Design and Discrete Element (DEM) Simulation Analysis of Grassland Ecological Cleaning and Restoration Vehicle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Design and Analysis
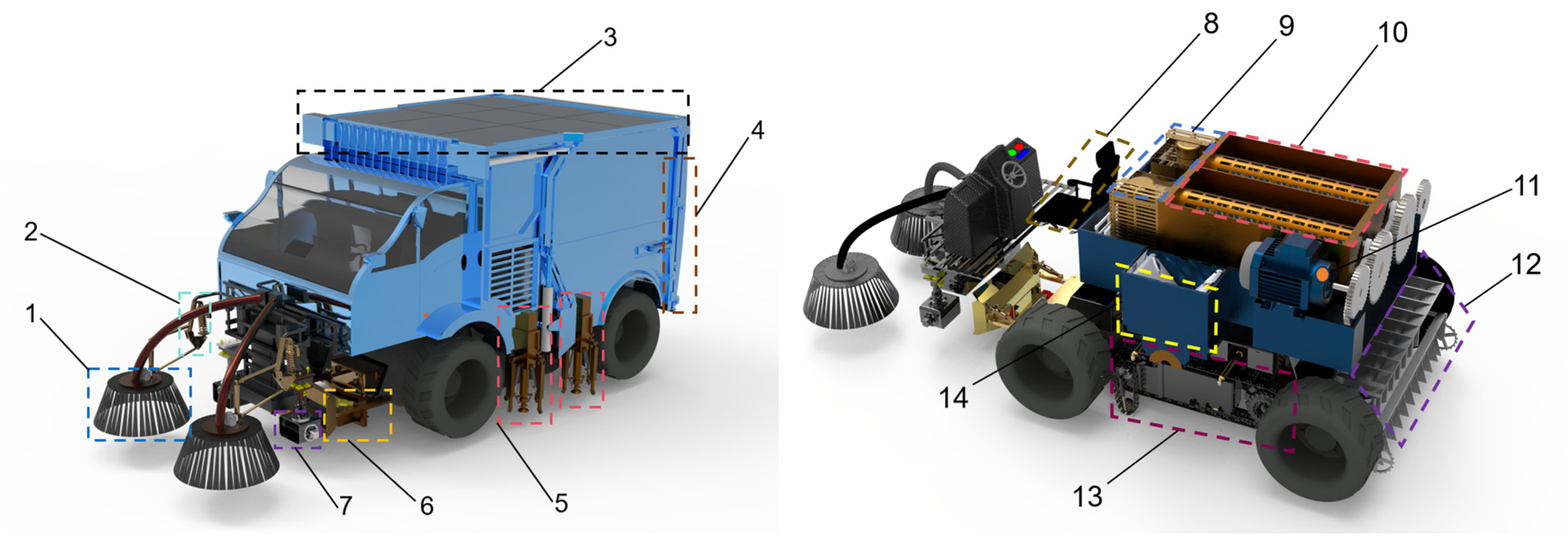
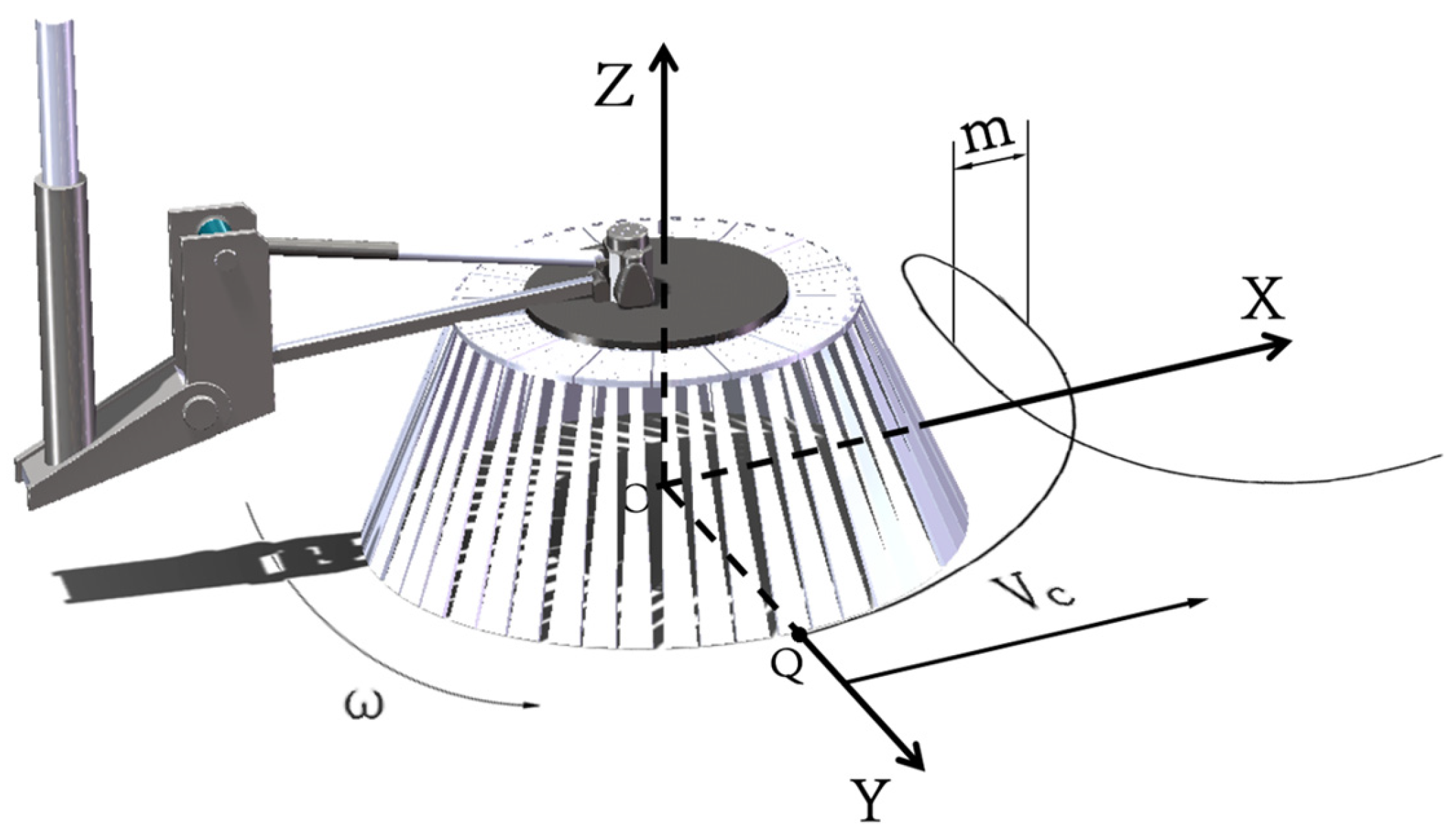
2.1. Structure and Working Principle of Grassland Ecological Cleaning and Restoration Vehicle
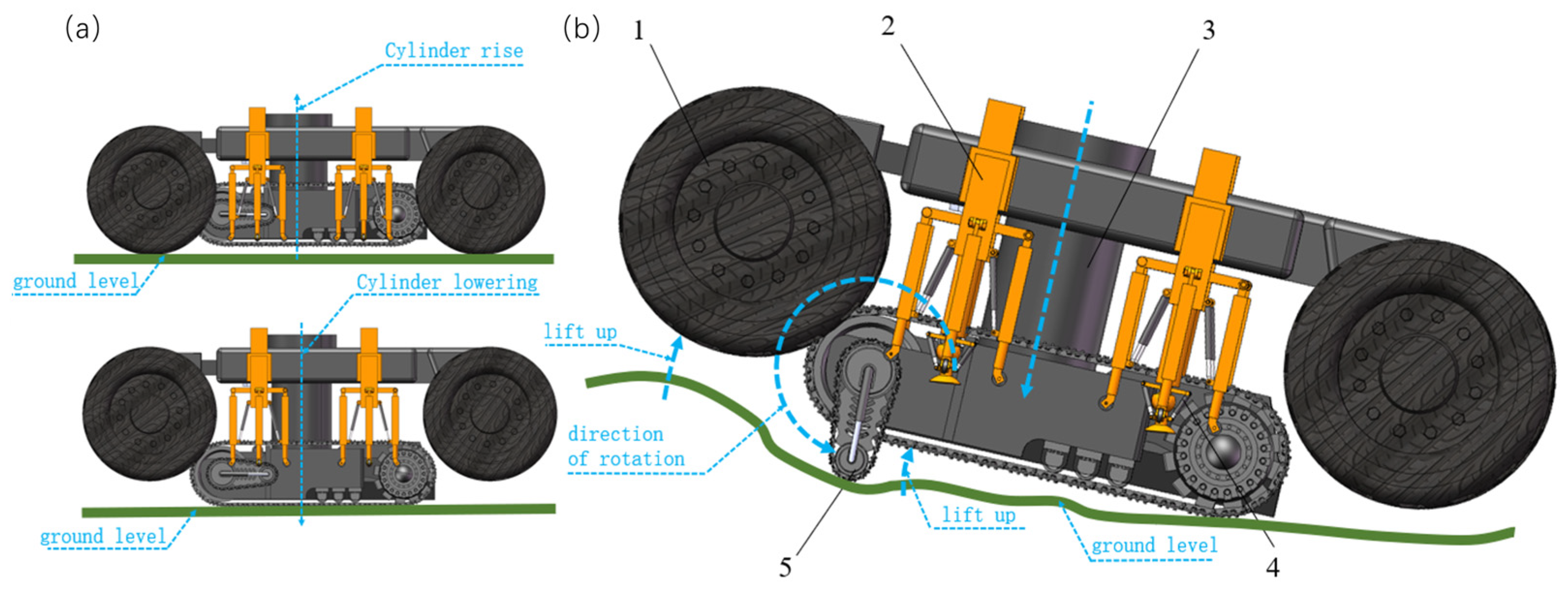
2.2. Working Mechanism of Wheel–Track Composite Obstacle-Crossing Device
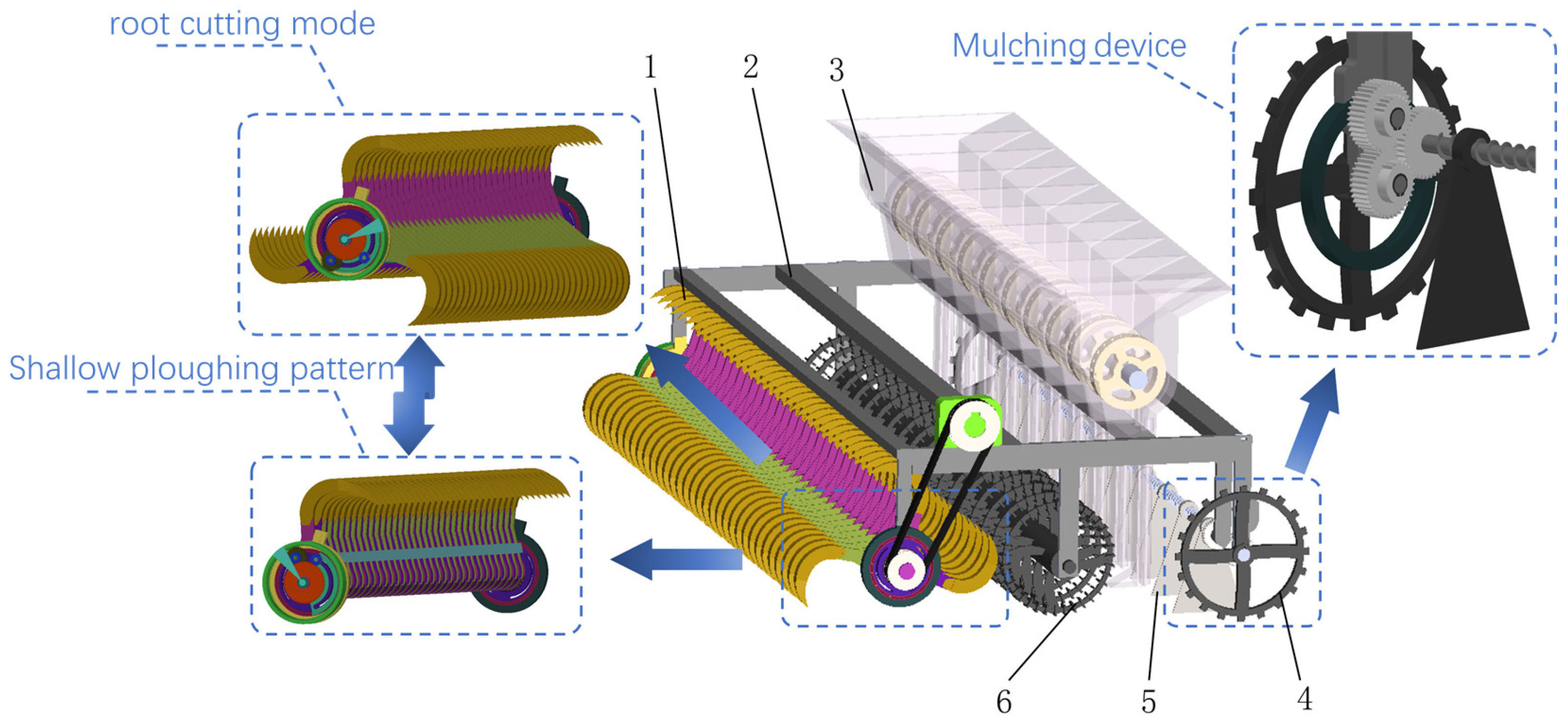
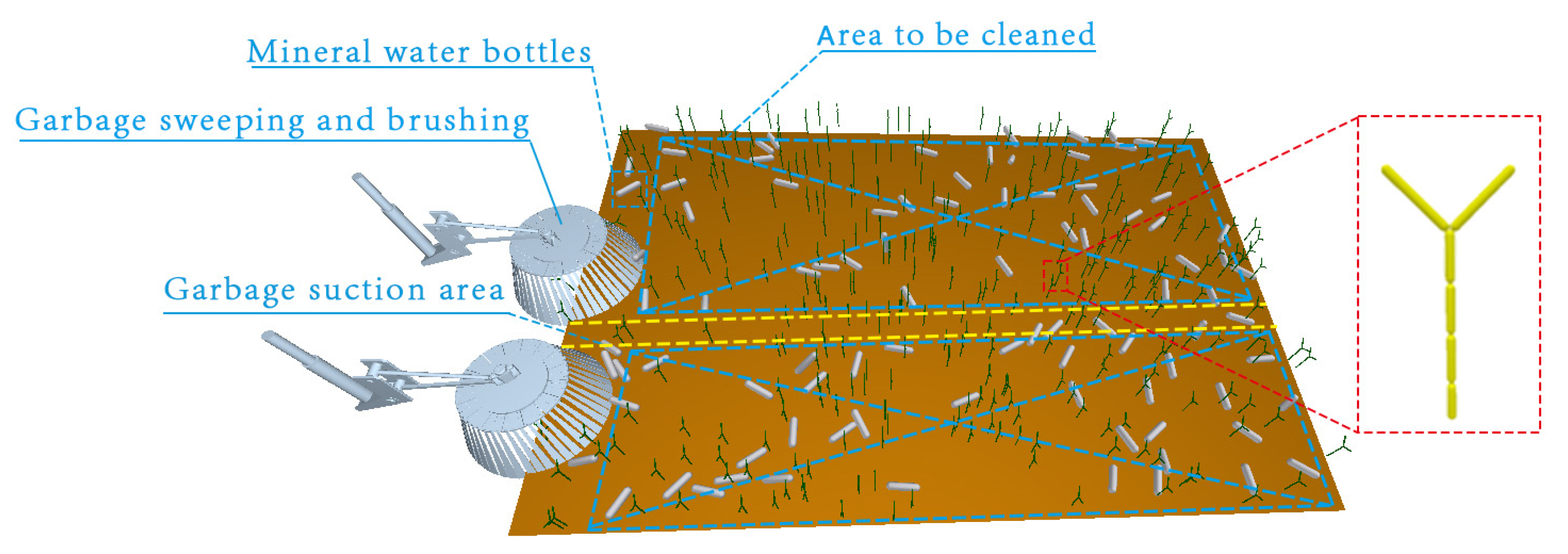
2.3. Design of Sweeping Device
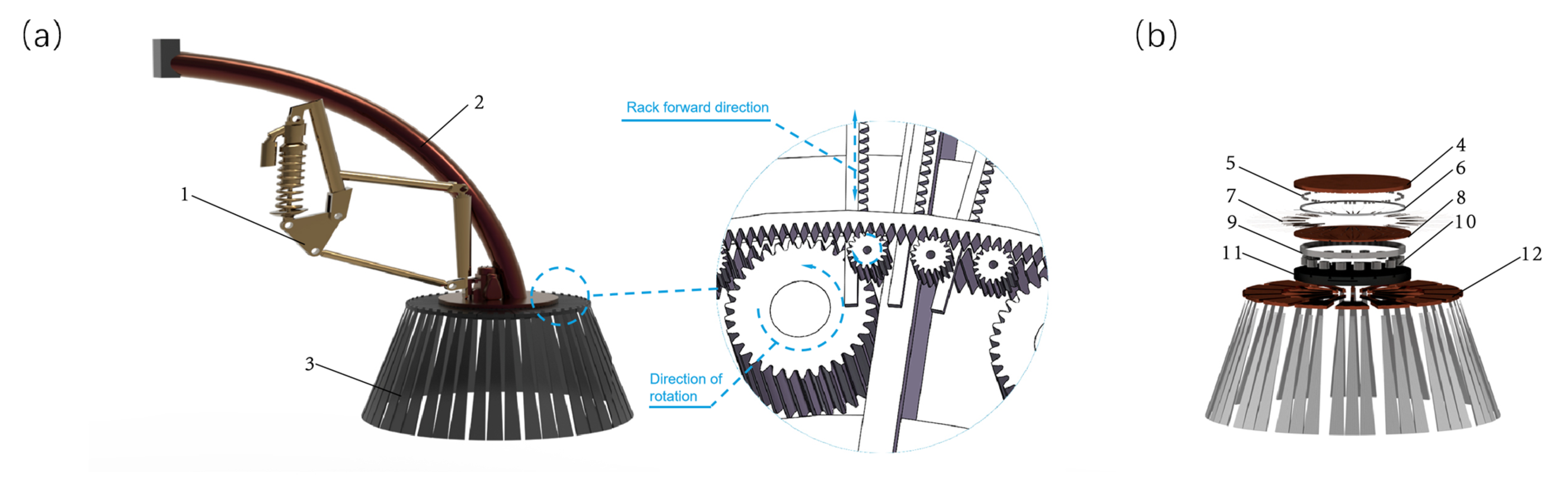
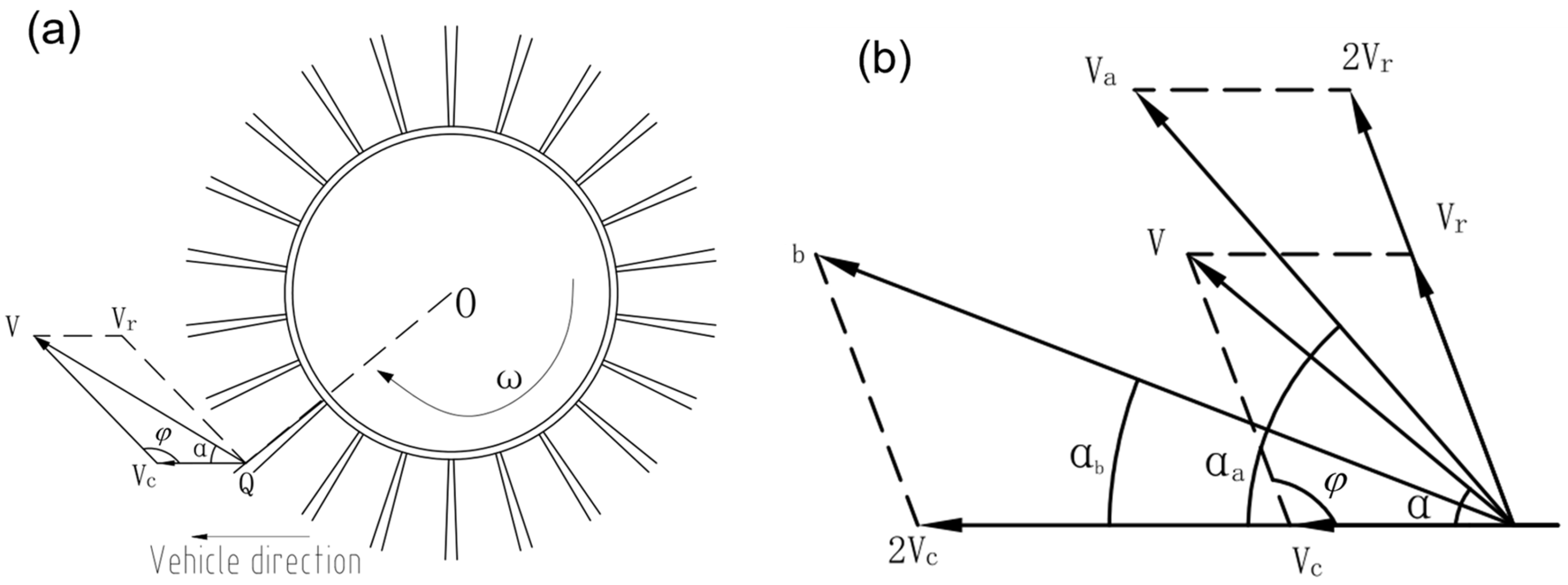
2.3.1. Structural Design of Disk Brush with Variable Radius and Angle
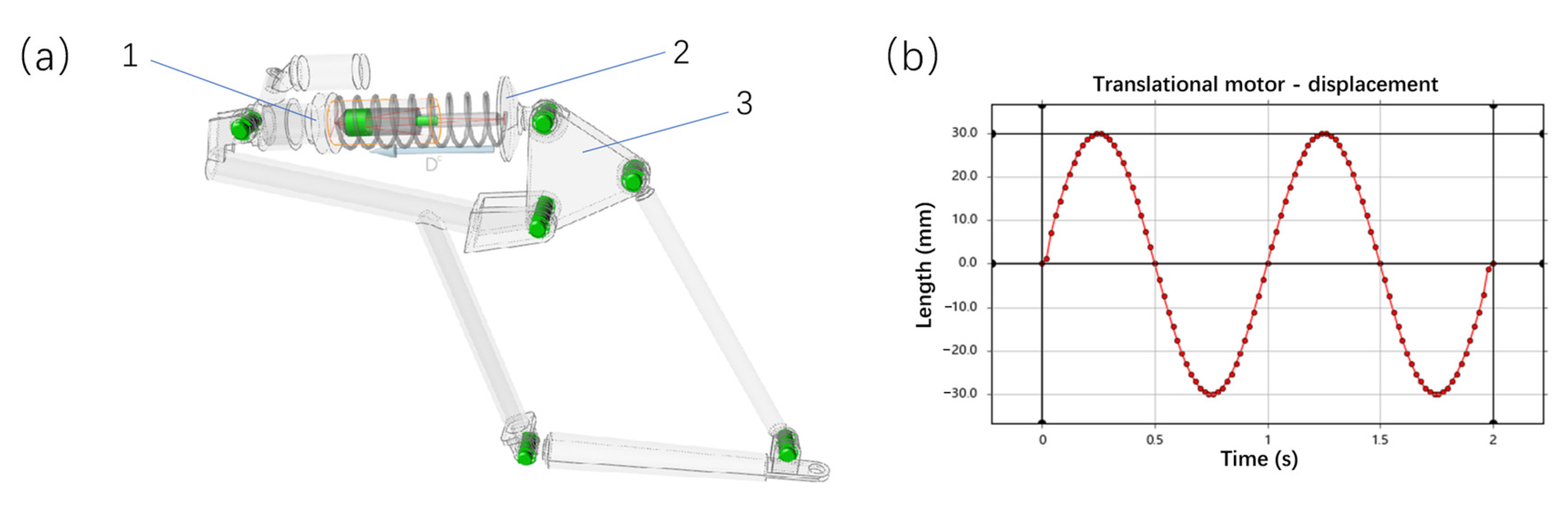
2.3.2. Motion Analysis of Disk Brush Swivel Arm Mechanism
2.3.3. Static Force Analysis of Disk Brush Swivel Arm Mechanism
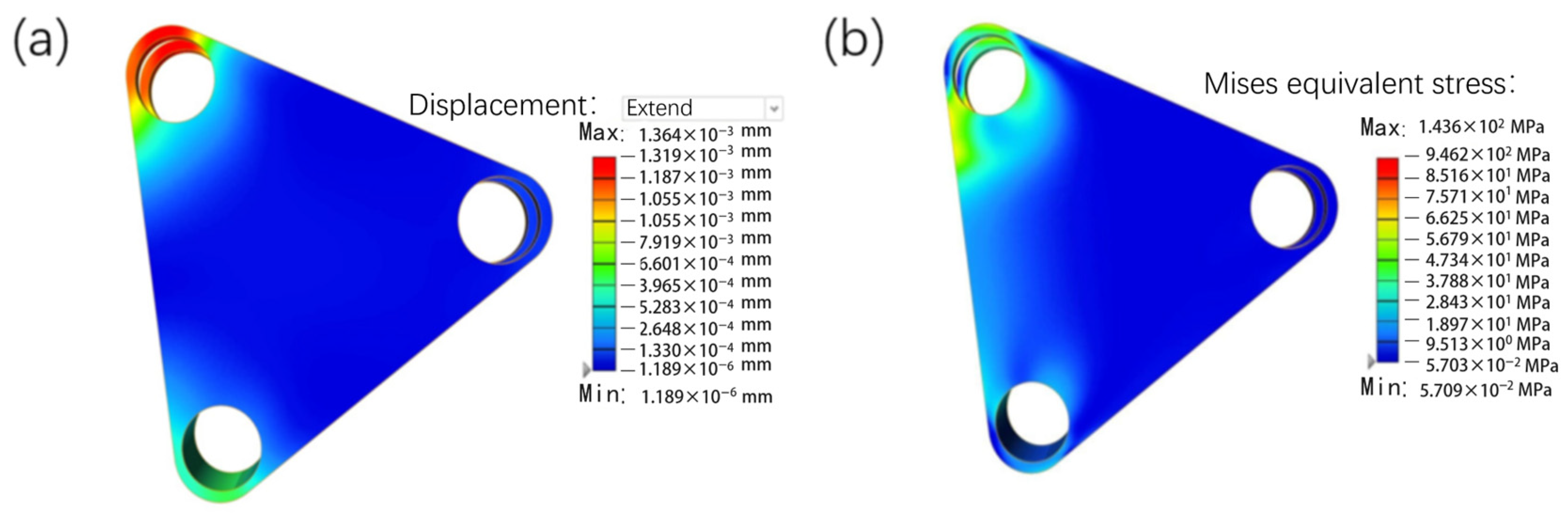
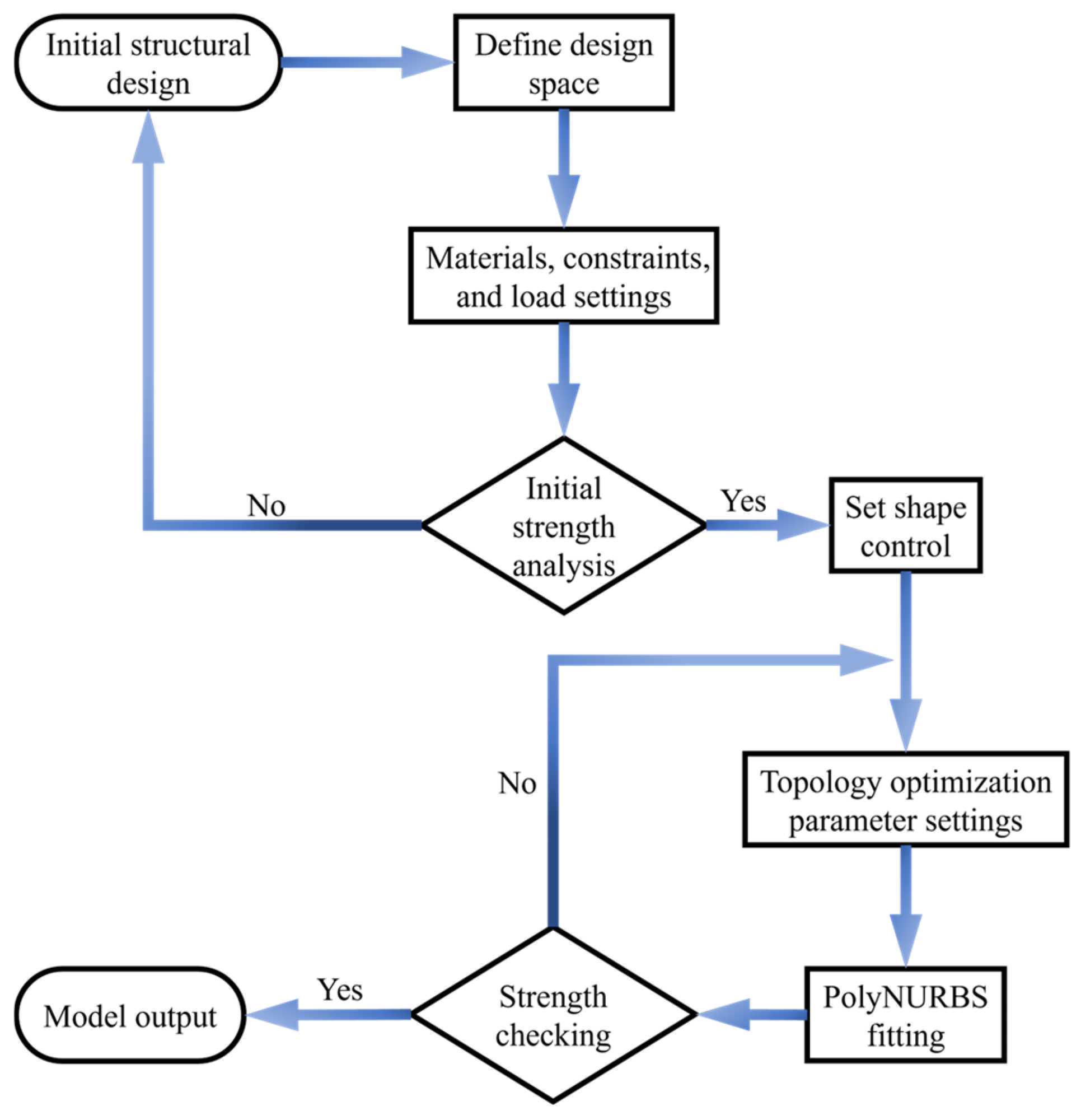
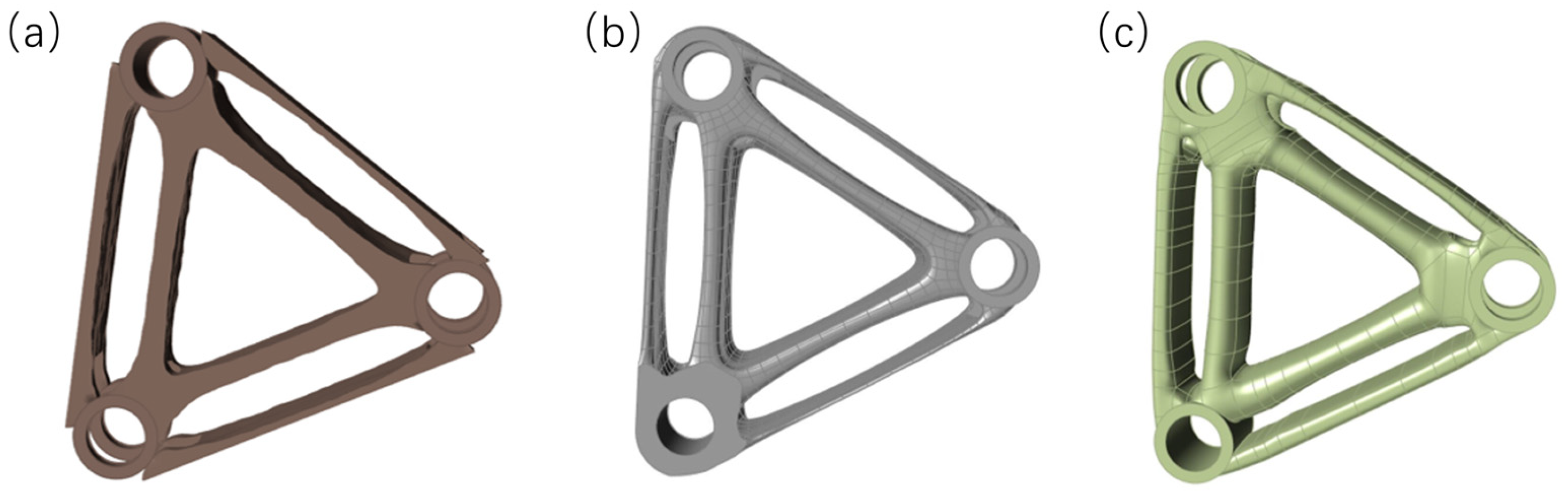
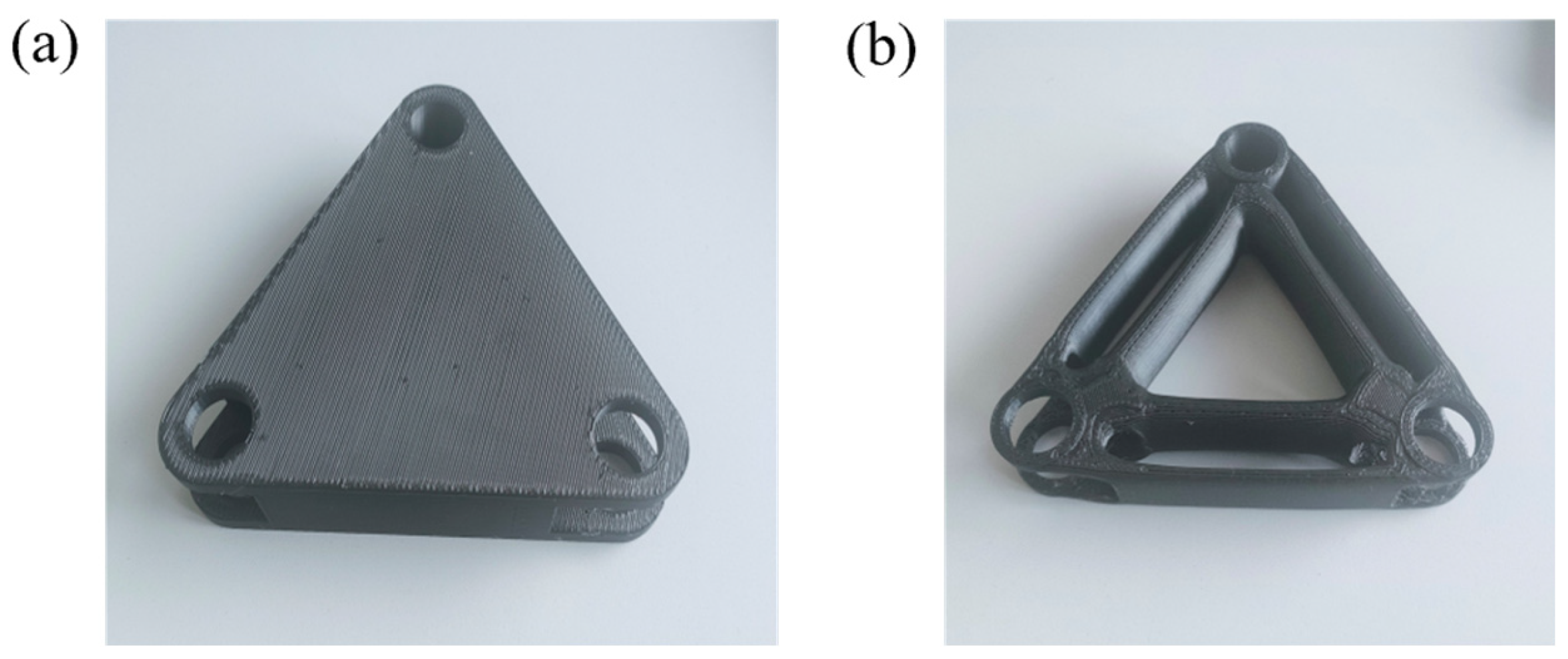
2.3.4. Optimization of Disk Brush Swivel Arm Topology
- ρ—lative density of the ith cell;
- Vi—Volume of the ith cell;
- Vo—original volume;
- α—Percentage reduction in volume;
- f(ρ)—objective function;
- g(ρ)—constraint function.
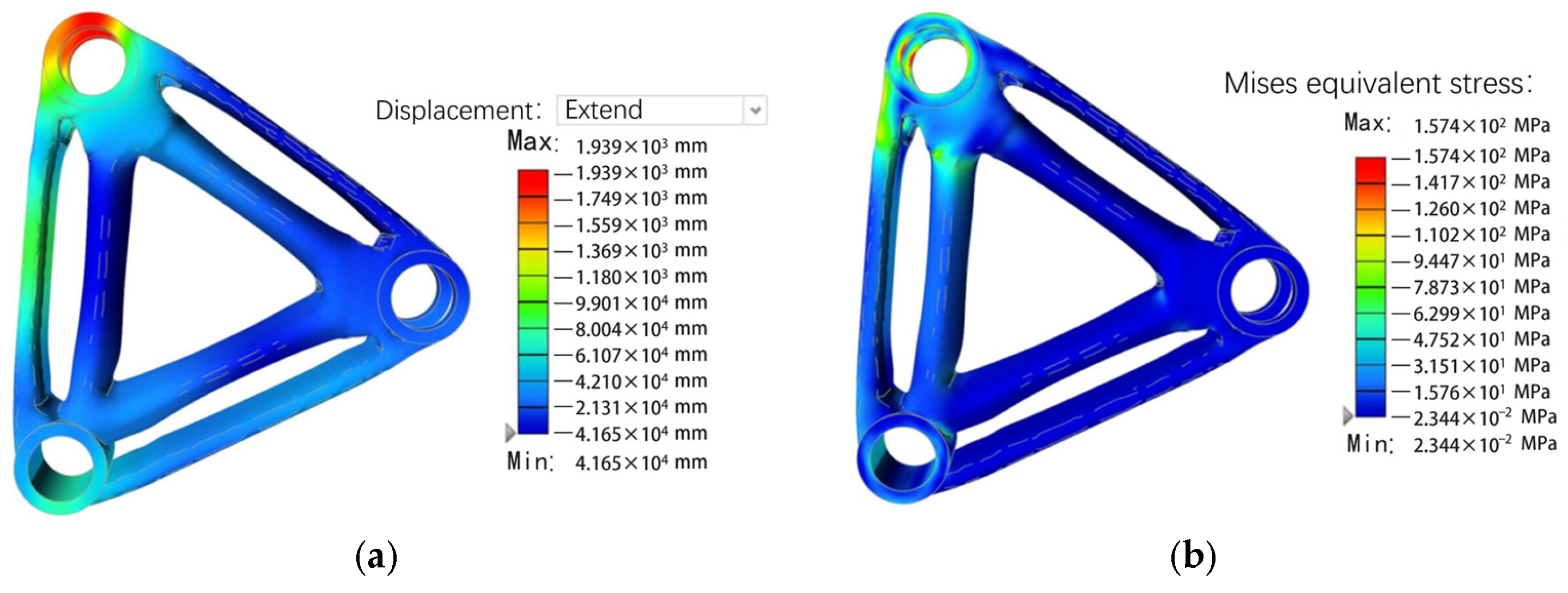
2.3.5. Calibration of the Results of the Topology Optimization of the Disk Brush Swivel Arm
2.4. Design of the Waste Disposal Unit
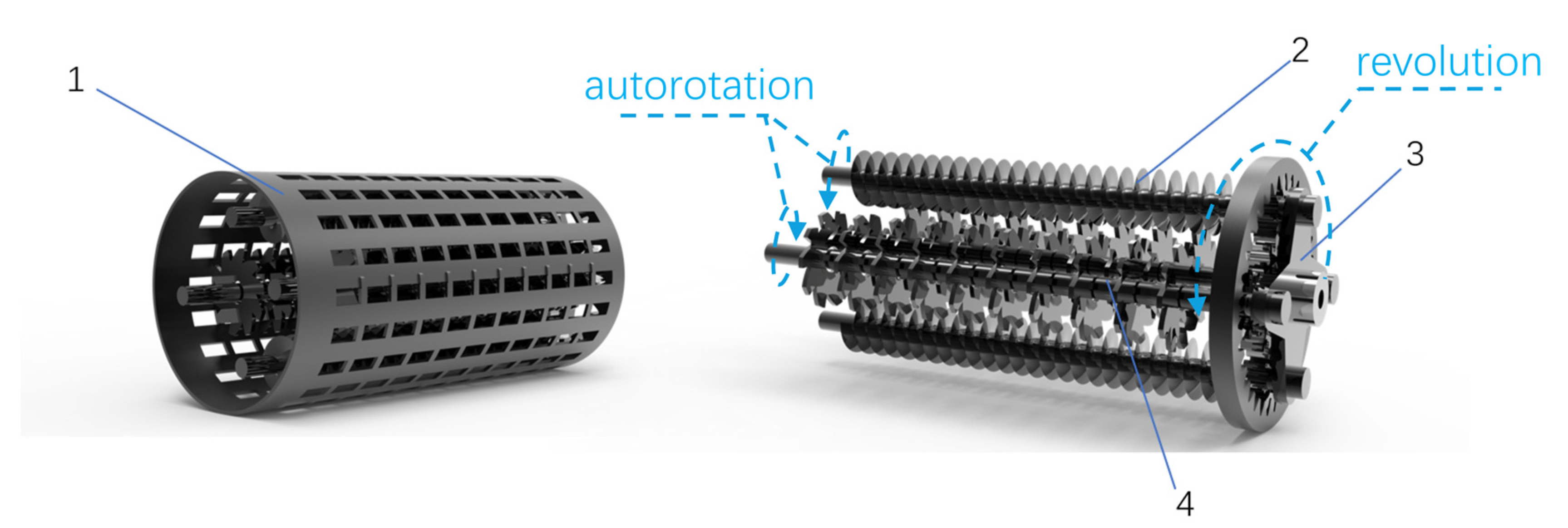
2.4.1. Mechanism of the Spiral Knife Waste Shredding Device
2.4.2. Kinematic Analysis of Spiral Knife Waste Shredding Devices
2.5. Working Mechanism of Centre of Mass Leveling Device
2.6. Grass Seed Sowing Device Working Mechanism
3. Methodology and Simulation
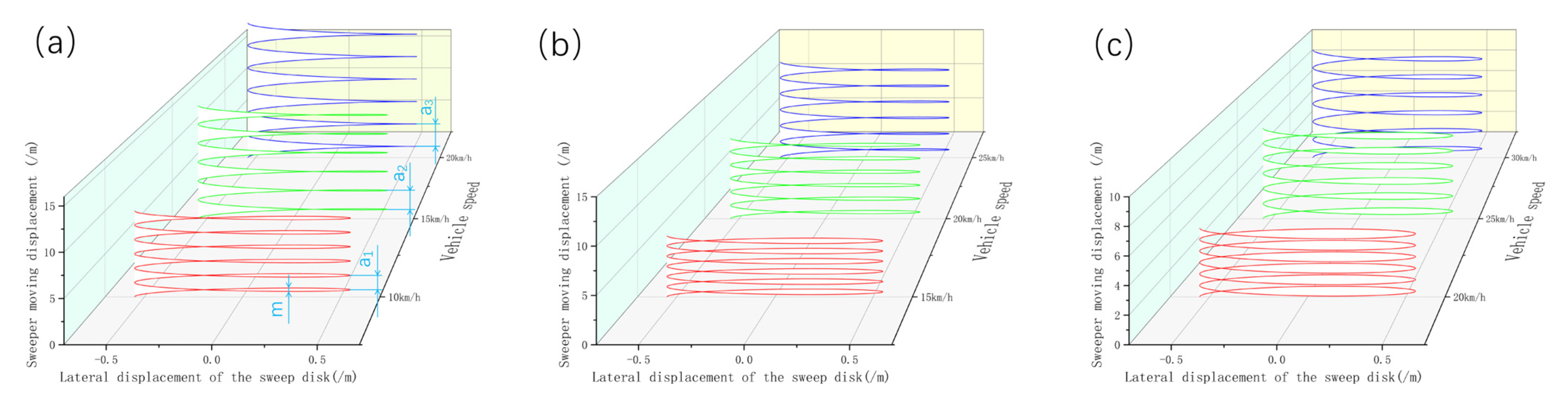
3.1. Parametric Modeling of Disk Brush Movement
3.2. Discrete Element Simulation Modeling and Parameterization of the Cleaning Process
3.2.1. Discrete Element Method (Math.)
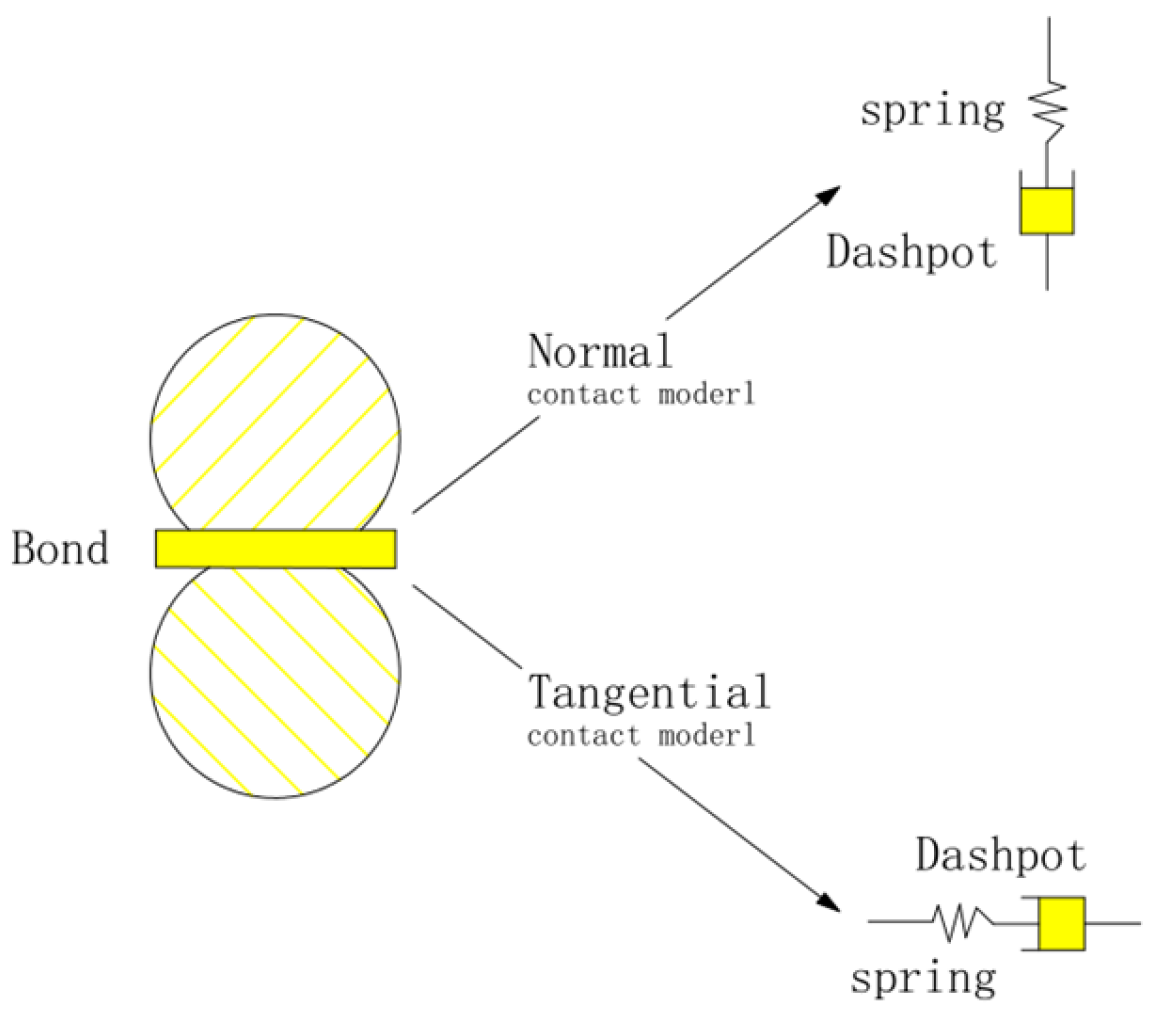
3.2.2. Contact Model
3.2.3. Venue Construction
4. Results and Discussion
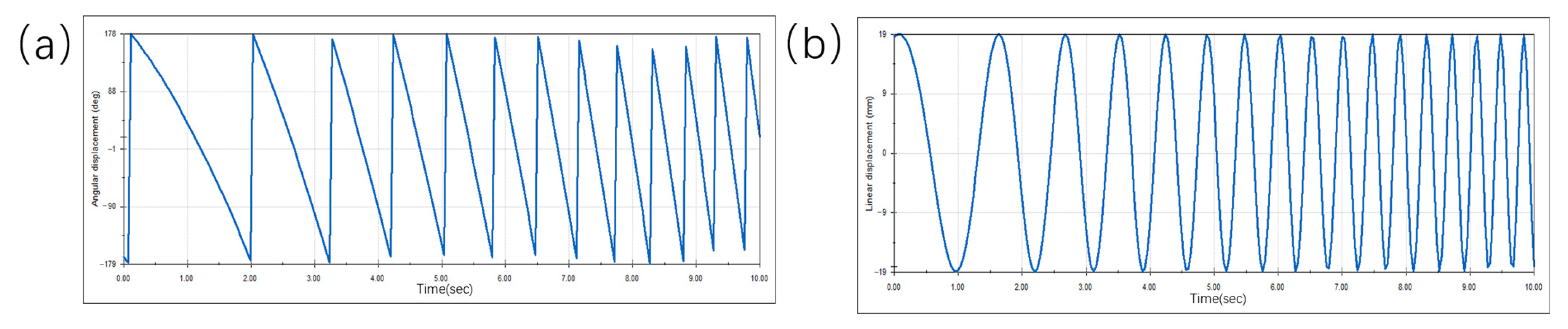
4.1. Analysis of the Results of the Disk Brush Motion Parameters
