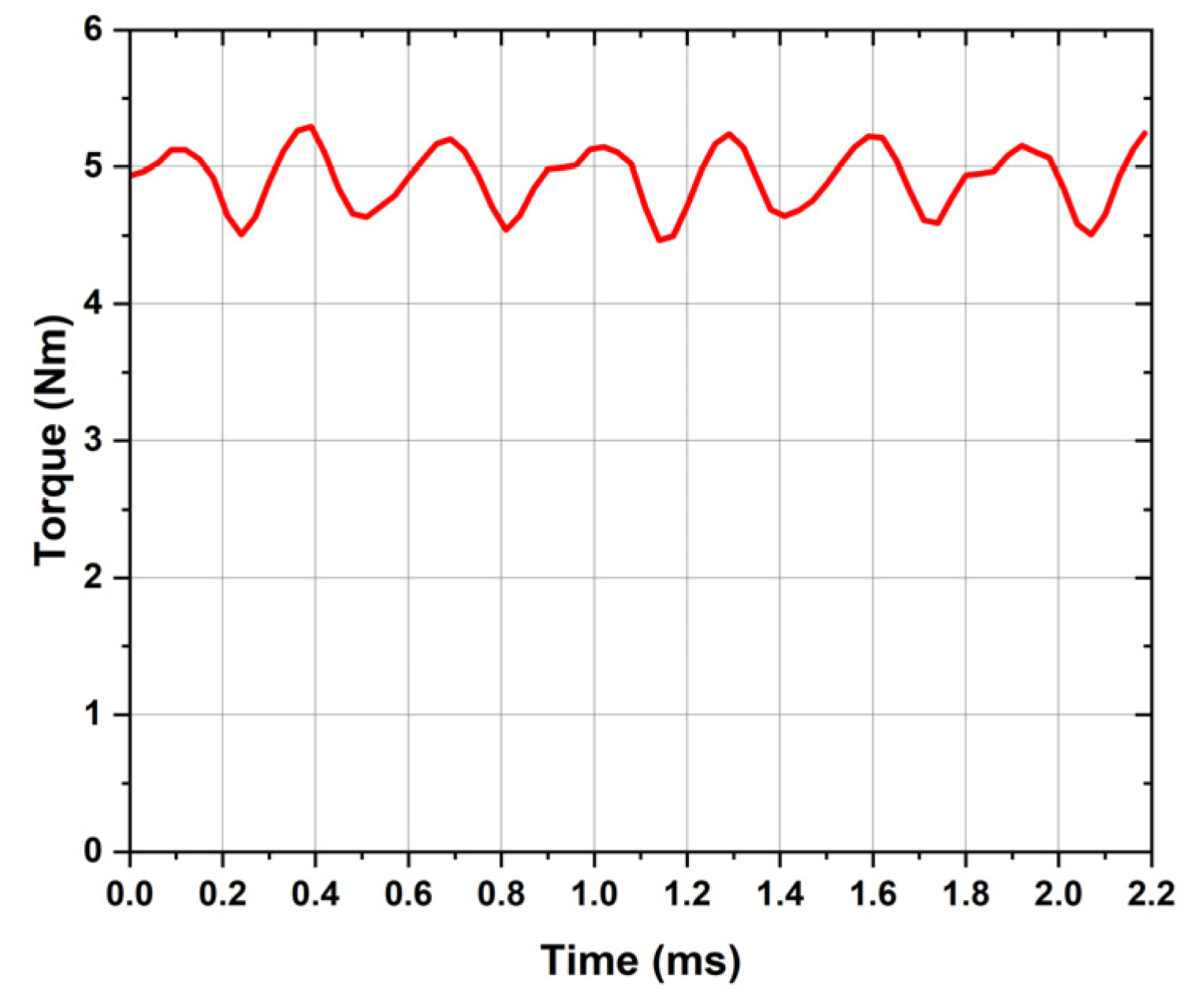
5. PMSM Operation Mode
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Cost-Effective High Torque Density Bi-Magnet Machines Utilizing Rare Earth and Ferrite Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheramin, M.; Saha, A.K.; Cheng, J.; Paul, S.K.; Jin, H. Resilient NdFeB magnet recycling under the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic: Stochastic programming and Benders decomposition. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 155, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.E.; Kaya, O.; Stopic, S.; Gürmen, S.; Friedrich, B. NdFeB Magnets Recycling Process: An Alternative Method to Produce Mixed Rare Earth Oxide from Scrap NdFeB Magnets. Metals 2021, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Rao, Y.T.; Bhattacherjee, H. Brushless induction excited synchronous motor (BinSyM): A new motor for high power applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 7th Power India International Conference (PIICON), Bikaner, India, 25–27 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; An, Q.; Sun, L.; Lipo, T.A. Performance Investigation of a Brushless Synchronous Machine with Additional Harmonic Field Windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6756–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Boscaglia, L. Electromagnetic Performance Investigation of a Brushless Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Long-Distance Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2025, 11, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Atiq, S.; Kwon, B. Consequent-Pole