Research on the Entrance Damage of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer/Ti6Al4V Stacks in Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Robot Drilling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Robot Kinematics Analysis
2.1. Robot Kinematics Model Based on the Modified D-H Method
2.2. Kinematics Performance Analyzing
3. Robot Stiffness Performance Analysis
3.1. Robot Static Stiffness Model
3.2. Robot Stiffness Performance Index
4. Optimization Analysis of Drilling Posture
4.1. Kinematics Performance Optimization
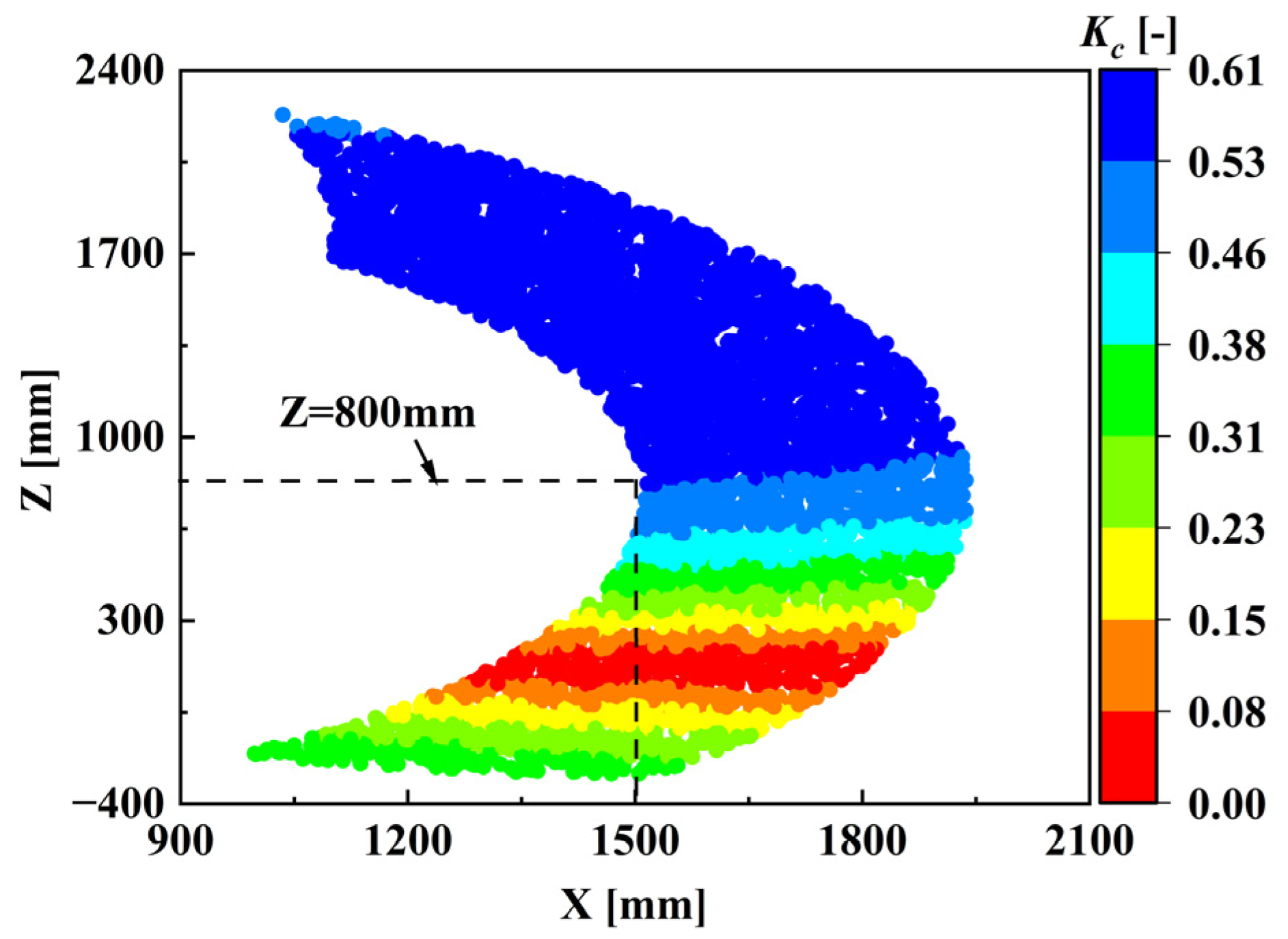
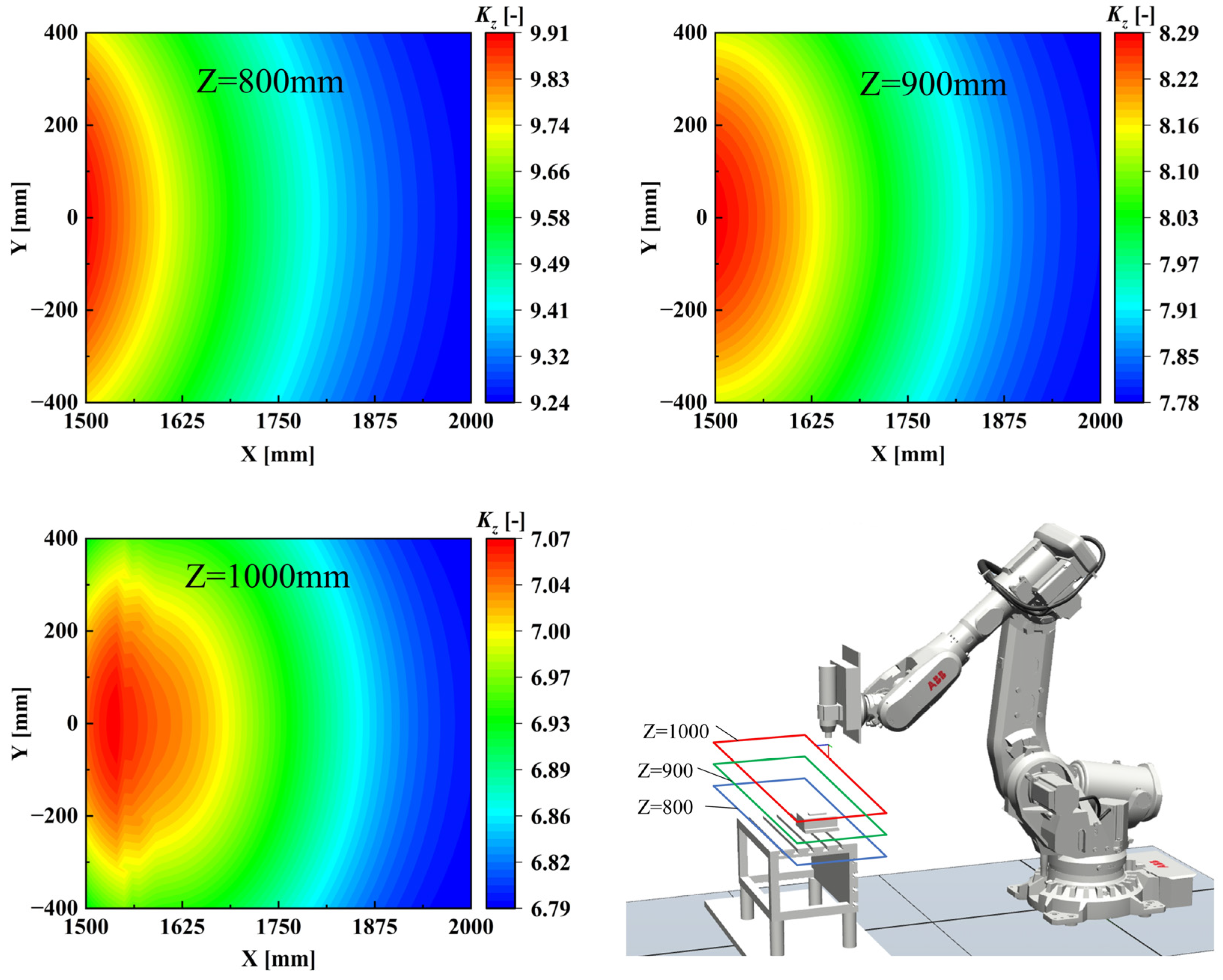
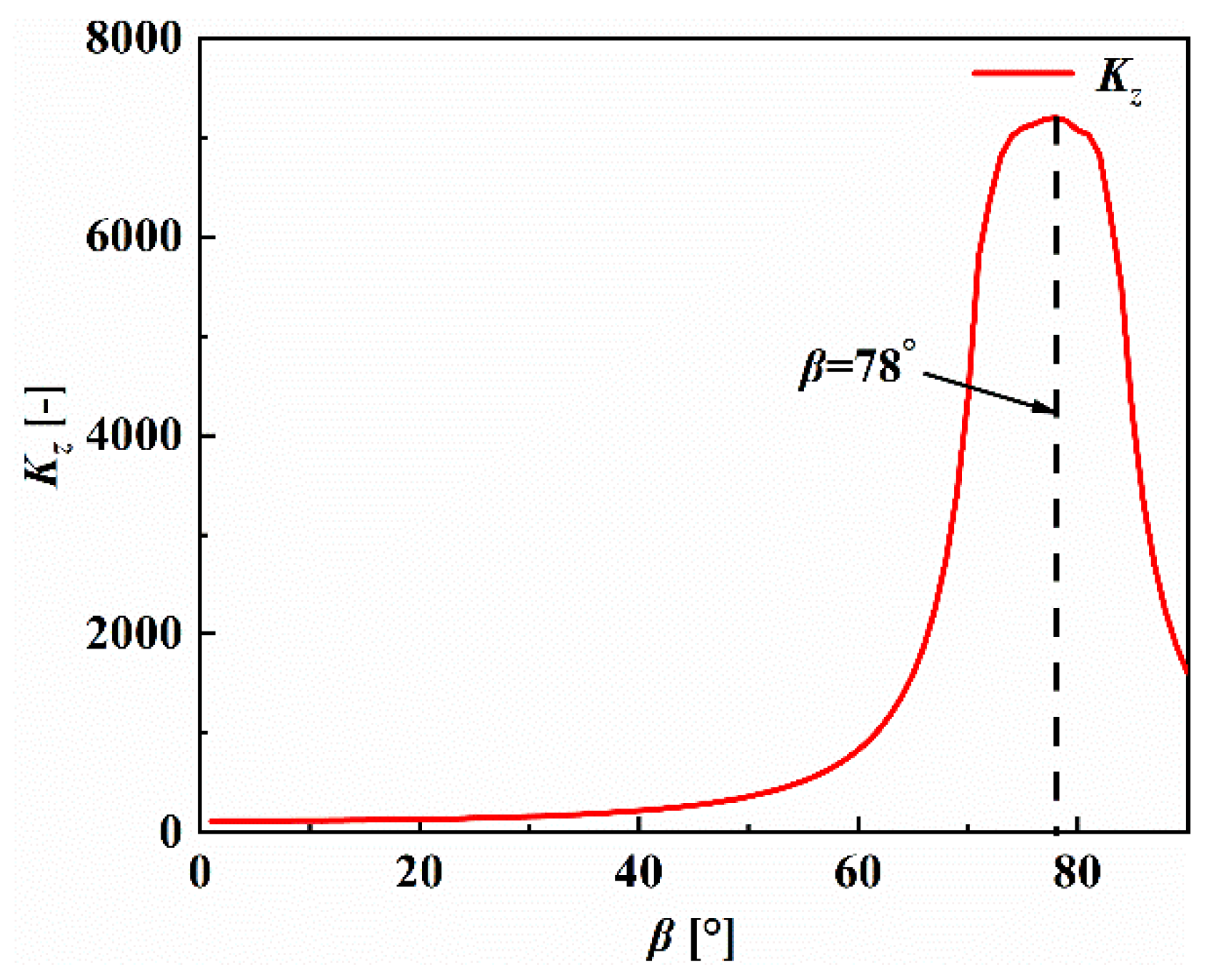
4.2. Optimization Analysis of Machining Plane Stiffness
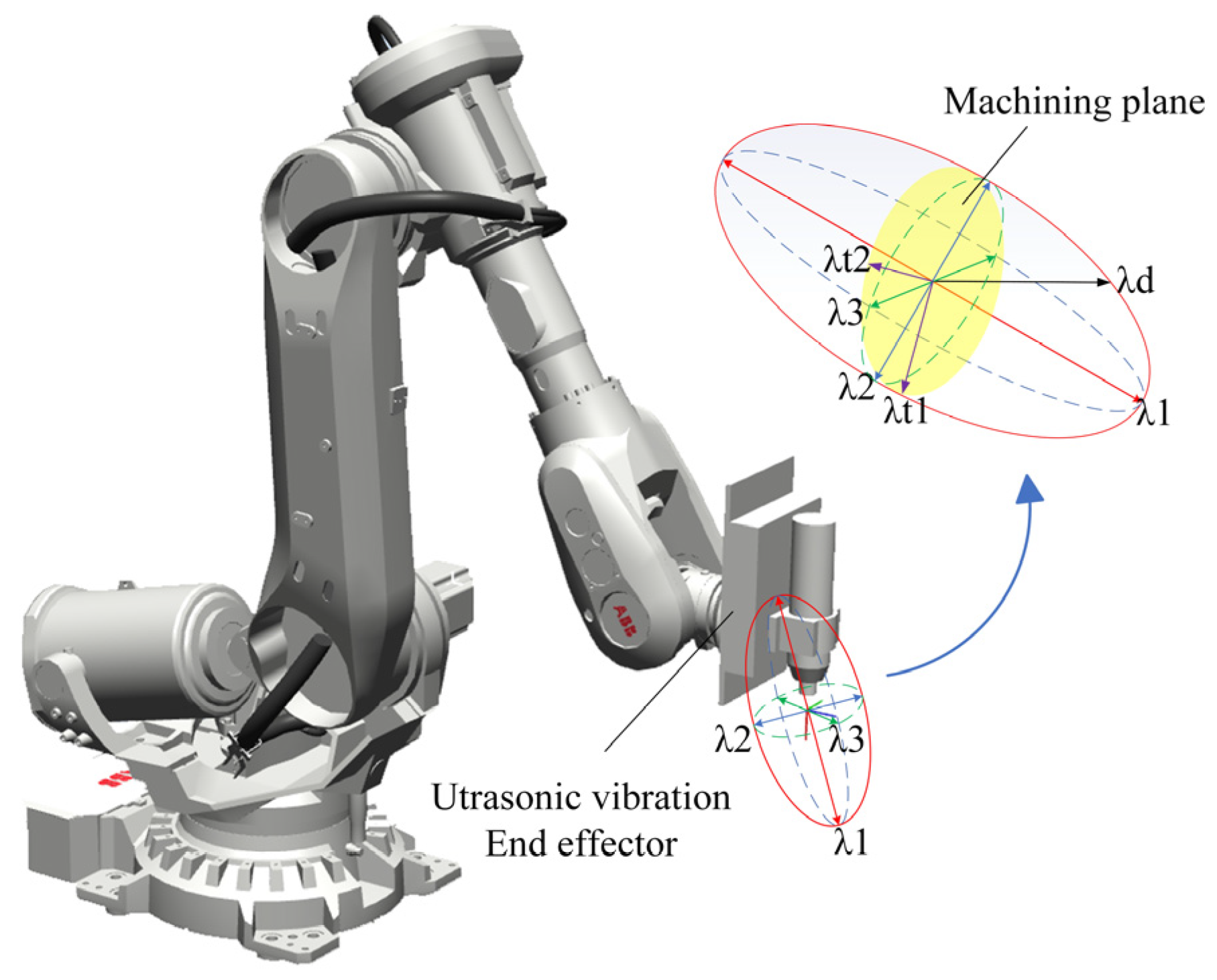
4.3. Robot End-Effector Redundancy Optimization
5. Experimental Conditions and Schemes
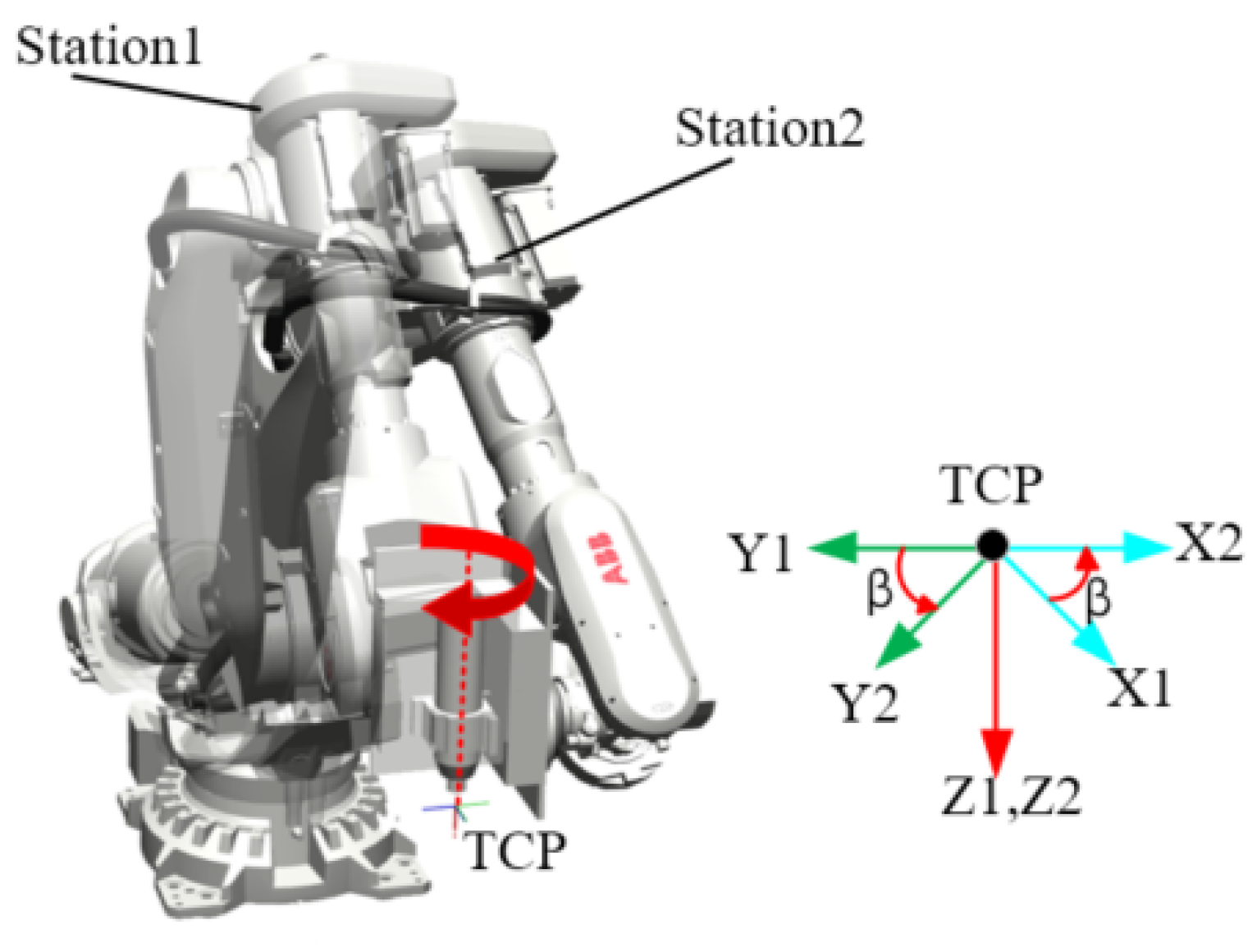
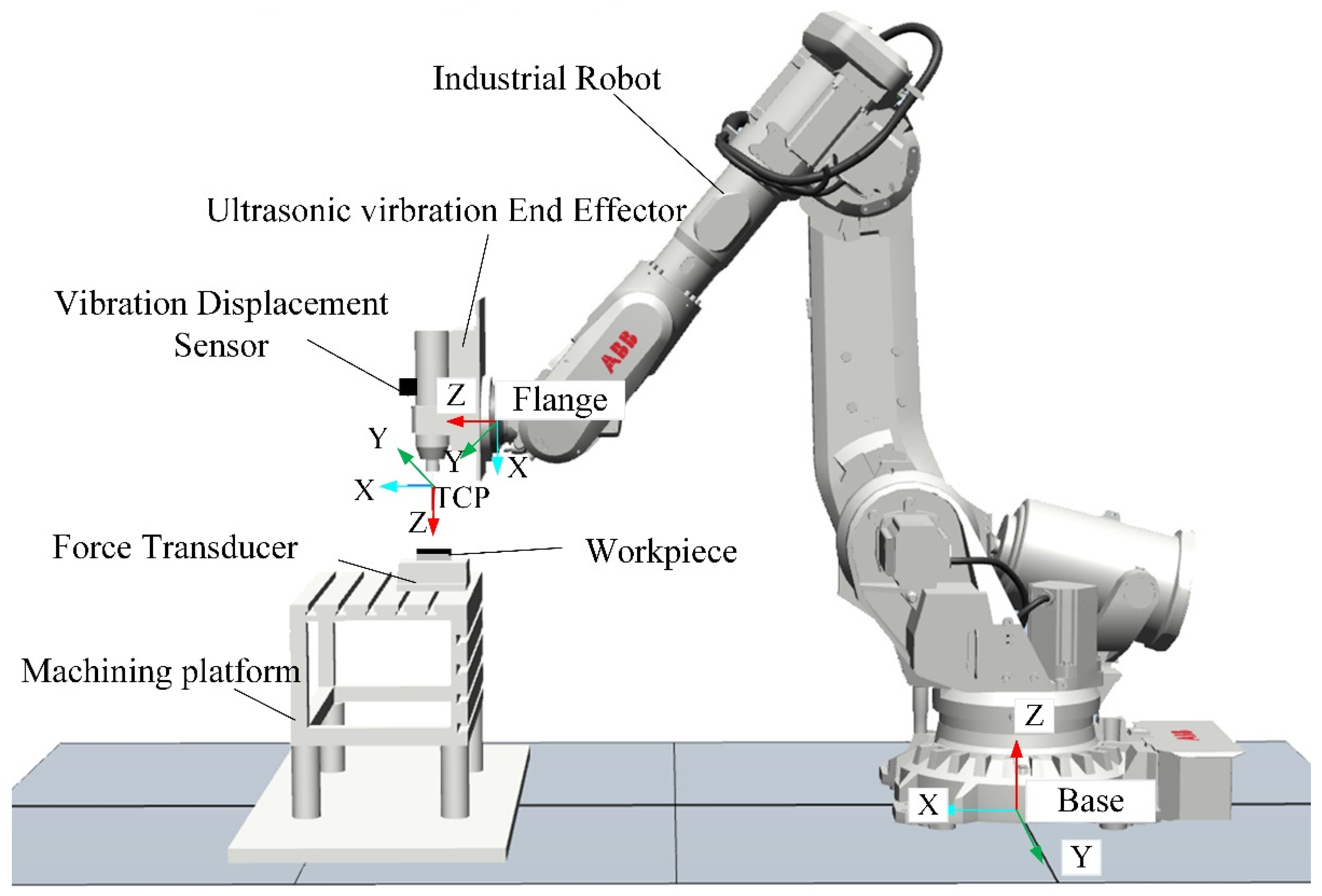
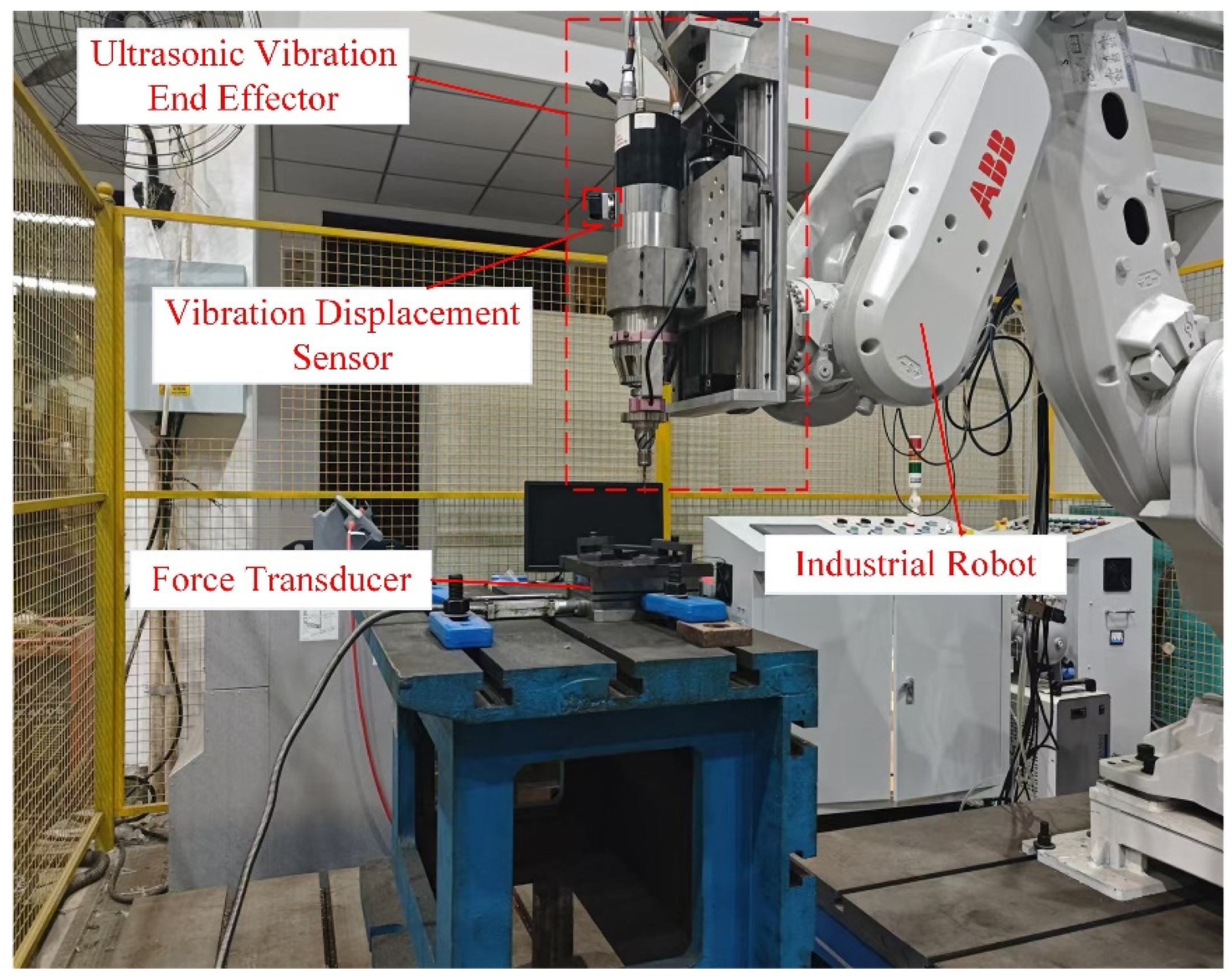
5.1. Experimental System
5.2. Tool and Workpiece
5.3. Experimental Method
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Theoretical Verification and Analysis
6.2. Vibration in Drilling Process
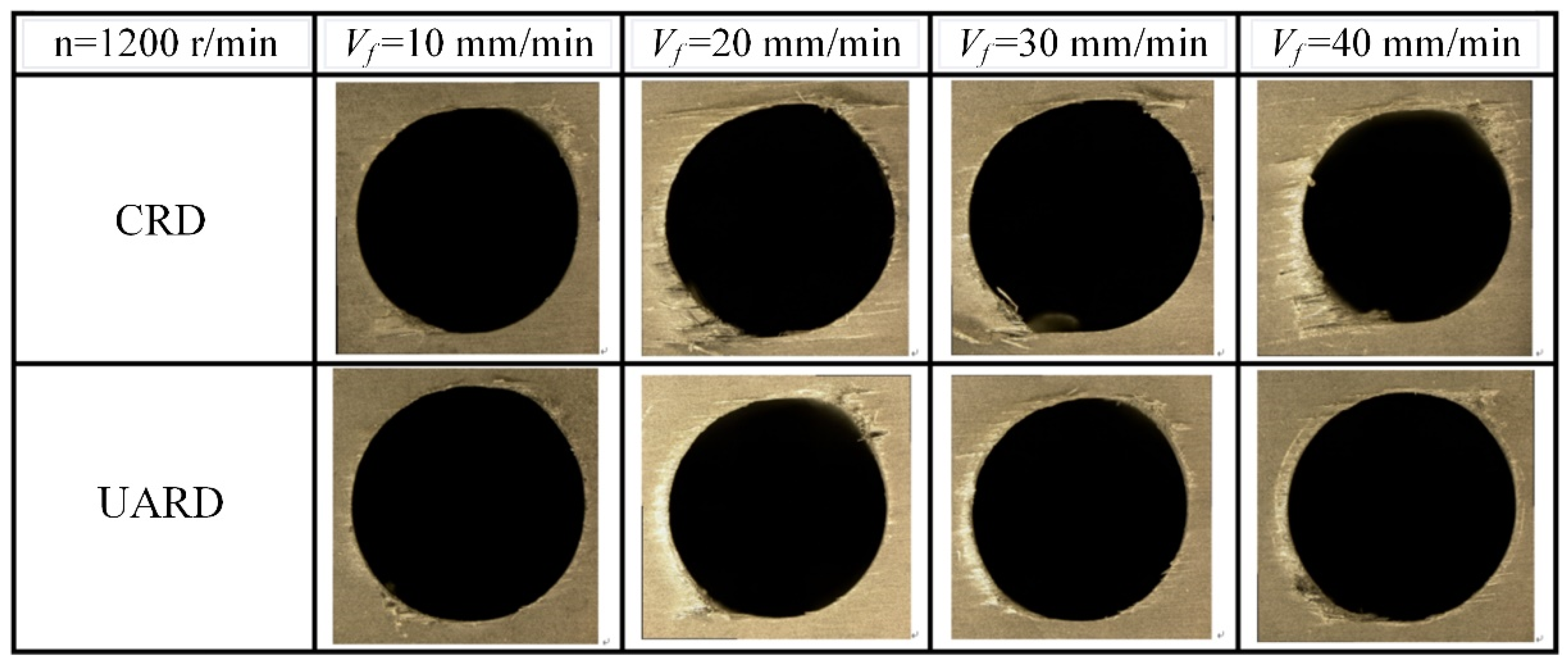
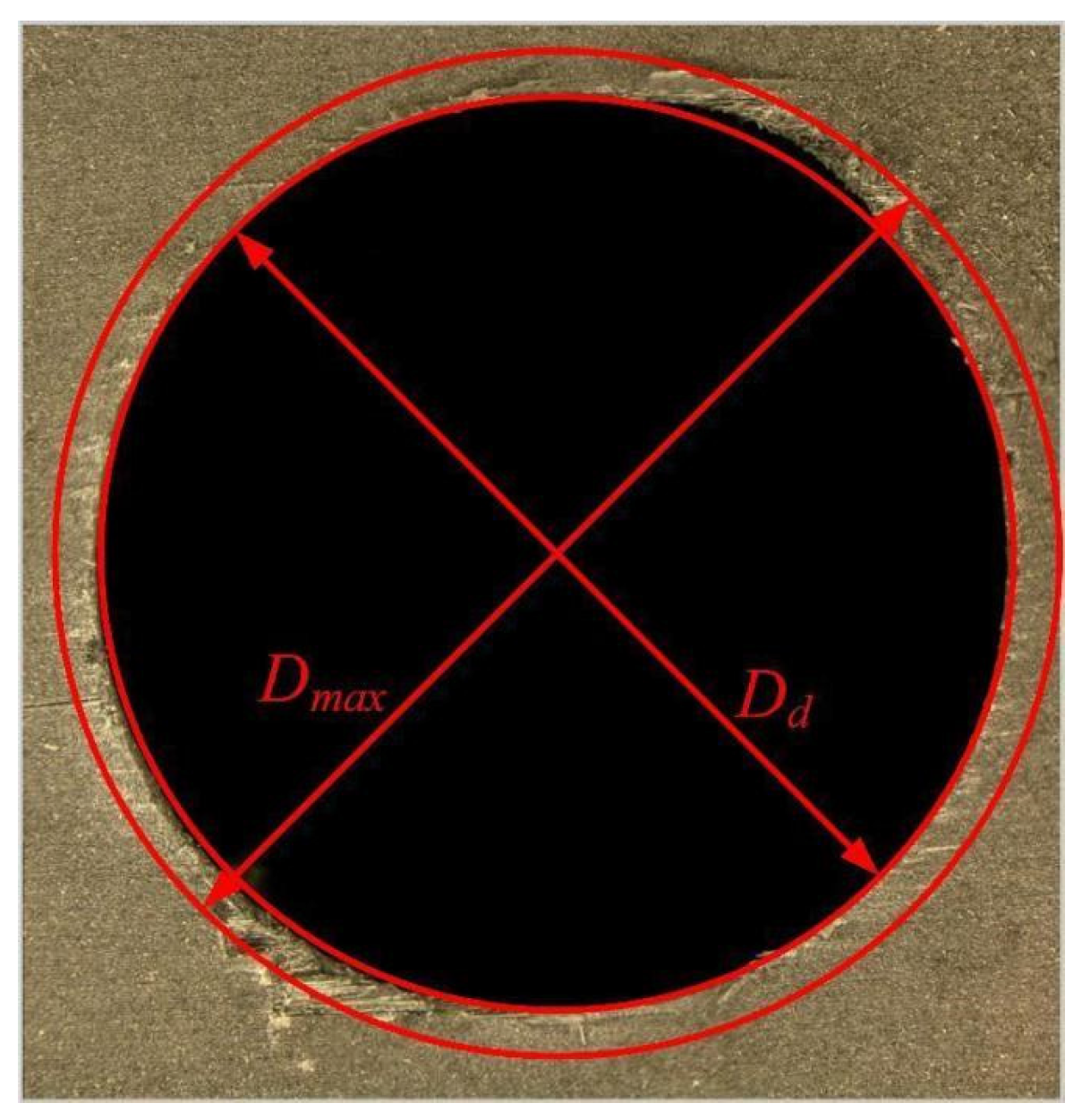
6.3. CFRP Entrance Delamination
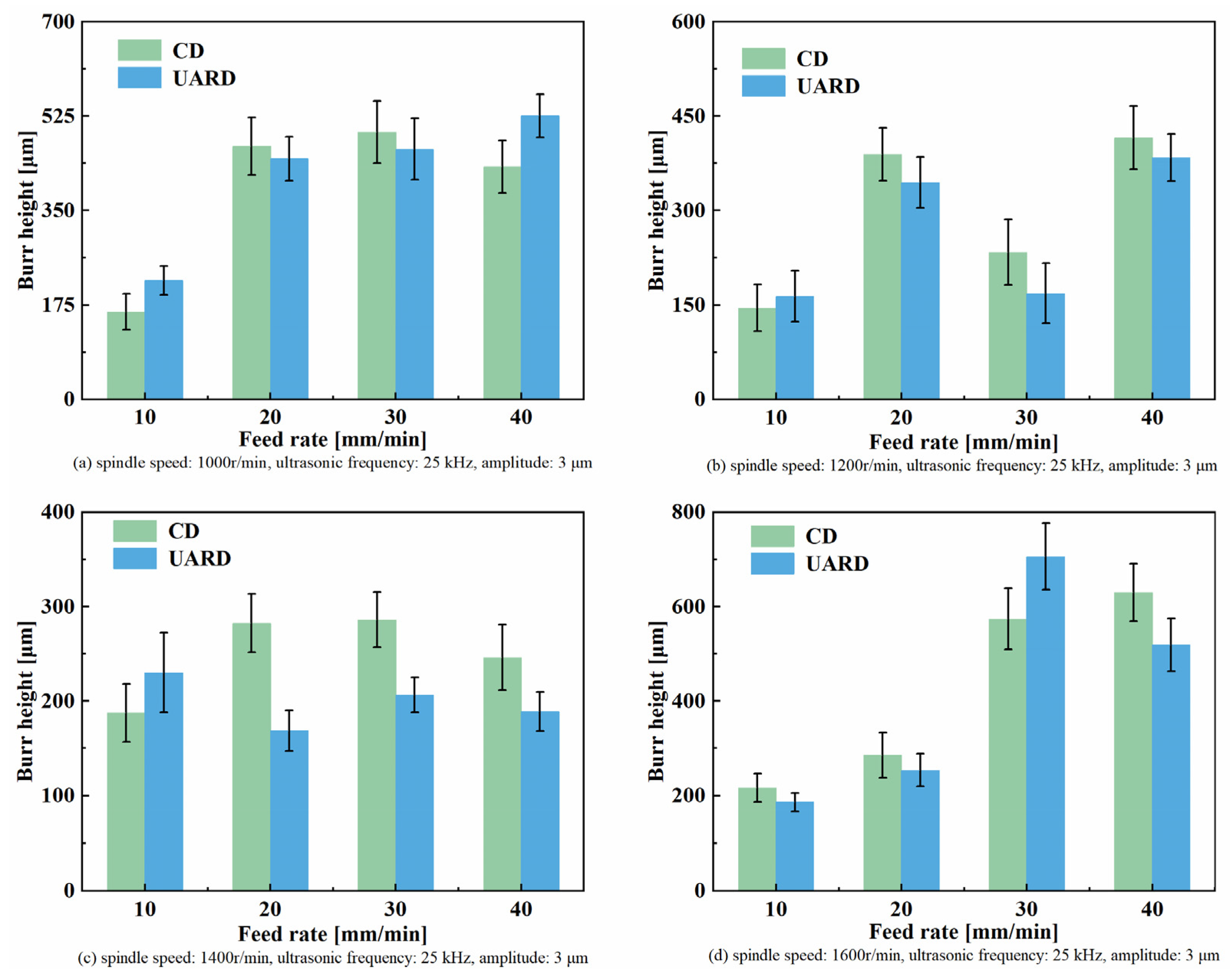
6.4. CFRP Entrance Burr Height
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- By optimizing the calculated machining area and machining posture, the quality and stability of robotic drilling are improved.