4.2. Analysis of Disk Brush Simulation Results
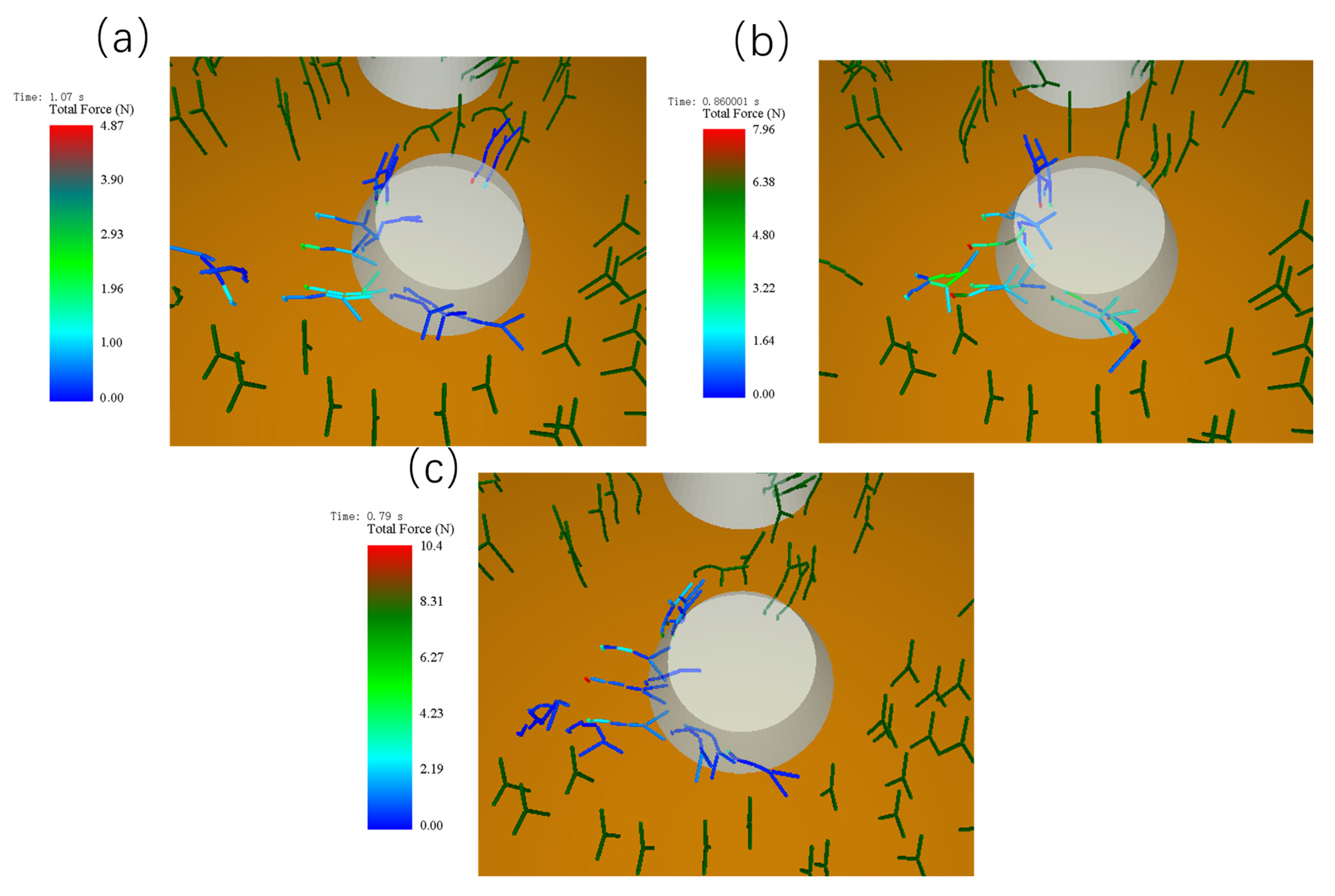
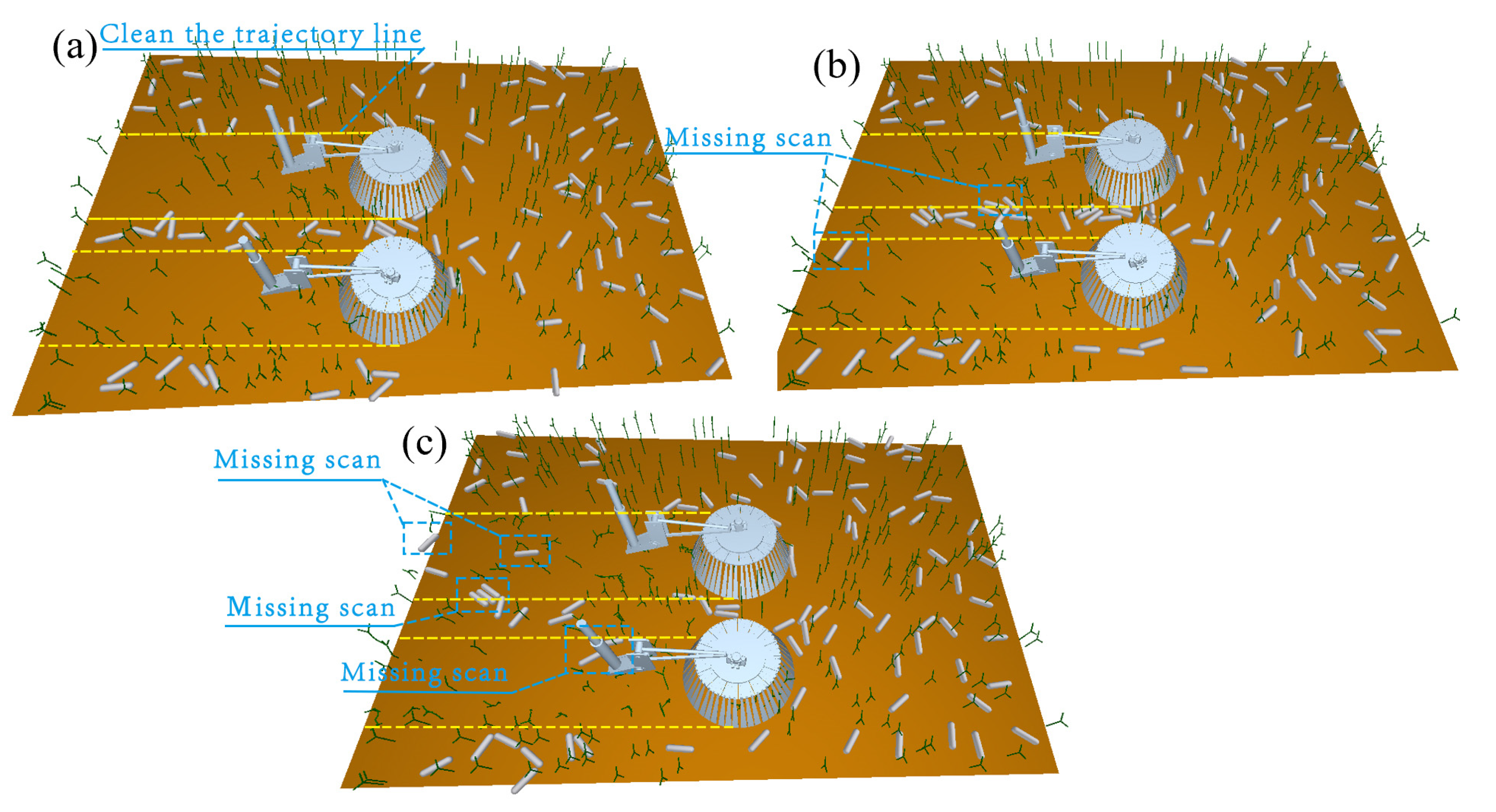
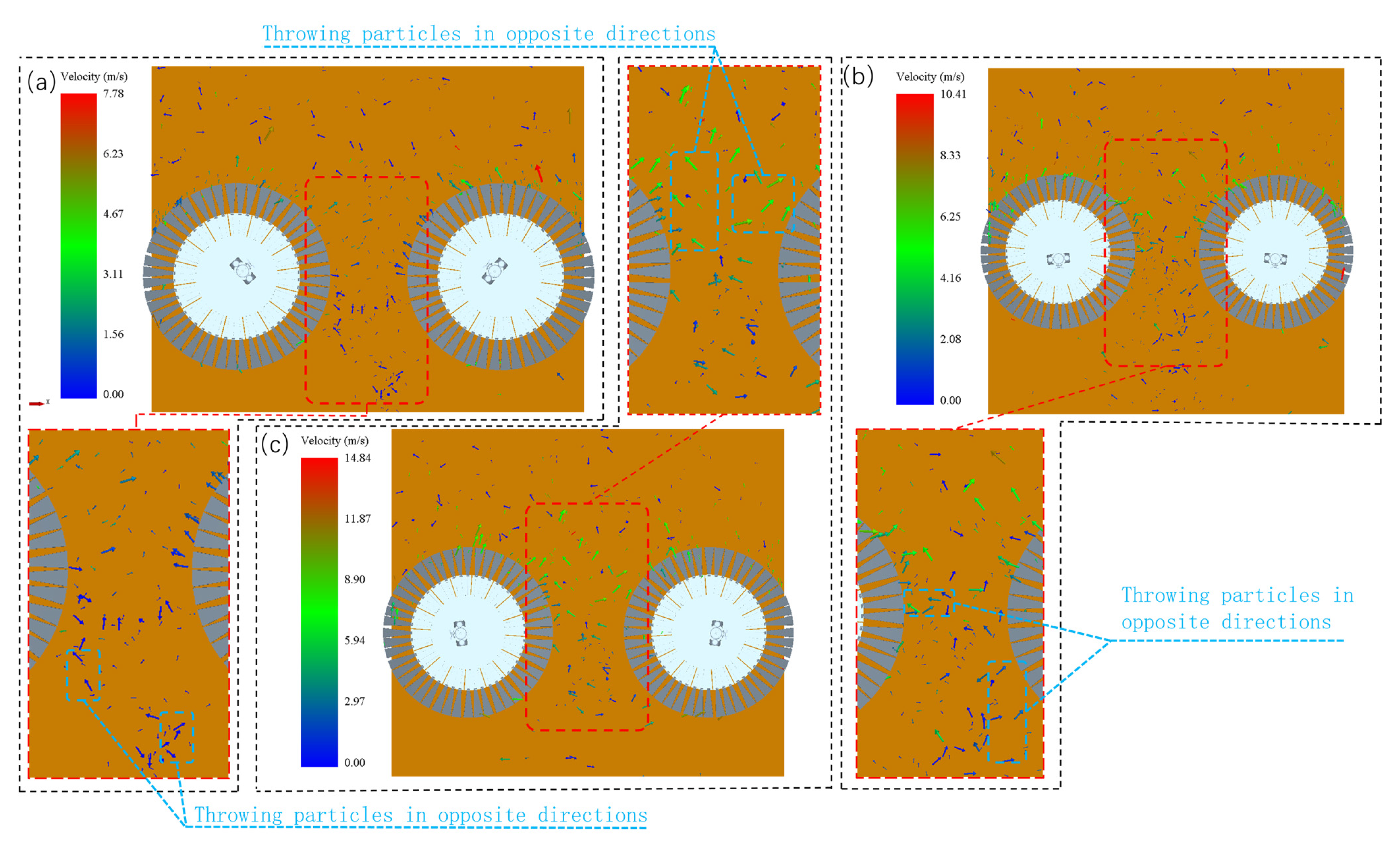
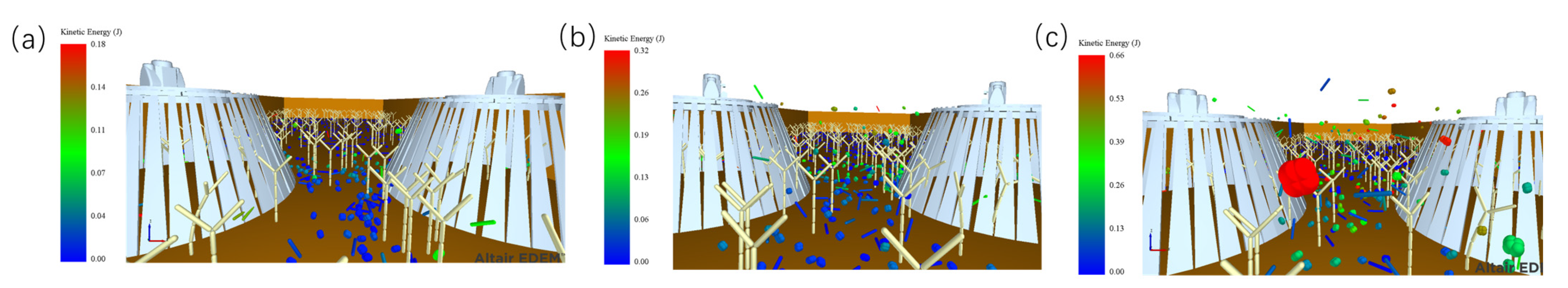
4.2.1. Effects of Rotational Speed and Vehicle Speed on Gramineous Plants
4.2.2. Effect of R/MIN and Vehicle Speed on Garbage Collection
4.3. Discrete Element Simulation and Parameterization of the Seeding Process
4.3.1. Discrete Element Simulation Modeling Parameter Settings
4.3.2. One-Way Experimental Analysis
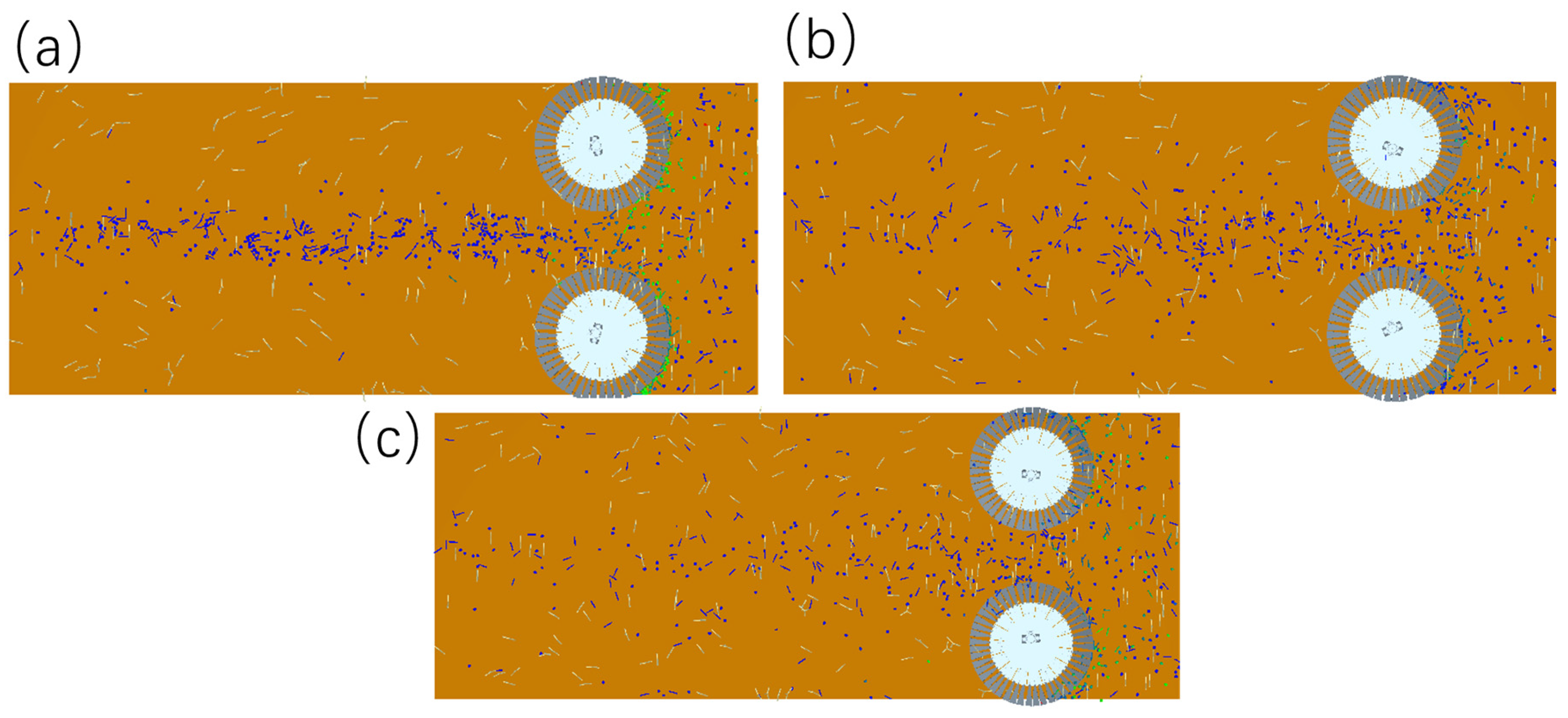
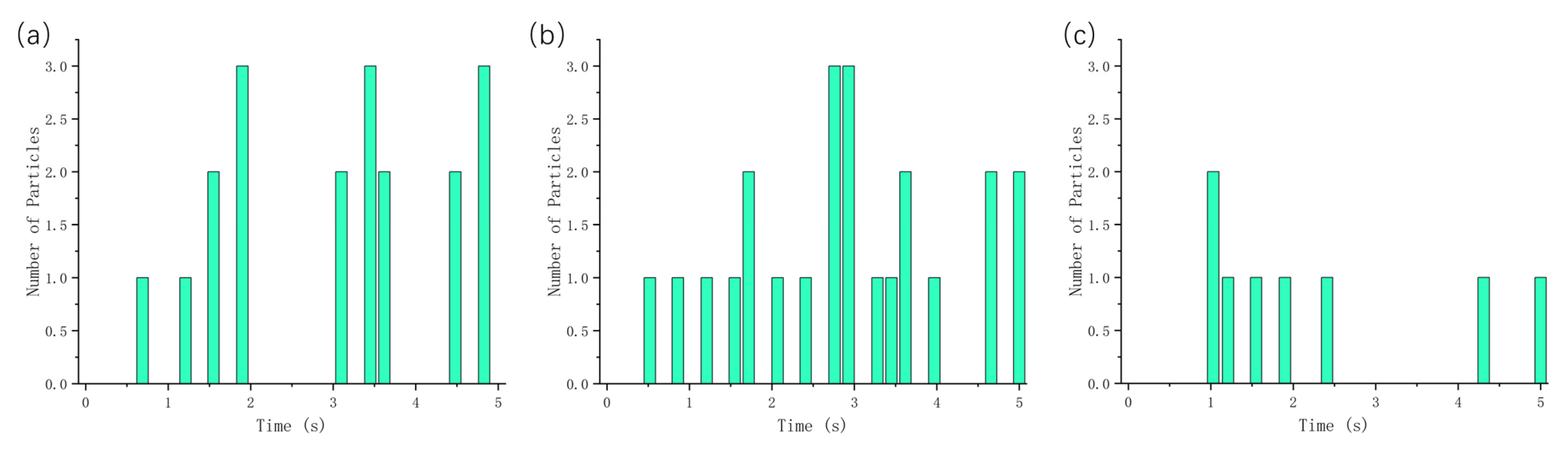
4.3.3. Influence of the Number of Slots on the Amount of Seed Discharged
4.3.4. Orthogonal Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Ma, J. A new type of environmentally friendly self-loading rubbish truck. Spec. Purp. Veh. 2019, 9, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Zhou, G.; Yuan, T.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Shao, J.; Zhou, X. Grazing Intensity Significantly Changes the C:N:P Stoichiometry in Grassland Ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettlaff, M.A.; Erbilgin, N.; Cahill, J.F., Jr. An Invasive Grass and Litter Impact Tree Encroachment into a Native Grassland. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2021, 24, e12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.R.; Dharmale, S. Eco Efficiency Optimization of Municipal Solid Waste Management. IJRASET 2023, 11, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, R.; Xiang, Y. Study on the Influence of Village Form of Famous Tourism Village on the Layout of Garbage Collection Points—A Case Study of Famous Tourism Village in Guilin City. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 446, 032024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.N. A Model for the Optimal Allocation of Trucks for Solid Waste Management. Waste Manag. Res. 1996, 14, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, D.; Dorronsoro, B.; Ruiz, P. Sustainable Waste Collection Optimization Using Electric Vehicles. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 105, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zuo, C.; Yin, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, A. Simplified Calculation of Pressure on Buried Pipelines by Vehicle Loads. Eng. Constr. Des. 2020, 22, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Xie, Y. Discussion on the technical status and development trend of self-loading rubbish truck loading mechanism. Spec. Purp. Veh. 2022, 11, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Diao, A.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S. Design of an Automatic Ground Cleaning Machine for Dedusting Rooms of Chicken Houses. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajian, R.; Sun, J.-Q.; Ehsani, R. Design of an Integrated Controller for a Sweeping Mechanism of a Low-Dust Almond Pickup Machine. Sensors 2023, 23, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.; Luo, K.; Yan, L. Structure Design and Configuration Optimization of the Reconfigurable Deformed Tracked Wheel Based on Terramechanics Characteristics. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2023, 108, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioso, A.; di Maria, E.; Giannoccaro, N.I.; Ishii, K. Multibody Modeling of a New Wheel/Track Reconfigurable Locomotion System for a Small Farming Vehicle. Machines 2022, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, D.L.; Olson, R.A.; Schuman, G.E. Long-Term Effects of Mechanical Renovation of a Mixed-Grass Prairie: I. Plant Production. Arid. Land Res. Manag. 2004, 18, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, A.; Uchida, K. Grassland Legacy Remaining in Vegetation and Seedbank Species Diversity: Evaluation in Abandoned Grasslands and Plantation Forests. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 36, e02134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacigin, V.V.; Guskov, V.V. The Basis of Tractor Performance Theory: Part 1—General Laws of Soil Strength and Deformation. J. Terramech. 1968, 5, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, A.; Usowicz, B.; Lipiec, J. Effects of Tractor Traffic on Spatial Variability of Soil Strength and Water Content in Grass Covered and Cultivated Sloping Vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 84, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuferev, S.S.; Lesovskaya, M.I.; Olentsova, Y.A. Optimal Weight and Power Parameters of Crawler Tractors to Reduce Pressure on the Soil. IOP Conf. Ser.Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 315, 052009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tong, X.; Hou, Z. Design of suspension rocker arms and their topology optimization for Formula Racing cars. Agric. Equip. Veh. Eng. 2017, 55, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Guo, A.; Kong, D.; Wu, J.; Qu, P.; Wang, S.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C.; et al. Preparation of Bouligand Biomimetic Ceramic Composites and the Effect of Different Fiber Orientations on Mechanical Properties. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 132, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, A.; Sheng, X.; Tang, R.; Qu, P.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Yin, L.; Sui, S.; Guo, S. Preparation of 316L Stainless Steel/WC Gradient Layered Structures with Excellent Strength-Elongation Synergy Using Laser Powder Bed Fusion. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 133, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhu, J. Topology Optimization Design of 3D Continuum Structure with Reserved Hole Based on Variable Density Method. JESTR 2016, 9, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Zhao, Y. Topology Optimization of Heat Sink Based on Variable Density Method. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Fan, W. Topology optimization design of complex antenna support structures for star-carried articulated spreading antennas. Mech. Des. 2022, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coranic, T.; Gaspar, S.; Pasko, J. Utilization of Optimization of Internal Topology in Manufacturing of Injection Moulds by the DMLS Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Lee, K. Optimal Design of Rib Structures Using the Topology Optimization Technique. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1997, 211, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ypsilantis, K.