A Study on New Straight Shape Design to Reduce Cogging Torque of Small Wind Power Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition and Equation of Cogging Torque
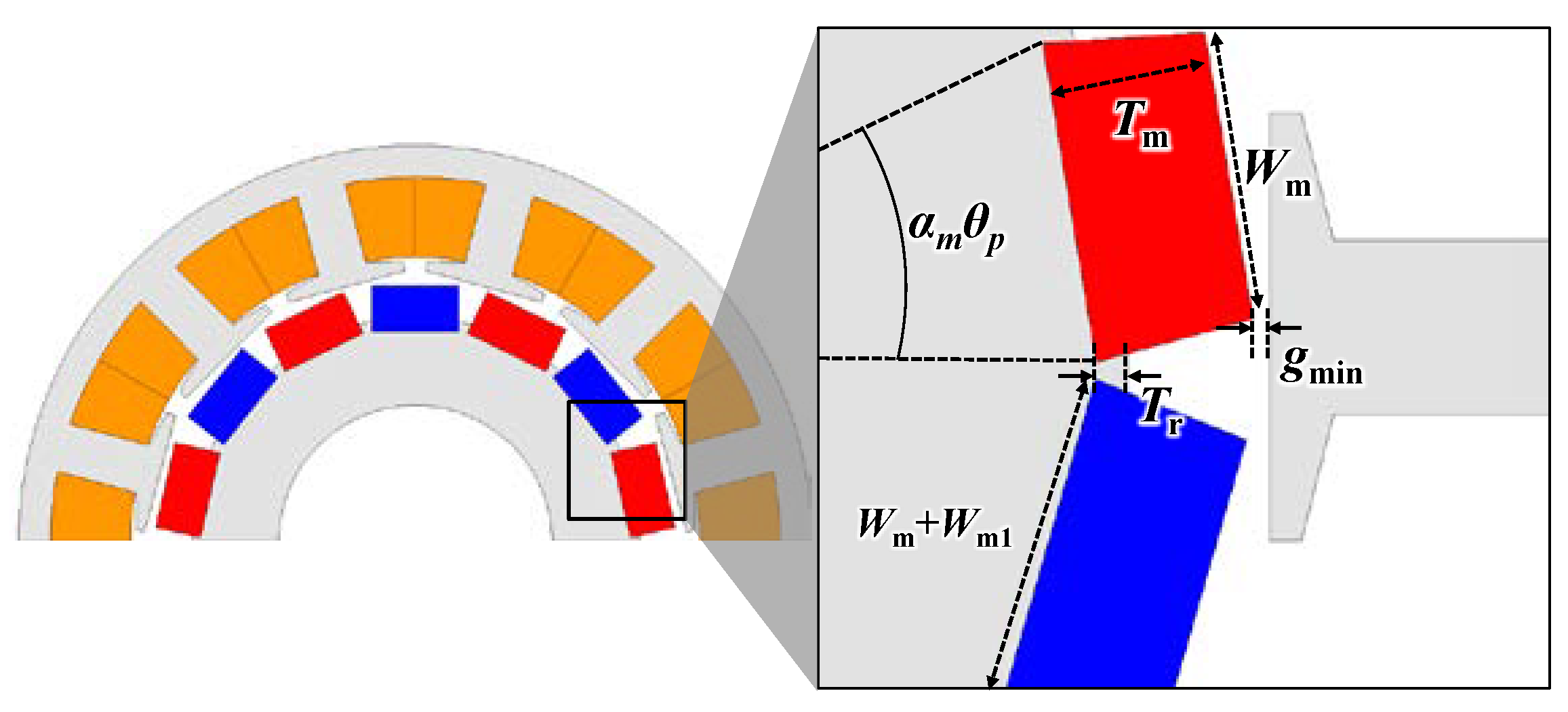
3. Specifications and Shape of Proposed Generator
3.1. Specifications of Generator
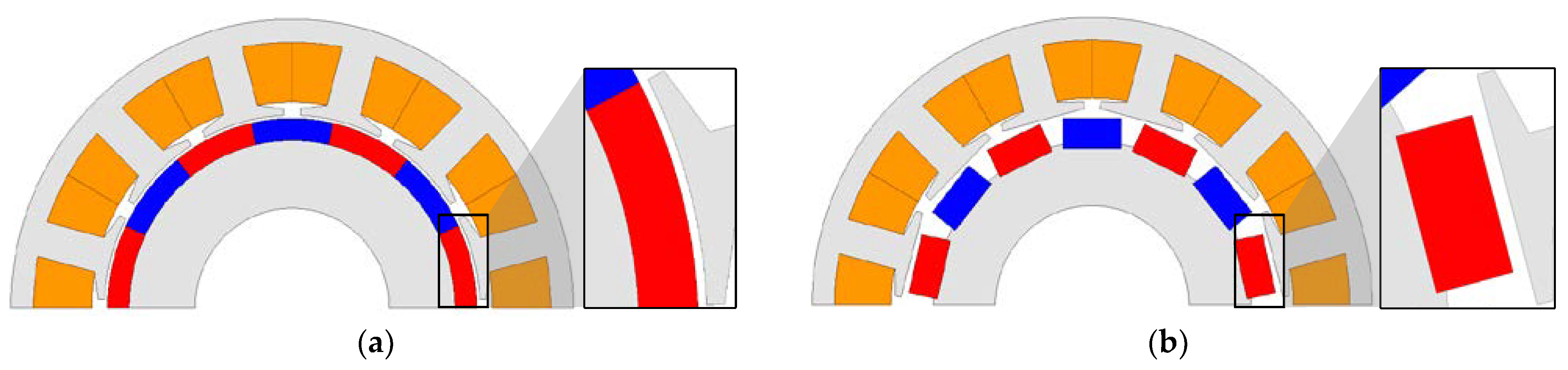
3.2. Comparison of Base and Proposed Models
4. Electromagnetic Design of Proposed Wind Generator
4.1. Pole Slot Combinations
4.2. Airgap
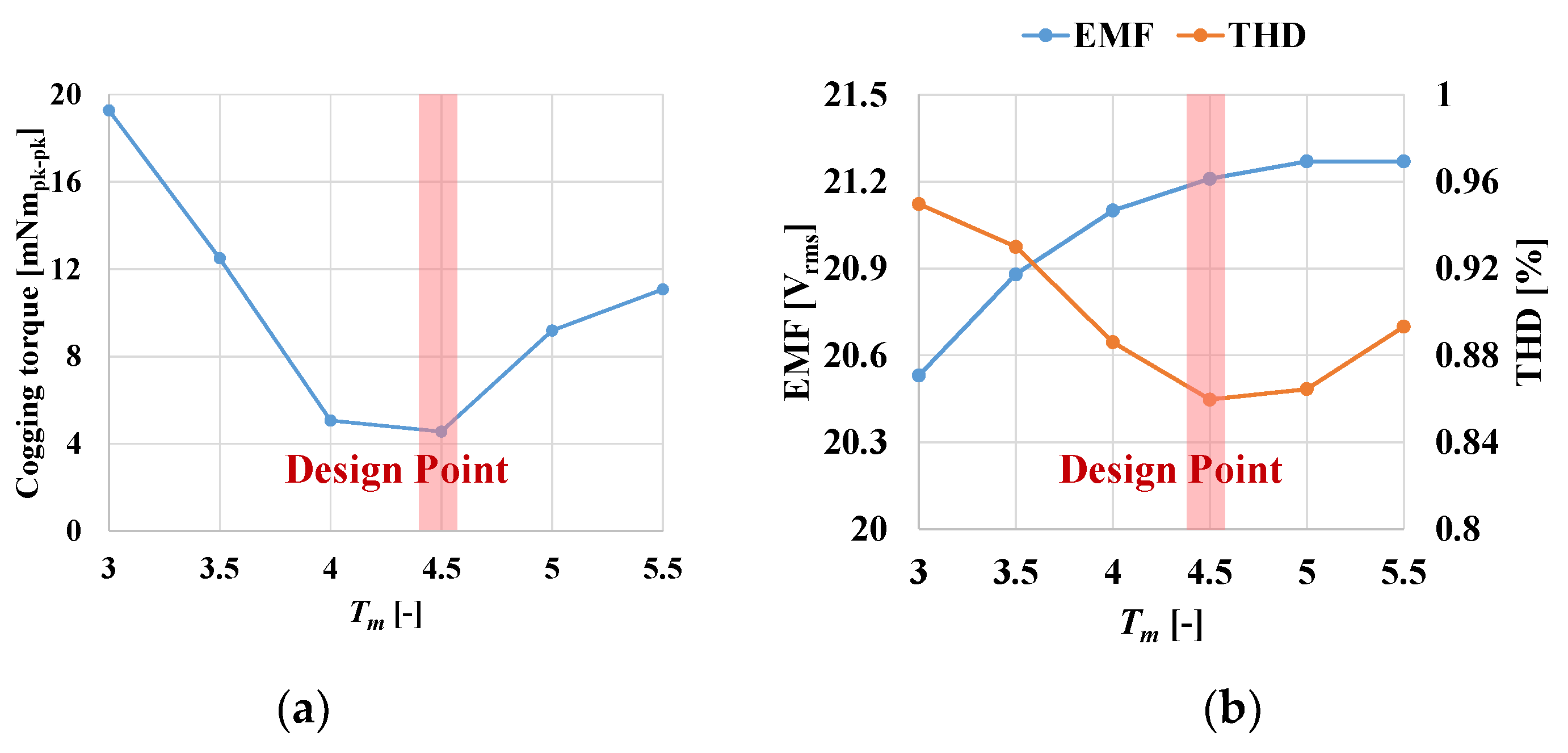
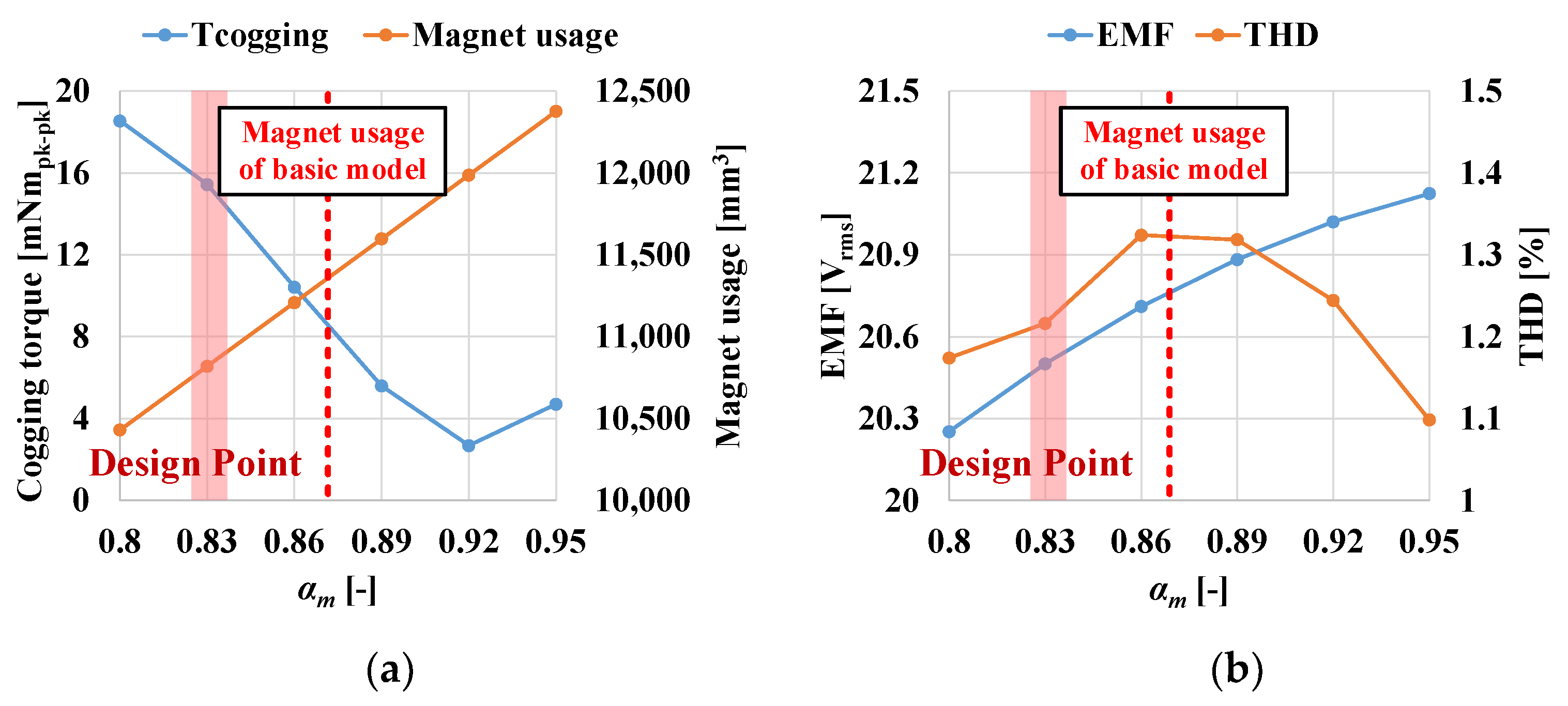
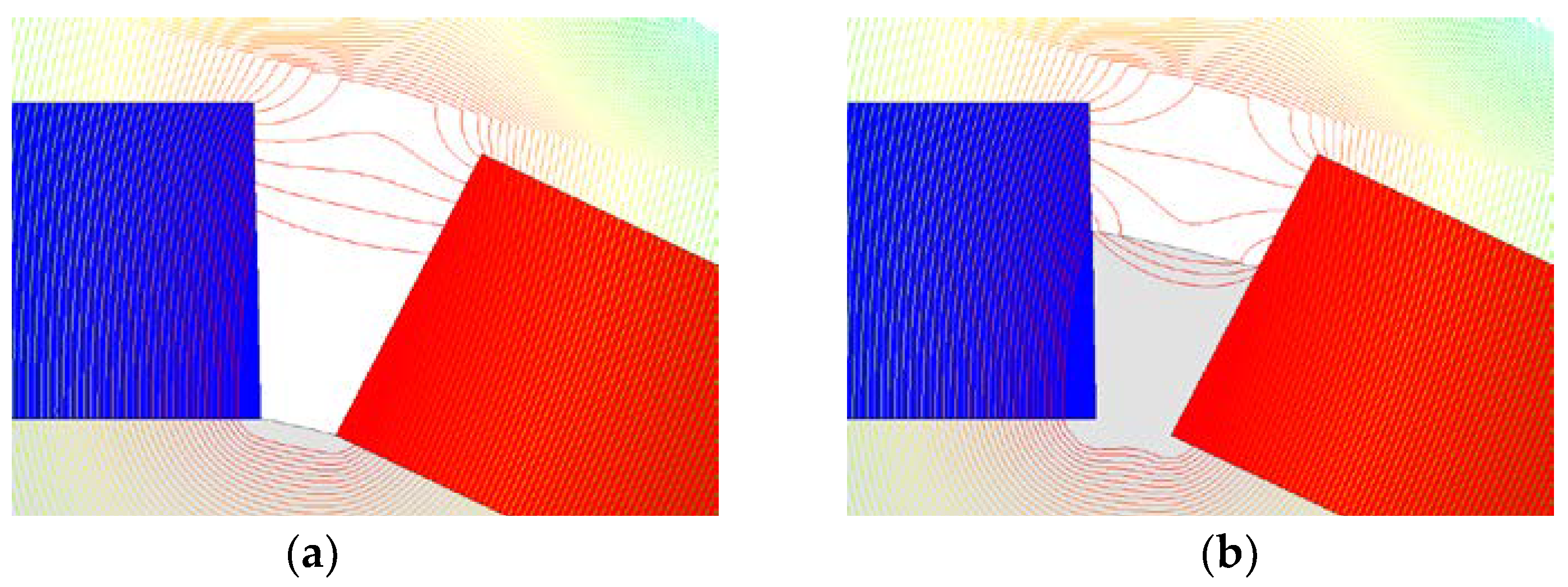
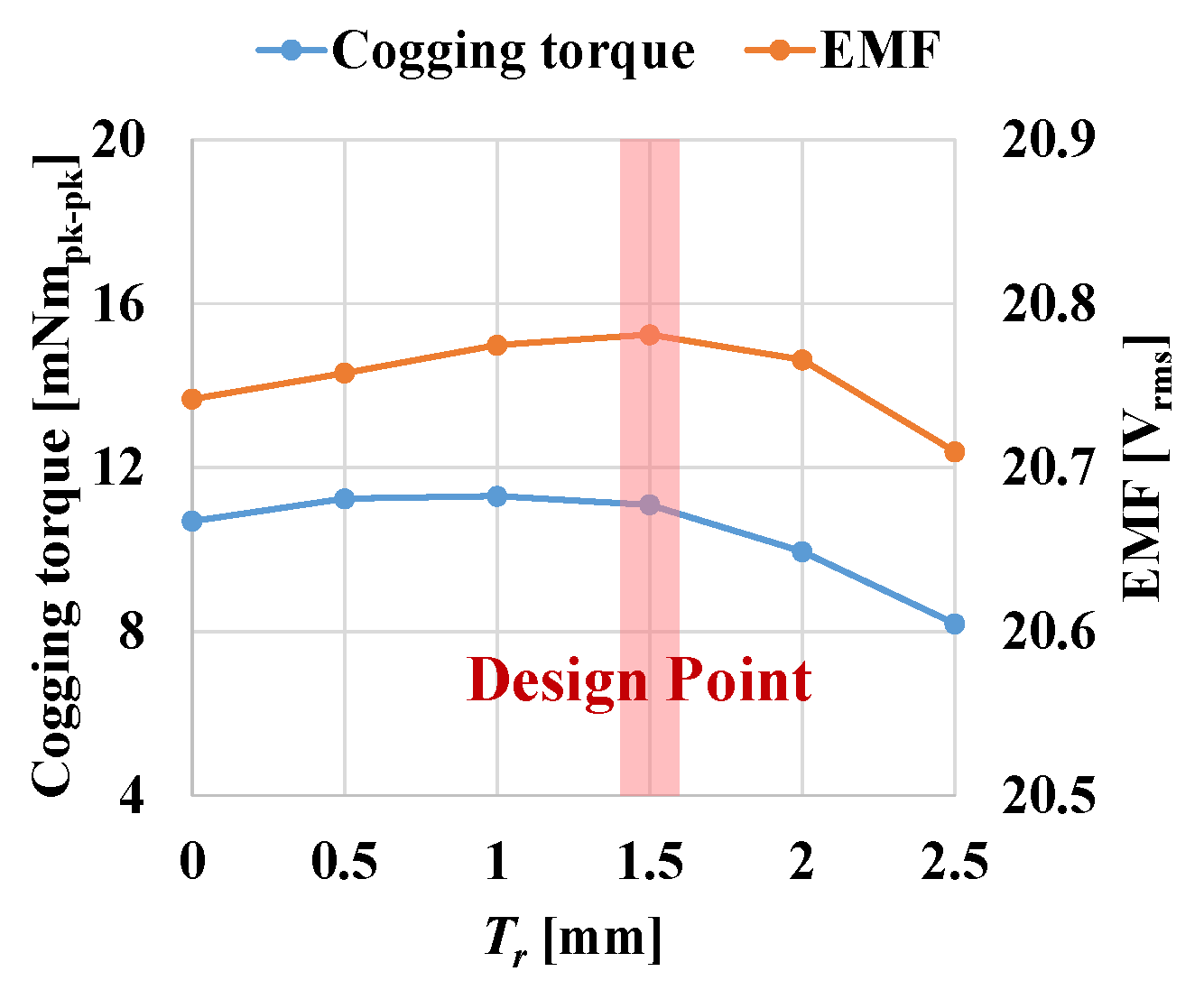
4.3. Magnet
4.4. Rotor Core
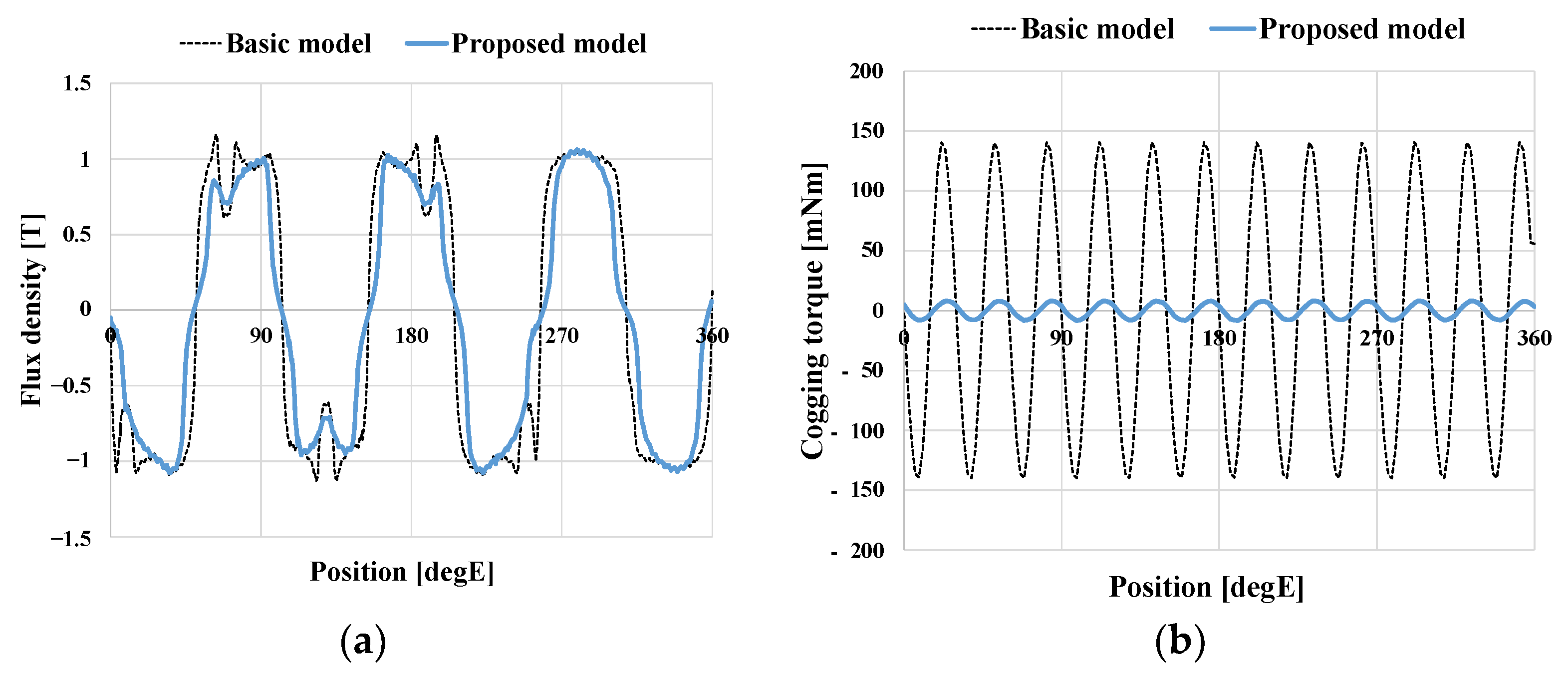
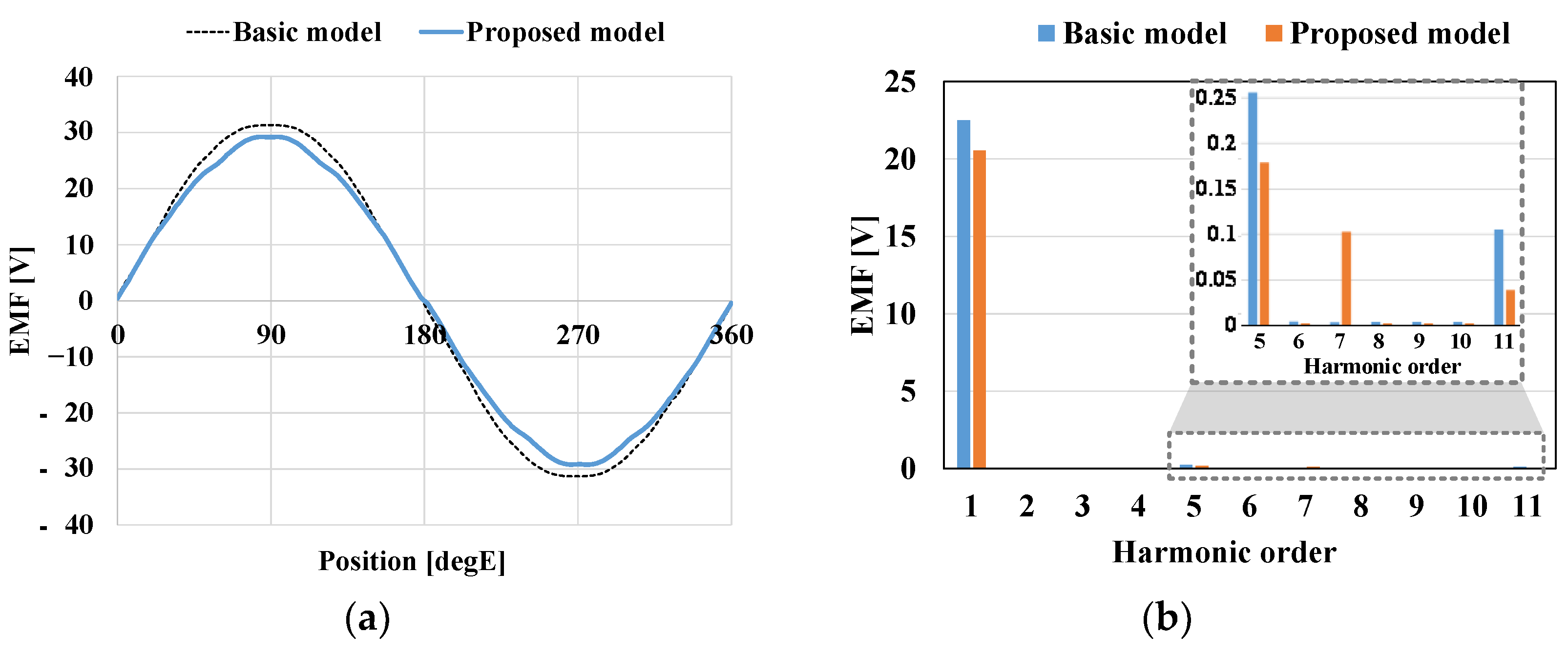
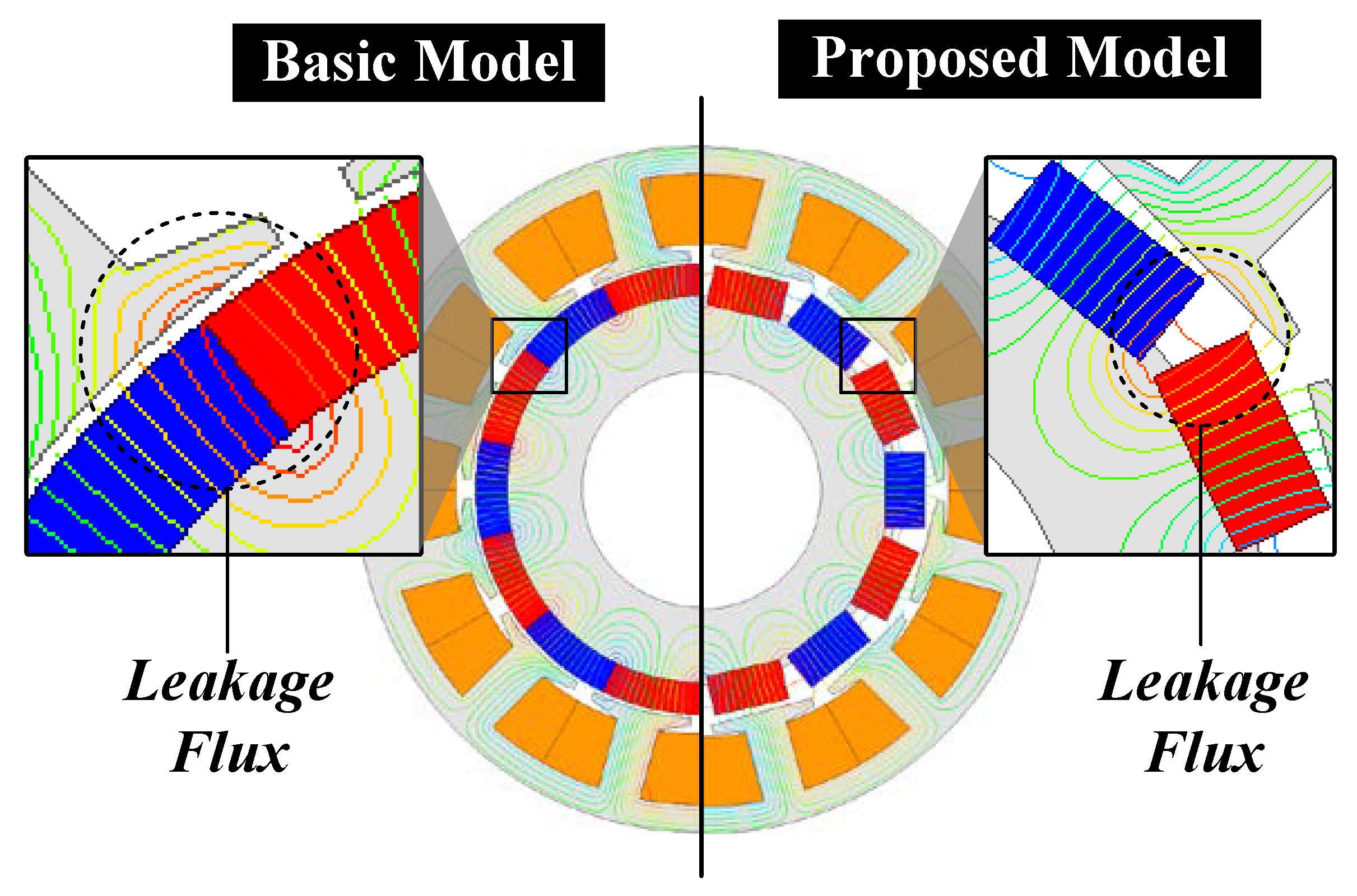
4.5. FEA Results of Final Model
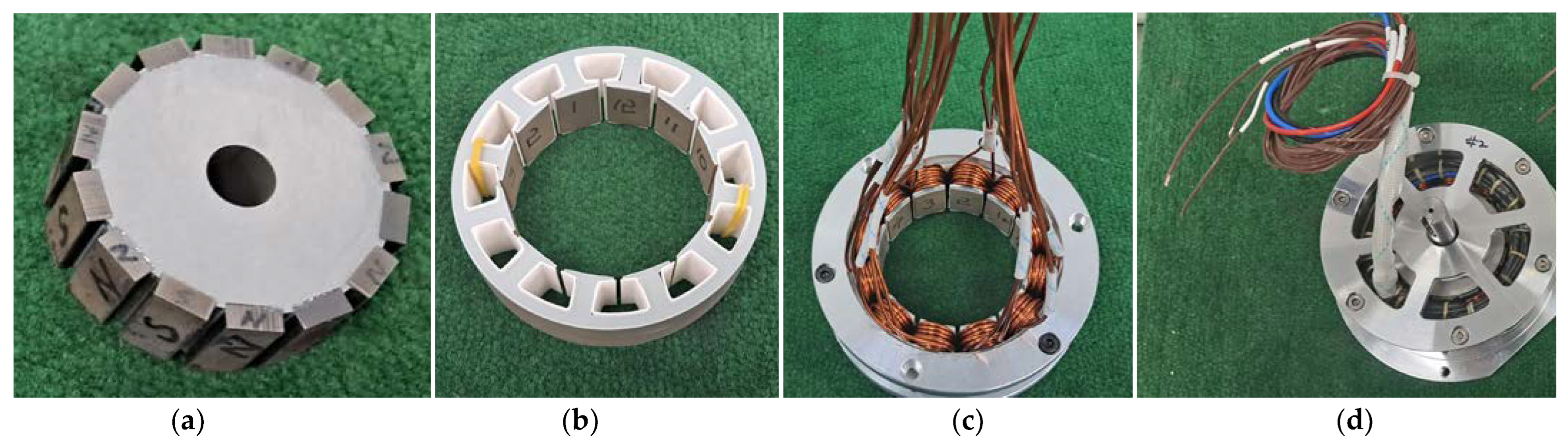
4.6. Manufacture and Experiment Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seangwong, P.; Chamchuen, S.; Fernando, N.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. A Novel Six-Phase V-Shaped Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Generator for Wind Power Generation. Energies 2022, 15, 9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seangwong, P.; Fernando, N.