- (2)
- Compared with conventional robotic drilling, in ultrasonic-assisted robotic drilling, the entrance quality of CFRP is improved and the vibration during the drilling process is significantly reduced.
- (3)
- At an ultrasonic vibration frequency of 25 kHz, an amplitude of 3 μm, a spindle speed of 1400 r/min, and a feed rate of 30 mm/min, the lowest CFRP entrance delamination factor obtained by ultrasonic-assisted robotic drilling was 1.09. Moreover, the CFRP entrance burr height obtained by ultrasonic-assisted robotic drilling is the lowest when the ultrasonic vibration frequency is 25 kHz, the amplitude is 3 μm, the spindle speed is 1600 r/min, and the feed rate is 10 mm/min, which is 186.3 μm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caro, S.; Dumas, C.; Garnier, S.; Furet, B. Workpiece Placement Optimization for Machining Operations with a KUKA KR270-2 Robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; IEEE: Karlsruhe, Germany; pp. 2921–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Leali, F.; Vergnano, A.; Pini, F.; Pellicciari, M.; Berselli, G. A Workcell Calibration Method for Enhancing Accuracy in Robot Machining of Aerospace Parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Drust, M.; Ansaloni, M.; Lehmann, C.; Pellicciari, M.; Leali, F.; Gunnink, J.W.; Verl, A. Improving Robotic Machining Accuracy through Experimental Error