-I.; Kazakis, G.; Faes, M.G.R.; Ivens, J.; Lagaros, N.D.; Moens, D. A Topology-Based in-Plane Filtering Technique for the Combined Topology and Discrete Fiber Orientation Optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 417, 116400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, D.; Duan, C.; Lin, J.; Ma, Y. Topology optimization and lightweight design of scroll compressor frame for a certain model. Mech. Des. 2022, 39, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. Research on Product Innovation Design Based on Reverse Engineering and 3D Printing Technology. Mech. Des. 2015, 32, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubov, V.V.; Domnitskiy, A.A.; Kargin, R.V. Calculation and Choice of Grip Parameters for Garbage Truck Manipulator. Procedia Eng. 2015, 129, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, Q. Wide spreader for sowing turfgrass seed. Foreign For. 1983, 2, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Holopainen, R.; Salonen, E.-M. Modelling the Cleaning Performance of Rotating Brush in Duct Cleaning. Energy Build. 2002, 34, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Huggins, C. Opportunities to Mitigate Particle Drift from Ground-Based Preemergent Herbicide Applications. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2023, 39, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alian, M.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Upreti, S.R.; Wu, J. Using Discrete Element Method to Analyze the Mixing of the Solid Particles in a Slant Cone Mixer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, C. Scaling Law and Mechanism for the Formation of Stripe Patterns in a Binary Mixture of Granular Materials under Horizontal Vibration. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2013, 63, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hao, C. Optimization of Particle Distribution for Asphalt Mixtures in Screw Conveyer of Paver Based on Discrete Element Method and Response Surface Methodology. Adv. Theory Simul. 2023, 6, 2300252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, D.; Gui, W.; Huang, J. Influence of Charging Parameters on the Burden Flow Velocity and Distribution on the Blast Furnace Chute Based on Discrete Element Method. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sun, K.; Tian, Y. A Review of the Application of Discrete Element Method in Agricultural Engineering: A Case Study of Soybean. Processes 2022, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, M.; Jiang, X. A Review of Contact Models’ Properties for Discrete Element Simulation in Agricultural Engineering. Agriculture 2024, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Hua, Z.; Xing, J.; Ma, W. Simulation and Verification for Seed-Filling Performance of Cell Wheel Precision Seed Metering Device Based on Discrete Element Method. MATEC Web. Conf. 2018, 169, 01035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramírez-Aragón, C.; Ordieres-Meré, J.; Alba-Elías, F.; González-Marcos, A. Comparison of Cohesive Models in EDEM and LIGGGHTS for Simulating Powder Compaction. Materials 2018, 11, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Guo, A.; Guo, S.; Sui, S.; Yang, W.; Tang, R.; Li, X.; Qu, P.; Wang, M.; Lin, X. Laser Powder Bed Fusion for the Fabrication of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Lattice Structures: Synergistic Macroscopic and Microscopic Optimization. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Guo, A.; Wu, H.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Qu, P.; Wang, S.; Guo, S. Four-Dimensional Printing of Polymer-Derived Ceramics with High-Resolution, Reconfigurability, and Shape Memory Effects. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 83, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirapornvaree, I.; Suppadit, T.; Kumar, V. Assessing the Economic and Environmental Impact of Jasmine Rice Production: Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Costs Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Machinery Industry Federation. JB/T 7303-2007; Road Sweeper. China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, C.; Cao, J. Design and Experiment of the Buckwheat Hill-Drop Planter Hole Forming Device. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Qi, B.; Zhang, W.; Song, S.; Wu, Y.; Xia, Q.Q.; Wang, Y. Calibration and Testing of Discrete Element Simulation Parameters for Spinach Seeds. Comp. Part. Mech. 2024, 1–12, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xue, D.; Guan, W.