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. E-Core and C-Core Switched Flux Permanent Magnet Generators for Wind Power Generation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 138590–138601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, S.-J. Multiobjective Optimization Design of Small-Scale Wind Power Generator with Outer Rotor Based on Box–Behnken Design. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Jurado, F.; Schmitt, K.; Chamana, M. Electricity Generation from Cow Manure Compared to Wind and Photovoltaic Electric Power Considering Load Uncertainty and Renewable Generation Variability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 3543–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, B.; Kumar, M.K.; Akuru, U.B. Design and Performance Assessment of a Small-Scale Ferrite-PM Flux Reversal Wind Generator. Energies 2020, 13, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, G.; Rao, F. Analysis and Design of Novel Axial Field Flux-Modulation Permanent Magnet Machines for Direct Drive Application. Machines 2022, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Koo, D.-H.; Moon, S.-R.; Han, C.-K. Design of an Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Generator for a Portable Hand Crank Generating System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-M.; Park, H.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Han, C.; Choi, M.-S. Analysis on the Magnetic Force Characteristics of Segmented Magnet Used in Large Permanent-Magnet Wind Power Generator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3981–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G. Design Optimization of a HTS-Modulated PM Wind Generator. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2021, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gracia, M.; Jiménez Romero, Á.; Herrero Ciudad, J.; Martín Arroyo, S. Cogging Torque Reduction Based on a New Pre-Slot Technique for a Small Wind Generator. Energies 2018, 11, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-F.; Yeh, Y.-H. Rotor Eccentricity Effect on Cogging Torque of PM Generators for Small Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 1897–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Yang, I.-J.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.-H. Alternative Bridge Spoke Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator Design for Wind Power Generation Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 152819–152828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Pyo, H.