Hybrid Brushless Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8206205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.K.; Basak, S.; Chakraborty, C. An Optimal Excitation Control Technique for Brushless Induction Excited Synchronous Motor (BINSYM). IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirewal, G.J.; Ayub, M.; Atiq, S.; Kwon, B.-I. Analysis of a Brushless Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine Employing a Stator Harmonic Winding. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 151392–151402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; An, Q.; Gao, X.; Sun, L.; Lipo, T.A. Principle of Operation and Performance of a Synchronous Machine Employing a New Harmonic Excitation Scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y. Extended-Kalman-Filter-Based Field Current Estimation for Brushless Electrically Excited Synchronous Machines Using Stator Current Measurements. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2025, 11, 5042–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallantla, M.; Kumar, P. A Line-Commutated Thyristor Bridge Emulated Rotating Power Electronic Converter (LCTEPC) with Mode-Switching Algorithm for Brushless Exciter Applications. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 10–11 February 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Atiq, S.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B. PM Assisted, Brushless Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine. J. Magn. 2016, 21, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, L.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Ma, J.; Li, R.; Yin, Z.; Du, G. Identification Methods for Rotating Diode Rectifier Open Circuit Failures Without Rotor Position Information in Brushless Exciter Systems of Wound Field Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirewal, G.J.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B. Torque ripple reduction in brushless wound rotor synchronous machine by two-phase excitation winding. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2019, 59, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, G.; Ali, Q.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.-I. Novel Brushless Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine With Zero-Sequence Third-Harmonic Field Excitation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 8106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Nam, K. Inductance Measurement and Parameter Identification for a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, S.; Kawaguchi, T. Excitation scheme of brushless self-excited-type three-phase synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y. Design optimization of brushless synchronous machines with wound-field excitation for hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015; pp. 2769–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Lim, M.