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z. Performance Optimization of a Spoon Precision Seed Metering Device Based on a Maize Seed Assembly Model and Discrete Element Method. Processes 2023, 11, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M. Comparative study on establishment effect of summer/fall seeded duckweed + perennial ryegrass + white clover grasses. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2021, 36, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar]





| Name | Overall Size (mm) | Overall Mass (kg) | Working Width (mm) | Rated Load (kg) | Authorized Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| parameters | 6890 × 1890 × 2640 | 9800 | 1900 | 4300 | 1 |
| Maximum Displacement/mm | Maximum von Mises Equivalent Force/Mpa | Mass/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial model | 1.364 × 10−2 mm | 143.6 Mpa | 15.909 kg |
| Optimized model | 1.939 × 10−3 mm | 157.4 Mpa | 7.091 kg |
| Nature of Sample | Value | Nature of the Model | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of grass plants | 200 | Normal Stiffness/N/m2 | 1 × 109 |
| Contact model | Linear contact bond | Shear Stiffness/N/m2 | 3 × 108 |
| Shear modulus/Pa | 1 × 108 | Normal Strength/Pa | 5 × 107 |
| Friction coefficient | 0.5 | Shear Strength/Pa | 5 × 107 |
| Stem density/(kg/m3) | 100 |
| Speed Ratio Coefficient λ | Disk Brush Speed/(r·min−1) | Vehicle Speed/(km·h−1) | Cleaning Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.826 | 90 | 10 | 98.9 |
| 1.866 | 130 | 15 | 85.1 |
| 1.356 | 200 | 30 | 81.5 |
| Characteristics | Parameter | Numerical |
|---|---|---|
| Seed characteristics | Poisson’s ratio | 0.362 |
| Density (kg·m−3) | 1.04 × 103 | |
| Shear modulus (Pa) | 5.06 × 107 | |
| Aluminum alloy | Poisson’s ratio | 0.394 |
| Density (kg·m−3) | 2.05 × 103 | |
| Shear modulus (Pa) | 7.9 × 108 | |
| Coefficient of restitution | Seed–seed | 0.501 |
| Seed–seed guide mechanism | 0.500 | |
| Coefficient of static friction | Seed–seed | 0.213 |
| Seed–seed guide mechanism | 0.300 | |
| Coefficient of rolling friction | Seed–seed | 0.035 |