-J.; Kim, W.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.-D. Design of Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Low Capacity Wind Turbine Considering Magnetization and Cogging Torques. Machines 2023, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bianchi, N.; Ji, J.; Zhao, W. Improving Torque Analysis and Design Using the Air-Gap Field Modulation Principle for Permanent-Magnet Hub Machines. Energies 2023, 16, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ahmed, S.; Massoud, A.M.; Elserougi, A.A. An Improved Performance Direct-Drive Permanent Magnet Wind Generator Using a Novel Single-Layer Winding Layout. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 5124–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y. Investigation of Post-Demagnetization Torque Ripple in Fractional-Slot Surface-Mounted PM Wind Power Generators After Short Circuit Faults. IEEE Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-M.; Seo, H.-J.; Park, Y.-S.; Park, H.-I.; Choi, J.-Y. Design and Electromagnetic Field Characteristic Analysis of 1.5 kW Small Scale Wind Power Generator for Substitution of Nd-Fe-B to Ferrite Permanent Magnet. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2933–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryca, Z.; Różowicz, S.; Różowicz, A.; Pakosz, A.; Leśko, M.; Wachta, H. Impact of Selected Methods of Cogging Torque Reduction in Multipolar Permanent-Magnet Machines. Energies 2020, 13, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Zou, J.; Li, Y. Minimization of Cogging Force in Fractional-Slot Permanent Magnet Linear Motors with Double-Layer Concentrated Windings. Energies 2016, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, M.G.; da Silva, F.F.; Branco, P.J.d.C. Operational Analysis of an Axial and Solid Double-Pole Configuration in a Permanent Magnet Flux-Switching Generator. Energies 2024, 17, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torn, V.; Seangwong, P.; Fernando, N.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. Performance Improvement of Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Wind Generator Using Magnetic Flux Barrier Design. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsal, M.; Cumhur, B.; Demir, Y.; Yolacan, E.; Aydin, M. Rotor Design Optimization of a New Flux-Assisted Consequent Pole Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Torque