-S. Design of High-Power Density and High Efficiency Wound-Field Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicle Traction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 46677–46685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, F.; Qian, C.; Hu, X.; Zhou, G. Automated Monitoring of the Uniform Demagnetization Faults in Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors: Practical Methods and Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrell, D.G. Are wound-rotor synchronous motors suitable for use in high efficiency torque-dense automotive drives? In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 4880–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Sun, D.; Sun, L.; Lipo, T.A. Dual Third Harmonic-Current Excitation Principle of a Brushless Synchronous Machine Based on Double Three-Phase Armature Windings. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, M.; Tiitinen, J. Vector Controlled PWM Current-Source-Inverter-Fed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive with a Low-Pass Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.S.H.; Ahmad, H.; Sirewal, G.J.; Ro, J.-S. Simplified Brushless Wound Field Synchronous Machine Topology Based on a Three-Phase Rectifier. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 8637–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Kwon, B. Novel single inverter fed brushless wound rotor synchronous machine. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Magnetics Conference (INTERMAG), Dublin, Ireland, 24–28 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.F.; Wang, C.; Kamper, M.J. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, P.; Pyrhönen, J.; Nerg, J. Design Aspects of High-Speed Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Rahman, M.F.; Zhong, L.; Lim, K.W. A Novel Direct Torque Control for Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Drive with Low Ripple in Torque and Flux—A Speed-Sensorless Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ruxi, S.; Zhao, L. A New Rotor Position Detection Method for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drive at Zero and Very Low Speed. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direct Drive Motor Specification. Fisher & Paykel Technologies. Available online: https://www.fisherpaykeltechnologies.com/technology/direct-drive-motors (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- In Geun Ahn. Stator of Motor and Washing Apparatus Having the Same. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20110016929 (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Scuiller, F. General, Compact and Easy-to-Compute Winding Factor Formulation. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Siddiqi, M.R.; Ali, Q.; Yazdan, T.; Hussain, A.; Hur, J. Brushless Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine Topology Using Concentrated Winding for Dual Speed Applications. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 119560–119567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



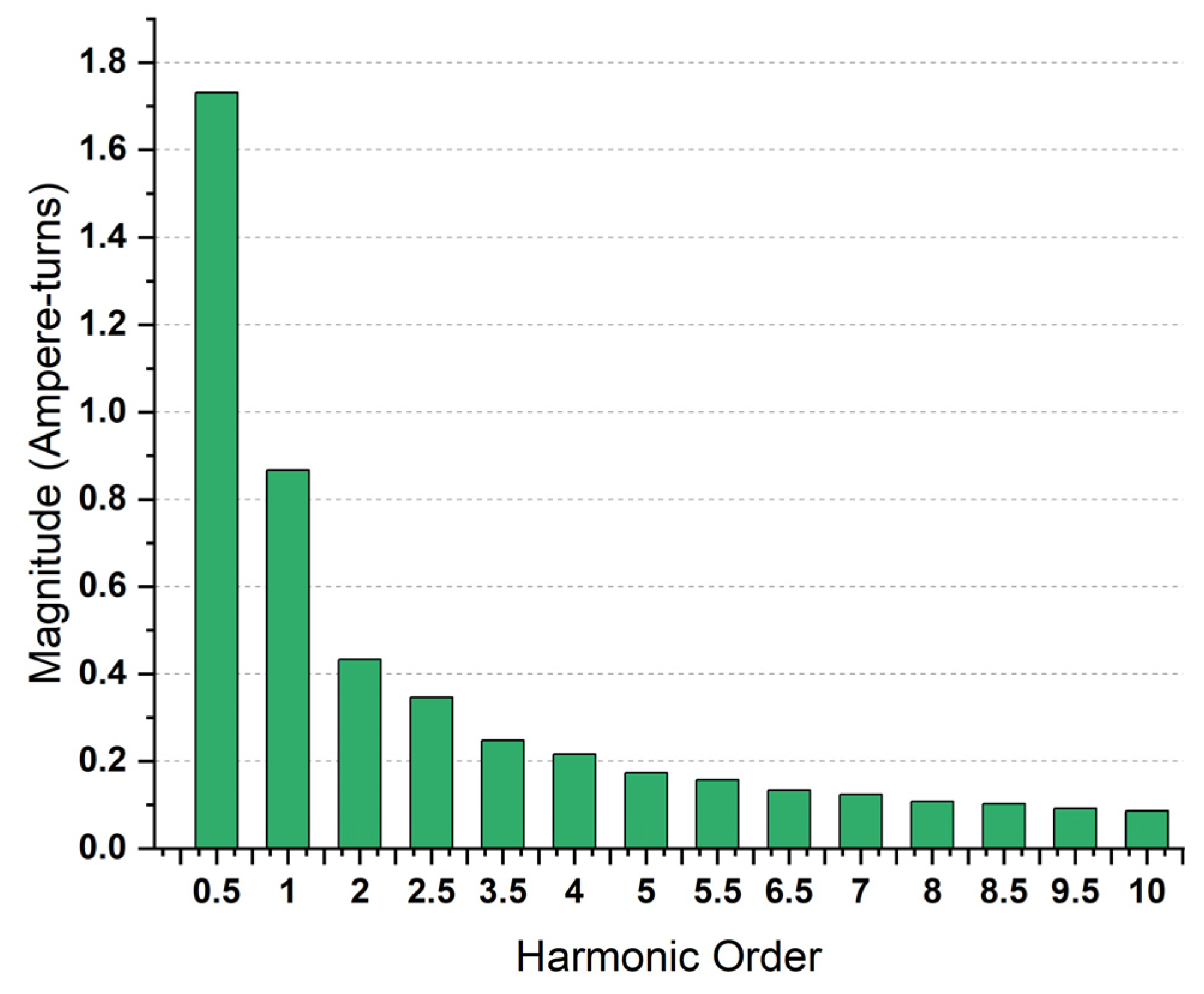
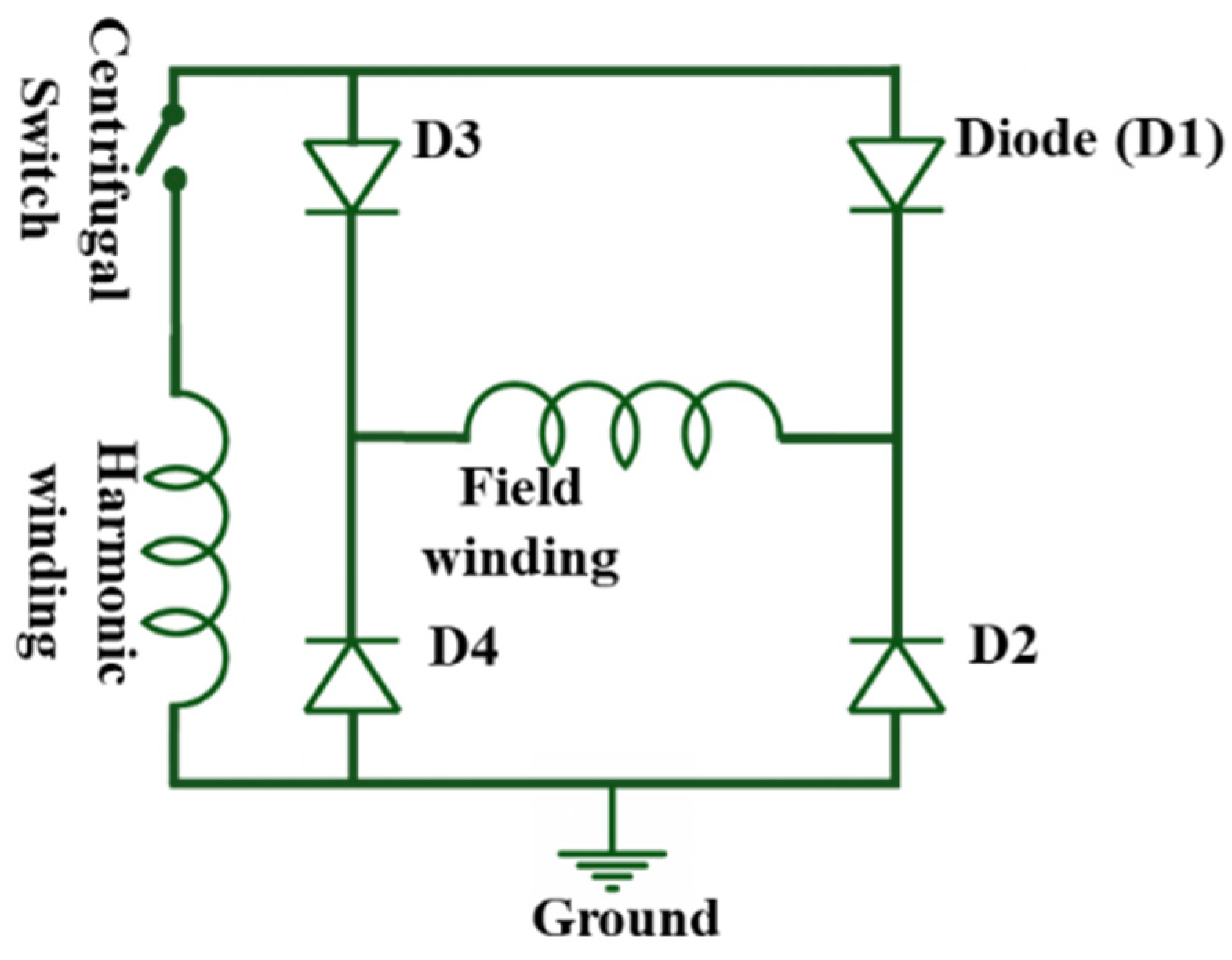

| Fundamental Frequency | Harmonic Order | Number of Poles | Synchronous Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 Hz | 0.5 | 24 | 150 r/min |
| 60 Hz | 1 | 48 | 300 r/min |
| Parameter | Unit | C-WRSM | BL-WRSM | HB-WRSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | ||||