| Seed–seed guide mechanism | 0.030 | |
| Other parameters | Gravitational acceleration (m·s−2) | 9.81 |
| Considerations | Factor A (Seeding Disk Speed) | Factor B (Vehicle Speed) | Factor C (Number of Slots) | Seed Dispenser | Row Spacing/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 50 | 9.17 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 62 | 12.5 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 65 | 19.44 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 74 | 10.56 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 73 | 14.58 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 63 | 29.17 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 53 | 11.67 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 42 | 20.83 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 52 | 31.25 |
| average value 1 | 59.000 | 59.000 | 51.667 | ||
| average value 2 | 70.000 | 59.000 | 62.667 | ||
| average value 3 | 49.000 | 60.000 | 63.667 | ||
| extremely poor R | 21.000 | 1.000 | 12.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, L.; Guo, A.; Liu, C.; Guo, M.; Yang, D.; Gao, X.; Wu, H. Design and Discrete Element (DEM) Simulation Analysis of Grassland Ecological Cleaning and Restoration Vehicle. Machines 2025, 13, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13020114
Yin L, Guo A, Liu C, Guo M, Yang D, Gao X, Wu H. Design and Discrete Element (DEM) Simulation Analysis of Grassland Ecological Cleaning and Restoration Vehicle. Machines. 2025; 13(2):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13020114
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Lvfa, Anfu Guo, Chang Liu, Minghui Guo, Dechao Yang, Xianxiang Gao, and Hailong Wu. 2025. "Design and Discrete Element (DEM) Simulation Analysis of Grassland Ecological Cleaning and Restoration Vehicle" Machines 13, no. 2: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13020114
APA StyleYin, L., Guo, A., Liu, C., Guo, M., Yang, D., Gao, X., & Wu, H. (2025). Design and Discrete Element (DEM) Simulation Analysis of Grassland Ecological Cleaning and Restoration Vehicle. Machines, 13(2), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13020114