Motor for Low-Speed Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, J.; Niu, S.; Wang, Q. Slot-PM-Assisted Hybrid Reluctance Generator with Self-Excited DC Source for Stand-Alone Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Huang, S.; Gao, J.; Lu, K. Cogging Torque Reduction by Slot-Opening Shift for Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 4028–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-M. Cogging Torque and Acoustic Noise Reduction in Permanent Magnet Motors by Teeth Pairing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 3144–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, J.; Viarouge, P. Synthesis of high performance PM motors with concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 17, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K. A Study on Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Considering Axial Flux Leakage Through End Plate. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | 150 | W |
| Voltage | 20 | V |
| Base Speed | 2000 | RPM |
| Cogging Torque | 15 | mNmpk-pk |
| THD of EMF (Line-Line) | 5 | % |
| Parameter | Basic Model | Proposed Model | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power | 156.8 | 157.2 | W |
| Efficiency | 91.2 | 90.9 | % |
| EMF | 22.5 | 20.5 | Vrms |
| THD of EMF (Line-Line) | 1.3 | 1.3 | % |
| Cogging Torque | 280.7 | 16.2 | mNmpk-pk |
| Nslot\Npole | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.866 | - | 0.866 | 0.5 | - | 0.5 | 0.866 |
| 9 | 0.617 | 0.866 | 0.945 | 0.945 | 0.866 | 0.617 | 0.328 |
| 12 | - | - | 0.866 | 0.933 | - | 0.933 | 0.866 |
| 15 | - | - | 0.621 | 0.866 | - | 0.951 | 0.951 |
| 18 | - | - | - | 0.647 | 0.866 | 0.902 | 0.945 |
| Variable | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| PM Thickness (Tm) | 4.5 | mm |
| PM Width (Wm) | 8.9 | mm |
| Additional Inner PM Width (Wm1) | 0.2 | mm |
| Pole Arc Ratio (αm) | 0.83 | mm |
| PM Insertion Depth (Tr) | 1.5 | mm |
| Parameter | Basic Model | Final Model | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator Outer Diameter | 87 | 87 | mm |
| Stack Length | 20 | 20 | mm |
| Power | 156.8 | 156.8 | W |
| Voltage | 20.5 | 20.1 | Vrms |
| Base Speed | 2000 | 2000 | RPM |
| Cogging Torque | 280.7 | 11.7 | mNmpk-pk |
| THD | 1.3 | 1.4 | % |
| Copper Loss | 4.5 | 5.6 | W |
| Core Loss | 7.1 | 6.6 | W |
| Magnet Loss | 0.7 | 0.4 | W |
| Efficiency | 91.2 | 91.0 | % |