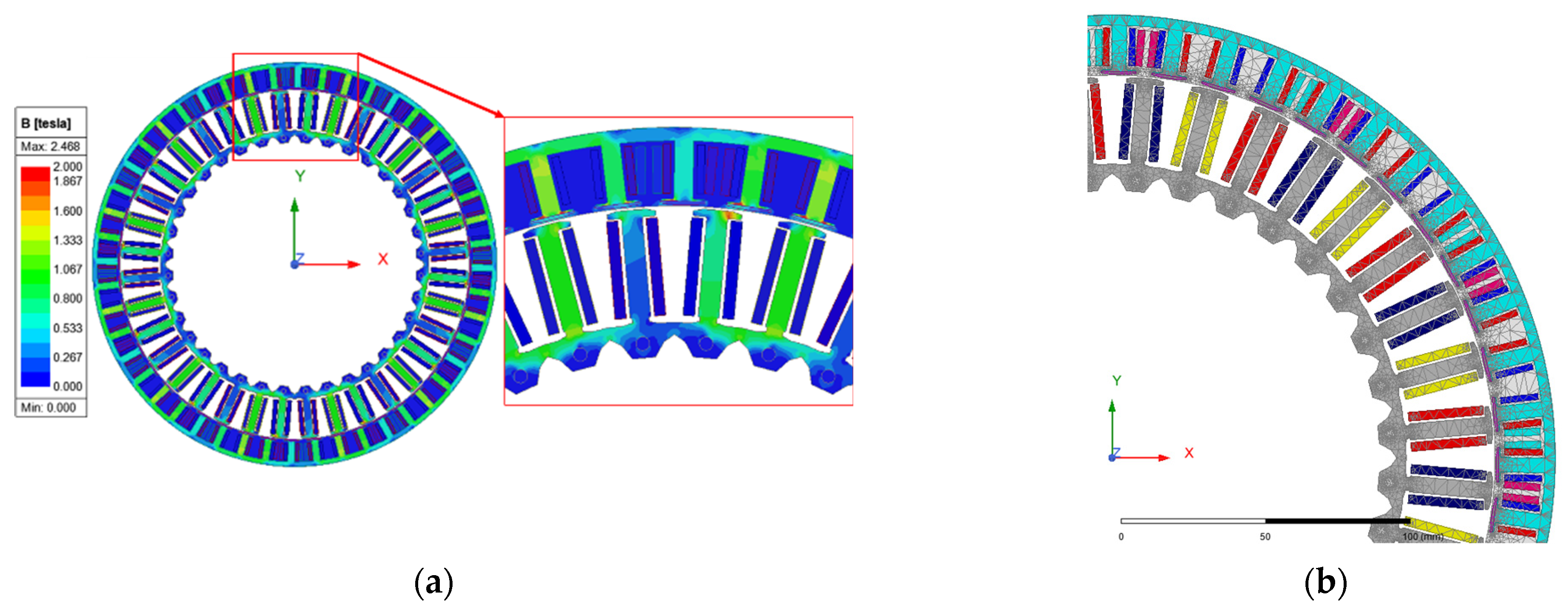
| Number of slots | - | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| Field winding poles | - | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| Harmonic winding poles | - | - | 24 | 24 |
| Stator OD/ID | mm | 265/186 | 265/186 | 265/186 |
| Rotor OD/ID | mm | 308/267 | 308/267 | 308/267 |
| Air-gap length | mm | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Axial length | mm | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Washing mode speed | r/min | 46 | 46 | 46 |
| Drying mode speed | r/min | 1370 | 1370 | 1370 |
| Frequency in washing mode | Hz | 18.4 | 18.4 | 18.4 |
| Frequency in drying mode | Hz | 548 | 548 | 548 |
| Number of magnets | - | - | - | 48 |
| Magnet material | - | - | - | NdFe30 |
| Fundamental Frequency | Washing Mode | Dry Mode | Washing Mode | Dry Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torque [Nm] | Torque Ripple [%] | |||
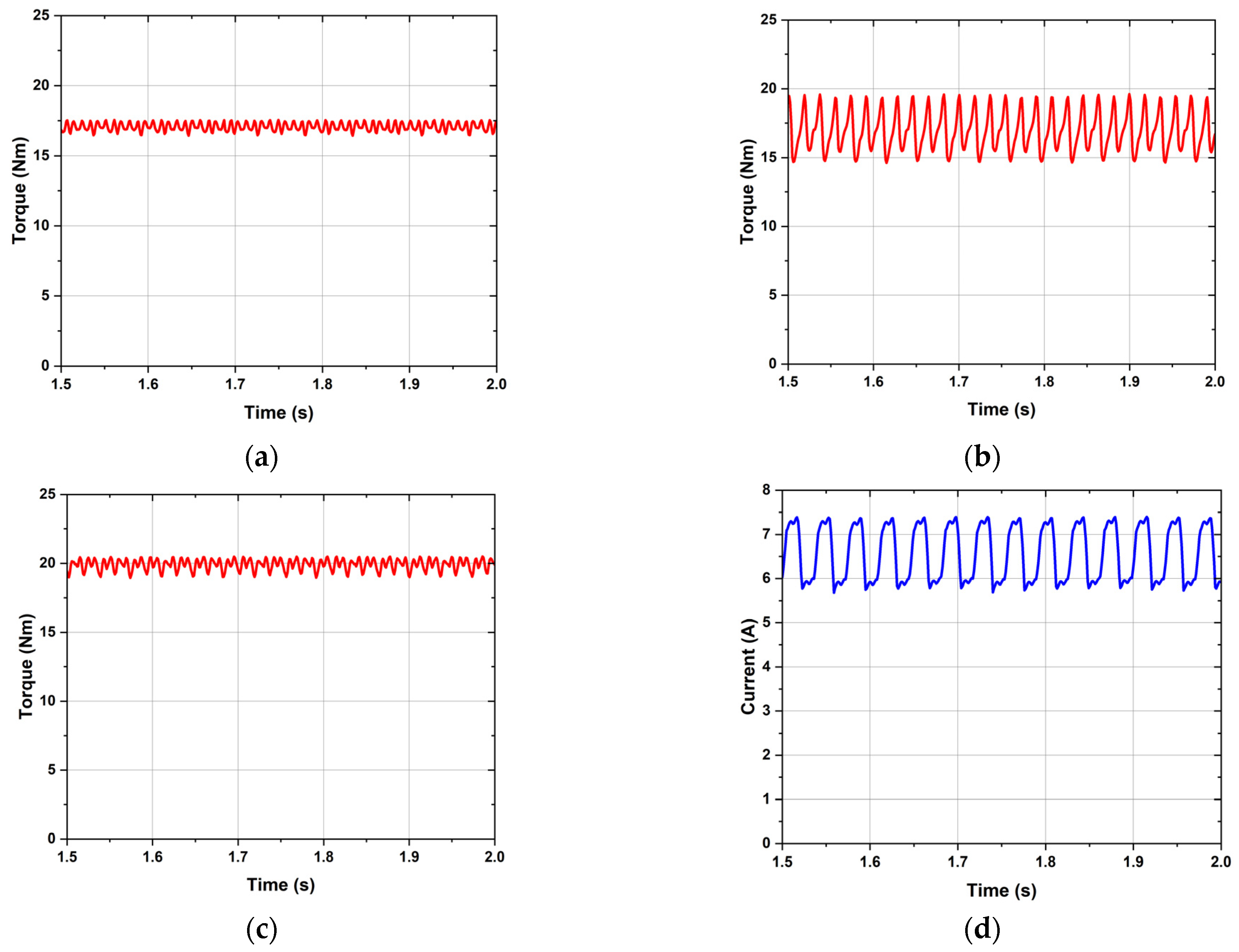
| C-WRSM | 17.14 | 3.37 | 5.22 | 8.81 |
| BL-WRSM | 16.39 | 3.04 | 25.12 | 39.77 |
| HB-WRSM | 19.41 | 5.46 | 7.86 | 93.0 |
| Parameter | C-WRSM | BL-WRSM | HB-WRSM | PMSM Mode | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wash | Dry | Wash | Dry | Wash | Dry | Dry | |
| Average torque [Nm] | 17.14 | 3.37 | 16.34 | 3.03 | 19.41 | 5.47 | 4.91 |
| Torque ripple [%] | 5.22 | 8.81 | 25.12 | 39.77 | 7.86 | 93.0 | 20.0 |
| Harmonic current [A] | 0 | 0 | 5.70 | 3.63 | 1.78 | 10.86 | 0 |
| Field current [A] | 5.83 | 4.16 | 6.26 | 4.87 | 1.85 | 13.64 | 0 |