Investigation and Modular Compensation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J. Chatter Analysis of Robotic Machining Process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 173, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Gan, Z.; Pan, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhu, Z. Machining with Flexible Manipulator: Toward Improving Robotic Machining Performance. In Proceedings of the Proceedings, 2005 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Monterey, CA, USA, 24–28 July 2005; IEEE: Monterey, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 1127–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Xie, H.-L.; Wang, Q.-H.; Zhou, X.-F. Region-Based Toolpath Generation for Robotic Milling of Freeform Surfaces with Stiffness Optimization. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 64, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamani, M.; Gauthier, S.; Chatelain, J.-F. A Study of the Combined Effects of Machining Parameters on Cutting Force Components during High Speed Robotic Trimming of CFRPs. Measurement 2015, 59, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J. Active Stiffness Control of a Manipulator in Cartesian Coordinates. In Proceedings of the 1980 19th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control including the Symposium on Adaptive Processes, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 10–12 December 1980; IEEE: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1980; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Abele, E.; Weigold, M.; Rothenbücher, S. Modeling and Identification of an Industrial Robot for Machining Applications. CIRP Ann. 2007, 56, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Peng, F.; Yan, R.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Fan, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhu, Z. Stiffness Performance Index Based Posture and Feed Orientation Optimization in Robotic Milling Process. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 55, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikag, H.; Sims, N.D.; Ozturk, E. Cartesian Stiffness Optimization for Serial Arm Robots. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Liao, W.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Stiffness Analysis and Optimization in Robotic Drilling Application. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Dong, H.; Ke, Y. Stiffness-Oriented Posture Optimization in Robotic Machining Applications. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2015, 35, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Wang, Q.-H.; Xie, H.; Li, J.-R.; Zhou, X.; Hua, P. Optimization of Robot Posture and Workpiece Setup in Robotic Milling with Stiffness Threshold. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-A.; Tang, K.; Wang, C.-Y. Collision-Free and Smooth Joint Motion Planning for Six-Axis Industrial Robots by Redundancy Optimization. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 68, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Posada, J.; Schneider, U.; Sridhar, A.; Verl, A. Automatic Motion Generation for Robotic Milling Optimizing Stiffness with Sample-Based Planning. Machines 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, S.; Dumas, C.; Caro, S.; Furet, B. Quality Certification and Productivity Optimization in Robotic-Based Manufacturing. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, L.T.; Gonul, B. Effect of Quasi-Static Motion on the Dynamics and Stability of Robotic Milling. CIRP Ann. 2021, 70, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratena, T.; Vavruska, P.; Sveda, J.; Valasek, M. Postprocessor for Verification of Robot Movements with Additional Axis after Toolpath Optimization. Procedia CIRP 2021, 101, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, C.; Matei, A.; Zarges, J.; Ulbrich, S.; Weigold, M. Optimal Design for Compliance Modeling of Industrial Robots with Bayesian Inference of Stiffnesses. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 2023, 17, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Gururaja, S. Investigation of Hole Quality in Drilled Ti/CFRP/Ti Laminates Using CO2 Laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Niu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Niu, J. Surface/Subsurface Damage Mechanisms and Inhibition Strategies in Machining of Hard and Brittle Materials: A Systematic Review. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 54, 105088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onawumi, P.Y.; Roy, A.; Silberschmidt, V.V.; Merson, E. Ultrasonically Assisted Drilling of Aerospace CFRP/Ti Stacks. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Qiu, X.; Niu, Q.; Li, C.; Ko, T.J. Study on the Mechanism and Performance of Longitudinal-Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Drilling CFRP/Ti Stack. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 92, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Kang, R.; Dong, Z.; Yin, S.; Bao, Y.; Guo, D. Hole Quality in Longitudinal–Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Drilling of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 15, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zheng, K.; Liao, W. Stability of Lateral Vibration in Robotic Rotary Ultrasonic Drilling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 145, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarbashi, S.H.H.; Khan, W.; Angeles, J. The Jacobian Condition Number as a Dexterity Index in 6R Machining Robots. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2012, 28, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alici, G.; Shirinzadeh, B. Enhanced Stiffness Modeling, Identification and Characterization for Robot Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarbashi, S.H.H.; Khan, W.; Angeles, J. Posture