| Parameter | FEA | Experiment | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power | 156.8 | 160.4 | W |
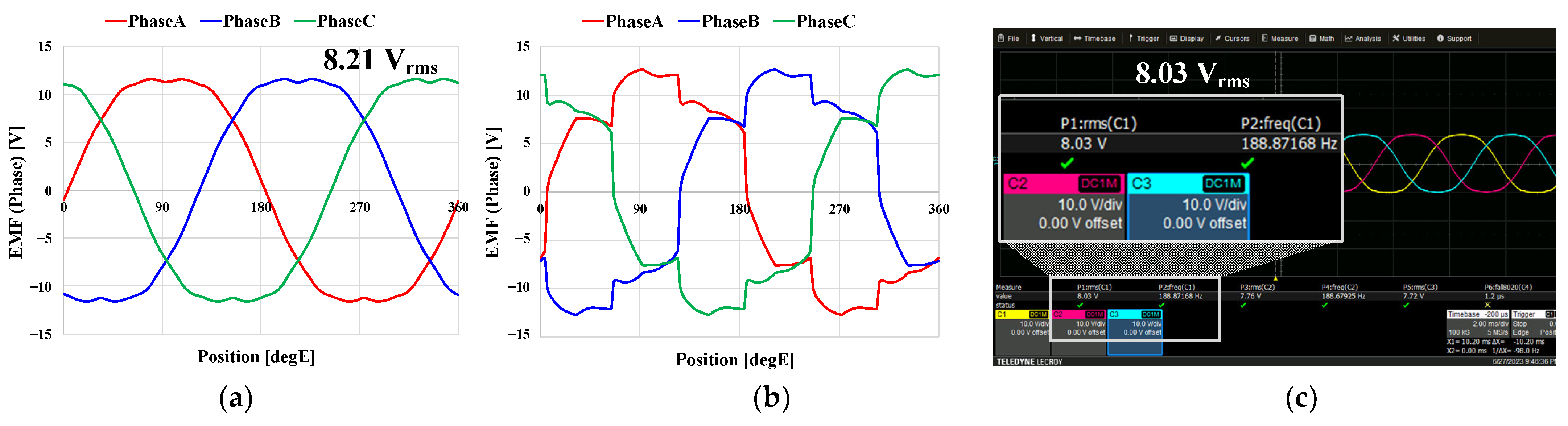
| EMF (@1600 RPM) | 8.21 | 8.03 | Vrms |
| Voltage | 20.1 | 20.0 | V |
| Efficiency | 91.0 | 90.8 | % |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Lee, J.; Ham, S.; Chun, Y.; Kim, H. A Study on New Straight Shape Design to Reduce Cogging Torque of Small Wind Power Generator. Machines 2024, 12, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12060412
Kang J, Lee J, Ham S, Chun Y, Kim H. A Study on New Straight Shape Design to Reduce Cogging Torque of Small Wind Power Generator. Machines. 2024; 12(6):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12060412
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Junho, Ju Lee, Sanghwan Ham, Yondo Chun, and Hyunwoo Kim. 2024. "A Study on New Straight Shape Design to Reduce Cogging Torque of Small Wind Power Generator" Machines 12, no. 6: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12060412
APA StyleKang, J., Lee, J., Ham, S., Chun, Y., & Kim, H. (2024). A Study on New Straight Shape Design to Reduce Cogging Torque of Small Wind Power Generator. Machines, 12(6), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12060412