| Output power [W] | 82.54 | 484.25 | 78.90 | 435.80 | 93.46 | 783.87 | 704.13 |
| Core loss [W] | 1.62 | 18.72 | 1.45 | 11.59 | 1.17 | 86.32 | 23.76 |
| Rotor copper loss [W] | 41.12 | 20.93 | 55.48 | 31.99 | 4.87 | 254.46 | 0 |
| Stator copper loss [W] | 87.33 | 33.48 | 87.33 | 33.48 | 87.33 | 33.48 | 33.48 |
| Efficiency [%] | 38.82 | 86.87 | 35.35 | 84.97 | 50.02 | 67.68 | 92.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.; Ali, Q.; Sirewal, G.J.; Kumar, K.; Choi, G. Hybrid Brushless Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine with Dual-Mode Operation for Washing Machine Applications. Machines 2025, 13, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13050342
Ahmed S, Ali Q, Sirewal GJ, Kumar K, Choi G. Hybrid Brushless Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine with Dual-Mode Operation for Washing Machine Applications. Machines. 2025; 13(5):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13050342
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Sheeraz, Qasim Ali, Ghulam Jawad Sirewal, Kapeel Kumar, and Gilsu Choi. 2025. "Hybrid Brushless Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine with Dual-Mode Operation for Washing Machine Applications" Machines 13, no. 5: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13050342
APA StyleAhmed, S., Ali, Q., Sirewal, G. J., Kumar, K., & Choi, G. (2025). Hybrid Brushless Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine with Dual-Mode Operation for Washing Machine Applications. Machines, 13(5), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13050342