Optimization in Robot-Assisted Machining Operations. Mech. Mach. Theory 2012, 51, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Tian, W.; Liao, W.; Zhang, L.; Bu, Y. Processing Configuration Off-Line Optimization for Functionally Redundant Robotic Drilling Tasks. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 110, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, T.; Duan, Z.; Suo, Y.; Zhang, C. Ultrasonic Assisted Pecking Drilling Process for CFRP/Ti Laminated Materials. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 108, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Link i | ai−1 [mm] | αi−1 [°] | di [mm] | θi [°] | Range of Joint Angle [°] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 780 | 0 | −170~170 |
| 2 | 320 | −90 | 0 | −90 | −60~85 |
| 3 | 1125 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −180~70 |
| 4 | 200 | −90 | 1142.5 | 0 | −300~300 |
| 5 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 0 | −130~130 |
| 6 | 0 | −90 | 200 | 180 | −360~360 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile strength [MPa] | 5523 |
| Modulus of elongation [GPa] | 252 |
| Density [g/cm3] | 1.81 |
| Breaking elongation [%] | 2.1 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Density [g/cm3] | 4.52 |
| Poisson ratio [-] | 0.343 |
| Tensile strength [MPa] | 902 |
| Yield strength [MPa] | 824 |
| Elongation [%] | 10 |
| Shrinkage ratio [%] | 30 |
| Variables | Value |
|---|---|
| Spindle speed [r/min] | 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600 |
| Feed rate [mm/min] | 10, 20, 30, 40 |
| Ultrasonic vibration frequency [kHz] | 25, 0 |
| Ultrasonic amplitude [μm] | 3, 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiao, F.; Li, Y. Research on the Entrance Damage of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer/Ti6Al4V Stacks in Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Robot Drilling. Machines 2024, 12, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120881
Zhong H, Zhang Z, Wang X, Jiao F, Li Y. Research on the Entrance Damage of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer/Ti6Al4V Stacks in Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Robot Drilling. Machines. 2024; 12(12):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Hao, Ziqiang Zhang, Xue Wang, Feng Jiao, and Yuanxiao Li. 2024. "Research on the Entrance Damage of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer/Ti6Al4V Stacks in Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Robot Drilling" Machines 12, no. 12: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120881
APA StyleZhong, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Jiao, F., & Li, Y. (2024). Research on the Entrance Damage of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer/Ti6Al4V Stacks in Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Robot Drilling. Machines, 12(12), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120881






